Abstract
This paper presents several transformative scenarios of municipal solid waste landfilling sites from technical and ecological points of view, applicable to upper-middle-income countries, as per the classification of the World Bank. Our approach is based on numerical simulations of greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions in 2012 and 2025 and numerical simulations of methane emissions in a selected landfilling site, Oued Smar, in Algiers (Algerian capital city), according to the LandGem and IPCC models. Business-as-usual, landfill gas flaring, and electricity generation scenarios are considered in the numerical simulations. Finally, a novel metric dividing the recoverable electrical power by the amount of avoided greenhouse gas emissions is suggested. This paper reveals that the LandGem results were closer to reality and exhibited slightly higher values of energy recovery. A novel “techno-ecological” metric, computed as the ratio of energy recovery to avoided amounts of GHG emissions, was suggested for controlling landfill transformation. Accordingly, transitioning from uncontrolled landfilling to energy recovery could reduce GHG emissions by up to 99.87%, with a generated power of 0.89 W per ton of CO2-eq avoided by 2025.
1. Introduction
The management of municipal solid waste (MSWM) is an important challenge for developing countries [1], particularly in the context of rapid urbanization and increasing generation of waste. Effective Solid Waste Management (SWM) is expected to mitigate health and environmental impacts related to solid wastes and their composition, conserve natural resources, and improve urban livability [2]. The Waste Framework Directive lays out some basic waste management principles. It requires waste to be managed without affecting human and environmental health, without any risks to water, air, soil, plants, and animals, and with the least possible odor and noise [3]. According to the waste management hierarchy presented in Figure 1, landfilling is the least preferred waste treatment option due to its numerous adverse environmental and health impacts, including air pollution, gas emissions, leachate contaminating ground and surface water, high possibility of open fires, alteration of fauna, and others [4].
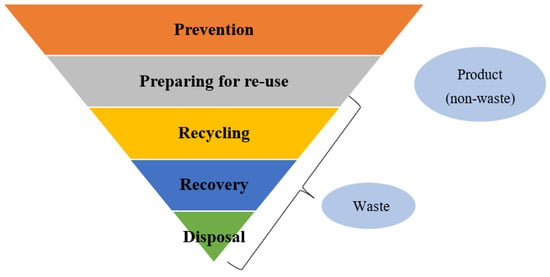
Figure 1.
Waste management hierarchy (Source: the authors based on [5]).
Globally, the open dumping of solid waste generates approximately 1.6 billion tons of CO2 equivalent annually, accounting for around 5% of global emissions, with the majority originating from decomposing food waste [6]. As illustrated in Figure 2, annual GHG emissions from developed countries (e.g., Germany, Japan, or Canada) and upper-middle-income countries (e.g., Brazil, Mexico, or South Africa) reveal important contrasts in waste sector contributions.
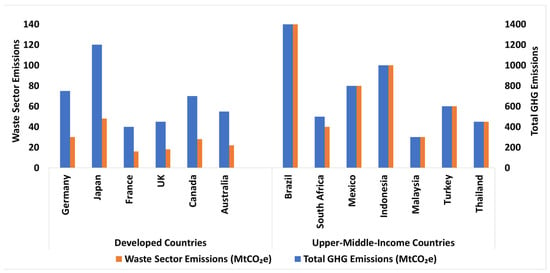
Figure 2.
Comparative analysis of total GHG emissions and waste sector contributions: developed vs. upper-middle-income countries (source: the authors using [7]).
Developed countries such as Germany (750 MtCO2e total emissions) and Japan (1200 MtCO2e) exhibit reduced waste sector contributions, with waste accounting for 4% of the total GHG (30 MtCO2e and 48 MtCO2e, respectively, shown as blue bars in Figure 2). These low percentages reflect the use of advanced waste management systems like recycling and energy recovery. Conversely, upper-middle-income countries such as Brazil (1400 MtCO2e total emissions) and Indonesia (1000 MtCO2e) face significantly higher waste sector impacts, with waste contributing 10% of the total emissions (140 MtCO2e and 100 MtCO2e, respectively; represented by orange bars in Figure 2). These disparities are exemplified by South Africa, where landfills contribute 8% (40 MtCO2e) of its 500 MtCO2e total emissions, reflecting systemic reliance on open dumping and uncontrolled landfills [6,7,8].
Landfilling practices vary significantly across regions, ranging from open dumps, meaning that waste is disposed of in unregulated and often uncontrolled areas [9,10], to sanitary landfills, which are engineered systems designed to include leachate and gas collection, waste compaction, and daily site covering [11]. Globally, around 37% of waste is landfilled, 8% of which is disposed of in sanitary landfills, while 31% is disposed of in open dumping. Open dumping is popular in 93% of the lower-income countries and in 2% of the high-income ones. Upper-middle-income countries, including North Africa and particularly Algeria, open dump around 54% of their waste [12,13].
Despite its well-documented environmental drawbacks, landfilling remains a widely practiced waste management strategy in many regions, including Algeria, where 60–70% of municipal waste is disposed of in open dumpsites and 30–40% in sanitary landfills [13]. The high organic fraction of Algerian waste, particularly food waste (over 62%), is both a challenge and an opportunity. Landfill gas, which contains around 50% methane, can be captured and utilized for energy production, thereby reducing greenhouse gas emissions and displacing fossil fuels [14]. However, the transition from open dumping to sanitary landfilling and energy recovery remains underexplored, particularly in upper-middle-income countries where waste management systems are often underdeveloped and underfunded.
The current literature on MSWM in upper-middle-income countries reveals several critical gaps that hinder the development of effective and sustainable waste management strategies:
- Inconsistent Waste Characterization: There is a lack of standardized methods for waste characterization, leading to inconsistencies in data collection, analysis, and planning [15]. This inconsistency complicates the development of tailored waste management solutions.
- Limited Focus on Transition Strategies: While the transition from open dumps to sanitary landfills is often discussed in theoretical terms, there is limited research on the practical challenges and ecological consequences of such transitions [16]. This gap is particularly important in upper-middle-income countries, where financial and technical constraints often impede progress.
- Regional Variations in Methane Emission Models: The existing models for estimating methane emissions from landfills often fail to account for regional variations in waste composition, climate, and socio-economic factors [17]. This limitation reduces the accuracy of emission estimates and undermines the effectiveness of mitigation strategies.
- Feasibility of Energy Recovery: The economic and technical feasibility of energy recovery from landfill gases remains controversial, particularly in countries with limited financial resources. While the potential benefits of energy recovery are widely recognized, the practical implementation of such systems is often hindered by high costs and technical challenges.
Several studies have estimated the potential for energy recovery from municipal solid waste (MSW) in upper-middle-income countries, highlighting various methods and specific regional contexts. For instance, Shovon et al. [18] reviewed energy recovery strategies from solid waste in developing countries, focusing on thermochemical and biochemical techniques. Their findings suggest that thermochemical methods—such as incineration, pyrolysis, and gasification—are particularly well suited to these regions due to their ability to handle large waste volumes efficiently. In contrast, studies like those by dos Muchangos et al. [19], which focused on Maputo, Mozambique, provide a more localized perspective by assessing greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions under different waste management scenarios—open dumps, GHG flaring, and recycling with biological treatment. However, no studies have linked the environmental impact of landfilling in upper-middle-income countries to their energetic potential based on iterative transitions in solid waste management scenarios with wider applicability. Such an approach may include transitioning from uncontrolled landfilling to landfill gas flaring as a first iteration and then to electrical energy recovery as an ultimate goal. The high dependence on landfilling and the high organic fraction of waste makes landfill gas extraction in upper-middle-income countries, specifically Algeria as a case study, an attractive working scenario both technically and ecologically.
The Algerian context provides an interesting case study for addressing these gaps. The quantity of household and similar waste generated in Algeria amounted to around 13 million tons in 2018 and is expected to exceed 20 million tons by 2035 [20]. The Algerian waste composition, which consists of more than 62% food waste [21], reflects the broader challenges faced by upper-middle-income countries, which share similar consumption patterns and waste management strategies based primarily on landfilling [22,23]. This situation needs a dual focus: first, on mitigating the environmental impact of uncontrolled landfilling, particularly in terms of greenhouse gas emissions [24,25], and second, on harnessing the technical and ecological benefits of landfill gas recovery for energy production [26]. Recent studies have highlighted the critical situation of municipal waste management in Algeria. For instance, Kebaili et al. [27] examined municipal waste management in Algiers, emphasizing the excessive production of household waste and the urgent need for improved waste management practices.
Our study addresses the gaps identified in the literature review by proposing an integrated approach to transitioning MSW landfilling practices in upper-middle-income countries, using Algeria as a case study. The methodology is designed to provide a comprehensive framework for improving waste management practices, with a focus on both environmental and energetic outcomes. Specifically, this study includes the following components:
1.1. Numerical Simulations of Greenhouse Gas Emissions
Using the LandGem and IPCC models, we simulate greenhouse gas emissions for 2012 and 2025. Our study refers to the World Band report related to worldwide solid waste management, according to several demographic and economic indicators, based on the year 2012 and expectations for the year 2025. Thus, this study is timely aligned with the data provided in the aforementioned report for consistency and reliability reasons. The models are applied to the Oued Smar landfill in Algiers [28]. These simulations provide a detailed understanding of the environmental impact of landfilling under different scenarios.
1.2. Energy Recovery Modeling
We develop a numerical model for electric energy recovery from landfill gas using the Rankine–Hirn cycle [29] and Siemens D-R B Standard multi-stage steam turbine. This model estimates the potential energy recovery per ton of waste and energy gain per avoided ton of CO2-equivalent emissions, providing valuable insights into the feasibility of energy recovery in upper-middle-income countries.
1.3. Scenario Analysis
We model and simulate transformative scenarios, including the transition from uncontrolled landfilling to landfill gas flaring and, ultimately, to energy recovery. This approach provides tailored recommendations for upper-middle-income countries considering their unique waste compositions, climatic conditions, and socio-economic contexts.
2. Materials and Methods
As illustrated in Figure 3, the analysis began by applying the Waste Reduction Model (WARM) to evaluate greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions under three distinct waste management scenarios: (1) simple landfilling (business as usual), (2) landfill gas flaring, and (3) energy recovery. This step identifies the scenario with the highest potential for minimizing environmental impacts. For the energy recovery scenario, a detailed assessment was conducted to quantify methane (CH4) emissions. This involved employing the LandGem and IPCC models, which provided robust and validated estimations [30]. Finally, the potential for electrical energy recovery was evaluated, leading to the computation of a novel metric, i.e., the ratio of power generated to avoided GHG emissions, to assess the energy and environmental efficiency of the selected scenario.
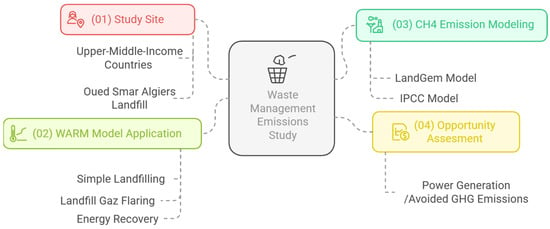
Figure 3.
Proposal method flowchart. Source: the authors.
2.1. Numerical Modeling and Simulations
2.1.1. Greenhouse Gas Emissions
To evaluate the impact of various waste management scenarios, we used the Waste Reduction Model (WARM) Version 16, developed by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) [31]. WARM is a widely recognized tool for assessing greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions and energy consumption associated with municipal solid waste management [32]. It allows for evaluating several waste management strategies, including source reduction, recycling, composting, landfilling, and combustion, enabling users to compare and analyze different scenarios. Numerous studies have demonstrated WARM’s effectiveness in identifying optimal waste management strategies and estimating GHG emissions and energy savings across diverse contexts [32,33,34]. Aligned with the IPCC 2006 guidelines for GHG inventories, WARM is recognized as a reliable tool for computing emissions from waste management systems [35]. Its user-friendly interface and ability to provide material-dependent, rapid, scenario-based assessments make it particularly valuable for decision-makers and stakeholders in developing sustainable waste management strategies.
WARM requires detailed data on the input fractions of individual materials in the waste stream, which are influenced by several factors, including cultural practices, economic development, climate, and energy sources [36,37]. Variability and uncertainty in waste stream composition can significantly affect assessments related to global warming potential, nutrient enrichment, and human toxicity [38]. To minimize these uncertainties and achieve a consistent composition, this study used waste composition data for upper-middle-income countries, provided by the World Bank [39], for the years 2012 and 2025. This ensured a more accurate assessment of waste management strategies and their related environmental impacts.
For the modeling, five material categories were considered: organic, paper, plastic, glass, metal, and others (which include all other municipal waste fractions). The composition and material categories used in the model are presented in Figure 3. This study utilized a functional unit of 1 ton of waste, and GHG emissions were expressed as tons of CO2-equivalent per ton of waste (ton CO2-eq/ton).
Three distinct scenarios were defined to facilitate a smooth transition from an uncontrolled baseline scenario, where waste streams are predominantly dumped or landfilled, to progressively more sustainable approaches. The second scenario incorporates landfill gas flaring, while the third relies on electrical energy recovery. These scenarios were analyzed for 2012 and 2025 waste compositions, consistent with the data provided in the aforementioned World Bank report, providing a comparative evaluation of their environmental impacts and sustainability potential.
2.1.2. Anaerobic Digestion and Biomethanation
Anaerobic digestion involves four stages: hydrolysis, acidogenesis, acetogenesis, and methanogenesis [40]. Hydrolysis is the first step in the conversion of organic material to biogas. In this stage, certain bacteria break down organic polymers like carbohydrates into simple sugars so that the next group of bacteria can further process the material. Hydrolysis refers to the cleavage of chemical bonds by the addition of water. Cations and anions react with water molecules, altering pH in the process to create the cleavage of H–O bonds. Hydrolysis is represented by the following equation:
Acidogenesis is the second step in the conversion of organic material to biogas. In this stage, certain bacteria, called acidogenic, convert simple sugars and amino acids into carbon dioxide, hydrogen, ammonia, and organic acids. This is the fermentation stage, where soluble compounds formed in the hydrolysis stage are degraded and converted into and by acidogenic bacteria (fermentative microorganisms); the important acid in this stage is , which is the most significant organic acid used as a substrate by CH4-forming microorganisms.
Acetogenesis is the third step in the conversion of organic materials to biogas. In this stage, certain bacteria, called acetogenic, convert organic acids into acetic acid, carbon dioxide, and hydrogen. The waste product of acetogenesis is the gas formed in the acidogenic stage of the AD process; hence, this stage is also known as the dehydrogenation stage.
Methanogenesis, or biological methanation, is a naturally occurring process that takes place in the later stages of digestion, in which organic material is microbiologically converted under anaerobic conditions to biogas [41]. Biomethanation involves three main physiological groups of microorganisms, namely, fermenting bacteria, organic-acid-oxidizing bacteria, and methanogenic archaea, which are strictly anaerobes highly vulnerable to small amounts of oxygen. The reactions of this conversion route are hydrogenotrophic methanogenesis and homoacetogenesis [42,43]. The solid and liquid leftover from this process, i.e., digestate, consists of material that the microbes cannot use and dead bacteria. Bacteria convert and into and .
The LandGem model [44] is first used to assess the yield of methane generated by the model landfilling. The model adopts a first-order equation for the decomposition rate, expressed by Equation (11).
In Equation (11), is the annual methane generation in the year of the computation (m3/year), is the methane generation rate (year−1), which is set at 0.050, is the potential methane generation capacity, which is set at 170 m3/ton, is the mass of waste accepted in the ith year (ton), and represents the age of ith section of waste mass accepted in the ith year. The index is incremented from 1 to , where refers to the difference between the year of computation and the year of waste acceptance.
The second model adopted in our study is IPCC, developed by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change [45]. This model considers the first-order decay equation shown in Equation (12).
where is the mass of decomposable degradable organic carbon at the start of the reaction, is the reaction constant, is time (years), and is the mass of decomposable degradable organic carbon at time .
The amount of decomposable organic carbon is computed by the model based on the yield of waste, as shown in Equation (13).
where is the mass of waste deposited in year “t”, is the degradable organic carbon under aerobic conditions, is the fraction of degradable organic carbon decomposing under anaerobic conditions, and is the methane correction factor.
The yield of deposited decomposable organic carbon remaining not decomposed at the end of deposition year “t”, is given by Equation (14).
Thus, the yield of deposited decomposable organic carbon during a deposition year “t”, is expressed according to Equation (15).
where is the month of reaction start, computed as the delay time in months .
Consequently, the yield of decomposable organic carbon accumulated at the end of deposition year “t”, is given by Equation (16).
The total yield of decomposed organic carbon in year “t”, is expressed by Equation (17).
The amount of methane generated from the decomposed organic carbon, is expressed as a function of the yield of decomposed organic carbon expressed earlier, as shown in Equation (18).
where represents the fraction of methane by volume of generated landfill gas and the ratio refers to the molecular weight ratio of methane to carbon.
Based on that, the total amount of emitted in year “t”, is given by:
where is the oxidation factor at year “t”, expressed as a fraction, is the mass of recovered methane in year “t”, and is the material fraction per waste category.
The model accounts for the cumulated deposited waste in the landfilling of Oued Smar reported in Figure 4, which is considered as a model site representing an upper-middle-income countries case, while Figure 5 shows cumulated deposited waste in the Oued Smar landfillling site–Algiers, Algeria
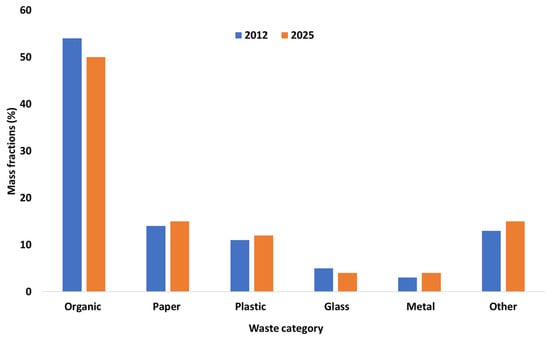
Figure 4.
Waste composition for upper-middle-income countries according to the World Bank [41].

Figure 5.
Cumulated deposited waste in the Oued Smar landfill site—Algiers, Algeria (opening: 1978, closing: 2003, covered duration: 80 years).
2.1.3. Electrical Energy Recovery
The possible electrical energy recovery from the emitted was studied through mathematical modeling and simulation based on the 11 MW Siemens D-R B standard multistage turbine; its characteristics are displayed in Table 1.

Table 1.
Characteristics of the 11 MW Siemens D-R B Standard multistage steam turbine.
The considered Hirn cycle uses a condensable fluid, which is cooled at an adequate temperature and pressure to be fully liquefied before compression. Under these conditions, the compression work is almost negligible compared to the expansion work. The compressed liquid is vaporized and superheated in the boiler by heat exchange with the hot source. In our case, the hot source consists of the heat coming from waste through the recovery of biogas and its combustion. The superheated water vapor is then expanded and condensed. The typical transformations taking place in this cycle are (i) the compression of water within a pump considered isentropic, (ii) the isobaric heating of liquid water in the two economizers, (iii) the isothermal vaporization in the vaporizer, (iv) the isobaric superheating of water vapors in the two superheaters, and, finally, (v) the isentropic expansion of vapors in the turbine.
In the first step, liquid water is supposed to be adiabatically compressed by the pump from P0 to P1 at a constant temperature, i.e., . The work needed for this compression is then:
where and are the enthalpies before and after the compression, expressed in kJ/kg, defined according to the enthalpy–pressure water diagram at the given pressures.
The second step after compression consists of the isobaric heating of water from T1 to T2 through the 1st and 2nd economizers. The heat needed for such a process is expressed as follows:
where represent the isobaric heat capacity of water as a function of temperature, expressed in J/kg·K.
The values of the constants appearing in Equation (23) are presented in Table 2.

Table 2.
Constant values of heat capacities.
The third step is the isothermal vaporization by pressure drop; the work needed for this transformation is:
In the fourth step, the water vapors go through the primary and secondary super heaters, passing from T3 to T4 at a constant pressure. The equations highlighting this step are:
where V3 and V4 are the specific volumes determined at the corresponding conditions, expressed in m3/kg.
In the last step, the obtained vapors enter the turbine and are expanded until P5. This expansion enables the turbine blades to rotate, producing a mechanical work expressed in the following equation:
where represents the isochoric heat capacity of water vapors as a function of temperature. The values of constants appearing in Equation (30) are given in Table 2.
The work of the Rankine–Hirn cycle is given by:
The mechanical power delivered by the cycle is given by:
where represents the mass flow rate of water used in the thermodynamic cycle and represents the mass flow rate of methane produced by the landfilling. is the molar enthalpy of methane combustion.
The efficiency is expressed as:
2.1.4. Techno-Ecological Assessment
The compromise of the technical performance of the energy recovery technique and its ecological impact were assessed through a novel metric expressed as the ratio of generated power per avoided GHG emissions, as shown in Equation (35).
where is the GHG emission from the considered scenario expressed in tons, i.e., CO2-eq/ton waste, according to WARM, while represents the emissions based on the electric energy recovery scenario. is the electric power recovered per ton of waste based on the LandGem and IPCC models. This metric was computed according to two transformative approaches: (i) from uncontrolled landfilling to energy recovery and (ii) from landfill gases flaring to energy recovery.
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Greenhouse Gas Emissions
The analysis of CO2 equivalent emissions across the three defined waste management scenarios (uncontrolled, LFG flaring, and energy recovery) provides important insights into the potential for reducing greenhouse gas emissions in the context of upper-middle-income countries. The results in terms of CO2 equivalent emissions expressed in tons of CO2 equivalent per ton of waste are presented in Figure 6a–c for the three scenarios.
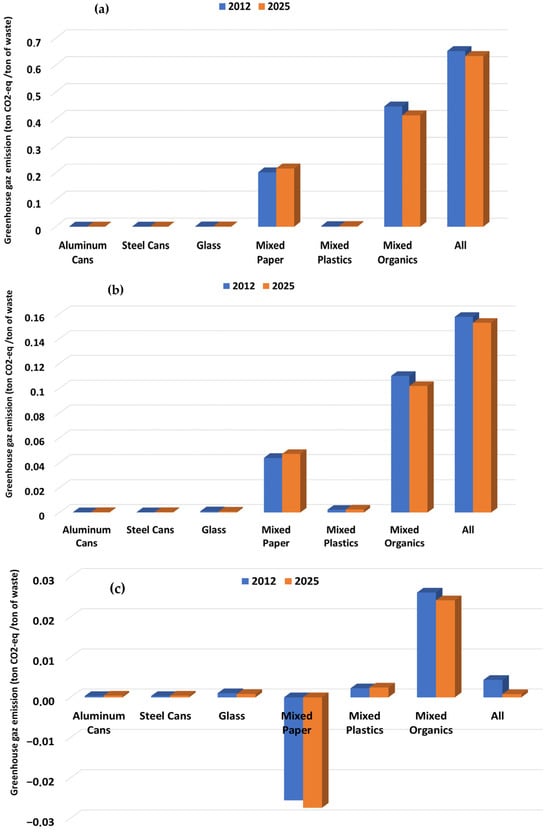
Figure 6.
Greenhouse gas emissions per ton of municipal waste considering uncontrolled landfilling (a), landfill gas flaring (b), and landfilling with energy recovery (c) in 2012 and 2025.
When comparing the “uncontrolled scenario” to the “LFG flaring” one, we notice a significant reduction in CO2 emissions by approximately 75.88%. This finding underscores the effectiveness of implementing LFG flaring as a strategy to mitigate greenhouse gas emissions associated with landfilling [46,47,48]. The substantial decrease is explained by the transition from methane gas emissions, which are 21-folds higher than an equivalent mass of CO2 emissions, which highlights the importance of adopting technologies that capture and combust landfill gas, thereby reducing the environmental impact of waste management practices. On the other hand, when transitioning from the uncontrolled scenario to the energy recovery scenario, the reduction in CO2 emissions exceeds 100%, indicating a negative emission potential of −0.0256 ton CO2/ton. This remarkable result points out the capacity of energy recovery processes not only to significantly reduce emissions but also to generate energy from waste. Such a transition promotes a circular economy, effectively diverting waste from landfills while simultaneously contributing to energy production.
When comparing the LFG flaring scenario with energy recovery for upper-middle-income countries, we find that energy recovery achieves a significantly greater reduction in CO2 emissions, with a drop of approximately 116.35%. This clearly demonstrates the superior benefits of energy recovery systems, which allow for a significant reduction in GHG emissions and also an optimization of resource recovery. In this context, studies show that LFG-to-energy transitions can cut emissions by 12% to 43% over a landfill’s lifespan [49]. For instance, in Cambodia, recovering electricity from LFG could lower emissions by as much as 83% compared to conventional landfilling [50]. Research from China reveals that LFG flaring can reduce emissions to 448–684 kg CO2-eq/t, while electricity production can further decrease this value to 214–277 kg CO2-eq/t [48]. A case study in Colombia also confirms that transitioning from open dumps or venting to LFG flaring or energy recovery significantly reduces global warming potential [51]. These findings highlight the crucial importance of shifting towards more sustainable waste management practices. Both landfill gas (LFG) flaring and energy recovery show significant potential in reducing CO2 equivalent emissions, especially when compared to the traditional, uncontrolled approach of landfilling.
Furthermore, the proportional drift in CO2 equivalent results in 2025 compared to 2012, as shown in Figure 6a–c, is due to a slight change in waste composition. This includes a decrease in organic content (Figure 3) and a corresponding increase in plastic, paper, and metal fractions. Since the primary source of CO2 emissions comes from the decomposition of organic matter, even a modest reduction in organic content results in a slight decrease in CO2 emissions. This reduction may be seen as diverting organic matter from landfilling, effectively considering it as avoided emissions, regardless of the waste management scenario.
3.2. Methane Emission: A Case Study
The results of estimating methane emissions over an 80-year period in the Oued Smar landfill site using the LandGem and IPCC models are shown in Figure 7. The time axis covers a period ranging from 1978, which is the site opening year, to 2058. The figure shows quasi-identical trends returned by both models for the evolutions of the methane emissions during the period 1978–1998, with a drastic increase from 0 to 10,000 tons of methane emitted from the Oued Smar site. The IPCC model (curve in blue) has a higher peak in methane emissions around 2003, with a value of 11,500 tons and a much faster decline than the LandGem model. A similar trend is observed in the LandGem model (orange curve), but the peak of around 10,600 tons is reached earlier in 1999; the emissions then gradually decrease until 2058. The decreasing rate is quasi-linear during this period according to the LandGem model, with an average rate of 160 tons of methane per year. The LandGem model demonstrates a slower decrease, suggesting a longer period of emissions than the IPCC model, which has a much faster slowdown.
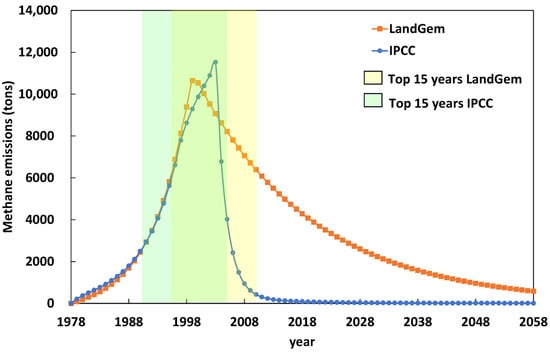
Figure 7.
Estimated methane emissions from the Oued Smar landfill according to the LandGem and IPCC models over 80 years. The yellow shaded area represents the most promising 15 years in terms of methane emissions according to the LandGem model, and the light blue shaded area represents the most promising 15 years in terms of methane emissions according to the LandGem model. The intersection of both periods is indicated by the light green shaded area.
The yellow shaded area in Figure 7 represents the most promising 15 years in terms of methane emissions according to the LandGem model, corresponding to the period ranging roughly between 1996 and 2010. According to the IPCC model, the 15 years characterized by the highest methane emissions are shown in the light blue shaded area between 1990 and 2005. Both models refer to the period from 1996 to 2005 as a common range for high methane emissions, with values comprised between 7000 and 11,000 tons of methane. These periods are mostly related to the opening and closing years of the landfilling (opening: 1978, closing: 2003), but also indirectly to the consumption habits of the population, which are affected by lifestyle, geography, and demography. The industrial revolution has also contributed to a certain orientation of consumption habits worldwide, including in upper-middle-income countries, in particular, Algeria. The most promising periods of methane emissions will be considered in the following section for the electrical energy recovery scenario.
3.3. Electrical Energy Recovery from Methanation
3.3.1. Rankine–Hirn Cycle Performance
The present section shows the results of simulations of a Rankine–Hirn cycle considering an 11 MW turbine and the recovery of methane produced from the Oued Smar landfill, based on the LandGem and IPCC models. The input parameters of the thermodynamic cycle are presented in Table 3.

Table 3.
The input parameters of an 11 MW Rankine–Hirn cycle.
The simulation results in terms of developed works and heats are reported in Table 4.

Table 4.
The simulation results of an 11 MW Rankine–Hirn cycle.
Based on the simulation results, the efficiency of the thermodynamic cycle, computed as the ratio of recovered electric power to the engaged heat power [52], is estimated at 36.01%. The thermodynamic cycle requires 1.493 MJ of heat per kg of water to operate. The combustion of methane is the heat source in our case; hence, according to the amount of methane generated yearly based on the LandGem and IPCC models, the available amount of heat per unit of time, i.e., the combustion power, is determined using Equation (33). The results are presented and discussed in the following section.
3.3.2. Electricity Generation
Figure 8 reports the heat power generated by methane combustion as a function of time over the 80-year period considered in the modeling of the methane emissions in the Oued Smar landfill site starting from 1978, based on the LandGem and IPCC models. Both models show an increase, a peak, and a decline in methane combustion heat over time. However, there are significant differences in the magnitude, timing, and duration of the maximum values between both models. According to the IPCC model, the heat of methane combustion peaks at around 20.3 MW in 2003, while based on the LandGem model, the heat of methane combustion peaks at around 18.7 MW, with a relative difference of 7.88%, but at an earlier time, around 1998. After the peak, the methane heat of combustion decreases rapidly, and the decrease is much faster in the IPCC model, with the same trends described earlier for methane emissions. These results are in good agreement with those demonstrated by Abdelli et al. [53] within the Algerian context.
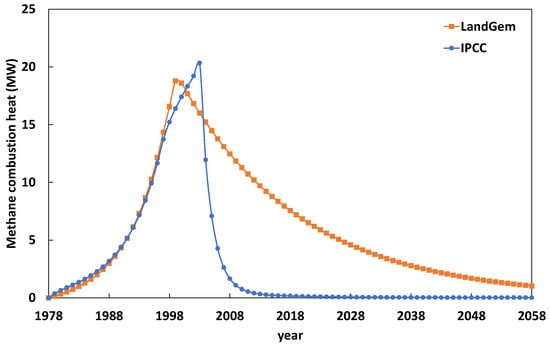
Figure 8.
Heat produced by methane combustion from the Oued Smar landfill according to the LandGem (orange line) and IPCC (blue line) models over 80 years starting from 1978 (opening year of the landfilling site).
As for the LandGem model, methane combustion is still active until 2058, whereas the IPCC model indicates no activity starting from 2020 onwards. Studies such as the one by Spokas et al. [54] claimed that methane oxidation rates and waste composition influence the behavior of methane emissions over the long term. This confirms the idea of long-term combustion, as indicated by the LandGem model. Scheutz et al. [55] pointed out that well-managed landfills equipped with gas collection systems show methane production curves similar to those predicted by the LandGem model, with methane emissions continuing for several decades, even after the landfill has reached its full capacity. LandGem’s slower decay curve is then consistent with the literature, showing that landfills continue to produce methane for a long time after they are closed because the anaerobic decomposition of waste can take several years or even decades to slow down.
The previous results reported in Figure 8 focus on the recoverable heat from the combustion of methane, without showing a direct link with the amount of solid waste responsible for the methanation. Thus, in the following figure (Figure 9), we suggest analyzing the amount of recoverable heat power divided by the amount of disposed solid waste in the landfilling site. This approach gives clear insights into the kinetics of energy recovery in parallel to solid waste disposal over time and offers a wider range of applicability for the present results by referring to the yield of solid waste disposed in the site rather than the site itself. Hence, an extrapolation to other sites with similar municipal solid waste composition (within upper-middle-income countries) becomes possible. The approach is applied considering both the LandGem and IPCC models.
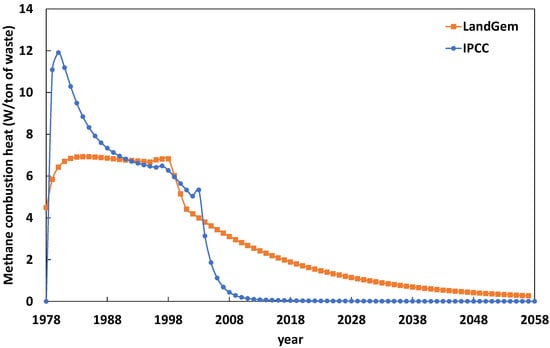
Figure 9.
Heat produced by methane combustion per ton of waste from the Oued Smar landfill according to the LandGem (orange line) and IPCC (blue line) models over 80 years starting from 1978 (opening year of the landfilling site).
Interestingly, the IPCC model shows that the highest recovery of energy per ton of disposed solid waste is achieved around the opening of the landfilling site, with values in the range of 7–12 W/ton during the period 1978–1988 (initial decade) and a maximum value achieved 4 years after opening (around 1982). According to the same model, the recoverable energy per ton of disposed solid waste decreases gradually during the period preceding the peak year of methane emissions, i.e., 2003, but abruptly drops afterward, until becoming negligible starting from 2008. In contrast, the LandGem model exhibits a considerable period of a steady-state regime in terms of recoverable energy per ton of disposed waste, which can be seen in Figure 9 as a plateau during the period 1978–1998 (almost 20 years). During this period, 6.8 W of heat is recoverable from each ton of disposed solid waste. Starting from 1998, which is the peak year of methane emissions according to the LandGem model, the amount of recoverable heat per ton of deposited solid waste gradually decreases, becoming null only around the end of the 80-year period. The hypotheses and approach of the LandGem model, which is more reflective of the reality within upper-middle-income countries, led to a more controllable operation of the landfilling site for energy recovery.
Finally, we discuss below the amounts of electrical power energy recovered from the site of Oued Smar using the Rankine–Hirn cycle presented earlier. Figure 10 shows a comparison of electrical power produced (in MW) during the 15 most productive years for methane emissions from the Oued Smar landfill using both the LandGem (blue bars) and IPCC (orange bars) models. Overall, the LandGem model predicts slightly higher values of generated powers than the IPCC model, though distinguishing trends of most productive years are visible. In particular, in the LandGem model, the highest power is produced in the fifth year, reaching a value of almost 7 MW. With the IPCC model, the electricity production peaks around year 13, slightly above 6 MW. In addition, the IPCC model shows more significant variations, with values of generated power starting at low levels (less than 2 MW in year 2) and increasing steadily until year 15. Referring to the Sonelgaz power project expected in the Oued Smar landfill, a peak of 6 MW of generated electrical power was announced [53], which is in the same order of magnitude as the results yielded by the present simulations. The results of energy recovery are thus validated.
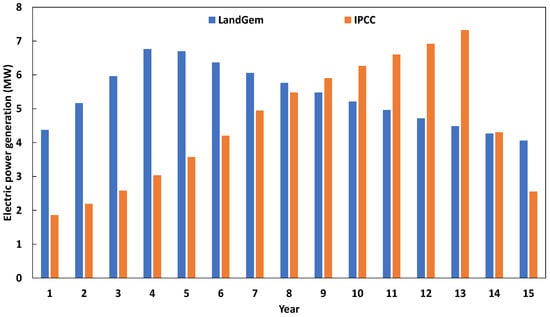
Figure 10.
Electrical power generated by the Oued Smar landfill during the 15 top CH4 production years according to the LandGem (blue line) and IPCC (orange line) models.
Technically speaking, the LandGem model predicts slightly higher values of generated electrical power, explained by the slower decay in methane emissions and, hence, the higher availability of methane for combustion over time.
3.3.3. Techno-Ecological Assessment
In the present section, the opportunity for energy recovery by transitioning from uncontrolled landfilling or landfill gas flaring to electricity production is directly linked to the ecological impact using a novel metric expressed as the ratio of generated electrical power to the amount of avoided GHG emissions when applying the considered transition.
The significance of the proposed metric requires broader cases of application with varied conditions and even other transition scenarios. Nonetheless, it is advanced here as a first instance with the aim of presenting preliminary results and perspectives for future studies.
3.3.4. First Transformative Approach: From Uncontrolled Landfilling to Energy Recovery
We first consider the scenario of a transition from uncontrolled landfilling to electricity generation (here called energy recovery). The proposed metric is computed based on the results retrieved with the LandGem and IPCC models in 2012 and 2025, which are the two reference years adopted by the World Bank report [41]. Figure 11 clearly shows that the LandGem model leads to the highest values of recoverable energy per ton of avoided GHG emissions, with 0.87 W/avoided ton CO2-Eq in 2012 and 0.89 W/avoided ton CO2-Eq in 2025. This slight difference is explained by the change in domestic solid waste composition predicted by the same report [39]. The IPCC model returns almost half of the previous values, with 0.41 and 0.42 W/avoided ton CO2-Eq computed in 2012 and 2025, respectively. Based on earlier results, the LandGem model returns results that are closer to reality. Thus, transitioning from the current state of uncontrolled landfilling to electrical energy recovery would offer a reduction of 99.87% in GHG emissions with a generated power of 0.89 W per each ton of CO2-eq of avoided emissions by 2025.
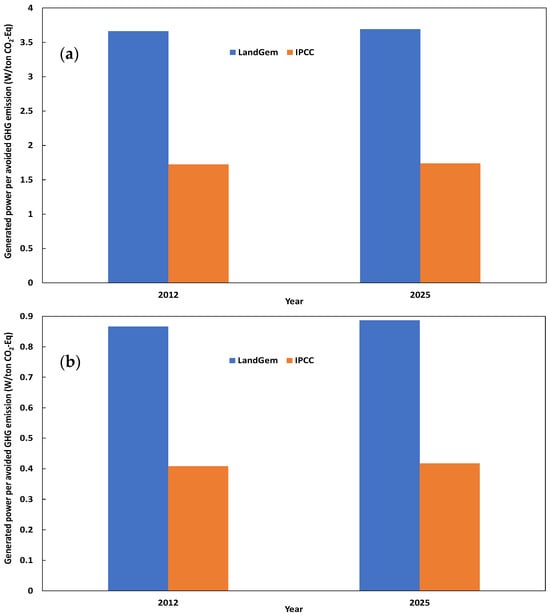
Figure 11.
Electrical power generated per ton of CO2-Eq of avoided GHG emissions when passing from uncontrolled landfilling to landfilling with energy recovery (a) and when passing from landfilling with landfill gas flaring to landfilling with energy recovery (b) according to the LandGem (blue bars) and IPCC (orange bars) models in 2012 and 2025.
3.3.5. Second Transformative Approach: From Landfill Gases Flaring to Energy Recovery
The second considered scenario supposes a transition from landfill gas flaring to electricity generation. The results show that the LandGem model returns values of 3.66 and 3.69 W/avoided ton CO2-Eq in 2012 and 2025, respectively, while the IPCC model predicts only 1.72 and 1.73 W/avoided ton CO2-Eq in 2012 and 2025, respectively. It is then confirmed that the LandGem model hypotheses, which are relatively reliable and verified [56], lead to the most affordable scenarios of energy recovery from landfilling sites. Compared to the direct transition from uncontrolled landfilling to electrical energy recovery, the gradual transformation passing through landfill gas flaring would first reduce 75.90% of GHG emissions. The second transformation would then consist of the transition from gas flaring to electrical energy recovery, accompanied by a reduction of 23.97% of GHG emissions (relative to the uncontrolled landfill scenario) and a generation of 3.69 W per each ton of CO2-eq of avoided emissions in the second transition by 2025.
4. Discussion
To provide a comprehensive and scientifically grounded perspective, a cross-sectional analysis of analogous studies conducted in various middle-income countries was undertaken. Research indicates that landfill gas-to-energy (LFGTE) projects have demonstrated significant potential in mitigating greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions while concurrently serving as a sustainable energy source. This is proved by case studies from regions like Brazil, Turkey, Hungary, Romania, and other countries, which highlight the environmental and economic benefits of such initiatives.
4.1. The Brazilian Example
In Brazil, LFGTE initiatives have been shown to offer substantial benefits in terms of GHG reduction and energy generation. For instance, studies estimate that the implementation of sanitary landfills in the southeast region could yield 11,795.7 gigawatt-hours (GWh) of electricity over a 20-year period while simultaneously reducing CO2 emissions by an average of 467.1 million metric tons annually [57]. A notable example of large-scale energy production from waste management is the Bandeirantes Biogas Plant in São Paulo, which exemplifies the feasibility and environmental benefits of such projects [58]. Furthermore, research conducted on a landfill in Rio de Janeiro highlighted that even basic flaring of landfill gases can lead to a significant reduction in methane emissions, underscoring the importance of methane capture and utilization in waste management systems [59].
4.2. The Turkish Example
Similarly, in Turkey, LFGTE projects have demonstrated both technical and economic feasibility. The Istanbul landfill gas project, for example, has shown significant reductions in GHG emissions alongside substantial increases in energy production. Studies estimated that utilizing all municipal solid waste (MSW) for landfill gas collection could meet approximately 1% of Turkey’s energy deficit by 2023 [60]. Assessments of various landfill areas have further validated the feasibility of these projects, considering factors such as gas production potential, energy capacity, and production costs [61]. The waste-to-energy sector in Turkey is relatively new, with a focus on landfill gas-to-power projects and an estimated potential of 750 MW for electricity generation [62]. Comparative analyses of waste management scenarios have shown that thermal conversion and material recycling are the most effective options for reducing climate change impacts, with incineration potentially saving up to 652,626 tCO2e y⁻¹ in emissions [63].
4.3. The Hungarian and Romanian Examples in Eastern Europe, in Relation to the German Example
In the Karlsruhe port on the Rhine, the former landfill became a so-called energy mountain. A student project co-authored by M. Bostenaru Dan was proposed as early as 1998 to convert the north of the port into a green area, along with greening the city of Karlsruhe, as port activities became more efficient and demanded less surface. The proposal was to use biodegradable geosynthetics. In 2002, a windmill was placed on the deposit, and since 2005, when a landfill ban law was introduced and no solid waste could be placed on its surface anymore, waste started to be transported along the Rhine to Mannheim for incineration. The number of windmills grew to four, while two were due to be replaced with a more efficient one with the help of the local technical university. Also, solar panels were placed on the southern slope of the landfill, and gas from the landfill was used for heating. This kind of renewable energy was the topic of the COST action “Renewable energy and landscape quality” led by a chair from the same federal land (Baden-Württemberg) in Germany, where the topic is very important since the ecological party is led through the prime minister of this particular federal land. So, the proposal of “energy mountain” (formerly “windmill mountain”) [64] can be easily related to the landscape/nature proposal from the student project. In the meantime, due to the recent cuts of Russian gas from Germany, the country has to rely now more and more on renewable energy given that nuclear and coal power plants are being dismantled.
In Pusztazamor, near Budapest, a similar proposal for wind, solar, and gas energy from landfills was studied by Emoke et al. [65]. Similar to the proposal in Germany, in Romania, geosynthetics are used in the conversion of landfills to environmentally friendly uses, as described in the studies of Mircea and Niculae [66,67].
From personal communication with Prof. Feodorov in Romania [68], there is currently a transition from the traditional formula of municipal waste burial to waste valorization plants, the so-called TMBs or Mechanical Biological Treatment plants. In an MBT, municipal waste is sorted; first, the recyclable waste (plastic, metal, glass, cardboard, textiles) is extracted, and out of what remains, about 55% is biodegradable waste. Biodegradable waste is first processed in anaerobic biodigestion plants with biogas extraction. The biogas is used to produce electricity and/or heat. Finally, the biodigestate (resulting from biodigesters) is composted in aerobic composting plants. Compost is used in agriculture, forestry, improvements in arid and desertified land, etc. This is the general functioning of a TMB.
4.4. Cross-Country Insights and Methodological Validation
In general, the findings of these case studies are consistent with broader trends observed in other middle-income countries. For instance, the trend identified using the LandGem model aligns with the findings of Fallahizadeh et al. [44], who simulated methane emissions from the Yasuj Landfill in Iran. In the same vein, Ramprasad et al. [69] applied the same model to evaluate methane emissions from the Tirupati municipal solid waste disposal site in India, revealing comparable temporal trends. Atabi et al. [70] further validated these findings by estimating methane emissions from the Kahrizak Landfill in Iran and comparing model predictions with experimental methane recovery rates recorded between 1994 and 2004. A similar approach was employed by Alam et al. [71] in their analysis of an open dumping site in Lahore, Pakistan.
However, challenges persist in regions with limited data availability. For example, in the case of the Oued Smar landfill in Algeria, direct comparison with experimental results is hindered by the lack of long-term methane emission data, which is a common issue in developing countries (particularly in African countries). Friedrich and Trois [8] highlighted the absence of a coherent framework for GHG accounting at the municipal level as a significant barrier to effective waste management and emission reduction strategies.
Methodological differences also influence emission estimates. As an example, Abdelli et al. [53] demonstrated that the IPCC model predicts a faster decline in methane emissions over time compared to the LandGem model. While the IPCC model may overestimate the rate of decay, the LandGem model appears to provide a more accurate representation of methane emission trends, as evidenced by ongoing emissions recorded at the Oued Smar landfill.
4.5. Challenges and Policy Implications
While the potential benefits of energy recovery from landfills are significant, there are several challenges that must be addressed in order to facilitate the transition from uncontrolled landfilling to energy recovery, particularly for countries that have ratified the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) and submitted their Determined National Contributions (DNCs). These commitments underscore the urgency of adopting sustainable waste management practices, including landfill gas (LFG) flaring and energy recovery, to meet national and international climate goals. Many countries have included waste-related mitigation strategies in their NDCs, with landfilling and waste-to-energy being the most common approaches [72].
4.6. Financial Constraints
In general, waste management has always been considered an expensive service requiring investments. As an example, the average percentage of municipal expenditures on solid waste management is approximately 11% for middle-income countries [73]. According to the World Bank, in order to manage the increasing global waste generation effectively, which is estimated to increase to 3.4 billion tons by 2050, an estimated 1000 new waste-to-energy (WtE) plants would be needed globally by 2050, assuming an average capacity of 500.000 tons per plant. However, the cost of these plants may vary depending on the technology and the conditions of the targeted country. For instance, a WtE plant with a capacity of 40.000 tons per annum (tpa) costs about USD 41 million, or USD 1026 per ton of annual capacity, and a medium-sized WtE plant with 250.000 tpa costs about USD 169 million, or USD 680 per ton of annual capacity [74].
For example, as an upper-middle-income country (UMIC), India generates around 58 million tons of MSW annually [75] and aims to build WtE plants to process this waste, targeting 500 MW of energy from waste by 2025 [76]. India would require approximately 100–150 WtE plants (according to the ratio of total waste generation/capacity per plant), which can be estimated at USD 102 to 420 million per plant [77,78].
Another example is Brazil, where recent data showed that the MSW generated was about 81.8 million tons, out of which 76.1 million tons were collected (93.0%) [79]. To manage this amount of waste, the country would need around 160 WtE plants, which may cost about USD 150 to 300 million per plant. In fact, recent reports summarized the fact that Brazil has the potential to build the equivalent of 118 WTE pants of 20 Mwe/plant in 28 metropolitan regions with 1 million inhabitants and 73 WTE plants in 25 municipalities with more than 600,000 inhabitants [80].
However, the financing of such large-scale investments can be challenging. To address these issues, governments and international organizations play a pivotal role in overcoming these challenges by providing financial support, subsidies, or tax incentives to encourage private sector participation in such projects. For example, mechanisms like the Clean Development Mechanism (CDM) under the Kyoto Protocol have successfully funded landfill gas (LFG)-to-energy projects in developing countries [81,82], emphasizing the potential for similar frameworks to support Algeria and other upper-middle-income countries in transitioning to sustainable waste management. Additionally, climate finance is critical for enabling developing nations to meet their Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs) under the Paris Agreement, as access to international public climate funds is essential for reducing emissions and implementing climate-related initiatives [83]. The integration of Emission Trading Schemes (ETSs) and carbon markets into NDCs also offers developing countries opportunities to access carbon finance, further supporting their climate mitigation efforts [83]. These financial mechanisms, combined with international cooperation, can significantly enhance the capacity of developing and upper-middle-income countries to adopt sustainable waste management practices and achieve their climate goals.
4.7. Technical Expertise and Regulatory Frameworks
As described before, the successful implementation of energy recovery technologies in upper-middle-income countries is hindered by significant challenges, particularly the lack of technical expertise [84]. Effective technology transfer, which is essential for overcoming these barriers, is often misunderstood and inadequately executed, as it requires more than the simple delivery of equipment. For technology transfer to be successful, it must encompass critical factors such as affordability, sustainable maintenance plans, comprehensive knowledge transfer, and local ownership to ensure long-term viability. Moreover, the deployment of energy recovery technologies in developing and upper-middle-income countries demands a holistic approach, integrating technical equipment, knowledge, skills, and organizational procedures. Initiatives like the Global Methane Initiative (GMI) have sought to promote methane recovery through partnerships between developed and developing nations [85]. However, many existing initiatives fail to address key components of knowledge transfer and are less common in climate-vulnerable countries, limiting their effectiveness [86].
4.8. Limitations and Future Research
Even though this study provides valuable insights into the potential of LFGTE projects in upper-middle-income countries, it also has some limitations that should be emphasized:
- (i)
- The reliance on the LandGEM and IPCC models introduces uncertainties due to assumptions about waste composition, degradation rates, and methane generation potential, which may not fully capture real-world variability. Moreover, the previous models do not adequately consider complex multi-source interactions that influence methane transport. Recent research [87] on reactive solute transport suggests that integrating boundary and internal source dynamics into multi-source models could enhance predictive accuracy, providing a potential avenue for refining landfill gas emission assessments.
- (ii)
- The case study of the Oued Smar landfill in Algeria may not be fully representative of other regions (which can limit the generalization of findings).
- (iii)
- This study focuses primarily on technical and ecological aspects, with limited consideration of economic feasibility, social acceptance, and policy frameworks, which are important for the successful implementation of LFGTE projects.
In the end, the proposed techno-ecological metric, even though it is innovative, requires further validation in diverse contexts to ensure its applicability.
5. Conclusions
Our study presents and applies an integrated approach to estimate greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions, specifically methane, and evaluate the potential for electrical energy recovery from municipal solid waste (MSW) landfilling sites in upper-middle-income countries. Three scenarios were analyzed: uncontrolled landfilling, landfill gas (LFG) flaring, and energy recovery. The results demonstrate that transitioning from the “uncontrolled landfill scenario” to the “LFG flaring” scenario achieves a significant reduction in CO2 emissions of approximately 75.90%, while transitioning to the “energy recovery” scenario results in an even greater reduction of 99.87%.
The case study of the Oued Smar landfill site, analyzed using both the LandGem and IPCC models, revealed a drastic increase in methane emissions during the first 20 years of operation. However, the IPCC model predicted a higher peak in methane emissions, occurring later, followed by a much faster decline compared to the LandGem model. The LandGem model’s predictions align more closely with real-world conditions, as the anaerobic decomposition of waste typically occurs over several years or even decades, leading to a slower decline in methane emissions.
Interestingly, the IPCC model indicates that the highest energy recovery per ton of deposited solid waste occurs shortly after opening the landfill. According to this model, recoverable energy decreases gradually until the peak methane emission year (2003), after which it drops abruptly. In contrast, the LandGem model shows a steady state of recoverable energy per ton of deposited waste for nearly 20 years, followed by a gradual decline until the end of the 80-year period. This suggests that the LandGem model provides a more realistic and controllable framework for energy recovery operations in landfilling sites.
Finally, the proposed “techno-ecological” metric, which evaluates the ratio of energy recovery to avoided GHG emissions, demonstrates that the LandGem model yields values twice greater than those obtained with the IPCC model. This confirms that the hypotheses of the LandGem model led to more realistic and economically feasible scenarios for energy recovery from landfills. Accordingly, transitioning from uncontrolled landfilling to electrical energy recovery could reduce GHG emissions by 99.87%, with a generated power of 0.89 W per ton of CO2-eq avoided by 2025.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, H.C., K.K. and C.F.B.; methodology, H.C., K.K. and I.G.; validation, H.A.A. and A.-I.P.; formal analysis, H.C.; investigation, K.K.; resources, H.C. and K.K.; data curation, I.G. and K.K.; writing—original draft preparation, H.C., K.K., C.F.B., I.G., M.B.-D. and H.A.A.; writing—review and editing, K.K., C.F.B., H.A.A. and A.-I.P.; visualization, K.K.; supervision, M.B.-D. and A.-I.P.; project administration, K.K.; funding acquisition, H.C., K.K., H.A.A., M.B.-D. and A.-I.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
All data used in this study are available in this manuscript.
Acknowledgments
We thank the National Higher School of Technology and Engineering and the Environmental Research Center (CRE) for their support. We thank also the General Directorate of Scientific Research and Technological Development—Algeria (DGRSDT).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders or institutions had no role in the design of this study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of this manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Roy, H.; Alam, S.R.; Bin-Masud, R.; Prantika, T.R.; Pervez, M.N.; Islam, M.S.; Naddeo, V. A Review on Charac-teristics, Techniques, and Waste-to-Energy Aspects of Municipal Solid Waste Management: Bangladesh Perspective. Sustain. Switz. 2022, 14, 10265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abubakar, I.R.; Maniruzzaman, K.M.; Dano, U.L.; AlShihri, F.S.; AlShammari, M.S.; Ahmed, S.M.S.; Al-Gehlani, W.A.G.; Alrawaf, T.I. Environmental Sustainability Impacts of Solid Waste Management Practices in the Global South. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2022, 19, 12717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jouhara, H.; Malinauskaite, J.; Spencer, N. Waste Prevention and Technologies in the Context of the EU Waste Framework Directive: Lost in Translation? Eur. Energy Environ. Law Rev. 2017, 26, 66–80. [Google Scholar]
- Eisted, R.; Christensen, T.H. Characterization of Household Waste in Greenland. Waste Manag. 2011, 31, 1461–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Hu, M.; Di Maio, F.; Sprecher, B.; Yang, X.; Tukker, A. An Overview of the Waste Hierarchy Frame-work for Analyzing the Circularity in Construction and Demolition Waste Management in Europe. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 803, 149892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Razzaq, A.; Sharif, A.; Najmi, A.; Tseng, M.-L.; Lim, M.K. Dynamic and Causality Interrelationships from Mu-nicipal Solid Waste Recycling to Economic Growth, Carbon Emissions, and Energy Efficiency Using a Novel Boot-strapping Autoregressive Distributed Lag. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2021, 166, 105372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crippa, M.; Guizzardi, D.; Pagani, F.; Banja, M.; Muntean, M.; Schaaf, E.; Monforti-Ferrario, F.; Becker, W.; Quadrelli, R.; Risquez Martin, A.; et al. CO₂ Emissions of All World Countries; European Union: Brussels, Belgium, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Friedrich, E.; Trois, C. Quantification of Greenhouse Gas Emissions from Waste Management Processes for Municipalities - A Comparative Review Focusing on Africa. Waste Manag. 2011, 31, 1585–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihai, F.-C.; Taherzadeh, M.J. Introductory Chapter: Rural Waste Management Issues at Global Level. In Solid Waste Management in Rural Areas; Mihai, F.-C., Ed.; InTech: Houston, TX, USA, 2017; ISBN 978-953-51-3485-5. [Google Scholar]
- Vincevica-Gaile, Z.; Burlakovs, J.; Fonteina-Kazeka, M.; Wdowin, M.; Hanc, E.; Rudovica, V.; Krievans, M.; Grinfelde, I.; Siltumens, K.; Kriipsalu, M.; et al. Case Study-Based Integrated Assessment of Former Waste Disposal Sites Transformed to Green Space in Terms of Ecosystem Services and Land Assets Recovery. Sustainability 2023, 15, 3256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamaruddin, M.A.; Norashiddin, F.A.; Hanif, M.H.M.; Shadi, A.M.H.; Yusoff, M.S.; Wang, L.K.; Wang, M.-H.S. Characterization and Measurement of Solid Waste; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Abderrahim, Y.; Bellal, S.E.; Sahnoun, M. Comparative Study of Waste Management Systems in Algeria and Other Countries : A Literature Review. In Proceedings of the 2023 International Conference on Decision Aid Scienc-es and Applications (DASA), Annaba, Algeria, 16 September 2023; IEEE: New York, NY, USA; pp. 164–169. [Google Scholar]
- Cheniti, H.; Kerboua, K.; Sekiou, O.; Aouissi, H.A.; Benselhoub, A.; Mansouri, R.; Zeriri, I.; Barbari, K.; Gilev, J.B.; Bouslama, Z. Life Cycle Assessment of Municipal Solid Waste Management within Open Dumping and Landfilling Contexts: A Strategic Analysis and Planning Responses Applicable to Algeria. Sustainability 2024, 16, 6930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Shemmeri, T.T. Thermodynamics, Performance Analysis and Computational Modelling of Small and Micro Com-bined Heat and Power (CHP) Systems; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Torkayesh, A.E.; Rajaeifar, M.A.; Rostom, M.; Malmir, B.; Yazdani, M.; Suh, S.; Heidrich, O. Integrating Life Cycle Assessment and Multi Criteria Decision Making for Sustainable Waste Management: Key Issues and Recom-mendations for Future Studies. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2022, 168, 112819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozbay, G.; Jones, M.; Gadde, M.; Isah, S.; Attarwala, T. Design and Operation of Effective Landfills with Min-imal Effects on the Environment and Human Health. J. Environ. Public Health 2021, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scharff, H.; Soon, H.-Y.; Taremwa, S.R.; Zegers, D.; Dick, B.; Zanon, T.V.B.; Shamrock, J. The Impact of Landfill Management Approaches on Methane Emissions. Waste Manag. Res. 2023, 42, 1052–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shovon, S.M.; Akash, F.A.; Rahman, W.; Rahman, M.A.; Chakraborty, P.; Hossain, H.M.Z.; Monir, M.U. Strate-gies of Managing Solid Waste and Energy Recovery for a Developing Country—A Review. Heliyon 2024, 10, e24736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Muchangos, L.S.; Tokai, A.; Hanashima, A. Greenhouse Gas Emissions and Cost Assessments of Municipal Solid Waste Treatment and Final Disposal in Maputo City. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2017, 21, 145–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djemaci, B. La Gestion Des Déchets Municipaux En Algérie: Analyse Prospective et Éléments d’efficacité. Bachelor’s Thesis, Université de Rouen, Rouen, France, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Gunsilius, E.; Spies, S.; García-Cortés, S.; Medina, M.; Dias, S.; Scheinberg, A.; Sabry, W.; Abdel-Hady, N.; dos Santos, A.-L.F.; Ruiz, S. Recovering Resources, Creating Opportunities. Integrating the Informal Sector into Solid Waste Management; Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ) GmbH: Eschborn, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Ghanimeh, S.; Gómez-Sanabria, A.; Tsydenova, N.; Štrbová, K.; Iossifidou, M.; Kumar, A. Two-Level Compari-son of Waste Management Systems in Low-, Middle-, and High-Income Cities. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2019, 36, 1281–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GRIFFITHS, U.K.; LEGOOD, R.; PITT, C. Comparison of Economic Evaluation Methods Across Low-Income, Middle-Income and High-Income Countries: What Are The Differences and Why? Health Econ. 2016, 25, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siddiqua, A.; Hahladakis, J.N.; Al-Attiya, W.A.K.A. An Overview of the Environmental Pollution and Health Effects Associated with Waste Landfilling and Open Dumping. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 58514–58536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaverková, M.D. Landfill Impacts on the Environment— Review. Geosci. Switz. 2019, 9, 431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Sharma, M.P. Estimation of GHG Emission and Energy Recovery Potential from MSW Landfill Sites. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2014, 5, 50–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kebaili, F.K.; Baziz-Berkani, A.; Aouissi, H.A.; Mihai, F.-C.; Houda, M.; Ababsa, M.; Azab, M.; Petrisor, A.-I.; Fürst, C. Characterization and Planning of Household Waste Management: A Case Study from the MENA Region. Sustainability 2022, 14, 5461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eddine, B.; Salah, M. Solid Waste as Renewable Source of Energy: Current and Future Possibility in Algeria. Int. J. Energy Environ. Eng. 2012, 3, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danel, Q. Étude Numérique et Expérimentale d’un Cycle de Rankine-Hirn de Faible Puissance Pour La Récu-pération d’énergie; Conservatoire National des Arts et Metiers—CNAM: Paris, France, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.; Yuan, W.; Xie, Y.; Fei, X.; Ren, F.; Wei, Y.; Jiao, G.; Li, M. Simulating CH4 Emissions from MSW Land-fills in China from 2003 to 2042 Using IPCC and LandGEM Models. Heliyon 2023, 9, e22943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency Waste Reduction Model (WARM). 2024. Available online: https://www.Epa.Gov/Warm (accessed on 13 January 2025).
- De Medeiros Engelmann, P.; Dos Santos, V.H.J.M.; Da Rocha, P.R.; Dos Santos, G.H.A.; Lourega, R.V.; De Lima, J.E.A.; Pires, M.J.R. Analysis of Solid Waste Management Scenarios Using the WARM Model: Case Study. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 345, 130687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costello, C.; McGarvey, R.; Birisci, E. Achieving Sustainability beyond Zero Waste: A Case Study from a Col-lege Football Stadium. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riedel, L.M. Environmental and Financial Impact of a Hospital Recycling Program. AANA J. 2011, 79, S8-14. [Google Scholar]
- Mohareb, E.A.; MacLean, H.L.; Kennedy, C.A. Greenhouse Gas Emissions from Waste Management—Assessment of Quantification Methods. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2011, 61, 480–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nizar, M.; Munir, E.; Munawar, E.; Irvan, I. Analysis of the Composition of Household Waste from the Com-munity within the Framework of a Waste Prevention and Reduction Strategy. Ecol. Eng. Environ. Technol. 2021, 22, 91–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zorpas, A.A.; Lasaridi, K.; Voukkali, I.; Loizia, P.; Chroni, C. Household Waste Compositional Analysis Varia-tion from Insular Communities in the Framework of Waste Prevention Strategy Plans. Waste Manag. 2015, 38, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slagstad, H.; Brattebø, H. Influence of Assumptions about Household Waste Composition in Waste Manage-ment {LCAs}. Waste Manag. 2013, 33, 212–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daniel Hoornweg and Perinaz Bhada-Tata. What a Waste: A Global Review of Solid Waste; World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Anukam, A.; Mohammadi, A.; Naqvi, M.; Granström, K. A Review of the Chemistry of Anaerobic Digestion: Methods of Accelerating and Optimizing Process Efficiency. Processes 2019, 7, 504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelidaki, I.; Karakashev, D.; Batstone, D.J.; Plugge, C.M.; Stams, A.J.M. Biomethanation and Its Potential. In Methods in Methane Metabolism, Part A; Rosenzweig, A.C., Ragsdale, S.W.B.T.-M.i.E., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2011; Volume 494, pp. 327–351. ISBN 0076-6879. [Google Scholar]
- LeeWays, C.; McCullough, L.L.; Hopple, A.M.; Keller, J.K.; Bridgham, S.D. Homoacetogenesis Competes with Hydrogenotrophic Methanogenesis for Substrates in a Peatland Experiencing Ecosystem Warming. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2022, 172, 108759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serna-García, R.; Tsapekos, P.; Treu, L.; Bouzas, A.; Seco, A.; Campanaro, S.; Angelidaki, I. Unraveling Preva-lence of Homoacetogenesis and Methanogenesis Pathways Due to Inhibitors Addition. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 376, 128922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fallahizadeh, S.; Rahmatinia, M.; Mohammadi, Z.; Vaezzadeh, M.; Tajamiri, A.; Soleimani, H. Estimation of Methane Gas by LandGEM Model from Yasuj Municipal Solid Waste Landfill, Iran. MethodsX 2019, 6, 391–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grisales, C.M.; Salazar, L.M.; Garcia, D.P. Treatment of Synthetic Dye Baths by Fenton Processes: Evaluation of Their Environmental Footprint through Life Cycle Assessment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 4300–4311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurniawan, T.A.; Liang, X.; Singh, D.; Othman, M.H.D.; Goh, H.H.; Gikas, P.; Kern, A.O.; Kusworo, T.D.; Shoqeir, J.A. Harnessing Landfill Gas (LFG) for Electricity: A Strategy to Mitigate Greenhouse Gas (GHG) Emissions in Jakarta (Indonesia). J. Environ. Manage. 2022, 301, 113882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanisavljević, N.; Ubavin, D.; Batinić, B.; Fellner, J.; Vujić, G. Methane Emissions from Landfills in Serbia and Potential Mitigation Strategies: A Case Study. Waste Manag. Res. J. Sustain. Circ. Econ. 2012, 30, 1095–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, N.; Zhang, H.; Shao, L.-M.; Lü, F.; He, P.-J. Greenhouse Gas Emissions during MSW Landfilling in China: Influence of Waste Characteristics and LFG Treatment Measures. J. Environ. Manage. 2013, 129, 510–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menikpura, S.; Sang-Arun, J.; Bengtsson, M. Climate Co-Benefits of Energy Recovery from Landfill Gas in De-veloping Asian Cities: A Case Study in Bangkok. Waste Manag. Res. J. Sustain. Circ. Econ. 2013, 31, 1002–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pheakdey, D.V.; Noudeng, V.; Xuan, T.D. Landfill Biogas Recovery and Its Contribution to Greenhouse Gas Mitigation. Energies 2023, 16, 4689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caicedo-Concha, D.M.; Sandoval-Cobo, J.J.; Stringfellow, A.; Colmenares-Quintero, R.F. An Evaluation of Fi-nal Disposal Alternatives for Municipal Solid Waste through Life Cycle Assessment: A Case of Study in Colombia. Cogent Eng. 2021, 8, 1956860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badr, O.; Probert, S.D.; O’Callaghan, P.W. Selecting a Working Fluid for a Rankine-Cycle Engine. Appl. Energy 1985, 21, 1–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelli, I.S.; Addou, F.Y.; Dahmane, S.; Abdelmalek, F.; Addou, A. Assessment of Methane Emission and Eval-uation of Energy Potential from the Municipal Solid Waste Landfills. Energy Sources Part Recovery Util. Environ. Eff. 2020, 46, 15688–15707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spokas, K.; Bogner, J.; Chanton, J.P.; Morcet, M.; Aran, C.; Graff, C.; Golvan, Y.M.-L.; Hebe, I. Methane Mass Balance at Three Landfill Sites: What Is the Efficiency of Capture by Gas Collection Systems? Waste Manag. 2006, 26, 516–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheutz, C.; Pedersen, G.B.; Costa, G.; Kjeldsen, P. Biodegradation of Methane and Halocarbons in Simulated Landfill Biocover Systems Containing Compost Materials. J. Environ. Qual. 2009, 38, 1363–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafey, A.; Siddiqui, F.Z. Modelling and Simulation of Landfill Methane Model. Clean. Energy Syst. 2023, 5, 100076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moraes, C.A.; Santos, L.D.L.C.D.; Oliveira, A.C.L.D.; Botelho, D.F.; Moltó Berenguer, J.; Renato, N.D.S. Biogas-Based Electricity Production from Landfills in Places of Irregular Disposal: Overview for the Southeast Region of Brazil. Energy 2024, 290, 130161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Barros Miranda Gomes, M.; Sacomano, J.B.; Papalardo, F.; da Silva, A.E. Production of Sustainable Electricity in Landfills: The Case of the Bandeirantes Landfill. In Advances in Production Management Systems. Innovative and Knowledge-Based Production Management in a Global-Local World; Grabot, B., Vallespir, B., Gomes, S., Bouras, A., Kiritsis, D., Eds.; IFIP Advances in Information and Communication Technology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; Volume 439, pp. 366–373. ISBN 978-3-662-44736-9. [Google Scholar]
- Lattanzi, I.E.; Prata Filho, D.D.A.; Quelhas, O.L.G. Modelagem Da Geração de Biogás Aplicando Metodologia CDM Para Redução de Emissões de Gases de Efeito Estufa: Estudo de Caso Do Aterro MTR Santa Maria Madalena, RJ, Brasil. Sist. Gest. 2020, 14, 483–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yılmaz, İ.H.; Abdulvahitoğlu, A. Evaluation of Municipal Solid Waste Options in Turkey: Scenarios for Energy Recovery, Carbon Mitigation and Consequent Financial Strategies. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2019, 147, 95–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kale, C.; Gökçek, M. A Techno-Economic Assessment of Landfill Gas Emissions and Energy Recovery Potential of Different Landfill Areas in Turkey. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 275, 122946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lise, W. Managing Waste for Energy Use in Turkey. In Towards 100% Renewable Energy; Uyar, T.S., Ed.; Springer Proceedings in Energy; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 305–312. ISBN 978-3-319-45658-4. [Google Scholar]
- Yaman, C. Investigation of Greenhouse Gas Emissions and Energy Recovery Potential from Municipal Solid Waste Management Practices. Environ. Dev. 2020, 33, 100484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Www.Energieberg.de: Energieberg.De. Available online: https://www.energieberg.de/home/ (accessed on 12 January 2025).
- Emoke, I.; Parvesh, T.; Tibor, P.; Peter, F.; Martin, M.; Gábor, M.; Tibor, F.; Gábor, T.; Zsolt, H.; Ulsbold, A. Development of Solar Irradiance and Wind Measuring Systems in the Pusztazamor Landfill Site Development of Solar Irra-diance and Wind Measuring Systems in the Pusztazamor Landfill Site. In Proceedings of the 13th ICEEE-2022, Budapest, Hungary, 17–18 November 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Mircea, M. Depozite de Deşeuri. Doctoral Dissertation, Universitatea Politehnică Timişoara Facultatea de Hidrotehnică, Timișoara, Romania, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Niculae, N.B.; Gheorghe, M.; Cornelia Aida, B. Depozitele Ecologice de Deşeuri—Componentă A Arhitecturii Dezvoltării Durabile. Bul. AGIR 2008. Available online: https://www.agir.ro/buletine/419.pdf (accessed on 13 January 2025).
- Feodorov, V. Waste. Personal Communication. Maria.Bostenaru@uauim.Ro. Available online: https://www.uauim.ro/en/university/faculty/maria-bostenaru-dan/ (accessed on 13 January 2025). (In Romanian).
- Ramprasad, C.; Teja, H.C.; Gowtham, V.; Vikas, V. Quantification of Landfill Gas Emissions and Energy Pro-duction Potential in Tirupati Municipal Solid Waste Disposal Site by LandGEM Mathematical Model. MethodsX 2022, 9, 101869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atabi, F.; Ali Ehyaei, M.; Ahmadi, M.H. Calculation of CH4 and CO2 Emission Rate in Kahrizak Landfill Site with Land GEM Mathematical Model. In Proceedings of the 4th World Sustainability Forum (Online), Basel, Switzerland, 1–30 November 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, A.; Chaudhry, M.N.; Ahmad, S.R.; Ullah, R.; Batool, S.A.; Butt, T.E.; Alghamdi, H.A.; Mahmood, A. Ap-plication of Landgem Mathematical Model for the Estimation of Gas Emissions From Contaminated Sites. a Case Study of a Dumping Site in Lahore, Pakistan. Environ. Prot. Eng. 2022, 48, 69–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, J.T.; Chertow, M.R.; Esty, D.C. Where Is Global Waste Management Heading? An Analysis of Solid Waste Sector Commitments from Nationally-Determined Contributions. Waste Manag. 2018, 80, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaza, S.; Yao, L.C.; Bhada-Tata, P.; Van Woerden, F. What a Waste 2.0: A Global Snapshot of Solid Waste Management to 2050; World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Dieter, M.; Dirk, H.; Christoph, H.; Thomas, G. Waste-to-Energy Options in Municipal Solid Waste Management: A Guide for Decision Makers in Developing and Emerging Countries; Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ) GmbH: Eschborn, Germany, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Pujara, Y.; Pathak, P.; Sharma, A.; Govani, J. Review on Indian Municipal Solid Waste Management Practices for Reduction of Environmental Impacts to Achieve Sustainable Development Goals. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 248, 109238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of New and Renewable Energy, Waste to Energy Programme: Programme on Energy from Urban, Industrial and Agricultural Wastes/Residues; New Delhi, India. 2022. Available online: https://mnre.gov.in/en/document/programme-on-energy-from-urban-industrial-agricultural-wastes-residues-and-municipal-solid-waste-2019-20-revised-guidelines-of-waste-to-energy-programme-reg/ (accessed on 13 January 2025).
- Azis, M.M.; Kristanto, J.; Purnomo, C.W. A Techno-economic Evaluation of Municipal Solid Waste (Msw) Conversion to Energy in Indonesia. Sustain. Switz. 2021, 13, 7232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, M.B. Cost-Benefit Analysis of a Waste to Energy Plant for Montevideo; and Waste to Energy in Small Islands. Master’s Thesis, Columbia University, New York, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Lino, F.A.M.; Ismail, K.A.R.; Castañeda-Ayarza, J.A. Municipal Solid Waste Treatment in Brazil: A Compre-hensive Review. Energy Nexus 2023, 11, 100232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISWA Working Group Energy Recovery. Waste-to-Energy Market in Brazil; ISWA Working Group Energy Recovery, ARBEN, WtERT–Brasil. 2020. Available online: https://wtert.org/wp-content/uploads/2020/11/Waste-to-Energy-Market-in-Brazil_ISWA-WGER-october2020.pdf (accessed on 13 January 2025).
- Moreira, H.M.; Giometti, A.B.D.R. Protocolo de Quioto e as Possibilidades de Inserção Do Brasil No Mecanis-mo de Desenvolvimento Limpo Por Meio de Projetos Em Energia Limpa. Contexto Int. 2008, 30, 9–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markgraf, C.; Kaza, S. Financing Landfill Gas Projects in Developing Countries; World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Caciagli, V. Emission Trading Schemes and Carbon Markets in the NDCs: Their Contribution to the Paris Agreement. In Theory and Practice of Climate Adaptation; Alves, F., Leal Filho, W., Azeiteiro, U., Eds.; Climate Change Management; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 539–571. ISBN 978-3-319-72873-5. [Google Scholar]
- Mabuza, L.O.K.; Brent, A.C.; Mapako, M. The Transfer of Energy Technologies in a Developing Country Con-text—Towards Improved Practice from Past Successes and Failures. Proc. World Acad. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2007, 22. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/242511628_The_Transfer_of_Energy_Technologies_in_a_Developing_Country_Context_-_Towards_Improved_Practice_from_Past_Successes_and_Failures (accessed on 13 January 2025).
- Talkington, C.; Pilcher, R.C.; Ruiz, F.A. Addressing Barriers to Global Deployment of Best Practices to Reduce Methane Emissions from Coal Mines. Carbon Manag. 2014, 5, 587–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weko, S.; Goldthau, A. Bridging the Low-Carbon Technology Gap? Assessing Energy Initiatives for the Global South. Energy Policy 2022, 169, 113192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.-H.; Luo, B.; Zhou, H.-T.; Chen, Y.-H. Generalized Solutions for Advection–Dispersion Transport Equa-tions Subject to Time- and Space-Dependent Internal and Boundary Sources. Comput. Geotech. 2025, 178, 106944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).