Abstract
The processing and disposal of municipal solid waste (MSW) are global problems, particularly in low- to middle-income states like Pakistan. These economic systems will need to tackle problems regarding municipal solid waste disposal to accomplish a sustainable future in waste management. Still, the determination of MSW procedures is frequently influenced by unstable, vague, and inadequately stated criteria. To deal with this issue, we designed an interactive model that uses intuitionistic fuzzy hypersoft sets (IFHSSs) to find the optimal thermochemical processing system for MSW. The main objective of this research is to define interactional operational laws for intuitionistic fuzzy hypersoft numbers and to use these laws to build interaction aggregation operators (AOs) and ordered AOs along with their basic characteristics. Based on developed operators, a novel Evaluation Based on the Distance from the Average Solution (EDAS) technique is proposed to integrate multiple attribute group decision making (MAGDM) issues. The suggested strategy is used to analyze five thermochemical treatment techniques for MSW, using a case study focusing on Pakistan’s particular MSW administration problems to choose the most economical technique. Therefore, the new structure is assessed with established methodologies to illustrate its stability. The comparison of results proves that the implications of the stated approach will be more effective and capable than the existing approaches.
1. Introduction
Several unexplored challenges exist for organizations, services, modern technologies, and infrastructure to move into MSW management. Pakistan discharges roughly 49.6 million tons of rubbish annually, with a yearly increase of over 2.4%. Pakistan lacks waste management infrastructure, like other low-income countries, causing significant environmental issues. A substantial amount of municipal waste can be disposed of through incineration, landfilling, or illegal dumping on empty plots of land, posing a significant risk to the overall well-being and safety of the public. According to the Pakistani administration’s estimations, around 87,000 tons of solid garbage are produced weekly, mainly from large towns and cities. Karachi, the most populous city in Pakistan, produces almost 16,500 tons of municipal waste daily. The responsibility of collecting waste in almost every one of Pakistan’s main areas falls within the authority of both local and regional governments. Roughly 60–70% of the solid waste produced in urban areas is gathered.
The world’s growing population, economic growth, and rate of urbanization have all been responsible for an unprecedented increase in the utilization of resources and, by extension, the quantity of waste production [1]. As a result, waste-management-related issues with the environment are now receiving a lot of attention and causing controversy [2]. A significant obstacle for relevant organizations in developing countries is the adequate supervision of MSW [3,4,5]. The main objective of solid waste management is to handle a wide range of challenges caused by inadequate handling of waste, among which are the health of the community, the environment, the use of resources, aesthetics, land use, and finances [6]. Wang et al. [7] addressed the properties and worldwide utilization of bauxite residue (red mud) in cement-based materials. They highlighted its ability to mitigate energy use, emissions of carbon dioxide, and waste from factory formation.
Approximately 37% of MSW is dumped in landfills, whereas 33% of MSW is directed to open sites [8] as part of global waste disposal initiatives. Wu et al. [9] analyzed refurbishment techniques for end-of-life and used goods, concluding that reusing recycled materials delivers superior sustainable benefits. Because there is a shortage of proper disposal facilities in Pakistan [10], open-pit disposal is the preferred approach for managing MSW. Pan et al. [11] evaluated acidogenic fermentation for food waste administration, exposing that CO2 splitting grows acetic acid fabrication by promoting acetate-producing organisms and limiting contending avenues. This waste, which amounts to 0.79 kg per person per day, negatively affects the globe’s climate, health, and biodiversity. The study provides solutions tailored to specific countries, identifies significant issues, and presents feasible solutions to promote worldwide progress in sustainability in both the economy and the environment [12]. Sohoo et al. [13] performed an exhaustive study of the open disposal method for MSW in Pakistan, particularly in Karachi. Aslam et al. [14] examined the performance of the solid waste disposal system in Karachi, using materials flow analysis to explore the transit of solid waste. Iqbal et al. [15] explored global challenges with managing municipal waste, focusing on middle-income and low-income countries like Pakistan. The growing production of MSW in Asian metropolitan areas, combined with insufficient waste disposal systems and energy limitations [16], raise serious threats to people’s health and the surroundings. Figure 1 shows the composition of MSW generated in Pakistan.
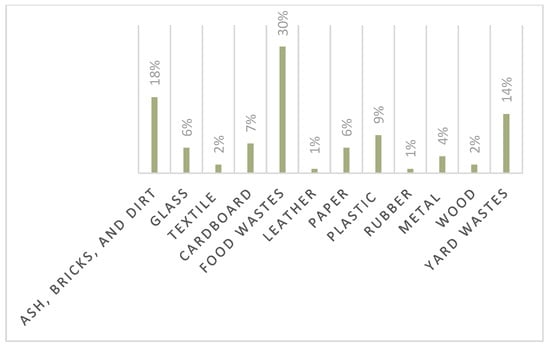
Figure 1.
Composition of MSW in Pakistan (https://www.trade.gov/country-commercial-guides/pakistan-waste-management, accessed on 12 January 2024).
Unfortunately, urban areas in Pakistan are emerging as the most severe instances of negligence and mismanagement in handling MSW, causing a significant decline in the climate and the standard of community life. Han et al. [17] highlighted that using a tailored bacterial population derived from organically decomposed food debris improves the effectiveness of aerobic decomposition by facilitating the proliferation of hydrolyzed bacteria. Liu et al. [18] described the Multifaceted Anomaly Detection Framework, which merges Electrical Resistivity Tomography with sophisticated machine learning models to enhance the detection and surveillance of harmful substances immensely. The authors investigated the thermal and catalytic pyrolysis procedures for reducing waste into beneficial goods, emphasizing their structures, obstacles, and possibilities for waste-to-energy applications [19]. Wang et al. [20] described a breakthrough in situ chemical injection strategy exploiting an Fe-Mn oxide-activated persulfate structure for the sterilization of groundwater contamination with BPA. Meng et al. [21] explored biofilm formation on microplastics in wetlands, confirming that the plastisphere substantially affects the variety of bacteria and biological processes.
This research concentrates on one specific scenario of executing the stated approach, which examines five thermochemical techniques for regulating MSW: thermal gasification, incineration, pyrolysis, thermal depolymerization, and plasma arc gasification. Five experts with distinct acquisition experiences participated in the evaluation, all delivering quantitative observations. A novel hybrid approach is presented to boost the credibility of the findings.
This research is organized as follows. Section 1 illustrates the significance of merging factors of uncertainty and incomplete information into decision-making strategies. Section 2 contains a detailed examination of the fundamental concepts that form the basis for the remainder of the study. Section 3 describes the interactional operational laws for IFHSS regulating IFHSS and presents the IFHSIWA and IFHSIOWA operators, along with their essential characteristics. Section 4 describes the IFHSIWG and IFHSIOWG operators, clearly explaining their distinctive features. Section 5 proposes a novel EDAS model that employs the operators mentioned above to deal with the obstacles of MAGDM. Section 6 performs an empirical study to evaluate the feasibility of the proposed approach, intending to identify the optimum thermochemical treatment method for managing MSW. The proposed technique is assessed using a thorough comparison study with previous methodologies in Section 7.
1.1. Literature Review
The following subsection reviews relevant research on strategies used to treat MSW. It then discusses the interaction between AOs and the EDAS approach.
The disposal of MSW has been considered a top priority these days, as it has grown to be a critical problem globally and an essential component of environmental protection and ecologically sound resource protection. Arikan et al. [22] applied three MAGDM approaches, namely PROMETHEE, TOPSIS, and fuzzy TOPSIS, to find appropriate alternatives for solid waste treatment. Zhuang et al. [23] indicated that the integration of ZnO into a Co3O4 heterojunction configuration substantially improves its enzymatic efficacy for purifying peroxymonosulfate-based organic water. Mir et al. [24] implemented the TOPSIS approach to choose the most effective strategy to handle solid waste. Wang et al. [25] introduced a MAGDM strategy for determining a suitable process to regulate MSW.
Coban et al. [26] used three different multi-criteria decision-making (MCDM) strategies, specifically TOPSIS, PROMETHEE I, and PROMETHEE II, to assess and examine eight situations in solid waste treatment. Afrane et al. [27] analyzed the best waste-to-energy conversion system for use in Ghana. Akram et al. [28] investigated MAGDM problems using a linguistic Pythagorean fuzzy structure. Paul et al. [29] applied cubic Pythagorean fuzzy numbers to represent the fuzzy attributes of the criteria values associated with the five thermochemical techniques used to process MSW. Roy et al. [30] implemented the TOPSIS technique in a credibility structure to solve problems with MSW management. Rahimi et al. [31] presented a new structure that integrates Geographic Information System techniques with fuzzy MCDM processes to locate dump sites for MSW disposal. Rani et al. [32] developed the Pythagorean fuzzy stepwise weight assessment ratio analysis to solve MCDM issues in medical waste disposal systems. Garg and Rani [33] presented the MULTIMOORA method in the IFS structure to measure the feasibility of several ways of handling waste materials. Barakati and Rani [34] presented a novel parametric divergence measure and planned a twofold normalization-based multi-aggregation technique for interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy sets (IVIFS) to deal with MCDM problems.
Zadeh [35] developed a framework for dealing with inconsistency by presenting the fuzzy set (FS) theory. Atanassov [36] introduced IFS to solve the drawbacks of FS. IFS is an FS extension integrating a membership degree (MD) with a non-membership degree (NMD). The structures mentioned above are insufficient when faced with the parametric representation of alternatives. Molodtsov [37] proposed the soft set (SS) as a conceptual structure to successfully tackle and resolve this problem. Several studies involve fuzzy set advancements with soft sets, especially fuzzy soft sets (FSS) [38] and intuitionistic fuzzy soft sets (IFSS) [39]. Smarandache [40] proposed the idea of hypersoft sets (HSS), which involves incorporating multiple multi-sub-parameters into the assigning function of an identified set of attributes. Saeed et al. [41] proposed a multi-fuzzy HSS structure that employs similarity and entropy measures to tackle MCDM challenges. Rahman et al. [42] proposed a mathematical structure for convexity and concavity in fuzzy HSS. Yolcu et al. [43] introduced essential operations for IFHSS. Zulqarnain et al. [44,45] developed the TOPSIS technique and aggregation operators (AOs) designed explicitly for IFHSS.
He et al. [46,47] proposed the intuitionistic fuzzy geometric interaction averaging operators and generalized intuitionistic fuzzy weighted geometric interaction and proposed the MADM model to resolve decision-making complications. Garg [48,49,50] presented the implementation of intuitionistic fuzzy Hamacher interactive weighted averaging, ordered weighted averaging, hybrid weighted averaging operators, interaction average, and geometric AOs in MCDM problems. Liu and Wang [51] introduced novel hammy mean AOs that integrate interaction in IFS. Garg [52] proposed interactive Einstein operational laws for IFS, which assisted in forming geometric interaction averaging AOs. Liu [53] enhanced the use of MADM techniques by implementing interaction AOs into the usual IFS framework. Garg and Arora [54] introduced prioritized interaction averaging AOs under IFSS. Several researchers have made major improvements in developing interaction AOs within different extensions of the FS theory [55,56,57,58,59,60,61,62].
Ghorabaee et al.’s [63] approach is considered a highly practical approach for numerically describing MAGDM difficulties that contain competing factors. Ghorabaee et al. [64] stated that the EDAS approach uses the average solution to calculate the importance of alternatives. It takes note of differences in the average solution by analyzing the positive distance from average (PDA) and negative distance from average (NDA) measures. Srivastava et al. [65] executed an investigation where they implemented the fuzzy EDAS approach to evaluate and rank autonomous maintenance characteristics from a technical perspective. Kahraman et al. [66] used the EDAS technique for solid waste management in an IF framework. Mishra et al. [67] implemented the EDAS method to investigate techniques for handling hospital waste, while Schitea et al. [68] engaged it to determine a suitable site within the IF context. Liu et al. [69] enlarged the EDAS technique to deal with Pythagorean fuzzy sets. Li et al. [70] constructed a novel EDAS method for Pythagorean fuzzy numbers to address decision-making obstacles. Zhang et al. [71] developed the EDAS method for picture fuzzy sets, while Darko and Liang [72] enhanced it by including Hamacher operators. Mishra et al. [73] explored the computation of attribute weights and used the EDAS method to evaluate the ranking of sustainable third-party reverse logistics providers.
1.2. Aim of the Proposed Study
The AOs in ref. [45] are insufficient for properly evaluating facts built into more secure categories that possess the exactitude required to produce precise outcomes. Let be two experts with weights and let be the parameters with their sub-parameters, such as and , where with weights . Let be an alternate, and then experts’ evaluation of the planned aspects in terms of IFHSNs. The obtained aggregated value using the IFHSWA [45] operator is . The validity of these AOs is unreliable, and only basic knowledge about the alternatives can be found. Thus, merging IFHSNs into the composition of interaction AOs offers an exciting and important way to investigate. The techniques described in [45] are inadequate for carefully examining information while observing previous theoretical structures and presenting obvious, practical implications.
This study is considered important for the following reasons.
- The IFHSS concept has abundant applications and can represent complicated information in a versatile and detailed manner. This makes it an important DM method that considers the overall environment.
- This research demonstrates the apparent convenience of interactional operations, which contributes to their specific variables. The study introduces interactive and interactive ordered AOs that have been optimized for IFHSS.
- The EDAS approach is widely employed due to its accessibility and effectiveness in delivering more favorable outcomes in the DM procedure. The execution of the EDAS approach used in this study boosts the robustness and dependability of the DM system, solving an apparent drawback in present approaches.
- Several researchers use various DM methodologies in different fuzzy structures for existing studies, such as TOPSIS, VIKOR, and EDAS. Still, there exists a lack of real-world studies on MSW management using the EDAS approach in an IFHSS context. This research handles this problem using the presented integrated model, which analyzes IFHSS information to identify the most effective thermochemical approach.
1.3. Research Problem and Contribution
This research analyzes five distinct alternatives and uses the intuitionistic fuzzy hypersoft EDAS technique for investigation. Municipalities must use appropriate solutions to mitigate the effects of trash disposal sites. The diverse composition of the collected waste, depicted in Figure 1, underscores the imperative for effective management to avert negative health impacts from infectious diseases and to mitigate the harmful consequences of climate change, particularly by controlling the release of methane and other deleterious gases. Moreover, the reality that 30% of MSW consists of food compounds stresses the importance of implementing waste-to-energy transformation.
Therefore, an intelligent selection of MSW disposal technologies is most important in managing the challenges caused by improperly handling MSW and encouraging waste-to-energy reprocessing. The EDAS approach is more effective for MAGDM than TOPSIS and VIKOR. This is because it concentrates on finding an average solution that takes into account both positive ideal and negative ideal solutions. The suggested strategy addresses significant challenges. How can one choose the optimum thermochemical treatment technique correctly in unreliable circumstances? How can we acquire data on the abilities of the MSW management group? How will the EDAS method be applied to create the MSW organizational structure to determine appropriate treatment processes?
This research presents multiple exciting developments, which can be briefly summarized as follows.
- (1)
- Integrating interactional operational laws in the IFHSS structure assisted in designing and presenting IFHSS interaction AOs. The operators provided are IFHSIWA, IFHSIOWA, IFHSIWG, and IFHSIOWG operators. We also adequately presented some significant aspects of these operators, particularly idempotency, boundedness, monotonicity, homogeneity, and shift-invariance.
- (2)
- The IFHSS structure uses the distinctive procedure EDAS to determine the most optimal alternative. This method delivers a practical solution for convoluted DM challenges and merges the prevailing DM theory through this novel strategy.
- (3)
- The proposed approach investigates and chooses the thermochemical treatment strategy in MSW management.
- (4)
- The approach executes detailed comparison and sensitivity evaluations, which are meticulously examined and evaluated. The research outcomes confirm the consistency and effectiveness of the proposed technique.
2. Preliminaries
This section recalls basic concepts, such as soft set (SS), fuzzy soft set (FSS), HSS, and IFHSS.
Definition 1
([37]). Let and be the universe of discourse and set of attributes, respectively. Let be the power set of and . A pair () is called an SS over . Its mapping is expressed as follows:
Also, it can be defined as follows:
Definition 2
([38]). Let be a universal set, let be a set of attributes, and let be a fuzzy power set of . Let , and then () is an FSS over ; its mapping can be stated as
The previous studies have challenges in solving scenarios when an expert considers a parameter’s sub-attributes. To solve this issue, Smarandache [40] introduced the idea of the hypersoft set as a solution.
Definition 3
([40]). Let be a universal set, and let () be a power set of and , ; represents the set of attributes and their corresponding sub-attributes, such as , where for each and . Assume is a collection of sub-attributes, where , , , and . Then, the pair is known as HSS, defined as follows:
It is also defined as
Definition 4
([40]). Let be a universal set, and let () be a power set of and ,; denotes the set of attributes and their corresponding sub-attributes, like , where for each and . Assume is a collection of sub-attributes, where , , , and . represents the intuitionistic fuzzy subsets of . Then, the pair is known as IFHSS, defined as follows:
It is also defined as , where , where and signify the membership and non-membership values of the sub-attributes, , and .
Example 1.
Let and represent the universe of discourse and attributes with their respective sub-attributes, e.g., teaching methodology = Subjects = , and Classes = , respectively. The group of attributes with succeeding conforming sub-attributes is specified as follows.
Let be a set of attributes, such as
Then, the IFHSS over is known as
Remark 1.
If is held, no one attribute has a sub-attribute. Then, IFHSS is condensed to IFSS [39].
IFHSN can be written as . Alternative ranking can be found using score functions, as follows:
where . It is not easy to differentiate the IFSNs and which alternative is most appropriate, in some cases, using the score function. For example, let and , and then and . Therefore, it is impossible to decide the best alternative. To overcome the above situation, an accuracy function has been developed, such as
Let and be two distinct IFHSNs; then, comparison laws are defined as follows:
- If , then .
- If , then.
- ➢
- If , then .
- ➢
- If , then .
Definition 5
([44]). Let , , and be three IFHSNs and . Then, the algebraic operational laws for IFHSNs are defined as follows:
- .
- .
- .
- .
A comprehensive evaluation of the aggregation operators under the IFHSS framework clearly shows that in particular situations, these aggregation operators generate undesirable outcomes. We promote the interaction AOs designed for IFHSNs to communicate and deal with such issues.
3. Interactive Aggregation Operators for Intuitionistic Fuzzy Hypersoft Sets
This section will construct a couple of interactive average AOs, such as IFHSIWA and IFHSIOWA operators, with their essential properties.
Definition 6.
Let
,
, and
be the three IFHSNs and
. Then, the interactional operational laws for IFHSNs are defined as follows:
- .
- .
- .
Definition 7.
Let
be an IFHSN;
and
represent the weights of experts and multi-sub-attributes along with stated conditions
,
,
, and
, where
and
. Then,
Theorem 1.
Let
be a family of IFHSNs. Then, the aggregated value of the IFHSIWA operator is also an IFHSN and
where and represent the experts’ and the sub-attribute weights within certain circumstances, , , , , and .
Proof.
The IFHSIWA operator can be proved using mathematical induction.
Let ; we obtain . Then,
For , we obtain . Then,
So, Equation (3) holds for and .
For and . Then,
And
So, Equation (3) holds for and .
Consider that Equation (3) holds for , . Then,
For and , we have
For simplicity,
, , , , , . Then,
It is verified that Equation (3) holds for , . So, we can say that Equation (3) holds , . □
Proposition 1.
Let be a family of IFHSNs. Also, let and be the weights of experts and sub-attributes, respectively, such as and .
3.1. Idempotency
If , then
Proof.
As we know, is a collection of IFHSNs. Then, by using Equation (3),
As and . So,
□
3.2. Boundedness
Let and . Then,
Proof.
We know is an IFHSN. Then,
As and . So,
Similarly,
Let . Then, inequities (4) and (5) could be turned into the following form:
and . From Equation (1), we have
and . Now, there are two possibilities
If and . Then,
If , then
. So, and . Hence,
If , then
. So, and . Hence,
Therefore, using Equations (6)–(8), we have
□
3.3. Shift Invariance
If is a collection of IFHSNs and is an IFHSN, then
Proof.
We have
So,
□
3.4. Homogeneity
Let be a family of IFHSNs, where . Then,
, where .
Proof.
As is a family of IFHSNs and , then
So,
□
3.5. Monotonicity
Let and be the two distinct families of IFHSNs. Then,
, if .
Proof.
Let , , and then , so is a decreasing function on . If , then .
as , , and . So,
Let , , and then . So, is decreasing on . If , then .
as , , and . So,
Hence,
□
Definition 8.
Let
be a family of IFHSNs. Then, the IFHSIOWA operator is defined as
Theorem 2.
Let
be a family of IFHSNs. Then, the aggregated value of the IFHSIOWA operator is also an IFHSN.
where is the leading element of the row and the column in , such as and . Also, and are the weights for experts and sub-attributes, such as 0, = 1, 0, and = 1.
Proof.
Similar to Theorem 1.
Moreover, the IFHSIOWA operator presents notable properties similar to the IFHSIWA operator, such as idempotency, boundedness, homogeneity, monotonicity, and shift-invariance. The following sections contain a comprehensive explanation of these characteristics. □
Proposition 2.
Let be a family of IFHSNs and and be the weight vectors of experts and sub-attributes, respectively, such as and , .
3.6. Idempotency
If , then
3.7. Boundedness
Let and . Then,
3.8. Shift Invariance
Let be a collection of IFHSNs and be an IFHSN. Then,
3.9. Homogeneity
Let be a family of IFHSNs. Then,
where .
3.10. Monotonicity
Let and be the two distinct families of IFHSNs. Then,
, if .
4. Interactive Geometric Aggregation Operators for Intuitionistic Fuzzy Hypersoft Sets
This section will present the IFHSIWG and IFHSIOWG operators specifically developed for IFHSNs and their essential characteristics.
Definition 9.
Let = be an IFHSN; and represent the weights of experts and multi-sub-attributes along with stated conditions 0, = 1, 0, and = 1. Then, IFHSIWG, , is defined as follows:
Theorem 3.
Let
=
be a family of IFHSNs. Then, the aggregated value of the IFHSIWG operator is also an IFHSN, and
where and represent the experts’ and sub-attribute weights within certain circumstances, 0, = 1, 0, and = 1.
Proof.
Similar to Theorem 1. □
Proposition 3.
Let be a family of IFHSNs and and be the weight vectors of experts and sub-attributes, respectively, such as and .
4.1. Idempotency
If , then
4.2. Boundedness
Let and . Then,
4.3. Shift Invariance
Let be a collection of IFHSNs and be an IFHSN. Then,
4.4. Homogeneity
Let be a family of IFHSNs. Then,
where .
4.5. Monotonicity
Let and be the two distinct families of IFHSNs. Then,
, if .
Definition 10.
Let
=
be a family of IFHSNs. Then, the IFHSIOWG operator is defined as
Theorem 4.
Let
=
be a family of IFHSNs. Then, the aggregated value of the IFHSIOWG operator is also an IFHSN, and
where is the largest element of the row and the column in , such as and . Also, and are the weight vectors for experts and sub-attributes, such as 0, = 1, 0, and = 1.
Proof.
Similar to Theorem 1.
Moreover, the IFHSIOWG operator presents notable properties similar to the IFHSIWG operator, such as idempotency, boundedness, homogeneity, monotonicity, and shift-invariance. The following sections contain a comprehensive explanation of these characteristics. □
Proposition 4.
Let be a family of IFHSNs and let , be the weights of experts and sub-attributes, respectively, such as and .
4.6. Idempotency
If , then
4.7. Boundedness
Let and . Then,
4.8. Shift Invariance
Let be a collection of IFHSNs and be an IFHSN. Then,
4.9. Homogeneity
Let be a family of IFHSNs. Then,
where .
4.10. Monotonicity
Let and be the two distinct families of IFHSNs. Then,
, if .
5. EDAS Technique Based on Developed Interaction Aggregation Operators
Experts from different areas of expertise, each with different viewpoints and opinions, may have conflicting opinions on the most productive approaches to employ. Cooperative methods for decision making are beneficial in such circumstances. Experts frequently implement intuitionistic fuzzy hypersoft values to indicate complexity and unpredictability when stating opinions. This research describes the “intuitionistic fuzzy hypersoft interaction-based EDAS method” as an approach to deal with the obstacles faced in MAGDM problems. The main objective of this technique is to build an effective basis for managing DM situations characterized by uncertainty and ambiguity. The impact of the EDAS technique is reliant upon two particular evaluations, the PDA and the NDA, which are effective at evaluating discrepancies between various alternatives. The EDAS approach reduces the need to systematically assess ideal and non-ideal solutions when applying MAGDM challenges. In this research, decision experts utilize IFHSNs to evaluate the combined values of the alternatives by assigning preference values. The following section describes the computational framework of the stated methodology.
Let be a set of alternatives and let be a group of experts. The weights of experts are given as and , . Let and represent the set of attributes with their corresponding multi-sub-attributes with weights , such as , , and they can be indicated as . The group of experts assesses the alternatives under the chosen sub-attributes in the form of IFHSNs, such as , where and , .
Therefore, to put into practice such an effective approach, the implementation of the subsequent steps must be undertaken.
Step 1: Experts evaluate matrices for alternatives in terms of IFHSNs under their considered sub-attributes.
Step 2: Therefore, the matrix undergoes consideration by categorizing parameters into two different categories: those involving costs and those about benefits. Normalization is unnecessary when the parameters are identical. However, if the decisions have distinct kinds of attributes, it is necessary to use the normalization procedure to normalize them. The procedures of normalization are described in the following way:
Step 3: Evaluate the ordered matrices for each alternative if using IFHSIOWA or IFHSIOWG operators. Otherwise, there is no need to find ordered matrices, and we can move forward to step 4 directly without finding ordered matrices.
Step 4: Equations (3), (9), (10), or (11) will determine aggregated decision matrices of the expert’s assessment. This is carried out while considering the weight of all of the experts.
Step 5: Find the average solution matrix using the following equation.
Step 6: Evaluate the PDA using Equation (14) and the NDA using Equation (16). In some situations, it is not easy to justify which alternative has a higher appraisal value. So, in such scenarios, we cannot decide which alternative is most appropriate. We will use Equation (15) to find the PDA and Equation for this. We will use (17) to find the NDA. Moreover, and represent the beneficial and non-beneficial criteria, respectively.
, , where
or
and
or
Step 7: For both the IFHSIWA and IFHSIOWA operators, compute the positive weighted distance and the negative weighted distance , which are given in Equations (18) and (19).
Or, use IFHSIWG and IFHSIOWG operators given in Equations (20) and (21):
where , such as and
Step 8: Normalize the values of and ,
where and are the maximum distances.
Step 9: Derive the integrative appraisal score
where
Step 10: After determining their relative values, each alternative will be placed in descending order of importance. The option with the best potential score is perceived to be most efficient, while the other option with the lowest total rating is perceived as least productive. Figure 2 presents a visual representation of the planned method.
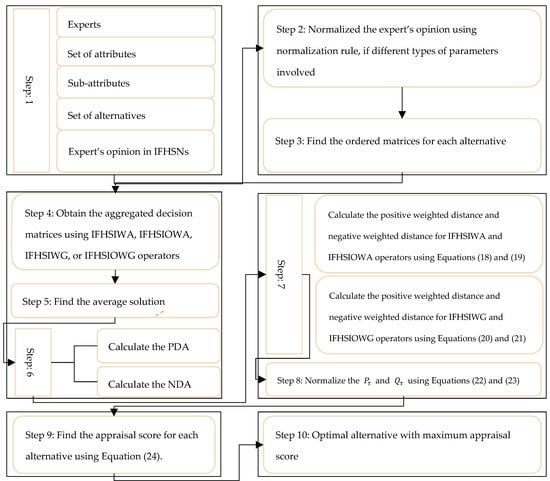
Figure 2.
Flow chart of the proposed EDAS model.
6. Application of the Proposed EDAS Method in MSW Management
The following section explores the practical significance of this model in assessing the optimal thermochemical waste disposal techniques for the disposal of MSW.
6.1. Case Study of MSW Management
The removal and disposal of MSW constitute an extensive ecological problem. Various techniques, including thermochemical processes, are used to manage and alleviate the impact of waste. Thermochemical treatments utilize heat to influence the waste products’ chemical structure. Several thermochemical techniques for disposal of MSW are outlined in the following order.
6.1.1. Incineration
One standard method for handling MSW is thermochemical incineration, which involves burning waste products at a high temperature with extra air present. Because inorganic substances are generally processed into ash through this procedure, organic trash ingredients oxidize into water and carbon dioxide. The eradication of potentially hazardous substances and the decrease in waste size are two advantages of the extreme temperatures obtained during combustion. Effective air quality management techniques, like scrubbers and electrostatic precipitation devices, must be developed to solve problems. After burning, hazardous ash may be left behind that needs to be managed and disposed of appropriately to prevent damage to surroundings. Also, how society perceives and absorbs a factor can lead to obstacles, as concerns regarding the purity of air and prospective safety risks can impact the authorization and execution of incineration sites.
6.1.2. Plasma Gasification
Plasma gasification is a complicated thermochemical mechanism that handles MSW. It uses elevated temperatures of ionized gases (plasma) to transform waste products into syngas, which are metallic substances and a glass-like remnant that is sterilized. In this method, waste is heated to high temperatures through an electromagnetic arc within a radiant flame, disintegrating complicated inorganic and organic substances. This method presents another benefit of reducing the quantity of trash and minimizing the harmful environmental effects attributed to conventional disposal methods. High initial expenditures, technological intricacy, and the requirement of complicated operation are some of the limitations that plasma gasification must overcome, considering its appealing characteristics. The project’s sustainability is significantly impacted by financial viability because of the massive capital expenses required to build plasma gasification plants. This technology also requires operators and servicing experts with the necessary expertise.
6.1.3. Thermal Depolymerization
Thermal depolymerization is a novel technique employed for disposing of MSW, providing an environmentally friendly method for managing various types of garbage. Throughout this process, organic substances are exposed to severe pressures and temperatures in an oxygen-free environment, decomposing into less complex particles. The considerable energy expenditure needed to achieve and sustain the desired temperatures and pressures shows a financial obstacle, necessitating effective energy recovery techniques. The successful implementation of thermochemical thermal depolymerization in municipal solid waste management strategies requires striking a balance between the advantages of resource rehabilitation and the difficulties of consumption of energy and material fluctuations.
6.1.4. Pyrolysis
Gases, liquids, and char are byproducts of the thermochemical process known as pyrolysis used to dispose of MSW. This process occurs in an oxygen-free environment. The thermal decomposition process is carried out by treating waste products at high temperatures ranging from 300 °C to 800 °C. Biofuels, heat, and important pharmaceuticals are just a few possible applications for the byproducts. Strong administration is required to prevent reaction degradation and enhance energy extraction performance. Maintaining an integrated approach to technological developments and economic feasibility and managing possible adverse ecological effects are necessary for the effective execution of pyrolysis as a thermochemical technique for dealing with MSW.
6.1.5. Thermal Gasification
One viable method for handling waste is thermal gasification, demonstrating the potential for adequately handling MSW. Carbon monoxide and hydrogen, two of the main substances found in syngas, are usable to provide heat and power or to generate biofuels and chemicals. Thermal gasification’s advantages are its ability to adapt to various municipal waste streams, its low negative environmental impact, and its great energy efficiency. Maintaining stability among scientific progress, financial stability, and environmental sustainability is crucial for effectively implementing thermal gasification as a thermochemical process for processing MSW. The flow chart of the thermochemical MSW disposal techniques and their benefits and limitations is presented in Figure 3.
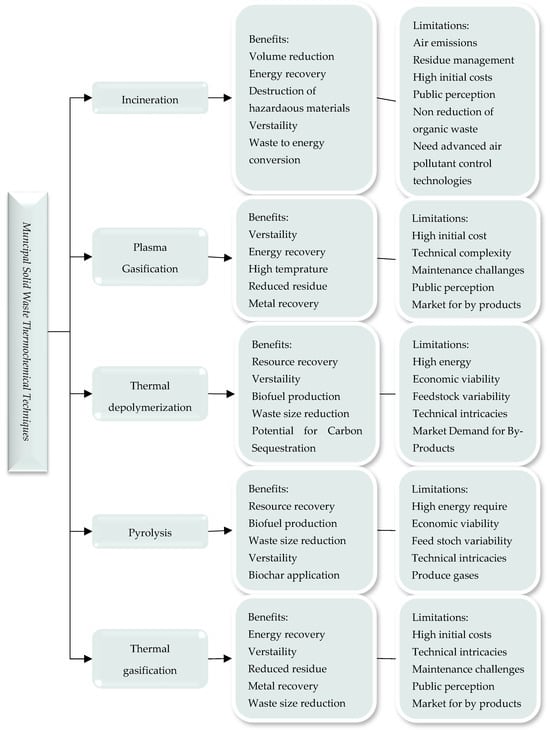
Figure 3.
Benefits and limitations of the thermochemical MSW disposal techniques.
6.2. Criteria Description
A detailed investigation has been carried out to assess thermochemical disposal techniques in MSW management, considering a variety of attributes with their corresponding sub-attributes. Proper decision making includes carefully evaluating several parameters; the complicated framework of the evaluation procedure reflects the multi-faceted characteristic of MSW administration.
6.2.1. Energy Recovery
Energy recovery plays a significant role in analyzing the effectiveness of thermochemical techniques for handling MSW. The main objective is to efficiently transform the energy generated by solid waste into consumable kinds of power, including heat, power, or synthetic gasoline. Also, thermochemical processes’ potential to reduce costs, cut emissions, and maintain ecological sustainability is essential for assessing how well they integrate power requirements with waste disposal. Economical and functional reliability, two of the most important sub-criteria in this assessment, are presented as follows.
Efficiency : The financial stability and environmental viability of waste-to-energy processes depend on the efficient use of the optimum proportion of energy and the smallest quantity of waste. Thermochemical method efficiency determines the feasibility of transforming waste material into useful products like heat, electricity, or synthetic fuels.
Integration Compatibility : The subsequent sub-criterion admits the significance of the kind of power generated and its compatibility with the prevailing energy systems. It realizes that distinct thermochemical methods may generate electricity, heat, or synthetic fuels.
6.2.2. Environmental Impact:
The environmental consequences and specifications for treating MSW using thermochemical techniques are necessary for the continued viability of waste disposal activities. It requires an accurate evaluation of potential ecological impacts and the execution of reliable procedures for dumping or recycling. Integrating measures that decrease the release of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere and adhere to existing environmental rules is essential for adopting an environmentally friendly approach to handling MSW using thermochemical techniques.
Control and reduction of emissions : The control and reduction of emissions are the top objectives when evaluating the environmental consequences of MSW waste disposal, particularly for thermochemical techniques. These techniques may culminate in the emission of pollutants, such as nitrogen oxides, sulfur dioxide, heavy metals, and dioxins.
6.2.3. Economic Viability
Financial viability factors are important in determining the practicality of disposing of MSW using thermochemical techniques. The competitiveness of thermochemical plants relies on effectively controlling expenses related to installing technology compared to the advantages obtained from energy recovery or the use of byproducts.
Revenue generation : Revenue-generating prospects, such as the sale of electricity or recovered materials, additionally enhance the fiscal viability of the plants. This demonstrates the necessity of ongoing technological innovation and optimization to reduce expenditures and improve the financial benefits of recycling waste into energy projects.
6.2.4. Resource Efficiency
The most critical consideration in assessing the treatment of MSW through thermochemical techniques is the sustainable efficiency of resources. This requires an integrated strategy to maximize energy, water, and auxiliary materials’ consumption. Two crucial sub-criteria in this context are maintaining a balance in energy use and conserving water supply.
Energy Balance : An important component in thermochemical operations is to preserve a favorable balance of energy, where the energy generated by waste exceeds the energy required to execute thermochemical processes.
Water Conservation : An essential aspect of thermochemical operation is properly handling water by preventing water use while maximizing productivity. This occurs through the use of technological advances and procedures that minimize the use of water and endorse reuse and recycling.
6.2.5. Regulatory Compliance
Evaluating the implementation of thermochemical approaches for handling MSW requires a thorough review of compliance with regulators. It incorporates detailed environmental, medical care, and protection rules. Within this framework, two essential sub-criteria are emissions control and residue management.
Emissions Control : An essential component of regulatory compliance in thermochemical waste treatment is the effective administration and reduction of pollutants to properly locate and eliminate particulates.
Residue Management : Another critical component in thermochemical waste disposal is properly handling byproducts, such as ash or slag, and maintaining a commitment to waste management standards to prevent soil and water pollution.
6.3. Numerical Example
A numerical example presents the significance and usability of the established model under IFHSS, and the developed approach was utilized to select an effective thermochemical waste disposal technique.
The team of five experts had weights to evaluate the ranking of the thermochemical waste disposal techniques . Professionals adopt the standards for the assortment of thermochemical waste disposal techniques, such as , which represents the attributes of the alternatives, and their corresponding sub-attribute is given as , , , , and . Let be a set of sub-attributes is a set of all multi-sub-attributes with weights . Specialists have access to alternatives in the form of IFHSNs.
The stakeholders will prioritize among the five alternatives based on their preferences in IFHSNs after analyzing each based on these five criteria and their related sub-attributes. The procedure is shown in the following diagram (see Figure 4).
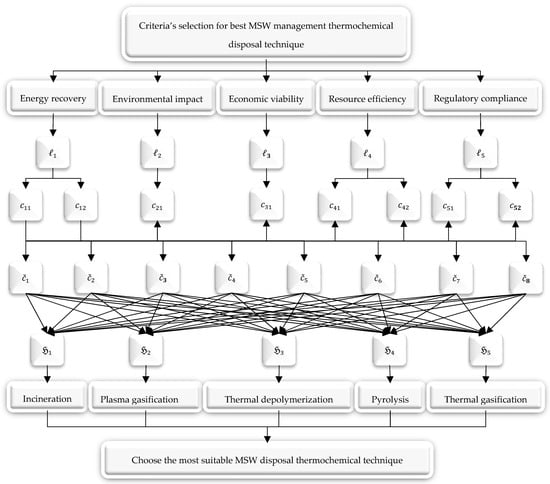
Figure 4.
Selection of thermochemical technique for MSW disposal.
The technique presented here assists in discovering the most optimal solution using the provided criteria. The selection method focuses on preserving environmental stability and safety for both humans and plants. The main objective of the MSW thermochemical technique is to ensure sustainable economic and social development. However, this research identifies potential risks to people’s safety, indicating its essential importance in promoting social prosperity. Through detailed study and meticulous evaluation of these variables, experts can recommend the most suitable and efficient thermochemical strategy for treating MSW. The experts’ opinions for each choice in Table 1 are presented using IFHSNs and then contained in the EDAS approach. This strategy combines the interaction AOs and interaction ordered AOs presented in Section 4 and Section 5, intending to determine the most economical thermochemical treatment process in MSW management.

Table 1.
Expert’s opinion for each alternative.
Step 1. The expert clarifies that the intuitionistic fuzzy hypersoft decision matrices for all potential outcomes are shown in Table 1.
Step 2: Economic viability. Let be the cost type parameter with sub-criteria . As we know, , the multi-sub-attributes and sub-criteria are involved in every multi-sub attribute, which shows that each attribute contains this cost type sub-criteria. So, it is necessary to normalize the decision matrix using Equation (12). The normalized decision matrix is presented in Table 2.

Table 2.
Normalized decision matrix.
Step 3: We will apply the IFHSIWA or IFHSIWG operators. Therefore, there is no need to find ordered matrices, and we can proceed to step 4 directly without finding ordered matrices.
Step 4: Equation (3) or (10) (IFHSIWA or IFHSIWG) operators will be used to determine the experts’ assessments’ aggregated decision matrices. Based on the defined parameters, the above operators verify all of the desired values for alternatives. The aggregated evaluation matrix implementing Equation (3) is laid out in Table 3.

Table 3.
Aggregated decision matrix using IFHSIWA operator.
Step 5: Find the average solution matrix using Equation (13).
Step 6: Evaluate the PDA using Equation (15) and the NDA using Equation (17). We cannot use Equations (14) or (16) to compute the PDA or the NDA, respectively. The PDA and NDA matrices are given in Table 4 and Table 5.

Table 4.
PDA matrix.

Table 5.
NDA matrix.
Step 7: Compute the positive weighted distance using Equation (18) and the negative weighted distance using Equation (19).
, , , , , , , , , and .
Step 8: Normalize the positive weighted distance using Equation (22) and the negative weighted distance using Equation (23), where, are given as , , , , , , , , , and .
Step 9: Calculate the appraisal value using Equation (24), such as , , , , and .
Step 10: Each alternative is rated in descending order of appraisal value. The feasible choice with the highest and lowest appraisal scores appears to be the poorest, .
The suggested method presents substantial improvements over the existing EDAS strategy. Employing real numbers, the prevailing EDAS methods do not express the analyzed information’s multi-sub-parametric MD and NMD values. Meanwhile, the proposed model enables experts to present their opinions more easily.
7. Comparative Analysis and Theoretical Implications
This section will perform a comprehensive evaluation by comparing and analyzing prior studies and investigating the implications of the proposed strategy.
7.1. Comparative Analysis
This subsection will analyze our proposed framework from three different viewpoints. We investigate our proposed EDAS technique against existing EDAS techniques in different fuzzy environments. Additionally, we will analyze the newly introduced EDAS model with relevant AOs within the IFHSS context. Finally, we examine our proposed approach with the TOPSIS approach in the IFHSS structure.
7.1.1. Comparison with Existing EDAS Approaches
It is observed that prevalent techniques, such as the fuzzy EDAS [65], exclusively compensate for the MD of alternates. In comparison, particular mathematical models, such as the IFS EDAS [66], incorporate the advantage of the MD and NMD while analyzing alternatives. Liu et al. [69] and Paul et al. [29] proposed the EDAS strategy for PFS and cubic PFS. Zhang et al. [71] presented the EDAS technique for picture fuzzy sets. Darko and Liang [72] enlarged the EDAS method using the q-rung orthopair fuzzy context. However, such techniques lack barriers concerning how to parameterize alternatives. A conceptual assessment of our novel EDAS approach to existing EDAS strategies for different fuzzy set configurations is discussed in Table 6.

Table 6.
Comparative analysis with existing EDAS models in different structures. n/a: not applicable.
The advanced EDAS technique effectively solves the essential difficulties raised by conventional EDAS strategies, particularly for maintaining the parameterized nature of alternates. Also, it efficiently addresses data related to sub-parameter forms and multi-sub-attributes of alternatives, which frequently get overlooked or not dealt with in other EDAS techniques. Given the importance of such variables in decision making, the proposed EDAS model addresses issues precisely. The feasibility of the developed EDAS model is shown by its ability to determine the most productive thermochemical method for disposing of MSW. Table 6 demonstrates that the proposed technique prevails over prior techniques in selecting the most optimal choice from the relevant prospects.
7.1.2. Comparison with Different Aggregation Operators
This method is extended within the framework of the intuitionistic fuzzy hypersoft set. So, this strategy is comparable to the multi-criteria decision-making approach developed by Zulqarnain et al. [45], which is based on the intuitionistic fuzzy hypersoft weighted average and weighted geometric AOs. The intuitionistic fuzzy hypersoft number is an extension of the intuitionistic fuzzy number. A comparison of our proposed approach with some prevalent operators under the same structure is given in Table 7, where score values and ranking orders are provided.

Table 7.
Comparison with different operators.
Table 7 demonstrates that pyrolysis is the optimum alternative for the thermochemical disposal approach to MSW in the decision-making procedures given in [45]. Figure 5 graphically represents the proposed EDAS method with different operators.
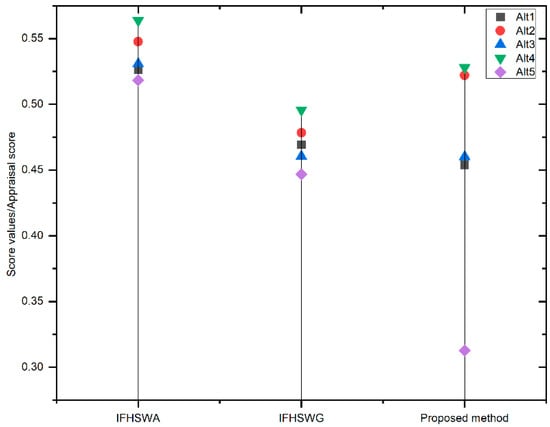
Figure 5.
Comparison with different operators.
7.1.3. Comparison with the TOPSIS Method
However, we explore the resemblances and disparities between the proposed strategy and the TOPSIS method [44]. was determined to be the most suitable alternative for the thermochemical technique of MSW disposal in the TOPSIS method [44]. The difference appears in the order of alternatives as an outcome of the procedure used to identify positive and negative ideal solutions, which is subsequently examined by considering the relative distances from these possible solutions. On the other hand, our proposed method depends on the principle of average solutions instead of implementing the optimal strategies, which includes the mathematical computation of comparable distances. The comparison of the results of Table 8 demonstrates that the developed EDAS approach, which entails the implementation of IFHSNs, delivers better precision in choosing the most suitable alternative for thermochemical MSW disposal processes. The distinction pertains to integrating more detailed data compared to IFS and IFSS and employing a unique technique to determine average solutions and calculate positive and negative distance measures.

Table 8.
Comparison with the TOPSIS method.
The graphical comparison of the proposed approach and the TOPSIS [44] method is demonstrated in Figure 6.
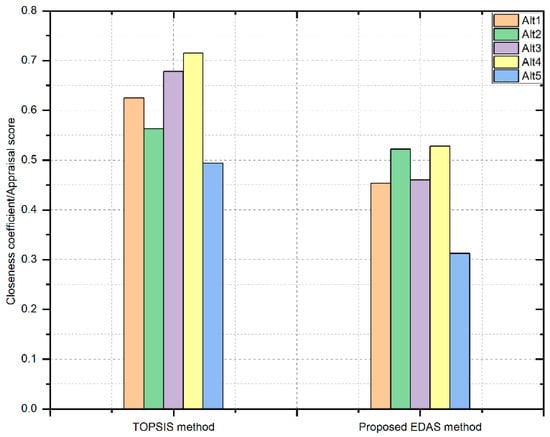
Figure 6.
Comparison with the TOPSIS method.
7.2. Discussion
After a comprehensive review of various research studies, it is determined that the EDAS approach used in this research is comparable to prior methods. However, the most significant advantage is integrating more details about the sub-parameters of alternatives, which attempts to address the fundamental confusion in empirical data. This approach delivers reliable and credible insights into objects, illuminating unclear and inaccurate aspects of the decision-making process. The stated EDAS approach provides greater effectiveness over existing methodologies and associated metrics by analyzing the level of perceptions and consistency across interpretations. Furthermore, it properly tackles issues related to parameterizing decisions and managing multiple sub-attributes, problems other EDAS techniques have not yet solved.
The assessments of the comparative study indicate a consensus between the ideal alternative identified by the proposed approach and the existing systems, validating the reliability and effectiveness of the proposed EDAS model. Therefore, the suggested EDAS strategy is a significant asset for decision makers, presenting more accurate and reliable findings than previous methodologies when managing instabilities and multiple sub-attributes.
7.3. Research Implications
The most important purpose of this paper is to present an adequate thermochemical waste disposal method for municipalities in Pakistan. Five thermochemical alternatives were explored for assessment. The conventional EDAS approach is frequently implemented as a multi-criteria decision-making strategy, and a substantial quantity of literature on the technique is available. This research uses a generalized distance function to extend the EDAS technique in the IFHSS structure. Several implications of this planned improvement are presented as follows.
7.3.1. Methodological Implications
The diagram shown in Figure 2, along with the details described in Section 5, demonstrate the sequential steps of the proposed approach. This approach uses the interaction aggregation and interaction-ordered AOs presented in Section 3 and Section 4 to organize the five experts’ decision matrices. The consequent fused decision matrix is applied to determine the average solution. This approach mainly uses the EDAS technique in an IFHSS framework. IFHSS–EDAS is characterized by its insistence on the average solution, which varies from the positive and negative ideal solutions determined in the TOPSIS approach [44]. This property imparts more benefit when comparing FS, IFS, FSS, and IFSS, stimulating the practicality of decision-making processes. The method’s applicability is demonstrated by its ability to be used by all municipal governments in Pakistan. The technique proposed here indicates the prospect of future study efforts, adding to the developing field of decision-making strategies.
7.3.2. Theoretical Implications
This study concentrates on an MAGDM problem regarding the most effective decisions about MSW disposal methods for municipalities in Pakistan. The theoretical applications of this hybrid approach will be stated in the following way.
Integrating IFHSS in the EDAS approach helps with the modeling of integral unpredictability and inaccuracy in the decision-making process. IFHSS effectively conveys complicated fuzzy facts by combining HSS and IFS knowledge. It enables amplification of the unpredictability of the data to calculate criteria weights.
The merging of the dynamically optimized methodology with IFHSS–EDAS improves its theoretical potential by effectively resolving the convoluted interactions between the parameters. When determining the best way to dump MSW, several factors require being taken into perspective, such as its impact on the surroundings, its affordability, its energy effectiveness, and its ability.
A detailed assessment of MSW disposal methods can be executed using the IFHSS–EDAS technique and irregular optimization. By implementing compromise research, stakeholders can review the functionality of various techniques over distinct parameters while simultaneously focusing on several criteria for assessment.
The execution of the IFHSS–EDAS technique complemented by dynamic stabilization indicates theoretical development regarding decision-making techniques for MSW. The theoretical repercussions include the ability to boost and enhance the approach, presenting prospects for future research.
7.3.3. Managerial Implications
This research investigates five thermochemical techniques for treating MSW: incineration, plasma arc gasification, thermal depolymerization, pyrolysis, and thermal gasification. However, according to the IFHSS–EDAS approach, pyrolysis () is the most effective technique for managing MSW based on the specified factors and sub-factors in Section 6.2.
Pyrolysis is when organic materials are heated without oxygen, causing them to disintegrate into smaller particles, including gases and liquid fuels. The process occurs inside of a pyrolysis reactor, a specially built container that operates at high temperatures (400–800 °C) and pressure. Pyrolysis is a flexible waste-to-energy approach capable of dealing with a wide range of resources, such as items that are difficult to recycle or dispose of, like rubber and agricultural residue.
Several managerial implications relate to the pyrolysis technique and need meticulous consideration. Here are a few of those features: it minimizes the detrimental impact of waste treatment on the surroundings by limiting the quantity of greenhouse gases released into the atmosphere and reducing the amount of fossil fuels used.
Using pyrolysis as an MSW management approach requires significant investments in technology and appliances. Therefore, it is important to precisely assess operational problems, such as the availability of adequate resources and the financial implications relating to gear and administration.
It may be essential to devote quite a bit of capital initially to implement pyrolysis as an MSW disposal method. However, it presents the prospect of financial rewards in the future. Alternatives include eliminating energy expenditures, minimizing trash disposal, and earning money from resale of waste products.
Before implementing pyrolysis, authorization from the regulatory organization with authority over waste and environmental handling techniques must be secured. This authorization is vital to prevent potential repercussions or legal problems.
Local communities and regulatory bodies are among several organizations that must be engaged in properly implementing pyrolysis. Although thoroughly describing precautions and protecting the environment is necessary, informing these stakeholders of pyrolysis’s conceivable benefits and risks is needed.
Workers and other stakeholders need educational and training initiatives to make the pyrolysis manufacturing process. Training personnel on the correct use of pyrolysis equipment and providing information about the method’s benefits and downsides are all part of this process.
Consequently, pyrolysis has been chosen for MSW management in part because of the EDAS approach. In light of the preceding information, pyrolysis can be implemented by Pakistani municipalities as an efficient and secure means of disposal of MSW, with an emphasis on environmental preservation and respect for the requirements and worries of all parties concerned.
Although our strategy enables mobility and resilience, it confronts limitations in complicated and unpredictable scenarios, particularly for computing expenses and manageability as the variety of feasible inputs grows.
8. Conclusions
The intuitionistic fuzzy hypersoft structure describes a novel technique in multi-attribute group decision-making processes, greatly enlarging the potential to integrate fuzzy data in a precise, logical paradigm. The proper handling of MSW persists as an important issue in Pakistan and other emerging economies due to poor policies and practices, resulting in adverse environmental effects. Prioritizing environmental concerns, cost-effectiveness, and extracting alternative energy sources from organic waste are essential to proper MSW disposal techniques. This research concentrates on five thermochemical MSW methods, integrating five criteria and their corresponding sub-criteria for classification.
We present interaction operational laws for IFHSNs and develop interactive aggregation and ordered aggregation operators, demonstrating their fundamental characteristics. The novel EDAS approach is presented to deal with the obstacles of MAGDM in the IFHSS structure using these interaction operators. The IFHSS–EDAS algorithm is implemented to determine the hierarchy of five alternatives, consequently determining pyrolysis as the best and most economical thermochemical MSW disposal approach in Pakistan. The comparative research and arguments demonstrate the viability and practicality of the presented approach, promoting its appropriateness to be implemented in all municipalities, taking into account financial and environmental considerations.
Moreover, the proposed research extended its practicality to the selection of sustainable resources, the selection of portfolios, the utilization of carbon capture, and the selection of storage sites. This study indicates the prospect of future research attempts because it implemented the novel idea of EDAS in the IFHSS environment and various optimization strategies. Further research will explore the distinct characteristics of Einstein-ordered and Einstein hybrid aggregation operators. Also, the technique stated in this article will be extended to include Pythagorean fuzzy hypersoft sets and q-rung orthopair fuzzy hypersoft sets. Moreover, studies will be performed to integrate IFHSNs with other MAGDM methods, evaluating their implications in medical diagnostics, material selection, pattern identification, and biomedical waste management. The prospective development of multiple topological, algebraic, and ordered structures in the IFHSS context will boost decision-making approaches in these areas.
Author Contributions
R.M.Z.: methodology, conceptualization, design, analysis, writing—original draft, writing—review and editing. H.W.: methodology, supervision, writing—original draft, writing—review and editing. I.S.: validation, design, analysis, writing—original draft. R.A.: funding, formal analysis, writing—original draft. H.N.: software, analysis, formal analysis, validation, writing—original draft. S.A.V.: writing—original draft, methodology, validation, formal analysis. M.I.A.: conceptualization, design, analysis, writing—original draft. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by King Khalid University grant number RGP2/218/45.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available within the article.
Acknowledgments
The authors extend their appreciation to the Deanship of Research and Graduate Studies at King Khalid University for funding this work through a Large Group Project under grant number RGP2/218/45.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they do not have any conflicts of interest.
References
- Ngoc, U.N.; Schnitzer, H. Sustainable solutions for solid waste management in Southeast Asian countries. Waste Manag. 2009, 29, 1982–1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, M.; Agrawal, M. Greenhouse gas emissions from municipal solid waste management: A review of global scenario. In Carbon Footprint Case Studies: Municipal Solid Waste Management, Sustainable Road Transport and Carbon Sequestration; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 123–160. [Google Scholar]
- Cetrulo, T.B.; Marques, R.C.; Cetrulo, N.M.; Pinto, F.S.; Moreira, R.M.; Mendizábal-Cortés, A.D.; Malheiros, T.F. Effectiveness of solid waste policies in developing countries: A case study in Brazil. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 205, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleluia, J.; Ferrão, P. Characterization of urban waste management practices in developing Asian countries: A new analytical framework based on waste characteristics and urban dimension. Waste Manag. 2016, 58, 415–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, F.; Zhou, H. Can the energy conservation and emission reduction demonstration city policy enhance urban domestic waste control? Evidence from 283 cities in China. Cities 2024, 154, 105323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, R.E.; Farahbakhsh, K. Systems approaches to integrated solid waste management in developing countries. Waste Manag. 2013, 33, 988–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, Y. Synergistic utilization, critical mechanisms, and environmental suitability of bauxite residue (red mud) based multi-solid wastes cementitious materials and special concrete. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 361, 121255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mir, I.S.; Cheema, P.P.S.; Singh, S.P. Implementation analysis of solid waste management in Ludhiana city of Punjab. Environ. Chall. 2021, 2, 100023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Cao, J.; Shao, Q. How to select remanufacturing mode: End-of-life or used product? In Environment, Development and Sustainability; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2024; pp. 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- Sohoo, I.; Ritzkowski, M.; Sohu, Z.A.; Cinar, S.Ö.; Chong, Z.K.; Kuchta, K. Estimation of methane production and electrical energy generation from municipal solid waste disposal sites in Pakistan. Energies 2021, 14, 2444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.R.; Shang-Guan, P.K.; Li, S.H.; Zhang, C.H.; Lou, J.M.; Guo, L.; Liu, L.; Lu, Y. The influence of carbon dioxide on fermentation products, microbial community, and functional gene in food waste fermentation with uncontrol pH. Environ. Res. 2024, 267, 120645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amin, N.; Aslam, M.; Yasin, M.; Hossain, S.; Shahid, M.K.; Inayat, A.; Samir, A.; Ahmad, R.; Murshed, M.N.; Khurram, M.S.; et al. Municipal solid waste treatment for bioenergy and resource production: Potential technologies, techno-economic-environmental aspects and implications of membrane-based recovery. Chemosphere 2023, 323, 138196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sohoo, I.; Ritzkowski, M.; Guo, J.; Sohoo, K.; Kuchta, K. Municipal solid waste management through sustainable landfilling: In view of the situation in Karachi, Pakistan. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aslam, S.; Ali, F.; Naseer, A.; Sheikh, Z. Application of material flow analysis for the assessment of current municipal solid waste management in Karachi, Pakistan. Waste Manag. Res. 2022, 40, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, A.; Yasar, A.; Tabinda, A.B.; Haider, R.; Sultan, I.A.; Kedwii, A.A.; Chaudhary, M.M.; Sheikh, M.M.; Nizami, A.S. Waste as Resource for Pakistan: An Innovative Business Model of Regenerative Circular Economy to Integrate Municipal Solid Waste Management Sector. Sustainability 2023, 15, 6281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohoo, I.; Ritzkowski, M.; Heerenklage, J.; Kuchta, K. Biochemical methane potential assessment of municipal solid waste generated in Asian cities: A case study of Karachi, Pakistan. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 135, 110175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, Q.; He, X.; Song, Y.; Tian, L.; Wu, H. Improving aerobic digestion of food waste by adding a personalized microbial inoculum. Curr. Microbiol. 2024, 81, 277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, R.; Jiang, S.; Ou, J.; Kouadio, K.L.; Xiong, B. Multifaceted anomaly detection framework for leachate monitoring in landfills. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 368, 122130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Salem, S.M.; Antelava, A.; Constantinou, A.; Manos, G.; Dutta, A. A review on thermal and catalytic pyrolysis of plastic solid waste (PSW). J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 197, 177–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, N.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, X.; Guan, Q. Fe-Mn oxide activating persufate for the in-situ chemical remediation of organic contaminated groundwater. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 355, 129566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, L.; Liang, L.; Shi, Y.; Yin, H.; Li, L.; Xiao, J.; Huang, N.; Zhao, A.; Xia, Y.; Hou, J. Biofilms in plastisphere from freshwater wetlands: Biofilm formation, bacterial community assembly, and biogeochemical cycles. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 476, 134930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arıkan, E.; Şimşit-Kalender, Z.T.; Vayvay, Ö. Solid waste disposal methodology selection using multi-criteria decision making methods and an application in Turkey. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 142, 403–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, Q.; Li, X.; Lian, X.; Hu, H.; Wang, N.; Wu, J.; Miao, K.; Feng, G.; Luo, X. Catalysis Enhancement of Co3O4 through the Epitaxial Growth of Inert ZnO in Peroxymonosulfate Activation: The Catalytic Mechanism of Surface Hydroxyls in Singlet Oxygen Generation. Cryst. Growth Des. 2024, 25, 319–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mir, M.A.; Ghazvinei, P.T.; Sulaiman, N.M.N.; Basri, N.E.A.; Saheri, S.; Mahmood, N.Z.; Jahan, A.; Begum, R.A.; Aghamohammadi, N.J.J.O.E.M. Application of TOPSIS and VIKOR improved versions in a multi criteria decision analysis to develop an optimized municipal solid waste management model. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 166, 109–115. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Ren, J.; Goodsite, M.E.; Xu, G. Waste-to-energy, municipal solid waste treatment, and best available technology: Comprehensive evaluation by an interval-valued fuzzy multi-criteria decision making method. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 172, 887–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coban, A.; Ertis, I.F.; Cavdaroglu, N.A. Municipal solid waste management via multi-criteria decision making methods: A case study in Istanbul, Turkey. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 180, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afrane, S.; Ampah, J.D.; Agyekum, E.B.; Amoh, P.O.; Yusuf, A.A.; Fattah, I.M.R.; Agbozo, E.; Elgamli, E.; Shouran, M.; Mao, G.; et al. Integrated AHP-TOPSIS under a fuzzy environment for the selection of waste-to-energy technologies in Ghana: A performance analysis and socio-enviro-economic feasibility study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 8428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akram, M.; Ramzan, N.; Deveci, M. Linguistic Pythagorean fuzzy CRITIC-EDAS method for multiple-attribute group decision analysis. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2023, 119, 105777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, T.K.; Jana, C.; Pal, M. Multi-criteria group decision-making method in disposal of municipal solid waste based on cubic Pythagorean fuzzy EDAS approach with incomplete weight information. Appl. Soft Comput. 2023, 144, 110515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, J.; Adhikary, K.; Kar, S. Credibilistic TOPSIS model for evaluation and selection of municipal solid waste disposal methods. In Advances in Waste Management: Select Proceedings of Recycle 2016; Springer: Singapore, 2019; pp. 243–261. [Google Scholar]
- Rahimi, S.; Hafezalkotob, A.; Monavari, S.M.; Hafezalkotob, A.; Rahimi, R. Sustainable landfill site selection for municipal solid waste based on a hybrid decision-making approach: Fuzzy group BWM-MULTIMOORA-GIS. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 248, 119186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, P.; Mishra, A.R.; Krishankumar, R.; Ravichandran, K.S.; Gandomi, A.H. A new Pythagorean fuzzy based decision framework for assessing healthcare waste treatment. IEEE Trans. Eng. Manag. 2020, 69, 2915–2929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, H.; Rani, D. An efficient intuitionistic fuzzy MULTIMOORA approach based on novel aggregation operators for the assessment of solid waste management techniques. Appl. Intell. 2022, 52, 4330–4363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Barakati, A.; Rani, P. Assessment of healthcare waste treatment methods using an interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy double normalization-based multiple aggregation approach. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2023, 26, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zadeh, L.A. Fuzzy sets. Inf. Control 1965, 8, 338–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atanassov, K.T. Intuitionistic Fuzzy Sets. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 1986, 20, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molodtsov, D. Soft set theory—First results. Comput. Math. Appl. 1999, 37, 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maji, P.K.; Biswas, R.; Roy, A.R. Fuzzy soft sets. J. Fuzzy Math. 2001, 9, 589–602. [Google Scholar]
- Maji, P.K.; Biswas, R.; Roy, A.R. Intuitionistic fuzzy soft sets. J. Fuzzy Math. 2001, 9, 677–692. [Google Scholar]
- Smarandache, F. Extension of soft set to hypersoft set, and then to plithogenic hypersoft set. Neutrosophic Sets Syst. 2018, 22, 168–170. [Google Scholar]
- Saeed, M.; Ahsan, M.; Abdeljawad, T. A development of complex multi-fuzzy hypersoft set with application in MCDM based on entropy and similarity measure. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 60026–60042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, A.U.; Saeed, M.; Smarandache, F. A theoretical and analytical approach to the conceptual framework of convexity cum concavity on fuzzy hypersoft sets with some generalized properties. Soft Comput. 2022, 26, 4123–4139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yolcu, A.; Smarandache, F.; Öztürk, T.Y. Intuitionistic fuzzy hypersoft sets. Commun. Fac. Sci. Univ. Ank. Ser. A1 Math. Stat. 2021, 70, 443–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zulqarnain, R.M.; Xin, X.L.; Saeed, M. Extension of TOPSIS method under intuitionistic fuzzy hypersoft environment based on correlation coefficient and aggregation operators to solve decision making problem. AIMS Math. 2020, 6, 2732–2755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zulqarnain, R.M.; Siddique, I.; Ali, R.; Pamucar, D.; Marinkovic, D.; Bozanic, D. Robust aggregation operators for intuitionistic fuzzy hypersoft set with their application to solve MCDM problem. Entropy 2021, 23, 688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Chen, H.; Zhou, L.; Liu, J.; Tao, Z. Intuitionistic fuzzy geometric interaction averaging operators and their application to multi-criteria decision making. Inf. Sci. 2014, 259, 142–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Chen, H.; Zhou, L.; Han, B.; Zhao, Q.; Liu, J. Generalized intuitionistic fuzzy geometric interaction operators and their application to decision making. Expert Syst. Appl. 2014, 41, 2484–2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, H. Some series of intuitionistic fuzzy interactive averaging aggregation operators. SpringerPlus 2016, 5, 999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, H. Generalized interaction aggregation operators in intuitionistic fuzzy multiplicative preference environment and their application to multicriteria decision-making. Appl. Intell. 2018, 48, 2120–2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, H. Generalized intuitionistic fuzzy multiplicative interactive geometric operators and their application to multiple criteria decision making. Int. J. Mach. Learn. Cybern. 2016, 7, 1075–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Wang, Y. Intuitionistic fuzzy interaction Hamy mean operators and their application to multi-attribute group decision making. Group Decis. Negot. 2019, 28, 197–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, H. Generalized intuitionistic fuzzy interactive geometric interaction operators using Einstein t-norm and t-conorm and their application to decision making. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2016, 101, 53–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P. Multiple attribute decision-making methods based on normal intuitionistic fuzzy interaction aggregation operators. Symmetry 2017, 9, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, H.; Arora, R. Novel scaled prioritized intuitionistic fuzzy soft interaction averaging aggregation operators and their application to multi criteria decision making. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2018, 71, 100–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, G. Pythagorean fuzzy interaction aggregation operators and their application to multiple attribute decision making. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 2017, 33, 2119–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Lu, M.; Wei, G.; Wei, Y. Some novel Pythagorean fuzzy interaction aggregation operators in multiple attribute decision making. Fundam. Informaticae 2018, 159, 385–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Garg, H.; Li, N. Pythagorean fuzzy interactive Hamacher power aggregation operators for assessment of express service quality with entropy weight. Soft Comput. 2021, 25, 973–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zulqarnain, R.M.; Xin, X.L.; Garg, H.; Ali, R. Interaction aggregation operators to solve multi criteria decision making problem under pythagorean fuzzy soft environment. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 2021, 41, 1151–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riaz, M.; Garg, H.; Farid HM, A.; Aslam, M. Novel q-rung orthopair fuzzy interaction aggregation operators and their application to low-carbon green supply chain management. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 2021, 41, 4109–4126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farid HM, A.; Riaz, M. Some generalized q-rung orthopair fuzzy Einstein interactive geometric aggregation operators with improved operational laws. Int. J. Intell. Syst. 2021, 36, 7239–7273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zulqarnain, R.M.; Siddique, I.; Eldin, S.M.; Gurmani, S.H. Extension of interaction aggregation operators for the analysis of cryptocurrency market under q-rung orthopair fuzzy hypersoft set. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 126627–126650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zulqarnain, R.M.; Siddique, I.; Iampan, A.; Awrejcewicz, J.; Bednarek, M.; Ali, R.; Asif, M. Novel multicriteria decision making approach for interactive aggregation operators of q-rung orthopair fuzzy soft set. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 59640–59660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keshavarz Ghorabaee, M.; Zavadskas, E.K.; Olfat, L.; Turskis, Z. Multi-criteria inventory classification using a new method of evaluation based on distance from average solution (EDAS). Informatica 2015, 26, 435–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorabaee, M.K.; Zavadskas, E.K.; Amiri, M.; Turskis, Z. Extended EDAS method for fuzzy multi-criteria decision-making: An application to supplier selection. Int. J. Comput. Commun. Control 2016, 11, 358–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, P.; Mustafa, A.; Khanduja, D.; Chowdhary, S.K.; Kumar, N.; Shukla, R.K. Prioritizing autonomous maintenance system attributes using fuzzy EDAS approach. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2020, 167, 1941–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahraman, C.; Keshavarz Ghorabaee, M.; Zavadskas, E.K.; Cevik Onar, S.; Yazdani, M.; Oztaysi, B. Intuitionistic fuzzy EDAS method: An application to solid waste disposal site selection. J. Environ. Eng. Landsc. Manag. 2017, 25, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, A.R.; Mardani, A.; Rani, P.; Zavadskas, E.K. A novel EDAS approach on intuitionistic fuzzy set for assessment of health-care waste disposal technology using new parametric divergence measures. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 272, 122807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schitea, D.; Deveci, M.; Iordache, M.; Bilgili, K.; Akyurt, I.Z.; Iordache, I. Hydrogen mobility roll-up site selection using intuitionistic fuzzy sets based WASPAS, COPRAS and EDAS. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 8585–8600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Rani, P.; Pachori, K. Sustainable circular supplier selection and evaluation in the manufacturing sector using Pythagorean fuzzy EDAS approach. J. Enterp. Inf. Manag. 2022, 35, 1040–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Liu, J.; Wei, C.; Liu, J. A new EDAS method based on prospect theory for Pythagorean fuzzy set and its application in selecting investment projects for highway. Kybernetes 2022, 51, 2636–2651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Wei, G.; Gao, H.; Wei, C.; Wei, Y. EDAS method for multiple criteria group decision making with picture fuzzy information and its application to green suppliers selections. Technol. Econ. Dev. Econ. 2019, 25, 1123–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darko, A.P.; Liang, D. Some q-rung orthopair fuzzy Hamacher aggregation operators and their application to multiple attribute group decision making with modified EDAS method. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2020, 87, 103259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, A.R.; Rani, P.; Pandey, K. Fermatean fuzzy CRITIC-EDAS approach for the selection of sustainable third-party reverse logistics providers using improved generalized score function. J. Ambient Intell. Humaniz. Comput. 2022, 13, 295–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).