Long-Term Effects of Crop Treatments and Fertilization on Soil Stability and Nutrient Dynamics in the Loess Plateau: Implications for Soil Health and Productivity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. The Geographical Map of Study Site of Changwu County Loess Plateau
2.3. Soil Sampling and Fertilization Under Different Land Use
2.4. Bulk Density
2.5. Root Biomass
2.6. Sampling Procedures Used in the Determination of Aggregate Size Fractions
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Soil Bulk Density, Root Biomass, and Biological Yield in Alfalfa and Grain Yield in Wheat Fields
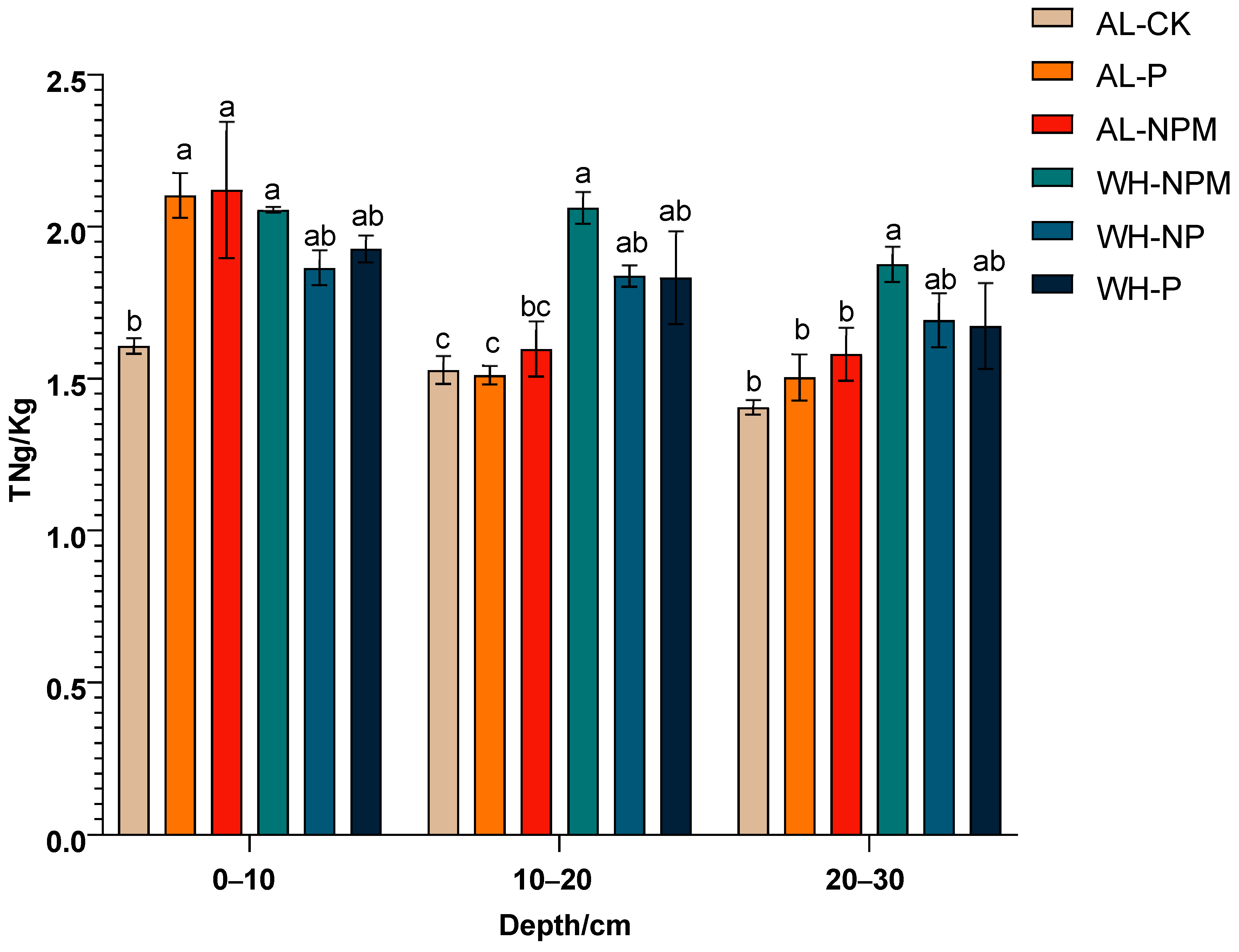
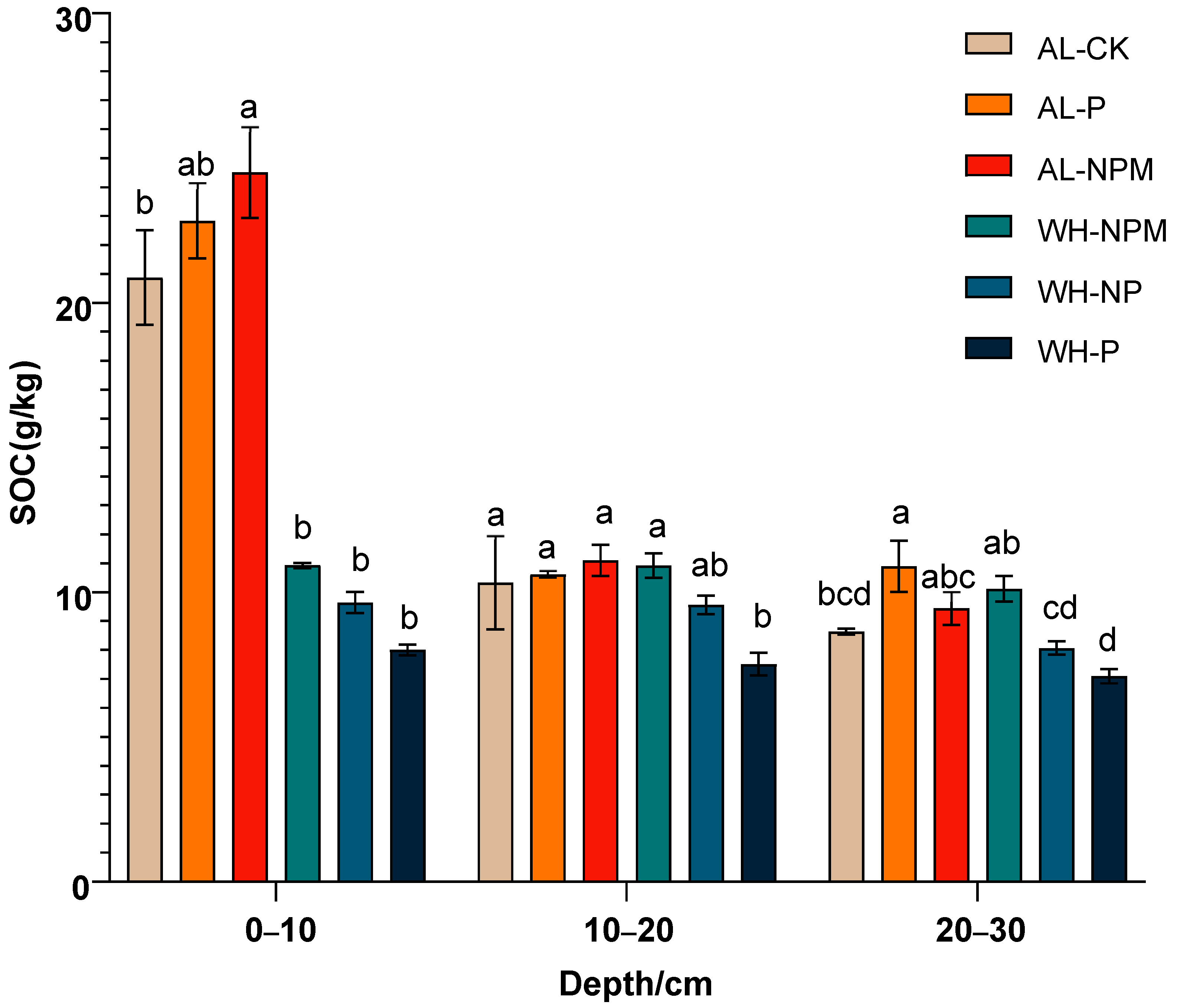
3.2. Soil Nutrient Concentrations
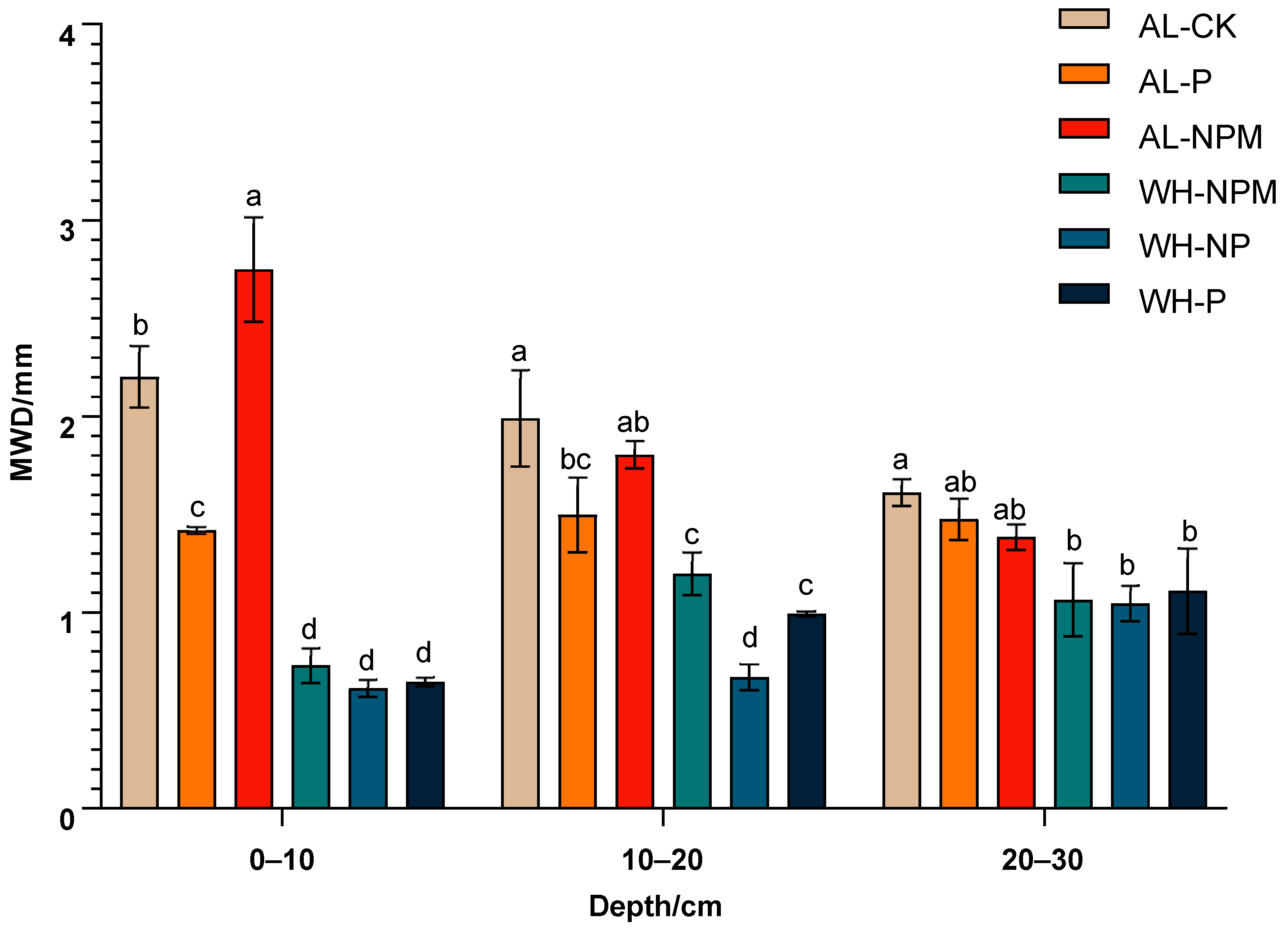
3.3. Soil Aggregate Stability
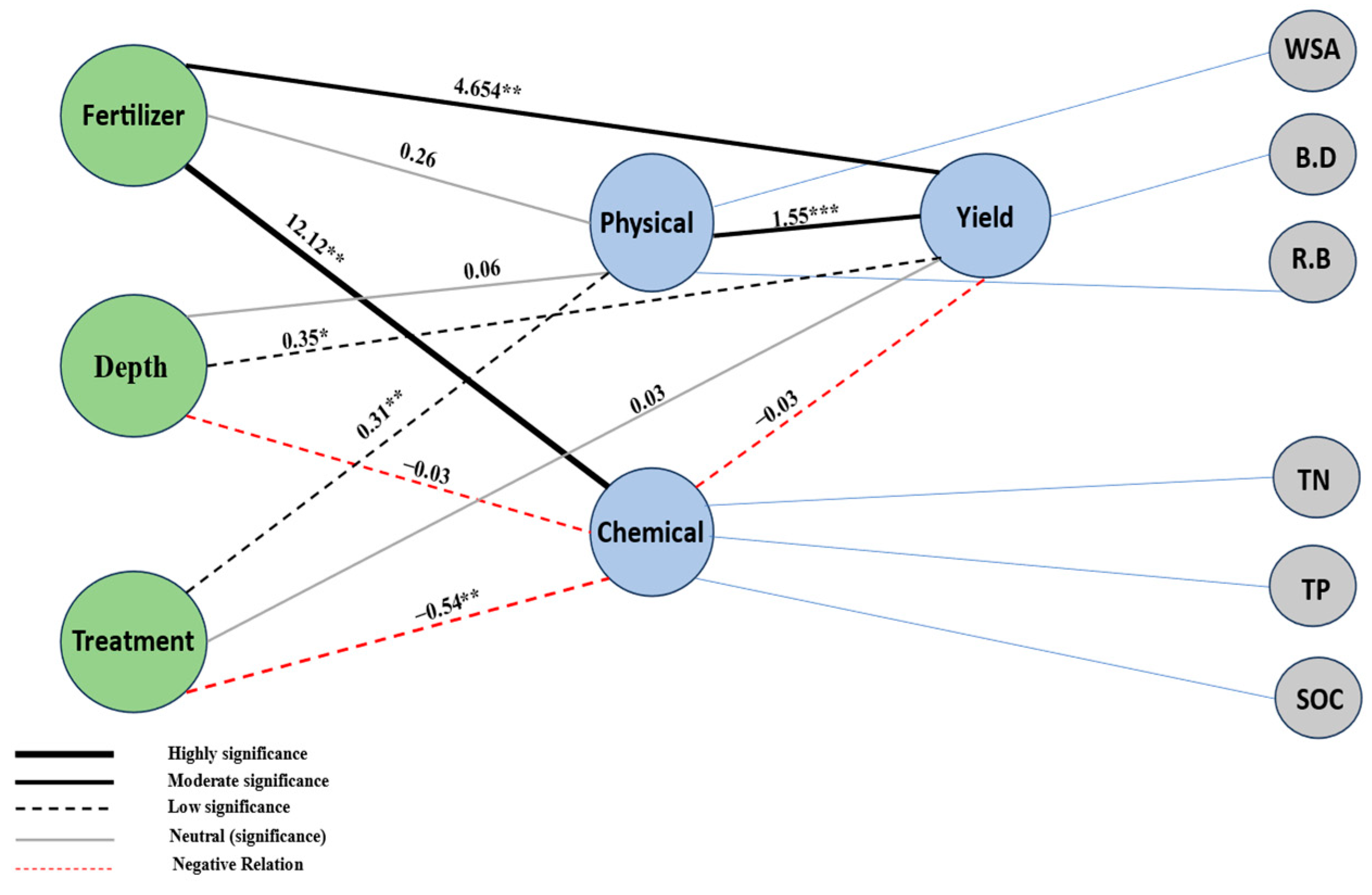
3.4. Correlation Patterns and Partial Least Squares Modeling (PLS-M) Outputs
4. Discussion
4.1. Yield Comparison Between Alfalfa and Wheat
4.2. Nutrient Management and Soil Dynamics
4.3. Effects of Fertilization on Soil Aggregation and Stability
4.4. Interpretation of Correlation Patterns and Partial Least Squares Modeling (PLS-M) Outputs
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jiang, C.; Zhang, H.; Wang, X.; Feng, Y.; Labzovskii, L. Challenging the land degradation in China’s Loess Plateau: Benefits, limitations, sustainability, and adaptive strategies of soil and water conservation. Ecol. Eng. 2019, 127, 135–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patial, D.; Sankhyan, N.K.; Sharma, R.P.; Dev, P.; Anjali. Assessing Soil Physical and Chemical Properties Under Long Term Fertilization After Forty-Eight Years in North-Western Himalayas. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2022, 53, 2257–2270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ping, Z.; Anbang, W.; Xinbao, Z.; Xiubin, H. Soil conservation and sustainable eco-environment in the Loess Plateau of China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2013, 68, 633–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, R.; Bhatia, A.; Ghosh, B.N.; Santra, P.; Mandal, D.; Kumar, G.; Chaudhari, S.K. Soil degradation and mitigation in agricultural lands in the Indian Anthropocene. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2023, 74, e13388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, R.; Ghosh, B.N.; Mishra, P.K.; Mandal, B.; Rao, C.S.; Sarkar, D.; Franzluebbers, A.J. Soil degradation in India: Challenges and potential solutions. Sustainability 2015, 7, 3528–3570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prashanth, M.; Kumar, A.; Dhar, S.; Verma, O.; Rai, S.K.; Kouser, B. Land use/land cover change and its implication on soil erosion in an ecologically sensitive Himachal Himalayan watershed, Northern India. Front. For. Glob. Change 2023, 6, 1124677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco-Sepúlveda, R.; Enríquez-Narváez, F.; Lima, F. Effectiveness of conservation agriculture (tillage vs. vegetal soil cover) to reduce water erosion in maize cultivation (Zea mays L.): An experimental study in the sub-humid uplands of Guatemala. Geoderma 2021, 404, 115336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, M.R.; van Es, H.M.; Schindelbeck, R.; Ristow, A.J.; Ryan, M. No-till and cropping system diversification improve soil health and crop yield. Geoderma 2018, 328, 30–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Hu, F.; Chen, X.; Huang, Q.; Jiao, J.; Zhang, B.; Li, H. Organic amendments with reduced chemical fertilizer promote soil microbial development and nutrient availability in a subtropical paddy field: The influence of quantity, type and application time of organic amendments. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2009, 42, 166–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.L.; Liu, K.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, H.; Li, D.; Li, J.; Shen, R. Balanced fertilization over four decades has sustained soil microbial communities and improved soil fertility and rice productivity in red paddy soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 793, 148664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, G.; Dhar, S.; Kumar, A.; Choudhary, A.; Dass, A.; Sharma, V.; Shukla, L.; Upadhyay, P.K.; Das, A.; Jinger, D.; et al. Microbes-mediated integrated nutrient management for improved rhizo-modulation, pigeonpea productivity, and soil bio-fertility in a semi-arid agro-ecology. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 924407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, D. Sustainable soil management for food security. Soil Use Manag. 2023, 39, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, W.; Chen, C.; Ma, Y.; Guo, S.; Liu, M.; Gao, Q.; Zhao, H. The combined application of mineral fertilizer and organic amendments improved the stability of soil water-stable aggregates and C and N accumulation. Agronomy 2022, 12, 469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, Y.; Lu, S. Does long-term inorganic and organic fertilization affect soil structural and mechanical physical quality of paddy soil? Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2020, 66, 625–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viet, H.Q. Influence of 96 years of mineral and organic fertilization on selected soil properties: A case study from long-term field experiments in Skierniewice, central Poland. Soil Sci. Annu. 2023, 74, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gyssels, G.; Poesen, J.; Bochet, E.; Li, Y. Impact of plant roots on the resistance of soils to erosion by water: A review. Prog. Phys. Geogr. 2005, 29, 189–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahat, M.M.; Alananbeh, K.M.; Othman, Y.A.; Leskovar, D.I. Soil Health and Sustainable Agriculture. Sustainability 2020, 12, 4859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu-Xu, L.; González-Hernández, A.I.; Camañes, G.; Vicedo, B.; Scalschi, L.; Llorens, E. Harnessing Green Helpers: Nitrogen-Fixing Bacteria and Other Beneficial Microorganisms in Plant–Microbe Interactions for Sustainable Agriculture. Horticulturae 2024, 10, 621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehman, R.M.; Acosta-Martinez, V.; Buyer, J.S.; Cambardella, C.A.; Collins, H.P.; Ducey, T.F.; Halvorson, J.J.; Jin, V.L.; Johnson, J.M.; Kremer, R.J.; et al. Soil biology for resilient, healthy soil. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2015, 70, 12A–18A. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, H.X.; Qin, J.H.; Sun, Z.X.; Guo, Z.L.; Wang, J.G. Erosion-reducing effects of plant roots during concentrated flow under contrasting textured soils. Catena 2021, 203, 105378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosier, S.; Córdova, S.C.; Robertson, G.P. Restoring soil fertility on degraded lands to meet food, fuel, and climate security needs via perennialization. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2021, 5, 706142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gowthamchand; Dhaliwal, S.S.; Sharma, V.; Verma, G.; Singh, J.; Kaur, M. Variation of physico-chemical properties among different soil orders under different land use systems of the Majha Region in North-Western India. Sustainability 2023, 15, 4779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, K.; Zhu, B. Phosphorus loss through surface runoff and leaching in response to the long-termapplication of different organic amendments on sloping croplands. J. Soils Sediments 2020, 20, 3459–3471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalhoro, S.A.; Xu, X.; Ding, K.; Chen, W.; Shar, A.G.; Rashid, M. The effects of different land uses on soil hydraulic properties in the Loess Plateau, Northern China. Land Degrad. Dev. 2018, 29, 3907–3916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böhm, W. Methods of Studying Root Systems; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Maleki, S.; Karimi, A.; Mousavi, A.; Kerry, R.; Taghizadeh-Mehrjardi, R. Delineation of soil management zone maps at the regional scale using machine learning. Agronomy 2023, 13, 445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L. Advances and perspectives on soil water research in China’s Loess Plateau. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2019, 199, 102962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, K.; Xu, X.; Chen, W.; Kalhoro, S.A. Soil aggregates and infiltration characteristics under different vegetations in Changwu tableland slope of northwestern China. Soil Sci. 2017, 39, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Li, Z.; Zhang, T. Impact of different fertilization regimes on root biomass and nutrient dynamics in cropping systems. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2015, 81, 50–58. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Y.; Su, B.; Currie, W.S.; Dukes, J.S.; Finzi, A.; Hartwig, U.; Field, C.B. Progressive nitrogen limitation of ecosystem responses to rising atmospheric carbon dioxide. Bioscience 2004, 54, 731–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Yang, Y.; Dang, T.; Zhu, Y.; Huang, M. Responses of Wheat Yield under Different Fertilization Treatments to Climate Change Based on a 35-Year In Situ Experiment. Agriculture 2022, 12, 1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gai, X.; Liu, H.; Liu, J.; Zhai, L.; Yang, B.; Wu, S.; Wang, H. Long-term benefits of combining chemical fertilizer and manure applications on crop yields and soil carbon and nitrogen stocks in North China Plain. Agric. Water Manag. 2018, 208, 384–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Hao, M.; Zhang, Y.; Li, L. Effects of continuous cropping of wheat and alfalfa on soil enzyme activities and nutrients. Yingyong Shengtai Xuebao 2014, 25, 3191–3196. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Otremba, K.; Kozłowski, M.; Tatuśko-Krygier, N.; Pająk, M.; Kołodziej, B.; Bryk, M. Impact of alfalfa and NPK fertilization in agricultural reclamation on the transformation of Technosols in an area following lignite mining. Land Degrad. Dev. 2021, 32, 1179–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triberti, L.; Nastri, A.; Baldoni, G. Long-term effects of crop rotation, manure and mineral fertilisation on carbon sequestration and soil fertility. Eur. J. Agron. 2016, 74, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Garrido, R.; Madejón, E.; Murillo, J.; Moreno, F. Short and long-term distribution with depth of soil organic carbon and nutrients under traditional and conservation tillage in a Mediterranean environment (southwest Spain). Soil Use Manag. 2011, 27, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.; Zhao, L.; Wu, X.; Fang, H.; Zhao, Y.; Yue, G.; Liu, G.; Chen, H. Vertical patterns and controls of soil nutrients in alpine grassland: Implications for nutrient uptake. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 607–608, 855–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clément, C.; Schneider, H.; Dresbøll, D.; Lynch, J.; Thorup-Kristensen, K. Root and xylem anatomy varies with root length, root order, soil depth, and environment in intermediate wheatgrass (Kernza®) and alfalfa. Ann. Bot. 2022, 130, 367–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puccio, G.; Ingraffia, R.; Giambalvo, D.; Amato, G.; Frenda, A. Morphological and Physiological Root Traits and Their Relationship with Nitrogen Uptake in Wheat Varieties Released from 1915 to 2013. Agronomy 2021, 11, 1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Hao, W.; Zhang, Y.; Liang, W. Changes in Soil Nutrients with Profile Depth in Aquic Brown Soil under Different Land Use. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2006, 20, 93–96, 122. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, L.; Huang, Y.; Zhao, J.; Zhou, J.; Abbas, F. Effects of planting structure on soil water-stable aggregates, microbial biomass and enzyme activity in a catchment of Loess Plateau terraces, China. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2020, 159, 103819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalhoro, S.; Xu, X.; Chen, W.; Hua, R.; Raza, S.; Ding, K. Effects of Different Land-Use Systems on Soil Aggregates: A Case Study of the Loess Plateau (Northern China). Sustainability 2017, 9, 1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jokela, W.; Posner, J.; Hedtcke, J.; Balser, T.; Read, H. Midwest cropping system effects on soil properties and on a soil quality index. Agron. J. 2011, 103, 1552–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šimanský, V.; Balashov, E.; Horák, J. Water stability of soil aggregates and their ability to sequester carbon in soils of vineyards in Slovakia. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2016, 62, 177–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, P.; Liu, S.; Ye, Y.; Zhang, W.; He, X.; Su, Y.; Wang, K. Soil carbon and nitrogen accumulation following agricultural abandonment in a subtropical karst region. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2018, 132, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Cheng, G.; Feng, H.; Sun, B.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, H.; Chen, J.; Dyck, M.; Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; et al. Effects of straw and biochar amendments on aggregate stability, soil organic carbon, and enzyme activities in the Loess Plateau, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 10108–10120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiang, M.; Zhang, X.; Zhuang, X.; Zhang, H. Effect of Organic Amendment and Mineral Fertilizer on Soil Aggregate Stability and Maize Yield on the Loess Plateau of China. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2024, 33, 2255–2265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.; Zhou, Y.; Zhou, X.; Zhou, W. Soil organic carbon and soil aggregate stability associated with aggregate fractions in a chronosequence of citrus orchards plantations. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 293, 112847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavalieri-Polizeli, K.; Marcolino, F.; Tormena, C.; Keller, T.; Moraes, A. Soil Structural Quality and Relationships With Root Properties in Single and Integrated Farming Systems. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 901302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Dai, L.; Xie, L.; Zhao, S.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Z. Hydrological connectivity improves soil nutrients and root architecture at the soil profile scale in a wetland ecosystem. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 762, 143162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Yuan, X.; Ge, L.; Li, Q.; Li, Z.; Wang, L.; Liu, Y. Rhizosphere effects promote soil aggregate stability and associated organic carbon sequestration in rocky areas of desertification. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2020, 304, 107126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lal, R. Restoring Soil Quality to Mitigate Soil Degradation. Sustainability 2015, 7, 5875–5895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, L.; Huang, M. Fine root distributions and water consumption of alfalfa grown in layered soils with different layer thicknesses. Soil Res. 2016, 54, 730–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gangwar, R.K.; Makádi, M.; Demeter, I.; Táncsics, A.; Cserháti, M.; Várbíró, G.; Szegi, T. Comparing soil chemical and biological properties of salt affected soils under different land use practices in Hungary and India. Eurasian Soil Sci. 2021, 54, 1007–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delcourt, N.; Rébufa, C.; Dupuy, N.; Boukhdoud, N.; Brunel, C.; Abadie, J.; Farnet-Da Silva, A.M. Infrared spectroscopy as a useful tool to predict land use depending on Mediterranean contrasted climate conditions: A case study on soils from olive-orchards and forests. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 686, 179–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, X.; Chen, S.; Sun, H.; Shao, L. Subsoil compaction and irrigation regimes affect the root–shoot relation and grain yield of winter wheat. Agric. Water Manag. 2015, 154, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Z.; Shen, J.; Blackwell, M.; Li, H.; Zhao, B.; Yuan, H. Combined applications of nitrogen and phosphorus fertilizers with manure increase maize yield and nutrient uptake via stimulating root growth in a long-term experiment. Pedosphere 2016, 26, 26–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Land Use | Bulk Density | Root Biomass | |
|---|---|---|---|
| (g cm−3) | mg cm−3 | ||
| Soil Layers (cm) | |||
| 0–10 | AL-CK | 1.15 ± 0.01 bc | 0.11 ± 1.07 ab |
| AL-P | 1.09 ± 0.02 c | 0.09 ± 0.98 ab | |
| AL-NPM | 1.10 ± 0.06 c | 0.31 ± 1.09 a | |
| WH-NPM | 1.16 ± 0.06 b | 0.04 ± 0.37 c | |
| WH-NP | 1.18 ± 0.02 ab | 0.03 ± 0.28 c | |
| WH-P | 1.20 ± 0.03 a | 0.02 ± 0.21 c | |
| 10–20 | AL-CK | 1.32 ± 0.03 a | 0.02 ± 0.20 c |
| AL-P | 1.33 ± 0.03 a | 0.06 ± 0.25 b | |
| AL-NPM | 1.24 ± 0.02 c | 0.09 ± 0.30 a | |
| WH-NPM | 1.30 ± 0.04 b | 0.07 ± 0.69 ab | |
| WH-NP | 1.32 ± 0.00 a | 0.03 ± 0.31 c | |
| WH-P | 1.30 ± 0.01 b | 0.02 ± 0.19 c | |
| 20–30 | AL-CK | 1.36 ± 0.06 bc | 0.04 ± 0.60 a |
| AL-P | 1.44 ± 0.03 b | 0.03 ± 0.11 b | |
| AL-NPM | 1.37 ± 0.02 bc | 0.05 ± 0.16 ab | |
| WH-NPM | 1.35 ± 0.03 c | 0.02 ± 0.21 c | |
| WH-NP | 1.47 ± 0.00 a | 0.01 ± 0.12 c | |
| WH-P | 1.45 ± 0.04 ab | 0.01 ± 0.07 c |
| Plot | Crop Type | Total Yield (kg/ha) |
|---|---|---|
| AL-CK | Alfalfa | 24,555 b |
| AL-P | Alfalfa | 33,240 a |
| AL-NPM | Alfalfa | 34,900 a |
| WH-NPM | Wheat | 5094.75 c |
| WH-NP | Wheat | 3924.75 d |
| WH-P | Wheat | 1055 e |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ullah Khan, F.; Zaman, F.; Qu, Y.; Wang, J.; Darmorakhtievich, O.H.; Wu, Q.; Fahad, S.; Du, F.; Xu, X. Long-Term Effects of Crop Treatments and Fertilization on Soil Stability and Nutrient Dynamics in the Loess Plateau: Implications for Soil Health and Productivity. Sustainability 2025, 17, 1014. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17031014
Ullah Khan F, Zaman F, Qu Y, Wang J, Darmorakhtievich OH, Wu Q, Fahad S, Du F, Xu X. Long-Term Effects of Crop Treatments and Fertilization on Soil Stability and Nutrient Dynamics in the Loess Plateau: Implications for Soil Health and Productivity. Sustainability. 2025; 17(3):1014. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17031014
Chicago/Turabian StyleUllah Khan, Farhat, Faisal Zaman, Yuanyuan Qu, Junfeng Wang, Ojimamdov Habib Darmorakhtievich, Qinxuan Wu, Shah Fahad, Feng Du, and Xuexuan Xu. 2025. "Long-Term Effects of Crop Treatments and Fertilization on Soil Stability and Nutrient Dynamics in the Loess Plateau: Implications for Soil Health and Productivity" Sustainability 17, no. 3: 1014. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17031014
APA StyleUllah Khan, F., Zaman, F., Qu, Y., Wang, J., Darmorakhtievich, O. H., Wu, Q., Fahad, S., Du, F., & Xu, X. (2025). Long-Term Effects of Crop Treatments and Fertilization on Soil Stability and Nutrient Dynamics in the Loess Plateau: Implications for Soil Health and Productivity. Sustainability, 17(3), 1014. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17031014








