Analyzing Eutrophication Conditions in the Gulf of Mexico Using the SIMAR Integral Marine Water Quality Index (ICAM-SIMAR-Integral)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Description of the SIMAR Integral Marine Water Quality Index (ICAM-SIMAR-Integral)
- Selection of environmental parameters for marine water quality
- -
- Chlorophyll-a concentration (mg/m3) or CHL: Satellite biological parameter, indicator of the presence of phytoplankton on the sea surface and related to possible contamination by organic matter, available since 4 September 1997 [22].
- -
- Nitrate concentration (mmol m−3) or NO3: Chemical parameter obtained from numerical models, an indicator of the presence of nutrients at the sea surface, available since 1 January 1993 [23].
- -
- Phosphate concentration (mmol m−3) or PO4: Chemical parameter obtained from numerical models, an indicator of the presence of nutrients at the sea surface, available since 1 January 1993 [24].
- -
- Diffuse attenuation coefficient of incident irradiance at 490 nm (m−1) or KD490: Satellite optical parameter used as an indicator of turbidity, available since 4 September 1997 [25].
- -
- Dissolved oxygen at the sea surface (mmol/m3) or O2: Chemical parameter derived from models, which can be affected by changes in salinity, temperature, or the presence of organic matter, available since 1 January 1993 [26].
- B.
- Generation of the sub-indices for each parameter
- -
- Chlorophyll-a sub-index (CHL):
- -
- Phosphate sub-index (PO4):
- -
- Sub-index of the diffuse attenuation coefficient (KD490):
- C.
- Assignment of parameter weighting values
- D.
- Calculation of the SIMAR Integral Marine Water Quality Index (ICAM-SIMAR-Integral) using an aggregation function
2.2. Evaluation of the Spatial and Temporal Variability of the ICAM-SIMAR-Integral
2.2.1. Study Sites
2.2.2. Data Processing for the Spatio-Temporal Evaluation of the Index
2.3. Validation of the ICAM-SIMAR-Integral
| TRIX | ICAM-SIMAR-Integral | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Source | Site | No. | Period | Mean | Median | Mean | Median |
| Herrera-Silveira and Morales-Ojeda [46] | Celestun | 1 | Three times a year from 2002 to 2006 | - | 4.43 | 53.63 | 54.35 |
| Sisal | 2 | - | 4.61 | 54.48 | 55.76 | ||
| Progreso | 3 | - | 5.17 | 53.64 | 54.93 | ||
| Telchac | 4 | - | 4.47 | 53.91 | 55.30 | ||
| Dzilam de Bravo | 5 | - | 3.57 | 51.55 | 52.37 | ||
| Ría Lagartos | 6 | - | 4.41 | 55.50 | 56.24 | ||
| Aranda-Cirerol [12] | Celestún | 7 | March to May 2000 | 5.23 | - | 58.14 | 57.96 |
| 8 | July to September 2000 | 4.80 | - | 50.80 | 51.07 | ||
| 9 | November 2000 to January 2001 | 5.46 | - | 55.06 | 55.24 | ||
| Sisal | 10 | March to May 2000 | 5.08 | - | 58.52 | 58.22 | |
| 11 | July to September 2000 | 5.10 | - | 49.32 | 49.41 | ||
| 12 | November 2000 to January 2001 | 4.89 | - | 56.95 | 58.58 | ||
| Progreso | 13 | March to May 2000 | 4.79 | - | 57.21 | 56.91 | |
| 14 | July to September 2000 | 5.16 | - | 47.60 | 47.52 | ||
| 15 | November 2000 to January 2001 | 4.99 | - | 56.57 | 57.82 | ||
| Dzilam de Bravo | 16 | March to May 2000 | 5.20 | - | 55.36 | 55.88 | |
| 17 | July to September 2000 | 5.17 | - | 46.37 | 46.38 | ||
| 18 | November 2000 to January 2001 | 4.78 | - | 55.51 | 55.45 | ||
| Ayala-Rodríguez [47] | Santa María | 19 | Monthly monitoring from November 2004 to February 2006 | 6.68 | - | 29.10 | 28.70 |
| Topolobampo | 20 | 5.99 | - | 37.14 | 35.52 | ||
| Ohuira | 21 | 6.13 | - | 38.75 | 38.25 | ||
| Escobedo-Urias [48] | Topolobampo | 22 | 2004 | 5.74 | - | 38.98 | 37.70 |
| 23 | 2005 | 5.82 | - | 37.44 | 35.79 | ||
| 24 | 2006 | 6.07 | - | 36.06 | 34.95 | ||
| 25 | 2007 | 6.20 | - | 36.20 | 35.42 | ||
| Navachiste-Macapule | 26 | 1998 | 4.95 | - | 41.14 | 40.89 | |
| 27 | 2000 | 5.09 | - | 39.24 | 38.71 | ||
| 28 | 2002 | 5.27 | - | 40.04 | 39.73 | ||
| 29 | 2003 | 5.43 | - | 40.46 | 40.15 | ||
| Cacheux [49] | Guaymas | 30 | September 2018 | 4.50 | - | 44.36 | 42.61 |
| 31 | December 2018 | 4.50 | - | 43.21 | 44.24 | ||
| 32 | February 2019 | 6.00 | - | 37.88 | 37.74 | ||
| 33 | April 2019 | 4.50 | - | 37.09 | 37.39 | ||
| Cervantes-Duarte et al. [50] | Bahía de Magdalena | 34 | 2015 | - | 5.38 | 52.68 | 53.94 |
| 35 | 2016 | - | 5.61 | 50.47 | 52.54 | ||
| 36 | 2017 | - | 5.85 | 45.86 | 46.73 | ||
| 37 | 2018 | - | 5.91 | 47.82 | 49.13 | ||
| Reyes-Velarde et al. [51] | Santa María-La Reforma | 38 | September 2018 | 4.39 | 4.88 | 44.30 | 46.10 |
| 39 | December 2018 | 4.48 | 5.21 | 32.30 | 34.51 | ||
| 40 | February 2019 | 6.31 | 6.38 | 27.84 | 28.34 | ||
| 41 | April 2019 | 4.61 | 4.70 | 50.80 | 51.22 | ||
3. Results and Discussion
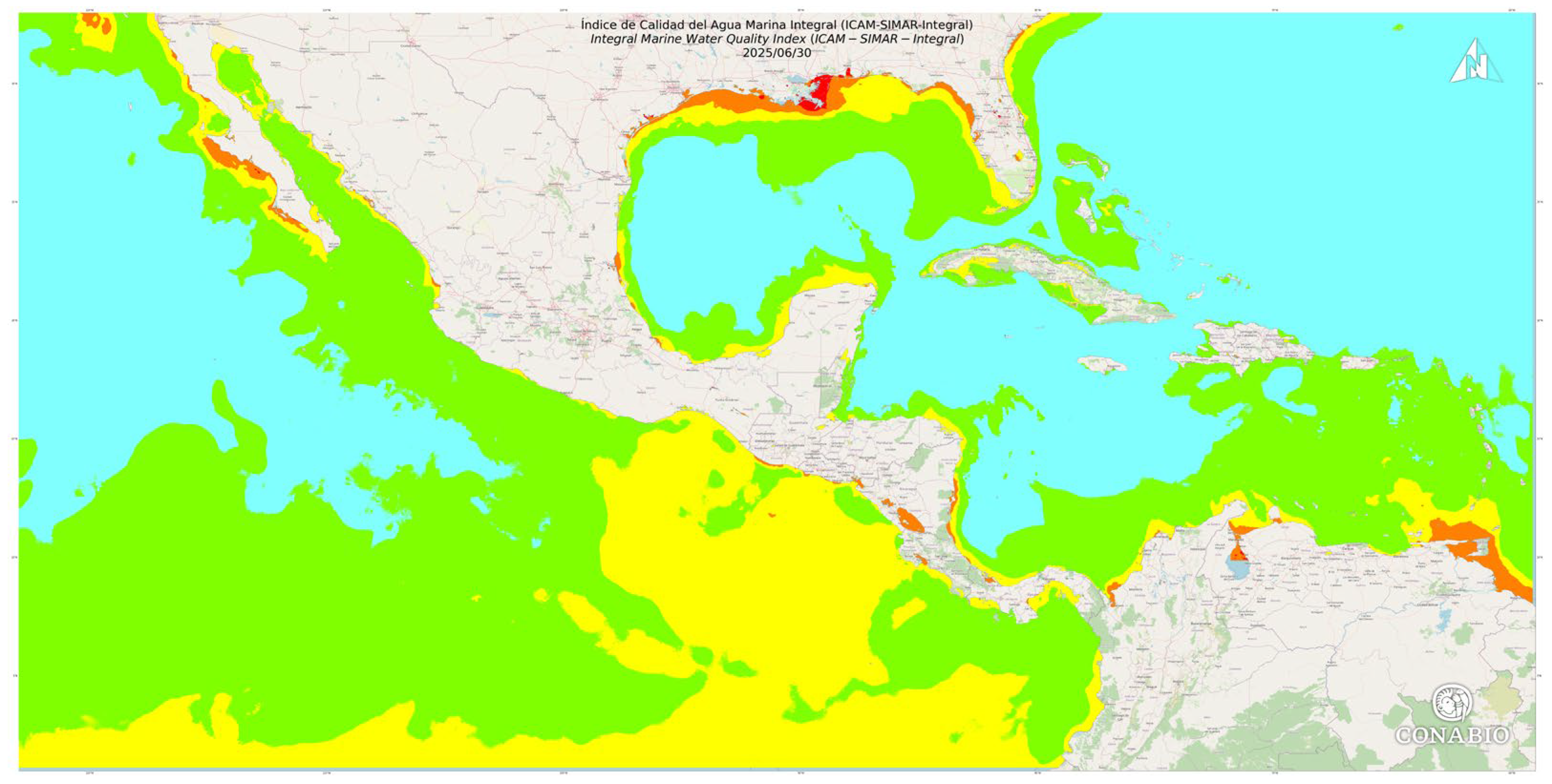
3.1. Visualization of ICAM-SIMAR-Integral on the SIMAR Operational Explorer
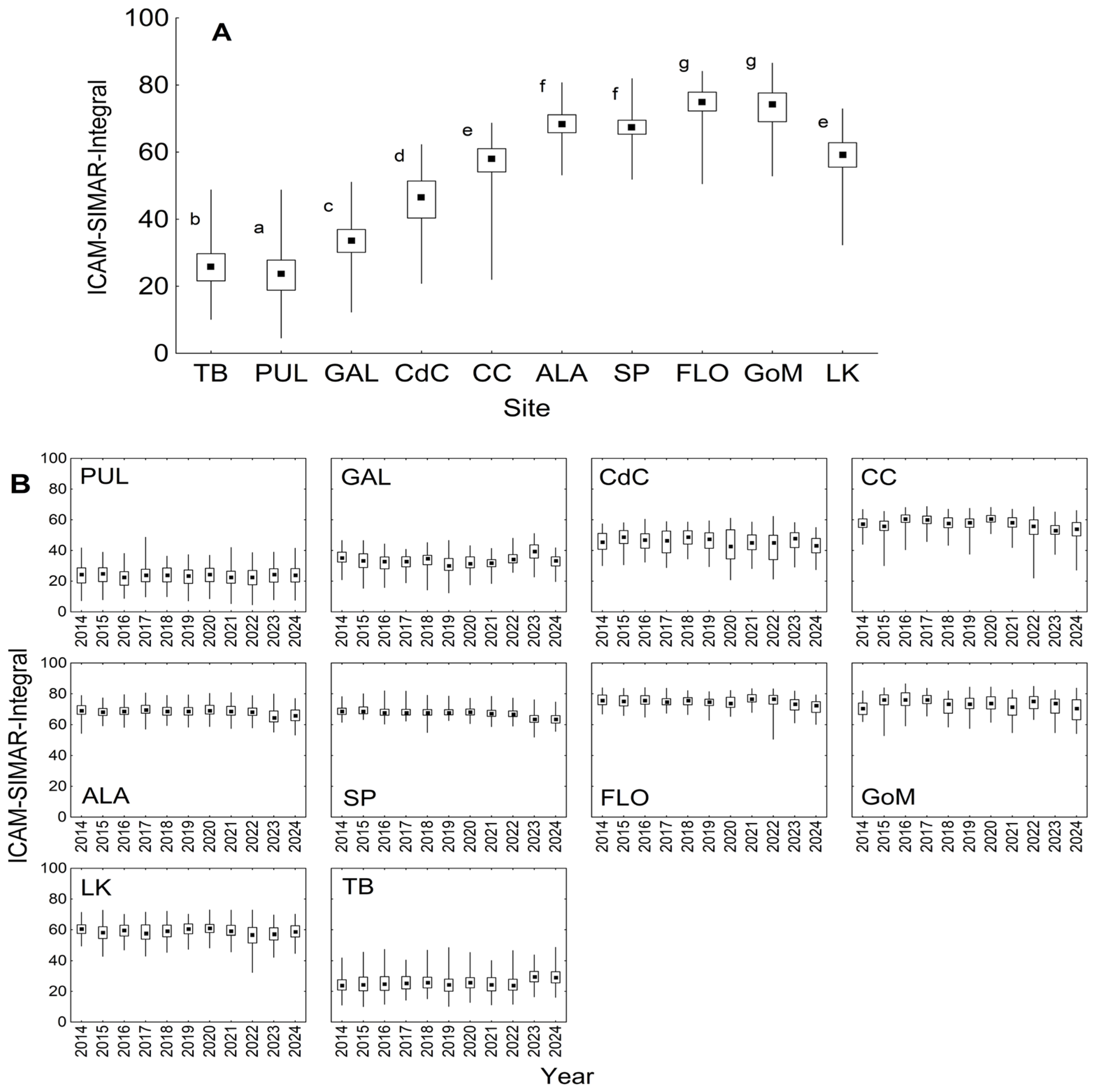
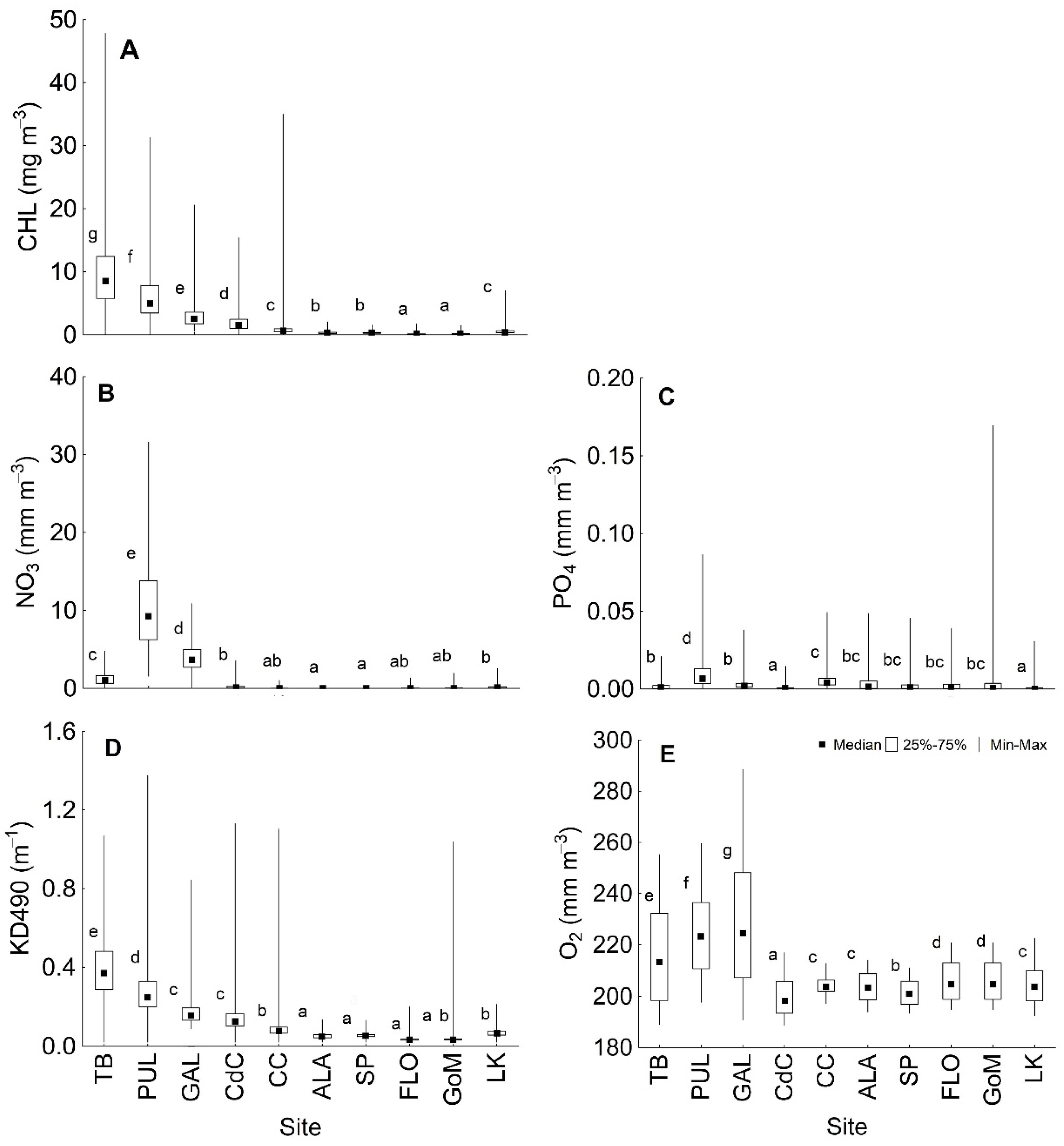
3.2. Spatiotemporal Variability of Metrics
3.3. Validation of the ICAM-SIMAR-Integral
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SIMAR | Marine and Coastal Information and Analysis System |
| TRIX | Trophic Index |
| WQIs | Water Quality Indices |
| ICAM | Marine Water Quality Index |
References
- Javed, S.; Ali, A.; Ullah, S. Spatial Assessment of Water Quality Parameters in Jhelum City (Pakistan). Environ. Monit. Assess. 2017, 189, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riechers, M.; Brunner, B.P.; Dajka, J.-C.; Dușe, I.A.; Lübker, H.M.; Manlosa, A.O.; Sala, J.E.; Schaal, T.; Weidlich, S. Leverage Points for Addressing Marine and Coastal Pollution: A Review. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 167, 112263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holsman, K.K.; Haynie, A.C.; Hollowed, A.B.; Reum, J.C.P.; Aydin, K.; Hermann, A.J.; Cheng, W.; Faig, A.; Ianelli, J.N.; Kearney, K.A.; et al. Ecosystem-based fisheries management forestalls climate-driven collapse. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McQuatters-Gollop, A.; Guérin, L.; Arroyo, N.L.; Aubert, A.; Artigas, L.F.; Bedford, J.; Corcoran, V.; Dierschke, S.A.M.; Elliott, S.C.V.; Geelhoed, A.; et al. Assessing the state of marine biodiversity in the Northeast Atlantic. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 141, 109–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syeed, M.M.M.; Hossain, M.S.; Karim, M.R.; Uddin, M.F.; Hasan, M.; Khan, R.H. Surface Water Quality Profiling Using the Water Quality Index, Pollution Index and Statistical Methods: A Critical Review. Environ. Sustain. Indic. 2023, 18, 100247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santamaría-del-Angel, E.; Sebastias-Frasquet, M.; Millán-Nuñez, R.; González-Silvera, A.; Cajal-Medrano, R. Anthropocentric bias in management policies. Are we efficiently monitoring our ecosystem? In Coastal Ecosystems: Experiences and Recommendations for Environmental Monitoring Programs; Sebastiá-Frasquet, M., Ed.; Nova Science Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 1–12. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/296950802_Anthropocentric_BIAS_in_management_policies_Are_we_efficiently_monitoring_our_ecosystems (accessed on 15 December 2025).
- Uddin Md, G.; Moniruzzaman, M.d.; Quader, M.A.; Hasan, M.A. Spatial Variability in the Distribution of Trace Metals in Groundwater around the Rooppur Nuclear Power Plant in Ishwardi, Bangladesh. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2018, 7, 220–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meran, G.; Siehlow, M.; Von Hirschhausen, C. Integrated Water Resource Management: Principles and Applications. In The Economics of Water; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 23–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, D. Water Quality Assessments: A Guide to the Use of Biota, Sediments and Water in Environmental Monitoring, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: London, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CEDEX La Calidad de las Aguas. Libro Blanco del Agua en España; Ministerio de Medio Ambiente: Madrid, Spain, 2000. Available online: https://ceh.cedex.es/web/documentos/LBA/LBA.pdf (accessed on 15 December 2025).
- Abirami, A. Marine Pollution and Waste Management. J. Law Leg. Res. Dev. 2024, 1, 20–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aranda Cirerol, N. Eutrofización y Calidad del Agua de Una Zona costera Tropical; Universitat de Barcelona, 2004. Available online: https://hdl.handle.net/2445/35296 (accessed on 15 December 2025).
- Uddin, M.G.; Nash, S.; Rahman, A.; Olbert, A.I. A Comprehensive Method for Improvement of Water Quality Index (WQI) Models for Coastal Water Quality Assessment. Water Res. 2022, 219, 118532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.K.; Gupta, S.K.; Patil, R.S. A Comparison of Water Quality Indices for Coastal Water. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 2003, 38, 2711–2725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vollenweider, R.A.; Giovanardi, F.; Montanari, G.; Rinaldi, A. Characterization of the Trophic Conditions of Marine Coastal Waters with Special Reference to the NW Adriatic Sea: Proposal for a Trophic Scale, Turbidity and Generalized Water Quality Index. Environmetrics 1998, 9, 329–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin Md, G.; Nash, S.; Olbert, A.I. A Review of Water Quality Index Models and Their Use for Assessing Surface Water Quality. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 122, 107218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mumby, P.J.; Green, E.P.; Edwards, A.J.; Clark, C.D. The Cost-Effectiveness of Remote Sensing for Tropical Coastal Resources Assessment and Management. J. Environ. Manag. 1999, 55, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malthus, T.J.; Mumby, P.J. Remote Sensing of the Coastal Zone: An Overview and Priorities for Future Research. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2003, 24, 2805–2815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chollett, I.; Mumby, P.J.; Müller-Karger, F.E.; Hu, C. Physical Environments of the Caribbean Sea. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2012, 57, 1233–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horton, R.K. An index-number system for rating water quality. J. Water Pollut. Control. Fed. 1965, 37, 300–306. [Google Scholar]
- Marine Water Quality Alert System (SATwality Marine-Coastal Information Analysis System (SIMAR). CONABIO. México. Available online: https://simar.conabio.gob.mx/explorer/ (accessed on 11 October 2024).
- Cerdeira-Estrada, S.; Martell-Dubois, R.; Valdéz, J.; Ressl, R. Daily 1-km Satellite Chlorophyll-a Concentration (CHL). Satellite-Based Ocean Monitoring System (SATMO). Marine-Coastal Information and Analysis System (SIMAR), CONABIO, Mexico, 2018. Available online: https://simar.conabio.gob.mx/explorer/?satmo=chl1 (accessed on 15 December 2025).
- Cerdeira-Estrada, S.; Martell-Dubois, R.; Valdéz-Chavarin, J.; Rosique-de la Cruz, L.; Perera-Valderrama, S.; López-Perea, J.; Caballero-Aragón, H.; Ressl, R. Nitrate Concentration in Surface Sea Water (NO3) at 1 km. Ocean-Atmosphere Climate Model System (SIMOD). Marine-Coastal Information and Analysis System (SIMAR), CONABIO, Mexico, 2021. Available online: https://simar.conabio.gob.mx (accessed on 15 December 2025).
- Cerdeira-Estrada, S.; Martell-Dubois, R.; Valdéz, J.; Ressl, R. Daily 1-km Satellite Diffuse Attenuation Coefficient of the Downwelling Irradiance at 490 nm (KD490) at 1-km. Satellite-Based Ocean Monitoring System (SATMO). Marine-Coastal Information and Analysis System (SIMAR), CONABIO, México, 2021. Available online: https://simar.conabio.gob.mx (accessed on 26 October 2020).
- Cerdeira-Estrada, S.; Martell-Dubois, R.; Valdéz, J.; Ressl, R. Daily 1-km Satellite Secchi Disk Depth (ZSD). Satellite-Based Ocean Monitoring System (SATMO). Marine-Coastal Information and Analysis System (SIMAR), CONABIO, Mexico, 2018. Available online: https://simar.conabio.gob.mx (accessed on 26 October 2020).
- Cerdeira-Estrada, S.; Martell-Dubois, R.; Valdéz-Chavarin, J.; Rosique-de la Cruz, L.; Perera-Valderrama, S.; López-Perea, J.; Caballero-Aragón, H.; Ressl, R. Dissolved Oxygen on the Sea Surface (O2) at 1 km. Ocean-Atmosphere Climate Model System (SIMOD). Marine-Coastal Information and Analysis System (SIMAR), CONABIO, Mexico, 2021. Available online: https://simar.conabio.gob.mx/explorer/?satmo=o2 (accessed on 15 December 2025).
- OCEANCOLOUR_GLO_BGC_L4_MY_009_104. Copernicus Marine Service Information (CMEMS). Marine Data Store (MDS). Available online: https://data.marine.copernicus.eu/product/OCEANCOLOUR_GLO_BGC_L4_MY_009_104/description (accessed on 11 December 2025).
- NEMO-PICIS GLOBAL_ANALYSISFORECAST_BGC_001_028 Copernicus Marine Service Information (CMEMS). Marine Data Store (MDS). Available online: https://data.marine.copernicus.eu/product/GLOBAL_ANALYSISFORECAST_BGC_001_028/description (accessed on 11 December 2025).
- CMEMS-OC-QUID-009-101to104-111-113-116-11830. Copernicus Marine Service Information (CMEMS). Marine Data Store (MDS). Available online: https://documentation.marine.copernicus.eu/QUID/CMEMS-OC-QUID-009-101to104-111-113-116-118.pdf (accessed on 11 December 2025).
- CMEMS-GLO-QUID-001-028. Copernicus Marine Service Information (CMEMS). Marine Data Store (MDS). Available online: https://documentation.marine.copernicus.eu/QUID/CMEMS-GLO-QUID-001-028.pdf (accessed on 11 December 2025).
- Srivastava, G.; Kumar, P. Water quality index with missing parameters. Int. J. Res. Eng. Technol. 2013, 02, 609–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banda, T.D.; Kumarasamy, M.V. Development of Water Quality Indices (WQIs): A Review. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2020, 29, 2011–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, M.G.; Nash, S.; Mahammad Diganta, M.T.; Rahman, A.; Olbert, A.I. Robust Machine Learning Algorithms for Predicting Coastal Water Quality Index. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 321, 115923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, M.G.; Nash, S.; Rahman, A.; Olbert, A.I. Performance Analysis of the Water Quality Index Model for Predicting Water State Using Machine Learning Techniques. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2023, 169, 808–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, D.M.; Glibert, P.M.; Burkholder, J.M. Harmful Algal Blooms and Eutrophication: Nutrient Sources, Composition, and Consequences. Estuaries 2002, 25, 704–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, K.R.; Gorley, R.N. PRIMER v7: User Manual/Tutorial; PRIMER-E, Ltd.: Plymouth, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Penna, N.; Capellacci, S.; Ricci, F. The Influence of the Po River Discharge on Phytoplankton Bloom Dynamics along the Coastline of Pesaro (Italy) in the Adriatic Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2004, 48, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zar, J.H. Biostatistical Analysis, 4th ed.; Prentice Hall International: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, W.; Chen, W.; Liang, Y. Feasibility Study on the Least Square Method for Fitting Non-Gaussian Noise Data. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Appl. 2018, 492, 1917–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilcoxon, F. Individual Comparisons by Ranking Methods. Biom. Bull. 1945, 1, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilcoxon, F.; Katti, S.K.; Wilcox, R.A. Critical Values and Probability Levels for the Wilcoxon Rank Sum Test and the Signed Rank Test; American Cyanamid Co., & Lederle Lab.: Pearl River, NY, USA, 1963. Available online: https://books.google.cl/books/about/Critical_Values_and_Probability_Levels_f.html?id=GS3aGAAACAAJ (accessed on 15 December 2025).
- Wilcoxon, F.; Katti, S.K.; Wilcox, R.A. Critical Values and Probability Levels for the Wilcoxon Rank Sum Test and the Wilcoxon Signed Rank Test. In Selected Tables in Mathematical Statistics; Amer Mathematical Society: Providence, RI, USA, 1970; Volume 1, pp. 171–259. [Google Scholar]
- Perdices, M. Null Hypothesis Significance Testing, p-Values, Effects Sizes and Confidence Intervals. Brain Impair. 2018, 19, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rey, D.; Neuhäuser, M. Wilcoxon-Signed-Rank Test. In International Encyclopedia of Statistical Science; Lovric, M., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 1658–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maggio, S.; Sawilowsky, S.S. A New Maximum Test via the Dependent Samples T-Test and the Wilcoxon Signed-Ranks Test. Appl. Math. 2014, 5, 110–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera-Silveira, J.A.; Morales-Ojeda, S.M. Evaluation of the Health Status of a Coastal Ecosystem in Southeast Mexico: Assessment of Water Quality, Phytoplankton and Submerged Aquatic Vegetation. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2009, 59, 72–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayala Rodríguez, G.A. Grupos Funcionales del Fitoplancton y Estado Trófico del Sistema Laguna Topolobam-po-Ohuira-Santa María. Thesis, Instituto Politécnico Nacional. Centro Interdisciplinario de Ciencias Marinas, 2008. Available online: http://www.repositoriodigital.ipn.mx/handle/123456789/13651 (accessed on 13 November 2025).
- Escobedo Urias, D.C. Diagnóstico y Descripción del Proceso de Eutrofización en Lagunas Costeras del Norte de Sinaloa. The-sis, Instituto Politécnico Nacional. Centro Interdisciplinario de Ciencias Marinas, 2010. Available online: https://agua.org.mx/wp-content/uploads/2019/11/Diagn%C3%B3stico-y-descripci%C3%B3n-del-proceso-de-eutrofizaci%C3%B3n-en-Lagunas-costeras-del-Norte-de-Sinaloa.pdf (accessed on 13 November 2025).
- Cacheux Martínez, E. Condición y Tendencia Ambiental de la Bahia de Guaymas, Sonora, México. 2019. Available online: https://rinacional.tecnm.mx/jspui/handle/TecNM/7352 (accessed on 15 December 2025).
- Cervantes-Duarte, R.; Jimenez-Quiroz, M.D.C.; Funes-Rodriguez, R.; Hernandez-Trujillo, S.; Gonzalez-Armas, R.; Ana-ya-Godinez, E. Interannual Variability in the Trophic Status and Water Quality of Bahía Magdalena, Mexico, During the 2015–2018 Period: TRIX. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2021, 42, 101638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes-Velarde, P.M.; Alonso-Rodríguez, R.; Domínguez-Jiménez, V.P.; Calvario-Martínez, O. The Spatial Distribution and Seasonal Variation of the Trophic State TRIX of a Coastal Lagoon System in the Gulf of California. J. Sea Res. 2023, 193, 102385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehrter, J.C.; Ko, D.S.; Murrell, M.C.; Hagy, J.D.; Schaeffer, B.A.; Greene, R.M.; Gould, R.W.; Penta, B. Nutrient Distributions, Transports, and Budgets on the Inner Margin of a River-Dominated Continental Shelf: Louisiana Shelf Nutrient Dynamics. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2013, 118, 4822–4838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greening, H.; Janicki, A.; Sherwood, E.T.; Pribble, R.; Johansson, J.O.R. Ecosystem Responses to Long-Term Nutrient Management in an Urban Estuary: Tampa Bay, Florida, USA. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2014, 151, A1–A16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yáñez-Arancibia, A.; Day, J. Ecological Characterization of Terminos Lagoon, a Tropical Lagoon-Estuarine System in the Southern Gulf of Mexico. Ecology of Coastal Ecosystems in the Southern Gulf of Mexico Region of the Lagoon of Términos 5: 1–26. 1982. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/284543972_Ecological_characterization_of_Terminos_Lagoon_a_tropical_lagoon-estuarine_system_in_the_Southern_Gulf_of_Mexico (accessed on 15 December 2025).
- Herrera-Silveira, J.A.; Comin, F.A.; Aranda-Cirerol, N.; Troccoli, L.; Capurro, L. Coastal Water Quality Assessment in the Yucatan Peninsula: Management Implications. Ocean. Coast. Manag. 2004, 47, 625–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grenz, C.; Fichez, R.; Silva, C.Á.; Benítez, L.C.; Conan, P.; Esparza, A.C.R.; Denis, L.; Ruiz, S.D.; Douillet, P.; Martinez, M.E.G.; et al. Benthic Ecology of Tropical Coastal Lagoons: Environmental Changes over the Last Decades in the Términos Lagoon, Mexico. Comptes Rendus. Géoscience 2017, 349, 319–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo, M.M.; Carrillo, L.; Jarquín-Sánchez, A.; Alcérreca-Huerta, J.C.; Álvarez-Merino, A.; Lázaro-Vázquez, A. Transport of Nutrients into the Southern Gulf of Mexico by the Grijalva–Usumacinta Rivers. Hydrol. Process. 2023, 37, e14838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Terrones, L.; Rebolledo-Vieyra, M.; Merino-Ibarra, M.; Soto, M.; Le-Cossec, A.; Monroy-Ríos, E. Groundwater Pollution in a Karstic Region (NE Yucatan): Baseline Nutrient Content and Flux to Coastal Ecosystems. Water Air Soil. Pollut. 2011, 218, 517–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapointe, B.E.; Brewton, R.A.; Herren, L.W.; Porter, J.W.; Hu, C. Nitrogen Enrichment, Altered Stoichiometry, and Coral Reef Decline at Looe Key, Florida Keys, USA: A 3-Decade Study. Mar. Biol. 2019, 166, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caballero-Aragón, H.; Alcolado, P.M. Condición de arrecifes de coral sometidos a presiones naturales recientes: Bajos de Sancho Pardo, Cuba. Rev. Mar. Cost. 2011, 3, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favoretto, F.; Mascareñas-Osorio, I.; León-Deniz, L.; González-Salas, C.; Pérez-España, H.; Rivera-Higueras, M.; Ruiz-Zárate, M.-Á.; Vega-Zepeda, A.; Villegas-Hernández, H.; Aburto-Oropeza, O. Being Isolated and Protected Is Better Than Just Being Isolated: A Case Study From the Alacranes Reef, Mexico. Front. Mar. Sci. 2020, 7, 583056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebich, R.A.; Houston, N.A.; Mize, S.V.; Pearson, D.K.; Ging, P.B.; Evan Hornig, C. Sources and Delivery of Nutrients to the Northwestern Gulf of Mexico from Streams in the South-Central United States1: Sources and Delivery of Nutrients to the Northwestern Gulf of Mexico from Streams in the South-Central United States. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2011, 47, 1061–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheffer, M.; Carpenter, S.; Foley, J.A.; Folke, C.; Walker, B. Catastrophic Shifts in Ecosystems. Nature 2001, 413, 591–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doney, S.C.; Fabry, V.J.; Feely, R.A.; Kleypas, J.A. Ocean Acidification: The Other CO2 Problem. Annu. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2009, 1, 169–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gulev, S.K.; Thorne, P.W.; Ahn, J.; Dentener, F.J.; Domingues, C.M.; Gerland, S.; Gong, D.; Kaufman, D.S.; Nnamchi, H.C.; Quaas, J.; et al. Changing state of the climate system. In Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Masson-Delmotte, V., Zhai, P., Pirani, A., Connors, S.L., Péan, C., Berger, S., Caud, N., Chen, Y., Goldfarb, L., Gomis, M.I., et al., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2021; pp. 287–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stenseth, N.C.; Mysterud, A.; Ottersen, G.; Hurrell, J.W.; Chan, K.-S.; Lima, M. Ecological Effects of Climate Fluctuations. Science 2002, 297, 1292–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schafer, T.; Dix, N.; Dunnigan, S.; Reddy, K.R.; Osborne, T.Z. Impacts of Hurricanes on Nutrient Export and Ecosystem Metabolism in a Blackwater River Estuary Complex. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Reyes, M.; Sydeman, W.J.; Schoeman, D.S.; Rykaczewski, R.R.; Black, B.A.; Smit, A.J.; Bograd, S.J. Under Pressure: Climate Change, Upwelling, and Eastern Boundary Upwelling Ecosystems. Front. Mar. Sci. 2015, 2, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glibert, P.M.; Maranger, R.; Sobota, D.J.; Bouwman, L. The Haber Bosch–Harmful Algal Bloom (HB–HAB) Link. Environ. Res. Lett. 2014, 9, 105001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seybold, E.C.; Dwivedi, R.; Musselman, K.N.; Kincaid, D.W.; Schroth, A.W.; Classen, A.T.; Perdrial, J.N.; Adair, E.C. Winter Runoff Events Pose an Unquantified Continental-Scale Risk of High Wintertime Nutrient Export. Environ. Res. Lett. 2022, 17, 104044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, R.E. Water Quality at the End of the Mississippi River for 120 Years: The Agricultural Imperative. Hydrobiologia 2024, 851, 1219–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wetz, M.S.; Cira, E.K.; Sterba-Boatwright, B.; Montagna, P.A.; Palmer, T.A.; Hayes, K.C. Exceptionally High Organic Nitrogen Concentrations in a Semi-Arid South Texas Estuary Susceptible to Brown Tide Blooms. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2017, 188, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Barnes, B.; Qi, L.; Corcoran, A. A Harmful Algal Bloom of Karenia Brevis in the Northeastern Gulf of Mexico as Revealed by MODIS and VIIRS: A Comparison. Sensors 2015, 15, 2873–2887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poor, N.; Pribble, R.; Greening, H. Direct Wet and Dry Deposition of Ammonia, Nitric Acid, Ammonium and Nitrate to the Tampa Bay Estuary, FL, USA. Atmos. Environ. 2001, 35, 3947–3955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, T.S.; DiMarco, S.F.; Cowan, J.H.; Hetland, R.D.; Chapman, P.; Day, J.W.; Allison, M.A. The Science of Hypoxia in the Northern Gulf of Mexico: A Review. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 1471–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabalais, N.N.; Turner, R.E.; Wiseman, W.J. Gulf of Mexico Hypoxia, A.K.A. “The Dead Zone”. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 2002, 33, 235–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cervantes-Díaz, G.Y.; Hernández-Ayón, J.M.; Zirino, A.; Herzka, S.Z.; Camacho-Ibar, V.; Norzagaray, O.; Barbero, L.; Montes, I.; Sudre, J.; Delgado, J.A. Understanding Upper Water Mass Dynamics in the Gulf of Mexico by Linking Physical and Biogeochemical Features. J. Mar. Syst. 2022, 225, 103647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santamaría-del-Ángel, E.; Millan-Nuñez, R.; Gonzalez-Silvera, A.; Cajal, R. Comparison of in Situ and Remotely-Sensed Chl-a Concentrations: A Statistical Examination of the Match-up Approach. In Handbook of Satellite Remote Sensing Image Interpretation: Applications for Marine Living Resources Conservation and Management; Morales, J., Stuart, V., Platt, T., Sathyendranath, S., Eds.; EU PRESPO and IOCCG: Dartmouth, Canada, 2011; pp. 241–260. [Google Scholar]
- Keith, L.H. Environmental Sampling and Analysis: A Practical Guide; CRC Press: New York, NY, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellerin, B.A.; Stauffer, B.A.; Young, D.A.; Sullivan, D.J.; Bricker, S.B.; Walbridge, M.R.; Clyde, G.A.; Shaw, D.M. Emerging Tools for Continuous Nutrient Monitoring Networks: Sensors Advancing Science and Water Resources Protection. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2016, 52, 993–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Shi, W. The NIR-SWIR Combined Atmospheric Correction Approach for MODIS Ocean Color Data Processing. Opt. Express 2007, 15, 15722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mobley, C.D.; Werdell, J.; Franz, B.; Ziauddin, A.; Bailey, S. Atmospheric Correction for Satellite Ocean Color Radiometry; National Aeronautics and Space Administration: Washington, DC, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Parameter | min | max |
|---|---|---|
| CHL (mg/m3) | 0.02 | 7 |
| NO3 (mmol m−3) | 0.0004 | 11 |
| PO4 (mmol m−3) | 0.00003 | 0.8 |
| KD490 (m−1) | 0.020 | 0.8 |
| O2 (mmol m−3) | 134 | 290 |
| Trophic Level | Color | Interval |
|---|---|---|
| Oligotrophic | 71–100 | |
| Mesotrophic | 51–70 | |
| Eutrophic | 31–50 | |
| Supertrophic | 11–30 | |
| Hipertrophic | 0–10 |
| Site | Acronym | Lat N | Lon W | Representative Of: |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Southwest Pass | TB | 27.7740 | 82.5170 | Estuarine zone |
| Pulaski Shoals Light | PUL | 28.9050 | 89.4280 | Estuarine zone |
| Galveston | GAL | 29.2320 | 94.4130 | Estuarine zone |
| Ciudad del Carmen | CdC | 18.7039 | 91.8357 | Estuarine zone |
| Cabo Catoche | CC | 21.7646 | 87.0513 | Coastal upwelling |
| Arrecife de Alacranes | ALA | 22.4696 | 89.7008 | Coral reef |
| Bajos de Sancho Pardo | SP | 22.1747 | 84.7698 | Coral reef |
| Estrecho de Florida | FLO | 23.7631 | 82.3661 | Open ocean waters |
| Mid Gulf | GoM | 25.8881 | 89.6581 | Open ocean waters |
| Long Key | LK | 24.6280 | 81.1090 | Coral reef |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Caballero-Aragón, H.; Santamaría-del-Ángel, E.; Cerdeira-Estrada, S.; Martell-Dubois, R.; Rosique-de-la-Cruz, L.; Valdez-Chavarin, J. Analyzing Eutrophication Conditions in the Gulf of Mexico Using the SIMAR Integral Marine Water Quality Index (ICAM-SIMAR-Integral). Sustainability 2025, 17, 11354. https://doi.org/10.3390/su172411354
Caballero-Aragón H, Santamaría-del-Ángel E, Cerdeira-Estrada S, Martell-Dubois R, Rosique-de-la-Cruz L, Valdez-Chavarin J. Analyzing Eutrophication Conditions in the Gulf of Mexico Using the SIMAR Integral Marine Water Quality Index (ICAM-SIMAR-Integral). Sustainability. 2025; 17(24):11354. https://doi.org/10.3390/su172411354
Chicago/Turabian StyleCaballero-Aragón, Hansel, Eduardo Santamaría-del-Ángel, Sergio Cerdeira-Estrada, Raúl Martell-Dubois, Laura Rosique-de-la-Cruz, and Jaime Valdez-Chavarin. 2025. "Analyzing Eutrophication Conditions in the Gulf of Mexico Using the SIMAR Integral Marine Water Quality Index (ICAM-SIMAR-Integral)" Sustainability 17, no. 24: 11354. https://doi.org/10.3390/su172411354
APA StyleCaballero-Aragón, H., Santamaría-del-Ángel, E., Cerdeira-Estrada, S., Martell-Dubois, R., Rosique-de-la-Cruz, L., & Valdez-Chavarin, J. (2025). Analyzing Eutrophication Conditions in the Gulf of Mexico Using the SIMAR Integral Marine Water Quality Index (ICAM-SIMAR-Integral). Sustainability, 17(24), 11354. https://doi.org/10.3390/su172411354











