Optimizing Environmental Comfort and Landscape Visibility in Traditional Villages via Digital Platforms: A Case Study of Dazhai Village, Chengbu County, Hunan
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
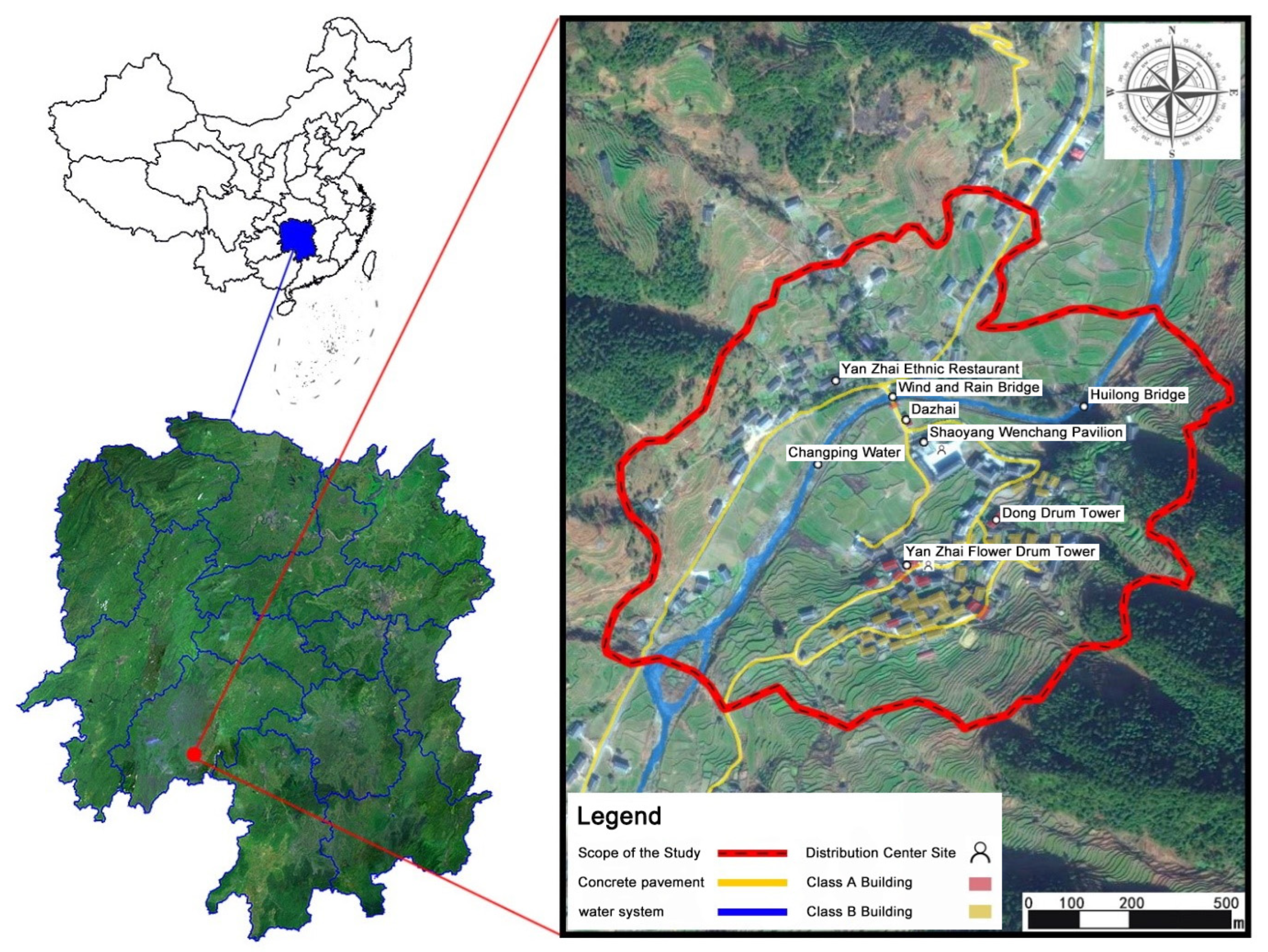
2.1. Overview of the Study Area
2.2. Data Sources and Processing
2.3. Environmental Comfort Analysis Model
2.4. Dynamic Touring Line Analysis Model
2.5. Multi-Dimensional Plot Value Evaluation Model
2.6. Three Models, Their Interrelationships, and Design Decision Logic
3. Results
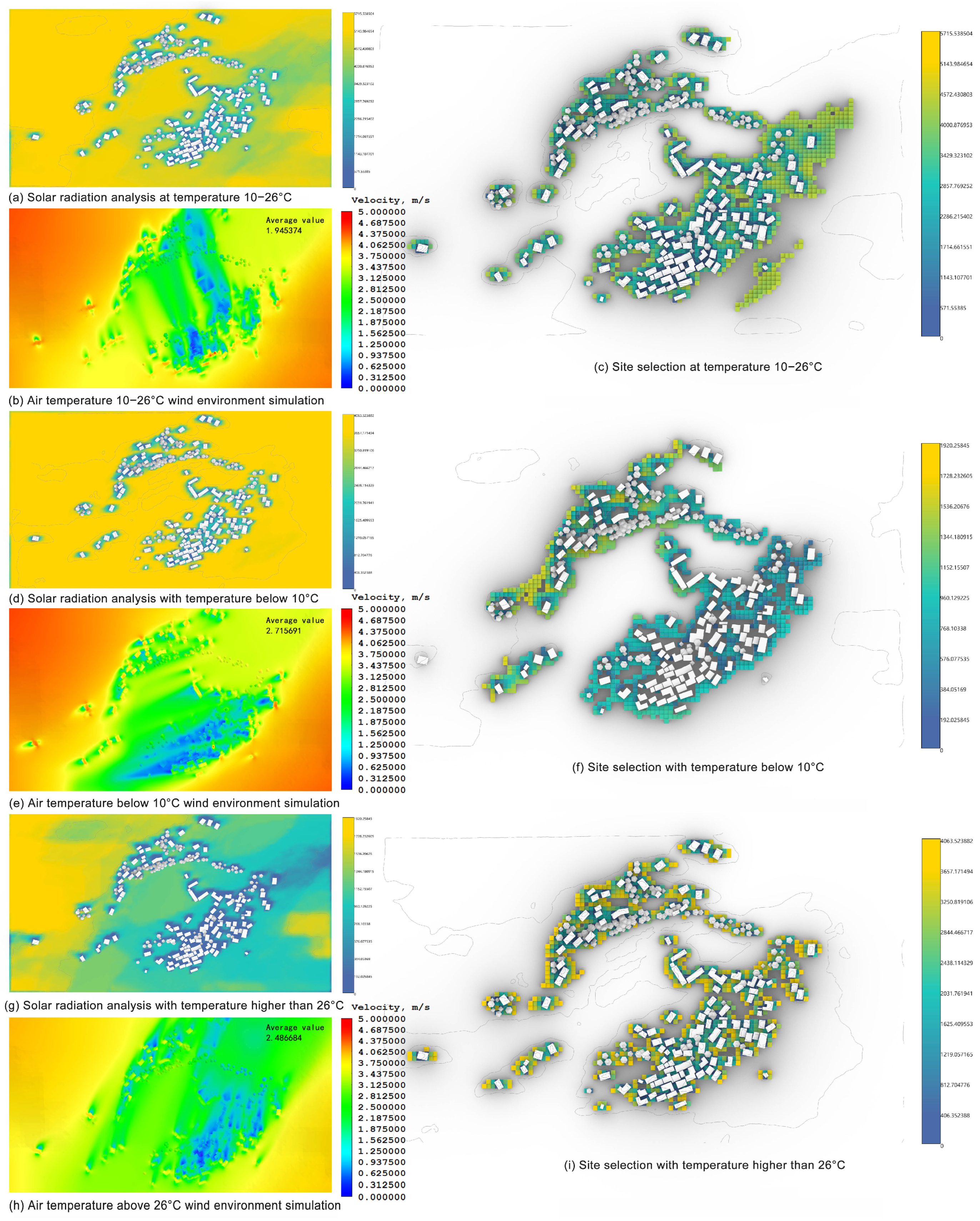
3.1. Climate Analysis of the Study Area
3.2. Perception Point Analysis and Activity Node Extraction
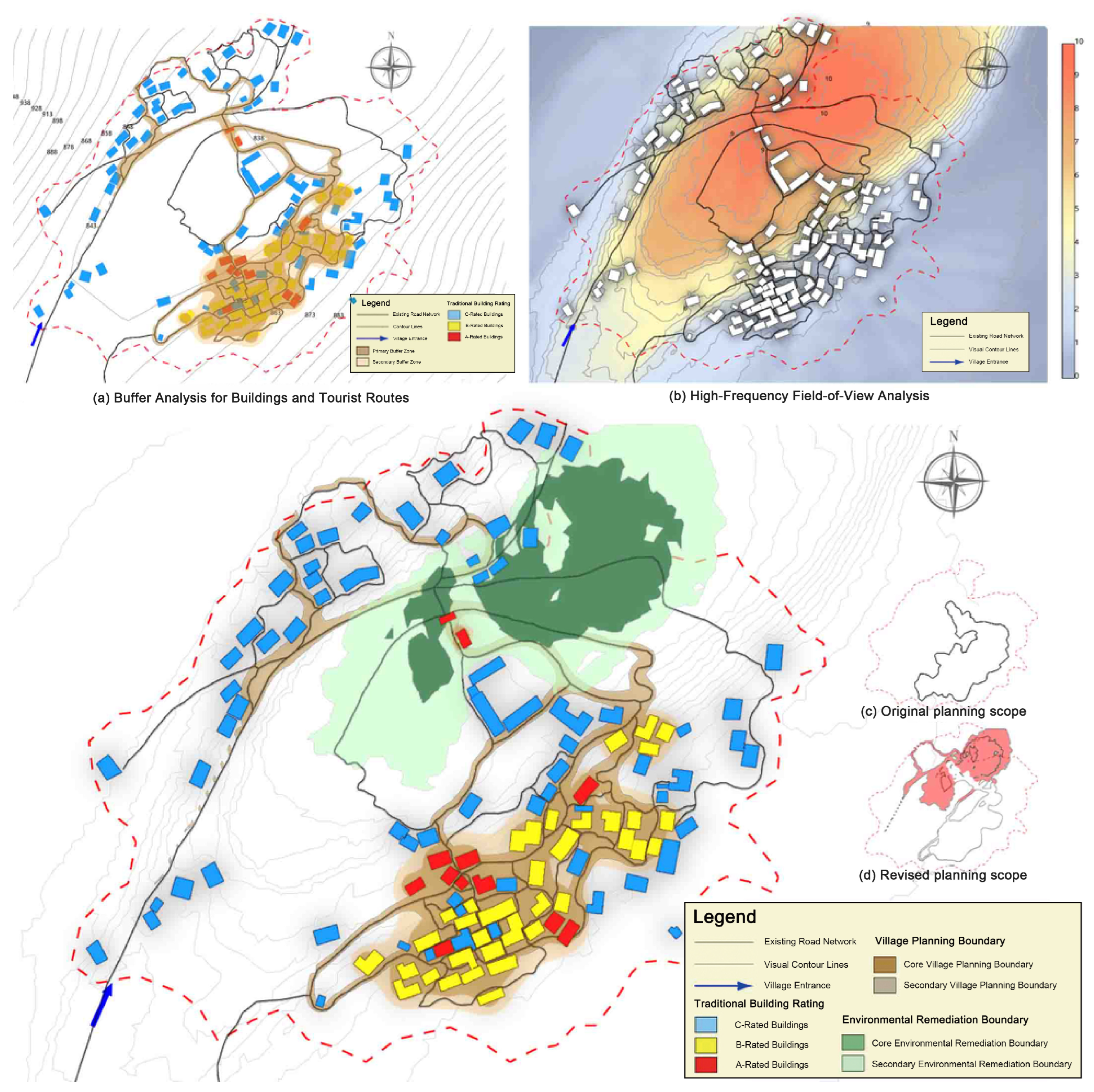
3.3. Tour Route Extraction and Optimization
3.4. Revision of Core Planning Boundaries
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
5.1. Extraction of Land Use Nodes and Tourist Routes Under Multiple Influences
5.2. Practicality and Limitations of Digital Platforms in Evaluating Human Comfort and Landscape Visibility
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yuan, C.; Kong, X.; Li, L.-Q.; Li, Y. Traditional Village Image Perception Research Based on Tourist UGC Data: A Case of Chengkan Village. Econ. Geogr. 2020, 40, 203–211. [Google Scholar]
- Tu, H.-F. Reflections on the Protection and Development of Traditional Chinese Villages in the Context of Rural Revitalization. Archit. Cult. 2023, 2023, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Lü, L. Spatial morphological traits, influencing factors and implications of typical traditional villages situated along the Jiangsu section of the Grand Canal. J. Nat. Resour. 2024, 39, 1993–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.-Z.; Fu, H.; Gong, J. Research on the Symbiotic Development Path of Traditional Villages from the Perspective of “Culture Driven”: Taking Five Traditional Villages in Xunxian County of Henan Province as An Example. Areal Res. Dev. 2021, 40, 169–173+180. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, J.; Zhang, X.; Hua, J. Research on the Effect and Mechanism of Digital Economy Empowering Rural Revitalization. Agric. Econ. Manag. 2025, 5, 53–65. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y. Mechanism and Empirical Test of Digital Economy Driving Rural Revitalization. Stat. Decis. 2025, 41, 11–16. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, M.; Zhu, H.; Tan, S.; Xu, Z. Reflections on Tourism-Driven Poverty Alleviation in Shihan Village, Qiongzhong Li and Miao Autonomous County. Tour. Overv. (Second Half Mon.) 2019, 162–163. [Google Scholar]
- Li, T.; Luo, Q.; Zhang, J.; Cheng, Y. Research on development of new business forms for traditional villagesin Northern Hainan volcano area based on the Grounded Theory: TakingMeixiao village in Haikou as a case. J. Nat. Resour. 2020, 35, 2079–2091. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, Y.-Q.; Chen, W.-Q.; Gao, H.; Ma, Y.H. Spatial Distribution Features and Controlling Factors of Traditional Villages in Henan Province. Areal Res. Dev. 2020, 39, 122–126. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.-B.; Wu, M.-M.; Li, X.; Wu, Z.C.; Li, W. Cognitive Reconstruction and the Evolution of Tourism Innovation in Traditional Village Community: A Case Study of Zhangguying Village in Hunan Province. Areal Res. Dev. 2021, 40, 92–96+102. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.-J.; Luo, D.-Y. Traditional Villages Need “Weak Landscape”—Exploration on the Practice of Traditional Village Landscape Construction. Landsc. Archit. 2018, 25, 26–31. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.-Y. The Research on the Application of Digital Technology in Ancient Villages Protection—Taking Jingxing County Daliangjiang Village as an Example. Master’s Thesis, Hebei Agricultural University, Shijiazhuang, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, R. Aesthetic Research on the Contemporary Multidimensional Building Skin. Ph.D. Thesis, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Bi, X.-J.; Liu, C.-H. Parametric Design of Energy Efficiency through Ladybug + Honeybee A Case Study on the Design of Office Complexes in Cold Regions in China. Archit. J. 2018, 65, 44–49. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Guo, Z.-F.; Ji, Y.-Z. Modeling and Realizing Generative Design A Case Study of the Assignment of Ji Village. Archit. J. 2015, 62, 94–98. [Google Scholar]
- Palmer, J.F. The contribution of a GIS-based landscape assessment model to a scientifically rigorous approach to visual impact assessment. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2019, 189, 80–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Wu, B.-H.; Zhao, Z.-F. A Sustainable Path Model for Tourism-based Revitalization of Traditional Villages Based on A Cultural Geography Perspective. Areal Res. Dev. 2020, 39, 73–78. [Google Scholar]
- Algeciras, J.A.R.; Consuegra, L.G.; Matzarakis, A. Spatial-temporal study on the effects of urban street configurations on human thermal comfort in the world heritage city of Camagüey-Cuba. Build. Environ. 2016, 101, 85–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.M.; Zhang, Y.F.; Zhao, L.H. Outdoor thermal comfort and activities in the urban residential community in a humid subtropical area of China. Energy Build. 2016, 133, 498–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.W.; Yang, F.; Zhang, Z.; Shao, Y.H.; Yuan, P.F. The effect of personal and microclimatic variables on outdoor thermal comfort: A field study in a cold season in Lujiazui CBD, Shanghai. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2018, 39, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, J.F.; English, D.B.K. An index of viewer sensitivity to scenery while engaged in recreation activities on U.S. National Forests. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2019, 189, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.-R. Study on the Visual Environment Design of Cultural Landscape of the “Huang Yong Ancient Road” in Taizhou, Zhejiang Province. Master’s Thesis, Zhejiang University of Technology, Hangzhou, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Nakashima, R.; Shioiri, S. Facilitation of visual perception in head direction: Visual attention modulation based on head direction. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0124367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S.-N.; Zhang, H.; He, B.-J.; Zhang, Y.-K. The Research on Visual Perception and Spatial Behavior in Traditional Chinese Villages Based on VR Experiment: A Case Study in Xiamei and Chengcun. New Archit. 2019, 39, 36–40. [Google Scholar]
- Xin, H.; Geng, X.; Li, C.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X. Assessment and lmpact Analysis of Urban Parks Resilience Based on PSR Model and Entropy Weight Method-A Case Study of shanghai. Fudan J. Nat. Sci. 2025, 64, 64–79. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, X.-J. The Production of Spectacle and the Restructuring of Rural Local Space-An Analysis of “Web-Star Village”. Ph.D. Thesis, Nanjing University, Nanjing, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Mou, T.-T.; Liu, Y.-F. Research on the Sight Line Organization of Vista View Landscape in Mountainous Park: Taking Phoenix Mountain National Forest Park as an Example. Chin. Landsc. Archit. 2017, 33, 91–94. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, J.; Yang, W.; Kong, Z.-H. ArcGIS Based Scenic Route Design of Traditional Villages: Kaiping Watchtowers. Planners 2015, 31, 90–94. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, N.; Jiang, X.-J.; Huang, J.-C.; Liu, H. Research on Tourism Planning of Traditional Village Space Based on Syntax Analysis: Take Xixiangping Village of Linzhou City in Henan Province as Example. Areal Res. Dev. 2019, 38, 111–115. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, S.-P.; Yun, Y.-X.; Tian, J. “Coordination” and “join”: Research on the Theory of “Source-Flow-Sink” Ventilated Corridor System Construction and Planning Strategy. Urban Dev. Stud. 2016, 23, 25–31. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Li, M.; Li, X.-Y. Research on Landscape Design of Fitness Facilities in Community Park Based on Human Comfort in Microclimate. Chin. Landsc. Archit. 2021, 37, 68–73. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, L.-J.; Sun, G.-N.; Wang, J.-J. Evaluation of Tourism Climate Comfortableness of Coastal Cities in the Eastern China. Prog. Geogr. 2009, 28, 713–722. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.-H. Evolution and Mechanism of Rural Settlement Pattern in Baiyun Mountain Tourist Area, Luoyang City. Areal Res. Dev. 2019, 38, 117–123. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, K.; Su, X.-L.; Su, K.-H.; Wang, Y. Research on Distribution Characteristic of Tourism Resource in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region Based on POI Big Data. Areal Res. Dev. 2021, 40, 103–108+114. [Google Scholar]




| Item | Index | Evaluation Standard |
|---|---|---|
| environmental comfort | dry-bulb temperature | The temperature of 10–26 °C indicates a high level of environmental comfort, and strong discomfort will be generated when the temperature is lower than 10 °C (cold) and higher than 26 °C (hot) [12,13,14] |
| solar radiation | Related to temperature, the site temperature increases with the increase in solar radiation | |
| wind direction and speed | Related to temperature, every 1 m/s increase in wind speed will make people feel that the temperature has dropped by 2–3 °C |
| Item | Index | Evaluation Standard |
|---|---|---|
| landscape visibility | visible quantity of building | The more visible the number of buildings, the more the number of stilted buildings in the field of vision, the better the human feeling, the greater the impact of village culture |
| visible area | The larger the field of view, the less occlusions in the field of view, the higher the spatial pleasure | |
| environmental comfort | percentage of comfort time | The higher the percentage of comfort time, the longer the comfort time, the higher the comfort |
| Evaluation Index | Expert (10 People) | Manager (10 People) | Villager and Tourist (50 People) | Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| landscape visibility | 6.4 | 5.6 | 5.3 | 5.83 |
| environmental comfort | 3.6 | 4.4 | 4.7 | 4.17 |
| visible quantity of building | 4.2 | 4.7 | 4.8 | 4.53 |
| visible area | 5.8 | 5.3 | 5.2 | 5.47 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, R.; Feng, S.; Wang, J.; Peng, W.; Tan, C. Optimizing Environmental Comfort and Landscape Visibility in Traditional Villages via Digital Platforms: A Case Study of Dazhai Village, Chengbu County, Hunan. Sustainability 2025, 17, 11147. https://doi.org/10.3390/su172411147
Li R, Feng S, Wang J, Peng W, Tan C. Optimizing Environmental Comfort and Landscape Visibility in Traditional Villages via Digital Platforms: A Case Study of Dazhai Village, Chengbu County, Hunan. Sustainability. 2025; 17(24):11147. https://doi.org/10.3390/su172411147
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Ruixue, Saisai Feng, Jieming Wang, Wengang Peng, and Chenyu Tan. 2025. "Optimizing Environmental Comfort and Landscape Visibility in Traditional Villages via Digital Platforms: A Case Study of Dazhai Village, Chengbu County, Hunan" Sustainability 17, no. 24: 11147. https://doi.org/10.3390/su172411147
APA StyleLi, R., Feng, S., Wang, J., Peng, W., & Tan, C. (2025). Optimizing Environmental Comfort and Landscape Visibility in Traditional Villages via Digital Platforms: A Case Study of Dazhai Village, Chengbu County, Hunan. Sustainability, 17(24), 11147. https://doi.org/10.3390/su172411147


_Li.png)


