Impact of Climate Change on Cyanobacteria Growth: A Case Study of Lama Dei Peligni Rock Paintings Conservation (Majella Massif—Abruzzo Region, Italy)
Abstract
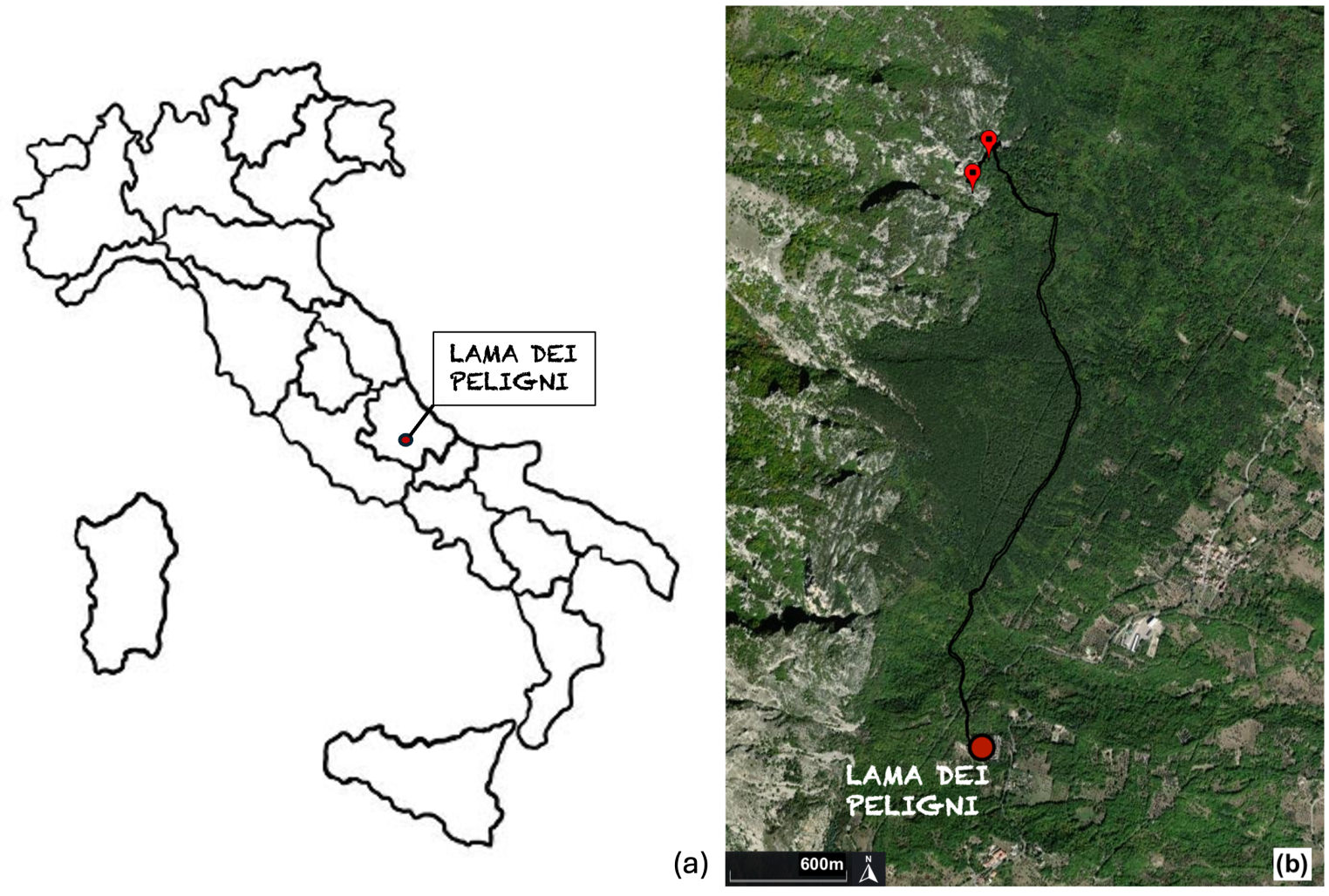
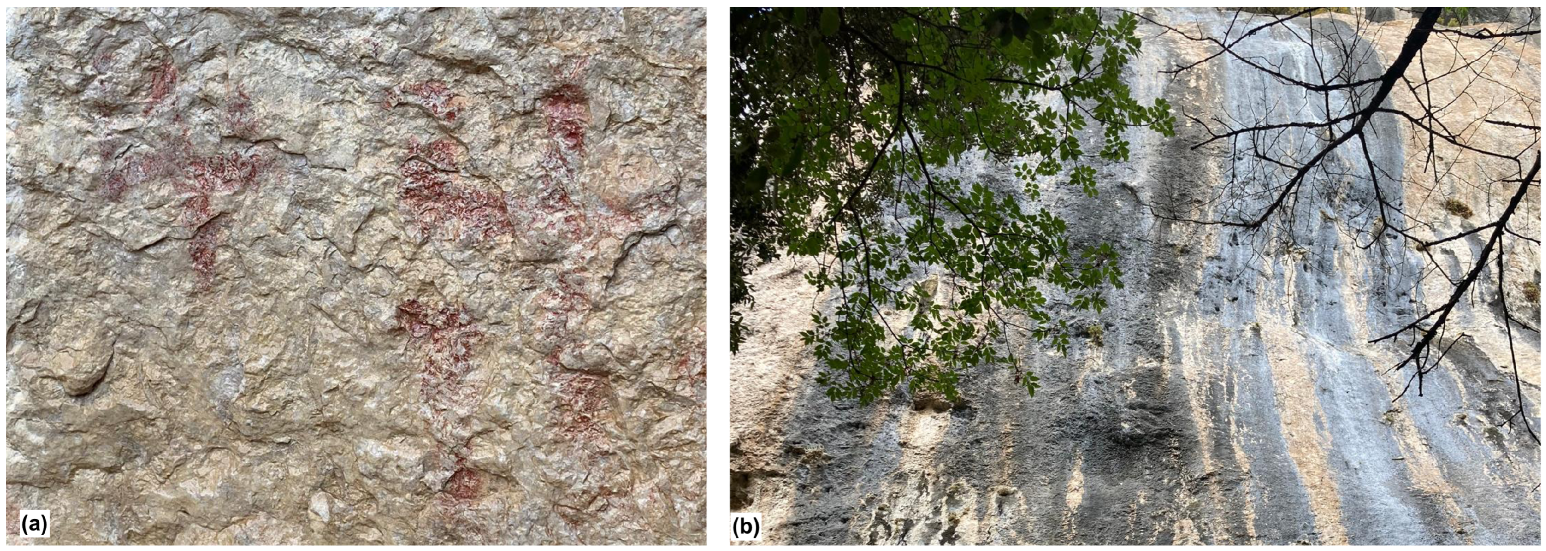
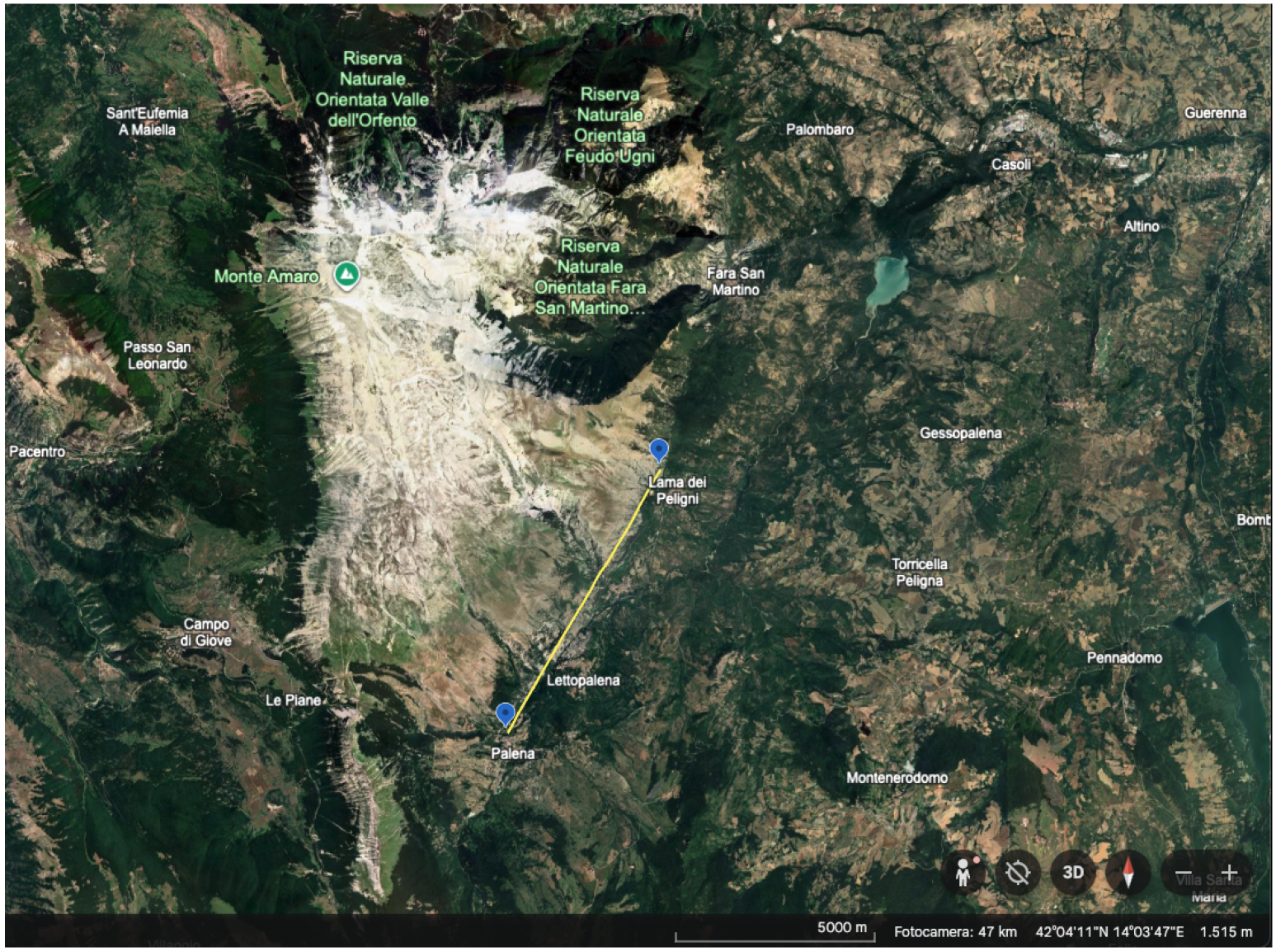
1. Introduction
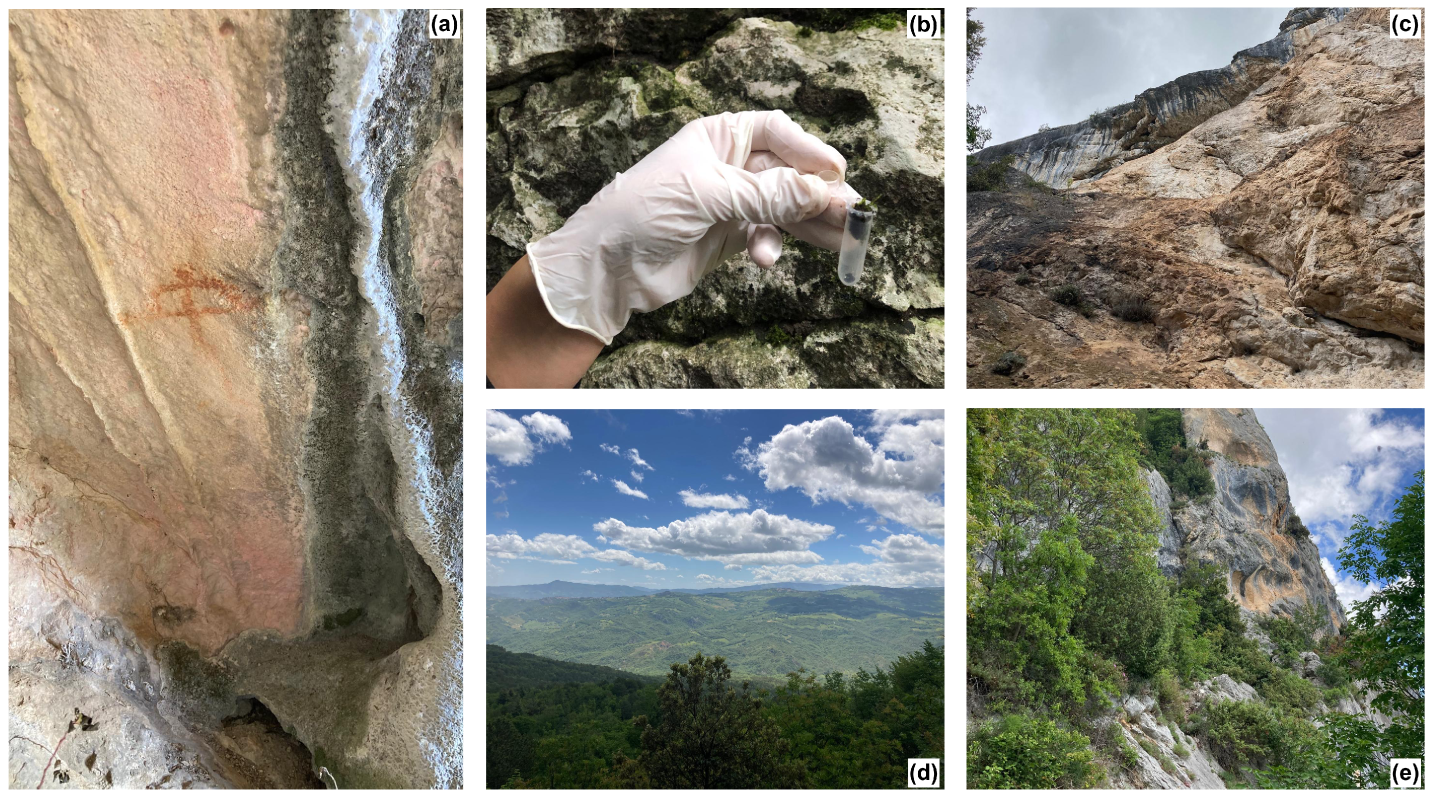
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Research Design
2.2. Atmospheric Analysis
2.3. Laboratory Tests
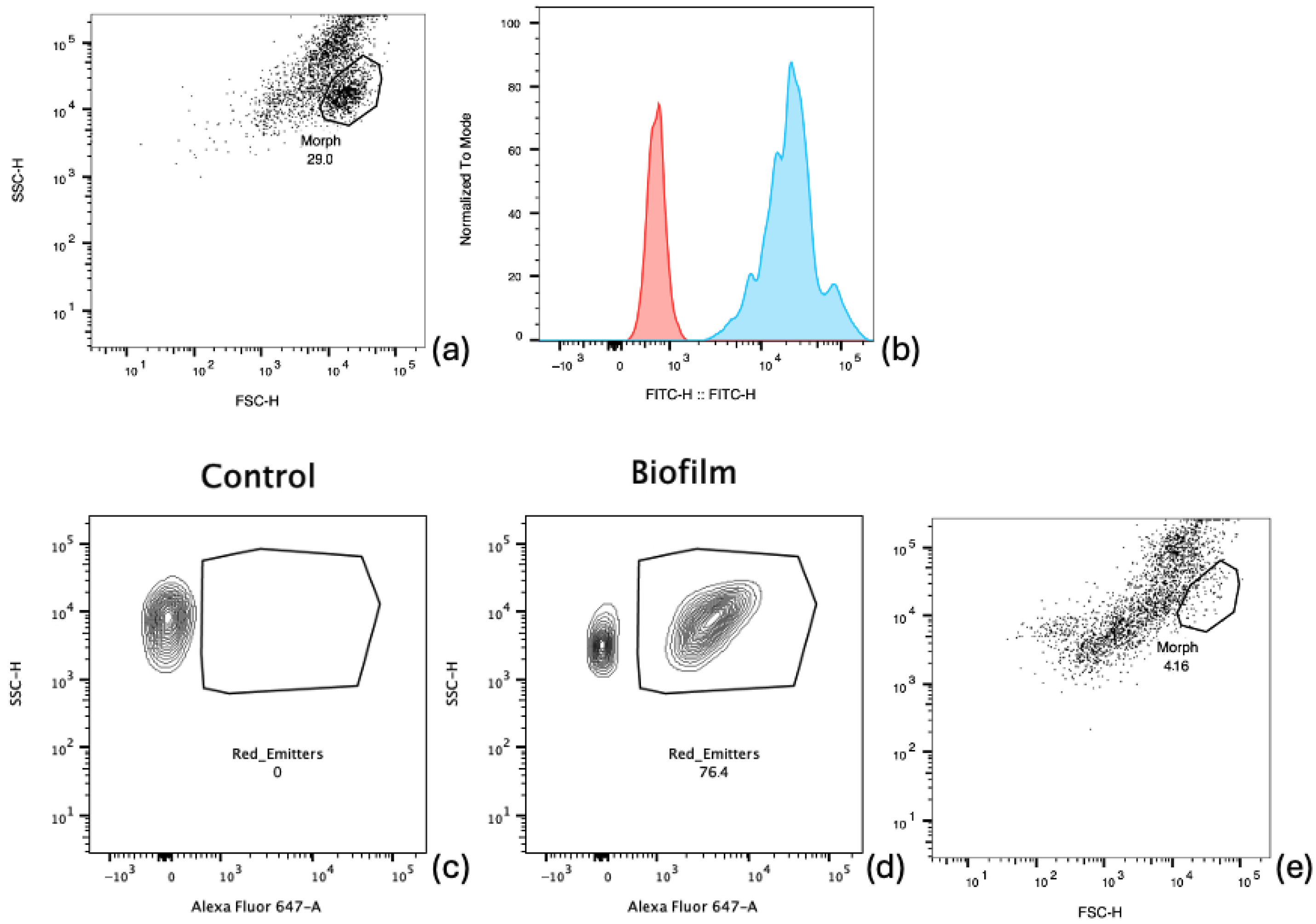
2.3.1. Cytometry Analysis
2.3.2. Genetics Analysis
2.3.3. Inductively Coupled Plasma–Mass Spectrometry (ICP-MS) Analysis
2.3.4. Shotgun Proteomics Analysis
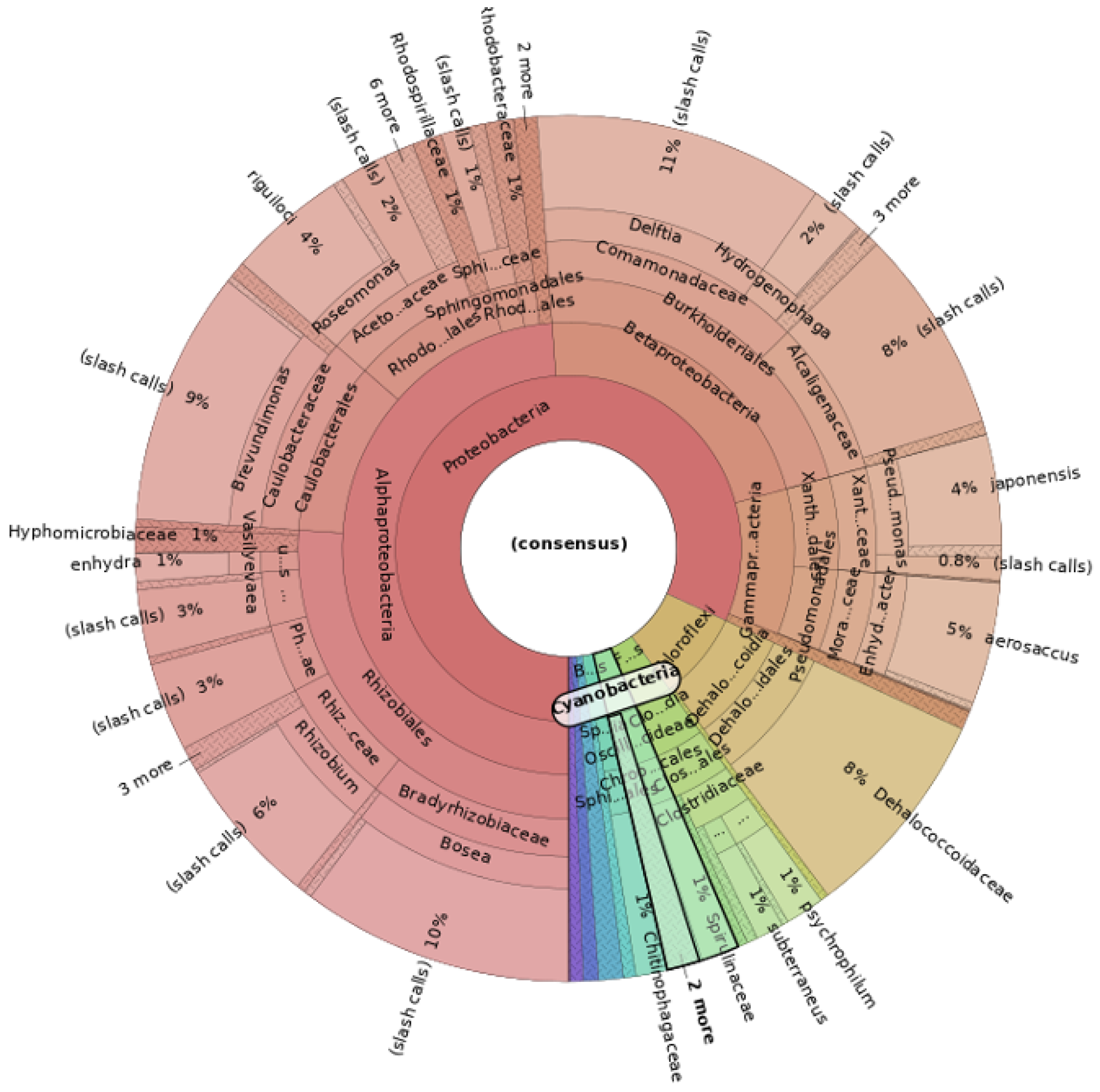
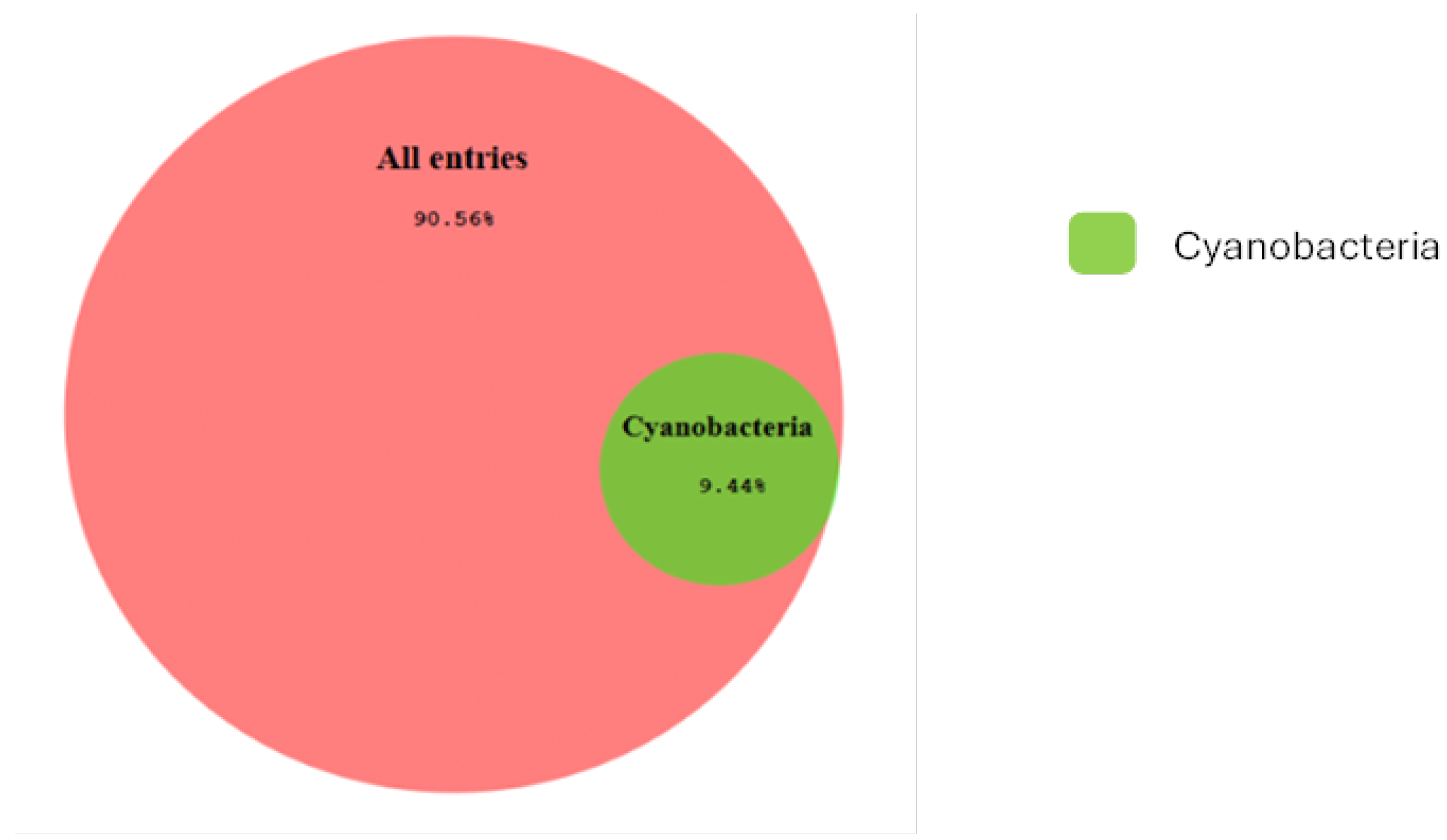
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Palmerini, G. L’arte Rupestre nel Parco Nazionale Della Maiella. Ricerche Storiche, Indagini in Corso e Nuove Prospettive; Ente Parco Nazionale della Maiella: Abruzzo, Italy, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Mattioli, T. L’arte Rupestre in Italia Centrale: Umbria, Lazio, Abruzzo; Ali&No: Perugia, Italy, 2007; Volume 4. [Google Scholar]
- Palmerini, G.; Beck, L.; Di Martino, L.; Gallet, X.; Lebon, M.; Manzi, A.; Nicoud, E.; Mariano, A.; Villa, V. # MaiellaRockArtProject: Nuove ricerche sull’arte rupestre dell’Appennino abruzzese. In Proceedings of the XXVIII Valcamonica Symposium: ROCK-ART, A HUMAN HERITAGE, Valcamonica, Italy, 28–31 October 2021; Centro Camuno di Studi Preistorici: Capo di Ponte, Italy, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Di Fraia, T. Le nuove scoperte di arte rupestre in Abruzzo: Verso un’interpretazione sistemica. L’RTE RUPESTRE. 2015. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/354836318_Le_nuove_scoperte_di_arte_rupestre_in_Abruzzo_verso_un’interpretazione_sistemica (accessed on 26 October 2025).
- Mattioli, T. Landscape analysis of a sample of rock-art sites in Central Italy. In Proceedings of the Layers of Perception: Proceedings of the 35th International Conference on Computer Applications and Quantitative Methods in Archaeology (CAA), Berlin, Germany, 2–6 April 2007; pp. 342–343. [Google Scholar]
- Nuhoglu, Y.; Oguz, E.; Uslu, H.; Ozbek, A.; Ipekoglu, B.; Ocak, I.; Hasenekoglu, I. The accelerating effects of the microorganisms on biodeterioration of stone monuments under air pollution and continental-cold climatic conditions in Erzurum, Turkey. Sci. Total Environ. 2006, 364, 272–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, R.; Kumar, A.V. Biodeterioration of Stone in Tropical Environments: An Overview; The Getty Conservation Institute: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Ortega-Morales, B.O.; Gaylarde, C.C.; Englert, G.E.; Gaylarde, P.M. Analysis of salt-containing biofilms on limestone buildings of the Mayan culture at Edzna, Mexico. Geomicrobiol. J. 2005, 22, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomaselli, L.; Lamenti, G.; Bosco, M.; Tiano, P. Biodiversity of photosynthetic micro-organisms dwelling on stone monuments. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2000, 46, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaylarde, P.M.; Gaylarde, C.C. Algae and cyanobacteria on painted buildings in Latin America. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2000, 46, 93–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crispim, C.A.; Gaylarde, C. Cyanobacteria and biodeterioration of cultural heritage: A review. Microb. Ecol. 2005, 49, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanardini, E.; Abbruscato, P.; Ghedini, N.; Realini, M.; Sorlini, C. Influence of atmospheric pollutants on the biodeterioration of stone. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2000, 45, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warscheid, T.; Braams, J. Biodeterioration of stone: A review. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2000, 46, 343–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheerer, S.; Ortega-Morales, O.; Gaylarde, C. Microbial deterioration of stone monuments—An updated overview. Adv. Appl. Microbiol. 2009, 66, 97–139. [Google Scholar]
- Ortega-Morales, O.; Montero-Muñoz, J.L.; Neto, J.A.B.; Beech, I.B.; Sunner, J.; Gaylarde, C. Deterioration and microbial colonization of cultural heritage stone buildings in polluted and unpolluted tropical and subtropical climates: A meta-analysis. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2019, 143, 104734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louati, M.; Ennis, N.J.; Ghodhbane-Gtari, F.; Hezbri, K.; Sevigny, J.L.; Fahnestock, M.F.; Cherif-Silini, H.; Bryce, J.G.; Tisa, L.S.; Gtari, M. Elucidating the ecological networks in stone-dwelling microbiomes. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 22, 1467–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sesana, E.; Gagnon, A.S.; Ciantelli, C.; Cassar, J.; Hughes, J.J. Climate change impacts on cultural heritage: A literature review. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Clim. Change 2021, 12, e710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.D.; Katayama, Y. Microbiota and biochemical processes involved in biodeterioration of cultural heritage and protection. Microorg. Deterior. Preserv. Cult. Herit. 2021, 37, 37–58. [Google Scholar]
- Macedo, M.F.; Miller, A.Z.; Dionísio, A.; Saiz-Jimenez, C. Biodiversity of cyanobacteria and green algae on monuments in the Mediterranean Basin: An overview. Microbiology 2009, 155, 3476–3490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urzì, C.; Realini, M. Colour changes of Notos calcareous sandstone as related to its colonisation by microorganisms. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 1998, 42, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gambino, M.; Sanmartín, P.; Longoni, M.; Villa, F.; Mitchell, R.; Cappitelli, F. Surface colour: An overlooked aspect in the study of cyanobacterial biofilm formation. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 659, 342–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega-Morales, O.; Guezennec, J.; Hernandez-Duque, G.; Gaylarde, C.C.; Gaylarde, P.M. Phototrophic biofilms on ancient Mayan buildings in Yucatan, Mexico. Curr. Microbiol. 2000, 40, 81–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorbushina, A.A. Life on the rocks. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 9, 1613–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillitte, O. Bioreceptivity: A new concept for building ecology studies. Sci. Total Environ. 1995, 167, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanmartín, P.; Miller, A.; Prieto, B.; Viles, H.A. Revisiting and reanalysing the concept of bioreceptivity 25 years on. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 770, 145314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, A.; Sanmartín, P.; Pereira-Pardo, L.; Dionísio, A.; Sáiz-Jiménez, C.; Macedo, M.; Prieto, B. Bioreceptivity of building stones: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 426, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viles, H.; Ahmad, H. Architectural controls on the bioreceptivity of sandstone to green algal colonization. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Biodeterioration of Stone Monuments-Second Edition, ECBSM2016, Cergy-Pontoise, France, 17–18 November 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Cattò, C.; Mu, A.; Moreau, J.W.; Wang, N.; Cappitelli, F.; Strugnell, R. Biofilm colonization of stone materials from an Australian outdoor sculpture: Importance of geometry and exposure. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 339, 117948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trovão, J.; Portugal, A. The impact of stone position and location on the microbiome of a marble statue. Microbe 2024, 2, 100040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohkubo, S.; Miyashita, H. A niche for cyanobacteria producing chlorophyll f within a microbial mat. ISME J. 2017, 11, 2368–2378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiedler, B.; Broc, D.; Schubert, H.; Rediger, A.; Börner, T.; Wilde, A. Involvement of Cyanobacterial Phytochromes in Growth Under Different Light Qualitities and Quantities. Photochem. Photobiol. 2004, 79, 551–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Qian, Y.; Wu, F.; Wang, Y.; Wang, W.; Gu, J.D. Biofilms on stone monuments: Biodeterioration or bioprotection? Trends Microbiol. 2022, 30, 816–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favero-Longo, S.E.; Viles, H.A. A review of the nature, role and control of lithobionts on stone cultural heritage: Weighing-up and managing biodeterioration and bioprotection. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 36, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinna, D. Coping with Biological Growth on Stone Heritage Objects: Methods, Products, Applications, and Perspectives; Apple Academic Press: Burlington, ON, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Cappitelli, F.; Cattò, C.; Villa, F. The control of cultural heritage microbial deterioration. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macchia, A.; Aureli, H.; Prestileo, F.; Ortenzi, F.; Sellathurai, S.; Docci, A.; Cerafogli, E.; Colasanti, I.A.; Ricca, M.; La Russa, M.F. In-situ comparative study of eucalyptus, basil, cloves, thyme, pine tree, and tea tree essential oil biocide efficacy. Methods Protoc. 2022, 5, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelova, B.; Traykov, I.; Boteva, S.; Tsvetkov, M.; Kenarova, A. Bacterial Metabolic Activity of High-Mountain Lakes in a Context of Increasing Regional Temperature. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaylarde, C.C. Influence of environment on microbial colonization of historic stone buildings with emphasis on cyanobacteria. Heritage 2020, 3, 1469–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- May, E.; Papida, S.; Abdulla, H.; Tayler, S.; Dewedar, A. Comparative studies of microbial communities on stone monuments in temperate and semi-arid climates. In Of Microbes and Art: The Role of Microbial Communities in the Degradation and Protection of Cultural Heritage; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2000; pp. 49–62. [Google Scholar]
- Perez-Monserrat, E.M.; Varas-Muriel, M.J.; Alvarez De Buergo, M.; Fort, R. Black layers of decay and color patterns on heritage limestone as markers of environmental change. Geosciences 2016, 6, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Bai, F.; Huang, J.; Lu, Y.; Wu, Y.; Yu, J.; Bai, S. The organisms on rock cultural heritages: Growth and weathering. Geoheritage 2021, 13, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Lan, W.; Yan, A.; Li, Y.; Katayama, Y.; Gu, J.D. Microbiome characteristics and the key biochemical reactions identified on stone world cultural heritage under different climate conditions. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 302, 114041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Wang, L.; Bai, C.; Wang, M.; Ma, T.; Ma, H.; Zhang, G.; Wang, W.; Guo, Z.; Sun, Y.; et al. Identification of the key factors influencing biodeterioration of open-air cultural heritage in the temperate climate zone of China. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2025, 196, 105954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Society for Microbiology. Microbes and Climate Change-Science, People & Impacts: Report on an American Academy of Microbiology Virtual Colloquium held on Nov. 5, 2021; American Society for Microbiology: Washington, DC, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Viles, H.A.; Cutler, N.A. Global environmental change and the biology of heritage structures. Glob. Change Biol. 2012, 18, 2406–2418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traversetti, L.; Bartoli, F.; Caneva, G. Wind-driven rain as a bioclimatic factor affecting the biological colonization at the archaeological site of Pompeii, Italy. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2018, 134, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orr, S.A.; Cassar, M. Exposure indices of extreme wind-driven rain events for built heritage. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albertano, P. Cyanobacterial biofilms in monuments and caves. In Ecology of Cyanobacteria II: Their Diversity in Space and Time; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 317–343. [Google Scholar]
- Drugă, B.; Ramm, E.; Szekeres, E.; Chiriac, C.; Hegedüs, A.; Stockenreiter, M. Long-term acclimation might enhance the growth and competitive ability of Microcystis aeruginosa in warm environments. Freshw. Biol. 2022, 67, 589–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsson-Francis, K.; de la Torre, R.; Cockell, C.S. Isolation of novel extreme-tolerant cyanobacteria from a rock-dwelling microbial community by using exposure to low Earth orbit. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 2115–2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiaudani, A.; Flamminii, F.; Consalvo, A.; Bellocci, M.; Pizzi, A.; Passamonti, C.; Cichelli, A. Rare Earth Element Variability in Italian Extra Virgin Olive Oils from Abruzzo Region. Foods 2024, 13, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potenza, F.; Cufaro, M.C.; Di Biase, L.; Panella, V.; Di Campli, A.; Ruggieri, A.G.; Dufrusine, B.; Restelli, E.; Pietrangelo, L.; Protasi, F.; et al. Proteomic analysis of marinesco–sjogren syndrome fibroblasts indicates pro-survival metabolic adaptation to SIL1 loss. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ucci, A.; Giacchi, L.; Cufaro, M.C.; Puri, C.; Ciocca, M.; Di Ferdinando, F.; Del Boccio, P.; Cappariello, A.; Rucci, N. Human osteosarcoma cell secretome impairs neonatal mouse calvarial osteogenic cells functions and modifies the nanoparticles-derived protein profile. Life Sci. 2025, 379, 123837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Instrument Parameters | |
|---|---|
| Nebulizer | Babington |
| Torch | Quartz glass torch |
| Spray chamber | Scott double-pass type at 2 °C |
| Sample cone Nickel | 1.00 mm aperture |
| Skimmer cone Nickel | 0.40 mm aperture |
| Plasma mode | Normal plasma |
| RF power (W) | 1550 |
| RF matching (V) | 1.8 |
| Sample depth (mm) | 10 |
| Nebulizer gas (L min−1) | 1.03 |
| Nebulizer pump (rps) | 0.1 |
| Plasma gas (L min−1) | 15 |
| Sampling period (s) | 0.3 |
| Repetitions 3 | 3 |
| Sample uptake rate (mL min−1) | 0.4 |
| Integration time (s) | 0.1 |
| MOSS | BLACKENED MOSS | SOIL | ROCK SURFACE |
|---|---|---|---|
| Co = 6.6 ± 0.2 | Co = 2.9 ± 1 | Co = 12.9 ± 5.7 | Co = 3.8 ± 2.7 |
| Cr = 2.2 ± 2.9 | Cr = 5.6 ± 2.2 | Cr = 1.5 ± 6.5 | Cr = 11.7 ± 4.7 |
| Al = 713.3 * ± 8.4 | Al = 3329.3 * ± 0.7 | Al = 435.2 * ± 1.7 | Al = 1532.3 * ± 2.4 |
| Ag = N/A ** | Ag = 0.23 ± 4.7 | Ag = N/A ** | Ag = N/A ** |
| As = 4.4 ± 5.1 | As = 2.01 ± 1.9 | As = 4.8 ± 0.6 | As = 12.6 ± 4.2 |
| Cd = 0.13 ± 3.4 | Cd = 5.4 ± 1.7 | Cd = 0.18 ± 10.9 | Cd = 624.2 * ± 1.3 |
| Cu = 16.9 ± 6.7 | Cu = 19.3 ± 2.3 | Cu = 16.2 ± 1 | Cu = 42.2 ± 3.1 |
| Mn = 25.2 ± 7.2 | Mn = 115.5 * ± 0.6 | Mn = 17.7 ± 1.7 | Mn = 188.4 * ± 2.7 |
| Ni = 56.3 ± 0.1 | Ni = 12.9 ± 0.9 | Ni = 107 ± 6.5 | Ni = 41.4 ± 8.7 |
| Pb = 1.9 ± 8.6 | Pb = 255.6 ± 4.9 | Pb = 1.4 ± 1 | Pb = 24.8 ± 6.9 |
| Se = 1.8 ± 13.4 | Se = 11.5 ± 7.2 | Se = 3.2 ± 16 | Se = 18 ± 6.9 |
| V = 11.7 ± 7 | V = 6.9 ± 0.8 | V = 12.1 ± 0.5 | V = 23.31 ± 1.6 |
| Zn = 17.9 ± 7.1 | Zn = 54.7 ± 1.7 | Zn = 22.2 ± 1.1 | Zn = 82.9 ± 3.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chiacchiaretta, P.; Prestileo, F.; Stella, E.M.; Aruffo, E.; Simeone, P.; Lanuti, P.; Di Lodovico, S.; Di Giulio, M.; Guarnieri, S.; Del Boccio, P.; et al. Impact of Climate Change on Cyanobacteria Growth: A Case Study of Lama Dei Peligni Rock Paintings Conservation (Majella Massif—Abruzzo Region, Italy). Sustainability 2025, 17, 10861. https://doi.org/10.3390/su172310861
Chiacchiaretta P, Prestileo F, Stella EM, Aruffo E, Simeone P, Lanuti P, Di Lodovico S, Di Giulio M, Guarnieri S, Del Boccio P, et al. Impact of Climate Change on Cyanobacteria Growth: A Case Study of Lama Dei Peligni Rock Paintings Conservation (Majella Massif—Abruzzo Region, Italy). Sustainability. 2025; 17(23):10861. https://doi.org/10.3390/su172310861
Chicago/Turabian StyleChiacchiaretta, Piero, Fernanda Prestileo, Eleonora Maria Stella, Eleonora Aruffo, Pasquale Simeone, Paola Lanuti, Silvia Di Lodovico, Mara Di Giulio, Simone Guarnieri, Piero Del Boccio, and et al. 2025. "Impact of Climate Change on Cyanobacteria Growth: A Case Study of Lama Dei Peligni Rock Paintings Conservation (Majella Massif—Abruzzo Region, Italy)" Sustainability 17, no. 23: 10861. https://doi.org/10.3390/su172310861
APA StyleChiacchiaretta, P., Prestileo, F., Stella, E. M., Aruffo, E., Simeone, P., Lanuti, P., Di Lodovico, S., Di Giulio, M., Guarnieri, S., Del Boccio, P., Spalluto, G., Cufaro, M. C., Gatta, V., Anaclerio, F., Alisi, C., Dietrich, S., Di Carlo, P., & Mascitelli, A. (2025). Impact of Climate Change on Cyanobacteria Growth: A Case Study of Lama Dei Peligni Rock Paintings Conservation (Majella Massif—Abruzzo Region, Italy). Sustainability, 17(23), 10861. https://doi.org/10.3390/su172310861


















