Can Agricultural Insurance Promote Agricultural Modernization?—Evidence from China During 2008–2023
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Theoretical Analysis and Research Hypotheses
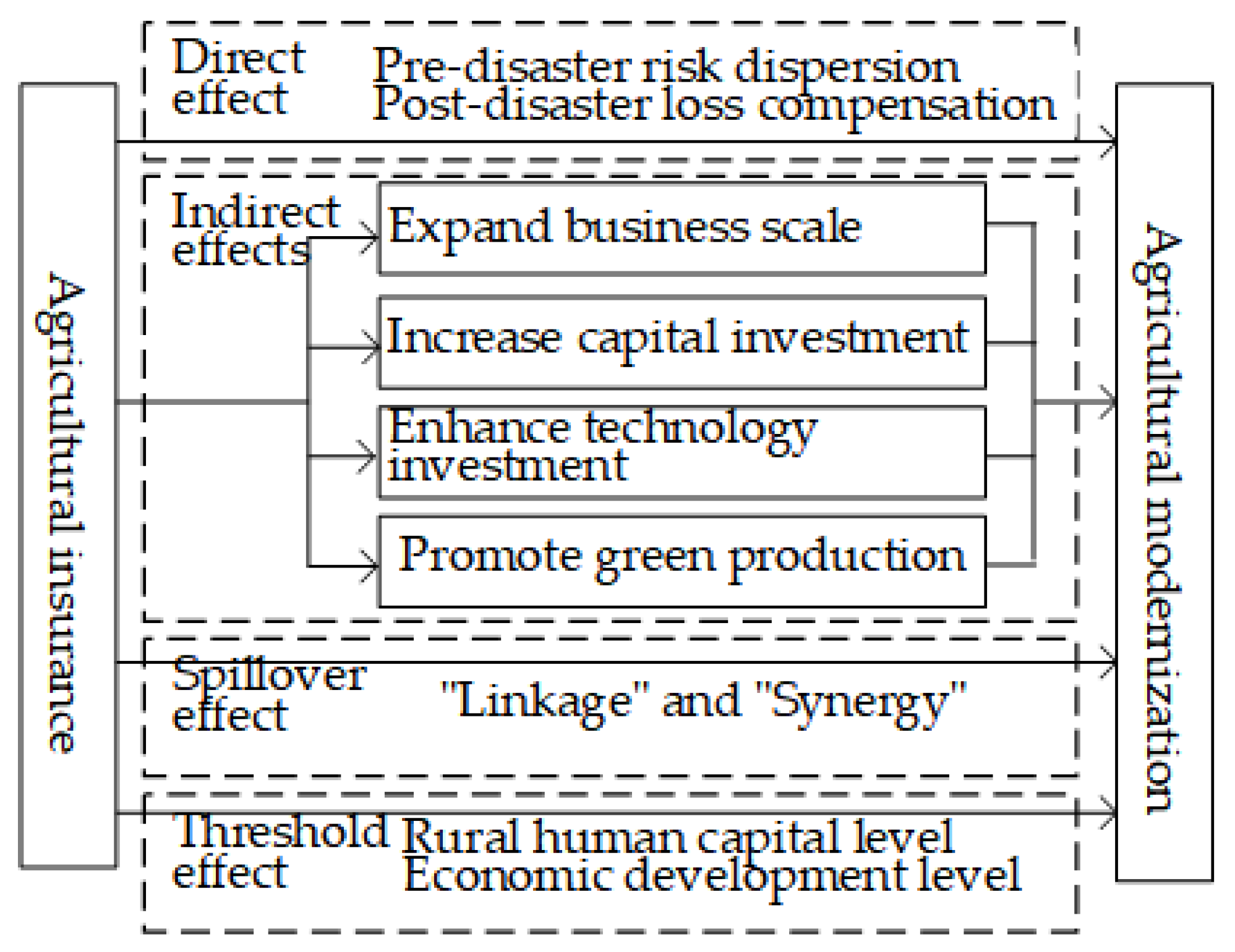
2.1. The Direct Effect of Agricultural Insurance on Agricultural Modernization
2.2. The Indirect Effect of Agricultural Insurance on Agricultural Modernization
2.3. The Spatial Spillover Effect of Agricultural Insurance on Agricultural Modernization
2.4. The Threshold Effect of Agricultural Insurance on Agricultural Modernization
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Model
3.1.1. Baseline Regression Model
3.1.2. Mediation Effect Model
3.1.3. Spatial Spillover Effect Model
3.1.4. Threshold Effect Model
3.2. Variable Selection
3.2.1. Core Explanatory Variable
3.2.2. Dependent Variable
3.2.3. Mediating Variables
3.2.4. Control Variables
3.3. Data Sources
4. Results
4.1. Baseline Regression Test
4.2. Robustness Test
4.2.1. Replace the Dependent Variable
4.2.2. Exclude Municipalities Directly Under the Central Government
4.2.3. Add Control Variables
4.2.4. Perform Tail-Reduction Processing
4.2.5. Lagged Explanatory Variable
4.3. Endogeneity Test
4.4. Mechanism Test
4.4.1. Mediation Effect Test
4.4.2. Spatial Spillover Effect Test
4.4.3. Threshold Effect Test
4.5. Heterogeneity Tests
4.5.1. Spatial Heterogeneity
4.5.2. Hierarchical Heterogeneity
5. Conclusions and Policy Implications
5.1. Conclusions
5.2. Policy Implications
5.2.1. Overall Suggestions for China
5.2.2. Differentiated Suggestions for China’s Eastern, Central, Western and North-Eastern Regions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fu, L.-S.; Qin, T.; Li, G.-Q.; Wang, S.-G. Efficiency of Agricultural Insurance in Facilitating Modern Agriculture Development: From the Perspective of Production Factor Allocation. Sustainability 2024, 16, 6223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Dijk, M.P. Crop Insurance, a Frugal Innovation in Tanzania, Helps Small Maize Farmers and Contributes to an Emerging Land Market. Land 2022, 11, 954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.; Tao, J.; Yi, L.; He, J.; Huang, Q. Dynamic Relationship between Agricultural Technology Progress, Agricultural Insurance and Farmers’ Income. Agriculture 2022, 12, 1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, L.; Zhu, D. The Role of Agricultural Insurance in the Coordinated Development of Green Agriculture and Farmers’ Income: Mechanism Analysis and Empirical Evidence. Contemp. Soc. Sci. 2025, 10, 45–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Möhring, N.; Dalhaus, T.; Enjolras, G.; Finger, R. Crop insurance and pesticide use in European agriculture. Agric. Syst. 2020, 184, 102902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodrich, B.; Yu, J.; Davidson, K.; Goh, G. Rainfall timing, forage growth, and insuring forage: Linking producer perceptions to observational data. Am. J. Agric. Econ. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Agrawal, G. Development, present status and performance analysis of agriculture insurance schemes in India. Int. J. Soc. Econ. 2020, 47, 461–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazell, P.; Varangis, P. Best practices for subsidizing agricultural insurance. Glob. Food Secur. 2020, 25, 100326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulte, E.; Lensink, R. Why agricultural insurance may slow down agricultural development. Am. J. Agric. Econ. 2022, 105, 1197–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, Y.X.; Jiang, S.Z.; Fei, Q. Can agriculture insurance help improve the level of green development in agriculture: Evaluation based on 13 major grain producing regions. Insur. Res. 2023, 11, 61–77. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, D.; Wang, X. How does agricultural insurance influence grain production scale? An income-mediated perspective. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2025, 9, 1524874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, T.; Yang, Y. How Agricultural Insurance Affects Farmers’ Household Savings Rate: Based on Two Phase Survey Data from Five Provinces. Agric. Technol. Econ. 2023, 5, 49–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, F.; Yi, F.; Zhang, Q. The Reducing Effect of Agricultural Insurance on the Use of ChemicalFertilizer: A Re-examination from the Perspective of Dual Constraints of Credit and Information. China Rural Econ. 2024, 10, 20–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Yang, R. Effect of agricultural insurance on the allocation of household labor resourcesunder the impact of income risk: Case study of Shandong, Henan and Guizhou. J. Arid. Land Resour. Environ. 2021, 35, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q. The Dynamic Effects of Agricultural Insurance Development on the Optimization of Agricultural Industrial Structure—Generalized Method of Moments Estimation Based on Dynamic Panel Model. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 831, 012039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazell, P.B.R. The appropriate role of agricultural insurance in developing countries. J. Int. Dev. 1992, 4, 567–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, A.S.A.F.; Begum, H.; Masud, M.M.; Al-Amin, A.Q.; Filho, W.L. Agriculture insurance for disaster risk reduction: A case study of Malaysia. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2020, 47, 101626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulewski, P.; Kłoczko-Gajewska, A. Farmers’ risk perception, risk aversion and strategies to cope with production risk: An empirical study from Poland. Stud. Agric. Econ. 2014, 116, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y. Introduction to Digital Insurance; Higher Education Press: Beijing, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Q.; Yin, R. A review of research on moderate scale management of agricultural land in China. China Land Sci. 2010, 24, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Mu, Y.; Hou, L. Does Participation in Agricultural Insurance Optimize Factor Allocation? An Analysis of Endogenous Farmers’ Insurance Decision-making and ItsEffect on Production. China Rural Econ. 2018, 10, 53–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, M.; Tian, M.; Wang, J. Digital Inclusive Finance, Agricultural Industrial Structure Optimization and Agricultural Green Total Factor Productivity. Sustainability 2022, 14, 11450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.-Y.; Zhu, T.-H.; Jia, W. Does Internet use promote the adoption of agricultural technology? Evidence from 1449 farm households in 14 Chinese provinces. J. Integr. Agric. 2022, 21, 282–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Gu, L. Can Policy-Based Agricultural Insurance Promote Agricultural Carbon Emission Reduction? Causal Inference Based on Double Machine Learning. Sustainability 2025, 17, 4086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Yin, Z. Has agricultural insurance promoted green development in Chinese agriculture? J. Huazhong Agric. Univ. Soc. Sci. Ed. 2024, 1, 49–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, R.; Li, J. The impact of agricultural production agglomeration on agricultural economic resilience: Based on spatial spillover and threshold effect test. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2024, 8, 1464732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiao, C. Analysis of Panel Data; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Z.; Ye, B. Mediation Effect Analysis: Development of Methods Models. Adv. Psychol. Sci. 2014, 22, 731–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffith, A.D. Spatial Econometrics: Methods and Models. Econ. Geogr. 2016, 65, 160–162. [Google Scholar]
- Hansen, B.E. Threshold effects in non-dynamic panels: Estimation, testing, and inference. J. Econom. 1999, 93, 345–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lium, W.; Sun, L.; Tuo, G. Research on the Impact Mechanism of Agricultural Insurance on Farmers’ Income: Based on the Moderated Mediating Effect. Agric. Technol. Econ. 2022, 6, 4–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L. Strategies to enhance the ability of rural households to resist economic risks under agricultural insurance system management. Glob. Vis. Res. 2025, 2, 56–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Tuo, G.; Long, W. Agricultural Risk and Agricultural Insurance; Higher Education Press: Beijing, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, L.; Qin, T.; Wang, S. The Factor Allocation Effect and Mechanism of Agricultural Insurance: Based on the Perspective of Supporting Modern Agricultural Development. Resour. Sci. 2022, 44, 1980–1993. [Google Scholar]
- State Council of China 2021. Advance Rural Revitalization Across the Board, Accelerate Agricultural and Rural Modernization. Available online: http://www.gov.cn/gongbao/content/2021/content_5591401.htm (accessed on 10 September 2024). (In Chinese)
- Liu, M.; Fang, X.; Ren, J. Accelerating the modernization of agriculture and rural areas in China. China Agric. Econ. Rev. 2023, 15, 871–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Huang, Q. Rural Public Science and Technology Services, Land Productivity, and Agricultural Modernization: Case Study of Southwest China. Land 2025, 14, 1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; You, X.; Sun, X.; Chen, J. Dynamic assessment and pathway optimization of agricultural modernization in China under the sustainability framework: An empirical study based on dynamic QCA analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 479, 144072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Piesse, J. Inequality and the Urban–rural Divide in China: Effects of Regressive Taxation. China World Econ. 2010, 18, 36–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, W.; Sun, Z. The Impact of the Digital Economy on High-Quality Development of Agriculture: A China Case Study. Sustainability 2023, 15, 5745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, H.; Dehong, L. Agricultural Insurance, Factor Allocation, and Farmers’ Income. J. S. China Agric. Univ. Soc. Sci. Ed. 2021, 20, 41–53. [Google Scholar]
| Target Layer | System Layer | System Layer | Definition | Unit | Attribute |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Agricultural Modernization | Agricultural Mechanization | Mechanical Power per Unit Cultivated Area | the ratio of total agricultural machinery power to cultivated land area | ten thousand kilowatts per thousand hectares | (+) |
| Agricultural Digitalization | Internet Penetration Rate | the ratio of the number of internet users in a region to the region’s population | % | (+) | |
| Digital Inclusive Finance | the development level of digital inclusive finance | — | (+) | ||
| Green Agriculture | Pesticide Usage per Unit of Cultivated Land | The ratio of pesticide usage to cultivated land area | Tons per thousand hectares | (−) | |
| Fertilizer Usage per Unit of Cultivated Land | ratio of agricultural fertilizer usage to cultivated land area | Tons per thousand hectares | (−) | ||
| Agricultural Development Level | Rural per Capital Disposable Income | the ratio of rural residents’ disposable income to the rural population | CNY per person | (+) | |
| Grain Yield per Unit Cultivated Land Area | the ratio of grain output to cultivated land area | ten thousand tons per thousand hectares | (+) | ||
| Agricultural Labor Productivity | The ratio of added value to employment in the primary industry | ten thousand CNY per person | (+) |
| Variables | Symbol | N | Mean | SD | Min | Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dependent variable | Lnmoa | 480 | 7.689 | 0.544 | 6.356 | 9.026 |
| Core explanatory variable | BZ | 480 | 24.73 | 1.754 | 1.147 | 27.63 |
| Mediating Variables | Scal | 480 | 10.02 | 0.651 | 8.739 | 11.88 |
| Cap | 480 | 2.714 | 0.975 | 0.225 | 6.438 | |
| Tec | 480 | 10.06 | 1.573 | 5.429 | 13.68 | |
| Gre | 480 | 2.109 | 0.515 | 0.909 | 3.181 | |
| Control variables | Pgdp | 480 | 5.481 | 3.252 | 0.970 | 20.03 |
| Prop | 480 | 10.00 | 5.405 | 0.200 | 28.70 | |
| Ope | 480 | 0.264 | 0.277 | 0.007 | 1.549 | |
| Lab | 480 | 0.218 | 0.113 | 0.0275 | 0.552 | |
| Edu | 480 | 7.801 | 0.661 | 5.878 | 10.32 |
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BZ | 0.005 *** | 0.004 *** | 0.004 *** | 0.004 *** | 0.004 *** | 0.004 *** |
| (2.83) | (3.05) | (3.12) | (3.26) | (3.47) | (3.09) | |
| Pgdp | −0.007 | −0.007 * | −0.002 | −0.002 | −0.004 | |
| (−1.54) | (−1.78) | (−0.35) | (−0.44) | (−0.77) | ||
| Prop | −0.072 *** | −0.056 *** | −0.057 *** | −0.057 *** | ||
| (−3.95) | (−3.42) | (−3.59) | (−3.67) | |||
| Ope | 0.090 ** | 0.082 ** | 0.082 ** | |||
| (2.66) | (2.30) | (2.29) | ||||
| Lab | −0.058 | −0.053 | ||||
| (−0.92) | (−0.88) | |||||
| Edu | 0.018 | |||||
| (1.38) | ||||||
| Constant | 6.757 *** | 6.798 *** | 6.825 *** | 6.772 *** | 6.791 *** | 6.667 *** |
| (167.88) | (191.37) | (205.94) | (162.92) | (153.34) | (63.42) | |
| Individual FE | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y |
| Time FE | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y |
| N | 480 | 480 | 480 | 480 | 480 | 480 |
| R2 | 0.996 | 0.996 | 0.997 | 0.997 | 0.997 | 0.997 |
| F | 2201.289 | 2502.477 | 3100.489 | 7407.450 | 10,923.180 | 9801.720 |
| Variable | Replace the Dependent Variable | Exclude Municipalities Directly Under the Central Government | Add Control Variables | Perform Tail-Reduction Processing | Lagged Explanatory Variable |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | |
| BZ | 0.014 *** | 0.003 ** | 0.004 *** | 0.009 ** | 0.003 *** |
| (2.78) | (2.43) | (3.21) | (2.45) | (3.07) | |
| L1.BZ | 0.003 ** | ||||
| (2.60) | |||||
| Pgdp | 0.005 | −0.001 | −0.004 | −0.004 | −0.003 |
| (0.27) | (−0.14) | (−0.73) | (−1.53) | (−0.67) | |
| Prop | 0.005 | −0.055 *** | −0.056 *** | −0.065 *** | −0.057 *** |
| (0.07) | (−4.38) | (−3.68) | (−3.96) | (−3.70) | |
| Ope | −0.069 | 0.056 * | 0.081 ** | 0.082 *** | 0.080 ** |
| (−0.64) | (1.84) | (2.36) | (3.84) | (2.24) | |
| Lab | 0.157 | −0.047 | −0.053 | −0.048 | −0.057 |
| (0.53) | (−0.75) | (−0.90) | (−1.32) | (−0.94) | |
| Edu | −0.135 | 0.027 | 0.017 | 0.006 | 0.017 |
| (−0.73) | (1.58) | (1.31) | (0.80) | (1.28) | |
| Natu | −0.009 | ||||
| (−1.07) | |||||
| Constant | 10.175 *** | 6.563 *** | 6.780 *** | 6.656 *** | 6.630 *** |
| (7.83) | (49.92) | (50.05) | (68.87) | (61.89) | |
| Time FE | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y |
| Individual FE | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y |
| R2 | 0.630 | 0.997 | 0.997 | 0.996 | 0.997 |
| N | 480 | 480 | 480 | 480 | 480 |
| Variable | (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IV-2SLS | ||||
| BZ | Lnmoa | BZ | Lnmoa | |
| Gap | −18.437 *** | −13.896 ** | ||
| (−3.11) | (−1.79) | |||
| BZ | 0.140 *** | 0.220 *** | ||
| (6.85) | (3.85) | |||
| Control variable | N | N | Y | Y |
| Constant | 25.311 *** | 23.768 *** | ||
| (33.12) | (16.69) | |||
| Kleibergen−Paap rk LM | 29.481 | 12.788 | ||
| [0.000] | [0.000] | |||
| Kleibergen−Paap Wald rk F | 52.864 | 23.830 | ||
| {16.38} | {16.38} | |||
| Time FE | Y | Y | Y | Y |
| Individual FE | Y | Y | Y | Y |
| N | 480 | 480 | 480 | 480 |
| R2 | 0.888 | 0.983 | 0.894 | 0.965 |
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | (7) | (8) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Scal | Lnmoa | Cap | Lnmoa | Tec | Lnmoa | Gre | Lnmoa | |
| BZ | 0.015 * | 0.003 * | 0.022 ** | 0.003 ** | 0.033 * | 0.003 ** | 0.021 * | 0.002 * |
| (1.74) | (2.03) | (2.47) | (2.57) | (2.02) | (2.26) | (2.00) | (1.78) | |
| Scal | 0.085 *** | |||||||
| (5.09) | ||||||||
| Cap | 0.042 ** | |||||||
| (2.12) | ||||||||
| Tec | 0.035 *** | |||||||
| (3.46) | ||||||||
| Gre | 0.070 *** | |||||||
| (1.78) | ||||||||
| Control variable | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y |
| Constant | 9.129 *** | 5.889 *** | 0.010 | 6.663 *** | 7.885 *** | 6.393 *** | 0.886 * | 6.605 *** |
| (17.50) | (33.90) | (0.28) | (62.06) | (9.09) | (46.18) | (1.98) | (55.68) | |
| Individual FE | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y |
| Time FE | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y |
| N | 480 | 480 | 480 | 480 | 480 | 480 | 480 | 480 |
| R2 | 0.717 | 0.997 | 0.929 | 0.997 | 0.939 | 0.997 | 0.392 | 0.997 |
| F | 128.34 | 17,042.59 | 260.87 | 58,083.78 | 801.40 | 17,866.57 | 25.55 | 54,266.32 |
| Year | Lnmoa | BZ | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Moran’s I | p-Value * | Moran’s I | p-Value * | |
| 2008 | 0.195 | 0.000 | 0.019 | 0.070 |
| 2009 | 0.192 | 0.000 | 0.041 | 0.020 |
| 2010 | 0.196 | 0.000 | −0.006 | 0.048 |
| 2011 | 0.199 | 0.000 | 0.038 | 0.020 |
| 2012 | 0.199 | 0.000 | 0.063 | 0.003 |
| 2013 | 0.200 | 0.000 | 0.058 | 0.005 |
| 2014 | 0.200 | 0.000 | 0.043 | 0.017 |
| 2015 | 0.197 | 0.000 | 0.065 | 0.003 |
| 2016 | 0.193 | 0.000 | 0.089 | 0.000 |
| 2017 | 0.191 | 0.000 | 0.083 | 0.001 |
| 2018 | 0.190 | 0.000 | 0.075 | 0.001 |
| 2019 | 0.189 | 0.000 | 0.081 | 0.001 |
| 2020 | 0.187 | 0.000 | 0.095 | 0.000 |
| 2021 | 0.187 | 0.000 | 0.086 | 0.000 |
| 2022 | 0.187 | 0.000 | 0.077 | 0.001 |
| 2023 | 0.186 | 0.000 | 0.070 | 0.002 |
| Test Method | Eigenvalue | Test Method | Eigenvalue |
|---|---|---|---|
| LM Spatial Lag | 517.287 *** | Wald Spatial Lag | 37.70 *** |
| LM Spatial Error | 241.277 *** | Wald Spatial Error | 43.18 *** |
| Robust LM Spatial Lag | 336.022 *** | Hausman Test | 20.60 *** |
| Robust LM Spatial Error | 60.012 *** | LR Test (Fixed Spatial Effect) | 64.40 *** |
| LR Spatial Lag | 101.97 *** | LR Test (Fixed Time Effect) | 1262.41 *** |
| LR Spatial Error | 119.64 *** |
| Variable | (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Geographic Distance Matrix | Geographic Distance Matrix | Spatial Adjacency Matrix | Economic Geography Nesting Matrix | |
| BZ | 0.005 *** | 0.006 *** | 0.004 *** | 0.004 *** |
| (3.98) | (3.31) | (3.31) | (3.47) | |
| W * BZ | 0.006 *** | 0.005 ** | 0.005 ** | 0.026 *** |
| (2.81) | (2.14) | (2.14) | (3.02) | |
| W * Lnmoa | 0.505 *** | 0.463 *** | 0.463 *** | 0.272 ** |
| (10.50) | (9.49) | (9.49) | (2.38) | |
| Direct Effect | 0.006 *** | 0.004 *** | 0.004 *** | 0.005 *** |
| (4.36) | (3.84) | (3.84) | (3.80) | |
| Indirect effects | 0.161 *** | 0.110 *** | 0.011 *** | 0.035 *** |
| (3.75) | (3.17) | (3.17) | (3.14) | |
| Total effect | 0.022 *** | 0.015 *** | 0.015 *** | 0.040 *** |
| (4.16) | (3.85) | (3.85) | (3.49) | |
| Control variable | Y | Y | Y | Y |
| Time FE | Y | Y | Y | Y |
| Individual FE | Y | Y | Y | Y |
| N | 480 | 480 | 480 | 480 |
| Log-L | 1083.0677 | 1115.0770 | 1115.0770 | 1079.2243 |
| R2 | 0.879 | 0.691 | 0.691 | 0.919 |
| Number of Threshold | Rural Human Capital Level (Edu) | Economic Development Level (Pgdp) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| F-Value | Threshold Value | F-Value | Threshold Value | |
| Single threshold | 34.68 ** | 7.1105 | 341.11 *** | 2.183 |
| Double threshold | 120.20 *** | 3.189 | ||
| Three thresholds | 143.36 *** | 13.617 | ||
| Threshold Range | Moderating Variables | |
|---|---|---|
| Rural Human Capital Level (Edu) (1) | Economic Development Level (Pgdp) (2) | |
| 0.066 | 0.027 | |
| (1.69) | (1.39) | |
| 0.075 * | 0.036 * | |
| (1.92) | (1.93) | |
| 0.046 ** | ||
| (2.48) | ||
| 0.029 | ||
| (1.45) | ||
| Control variable | Y | Y |
| N | 480 | 480 |
| F | 181.12 | 774.24 |
| R2 | 0.901 | 0.963 |
| Major Grain-Producing Areas (1) | Non-Grain-Producing Areas (2) | Eastern Region (3) | Central Region (4) | Western Region (5) | Northeast Region (6) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BZ | −0.017 * | 0.003 ** | 0.218 *** | 0.142 *** | 0.024 | −0.020 |
| (−2.17) | (2.81) | (6.54) | (6.84) | (1.53) | (−0.68) | |
| Pgdp | 0.009 | −0.011 * | 0.064 *** | 0.132 *** | 0.209 *** | 0.326 *** |
| (1.21) | (−1.89) | (7.49) | (10.46) | (13.12) | (8.92) | |
| Prop | −0.172 | −0.003 * | −1.828 *** | 0.527 | −0.140 *** | 0.902 *** |
| (−1.15) | (−1.81) | (−3.12) | (0.40) | (−3.77) | (2.98) | |
| Ope | 0.156 ** | 0.081 * | −0.166 * | 0.956 *** | −0.523 | −1.189 *** |
| (2.25) | (1.75) | (−1.93) | (5.49) | (0.99) | (−5.41) | |
| Lab | −0.043 | −0.007 | −0.366 ** | −0.526 | −0.254 | −0.858 |
| (−0.49) | (−0.08) | (−2.11) | (−1.42) | (−0.78) | (−0.78) | |
| Edu | 0.010 | 0.007 | −0.056 * | 0.094 | 0.192 *** | −0.081 |
| (0.54) | (0.51) | (−1.90) | (1.61) | (1.95) | (0.67) | |
| Constant | 7.214 *** | 6.757 *** | 2.949 *** | 2.745 *** | 4.742 *** | 6.300 *** |
| (27.39) | (75.76) | (3.61) | (3.44) | (9.04) | (4.29) | |
| Time FE | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y |
| Individual FE | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y |
| N | 208 | 272 | 160 | 96 | 176 | 48 |
| R2 | 0.999 | 0.997 | 0.971 | 0.954 | 0.942 | 0.976 |
| Full Sample | Primary Stage | Intermediate Stage | Advanced Stage | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | |
| BZ | 0.004 *** | 0.001 *** | −0.033 *** | 0.008 |
| (3.09) | (2.85) | (−2.95) | (0.45) | |
| Pgdp | −0.004 | −0.001 | −0.004 | −0.000 |
| (−0.77) | (0.06) | (−0.75) | (−0.11) | |
| Prop | −0.057 *** | 0.018 | 0.049 * | −0.058 |
| (−3.67) | (0.80) | (−1.97) | (−0.68) | |
| Ope | 0.082 ** | 0.155 *** | −0.053 ** | 0.023 |
| (2.29) | (3.50) | (−2.36) | (0.57) | |
| Lab | −0.053 | −0.032 | −0.070 | 0.039 |
| (−0.88) | (−0.57) | (−1.28) | (1.32) | |
| Edu | 0.018 | −0.002 | −0.001 | 0.004 |
| (1.38) | (0.07) | (−0.12) | (0.32) | |
| Constant | 6.667 *** | 6.746 *** | 7.710 *** | 7.120 *** |
| (63.42) | (34.90) | (23.97) | (14.45) | |
| Time FE | Y | Y | Y | Y |
| Individual FE | Y | Y | Y | Y |
| N | 480 | 144 | 192 | 144 |
| R2 | 0.997 | 0.996 | 0.997 | 0.995 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, H.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Q. Can Agricultural Insurance Promote Agricultural Modernization?—Evidence from China During 2008–2023. Sustainability 2025, 17, 10856. https://doi.org/10.3390/su172310856
Li H, Wang Q, Wang Q. Can Agricultural Insurance Promote Agricultural Modernization?—Evidence from China During 2008–2023. Sustainability. 2025; 17(23):10856. https://doi.org/10.3390/su172310856
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Hong, Qinmei Wang, and Qi Wang. 2025. "Can Agricultural Insurance Promote Agricultural Modernization?—Evidence from China During 2008–2023" Sustainability 17, no. 23: 10856. https://doi.org/10.3390/su172310856
APA StyleLi, H., Wang, Q., & Wang, Q. (2025). Can Agricultural Insurance Promote Agricultural Modernization?—Evidence from China During 2008–2023. Sustainability, 17(23), 10856. https://doi.org/10.3390/su172310856






