A Grey Wolf Optimization Approach for Solving Constrained Economic Dispatch in Power Systems
Abstract
1. Introduction
Proposed Innovation Study Contribution
- i.
- A constrained economic dispatch with integrated RESs within a multi-unit generation system to meet power balance demand using GWO is proposed;
- ii.
- A simulation environment is used to address power balance demand in a grid-tied RES-hybrid system.
- iii.
- Case studies and benchmark comparisons of the 3-unit, 6-unit, and 15-unit systems are presented.
2. Literature Review
3. Materials and Methods
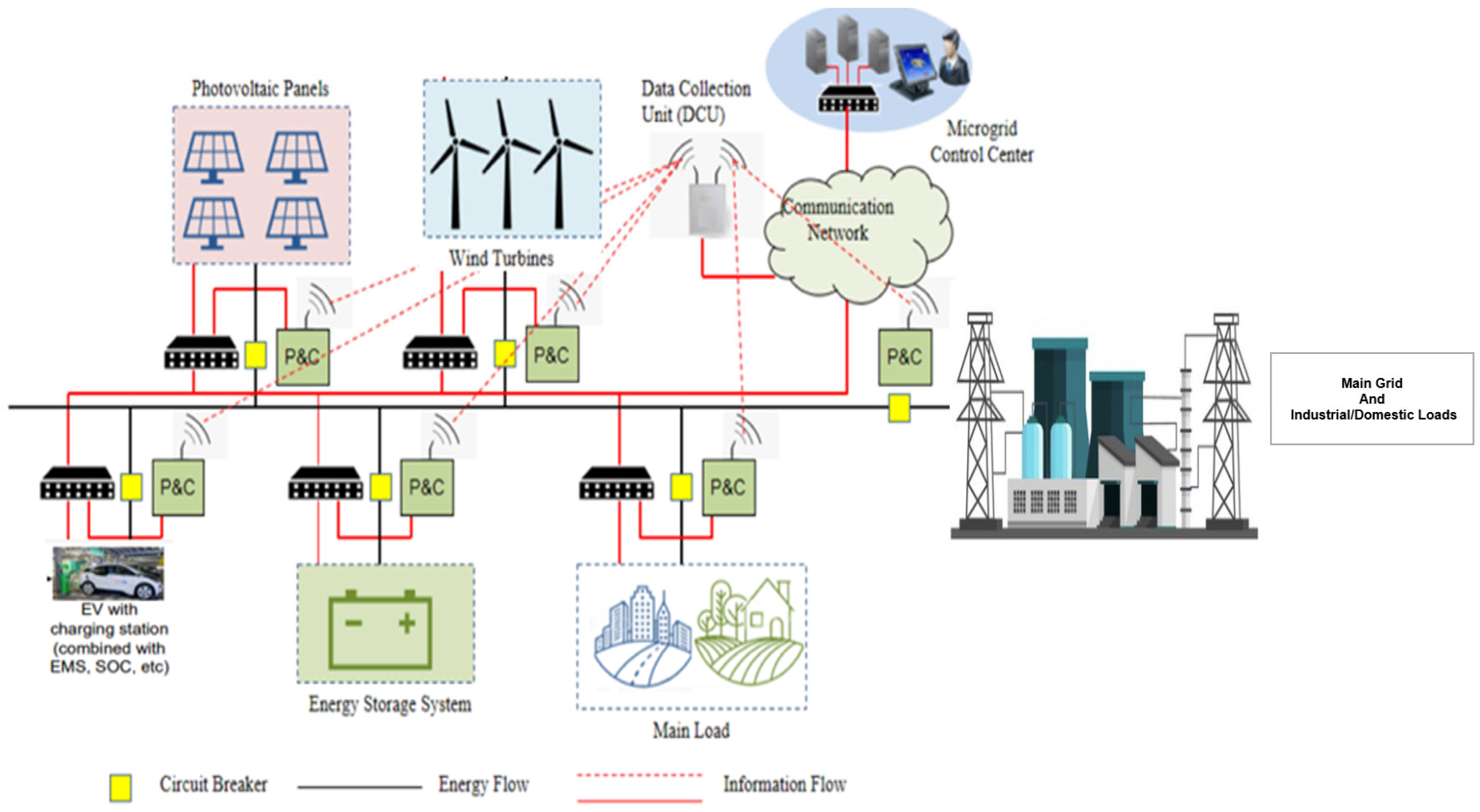
3.1. Materials
3.2. Methods
3.3. Description of the Test Systems
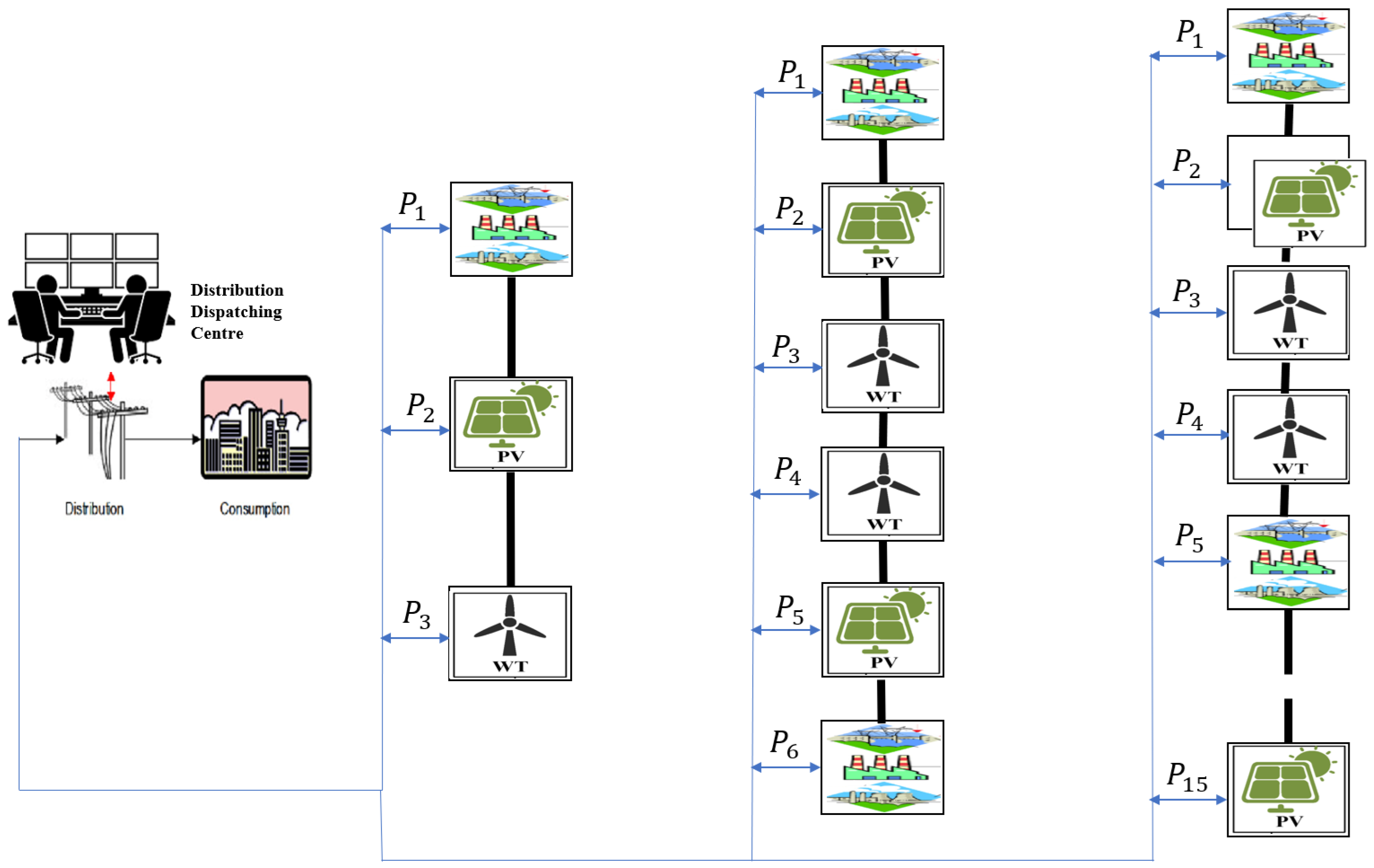
3.3.1. Test System 1
3.3.2. Test System 2
IEEE 14-, IEEE 30-, and IEEE 118-Bus Systems Comprising 3 Generators, 6 Generators, and 15 Generators, Using Monte Carlo UCF for RESs
- A power value denotes power i, as calculated by the ED solar generator model, . Monte Carlo replication produced a random irradiance rate that represents the RES’s functional-uncertainty cost.
- For the generator i ( in a Monte Carlo scenario), the irradiance random value is calculated using a log-normal probability distribution.
- The solar power-generated comparisons are derived from random irradiance.
- To estimate uncertainty cost, use the following formulas. If , use the underestimated state; if , use the overestimated state.
- Steps 2–4 are specified Monte Carlo repetitive scenarios.
- The entire accumulated cost expected value is determined; this is the UCF value.
- Steps 1–6 are repeated for each conceivable power value programmed into the economic dispatch model ().
3.4. Grey Wolf Algorithm for Solving Constrained ED Problems
3.4.1. Case 1: 3-Unit Generator System with the Demand of 850 MW Using Monte Carlo Uncertainty Cost Functions with RESs
3.4.2. Case 2: Six-Unit Generator System with 1263 MW Power Demand
3.4.3. Case 3: Fifteen-Unit Generator System with Demand of 2630 MW
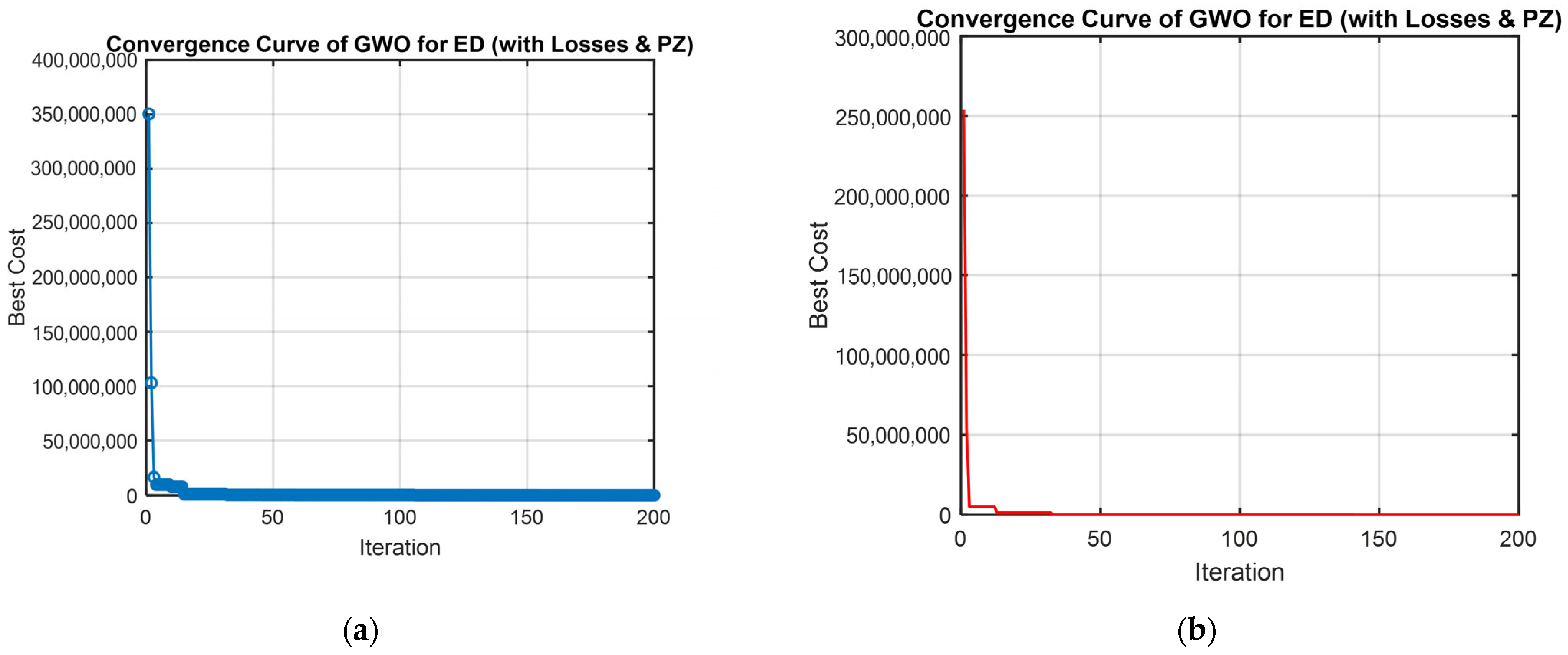
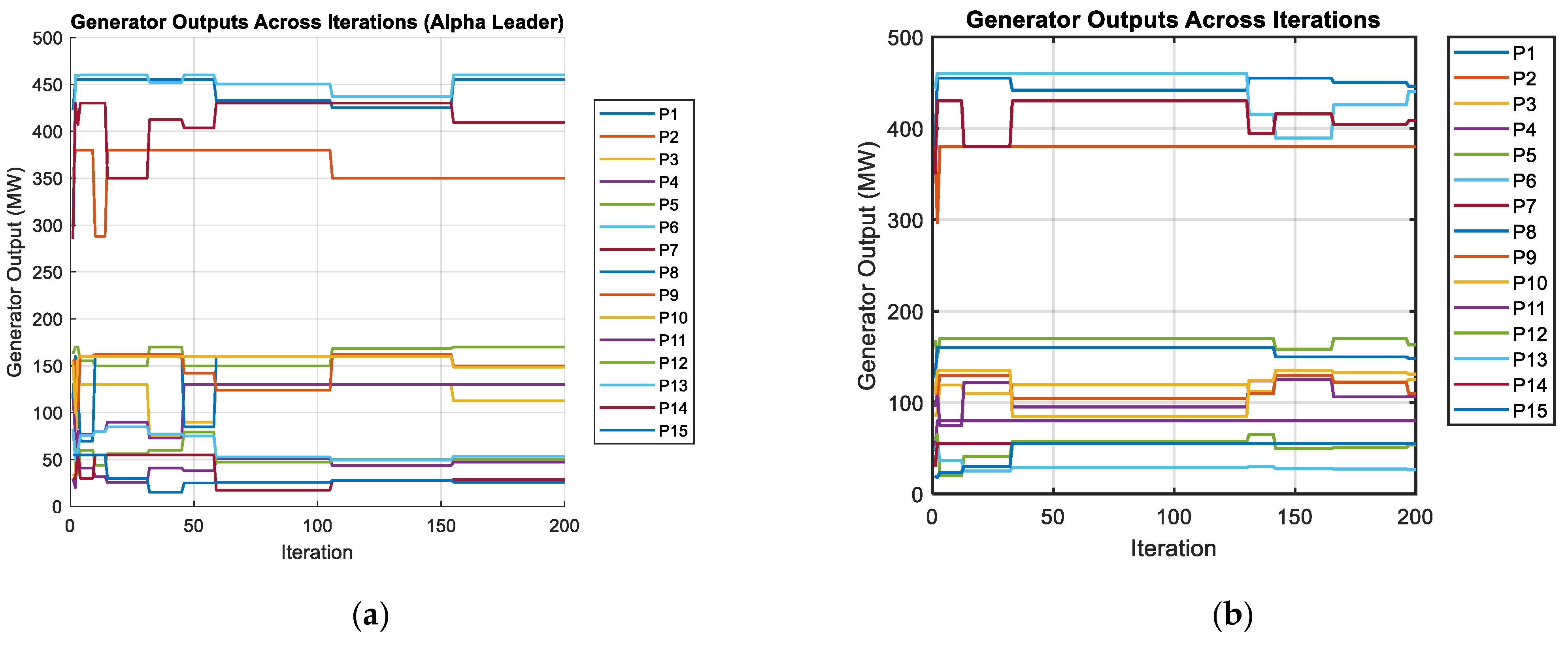
4. Results and Discussion
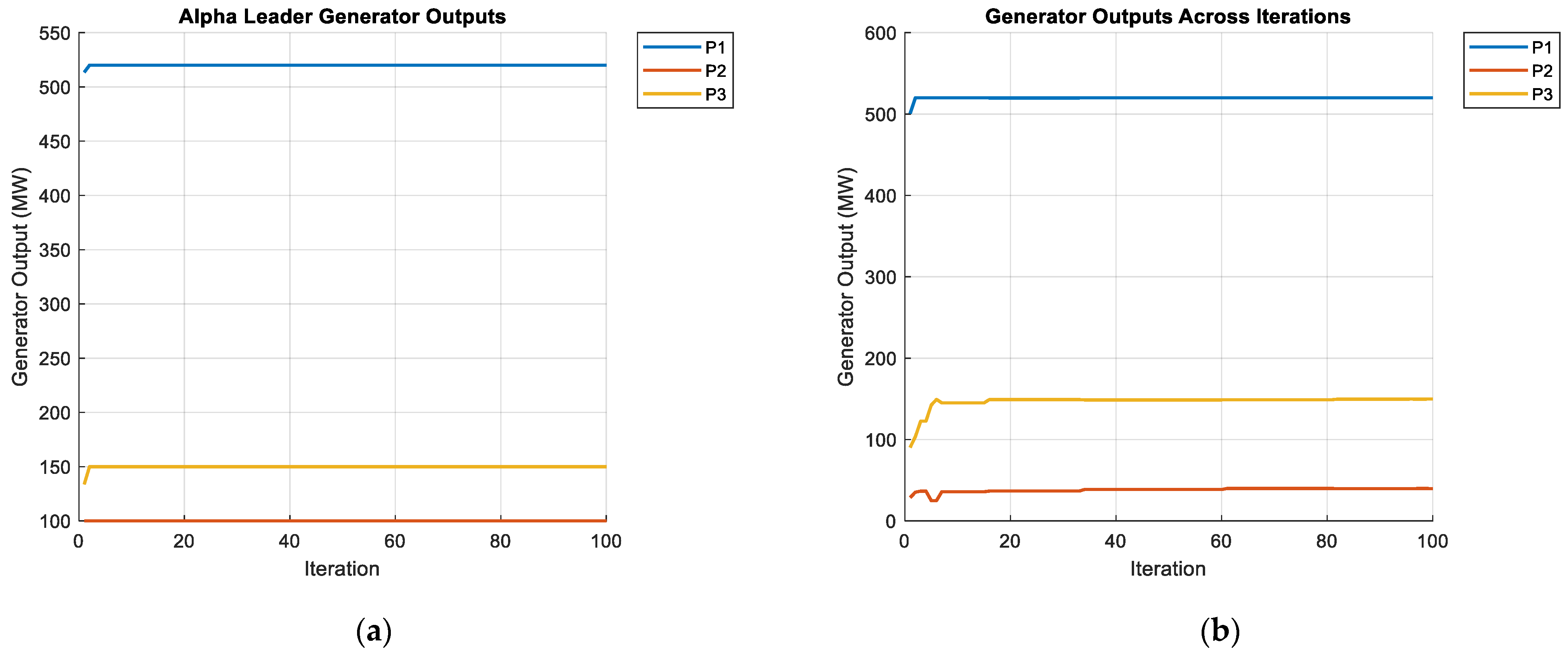
4.1. Test Case 1
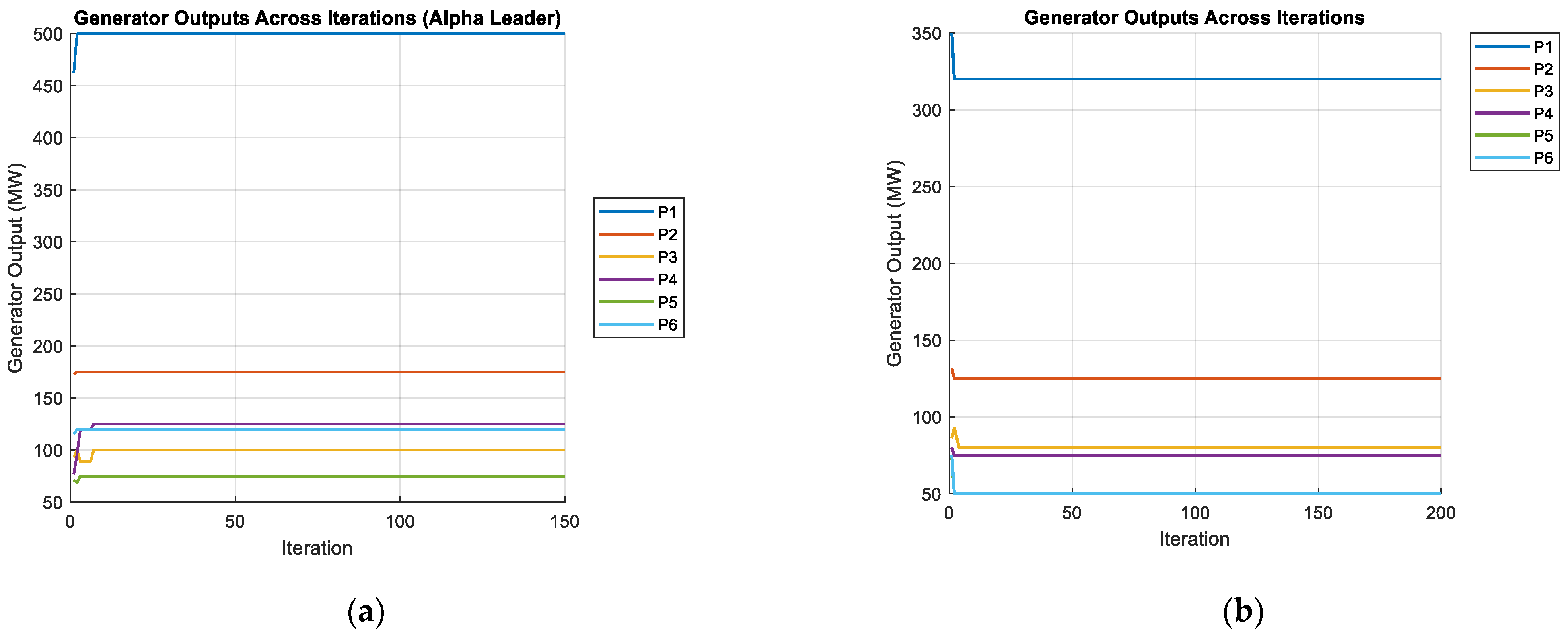
4.2. Test Case 2
4.3. Test Case 3
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gharehchopogh, F.S.; Ucan, A.; Ibrikci, T.; Arasteh, B.; Isik, G. Slime Mould Algorithm: A comprehensive survey of its variants and applications. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 2023, 30, 2683–2723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adenuga, O.T.; Krishnamurthy, S. Economic Power Dispatch of a Grid-Tied Photovoltaic-Based Energy Management System: Co-Optimization Approach. Mathematics 2023, 11, 3266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adenuga, O.T. Particle Swarm Optimization Method for Energy Management of the Hybrid System of an Electric Vehicle Charging Station. Ph.D. Thesis, Cape Peninsula University of Technology, Cape Town, South Africa, 2024. Available online: https://etd.cput.ac.za/bitstream/20.500.11838/4164/1/Adenuga%2c%20OT_223119016.pdf (accessed on 19 March 2025).
- Liang, Z.X.; Glover, J.D. A zoom feature for a dynamic programming solution to economic dispatch including transmission losses. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 1992, 7, 544–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Keib, A.A.; Ma, H.; Hart, J.L. Environmentally constrained economic dispatch using the Lagrangian relaxation method. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 1994, 9, 1723–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.L.; Wang, S.C. Branch- and bound scheduling for thermal generating units. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 1993, 8, 184–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodu, J.C.; Martin, P.; Merlin, A.; Pouget, J. An optimal formulation and solution of short-range operating problems for a power system with flow constraints. IEEE Proc. 1972, 60, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aravindhababu, P.; Nayar, K.R. Economic dispatch based on optimal lambda using radial basis function network. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2002, 24, 551–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parikh, J.; Chattopadhyay, D. A multi-area linear programming approach for analysis of economic operation of the Indian power system. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 1996, 11, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanda, J.; Hari, L.; Kothari, M.L. Economic emission dispatch with line flow constraints using a classical technique. IEE Proc. Gener. Trans. Distrib. 1994, 141, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goeritno, A. Implementation of the Coordination Equation for Determining the Transport-Related Losses in Economic Dispatch Phenomena. Math. Model. Eng. Probl. 2020, 07, 293–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adenuga, O.T.; Krishnamurthy, S. An MINLP Optimization Method to Solve the RES-Hybrid System Economic Dispatch of an Electric Vehicle Charging Station. World Electr. Veh. J. 2025, 16, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agnihotri, S.; Atre, A.; Verma, H.K. Equilibrium Optimizer for Solving Economic Dispatch Problem. In Proceedings of the PIICON 2020—9th IEEE Power India International Conference, Sonepat, India, 28 February–1 March 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visutarrom, T.; Chiang, T.C. Economic dispatch using metaheuristics: Algorithms, problems, and solutions. Appl. Soft Comput. 2023, 150, 110891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mundotiya, P.; Shrimal, S.; Koli, A.; Kansotia, G.; Meena, N.; Tiwari, H. Metaheuristic Optimization Techniques for Economic Dispatch in Power Generation: A Review. In Proceedings of the 2024 International Conference on Computer, Electronics, Electrical Engineering & their Applications (IC2E3), Srinagar Garhwal, India, 6–7 June 2024; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheta, A.; Ali, A.; Baareh, A.; Aljahdali, S. Meta-heuristic Search Algorithms for Solving the Economic Load Dispatch Problem. In Proceedings of the 2022 3rd International Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Robotics and Control (AIRC), Cairo, Egypt, 10–12 May 2022; pp. 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimzadeh Parizi, M.; Keynia, F.; Khatibi Bardsiri, A. Woodpecker Mating Algorithm for Optimal Economic Load Dispatch in a Power System with Conventional Generators. Int. J. Ind. Electron. Control Optim. 2021, 4, 221–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, J.; Yu, L.; Wang, J.; Li, N. A diversity-based parallel particle swarm optimization for nonconvex economic dispatch problem. Trans. Inst. Meas. Control 2022, 45, 452–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimoon, A.A.; Abdullah, M.N.; Yassim, H.M.; Raza, A.; Soomro, S.A. Lightning Search Algorithm for Economic Dispatch Solution Considering Practical Constraints and Transmission Loss. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE 4th International Conference in Power Engineering Applications (ICPEA), Pulau Pinang, Malaysia, 4–5 March 2024; pp. 214–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spea, S.R. Non-convex constrained economic power dispatch with prohibited operating zones and piecewise quadratic cost functions. Int. J. Electr. Comput. Eng. 2020, 10, 4469–4477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muraleedharan, S.; Babu, C.A.; Sasidharanpillai, A.K. Modified Opposition-Based Particle Swarm Optimization for Combined Economic and Emission Dispatch Problem. Electr. Power Compon. Syst. 2024, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, C.A. The solution of the economic dispatch problem via an efficient Teaching-Learning-Based Optimization method. Trans. Energy Syst. Eng. Appl. 2023, 4, 35–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassaymeh, S.; Abdullah, S.; Al-Betar, M.A.; Alweshah, M. Salp swarm optimizer for modeling the software fault prediction problem. J. King Saud Univ.—Comput. Inf. Sci. 2022, 34, 3365–3378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martınez, C.A.; Rivera, S.R. Quadratic Modelling of Uncertainty Costs for Renewable Generation and its Application on Economic Dispatch; Facultad de Ciencias Basicasc, Programa de Matemáticas, Universidad Nacional de Colombia: Bogotá, Colombia, 2018; Volume V, pp. 37–61. [Google Scholar]
- Arévalo, J.; Santos, F.; Rivera, S. Uncertainty Cost Functions for Solar Photovoltaic Generation, Wind Energy Generation, and Plug-In Electric Vehicles: Mathematical Expected Value and Verification by Monte Carlo Simulation. Int. J. Power Energy Convers. 2019, 10, 171–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, F.S.M.; Sichać, S.J.P.; Rodriguez, S.R.R. Formulación de funciones de Costo de Incertidumbre en Pequeñas Centrales Hidroeléctricas dentro de una Microgrid. Ing. USBmed 2017, 8, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varan, M.; Erduman, A.; Menevşeoğlu, F.A. Grey Wolf Optimization Algorithm-Based Optimal Reactive Power Dispatch with Wind-Integrated Power Systems. Energies 2023, 16, 5021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaing, Z.L. Particle swarm optimization to solving the economic dispatch considering the generator constraints. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2003, 18, 1187–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnamurthy, S.; Tzoneva, R.; Apostolov, A. Method for a Parallel Solution of a Combined Economic Emission Dispatch Problem. Electr. Power Compon. Syst. 2017, 45, 393–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Chang, H. Large-scale economic dispatch by genetic algorithm. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 1995, 10, 1919–1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Betar, M.A.; Awadallah, M.A.; Zitar, R.A.; Assaleh, K. Economic load dispatch using memetic sine cosine algorithm. J. Ambient Intell. Hum. Comput. 2023, 14, 11685–11713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, R.; Al-Roomi. Economic Load Dispatch Test Systems Repository; Dalhousie University, Electrical and Computer Engineering: Halifax, NS, Canada, 2016; Available online: https://www.al-roomi.org/economic-dispatch (accessed on 8 June 2023).
- Saadat, H. Power System Analysis; McGraw-Hill Companies: Columbus, OH, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Kuo, C.C. A novel coding scheme for practical economic dispatch by modified particle swarm approach. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2008, 23, 1825–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Q.; He, Y.; Hussain, S.; Lu, J.; Guerrero, J.M. Optimized energy storage configuration for enhanced flexibility in renewable-integrated power systems. J. Energy Storage 2025, 132, 117735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Ref. | Optimization Technique/Solution Approach | Objectives/Constraints Addressed | Test Power System Considered |
|---|---|---|---|
| [13] | Equilibrium Optimizer |
|
|
| [14] | Differential evolution-based algorithm (L-HMDE). |
|
|
| [15] | Metaheuristic Optimization Techniques |
|
|
| [16] | Crow Search Algorithm, and Differential Evolution (DE) Optimization Algorithm |
|
|
| [17] | Woodpecker Mating Algorithm |
|
|
| [18] | Diversity-based parallel particle swarm optimization (DPPSO) |
|
|
| [19] | Crow search algorithm |
|
|
| [20] | Genetic Algorithm variants |
|
|
| [21] | Lightning Search Algorithm (LSA) |
|
|
| [22] | Particle swarm optimization (PSO) algorithm |
|
|
| [23] | Salp Swarm Algorithm (SSSA) |
|
|
| [24] | Memetic Salp Swarm Algorithm (MSSA), |
|
|
| Bus No | Generator Limits [MW] | Fuel Cost Coefficients Without RESs | Fuel Cost Coefficients with RESs | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pmax | Pmin | ai [USD/MW2h] | bi [USD/MWh] | ci [USD/h] | ai [USD/MW2h] | bi [USD/MWh] | ci [USD/h] | ||
| 1 | 100 | 600 | 561 | 7.92 | 0.0016 | 561 | 7.92 | 0.0016 | |
| 2 | 100 | 400 | 310 | 7.85 | 0.0019 | 918.558 | 33.544 | 0.331 | |
| 5 | 50 | 200 | 78 | 7.97 | 0.0048 | 183.851 | 3.643 | 1.744 | |
| Transmission loss coefficients | |||||||||
| B01 | B | ||||||||
| 0.01890 | −0.00342 | −0.007660 | 0.0002940 | 0.0000901 | −0.0000507 | ||||
| 0.0000901 | 0.0005210 | 0.0000953 | |||||||
| B00 = 0.000014 | −0.0000507 | 0.0000953 | 0.0000953 | ||||||
| Bus No | Generator Limits [MW] | Fuel Cost Coefficients Without RESs | Fuel Cost Coefficients with RESs | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pmax | Pmin | ai [USD/MW2h] | bi [USD/MWh] | ci [USD/h] | ai [USD/MW2h] | bi [USD/MWh] | ci [USD/h] | |
| 1 | 100 | 500 | 240 | 7.00 | 0.0070 | 240 | 7.00 | 0.0070 |
| 2 | 50 | 200 | 200 | 10.0 | 0.0095 | 918.558 | 33.544 | 0.331 |
| 5 | 80 | 300 | 220 | 8.5 | 0.0090 | 183.851 | 3.643 | 1.744 |
| 8 | 50 | 150 | 200 | 11.0 | 0.0090 | 918.558 | 33.544 | 0.331 |
| 11 | 50 | 200 | 220 | 10.5 | 0.0080 | 183.851 | 3.643 | 1.744 |
| 13 | 50 | 120 | 190 | 12.0 | 0.0075 | 190 | 12.0 | 0.0075 |
| Transmission loss coefficients | ||||||||
| B01 | B | |||||||
| −0.3908 | −0.1279 | 0.7047 | 0.0017 | 0.0012 | 0.0007 | −0.0001 | -0.0005 | -0.0002 |
| 0.0012 | 0.0014 | 0.0009 | 0.0001 | -0.0006 | -0.0001 | |||
| 0.0591 | 0.2161 | −0.6635 | 0.0007 | 0.0009 | 0.0031 | 0.0000 | -0.0010 | -0.0006 |
| −0.0001 | 0.0001 | 0.0000 | 0.0024 | -0.0006 | -0.0008 | |||
| B00=0.056 | −0.0005 | −0.0006 | −0.0010 | 0.0006 | 0.0129 | −0.0002 | ||
| −0.0002 | −0.0001 | −0.0006 | 0.0008 | −0.0002 | 0.0150 | |||
| Bus No | Generator Limits [MW] | Fuel Cost Coefficients Without RESs | Fuel Cost Coefficients with RESs | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pmax | Pmin | ai [USD/MW2h] | bi [USD/MWh] | ci [USD/h] | ai [USD/MW2h] | bi [USD/MWh] | ci [USD/h] | |||
| 1 | 150 | 455 | 671 | 10.10 | 0.0003 | 671 | 10.10 | 0.0003 | ||
| 2 | 150 | 455 | 574 | 10.20 | 0.0001 | 574 | 10.20 | 0.0001 | ||
| 5 | 20 | 130 | 374 | 8.80 | 0.0011 | 918.558 | 33.544 | 0.331 | ||
| 4 | 20 | 130 | 374 | 8.80 | 0.0011 | 183.851 | 3.643 | 1.744 | ||
| 4 | 150 | 470 | 461 | 10.40 | 0.0002 | 461 | 10.40 | 0.0002 | ||
| 5 | 135 | 460 | 630 | 10.10 | 0.0003 | 630 | 10.10 | 0.0003 | ||
| 8 | 135 | 465 | 548 | 9.80 | 0.0003 | 548 | 9.80 | 0.0003 | ||
| 10 | 60 | 300 | 227 | 11.20 | 0.0003 | 227 | 11.20 | 0.0003 | ||
| 25 | 25 | 162 | 173 | 11.20 | 0.0008 | 918.558 | 33.544 | 0.331 | ||
| 26 | 25 | 160 | 175 | 10.70 | 0.0012 | 183.851 | 3.643 | 1.744 | ||
| 30 | 20 | 80 | 186 | 10.20 | 0.0035 | 918.558 | 33.544 | 0.331 | ||
| 37 | 20 | 80 | 230 | 9.90 | 0.0055 | 183.851 | 3.643 | 1.744 | ||
| 38 | 25 | 85 | 225 | 13.10 | 0.0003 | 918.558 | 33.544 | 0.331 | ||
| 63 | 15 | 55 | 309 | 12.10 | 0.0019 | 183.851 | 3.643 | 1.744 | ||
| 64 | 15 | 55 | 323 | 12.40 | 0.0044 | 323 | 12.40 | 0.004 | ||
| Algorithm | PSO with Evolutionary Technique [33] | Conventional Algebraic Method [35] | GA Method [29,32] | Memetic Sine Cosine Algorithm (SCA-βHC) [34] | Proposed GWO with Fuel Cost Coefficients | Proposed GWO with Fuel Cost Coefficients Using RES |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P1 | 32.604748 | 446.71 | 474.81 | 300.26 | 520 | 520 |
| P2 | 64.680578 | 173.01 | 178.64 | 400.00 | 100 | 39.9644 |
| P3 | 54.989919 | 265.00 | 262.21 | 149.73 | 150 | 149.6442 |
| Power Loss | 2.340470 | 2.3419 | 31.0960 | 3.0179 | 2.7237 | |
| Delivered | 152.34 | 1152.34 | 1276.03 | 1244.4640 | 770 | 706.88 |
| Fuel cost [USD] | 8234.07 | 8234.08 | 8234.10 | 8234.07 | 7598.1148 | 21,239.98 |
| %Deviation of FC for GWO compared to the literature | 7.65 | 7.81 | 7.69 | 7.27 | 0 | 179.5 |
| Algorithm | PSO with Evolutionary Technique [33] | PSO Method [29,31] | GA Method [29,32] | Memetic Sine Cosine Algorithm (SCA-βHC) [34] | Proposed GWO with Fuel Cost Coefficients | Proposed GWO with Fuel Cost Coefficients Using RES |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P1 | 440.576558 | 446.71 | 474.81 | 447.39 MW | 500 | 320 |
| P2 | 167.436910 | 173.01 | 178.64 | 173.31 MW | 175 | 125 |
| P3 | 278.235609 | 265.00 | 262.21 | 263.47 MW | 100 | 80 |
| P4 | 150.000000 | 139.00 | 134.28 | 138.55 MW | 125 | 75 |
| P5 | 157.606137 | 165.23 | 151.90 | 165.65 MW | 75 | 50 |
| P6 | 81.224444 | 86.78 | 74.18 | 87.19 MW | 120 | 50 |
| Power Loss | 12.079658 | 12.733 | 13.022 | 31.0960 | 24.3180 | 9.7161 |
| Delivered | 1275.079658 | 1275.7 | 1276.03 | 1244.4640 | 1070.6820 | 690.2839 |
| Fuel cost FC [USD] | 15,445.486621 | 15,447 | 15,459 | 15,444.48 | 13,397.0625 | 46,216,657.9535 |
| %Deviation of FC for GWO compared to the literature | 15.3 | 15.3 | 15.4 | 15.3 | 0 | 344 |
| Algorithm | PSO with Evolutionary Technique [33] | PSO Method [30,31] | GA Method [30,32] | Memetic Sine Cosine Algorithm (SCA-βHC) [34] | Proposed GWO with Fuel Cost Coefficients | Proposed GWO with Fuel Cost Coefficients Using RES |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P1 | 455.00 | 455.00 | 415.31 | 454.99 MW | 455.00 | 455 |
| P2 | 455.00 | 380.00 | 359.72 | 379.99 MW | 380.00 | 380 |
| P3 | 130.00 | 130.00 | 104.43 | 129.99 MW | 111.67 | 119.65 |
| P4 | 130.00 | 130.00 | 74.99 | 129.99 MW | 130.00 | 101.73 |
| P5 | 286.41 | 170.00 | 380.00 | 151.35 MW | 170.00 | 170 |
| P6 | 460.00 | 460.00 | 426.79 | 455.74 MW | 349.99 | 460 |
| P7 | 465.00 | 430.00 | 341.32 | 429.86 | 430.00 | 430 |
| P8 | 60.00 | 60.00 | 124.79 | 126.14 | 124.37 | 134.06 |
| P9 | 25.00 | 71.05 | 133.14 | 68.68 | 146.69 | 129.74 |
| P10 | 37.56 | 159.85 | 89.26 | 110.49 | 160.00 | 135 |
| P11 | 80.00 | 80.00 | 60.00 | 72.55 | 80.00 | 35 |
| P12 | 80.00 | 80.00 | 50.00 | 79.77 | 80.00 | 65 |
| P13 | 25.00 | 25.00 | 38.77 | 31.82 | 20.09 | 46.16 |
| P14 | 15.00 | 15.00 | 41.94 | 17.10 | 34.48 | 55 |
| P15 | 15.00 | 15.00 | 32.64 | 21.98 | 27.19 | 15.76 |
| Delivered | 2630.0 | 2630.0 | 2630.0 | 2660.51 | 2629.96 | |
| Power Loss | 28.97 | 30.90 | 13.02 | 30.50 | 2.85 | 102.10 |
| Fuel cost [USD] | 32,569 | 32,708 | 33,113 | 32,761.5 | 32,622.5 | 33,723.1 |
| %Deviation of FC for GWO compared to the literature | 0.164 | 0.26 | 1.50 | 0.4258 | 0 | 3.37 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Adenuga, O.T.; Krishnamurthy, S. A Grey Wolf Optimization Approach for Solving Constrained Economic Dispatch in Power Systems. Sustainability 2025, 17, 10648. https://doi.org/10.3390/su172310648
Adenuga OT, Krishnamurthy S. A Grey Wolf Optimization Approach for Solving Constrained Economic Dispatch in Power Systems. Sustainability. 2025; 17(23):10648. https://doi.org/10.3390/su172310648
Chicago/Turabian StyleAdenuga, Olukorede Tijani, and Senthil Krishnamurthy. 2025. "A Grey Wolf Optimization Approach for Solving Constrained Economic Dispatch in Power Systems" Sustainability 17, no. 23: 10648. https://doi.org/10.3390/su172310648
APA StyleAdenuga, O. T., & Krishnamurthy, S. (2025). A Grey Wolf Optimization Approach for Solving Constrained Economic Dispatch in Power Systems. Sustainability, 17(23), 10648. https://doi.org/10.3390/su172310648







