Sustainability of Supply Chains Through Digitalization: A Study on the Romanian Restaurant Industry
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
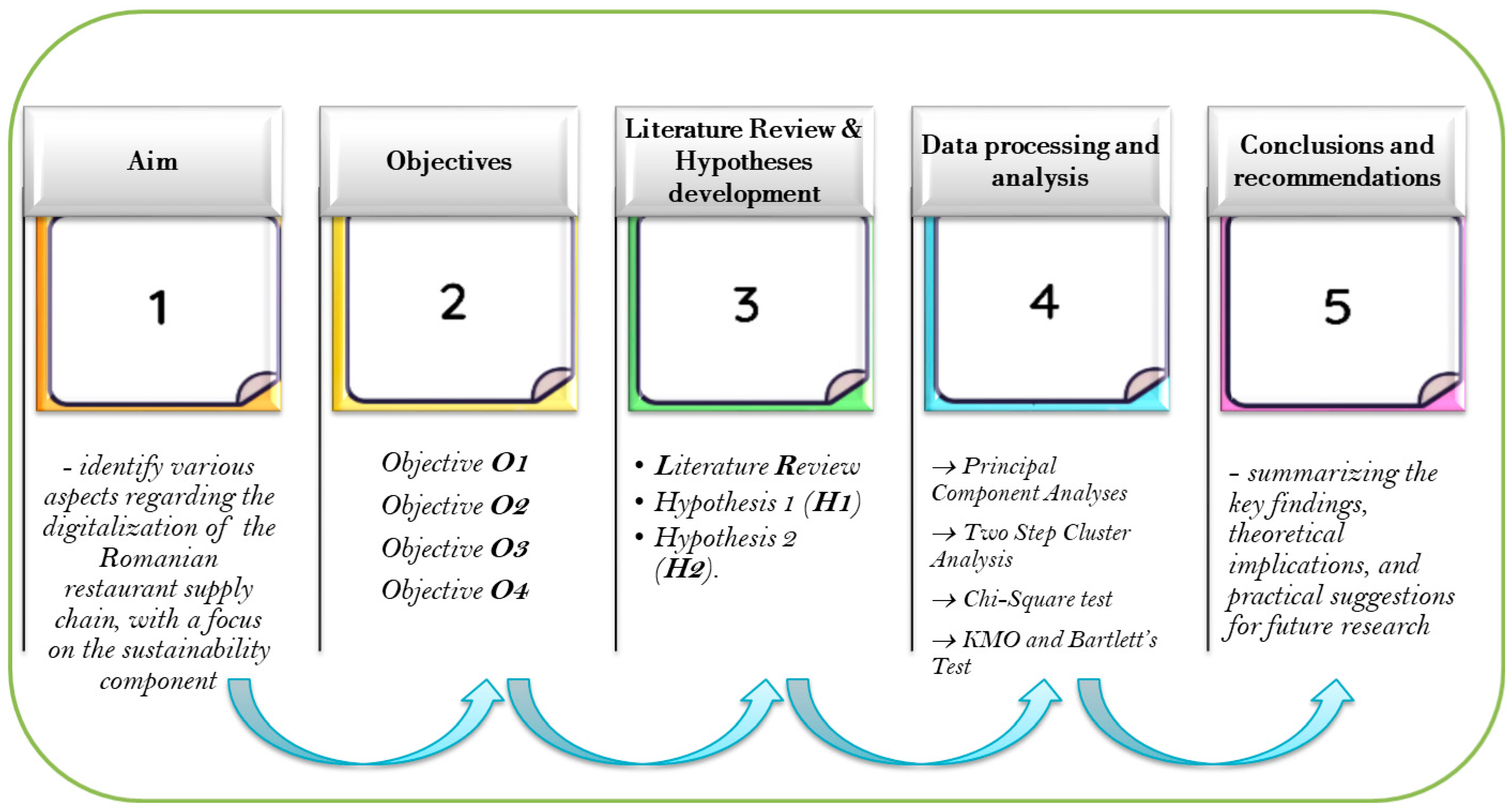
3. Research Method
- O1—Identifying the level of digitalization in the supply chain of restaurants in Romania;
- O2—Determining the relationship between the level of digitalization and the concern for sustainability;
- O3—Identifying the main barriers that prevent digitalization in the supply chain of restaurants in Romania;
- O4—Identifying the main factors that influence the adoption of digitalization in the supply chain.
3.1. Data Collection and Study Sample
3.2. Data Analysis Techniques
4. Results and Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sundarakani, B.; Manikas, I.; Gunasekaran, A. The Role of Digital Transformation in Achieving Sustainable Supply Chain Management in Industry 4.0: An Editorial Review Perspective. Int. J. Logist. Res. Appl. 2024, 27, 843–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkelmann, S.; Guennoun, R.; Möller, F.; Schoormann, T.; van der Valk, H. Back to a resilient future: Digital technologies for a sustainable supply chain. Inf. Syst. e-Bus. Manag. 2024, 22, 315–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, D.; Dolgui, A.; Sokolov, B. The impact of digital technology and Industry 4.0 on the ripple effect and supply chain risk analytics. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2018, 57, 829–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wynn, M.; Lam, C. Digitalisation and IT strategy in the hospitality industry. Systems 2023, 11, 501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García López, A.M.; Galindo Pérez de Azpillaga, L.; Foronda Robles, C. The flow of digital transition: The challenges of technological solutions for hotels. Soc. Indic. Res. 2025, 178, 1323–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunea, O.-I.; Corboș, R.-A.; Popescu, R.-I. Challenges for a Digital Sustainable Supply Chain in a Circular Economy Context. In Fostering Recovery Through Metaverse Business Modelling; Bucharest University of Economic Studies: Bucharest, Romania, 2022; pp. 731–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, B.; Qiu, H. How a hierarchical governance structure influences cultural heritage destination sustainability: A context of red tourism in China. J. Hosp. Tour. Manag. 2022, 50, 421–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bag, S.; Pretorius, J.H.C.; Gupta, S.; Dwivedi, Y.K. Role of institutional pressures and resources in the adoption of big data analytics powered artificial intelligence, sustainable manufacturing practices and circular economy capabilities. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2021, 163, 120420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, D.K.; Varshney, Y.; Awasthi, R.K.; Yadav, M.P.; Kumar, S.; Kumar, M. Digital Transformation and its Environmental Implications in Supply Chain Management. J. Big Data Anal. Bus. Intell. 2025, 2, 10–18. [Google Scholar]
- Chiu, J.-Z.; Hsieh, C.-C. The impact of restaurants’ green supply chain practices on firm performance. Sustainability 2016, 8, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naksuetrong, S.; Chunkamon, E. The influence of green supply chains on economic and environmental performance of restaurant business. J. Appl. Econ. Manag. Strategy 2024, 11, 53–69. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, Y.; Thoo, A.C.; Abdullah, M. Supplier selection criteria of restaurant: A cross-industry literature review. J. Tour. Hosp. Environ. Manag. 2024, 9, 159–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adekuaojo, I.O.; Fakeyede, O.G.; Udeh, C.A.; Daraojimba, C. The digital evolution in hospitality: A global review and its potential transformative impact on U.S. tourism. Int. J. Appl. Res. Soc. Sci. 2023, 5, 440–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasileiou, M.; Kyrgiakos, L.S.; Kleisiari, C.; Lappas, P.Z.; Tsinopoulos, C.; Kleftodimos, G.; Ntemou, A.; Kateris, D.; Moulogianni, C.; Vlontzos, G. Digital transformation of food supply chain management using blockchain: A systematic literature review towards food safety and traceability. Bus. Inf. Syst. Eng. 2025, 67, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazıcılar Sola, F.G.; Güzel, D. The role of supply chain transparency and supplier trust in the impact of blockchain technology adoption on new product development. Sustainability 2025, 17, 5171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erol, I.; Oztel, A.; Dogru, T.; Peker, I.; Neuhofer, I.O.; Benli, T. Supply chain resilience in the tourism and hospitality industry: A comprehensive examination of driving and restraining forces. Int. J. Hosp. Manag. 2024, 122, 103851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Androod, S.H.; Babakhan, M.; Biroki, N.; Khorasani, A.; Aslam, M.R.; Khan, S. Sustainability-related impacts of digitalization on supply chain management. Eng. Proc. 2024, 76, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruge, P.; Ban, O. Digitalisation in accommodation and food service activities in Romania and European Union. Ann. Univ. Oradea Econ. Sci. 2024, 33, 166–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Shrivastav, S.K.; Shrivastava, A.K.; Panigrahi, R.R.; Mardani, A.; Cavallaro, F. Sustainable supply chain management, performance measurement, and management: A review. Sustainability 2023, 15, 5290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekele, H.; Raj, S.; Singh, A.; Joshi, M.; Kajla, T. Digital Transformation and Environmental Sustainability in the Hospitality Industry: A Three-Wave Time-Lagged Examination. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 484, 144263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gariba, M.I.; Rehman, F.U.; Prokop, V.; Giglio, C. Be digital to be sustainable! The mediating role of sustainable supply chain practices in triggering the effects of digitalisation on Sustainable Development Goals in the European Union. Oeconomia Copernic. 2024, 15, 1383–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garti, M.O.; Arif, J.; Jawab, F.; Frichi, Y.; Benbrahim, F.Z. Factors impacting the sustainability of supply chain in Industry 5.0: An exploratory qualitative study in Morocco. Logistics 2025, 9, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vodenicharova, M.; Mihova, L. Sustainable supply chains in the food service industry. Indones. J. Sustain. Account. Manag. 2023, 7, 559–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeel, H.B.; Sabir, R.I.; Shahnawaz, M.; Zafran, M. Adoption of environmental technologies in the hotel industry: Development of sustainable intelligence and pro environmental behavior. Discov. Sustain. 2024, 5, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilies, V.I. Digital communications strategies in HoReCa industry: Case study Marty restaurants, Cluj Napoca. Prof. Commun. Transl. Stud. 2018, 11, 21–31. [Google Scholar]
- European Commission. Digital Economy and Society Index (DESI). 2024. Available online: https://digital-strategy.ec.europa.eu/en/policies/desi (accessed on 25 March 2025).
- Azmaiparashvili, M. Challenges and Prospects of Digital Transformation in Georgian Hotel Business. InterConf 2024, 49, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhuniya, S.; Pareek, S.; Sarkar, B. A supply chain model with service level constraints and strategies under uncertainty. Alex. Eng. J. 2021, 60, 6035–6052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saad, N.A.; Elgazzar, S.; Mlaker Kac, S. Investigating the impact of supply chain management practices on customer satisfaction through flexibility and technology adoption: Empirical evidence. Bus. Strategy Dev. 2023, 7, e326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Chen, L.; Ma, L. Supply chain product innovation and marketing strategies under different fairness concerns. Transp. Res. E Logist. Transp. Rev. 2024, 187, 103580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melnic, I.; Graur, A. Key performance indicators in the enterprise’s logistics activity. Rev. Econ. 2022, 1, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, R.V.; Harsh, H.O.; Ray, P.; Babu, A.K. Food quality traceability prototype for restaurants using blockchain and food quality data index. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 240, 118021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Băltescu, C.A.; Neacșu, N.A.; Madar, A.; Boșcor, D.; Zamfirache, A. Sustainable Development Practices of Restaurants in Romania and Changes during the COVID-19 Pandemic. Sustainability 2022, 14, 3798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssef, A.B.; Dutta, P.K.; Doshi, R.; Sajnani, M. (Eds.) AI, Blockchain, and Metaverse in Hospitality and Tourism Industry 4.0: Case Studies and Analysis; Chapman and Hall/CRC: New York, NY, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Lu, H.; Mangla, S.K. The Impact of Digital Traceability on Sustainability Performance: Investigating the Roles of Sustainability-Oriented Innovation and Supply Chain Learning. Supply Chain. Manag. Int. J. 2024, 29, 497–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutanto, J. Digital Supply Chains and Their Environmental Impact: A Dual Perspective on Performance. Politecnico di Milano, 2022. Available online: https://www.politesi.polimi.it/handle/10589/214084 (accessed on 27 March 2025).
- Wong, E.K.S.; Ting, H.Y.; Atanda, A.F. Enhancing supply chain traceability through blockchain and IoT integration: A comprehensive review. Green Intell. Syst. Appl. 2024, 4, 11–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brun, A.; Karaosman, H.; Barresi, T. Supply chain collaboration for transparency. Sustainability 2020, 12, 4429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franceli, J.C.; Novaes Zilber Turri, S. Adoption factors of enabling I4.0 technologies and benefits in the supply chain. Comput. Sci. Inf. Technol. 2021, 11, 9. [Google Scholar]
- Clemente-Almendros, J.A.; Nicoara-Popescu, D.; Pastor-Sanz, I. Digital transformation in SMEs: Understanding its determinants and size heterogeneity. Technol. Soc. 2024, 77, 102483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Restrepo-Morales, J.A.; Ararat-Herrera, J.A.; López-Cadavid, D.A.; Camacho-Vargas, A. Breaking the digitalization barrier for SMEs: A fuzzy logic approach to overcoming challenges in business transformation. J. Innov. Entrep. 2024, 13, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ocloo, E.C.; Coffie, I.S.; Bukari, Z.; Bashiru, S. Digitization of Small and Medium-Size Restaurant Enterprises: The Mediating Role of Owner/Manager IT Skill and Moderating Influence of COVID-19. Cogent Bus. Manag. 2024, 11, 2358549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhoondnejad, A.; Rosin, C.; Brennan, C. A Qualitative Study of Antecedents of Enduring Involvement and Its Role in Dining Experiences of Tourists. Int. J. Contemp. Hosp. Manag. 2022, 34, 993–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, C.; Dallasega, P.; Orzes, G.; Sarkis, J. Industry 4.0 Technologies Assessment: A Sustainability Perspective. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2020, 229, 107776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frederico, G.F.; Garza-Reyes, J.A.; Anosike, A.; Kumar, V. Supply Chain 4.0: Concepts, Maturity and Research Agenda. Supply Chain. Manag. Int. J. 2020, 25, 262–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guandalini, I. Sustainability through Digital Transformation: A Systematic Literature Review for Research Guidance. J. Bus. Res. 2022, 148, 456–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panigrahi, R.R.; Singh, N.; Muduli, K. Digital Technologies and Food Supply Chain: A Scoping View from 2010 to 2024. Int. J. Ind. Eng. Oper. Manag. 2025, 7, 150–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, A.S.; Brahmbhatt, M.N.; Bariya, A.R.; Nayak, J.B.; Singh, V.K. Blockchain Technology in Food Safety and Traceability Concern to Livestock Products. Heliyon 2023, 9, e16526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigala, E.G.; Gerwin, P.; Chroni, C.; Abeliotis, K.; Strotmann, C.; Lasaridi, K. Reducing Food Waste in the HORECA Sector Using AI-Based Waste-Tracking Devices. Waste Manag. 2025, 198, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masi, M.; De Rosa, M.; Charatsari, C.; Lioutas, E.D.; Vecchio, Y. Enhancing Value Creation in Short Food Supply Chains through Digital Platforms. Agric. Food Econ. 2025, 13, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghobakhloo, M. Industry 4.0, Digitization, and Opportunities for Sustainability. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 252, 119869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak, M.; Sangwan, M.; Hajoary, P.K.; Dinesh, K.K. Technology Adoption Strategy for Foodservice Businesses in an Emerging Economy Context: Policy Interventions Using the Longitudinal Influencer-Facilitator-Initiative (L-IFI) Framework. J. Foodserv. Bus. Res. 2025, 1–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almatooq, M.E.; Al Mubarak, M. The Role of Digital Technologies in Achieving Sustainability. In Sustainable Digital Technology and Ethics in an Ever-Changing Environment; Al Mubarak, M., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2025; Volume 236, pp. 639–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Principato, L.; Marchetti, S.; Barbarnera, M.; Ruini, L.; Capoccia, L.; Comis, C.; Secondi, L. Introducing Digital Tools for Sustainable Food Supply Management: Tackling Food Loss and Waste in Industrial Canteens. J. Ind. Ecol. 2023, 27, 1060–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, H.; Fan, Y. Digital Transformation, Supply Chain Integration and Supply Chain Performance: Evidence from Chinese Manufacturing Listed Firms. SAGE Open 2024, 14, 21582440241281616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malakar, P.; Khan, S.A.; Gunasekaran, A.; Mubarik, M.S. Digital Technologies for Social Supply Chain Sustainability: An Empirical Analysis Through the Lens of Dynamic Capabilities and Complexity Theory. IEEE Trans. Eng. Manag. 2025, 72, 664–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vukolić, D.; Gajić, T.; Cabral, Ó.; Veljović, S.; Knežević, S. Revolutionizing the Hospitality Industry: The Impact of AI Technologies on Efficient Food Management and Reduction of Food Waste. J. Tour. Futures 2025, 11, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathiya, V.; Nagalakshmi, K.; Raju, K. Tracking Perishable Foods in the Supply Chain Using Chain of Things Technology. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 21621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoeva, S.; Van Gompel, R.; Van den Bossche, L.; Rogge, E.; Slavova, P.; Grivins, M.; Mileiko, I. Understanding Collaboration in Short Food Supply Chains: A Focus on Collaborative Relationships, Interaction Mechanisms and Relational Benefits. Agric. Food Econ. 2024, 12, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duong, L.N.K.; Kumar, V.; He, Q. Collaboration for the Sustainable Food Supply Chain: A Bibliometric Analysis. Bus. Strategy Environ. 2025, 34, 1287–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quttainah, M.A.; Ayadi, I. The Impact of Digital Integration on Corporate Sustainability: Emissions Reduction, Environmental Innovation, and Resource Efficiency in the European. J. Innov. Knowl. 2024, 9, 100525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunasekaran, A.; Kamble, S.; Ghadge, A.; Kumar, V. Investments in Industry 4.0 Technologies and Supply Chain Finance: Approaches, Framework and Strategies. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2024, 62, 8049–8055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bindeeba, D.S.; Tukamushaba, E.K.; Bakashaba, R. Digital Transformation and Its Multidimensional Impact on Sustainable Business Performance: Evidence from a Meta-Analytic Review. Future Bus. J. 2025, 11, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Shen, Y. Unlocking the Potential of Supply Chain Digitalization for Enhancing Enterprise Green Transformation Performance: Evidence from China. Humanit. Soc. Sci. Commun. 2025, 12, 1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín Martín, D.; Maya García, J.; Romero, I. Determinants of digital transformation in the restaurant industry. Amfiteatru Econ. 2022, 24, 430–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alt, R. Digital Transformation in the Restaurant Industry: Current Developments and Implications. J. Smart Tour. 2021, 1, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, C.-H. Exploring Information Technology’s Adoption in Restaurants. Open Access Libr. J. 2020, 7, e6470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mladenova, I.; Vladimirov, Z.; Harizanova, O. Digital Transformation, Organisational Capabilities, and SME Performance—Size Matters. East. J. Eur. Stud. 2025, 16, 216–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Türkeș, M.C.; Bănacu, C.-S.; Stoenică, L. The Effect of Supply Chain Sustainability Practices on Romanian SME Performance. Sustainability 2024, 16, 2887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vehovar, V.; Manfreda, K.L. Overview: Online surveys. In The SAGE Handbook of Online Research Methods; Fielding, N., Lee, R.M., Blank, G., Eds.; Sage: London, UK, 2008; Volume 1, pp. 177–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sowa, P.; Pędziński, B.; Krzyżak, M.; Maślach, D.; Wójcik, S.; Szpak, A. The computer-assisted web interview method as used in the national study of ICT use in primary healthcare in Poland—Reflections on a case study. Stud. Log. Gramm. Rhetor. 2015, 43, 137–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolliffe, I.T.; Cadima, J. Principal component analysis: A review and recent developments. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2016, 374, 20150202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenacre, M.; Groenen, P.J.F.; Hastie, T.; Iodice D’Enza, A.; Markos, A.; Tuzhilina, E. Principal component analysis. Nat. Rev. Methods Primers 2022, 2, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, H.; Galera-Zarco, C. Tackling Food Waste and Loss through Digitalization in the Food Supply Chain: A Systematic Review and Framework Development. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2025, 217, 124175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaid, M.; Farooqi, R.; Azmi, S.N. Driving Sustainable Supply Chain Performance through Digital Transformation: The Role of Information Exchange and Responsiveness. Cogent Bus. Manag. 2025, 12, 2443047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
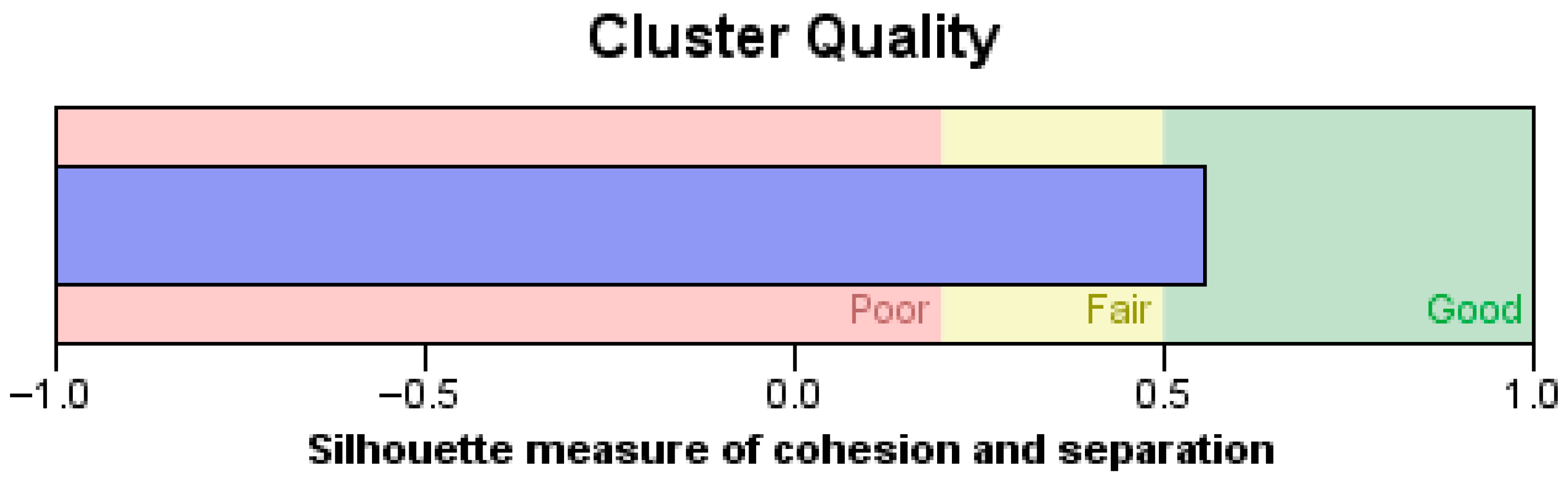
- Rousseeuw, P.J. Silhouettes: A graphical aid to the interpretation and validation of cluster analysis. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 1987, 20, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rugiubei, R.; Pînzaru, F. The Digitalization of Supply Chain Management in Romanian Companies: An Introductive Research. Proc. Int. Conf. Bus. Excell. 2022, 16, 1295–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Type of Restaurant | Frequency | Percent | Valid Percent | Cumulative Percent |
| Fast-Food Restaurant | 112 | 39.9 | 40.0 | 40.0 |
| Casual Restaurant | 56 | 19.9 | 20.0 | 60.0 |
| Premium Restaurant | 56 | 19.9 | 20.0 | 80.0 |
| Cafe | 56 | 19.9 | 20.0 | 100.0 |
| Total | 280 | 99.6 | 100.0 | |
| Restaurant Size | Frequency | Percent | Valid Percent | Cumulative Percent |
| 1–5 employees | 56 | 19.9 | 20.0 | 20.0 |
| 6–15 employees | 168 | 59.8 | 60.0 | 80.0 |
| Over 15 employees | 56 | 19.9 | 20.0 | 100.0 |
| Total | 280 | 99.6 | 100.0 | |
| Activity Duration in The Restaurant Industry | Frequency | Percent | Valid Percent | Cumulative Percent |
| 1–5 years | 56 | 19.9 | 20.0 | 20.0 |
| 6–10 years | 168 | 59.8 | 60.0 | 80.0 |
| Over 10 years | 56 | 19.9 | 20.0 | 100.0 |
| Total | 280 | 99.6 | 100.0 |
| The Restaurants’ Level of Digitalization Based on Application Areas | Type of Restaurant | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fast-Food | Casual Restaurant | Premium Restaurant | Cafe | Total | |
| 1—Very low level | 47.7% | 15.9% | 18.2% | 18.2% | 100.0% |
| 2—Low level | 39.6% | 20.9% | 19.8% | 19.8% | 100.0% |
| 3—Moderate level | 32.4% | 23.5% | 26.5% | 17.6% | 100.0% |
| 4—High level | 28.6% | 14.3% | 14.3% | 42.9% | 100.0% |
| 5—Very high level | 39.6% | 20.8% | 18.8% | 20.8% | 100.0% |
| Total | 39.7% | 20.1% | 20.1% | 20.1% | 100.0% |
| Does Your Restaurant Use Digital Technologies for Supply Management? | Type of Restaurant | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fast-Food | Casual Restaurant | Premium Restaurant | Cafe | Total | |
| Yes | 39.3% | 19.6% | 19.6% | 21.4% | 100.0% |
| No | 39.9% | 20.2% | 20.2% | 19.6% | 100.0% |
| Total | 39.7% | 20.1% | 20.1% | 20.1% | 100.0% |
| Chi-Square Tests | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Value | df | Asymptotic Significance (2-Sided) | |
| Pearson Chi-Square | 0.085 a | 3 | 0.994 |
| Likelihood Ratio | 0.084 | 3 | 0.994 |
| Linear-by-Linear Association | 0.054 | 1 | 0.817 |
| N of Valid Cases | 224 | ||
| The Level of Digitalization of Restaurants According to the Technologies Used in Supply | Type of Restaurant | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fast-Food | Casual Restaurant | Premium Restaurant | Cafe | Total | |
| 2—Low Level | 42.5% | 17.5% | 22.5% | 17.5% | 100.0% |
| 3—Moderate Level | 42.9% | 28.6% | 14.3% | 14.3% | 100.0% |
| 4—High Level | 22.2% | 22.2% | 22.2% | 33.3% | 100.0% |
| Total | 39.3% | 19.6% | 21.4% | 19.6% | 100.0% |
| Does Your Restaurant Use Digital Technologies for Supply Management? | Does Your Restaurant Implement Sustainable Measures in Its Supply Chain? | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| No | Yes | Total | |
| Yes | 19.6% | 80.4% | 100.0% |
| No | 21.4% | 78.6% | 100.0% |
| Total | 20.1% | 79.9% | 100.0% |
| Chi-Square Tests | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Value | df | Asymptotic Significance (2-Sided) | Exact Sig. (2-Sided) | Exact Sig. (1-Sided) | |
| Pearson Chi-Square | 0.083 a | 1 | 0.773 | ||
| Continuity Correction b | 0.009 | 1 | 0.923 | ||
| Likelihood Ratio | 0.083 | 1 | 0.774 | 0.454 | |
| Fisher’s Exact Test | 0.848 | ||||
| Linear-by-Linear Association | 0.083 | 1 | 0.773 | ||
| N of Valid Cases | 224 | ||||
| Descriptive Statistics | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | Std. Deviation | Analysis N | |
| The cost of technology | 4.2000 | 0.74967 | 280 |
| Ease of use | 4.0000 | 0.63359 | 280 |
| Market or regulatory pressure | 3.4714 | 0.69244 | 280 |
| Reducing food waste | 3.5536 | 1.09609 | 280 |
| Improving the relationship with suppliers | 3.0893 | 1.01735 | 280 |
| Increasing product transparency and traceability | 4.0000 | 0.63359 | 280 |
| KMO and Bartlett’s Test | ||
|---|---|---|
| Kaiser–Meyer–Olkin Measure of Sampling Adequacy | 0.541 | |
| Bartlett’s Test of Sphericity | Approx. Chi-Square | 541.693 |
| df | 15 | |
| Sig. | 0.000 | |
| Total Variance Explained | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Component | Initial Eigenvalues | Extraction Sums of Squared Loadings | Rotation Sums of Squared Loadings | ||||||
| Total | % of Variance | Cumulative % | Total | % of Variance | Cumulative % | Total | % of Variance | Cumulative % | |
| 1 | 2.337 | 38.948 | 38.948 | 2.337 | 38.948 | 38.948 | 2.334 | 38.894 | 38.894 |
| 2 | 1.335 | 22.250 | 61.198 | 1.335 | 22.250 | 61.198 | 1.338 | 22.304 | 61.198 |
| 3 | 0.968 | 16.136 | 77.333 | ||||||
| 4 | 0.735 | 12.258 | 89.592 | ||||||
| 5 | 0.497 | 8.286 | 97.877 | ||||||
| 6 | 0.127 | 2.123 | 100.000 | ||||||
| Rotated Component Matrix a | ||
|---|---|---|
| Component | ||
| 1 | 2 | |
| The cost of technology | 0.886 | −0.063 |
| Ease of use | 0.722 | 0.343 |
| Market or regulatory pressure | 0.189 | 0.747 |
| Reducing food waste | 0.403 | −0.553 |
| Improving the relationship with suppliers | −0.026 | 0.570 |
| Increasing product transparency and traceability | 0.911 | −0.167 |
| Descriptive Statistics | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | Std. Deviation | Analysis N | |
| Lack of digital skills of staff | 3.8000 | 1.60286 | 280 |
| Difficulties in integrating digital technologies with existing systems | 3.6000 | 0.49078 | 280 |
| Employee resistance to change | 3.0321 | 1.06207 | 280 |
| High initial investments for implementation | 3.5036 | 0.99820 | 280 |
| Lack of customized technological solutions for the restaurant industry | 4.2000 | 0.74967 | 280 |
| KMO and Bartlett’s Test | ||
|---|---|---|
| Kaiser–Meyer–Olkin Measure of Sampling Adequacy | 0.565 | |
| Bartlett’s Test of Sphericity | Approx. Chi-Square | 383.775 |
| df | 10 | |
| Sig. | 0.000 | |
| Total Variance Explained | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Component | Initial Eigenvalues | Extraction Sums of Squared Loadings | Rotation Sums of Squared Loadings | ||||||
| Total | % of Variance | Cumulative % | Total | % of Variance | Cumulative % | Total | % of Variance | Cumulative % | |
| 1 | 2.206 | 44.127 | 44.127 | 2.206 | 44.127 | 44.127 | 1.945 | 38.904 | 38.904 |
| 2 | 1.082 | 21.637 | 65.764 | 1.082 | 21.637 | 65.764 | 1.343 | 26.860 | 65.764 |
| 3 | 0.988 | 19.760 | 85.524 | ||||||
| 4 | 0.520 | 10.409 | 95.933 | ||||||
| 5 | 0.203 | 4.067 | 100.000 | ||||||
| Rotated Component Matrix a | ||
|---|---|---|
| Component | ||
| 1 | 2 | |
| Lack of digital skills of staff | 0.333 | 0.762 |
| Difficulties in integrating digital technologies with existing systems | 0.876 | 0.245 |
| Employee resistance to change | 0.402 | 0.558 |
| High initial investments for implementation | −0.351 | 0.625 |
| Lack of customized technological solutions for the restaurant industry | 0.885 | 0.001 |
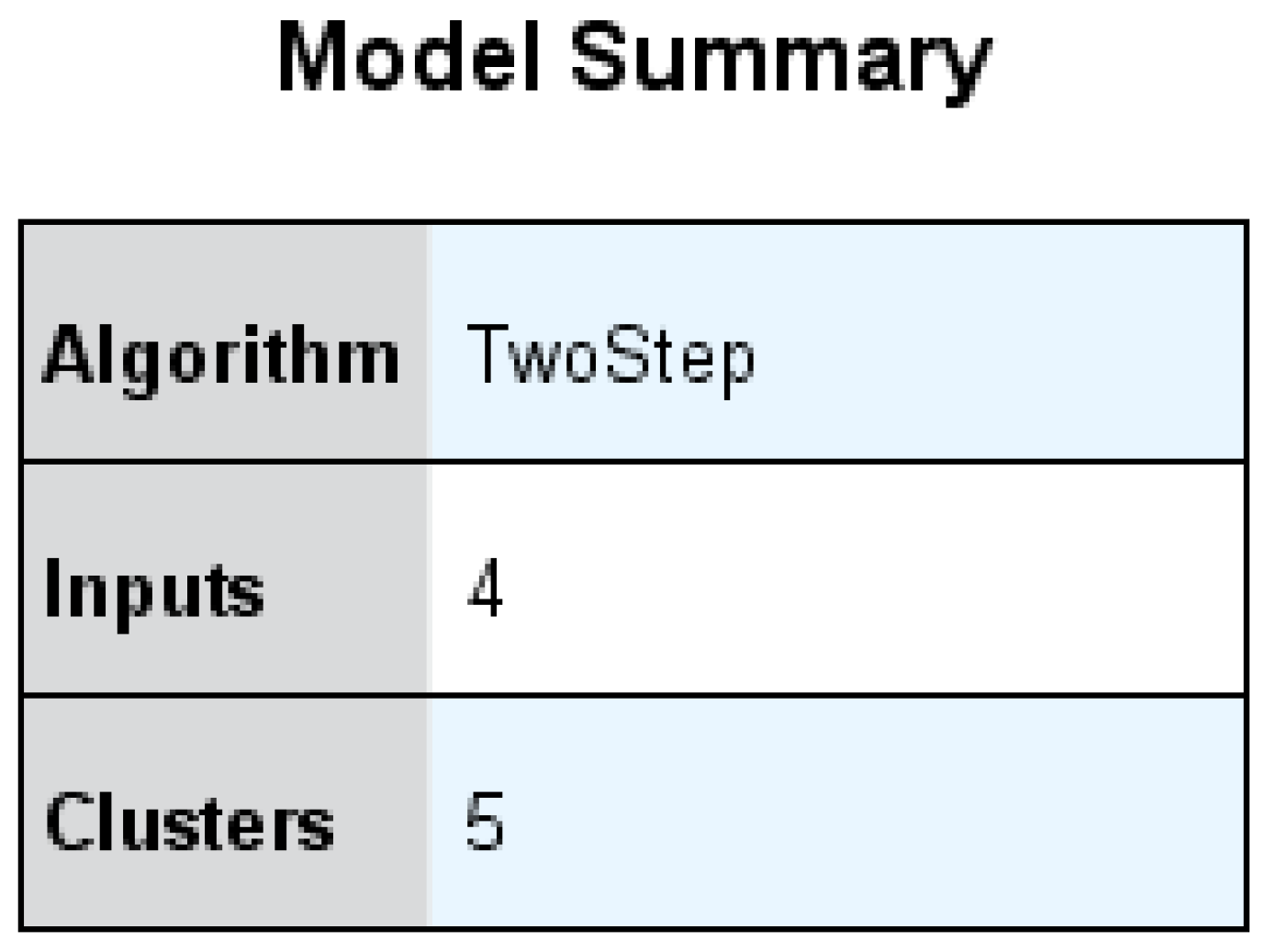
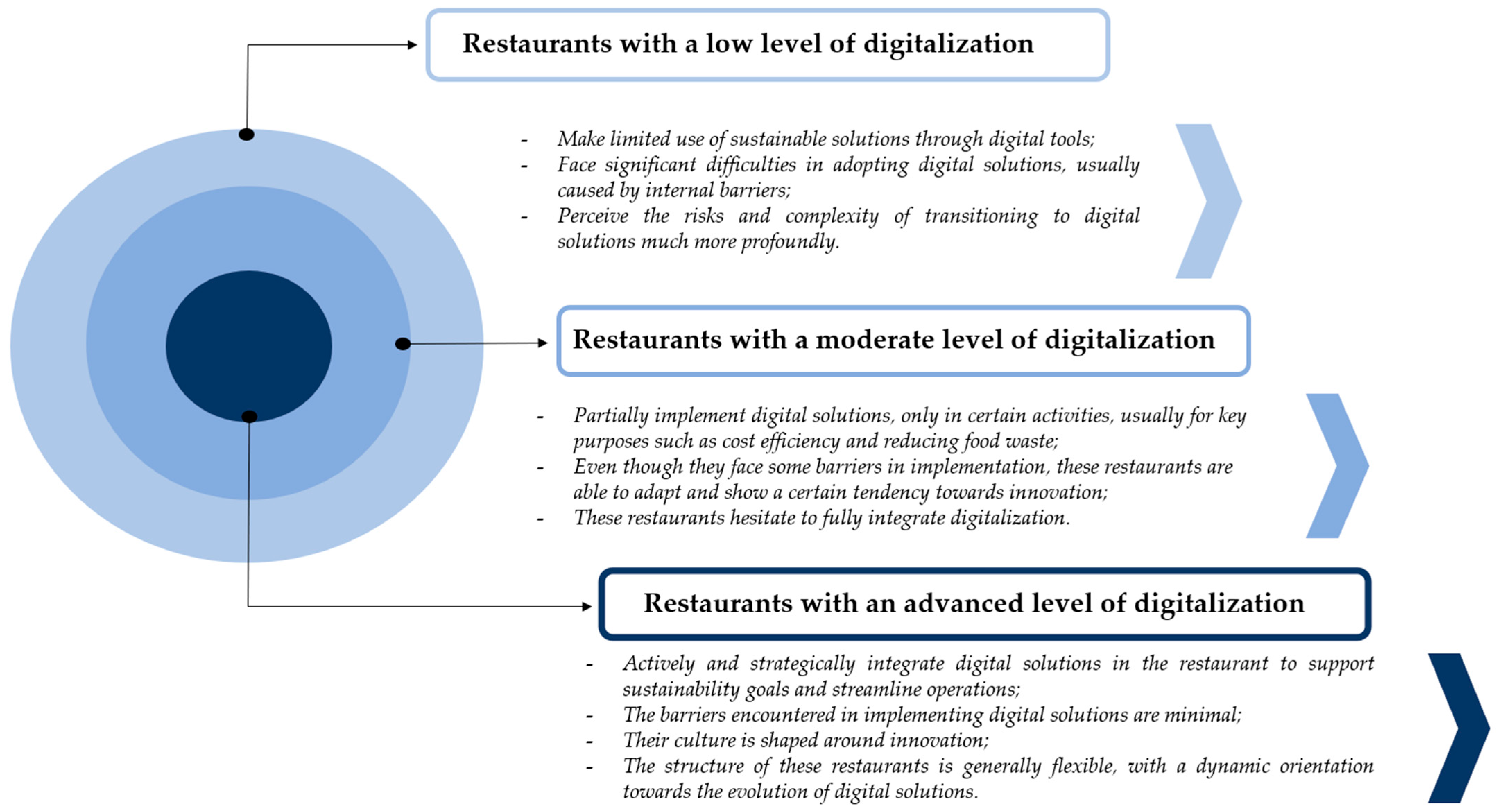
| Cluster | Type of Restaurant | Size of Restaurant | Industry Experience | Digitalization Level (Based on Sustainable Measures) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Cafe (100.0%) | 1–5 employees | 1–5 years (100.0%) | Mean =2.97 | Moderate level of digitalization |
| 2 | Premium Restaurant (100.0%) | 6–15 employees | Over 10 years | Mean =3.35 | Moderate level of digitalization |
| 3 | Fast-food (100.0%) | Over 15 employees | 6–10 years (100.0%) | Mean =3.26 | Moderate level of digitalization |
| 4 | Fast-food (100.0%) | 6–15 employees | 6–10 years (100.0%) | Mean =3.24 | Moderate level of digitalization |
| 5 | Casual Restaurant (100.0%) | 6–15 employees | 6–10 years (100.0%) | Mean = 3.12 | Moderate level of digitalization |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Grancea, A.; Neacșu, N.A.; Bălășescu, S.; Zamfirache, A. Sustainability of Supply Chains Through Digitalization: A Study on the Romanian Restaurant Industry. Sustainability 2025, 17, 10595. https://doi.org/10.3390/su172310595
Grancea A, Neacșu NA, Bălășescu S, Zamfirache A. Sustainability of Supply Chains Through Digitalization: A Study on the Romanian Restaurant Industry. Sustainability. 2025; 17(23):10595. https://doi.org/10.3390/su172310595
Chicago/Turabian StyleGrancea, Adrian, Nicoleta Andreea Neacșu, Simona Bălășescu, and Alexandra Zamfirache. 2025. "Sustainability of Supply Chains Through Digitalization: A Study on the Romanian Restaurant Industry" Sustainability 17, no. 23: 10595. https://doi.org/10.3390/su172310595
APA StyleGrancea, A., Neacșu, N. A., Bălășescu, S., & Zamfirache, A. (2025). Sustainability of Supply Chains Through Digitalization: A Study on the Romanian Restaurant Industry. Sustainability, 17(23), 10595. https://doi.org/10.3390/su172310595








