Effects of Salinity-Alkalinity and Degradation on Soil Phosphorus Fractions and Microbial Communities in the Songnen Plain, Northeast China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site and Soil Sampling
2.2. Soil Physicochemical Properties and P Fractionation Analysis
2.3. Soil Microbial Community Amplicon Sequencing
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Basic Soil Properties
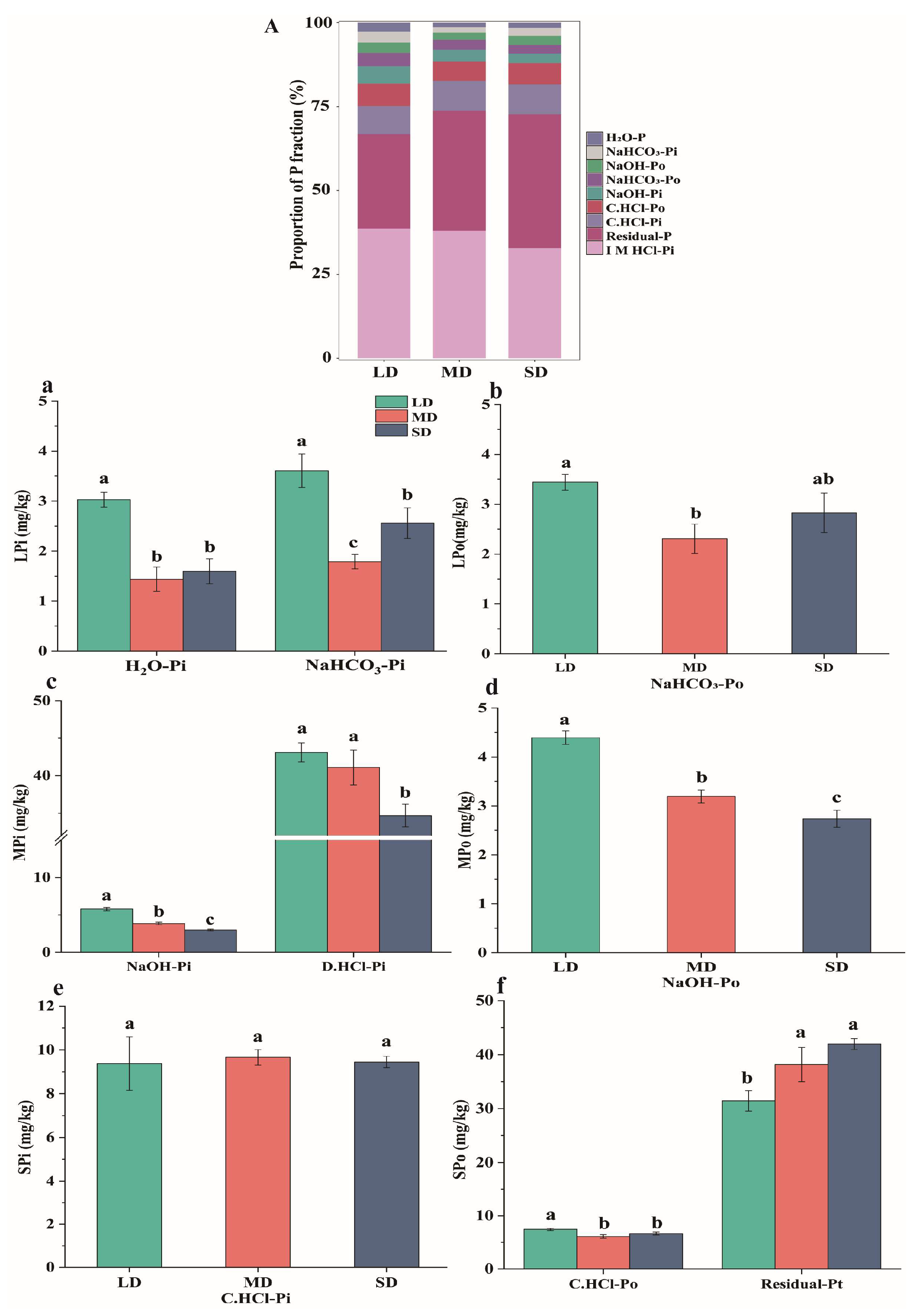
3.2. Characteristics of Soil P Fractions
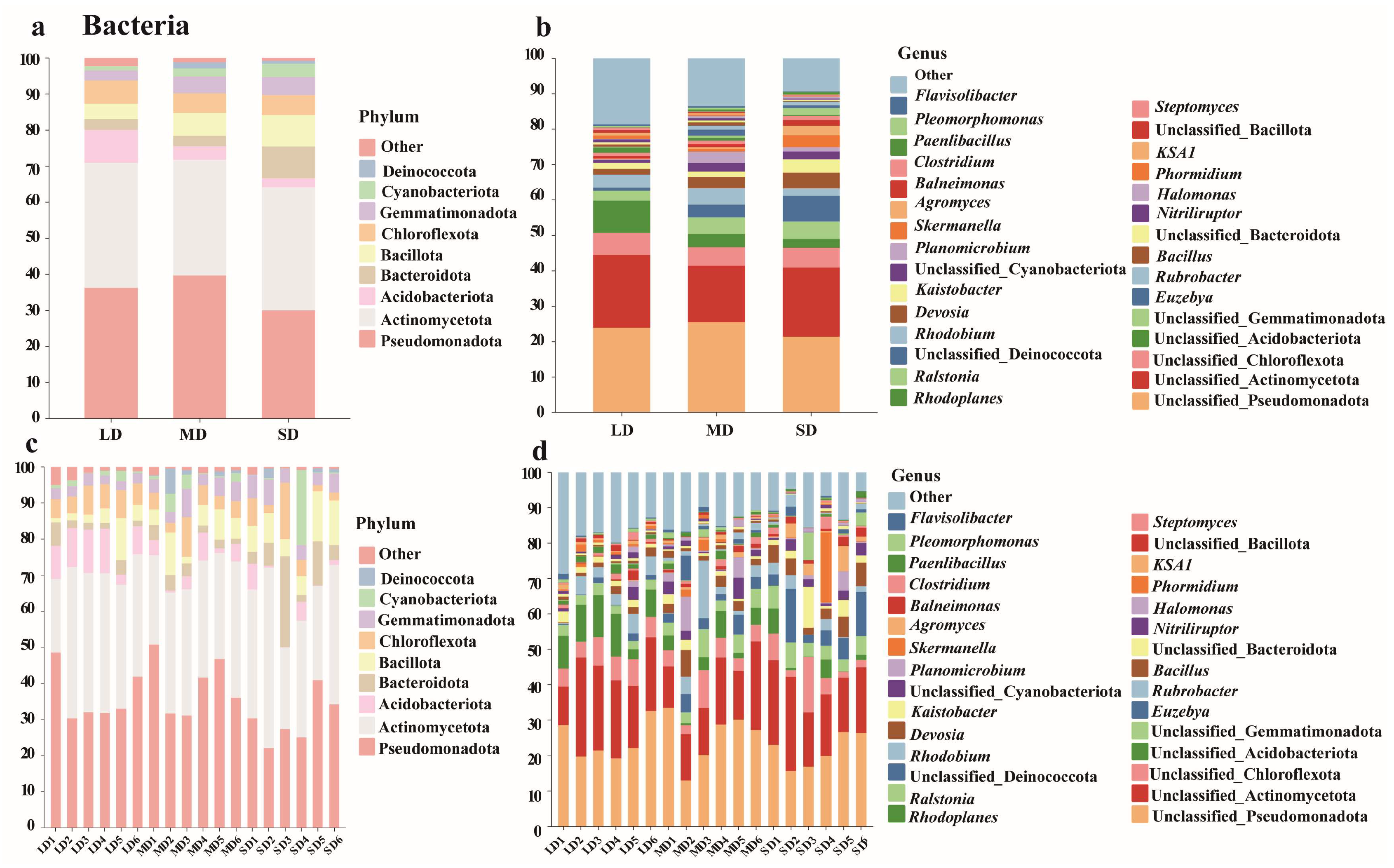
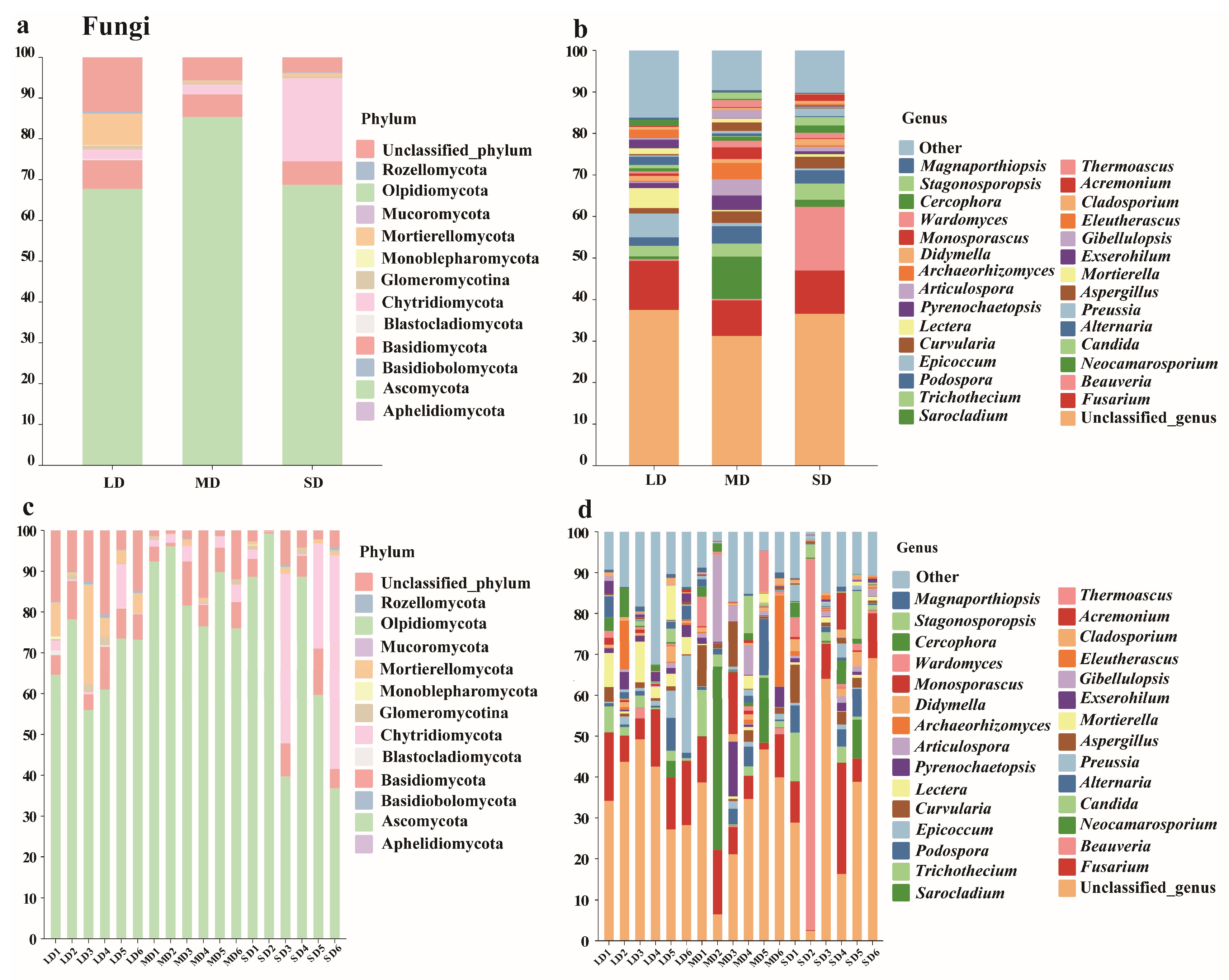
3.3. Microbial Community Composition
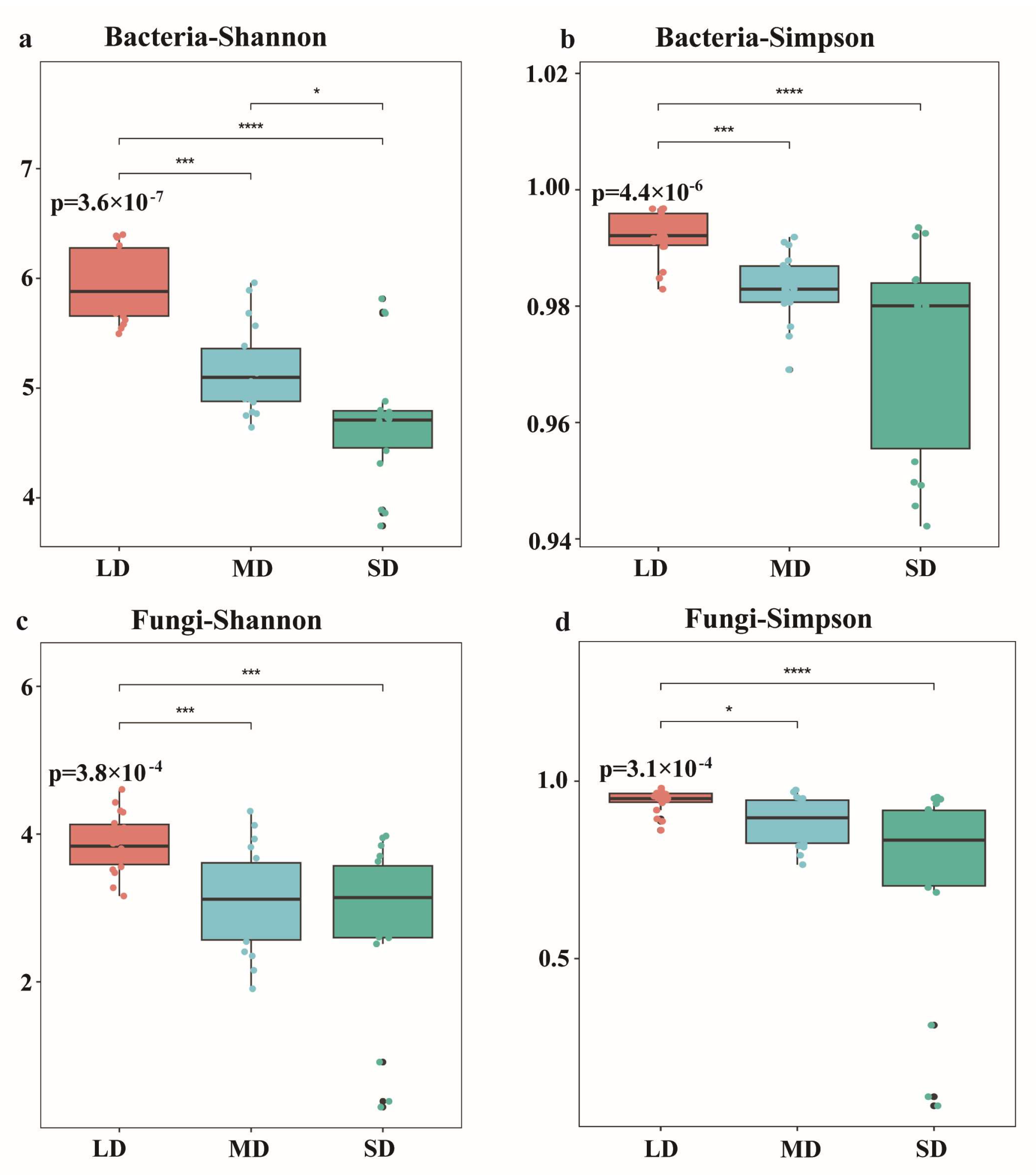
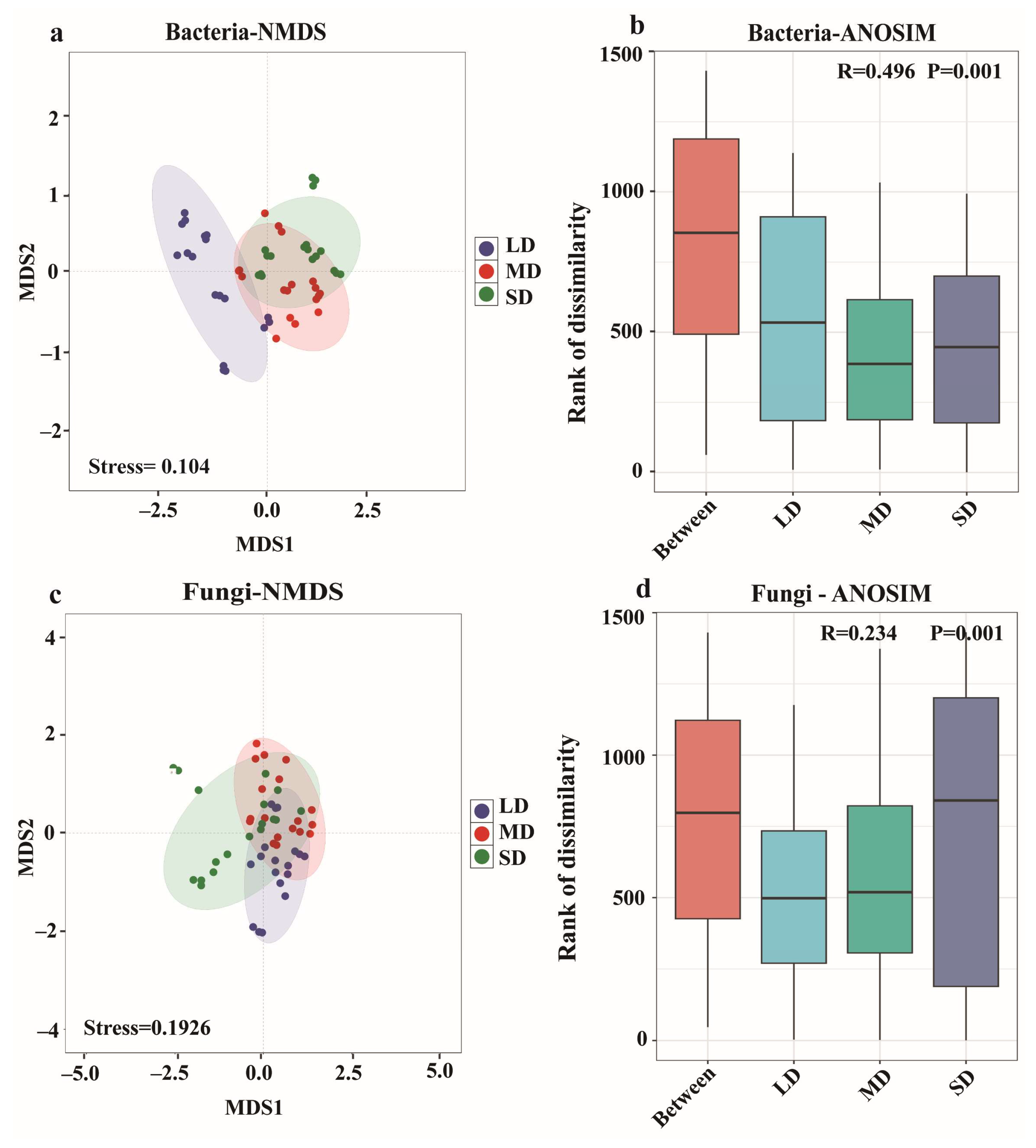
3.4. Alpha and Beta Diversity of Microbial Communities
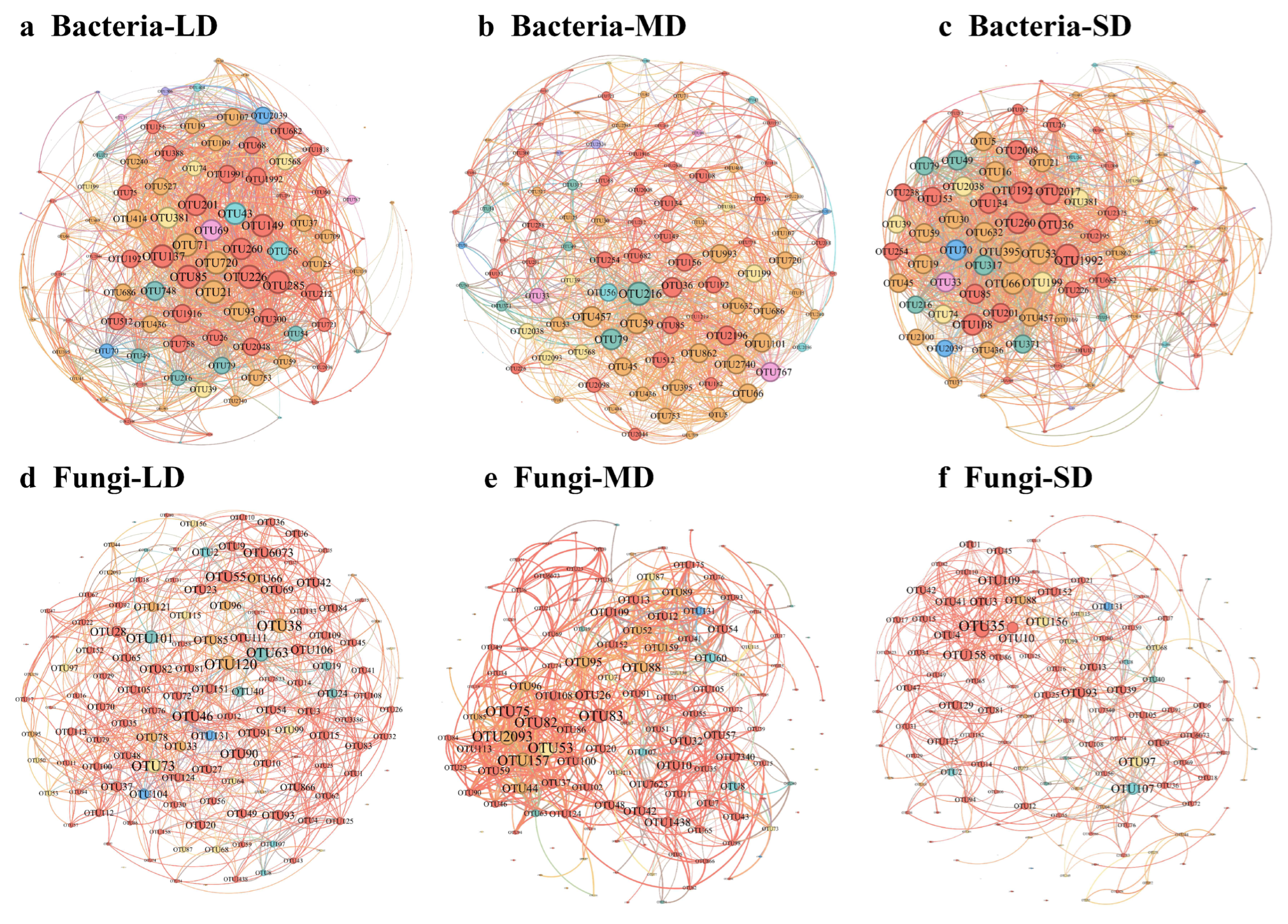
3.5. Co-Occurrence Network of Microbial Communities
3.6. Effects of Soil Physicochemical Properties and Microbial Communities on P Fractions
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of Saline-Alkaline Degradation on Soil Properties and P Availability
4.2. Effects of Saline-Alkaline Degradation on Microbial Communities
4.3. Microbial Community Driving P Dynamics in Saline-Alkaline Soils
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Sampling Site | Latitude (°) | Longitude (°) |
|---|---|---|
| Yujia | 45°25′33″ | 124°08′17″ |
| Qian’an | 45°19′46″ | 124°00′6″ |
| Dagangzi | 45°03′14″ | 123°56′56″ |
| San Tuanxiang | 44°34′57″ | 124°05′25″ |
| Chaganhua | 44°23′49″ | 123°43′20″ |
| Shuang Liao | 44°09′48″ | 123°54′44″ |
References
- Wang, J.; Ding, J.; Wang, Y.; Ge, X.; Lizaga, I.; Chen, X. Soil salinization in drylands: Measure, monitor, and manage. Ecol. Indic. 2025, 175, 113608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC. Climate Change 2023: Synthesis Report. Contribution of Working Groups I, II and III to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; IPCC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2003.
- Amin, A. Incubation time effect on releasing available phosphorus in saline sandy soil as a function of bone char application. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 29491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. Global Status of Salt-Affected Soils—Main Report; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2004. [CrossRef]
- Hassani, A.; Azapagic, A.; Shokri, N. Global predictions of primary soil salinization under changing climate in the 21st century. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 6663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.; Liu, Y.; Ferreira, J.F.; Wang, M.; Na, J.; Huang, J.; Liang, Z. Long-term combined effects of tillage and rice cultivation with phosphogypsum or farmyard manure on the concentration of salts, minerals, and heavy metals of saline-sodic paddy fields in Northeast China. Soil Tillage Res. 2022, 215, 105222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; An, F.; Ma, H.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, X.; Liu, Z. Variations on soil salinity and sodicity and its driving factors analysis under Microtopography in different hydrological conditions. Water 2016, 8, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costantini, E.; Branquinho, C.; Nunes, A.; Schwilch, G.; Stavi, I.; Valdecantos, A.; Zucca, C. Soil indicators to assess the effectiveness of restoration strategies in dryland ecosystems. Solid Earth 2016, 7, 397–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, G.; Banerjee, P.; Sharma, R.K.; Maity, J.P.; Etesami, H.; Shaw, A.K.; Huang, Y.; Huang, H.; Chen, C. Management of Phosphorus in Salinity-Stressed Agriculture for Sustainable Crop Production by Salt-Tolerant Phosphate-Solubilizing Bacteria—A Review. Agronomy 2021, 11, 1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiessen, H.; Moir, J.O. Characterization of Available P by Sequential Extraction. In Soil Sampling and Methods of Analysis; Canadian Society of Soil Science: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Maharjan, M.; Maranguit, D.; Kuzyakov, Y. Phosphorus fractions in subtropical soils depending on land use. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2018, 87, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niederberger, J.; Kohler, M.; Bauhus, J. Distribution of phosphorus fractions with different plant availability in German forest soils and their relationship with common soil properties and foliar P contents. Soil 2019, 5, 189–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Gao, J.; Yu, X.; Borjigin, Q.; Qu, J.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, S.; Li, Q.; Guo, J.; Li, D. Evaluation of the microbial community in various saline alkaline-soils driven by soil factors of the Hetao Plain, Inner Mongolia. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 28931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Huang, Y.; Zhou, D. Phosphorus fractions affect fungal compositions and functions under land use conversions in saline-alkali soil in northeastern China. Chem. Biol. Technol. Agric. 2024, 11, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallam, S.; Putnam, N.; Preston, C.; Detter, J.; Rokhsar, D.; Richardson, P.; DeLong, E. Reverse methanogenesis: Testing the hypothesis with environmental genomics. Science 2004, 305, 1457–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergkemper, F.; Schöler, A.; Engel, M.; Lang, F.; Krüger, J.; Schloter, M.; Schulz, S. Phosphorus Depletion in Forest Soils Shapes Bacterial Communities Towards Phosphorus Recycling Systems. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 8, 2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Z.; Liu, G.; Chen, H.; Chen, C.; Wang, J.; Ai, S.; Wei, D.; Li, D.; Ma, B.; Brookes, P. Long-Term Nutrient Inputs Shift Soil Microbial Functional Profiles of Phosphorus Cycling in Diverse Agroecosystems. ISME J. 2020, 14, 757–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, K.; Singh, B.; Singh, R. Effect of land rehabilitation on physicochemical and microbial properties of a sodic soil. Catena 2013, 109, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Jilani, G.; Akhtar, M.; Naqvi, S.; Rasheed, M. Phosphorus solubilizing bacteria: Occurrence, mechanisms and their role in crop production. J. Agric. Biol. Sci. 2009, 1, 48–58. [Google Scholar]
- Lozupone, C.; Knight, R. Global patterns in bacterial diversity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 11436–11440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, W.; Ni, Y.; Gao, N.; Bian, B.; Zheng, S.; Lin, X.; Chu, H. Bacterial community composition is shaped by soil secondary salinization and acidification brought on by high nitrogen fertilization rates. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2016, 108, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Sun, L.; Ling, N.; Zhu, C.; Chi, F.; Li, W.; Hao, X.; Zhang, W.; Bian, J.; Chen, L.; et al. Exploring soil factors determining composition and structure of the bacterial communities in saline-alkali soils of Songnen Plain. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 2902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zhang, S.; Li, Y.; Bu, K.; Zhang, Y.; Chang, L.; Zhang, Y. Dynamics of saline-alkali land and its ecological regionalization in western Songnen plain, China. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2010, 20, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Wang, Z.; Mao, D.; Jia, M.; Chang, S.; Li, X. Spatiotemporal variations of soil salinization in China’s West Songnen Plain. Land Degrad. Dev. 2023, 34, 2366–2378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Yu, P.; Chen, X.; Zhou, D.; Zheng, W. Facilitative and inhibitory effect of litter on seedling emergence and early growth of six herbaceous species in an early successional old field ecosystem. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 101860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Wu, J.; Cheng, M.; Xia, X. Global transfer of salinization on irrigated land: Complex network and endogenous structure. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 336, 117592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, N.; Shao, T.; Zhu, T.; Long, X.; Gao, X.; Liu, Z.; Shao, H.; Rengel, Z. Vegetation succession influences soil carbon sequestration in coastal alkali-saline soils in southeast China. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 9728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazhar, S.; Pellegrini, E.; Contin, M.; Bravo, C.; De Nobili, M. Impacts of salinization caused by sea level rise on the biological processes of coastal soils-a review. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 909415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Wang, X.; Zhou, J.; Zhou, W.; Zhou, S. Construction of Phosphate-Solubilizing Microbial Consortium and Its Effect on the Remediation of Saline-Alkali Soil. Microb. Ecol. 2025, 88, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornish, P. Research directions: Improving plant uptake of soil phosphorus, and reducing dependency on input of phosphorus fertiliser. Crop Pasture Sci. 2009, 60, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemkemeyer, M.; Schwalb, S.; Heinze, S.; Joergensen, R.; Wichern, F. Functions of elements in soil microorganisms. Microbiol. Res. 2021, 252, 126832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K. Microbial and Enzyme Activities of Saline and Sodic Soils. Land Degrad. Dev. 2016, 27, 706–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; van der Heijden, M.; Banerjee, S.; Liu, J.; Gu, H.; Zhou, N.; Yin, C.; Peng, B.; Liu, X.; Wang, B.; et al. The role of halophyte-induced saline fertile islands in soil microbial biogeochemical cycling across arid ecosystems. Commun. Biol. 2024, 7, 1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varshney, S.; Bhattacharya, A.; Gupta, A. Halo-alkaliphilic microbes as an effective tool for heavy metal pollution abatement and resource recovery: Challenges and future prospects. 3 Biotech 2023, 13, 400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokashe, N.; Chaudhari, B.; Patil, U. Operative utility of salt-stable proteases of halophilic and halotolerant bacteria in the biotechnology sector. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 117, 493–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Ruan, Y.; Chao, X.; Zhang, J.; Li, R.; Shen, Q. Rhizosphere microbial community manipulated by 2 years of consecutive biofertilizer application associated with banana Fusarium wilt disease suppression. Biol. Fertil. Soils. 2015, 51, 553–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, W.; Jiang, L.; Li, E.; Yang, X.; Yang, J. Salinity affects microbial function genes related to nutrient cycling in arid regions. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1407760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Pan, X.; Yu, W.; Ye, X.; Erdenebileg, E.; Wang, C.; Ma, L.; Wang, R.; Huang, Z.; Indree, T.; et al. Aridity and decreasing soil heterogeneity reduce microbial network complexity and stability in the semi-arid grasslands. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 151, 110342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manici, L.; Caputo, F.; De Sabata, D.; Fornasier, F. The enzyme patterns of Ascomycota and Basidiomycota fungi reveal their different functions in soil. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2024, 196, 105323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragot, S.; Kertesz, M.; Bünemann, E. phoD Alkaline Phosphatase Gene Diversity in Soil. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 81, 72819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Chen, S.; Chen, L.; Wang, D. Responses of soil microbial communities and their network interactions to saline-alkaline stress in cd-contaminated soils. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 252, 1609–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, D.; Wang, J.; Chen, K.; Lan, W.; Ye, Y.; Ma, X.; Lin, K. Responses of Soil Phosphorus Cycling-Related Microbial Genes to Thinning Intensity in Cunninghamia lanceolata Plantations. Forests 2024, 15, 440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, B.; Stegen, J.; Kim, M.; Dong, K.; Adams, J.; Lee, Y. Soil pH mediates the balance between stochastic and deterministic assembly of bacteria. ISME J. 2018, 12, 1072–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Sun, J. Soil Salinity Drives the Distribution Patterns and Ecological Functions of Fungi in Saline-Alkali Land in the Yellow River Delta, China. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 594284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pradhan, A.; Pahari, A.; Mohapatra, S.; Mishra, B. Phosphate-Solubilizing Microorganisms in Sustainable Agriculture: Genetic Mechanism and Application. In Advances in Soil Microbiology: Recent Trends and Future Prospects; Springer: Singapore, 2017; pp. 81–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rietz, D.; Haynes, R. Effects of irrigation-induced salinity and sodicity on soil microbial activity. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2003, 35, 845–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Cui, Z.; Cao, C. Effects of Secondary Salinization on Soil Phosphorus Fractions and Microbial Communities Related to Phosphorus Transformation in a Meadow Grassland, Northeast China. Agronomy 2025, 15, 960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, A.; Simpson, R. Soil microorganisms mediating phosphorus availability update on microbial phosphorus. Plant Physiol. 2011, 156, 989–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, S.; Singh, R.; Sharma, P. Response of Major Plant Nutrients to Salt Affected Environment. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. App. Sci. 2019, 8, 2188–2203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Yuan, L.; Zhang, J.; Li, H.; Bai, Z.; Chen, X.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, F. Phosphorus dynamics: From soil to plant. Plant Physiol. 2011, 156, 997–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Soil Type | pH | EC | SOC | TP | AP | TN | AN | AK mg/kg | C/N |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| µS/cm | g/kg | mg/kg | mg/kg | g/kg | mg/kg | ||||
| LD | 9.43 ± 0.12 b | 208.06 ± 25.72 c | 9.31 ± 0.90 a | 111.40 ± 8.53 a | 6.32 ± 0.16 a | 2.04 ± 0.10 a | 43.83 ± 6.02 | 151.23 ± 9.63 a | 4.58 ± 0.39 a |
| MD | 10.43 ± 0.35 a | 1004.67 ± 126.53 b | 7.26 ± 0.92 ab | 108.30 ± 26.65 a | 4.52 ± 0.60 b | 1.59 ± 0.12 b | 38.44 ± 9.88 b | 142.68 ± 9.47 a | 4.67 ± 0.50 a |
| SD | 10.50 ± 0.09 a | 1930.67 ± 255.52 a | 6.64 ± 0.54 b | 105.80 ± 8.46 a | 4.90 ± 0.75 b | 1.52 ± 0.11 b | 69.03 ± 9.16 a | 115.69 ± 6.29 b | 4.58 ± 0.39 a |
| Parameter | Bacterial | Fungi | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LD | MD | SD | LD | MD | SD | |
| Edges | 1561 | 1247 | 1474 | 999 | 890 | 668 |
| Average degree | 28.13 | 22.88 | 26.80 | 14.37 | 12.81 | 9.61 |
| Network density | 0.26 | 0.21 | 0.25 | 0.10 | 0.09 | 0.07 |
| Modularity | 0.58 | 1.46 | 0.48 | 1.31 | 0.77 | 0.81 |
| Clustering coefficient | 0.70 | 0.60 | 0.67 | 0.52 | 0.64 | 0.65 |
| Average path length | 1.91 | 2.11 | 2.08 | 2.47 | 2.84 | 3.51 |
| Positive correlation | 71.04 | 62.79 | 76.32 | 70.67 | 83.37 | 88.17 |
| Negative correlation | 28.96 | 37.21 | 23.68 | 29.33 | 16.63 | 11.83 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tian, Z.; Jia, X.; Chang, J.; Tian, L.; Ji, L.; Chang, C. Effects of Salinity-Alkalinity and Degradation on Soil Phosphorus Fractions and Microbial Communities in the Songnen Plain, Northeast China. Sustainability 2025, 17, 10527. https://doi.org/10.3390/su172310527
Tian Z, Jia X, Chang J, Tian L, Ji L, Chang C. Effects of Salinity-Alkalinity and Degradation on Soil Phosphorus Fractions and Microbial Communities in the Songnen Plain, Northeast China. Sustainability. 2025; 17(23):10527. https://doi.org/10.3390/su172310527
Chicago/Turabian StyleTian, Zhijie, Xueying Jia, Jingjing Chang, Lei Tian, Li Ji, and Chunling Chang. 2025. "Effects of Salinity-Alkalinity and Degradation on Soil Phosphorus Fractions and Microbial Communities in the Songnen Plain, Northeast China" Sustainability 17, no. 23: 10527. https://doi.org/10.3390/su172310527
APA StyleTian, Z., Jia, X., Chang, J., Tian, L., Ji, L., & Chang, C. (2025). Effects of Salinity-Alkalinity and Degradation on Soil Phosphorus Fractions and Microbial Communities in the Songnen Plain, Northeast China. Sustainability, 17(23), 10527. https://doi.org/10.3390/su172310527





