A Deep Learning-Based Method for Inrush Current Identification in Modern Sustainable Power Systems
Abstract
1. Introduction
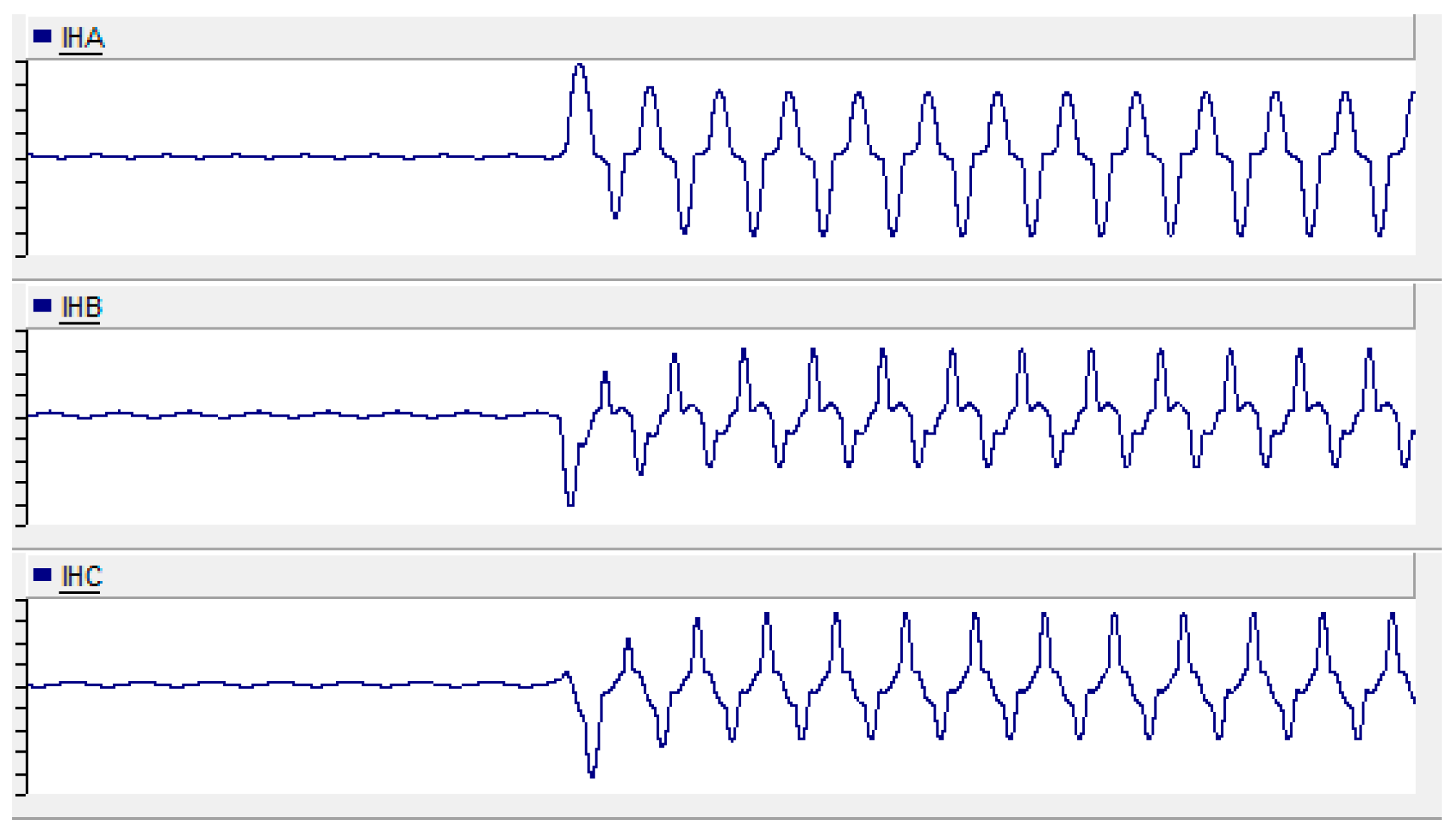
2. Classification and Generation Mechanisms of Magnetizing Inrush Current
2.1. Classification of Magnetizing Inrush Current
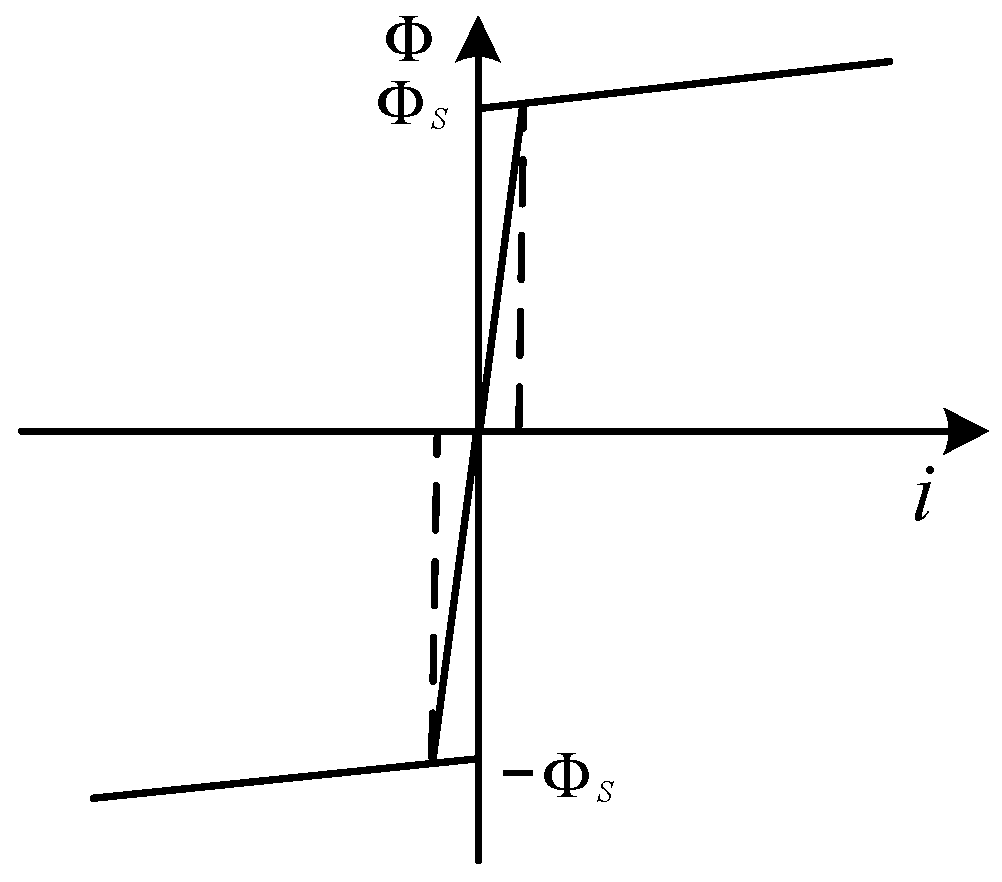
2.2. Generation Mechanisms of Magnetizing Inrush Current
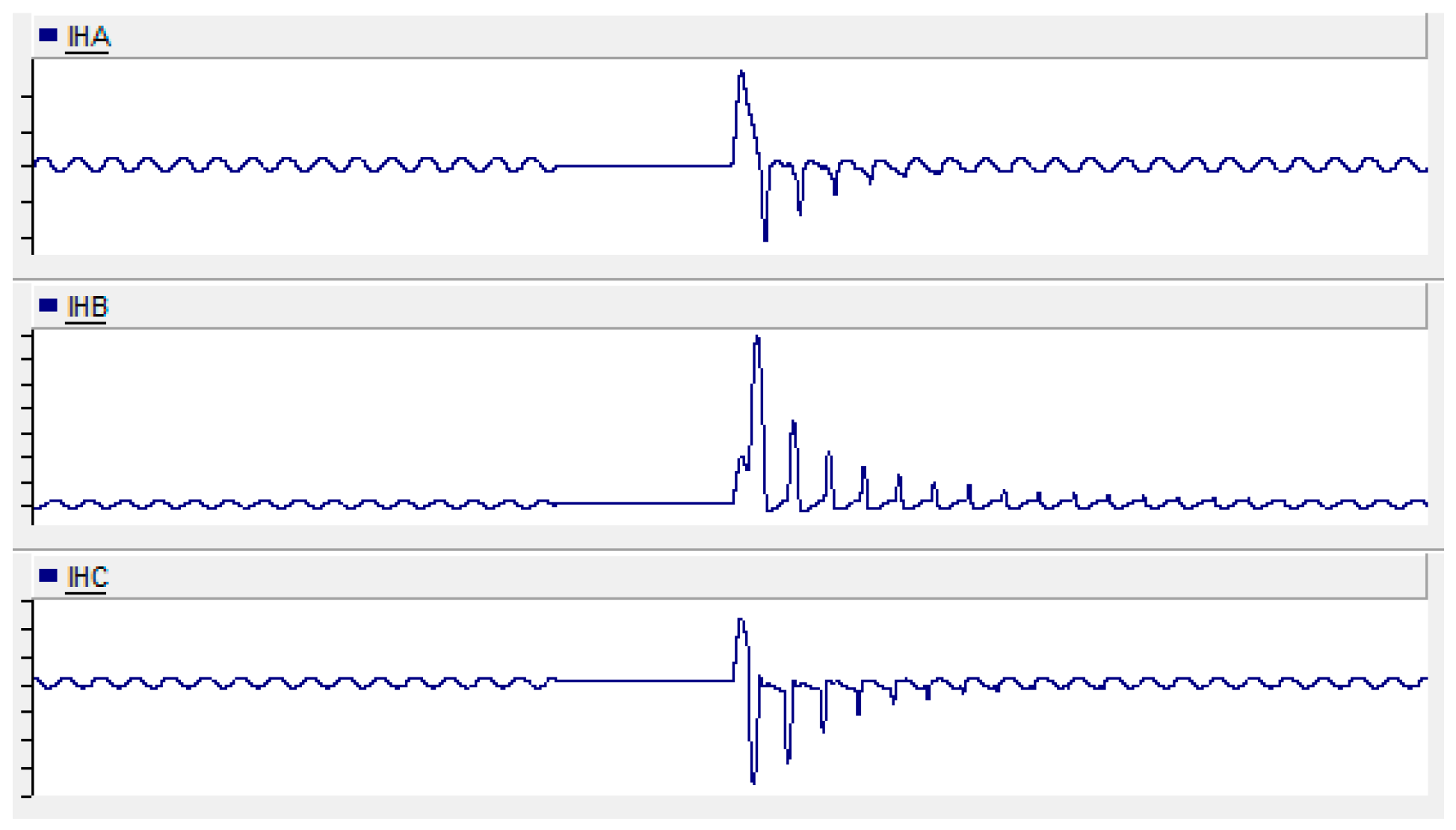
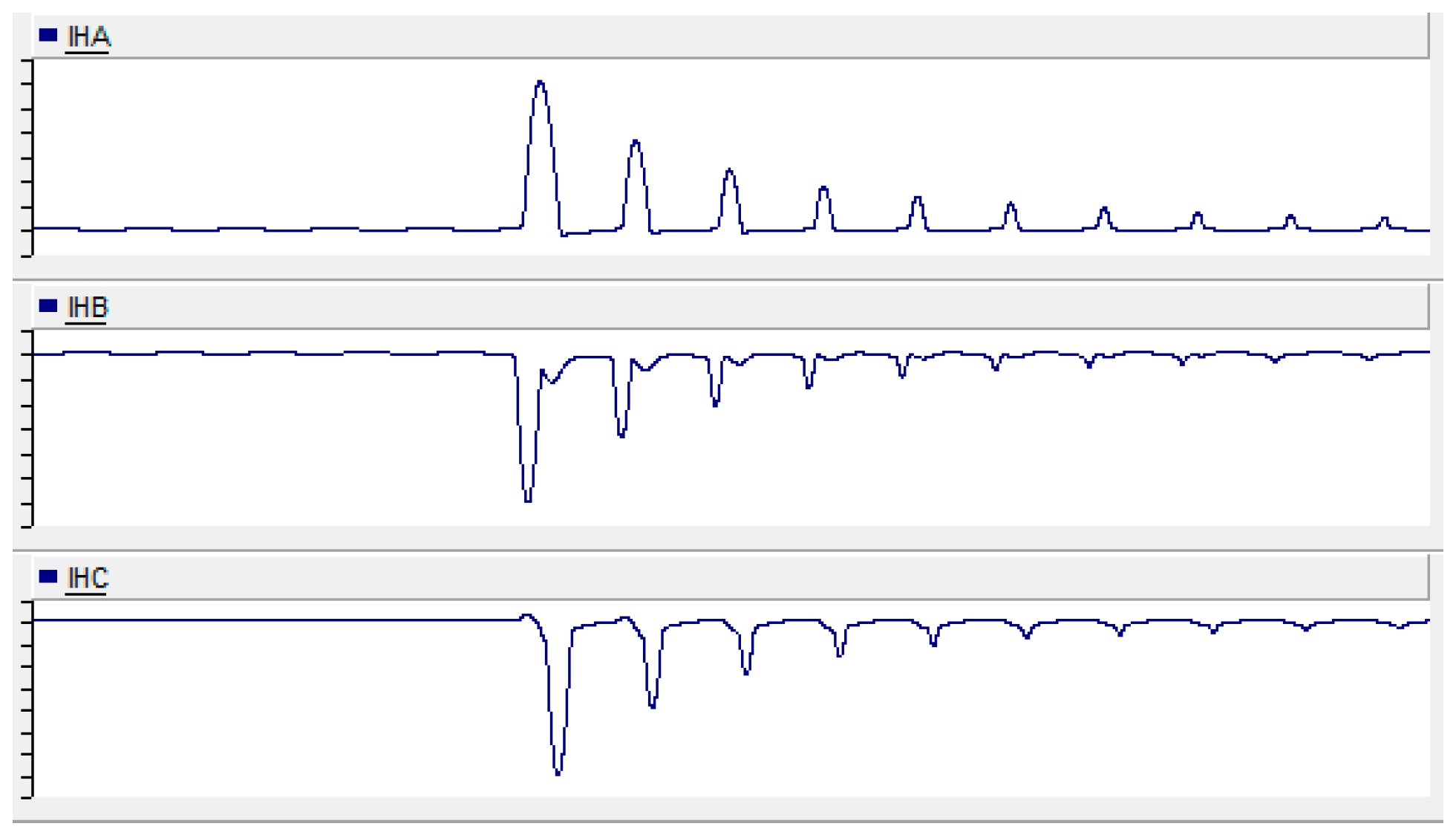
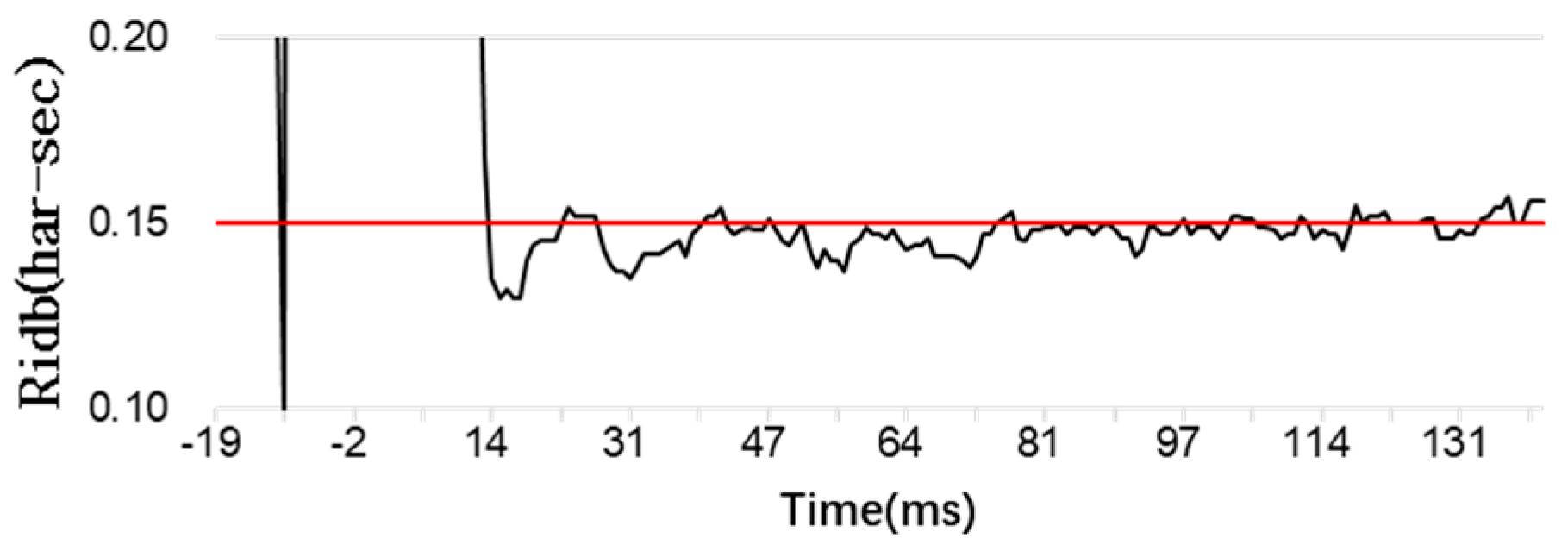
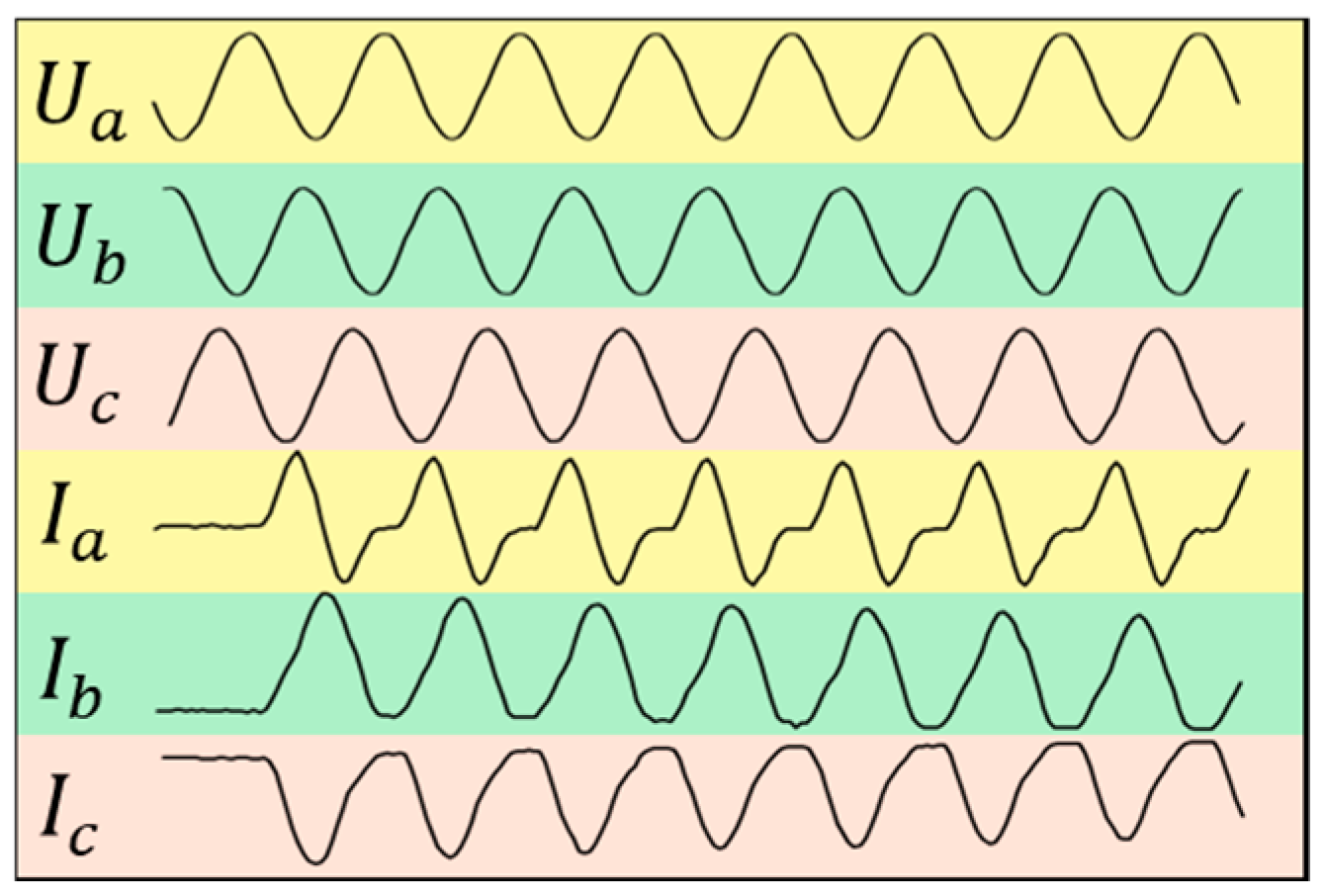
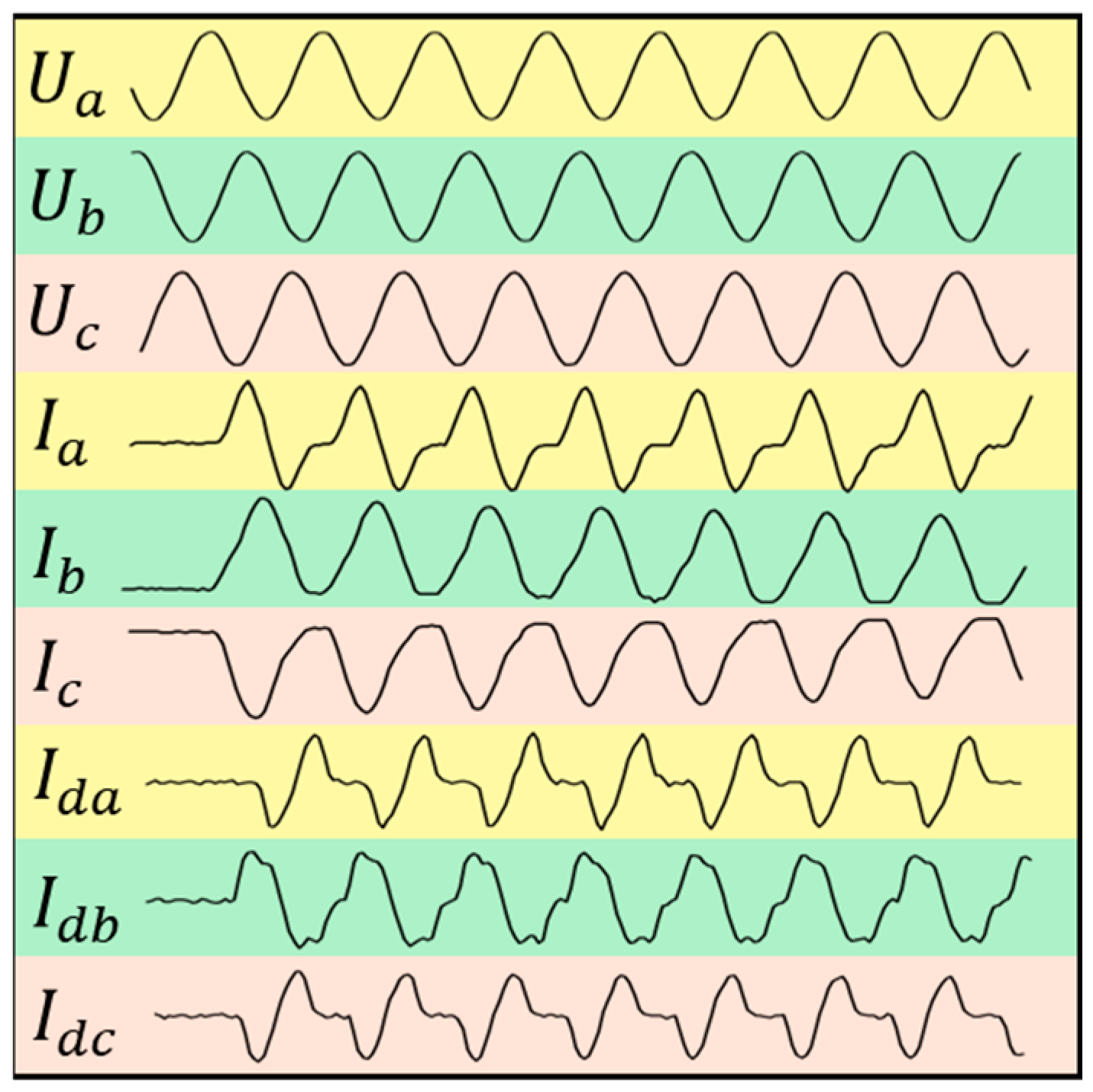
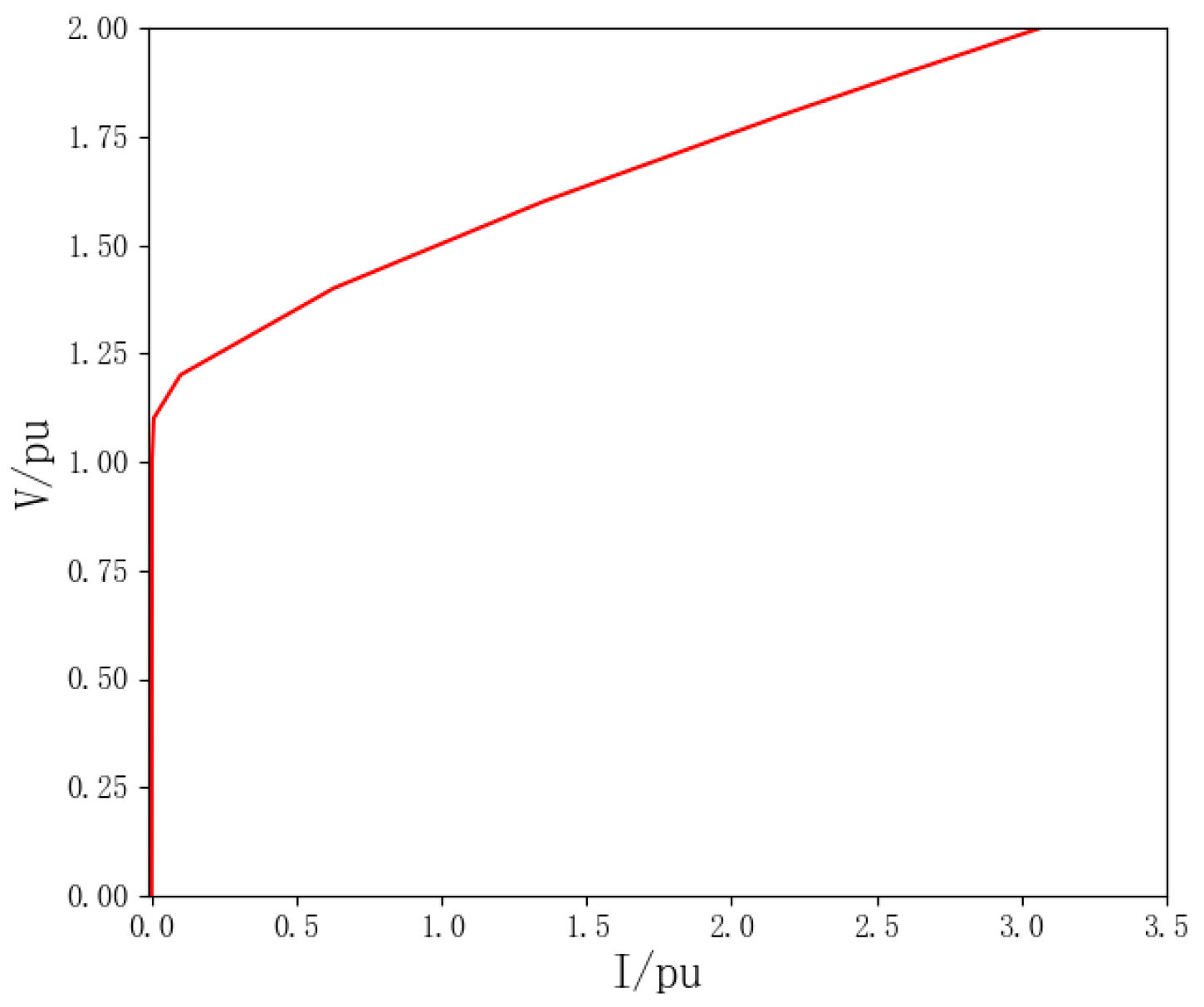
2.3. Harmonic Characteristics of Transformer Magnetizing Inrush Current
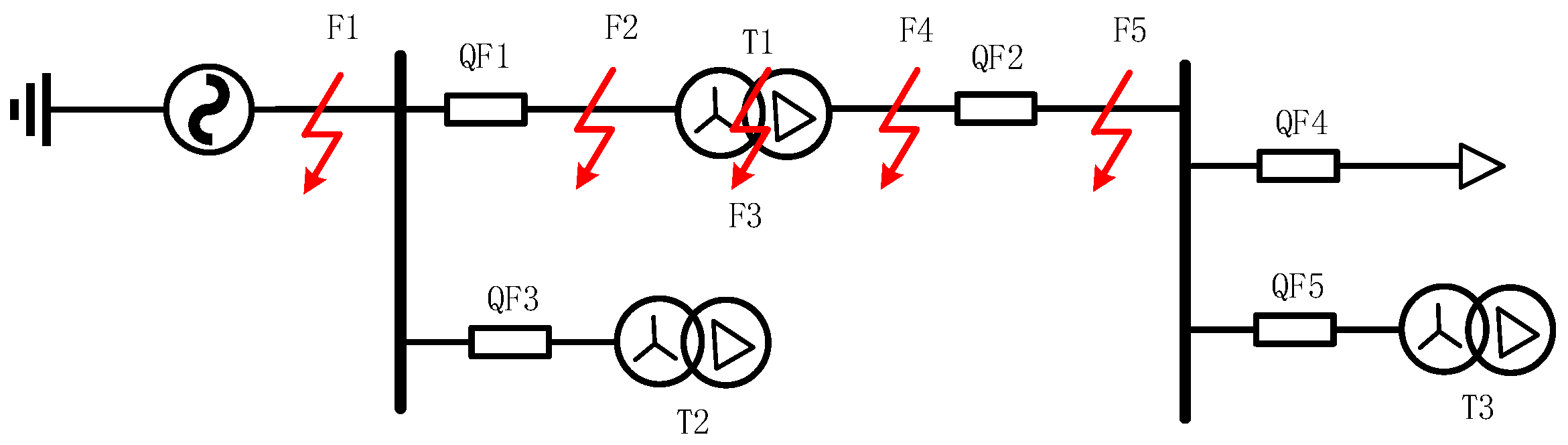
3. Data Curation Strategy
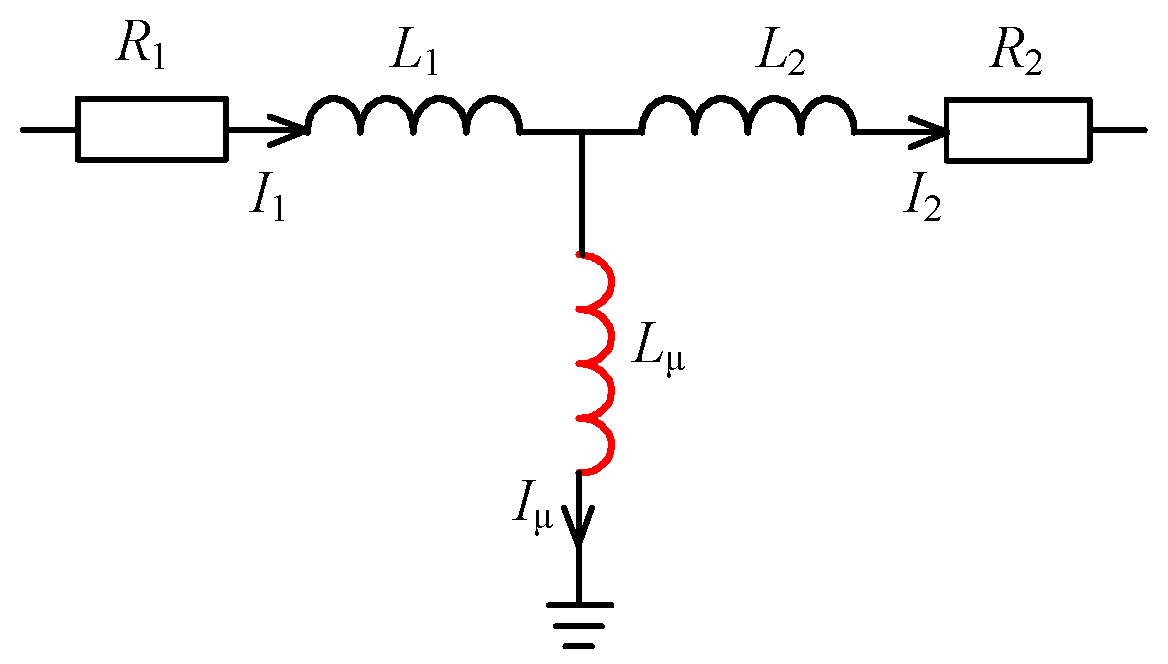
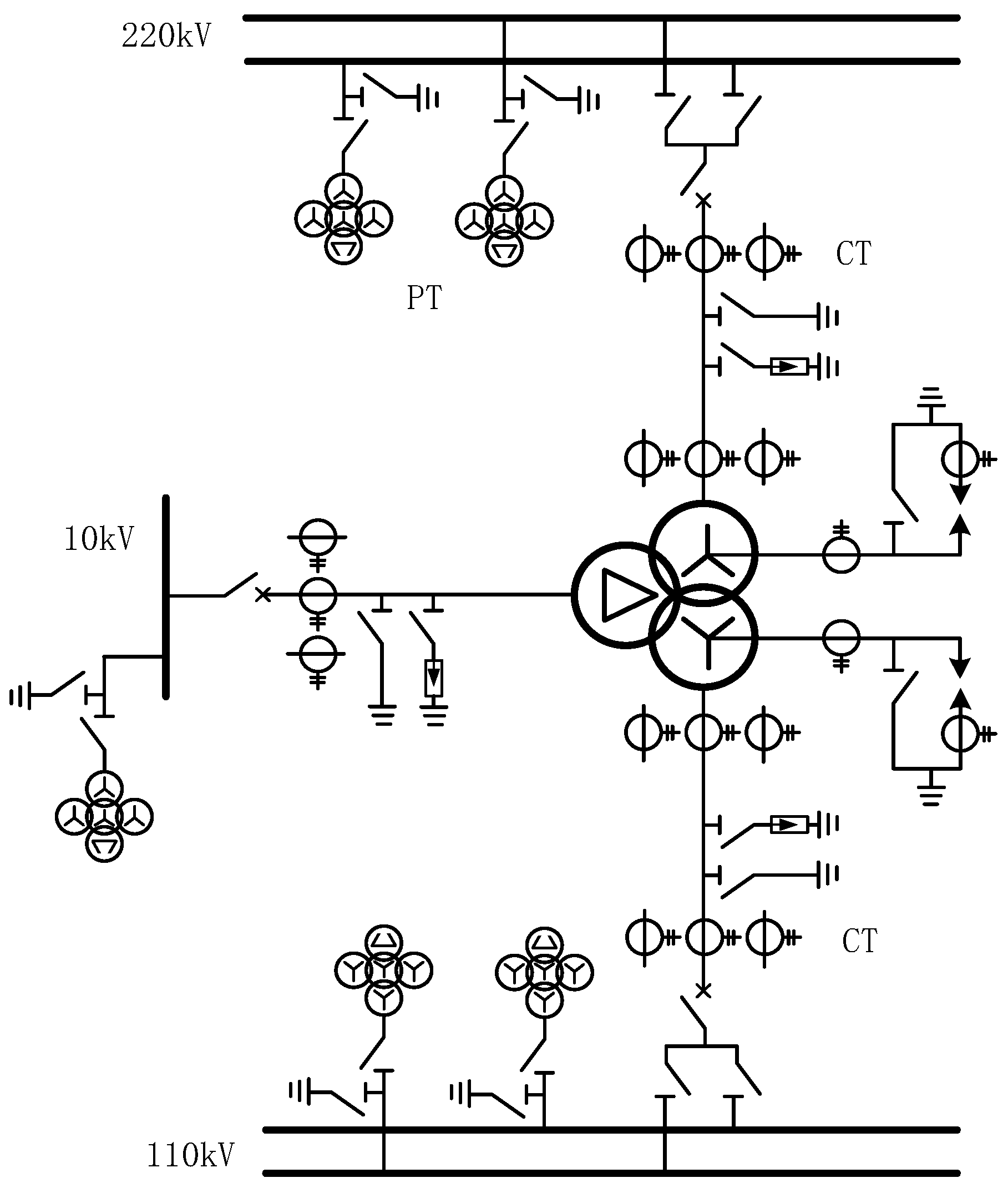
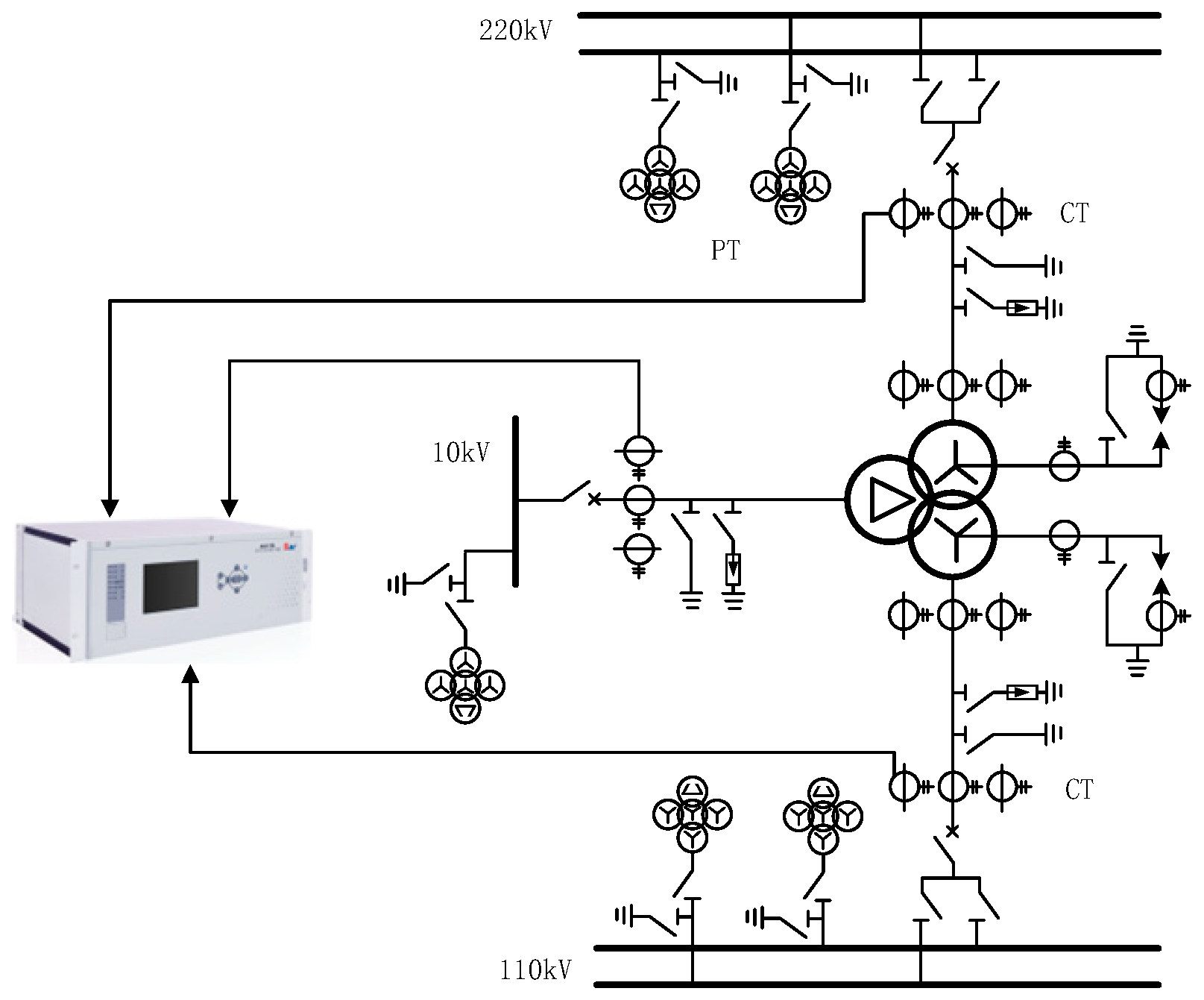
3.1. Instrument Transformer Configuration
3.2. Design of Data Scheme
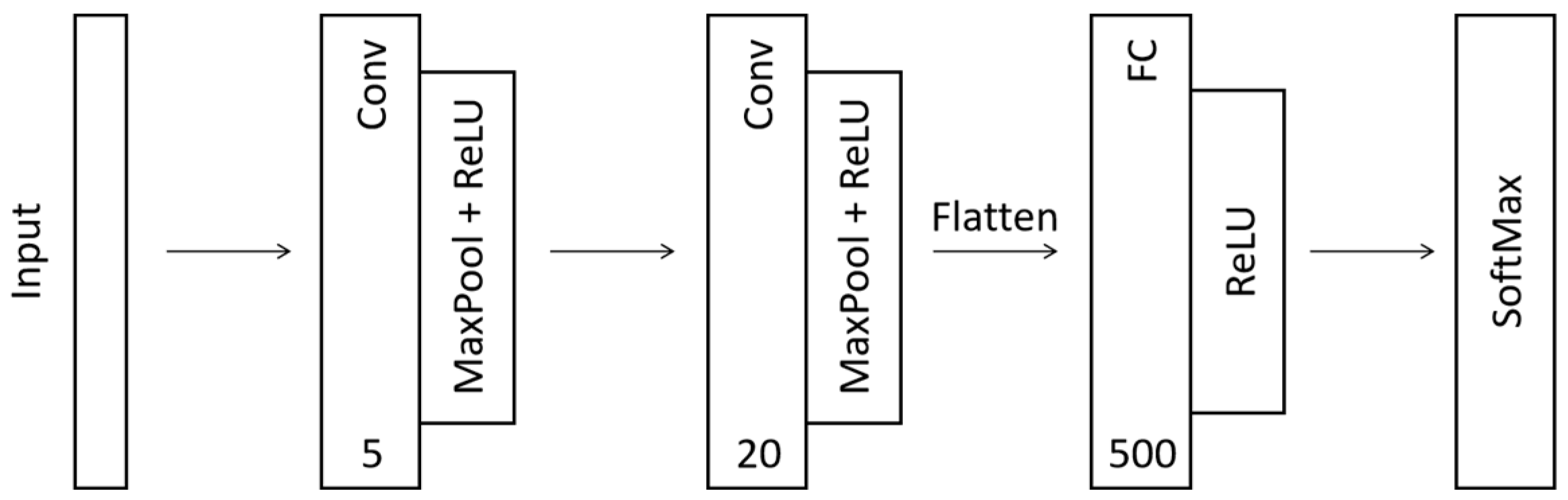
4. Design of Identification Model
5. Experimental Validation of the Proposed Methodology
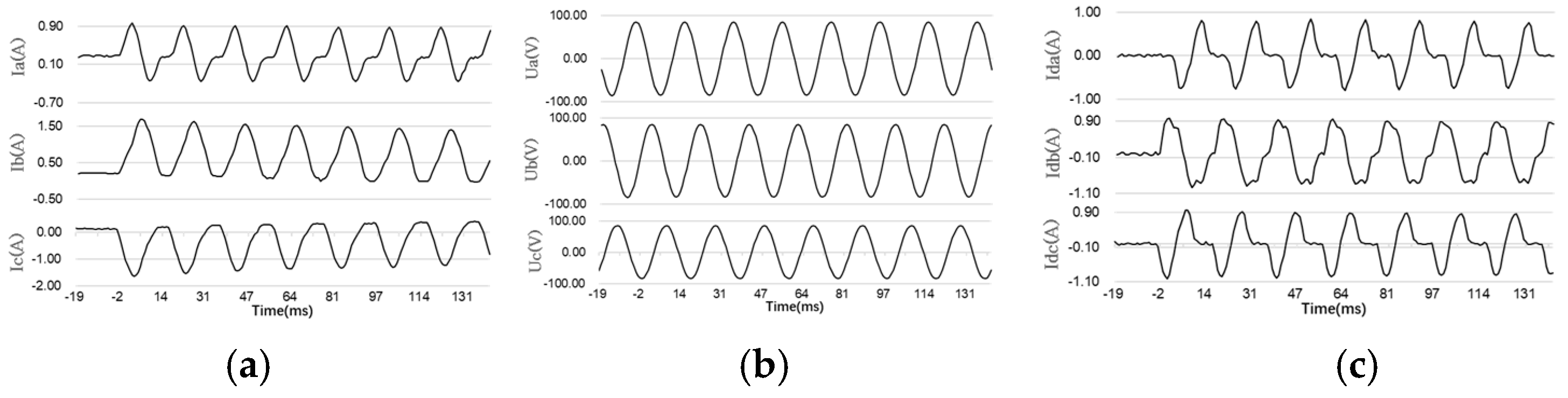
5.1. Dataset Generation
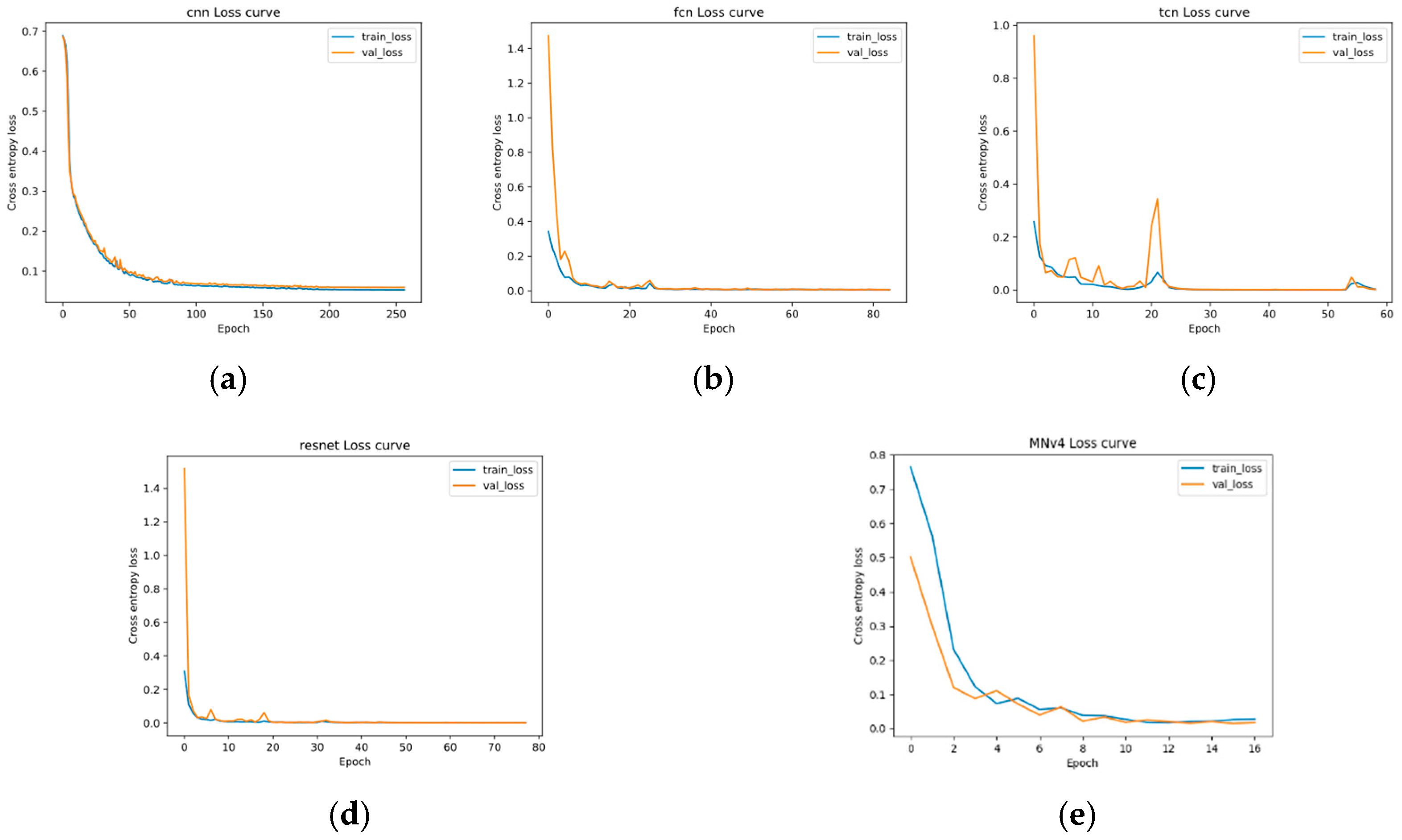
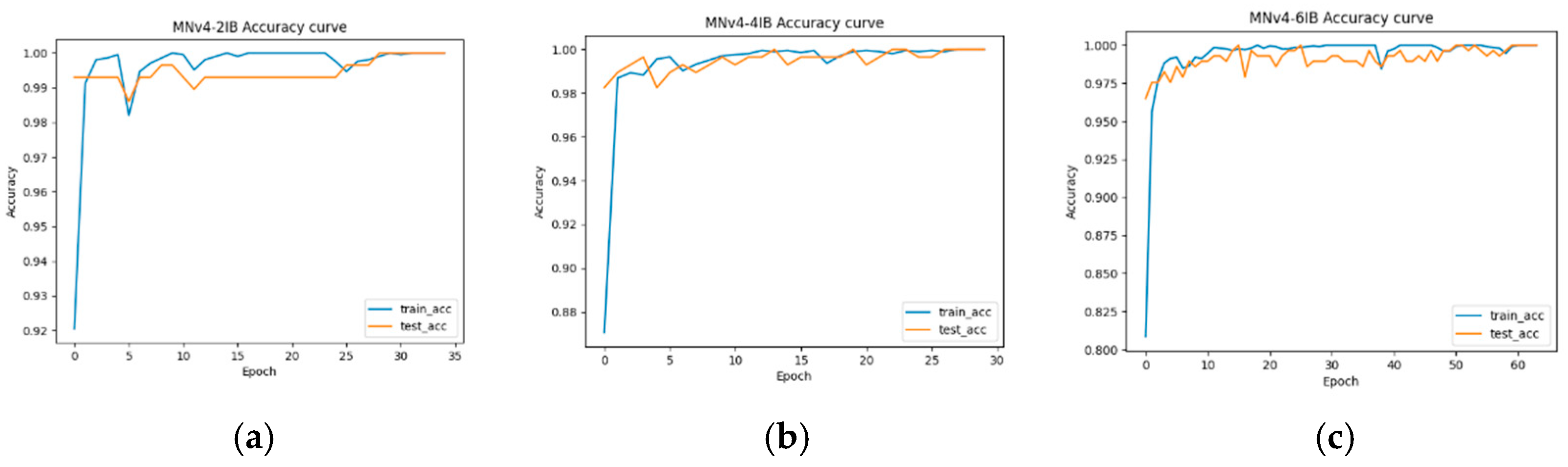
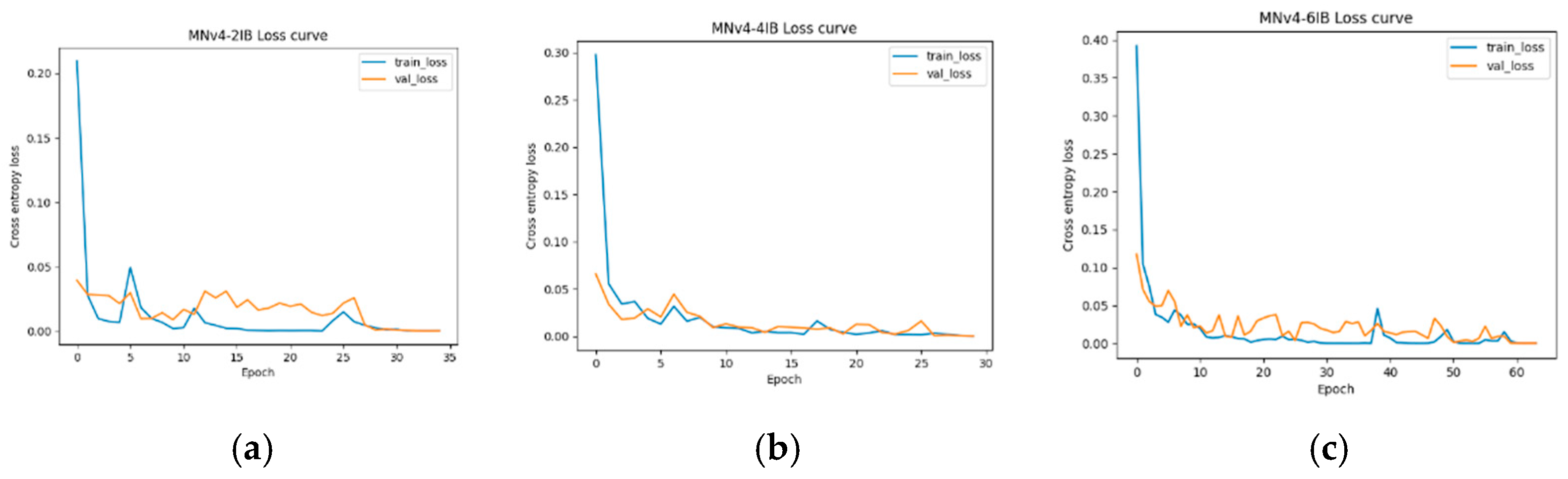
5.2. Model Training
5.3. Model Verification Results
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, B.; Yin, X. Power System Protective Relaying; China Electric Power Press: Beijing, China, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Xu, Z. Inrush current suppression strategy of three-phase transformer based on combined-switches. Electr. Power Autom. Equip. 2019, 39, 99–106. [Google Scholar]
- Jiao, Z.; Xing, W.; Wang, Z.; Jin, J. Features and Mechanism of Negative-sequenee Second Harmonics of Magnetizing Inrush Current in Transformers. Autom. Electr. Power Syst. 2015, 39, 146–151. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, C.; Yan, C.; Wu, H. Influence of Transformer Excitation Surge on Adjacent Generator and Solutions. Transformer 2023, 60, 28–30. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, D.; Yan, B.; Shen, C.; Zheng, G.; Lin, J.; Chen, C. A Novel Inrush Current Distinguishing Scheme Based on Second harmonic Component Decaying Characteristics of Transformer Current. Transformer 2023, 60, 28–34. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Sun, Q.; Zhang, H.; Wang, M. Identification of information entropy in transformer inrush current. Power Syst. Prot. Control 2017, 45, 107–111. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Peng, W.; Yao, B.; Fan, L.; Li, P.; Wang, X.; Du, Z.; Key Laboratory of Smart Grid of Ministry of Education (Tianjin University); China Electric Power Research Institute; State Grid Hubei Electric Power Research Institute. An Algorithm of Identifying Inrush Current of Converter Transformer Based on Waveform Cross-correlation of Composite Circulation and Zero Sequence Current Characteristics. Proc. CSEE 2020, 40, 8027–8039. [Google Scholar]
- Li, G.; Wang, J.; Tang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, S. Automatic identification method for excitation inrush current in power transformers based on wavelet theory. Electron. Des. Eng. 2024, 32, 31–35. [Google Scholar]
- Afrasiabi, S.; Afrasiabi, M.; Parang, B.; Mohammadi, M. Designing a composite deep learning based differential protection scheme of power transformers. Appl. Soft Comput. 2020, 87, 105975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afrasiabi, S.; Afrasiabi, M.; Parang, B.; Mohammadi, M.; Samet, H.; Dragicevic, T. Fast GRNN-based method for distinguishing inrush currents in power transformers. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2021, 69, 8501–8512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Liu, K.; Pu, H.; Yao, F.; Zhang, S. Identification of Inrush Current and Fault Current Based on Long Short-Term Memory Neural Network. J. Shanghai Jiao Tong Univ. 2024, 58, 730–738. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Liu, F.; Yang, W.; Peng, S.; Zhou, J. A survey of convolutional neural networks: Analysis, applications, and prospects. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2021, 33, 6999–7019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afrasiabi, S.; Afrasiabi, M.; Parang, B.; Mohammadi, M. Integration of accelerated deep neural network into power transformer differential protection. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2019, 16, 865–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, A.; Jiao, Z.; Li, Z.; Liang, Y. Discrimination between internal faults and inrush currents in power transformers based on the discriminative-feature-focused CNN. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2023, 223, 109701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atiyah, W.A.; Karimi, S.; Moradi, M. A novel approach for diagnosing transformer internal defects and inrush current based on 1DCNN and LSTM deep learning. J. Electr. Syst. 2024, 20, 2557–2572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y. Analysis and Research of the Transformer Inrush Current and the Sympathetic Inrush Current; North China Electric Power University: Beijing, China, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, E.; Sun, S.; Qi, Z.; Wu, Y. A new algorithm to prevent the mal-operation of transformer differential protection after removing external fault. Power Syst. Prot. Control 2011, 39, 27–30. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, W.; Bian, J.; Wu, Z. Principle and characteristics Of transformer sympathetic inrush. Electr. Power Autom. Equip. 2011, 31, 112–115. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, P.; Yu, X.; Li, Y.; Wang, T. Engineering application of transformer excitation inrush suppressor. Electr. Power Autom. Equip. 2012, 32, 145–149. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Lu, H.; Lan, L. Excitation Inrush Current Test and Simulation Analysis of Transformer in No-load closing Switching. High Volt. Appar. 2017, 53, 117–123. [Google Scholar]
- Le Guennec, A.; Malinowski, S.; Tavenard, R. Data augmentation for time series classification using convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the ECML/PKDD Workshop on Advanced Analytics and Learning on Temporal Data, Riva Del Garda, Italy, 19 September 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Yan, W.; Oates, T. Time series classification from scratch with deep neural networks: A strong baseline. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), Anchorage, AK, USA, 14–19 May 2017; pp. 1578–1585. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, S.; Kolter, J.Z.; Koltun, V. An empirical evaluation of generic convolutional and recurrent networks for sequence modeling. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1803.01271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail Fawaz, H.; Forestier, G.; Weber, J.; Idoumghar, L.; Muller, P.-A. Deep learning for time series classification: A review. Data Min. Knowl. Discov. 2019, 33, 917–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, D.; Leichner, C.; Delakis, M.; Fornoni, M.; Luo, S.; Yang, F.; Wang, W.; Banbury, C.; Ye, C.; Akin, B.; et al. MobileNetV4: Universal Models for the Mobile Ecosystem. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2404.10518v2. [Google Scholar]


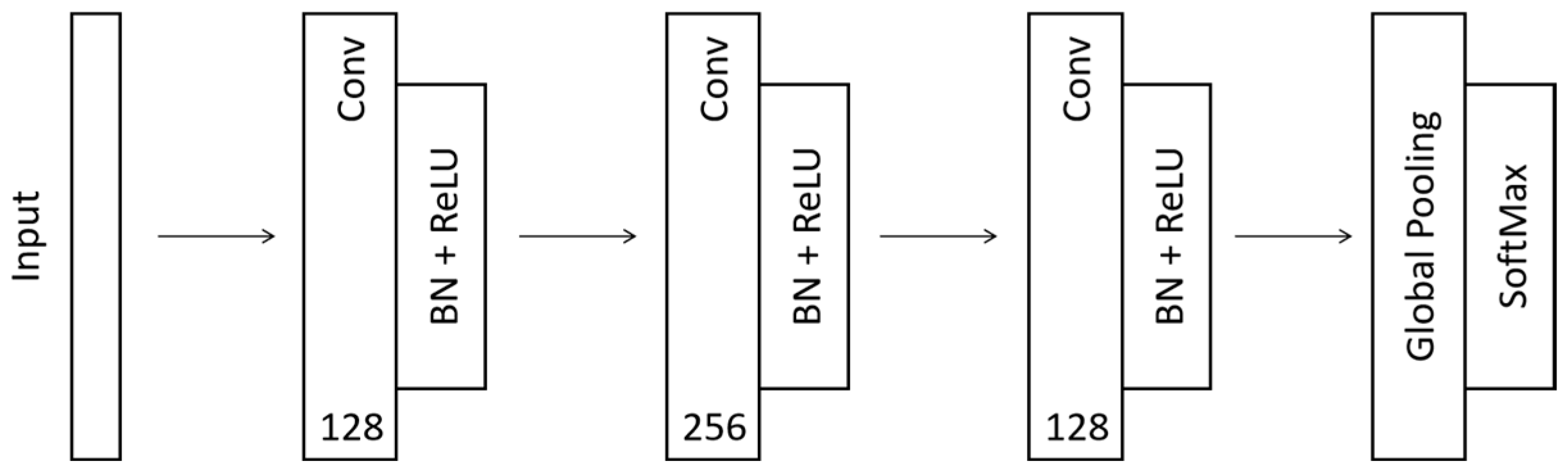
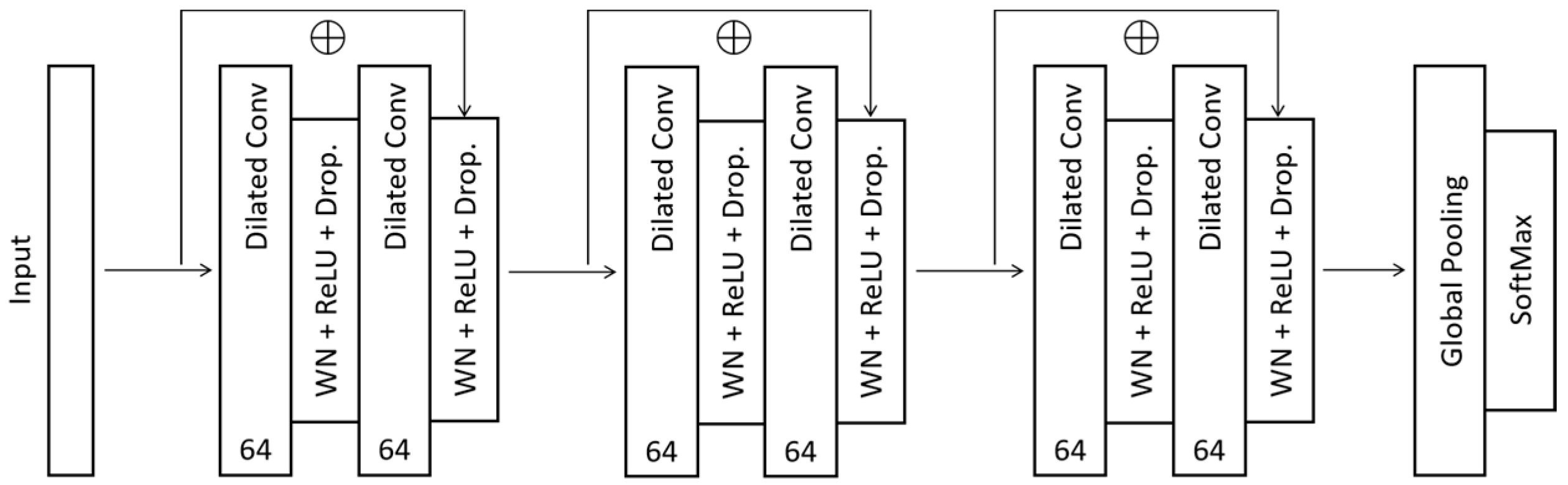
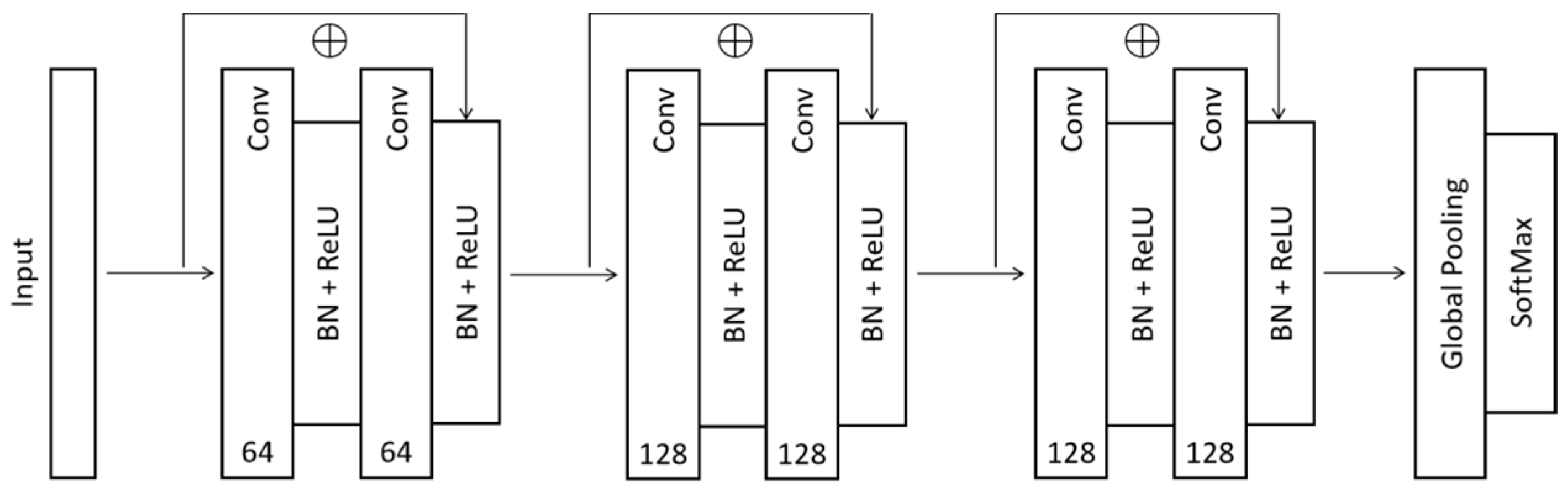
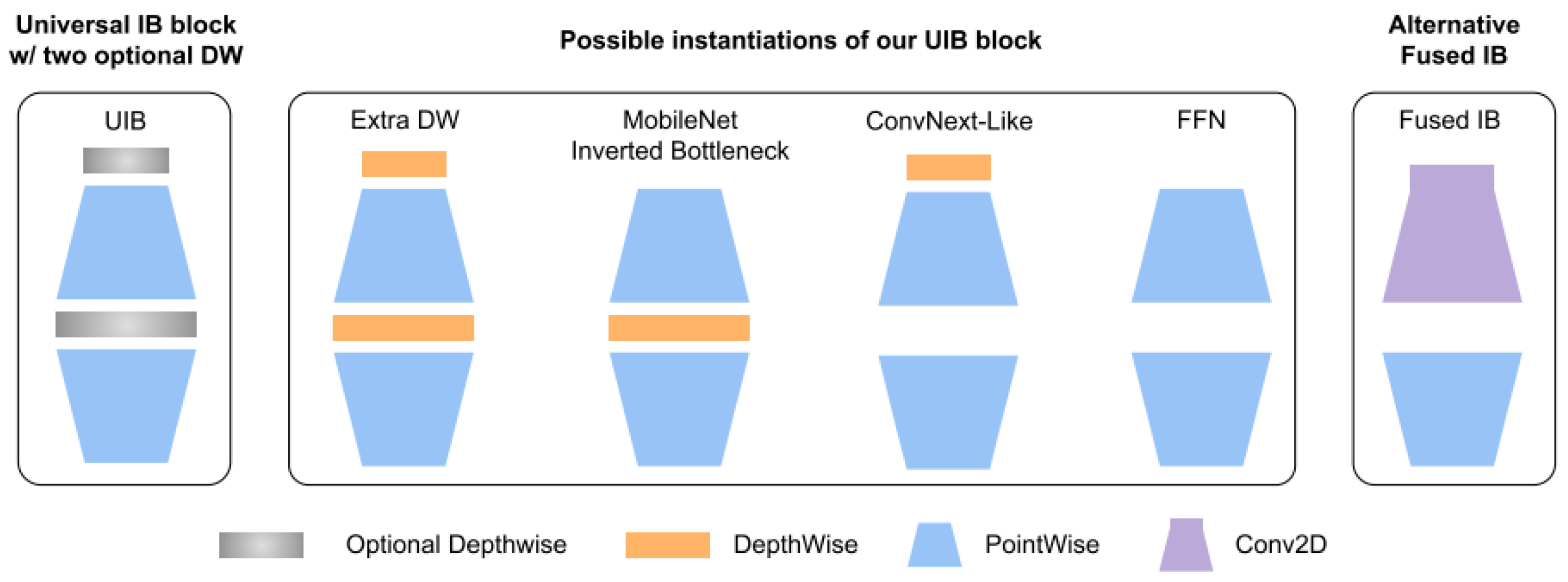
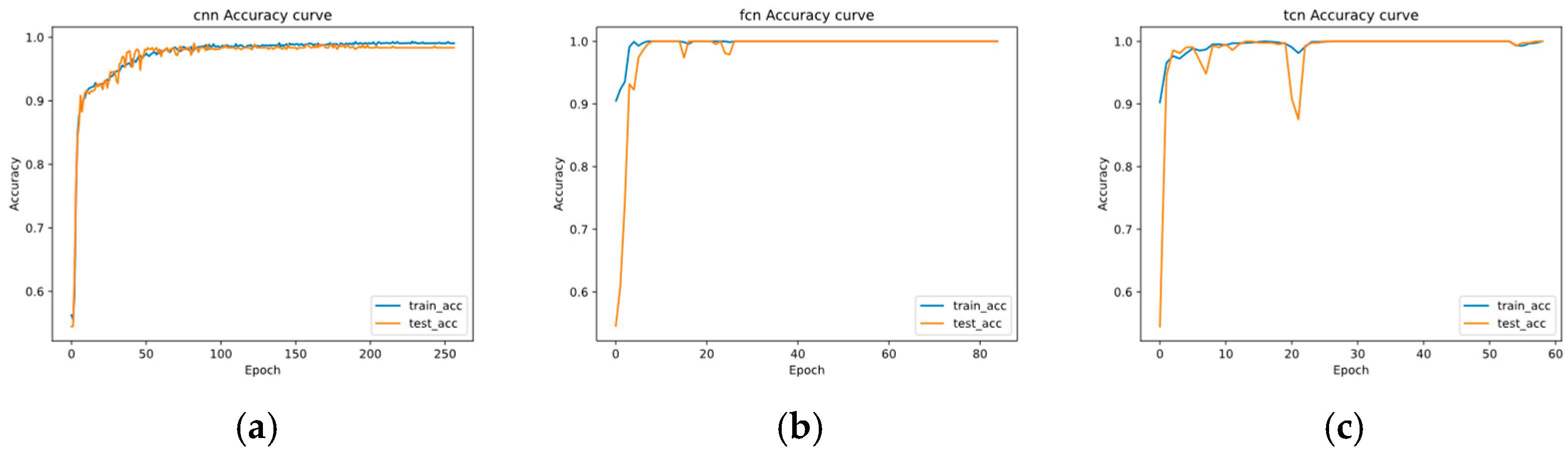
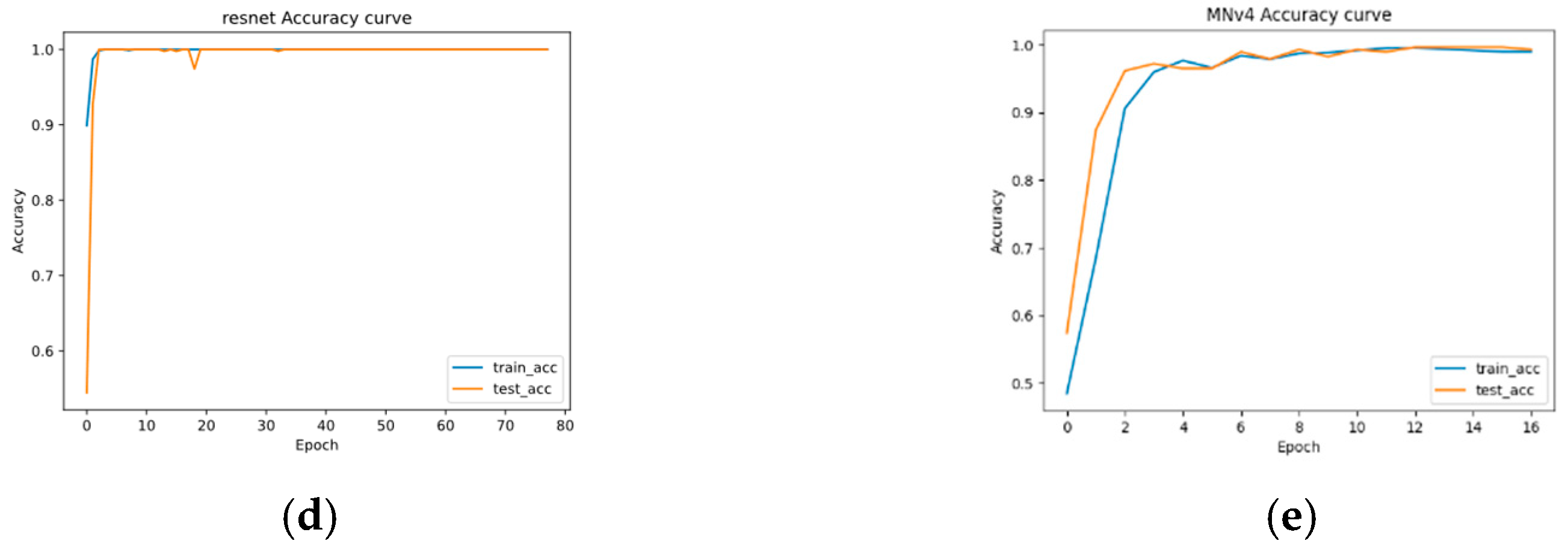
| Classification Model | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| t-LeNet | Simple structure, easy to converge | Poor feature extraction ability |
| FCN | Fewer parameters | Difficult to train, hard to converge |
| TCN | Can learn long-term scale dependencies | Complex structure, difficult to converge |
| ResNet | Stable training, easy to converge | Longer inference time |
| MNv4 | Low latency, fewer parameters, universally efficient architecture designs for mobile devices | Slightly lower accuracy |
| Hyperparameter Name | Value |
|---|---|
| Activation Function | ReLU |
| Learning Rate | 3 × 10−4 |
| Batch Size | 16 |
| Maximum Number of Epochs | 500 |
| Early Stopping Threshold | 10 |
| Weight Decay | 0.01 |
| Predicted Value | Actual Value | |
|---|---|---|
| Positive Sample | Negative Sample | |
| Positive Sample | TP | FP |
| Negative Sample | FN | TN |
| Model | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | F1-Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DTW-kNN | 0.988 | 0.989 | 0.988 | 0.988 |
| MLP | 0.987 | 0.987 | 0.987 | 0.987 |
| t-LeNet | 0.990 | 0.990 | 0.990 | 0.990 |
| FCN | 0.994 | 0.994 | 0.994 | 0.994 |
| TCN | 0.992 | 0.992 | 0.992 | 0.992 |
| ResNet | 0.998 | 0.998 | 0.998 | 0.998 |
| MNv4 | 0.997 | 0.997 | 0.997 | 0.997 |
| Input | Block | DW K1 | DW K2 | Expanded Dim | Output Dim | Stride |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2242 × 3 | Conv2D | - | 3 × 3 | - | 32 | 2 |
| 1122 × 32 | FusedIB | - | 3 × 3 | 32 | 32 | 2 |
| 562 × 32 | FusedIB | - | 3 × 3 | 96 | 64 | 2 |
| 282 × 64 | ExtraDW | 5 × 5 | 5 × 5 | 192 | 96 | 2 |
| 142 × 96 | IB | - | 3 × 3 | 192 | 96 | 1 |
| 142 × 96 | IB | - | 3 × 3 | 192 | 96 | 1 |
| 142 × 96 | IB | - | 3 × 3 | 192 | 96 | 1 |
| 142 × 96 | IB | - | 3 × 3 | 192 | 96 | 1 |
| 142 × 96 | ConvNext | 3 × 3 | - | 384 | 96 | 1 |
| 142 × 96 | ExtraDW | 3 × 3 | 3 × 3 | 576 | 128 | 2 |
| 72 × 128 | ExtraDW | 5 × 5 | 5 × 5 | 512 | 128 | 1 |
| 72 × 128 | IB | - | 5 × 5 | 512 | 128 | 1 |
| 72 × 128 | IB | - | 5 × 5 | 384 | 128 | 1 |
| 72 × 128 | IB | - | 3 × 3 | 512 | 128 | 1 |
| 72 × 128 | IB | - | 3 × 3 | 512 | 128 | 1 |
| 72 × 128 | AvgPool | - | 1 × 1 | - | 128 | 1 |
| 12 × 128 | Conv2D | - | 1 × 1 | - | 2 | 1 |
| Input | Block | DW K1 | DW K2 | Expanded Dim | Output Dim | Stride |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2242 × 3 | Conv2D | - | 3 × 3 | - | 32 | 2 |
| 1122 × 32 | FusedIB | - | 3 × 3 | 32 | 32 | 2 |
| 562 × 32 | FusedIB | - | 3 × 3 | 96 | 64 | 2 |
| 282 × 64 | ExtraDW | 5 × 5 | 5 × 5 | 192 | 96 | 2 |
| 142 × 96 | IB | - | 3 × 3 | 192 | 96 | 1 |
| 142 × 96 | ConvNext | 3 × 3 | - | 384 | 96 | 1 |
| 142 × 96 | ExtraDW | 3 × 3 | 3 × 3 | 576 | 128 | 2 |
| 72 × 128 | ExtraDW | 5 × 5 | 5 × 5 | 512 | 128 | 1 |
| 72 × 128 | IB | - | 5 × 5 | 512 | 128 | 1 |
| 72 × 128 | AvgPool | - | 1 × 1 | - | 128 | 1 |
| 12 × 128 | Conv2D | - | 1 × 1 | - | 2 | 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xing, W.; Xue, M.; Yan, Z.; Xiao, Y.; Chen, Q.; Li, Z. A Deep Learning-Based Method for Inrush Current Identification in Modern Sustainable Power Systems. Sustainability 2025, 17, 10502. https://doi.org/10.3390/su172310502
Xing W, Xue M, Yan Z, Xiao Y, Chen Q, Li Z. A Deep Learning-Based Method for Inrush Current Identification in Modern Sustainable Power Systems. Sustainability. 2025; 17(23):10502. https://doi.org/10.3390/su172310502
Chicago/Turabian StyleXing, Wu, Mingjun Xue, Ziheng Yan, Yang Xiao, Qi Chen, and Zongbo Li. 2025. "A Deep Learning-Based Method for Inrush Current Identification in Modern Sustainable Power Systems" Sustainability 17, no. 23: 10502. https://doi.org/10.3390/su172310502
APA StyleXing, W., Xue, M., Yan, Z., Xiao, Y., Chen, Q., & Li, Z. (2025). A Deep Learning-Based Method for Inrush Current Identification in Modern Sustainable Power Systems. Sustainability, 17(23), 10502. https://doi.org/10.3390/su172310502





