2.3.2. Hypotheses Development
(1) Entrepreneurship and organizational resilience
Higher-order theory suggests that top managers, as the core force of an organization, have different qualities and traits that lead to different cognitive and decision-making impacts on their members [
27]. Entrepreneurship is an important intangible production factor, which is a comprehensive manifestation of the personality traits and governance ability of top managers, and the sustainable and healthy development of enterprises cannot be separated from the driving role of managers [
28].
Organizational resilience is viewed as a dual-dimensional construct, comprising stability (robustness) and adaptability (flexibility). Stability reflects a firm’s capacity to maintain its essential functions under shocks, while adaptability captures its ability to reconfigure resources, innovate, and learn amid uncertainty. Entrepreneurship contributes differently to these two dimensions [
29]. At the cognitive level, entrepreneurs with strong psychological endurance and optimism can guide firms to remain calm and focused during crises, enhancing stability, while fostering positive mindsets that encourage exploration and learning, promoting adaptability [
30]. At the behavioral level, traits such as innovation, initiative, and prudence enable entrepreneurs to make quick yet strategic responses to external shocks, strengthening both operational stability and adaptive flexibility [
31]. At the contextual level, entrepreneurs’ environmental sensitivity and resource rationalization foster a culture of continuous learning and renewal, reinforcing stable operations while stimulating adaptive transformation. In summary, entrepreneurship enhances organizational resilience by integrating cognitive toughness, strategic action, and contextual learning. It simultaneously stabilizes organizational structure and improves adaptive capability, providing a comprehensive foundation for sustainable enterprise development.
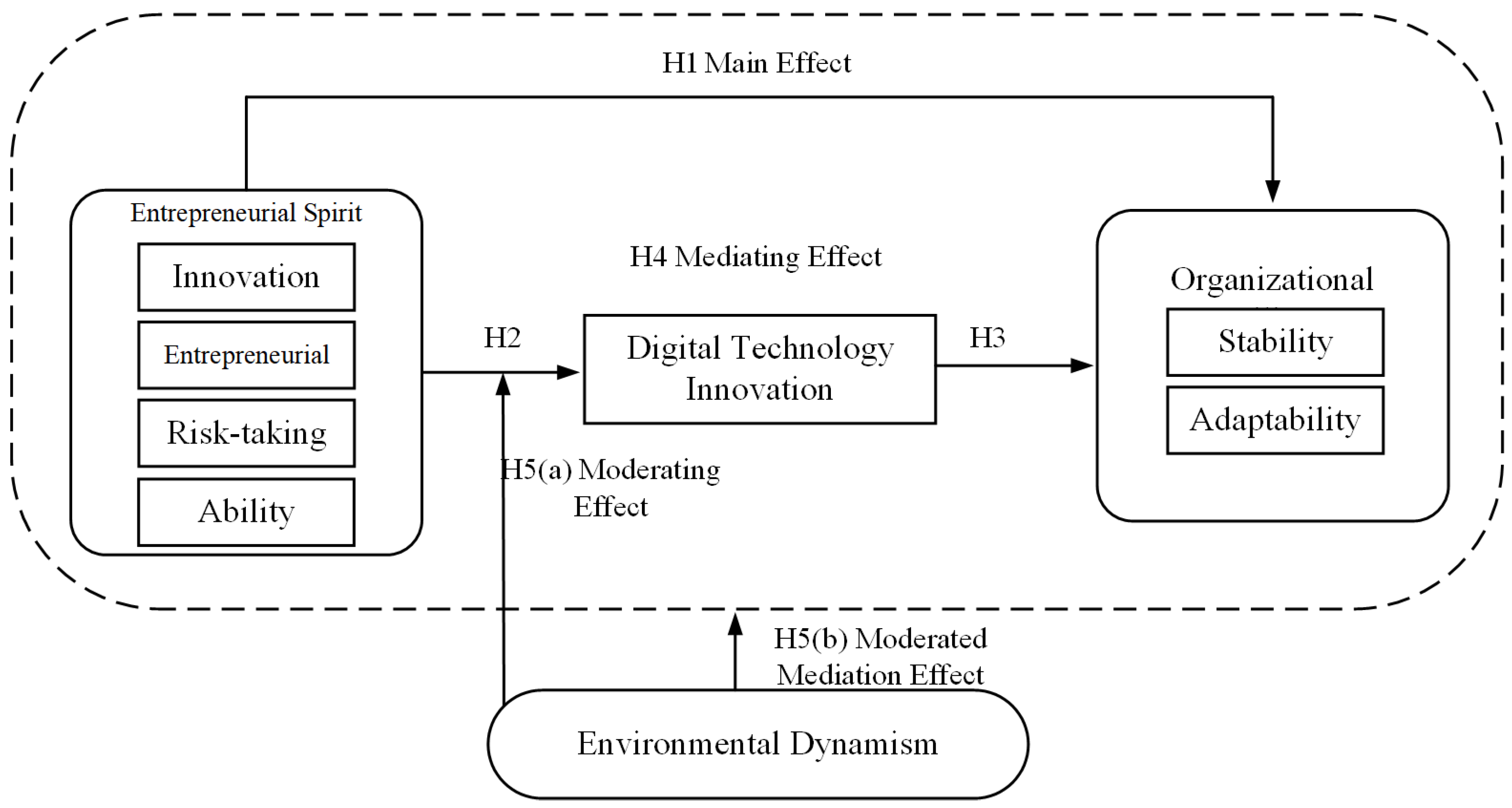
H1: Entrepreneurship positively affects organizational resilience.
(2) Entrepreneurship and Digital Technology Innovation
Based on the higher-order theory, this study argues that high entrepreneurship can provide guidance for business strategy development, and at the innovation level, this paper expects that entrepreneurship positively promotes digital technology innovation capability. Because innovation is a decision and action made to grasp the entrepreneurial opportunity, and the goal of grasping the opportunity is to be able to have independent core competitiveness, to create more and more value for the enterprise, so as to promote the sustainable development of the enterprise, employees, driven by managers, will also establish a sense of innovation, seek breakthroughs in work content and methods, and form an organizational learning atmosphere, so as to develop innovative and forward-looking products and services, which will help enterprises achieve innovative development [
32].
Specifically, at the strategic level, managers with a high level of entrepreneurship will look at problems from a long-term perspective and with a strategic overview, and will be good at formulating ambitious strategic visions to help the enterprise accomplish its set goals. At the innovation incentive level, managers are good at encouraging employees to be innovative and entrepreneurial, making innovation an assessment goal, and allowing employees to be good at identifying problems and innovating solutions. In such an environment, employees are more likely to successfully innovate and create ideas for change, contributing to the achievement of the enterprise’s innovative strategic goals. A survey found that some enterprises can survive and develop even in the case of resource shortage because they can creatively integrate existing resources as a means of solving the new problems encountered, and then look for new opportunities [
33].
In addition, entrepreneurship is more likely to explore market opportunities, pay attention to the hot industry dynamics, and efficiently utilize existing resources to create conditions for implementing innovative behaviors. In summary, managers with high entrepreneurship can enhance their industry status through entrepreneurial activities, respond quickly when the enterprise faces a crisis, and formulate a reasonable program for enterprise innovation and development. Therefore, it has a positive impact on the level of digital technology innovation. In summary, this paper argues that entrepreneurship can help enterprises identify and seize market opportunities and improve the level of digital technology innovation through the integration of resources. Therefore, this paper proposes Hypothesis 2:
H2: Entrepreneurship positively influences digital technology innovation.
(3) Digital technology innovation and organizational resilience
The existing literature suggests that organizational resilience is characterized by both stability and strain. The two seem to be contrary to each other, but in fact, a balance between the two is needed to achieve high organizational resilience. Stability allows the enterprise to shield its original state from impact when it encounters a crisis, avoiding the degradation or loss of its original functions. Contingency allows enterprises to defend against external risks, and through learning and changing in adversity, they can then achieve new innovations and further grow and expand. This paper argues that an enterprise’s digital technology innovation enhances its organizational resilience in terms of both stability and resilience.
Firstly, digital technological innovation improves organizational stability. In a dynamic environment, due to unexpected events and force majeure, the organization’s original business model or production line and financial chain can be damaged. The use of digital technologies such as big data and artificial intelligence enables the integration of these elements, facilitates communication between the top and bottom of the organization and the inside and outside of the organization, enhances the trust between members, and improves the efficiency of the organization’s business execution [
33]. When encountering an external crisis, it can not only integrate the existing resources, but also exert the production substitution effect, thus reducing the loss of the crisis on the enterprise. Therefore, digital technological innovation plays the role of a resource reserve for organizational action, and these backup resources can support its continuous operation, avoid the risks brought by external shocks, and enhance its risk-resistant ability.
Secondly, digital technological innovation enhances organizational resilience. Digital technology helps enterprises to improve their data computing ability by obtaining a large amount of more comprehensive information and then filtering and integrating useful information, helping enterprises to alleviate information asymmetry. Big data computing can help enterprises quickly perceive the internal and external environment, make predictions about future trends, and also help companies pay attention to real-time market dynamics, offering a reasonable prediction of possible risks. In addition, big data storage technology can record external environmental information as well as enterprise operation data, and these results can help enterprises analyze and reflect on the deficiencies in the process of coping with crises, so as to accumulate experience and feedback for the next step of optimization [
34]. Digital technological innovation also enhances the dynamic capability of enterprises, and the process of sensing, capturing, and then transforming data facilitates the process of enterprises adapting to the external environment and gaining a more comprehensive understanding of unknown risks, which in turn enhances the competitiveness and resistance of the organization. Therefore, this paper proposes Hypothesis 3:
H3: Digital technology innovation positively affects organizational resilience.
(4) The mediating role of digital technology innovation
Based on the dynamic capabilities perspective, entrepreneurship, digital technological innovation, and organizational resilience are strongly correlated. Digital technological innovation has changed the production mode in the past and boosted modernization and transformation. The application of digital technologies such as big data has enhanced the information processing and processing capabilities of enterprises and become a powerful tool for enterprises to gain competitive advantages in the market.
Firstly, entrepreneurship enables entrepreneurs to respond quickly to market demand, boosting the organization to make changes and create new value [
35]. The improvement of the level of digital technology innovation accelerates entrepreneurs’ adaptability to the environment, and at the same time, their competitive position in the market is improved, which effectively helps enterprises to withstand external crises, make rapid and effective strategic decisions, and optimize the structure of resources.
Secondly, in the market environment, where consumers’ demands are increasingly personalized, digital technology innovations lean more to the clients’ side through enterprises, giving rise to new business models. Digital technology innovation also reduces the cost of each link in the enterprise, so the saved resources can further improve and optimize digital technology, thus generating more and higher-quality digital technology and promoting enterprise value creation [
36]. Enterprise innovation can have a significant improvement on organizational capabilities; for those suffering from crisis and risk in particular, the integration of resources is key, helping the enterprise to recover from crisis and get on track, which has a positive impact on organizational resilience. Based on the above analysis, Hypothesis 4 is proposed:
H4: Digital technology innovation has a mediating effect on the relationship between entrepreneurship and organizational resilience.
(5) Moderating effects of environmental dynamics
In order to seek survival and development in a dynamic environment, enterprises need to make timely adjustments and changes, and the role of digital technology innovation cannot be ignored [
37]. If the enterprise always maintains agile insight and accurate judgment, such a virtuous cycle can greatly enhance the enterprise’s sustainable development ability and competitive advantage in the same industry. By continuously integrating its own resources to cope with environmental changes, it ultimately enhances the organizational resilience of the enterprise. Some enterprises have overinvested in the initial stage of digital technology innovation, resulting in the irrational use of resources and leading to a financial crisis. On the contrary, organizational resilience will be enhanced if enterprises fully grasp the external environment and their own actual situation, make full use of existing resources, and make accurate decisions, especially in the early stage, to ensure that digital technology innovation activities are carried out smoothly. Therefore, it is necessary to consider environmental dynamics when researching the impact of digital technology innovation and enterprise organizational toughness. Based on the above analysis, this paper proposes Hypotheses 5a and 5b:
H5a: Environmental dynamics positively moderate the impact of digital technological innovation on organizational resilience.
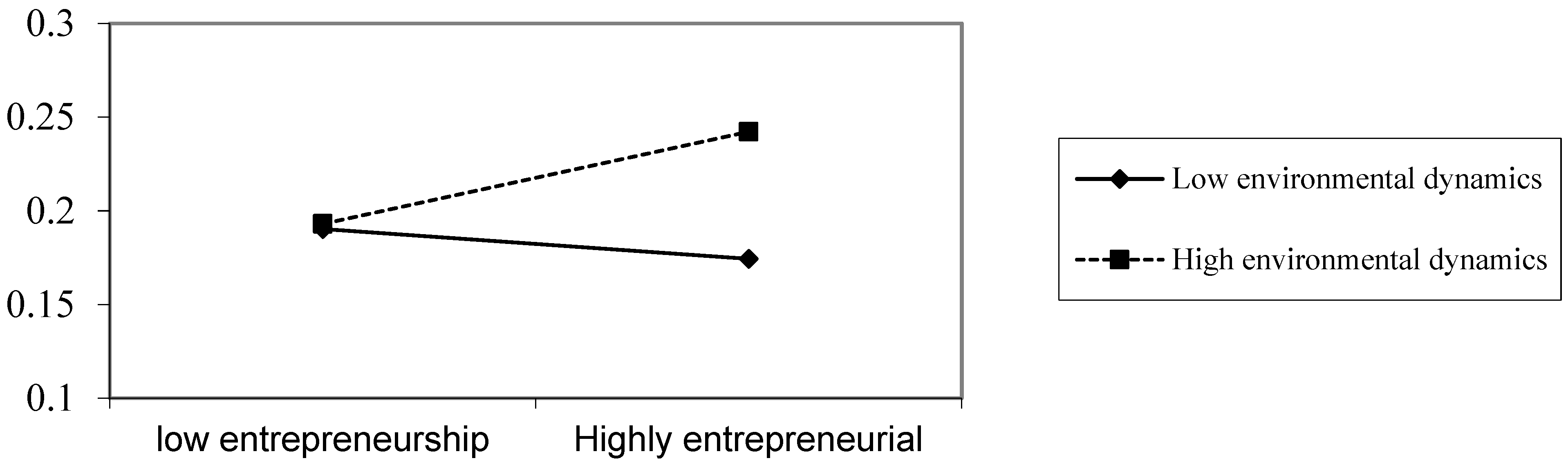
H5b: Environmental dynamism positively moderates the mediating effect of digital technological innovation between entrepreneurship and organizational resilience.
Based on the higher-order and dynamic capability theory, this paper introduces digital technological innovation and environmental dynamics to construct a research model to analyze and clarify the relationship between these four variables; this study not only broadens the research on the impact of entrepreneurship and organizational resilience, but also describes the path of entrepreneurship’s impact on organizational resilience, and further analyzes the boundary conditions of the process to provide theory and solutions for enterprises to cope with crises and challenges. The research model of this study is shown in
Figure 2: