Eco-Friendly Adsorbents: Innovative Strategies for Pesticide Removal from Soil and Wastewater
Abstract
1. Introduction
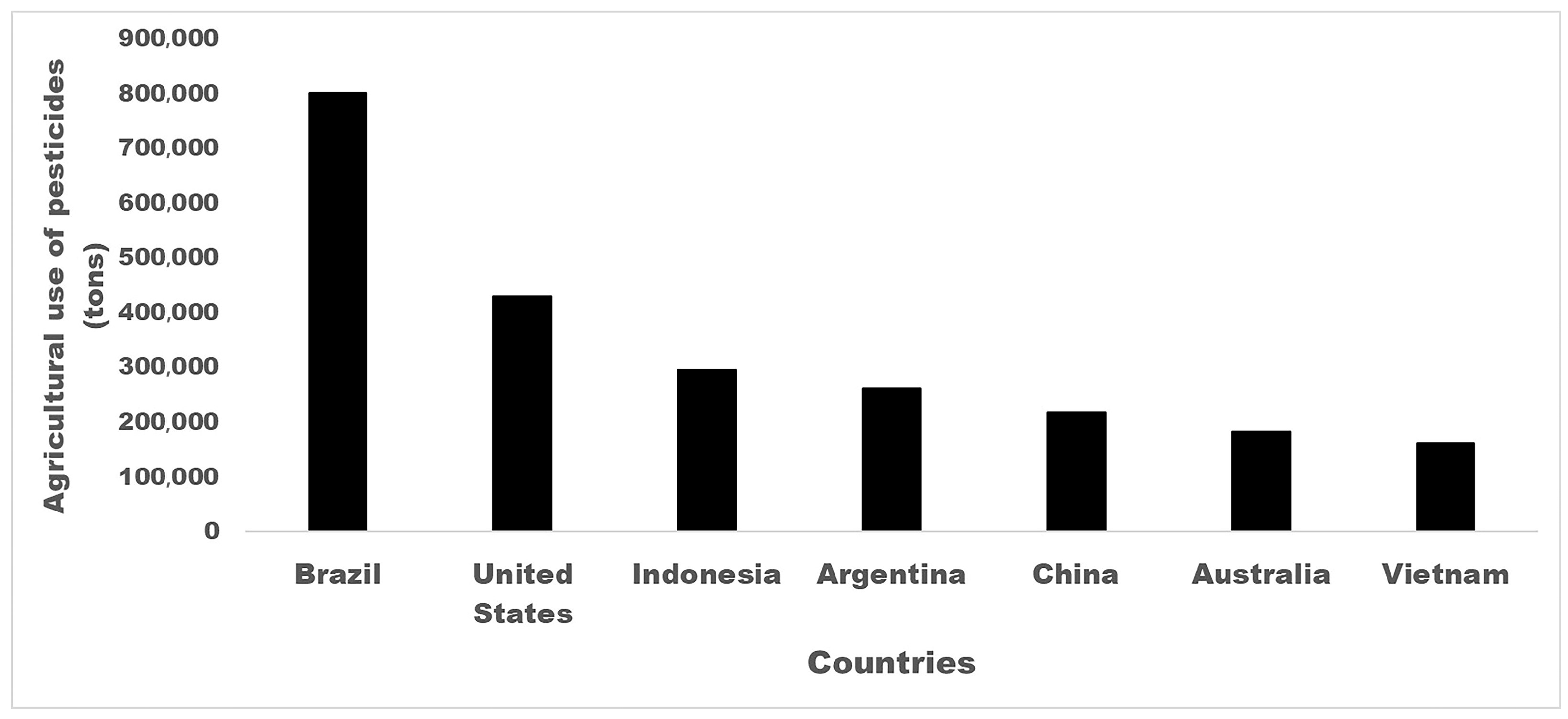
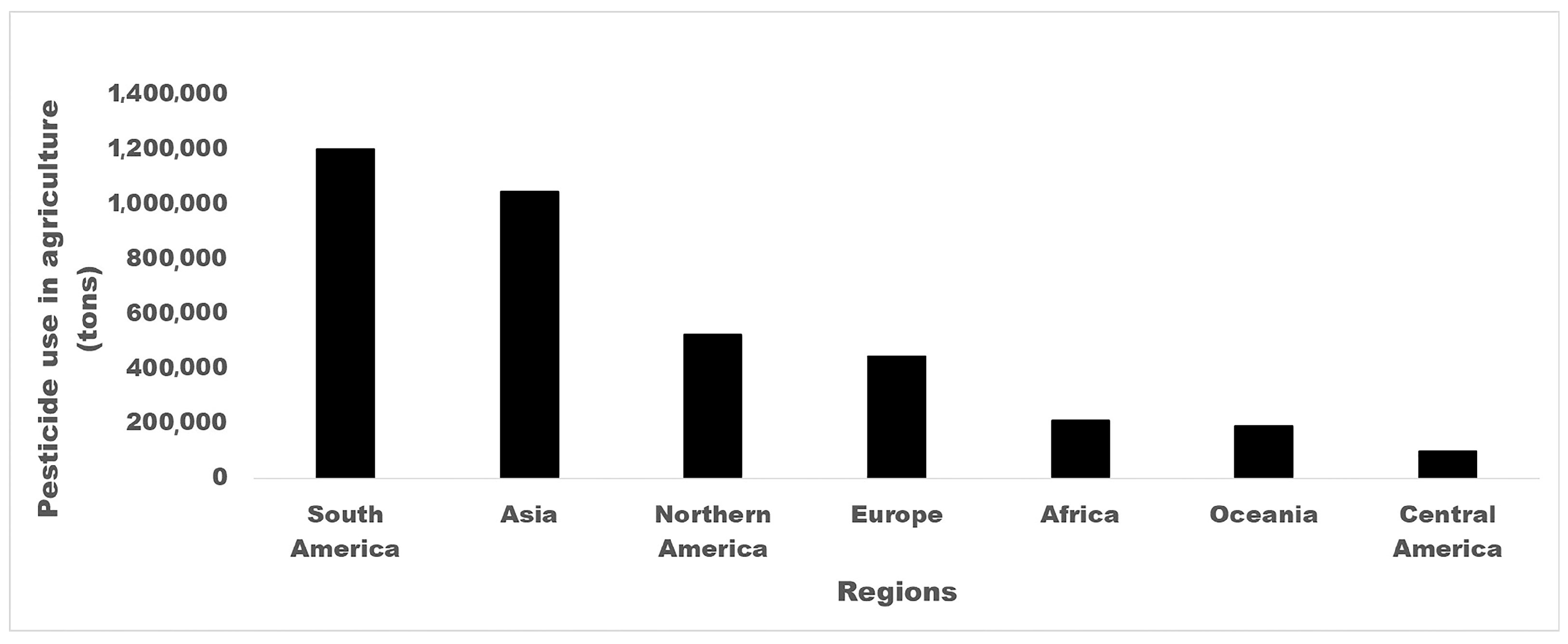
2. Pesticide Uses
3. Pesticide Removal
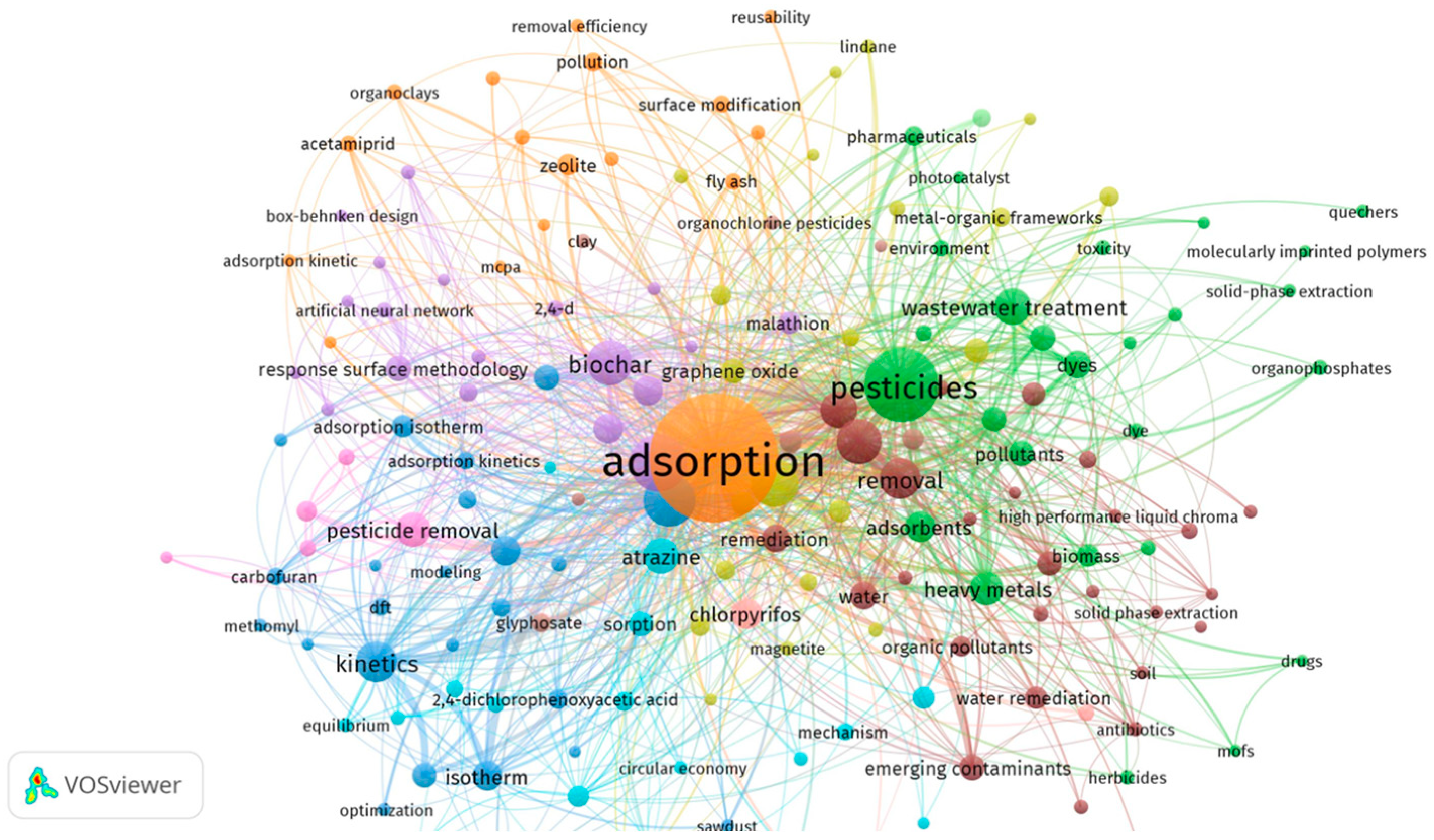
4. Green Adsorbents Strategy for Removing Pesticide Residues
5. Types of Green Adsorbents
Active Carbon Adsorbents
- Non-conventional low-cost adsorbents (NCLCAs)
- b.
- Agricultural solid waste
- c.
- Industrial by-products and solid waste
- d.
- Natural materials—zeolites
- e.
- Adsorbents from marine organisms
- f.
- Nanomaterial adsorbents
- g.
- Composite and nanomaterial adsorbents
- h.
- Miscellaneous adsorbents
- i.
- Cellulose-Based Green Adsorbents
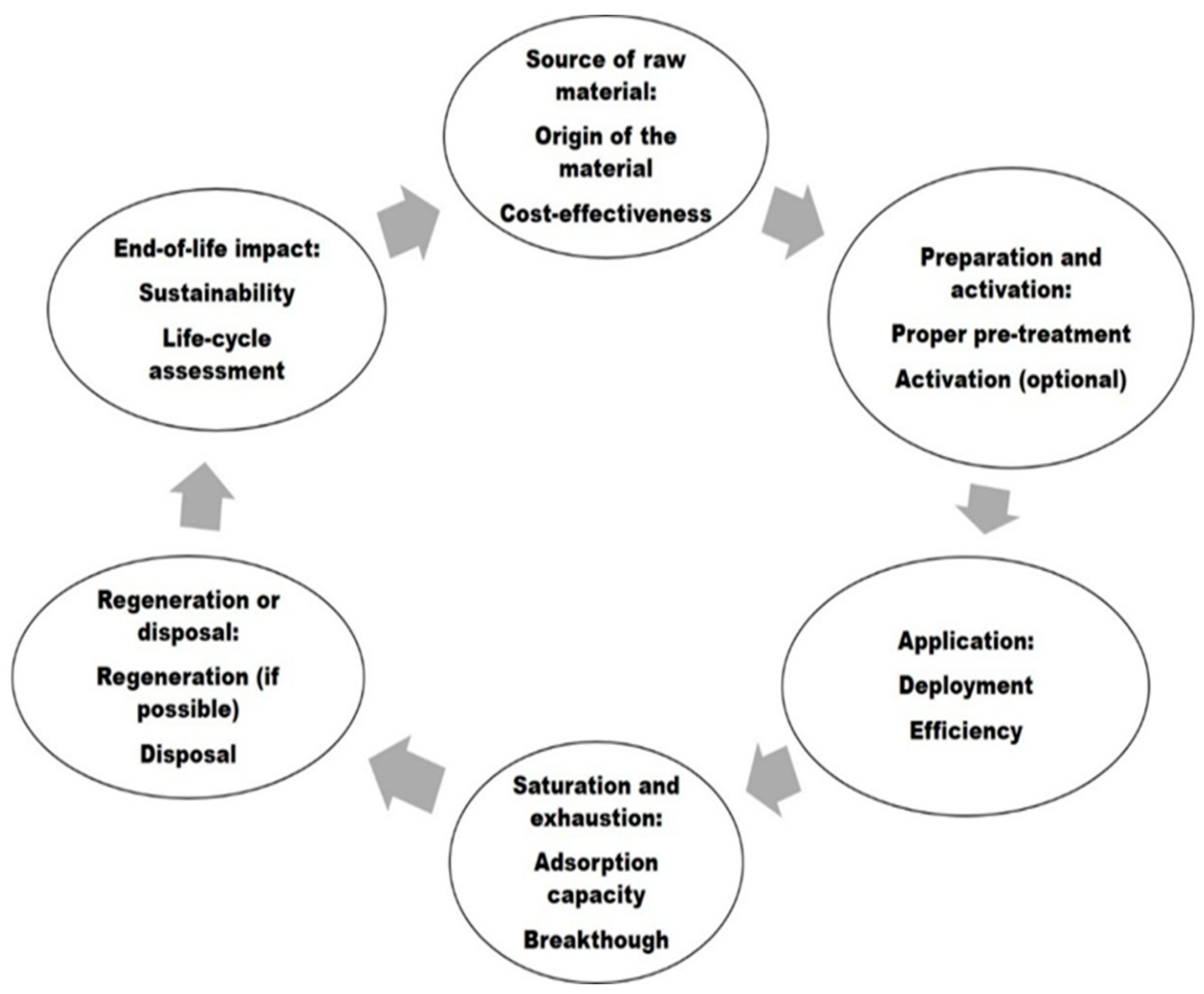
6. Life Cycle of the NCLCAs
7. Pesticide Adsorption Strategies with Some Examples of Green Adsorbents
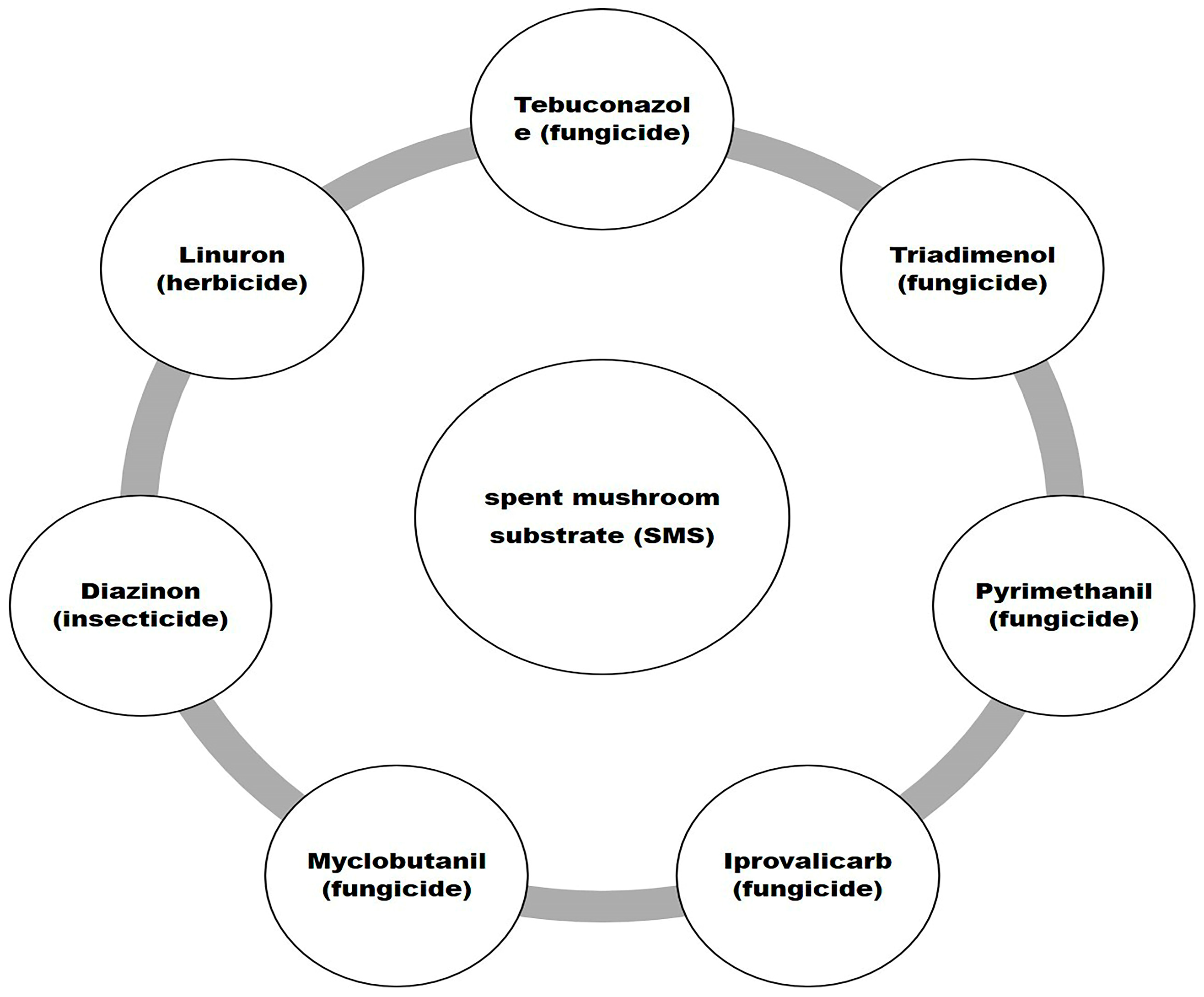
7.1. Pesticide Adsorption by Spent Mushroom Substrate
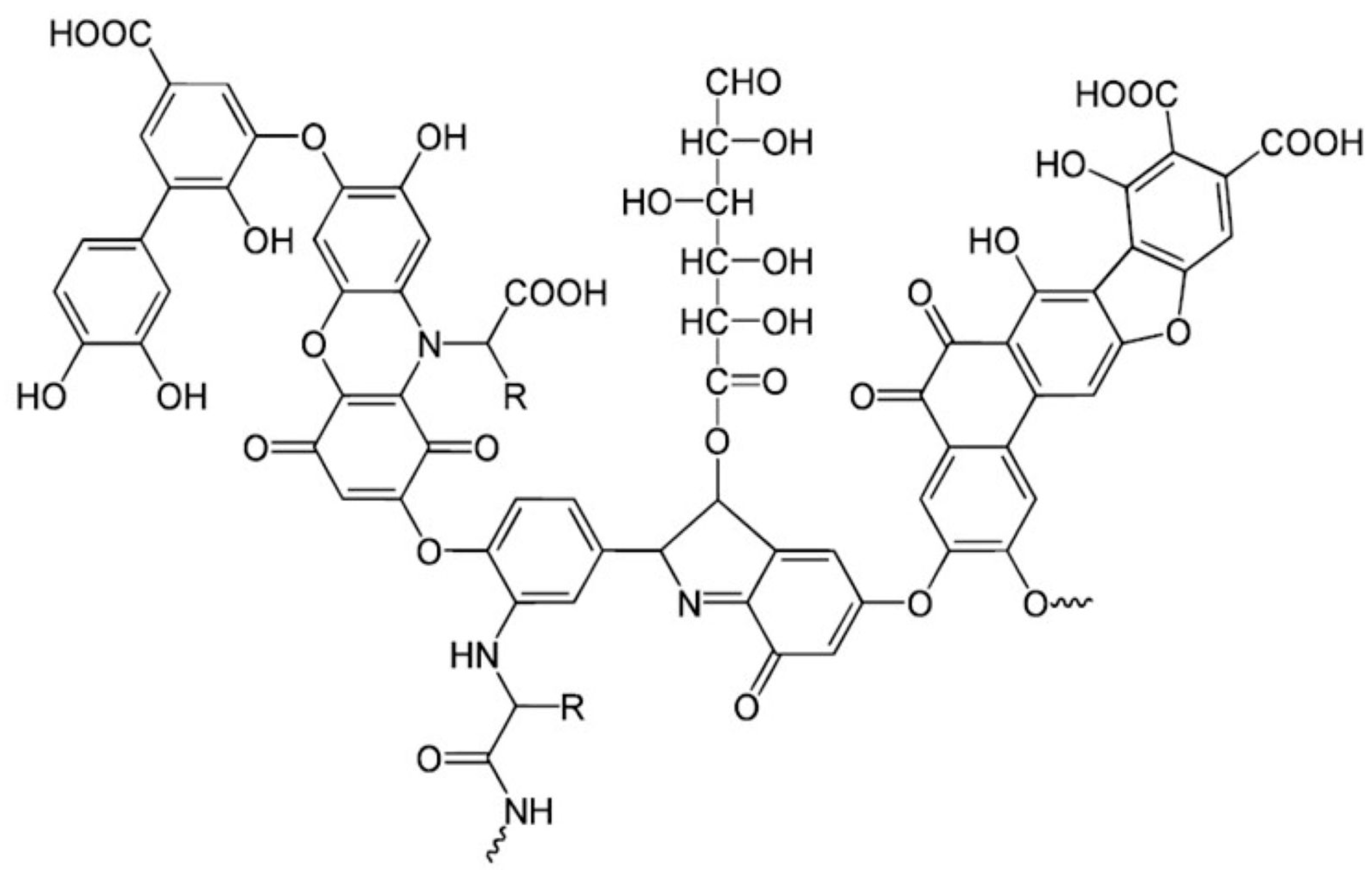
7.2. Pesticide Adsorption by Humic Acid
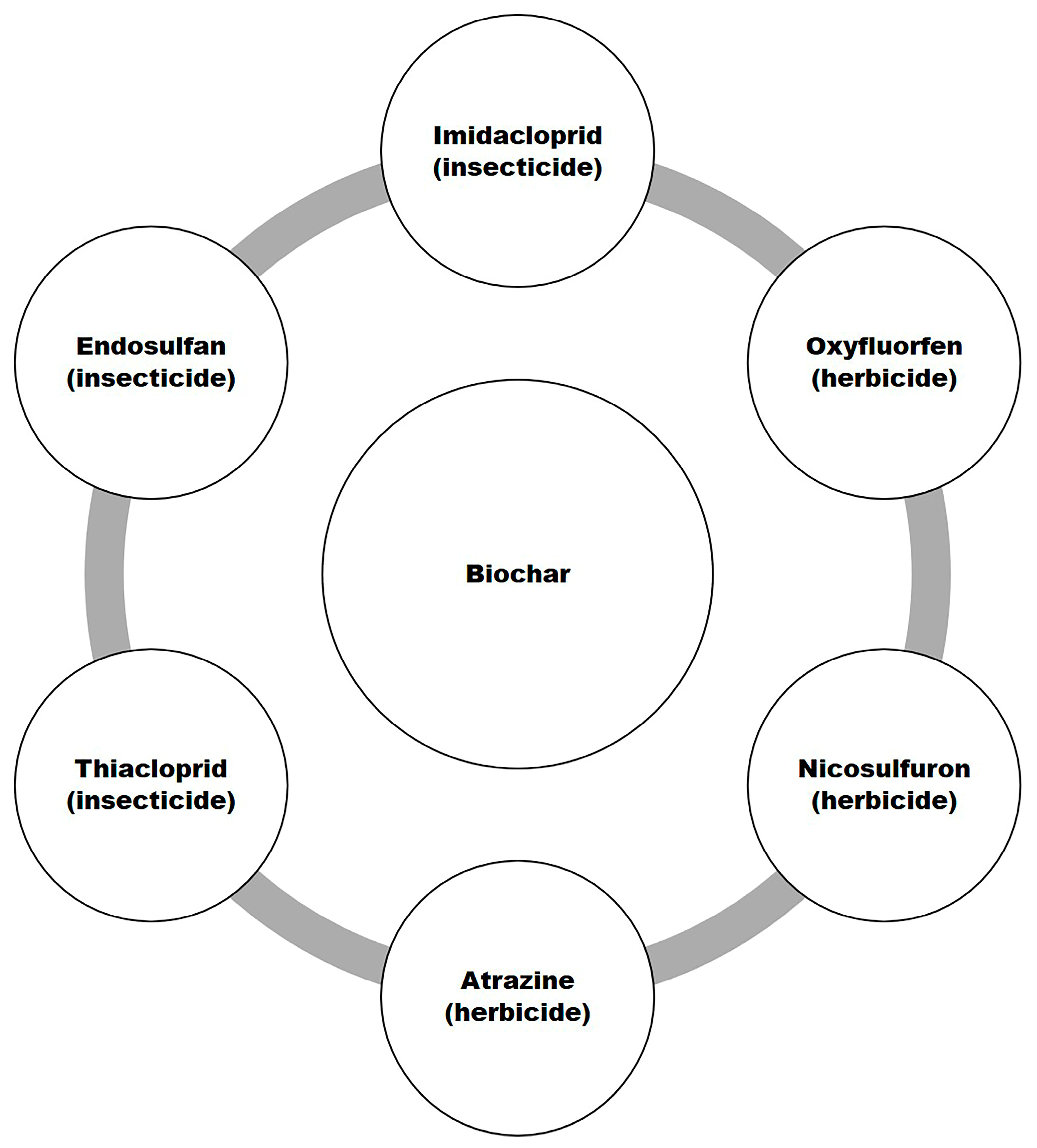
7.3. Pesticide Adsorption by Biochar
7.4. Pesticide Adsorption by Cellulose and Carboxymethyl Cellulose
7.5. Nanoadsorption for Pesticide Removal
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- FAO, 2022a. FAO, “FAOSTAT,” Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), [WWW Document]. Available online: https://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#search/Pesticide (accessed on 3 November 2025).
- Mohafrash, S.M.M.; Mossa, A.T.H. Disposal of Expired Empty Containers and Waste from Pesticides. Egypt. J. Chem. 2024, 67, 65–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gad, M.; Elmorsi, R.; Khalil, N.; Mossa, A.-T. Health Risk Assessment of Dietary Exposure to Pesticide Residues in Edible Tissue of Tilapia Fish from Lake Manzala, Egypt. Egypt. J. Chem. 2024, 67, 641–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USEPA Water Recycling and Reuse|Region 9: Water|US EPA. 2016. Available online: https://19january2017snapshot.epa.gov/www3/region9/water/recycling/index.html (accessed on 3 November 2025).
- Rippy, M.A.; Deletic, A.; Black, J.; Aryal, R.; Lampard, J.L.; Tang, J.Y.M.; McCarthy, D.; Kolotelo, P.; Sidhu, J.; Gernjak, W. Pesticide Occurrence and Spatio-Temporal Variability in Urban Run-off across Australia. Water Res. 2017, 115, 245–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Zhou, M.; Du, X.; Xu, X. Enhanced Mechanism of 2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic Acid Degradation by Electrochemical Activation of Persulfate on Blue-TiO2 Nanotubes Anode. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 254, 117560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almahri, A.; Abou-Melha, K.S.; Katouah, H.A.; Al-bonayan, A.M.; Saad, F.A.; El-Desouky, M.G.; El-Bindary, A.A. Adsorption and Removal of the Harmful Pesticide 2,4-Dichlorophenylacetic Acid from an Aqueous Environment via Coffee Waste Biochar: Synthesis, Characterization, Adsorption Study and Optimization via Box-Behnken Design. J. Mol. Struct. 2023, 1293, 136238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aksu, Z. Application of Biosorption for the Removal of Organic Pollutants: A Review. Process Biochem. 2005, 40, 997–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehghani, M.H.; Ahmadi, S.; Ghosh, S.; Othmani, A.; Osagie, C.; Meskini, M.; AlKafaas, S.S.; Malloum, A.; Khanday, W.A.; Jacob, A.O.; et al. Recent Advances on Sustainable Adsorbents for the Remediation of Noxious Pollutants from Water and Wastewater: A Critical Review. Arab. J. Chem. 2023, 16, 105303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satyam, S.; Patra, S. Innovations and Challenges in Adsorption-Based Wastewater Remediation: A Comprehensive Review. Heliyon 2024, 10, e29573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crini, G.; Lichtfouse, E. Green Adsorbents for Pollutant Removal: Fundamentals and Design; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; Volume 19, pp. 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunarathne, V.; Ashiq, A.; Ginige, M.P. Green Adsorbents for Pollutant Removal; Springer Nature: Durham, NC, USA, 2018; Volume 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.L.; Wang, Y.J.; Wang, Y.T.; Li, J.G.; Zeng, Y.N.; Guo, H.W.; Liu, H.; Dong, K.L.; Zhang, L.Y. Application and Innovation of Artificial Intelligence Models in Wastewater Treatment. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2024, 267, 104426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, M.F.; Haydar, S.; Bhatti, A.A.; Bari, A.J. Application of Artificial Neural Network for the Prediction of Biosorption Capacity of Immobilized Bacillus Subtilis for the Removal of Cadmium Ions from Aqueous Solution. Biochem. Eng. J. 2014, 84, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulhussein, S.A.; Alwared, A.I. The Use of Artificial Neural Network (ANN) for Modeling of Cu (II) Ion Removal from Aqueous Solution by Flotation and Sorptive Flotation Process. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2019, 13, 353–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WPR Pesticide Usage by Country 2025. Available online: https://worldpopulationreview.com/country-rankings/pesticide-usage-by-country (accessed on 10 November 2025).
- FAO Pesticides Use (RP). Available online: https://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#data/RP (accessed on 10 November 2025).
- Hathout, A.S.; Saleh, E.; Hussain, O.A.; Amer, M.M.; Mossa, A.T.H.; Yassen, A.A.A.; Fouzy, A.S.M. Determination of Pesticide Residues in Agricultural Soil Samples Collected from Sinai and Ismailia Governorates, Egypt. Egypt. J. Chem. 2022, 65, 407–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzouz, A.; Hausler, R.; El-Akhrass, M. Pesticides and removal approaches. In Sorbents Materials for Controlling Environmental Pollution; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 435–462. [Google Scholar]
- Bi, R.; Ou, M.; Zhou, S.; Geng, S.; Zheng, Y.; Chen, J.; Mo, R.; Li, Y.; Xiao, G.; Chen, X.; et al. Degradation strategies of pesticide residue: From chemicals to synthetic biology. Synth. Syst. Biotechnol. 2023, 8, 302–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.F.; Tang, J.; Nie, Z.H.; Wang, Y.D.; Ren, Y.; Zuo, L. Preparation and Application of Magnetic Fe3O4 Nanoparticles for Wastewater Purification. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2009, 68, 312–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Barick, K.C.; Bahadur, D. Novel and Efficient Three Dimensional Mesoporous ZnO Nanoassemblies for Envirnomental Remediation. Int. J. Nanosci. 2011, 10, 1001–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.-G.; Shen, H.-Y.; Pan, S.-D.; Hu, M.-Q.; Xia, Q.-H. Preparation and Characterization of Amino-Functionalized Nano-Fe3O4 Magnetic Polymer Adsorbents for Removal of Chromium (VI) Ions. J. Mater. Sci. 2010, 45, 5291–5301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradi, O.; Sadegh, H.; Shahryari-Ghoshekandi, R.; Norouzi, M. Application of Carbon Nanotubes in Nanomedicine: New Medical Approach for Tomorrow. In Medical Imaging: Concepts, Methodologies, Tools, and Applications; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2017; pp. 2021–2062. [Google Scholar]
- Sadegh, H.; Zare, K.; Maazinejad, B.; Shahryari-Ghoshekandi, R.; Tyagi, I.; Agarwal, S.; Gupta, V.K. Synthesis of MWCNT-COOH-Cysteamine Composite and Its Application for Dye Removal. J. Mol. Liq. 2016, 215, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, V.K.; Moradi, O.; Tyagi, I.; Agarwal, S.; Sadegh, H.; Shahryari-Ghoshekandi, R.; Makhlouf, A.S.H.; Goodarzi, M.; Garshasbi, A. Study on the Removal of Heavy Metal Ions from Industry Waste by Carbon Nanotubes: Effect of the Surface Modification: A Review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 46, 93–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurniawan, T.A.; Lo, W. Removal of Refractory Compounds from Stabilized Landfill Leachate Using an Integrated H2O2 Oxidation and Granular Activated Carbon (GAC) Adsorption Treatment. Water Res. 2009, 43, 4079–4091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudhoo, A.; Garg, V.K.; Wang, S. Removal of Heavy Metals by Biosorption. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2012, 10, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, A.K.; Singh, R.; Teja Pullela, R.; Pundir, V. Green Adsorbents for the Removal of Heavy Metals from Wastewater: A Review. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 57, 1468–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.B.; Nagpal, G.; Agrawal, S. Water Purification by Using Adsorbents: A Review. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2018, 11, 187–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyers, R.A. Encyclopedia of Environmental Analysis and Remediation. Encycl. Environ. Anal. Remediat. 1998, 26–68. Available online: https://www.wiley.com/en-us/Encyclopedia+of+Environmental+Analysis+and+Remediation%2C+Volume+8-p-9780471166290 (accessed on 10 November 2025).
- Radovic, L.R.; Moreno-Castilla, C.; Rivera-Utrilla, J. Carbon Materials as Adsorbents in Aqueous Solutions. Chem. Phys. Carbon 2001, 227–406. [Google Scholar]
- Cooney, D.O. Adsorption Design for Wastewater Treatment; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1998; ISBN 1566703336. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Zeng, Y.; Cheng, Z. Removal of Heavy Metal Ions Using Chitosan and Modified Chitosan: A Review. J. Mol. Liq. 2016, 214, 175–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okenicová, L.; Žemberyová, M.; Procházková, S. Biosorbents for Solid-Phase Extraction of Toxic Elements in Waters. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2016, 14, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volesky, B. Biosorption Process Simulation Tools. Hydrometallurgy 2003, 71, 179–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macek, T.; Mackova, M. Potential of Biosorption Technology. In Microbial Biosorption of Metals; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2011; pp. 7–17. [Google Scholar]
- Torres, E. Biosorption: A Review of the Latest Advances. Processes 2020, 8, 1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, A.G.; Pokrovsky, O.S.; Santana-Casiano, J.M.; González-Dávila, M. Bioadsorption of Heavy Metals. In Prospects and Challenges in Algal Biotechnology; Springer: Singapore, 2017; pp. 233–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haq, A.u.; Saeed, M.; Muneer, M.; Jamal, M.A.; Maqbool, T.; Tahir, T. Biosorption of Metribuzin Pesticide by Cucumber (Cucumis Sativus) Peels-Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Composite. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 5840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haq, A.U.; Saeed, M.; Usman, M.; Muneer, M.; Adeel, S.; Abbas, S.; Iqbal, A. Removal of Butachlor from Aqueous Solution Using Cantaloupe Seed Shell Powder: Kinetic, Equilibrium and Thermodynamic Studies. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 16, 6029–6042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastopoulos, I.; Karamesouti, M.; Mitropoulos, A.C.; Kyzas, G.Z. A Review for Coffee Adsorbents. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 229, 555–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dulman, V.; Cucu-Man, S.M. Wood Sawdust, Tree Bark and Wood Chips: Waste Lignocellulosic Materials for Dye Removal. In Sorption Processes and Pollution; Presses Universitaires de Franche-Comté: Besançon, France, 2010; pp. 233–269. [Google Scholar]
- Bhadoria, P.; Shrivastava, M.; Khandelwal, A.; Das, R.; Langyan, S.; Rohatgi, B.; Singh, R. Preparation of Modified Rice Straw-Based Bio-Adsorbents for the Improved Removal of Heavy Metals from Wastewater. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2022, 29, 100742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.K.; Kumar, A.; Joseph, P.E. Removal of Atrazine from Water by Low Cost Adsorbents Derived from Agricultural and Industrial Wastes. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2008, 80, 461–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boudesocque, S.; Guillon, E.; Aplincourt, M.; Martel, F.; Noël, S. Use of a Low-Cost Biosorbent to Remove Pesticides from Wastewater. J. Environ. Qual. 2008, 37, 631–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradi Dehaghi, S.; Rahmanifar, B.; Moradi, A.M.; Azar, P.A. Removal of Permethrin Pesticide from Water by Chitosan-Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Composite as an Adsorbent. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 2014, 18, 348–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miros-Kudra, P.; Sobczak, P.; Kopania, E. Removal of Heavy Metals from Aqueous Solutions with the Use of Lignins and Biomass. Fibres Text. East. Eur. 2022, 30, 99–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N. Adsorption of Herbicides on Coal Fly Ash from Aqueous Solutions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 168, 233–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behloul, M.; Lounici, H.; Abdi, N.; Drouiche, N.; Mameri, N. Adsorption Study of Metribuzin Pesticide on Fungus Pleurotus Mutilus. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2017, 119, 687–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhankhar, R.; Hooda, A. Fungal Biosorption-an Alternative to Meet the Challenges of Heavy Metal Pollution in Aqueous Solutions. Environ. Technol. 2011, 32, 467–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayangbenro, A.S.; Babalola, O.O. A New Strategy for Heavy Metal Polluted Environments: A Review of Microbial Biosorbents. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aksu, Z. Biosorption of Reactive Dyes by Dried Activated Sludge: Equilibrium and Kinetic Modelling. Biochem. Eng. J. 2001, 7, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, H.C.; Chen, K.M. Reuse of Activated Sludge Biomass: I. Removal of Basic Dyes from Wastewater by Biomass. Process Biochem. 2002, 37, 595–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crini, G. Non-Conventional Low-Cost Adsorbents for Dye Removal: A Review. Bioresour. Technol. 2006, 97, 1061–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karić, N.; Maia, A.S.; Teodorović, A.; Atanasova, N.; Langergraber, G.; Crini, G.; Ribeiro, A.R.L.; Đolić, M. Bio-Waste Valorisation: Agricultural Wastes as Biosorbents for Removal of (in)Organic Pollutants in Wastewater Treatment. Chem. Eng. J. Adv. 2022, 9, 100239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Messaoudi, N.; El Khomri, M.; El Mouden, A.; Bouich, A.; Jada, A.; Lacherai, A.; Iqbal, H.M.N.; Mulla, S.I.; Kumar, V.; Américo-Pinheiro, J.H.P. Regeneration and Reusability of Non-Conventional Low-Cost Adsorbents to Remove Dyes from Wastewaters in Multiple Consecutive Adsorption–Desorption Cycles: A Review. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2024, 14, 11739–11756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igwegbe, C.A.; Onukwuli, O.D.; Ighalo, J.O.; Okoye, P.U. Adsorption of Cationic Dyes on Dacryodes Edulis Seeds Activated Carbon Modified Using Phosphoric Acid and Sodium Chloride. Environ. Process. 2020, 7, 1151–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, M.Y.; Tam, Y.J. Bioremediation of Dyes Using Coconut Parts via Adsorption: A Review. SN Appl. Sci. 2020, 2, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorbani, F.; Kamari, S.; Zamani, S.; Akbari, S.; Salehi, M. Optimization and Modeling of Aqueous Cr(VI) Adsorption onto Activated Carbon Prepared from Sugar Beet Bagasse Agricultural Waste by Application of Response Surface Methodology. Surf. Interfaces 2020, 18, 100444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tissera, N.D.; Wijesena, R.N.; Yasasri, H.; de Silva, K.M.N.; de Silva, R.M. Fibrous Keratin Protein Bio Micro Structure for Efficient Removal of Hazardous Dye Waste from Water: Surface Charge Mediated Interfaces for Multiple Adsorption Desorption Cycles. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2020, 246, 122790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, A.; Kaur, H. Response Surface Optimization of Rhodamine B Dye Removal Using Paper Industry Waste as Adsorbent. Int. J. Ind. Chem. 2017, 8, 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeyemo, A.A.; Adeoye, I.O.; Bello, O.S. Adsorption of Dyes Using Different Types of Clay: A Review. Appl. Water Sci. 2017, 7, 543–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salinas-Hernández, C.; Díaz-Nava, M.C.; Solache-Ríos, M. Sorption and Desorption of Red 5 and Yellow 6 by a Fe-Zeolitic Tuff. Water. Air. Soil Pollut. 2012, 223, 4959–4968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Zhan, Y.; Wan, X.; He, S.; Yang, X.; Hu, J.; Zhang, G. Selective and Efficient Adsorption of Anionic Dyes by Core/Shell Magnetic MWCNTs Nano-Hybrid Constructed through Facial Polydopamine Tailored Graft Polymerization: Insight of Adsorption Mechanism, Kinetic, Isotherm and Thermodynamic Study. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 319, 114289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grifasi, N.; Ziantoni, B.; Fino, D.; Piumetti, M. Fundamental Properties and Sustainable Applications of the Natural Zeolite Clinoptilolite. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senila, M.; Cadar, O. Modification of Natural Zeolites and Their Applications for Heavy Metal Removal from Polluted Environments: Challenges, Recent Advances, and Perspectives. Heliyon 2024, 10, e25303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorodylova, N.; Michel, C.; Seron, A.; Joulian, C.; Delorme, F.; Bresch, S.; Garreau, C.; Giovannelli, F.; Michel, K. Modified Zeolite-Supported Biofilm in Service of Pesticide Biodegradation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 45296–45316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nhung, N.T.H.; Long, V.D.; Fujita, T. A Critical Review of Snail Shell Material Modification for Applications in Wastewater Treatment. Materials 2023, 16, 1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vakili, M.; Deng, S.; Shen, L.; Shan, D.; Liu, D.; Yu, G. Regeneration of Chitosan-Based Adsorbents for Eliminating Dyes from Aqueous Solutions. Sep. Purif. Rev. 2019, 48, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Wang, X. Adsorption of Ni(II) from Aqueous Solution Using Oxidized Multiwall Carbon Nanotubes. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2006, 45, 9144–9149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machida, M.; Mochimaru, T.; Tatsumoto, H. Lead(II) Adsorption onto the Graphene Layer of Carbonaceous Materials in Aqueous Solution. Carbon N. Y. 2006, 44, 2681–2688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayanda, O.S.; Mmuoegbulam, A.O.; Okezie, O.; Durumin Iya, N.I.; Mohammed, S.E.; James, P.H.; Muhammad, A.B.; Unimke, A.A.; Alim, S.A.; Yahaya, S.M. Recent Progress in Carbon-Based Nanomaterials: Critical Review. J. Nanopart. Res. 2024, 26, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, A.; Sharma, A.; Yadav, S.; Jule, L.T.; Krishnaraj, R. Nanomaterials for Remediation of Environmental Pollutants. Bioinorg. Chem. Appl. 2021, 2021, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asghar, N.; Hussain, A.; Nguyen, D.A.; Ali, S.; Hussain, I.; Junejo, A.; Ali, A. Advancement in nanomaterials for environmental pollutants remediation: A systematic review on bibliometrics analysis, material types, synthesis pathways, and related mechanisms. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2024, 22, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, L.; Catrina, G.-A.; Cernica, G.; Staicu, V.; Popescu, M.; Covaliu, C.I. Removal of Metals from Aqueous Solutions Using Sea Buckthorn Waste from Dietary Supplement Technology. Sustainability 2021, 13, 1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, M.Y.; Juang, R.S. Adsorption of Tannic Acid, Humic Acid, and Dyes from Water Using the Composite of Chitosan and Activated Clay. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2004, 278, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, L.S.; Lima, L.C.B.; Silva, F.C.; Matos, J.M.E.; Santos, M.R.M.C.; Santos Júnior, L.S.; Sousa, K.S.; da Silva Filho, E.C. Dye Anionic Sorption in Aqueous Solution onto a Cellulose Surface Chemically Modified with Aminoethanethiol. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 218, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, L.; Wang, L.; Li, F.; Tian, G.; Li, J.; Cai, Z.; Zhou, J.; Fu, Y. A Life-Cycle Integrated Model for Product Eco-Design in the Conceptual Design Phase. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 363, 132516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thoma, G.J.; Ellsworth, S.W.; Yan, M.J. Chapter 1: Principles of Green Food Processing (Including Lifecycle Assessment and Carbon Footprint). RSC Green Chem. 2018, 2018, 1–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngeno, E.C.; Mbuci, K.E.; Necibi, M.C.; Shikuku, V.O.; Olisah, C.; Ongulu, R.; Matovu, H.; Ssebugere, P.; Abushaban, A.; Sillanpää, M. Sustainable Re-Utilization of Waste Materials as Adsorbents for Water and Wastewater Treatment in Africa: Recent Studies, Research Gaps, and Way Forward for Emerging Economies. Environ. Adv. 2022, 9, 100282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez-Martín, A.; Sánchez-Martín, M.J.; Pose-Juan, E.; Rodríguez-Cruz, M.S. Effect of Different Rates of Spent Mushroom Substrate on the Dissipation and Bioavailability of Cymoxanil and Tebuconazole in an Agricultural Soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 550, 495–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrero-Hernández, E.; Andrades, M.S.; Marín-Benito, J.M.; Sánchez-Martín, M.J.; Rodríguez-Cruz, M.S. Field-Scale Dissipation of Tebuconazole in a Vineyard Soil Amended with Spent Mushroom Substrate and Its Potential Environmental Impact. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2011, 74, 1480–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Cruz, M.S.; Herrero-Hernández, E.; Ordax, J.M.; Marín-Benito, J.M.; Draoui, K.; Sánchez-Martín, M.J. Adsorption of Pesticides by Sewage Sludge, Grape Marc, Spent Mushroom Substrate and by Amended Soils. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2012, 92, 933–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marín-Benito, J.M.; Rodríguez-Cruz, M.S.; Andrades, M.S.; Sánchez-Martín, M.J. Assessment of Spent Mushroom Substrate as Sorbent of Fungicides: Influence of Sorbent and Sorbate Properties. J. Environ. Qual. 2012, 41, 814–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, J.A. Pesticide Manual 19th Edition-BCPC British Crop Production Council: BCPC British Crop Production Council. Available online: https://www.bcpc.org/product/the-pesticide-manual-19th-edition (accessed on 8 August 2024).
- Kulshreshtha, S. Removal of pollutants using spent mushrooms substrates. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2019, 17, 833–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freed, V.H.; Haque, R. Environmental Daynamics of Pesticides. Soil Sci. 1976, 121, 377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, R.; Sahoo, S.; Singh, H.; Nath, S. Humus Pesticide Interaction: The Fate of Pesticide in Soil Environment: An Overview. Int. J. Chem. Stud. 2019, 7, 3117–3123. [Google Scholar]
- Villaverde, J.; Kah, M.; Brown, C.D. Adsorption and Degradation of Four Acidic Herbicides in Soils from Southern Spain. Pest Manag. Sci. 2008, 64, 703–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kah, M.; Brown, C.D. Adsorption of Ionisable Pesticides in Soils. Rev. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2006, 188, 149–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butkovskyi, A.; Jing, Y.; Bergheim, H.; Lazar, D.; Gulyaeva, K.; Odenmarck, S.R.; Norli, H.R.; Nowak, K.M.; Miltner, A.; Kästner, M.; et al. Retention and Distribution of Pesticides in Planted Filter Microcosms Designed for Treatment of Agricultural Surface Runoff. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 778, 146114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blachnio, M.; Kusmierek, K.; Swiatkowski, A.; Derylo-Marczewska, A. Waste-Based Adsorbents for the Removal of Phenoxyacetic Herbicides from Water: A Comprehensive Review. Sustainability 2023, 15, 16516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ćwieląg-Piasecka, I.; Medyńska-Juraszek, A.; Jerzykiewicz, M.; Dębicka, M.; Bekier, J.; Jamroz, E.; Kawałko, D. Humic Acid and Biochar as Specific Sorbents of Pesticides. J. Soils Sediments 2018, 18, 2692–2702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milori, D.M.B.P.; Martin-Neto, L.; Bayer, C.; Mielniczuk, J.; Bagnato, V.S. Humification Degree of Soil Humic Acids Determined by Fluorescence Spectroscopy. Soil Sci. 2002, 167, 739–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, A.H.; de Oliveira, L.C.; Bellin, I.C.; Rocha, J.C.; Romão, L.P.C.; Dias Filho, N.L. Influence of Alkaline Extraction on the Characteristics of Humic Substances in Brazilian Soils. Thermochim. Acta 2005, 433, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barančíková, G.; Jarzykiewicz, M.; Gömöryová, E.; Tobiašová, E.; Litavec, T. Changes in Forest Soil Organic Matter Quality Affected by Windstorm and Wildfire. J. Soils Sediments 2018, 18, 2738–2747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loffredo, E.; Senesi, N. The Role of Natural Organic Matter (Humic Substances) on Adsorption of Pesticides Possessing Endocrine Disruptor Activity. In The Fate of Persistent Organic Pollutants in the Environment; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2007; pp. 369–383. ISBN 978-1-4020-6642-9. [Google Scholar]
- André, C.; Truong, T.T.; Robert, J.F.; Thomassin, M.; Guillaume, Y.C. Construction and Evaluation of a Humic Acid Column: Implication for Pesticide Risk Assessment. Anal. Chem. 2005, 77, 4201–4206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Doherty, J.; Zhao, B.; Kinchla, A.J.; Clark, J.M.; He, L. Effectiveness of Commercial and Homemade Washing Agents in Removing Pesticide Residues on and in Apples. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 9744–9752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senesi, N.; Loffredo, E.; D’Orazio, V.; Brunetti, G.; Miano, T.M.; La Cava, P. Adsorption of Pesticides by Humic Acids from Organic Amendments and Soils. In Humic Substances and Chemical Contaminants; Clapp, C.E., Hayes, M.H.B., Senesi, N., Bloom, P.R., Jardine, P.M., Eds.; Soil Science Social America: Madison, WI, USA, 2015; pp. 129–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amalina, F.; Razak, A.S.A.; Krishnan, S.; Sulaiman, H.; Zularisam, A.W.; Nasrullah, M. Biochar Production Techniques Utilizing Biomass Waste-Derived Materials and Environmental Applications—A Review. J. Hazard. Mater. Adv. 2022, 7, 100134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Issaka, E.; Fapohunda, F.O.; Amu-Darko, J.N.O.; Yeboah, L.; Yakubu, S.; Varjani, S.; Ali, N.; Bilal, M. Biochar-Based Composites for Remediation of Polluted Wastewater and Soil Environments: Challenges and Prospects. Chemosphere 2022, 297, 134163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haider, F.U.; Wang, X.; Zulfiqar, U.; Farooq, M.; Hussain, S.; Mehmood, T.; Naveed, M.; Li, Y.; Liqun, C.; Saeed, Q.; et al. Biochar Application for Remediation of Organic Toxic Pollutants in Contaminated Soils; An Update. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 248, 114322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, P.; Zou, Z.; Li, X.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, L.; Fu, J.; Wenyan, H. Biochar Changed the Distribution of Imidacloprid in a Plant–Soil–Groundwater System. Chemosphere 2022, 307, 136213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.Y.; Huang, W.D.; Guo, J.J.; Yang, Y.; Tao, R.; Feng, X. Use of Fe-Impregnated Biochar to Efficiently Sorb Chlorpyrifos, Reduce Uptake by Allium fistulosum L., and Enhance Microbial Community Diversity. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 5238–5243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, X.; Jiang, H.; Zhao, M.; Suo, F.; Zhang, C.; Zheng, H.; Sun, K.; Zhang, G.; Li, F.; Li, Y. Biochar Reduced Chinese Chive (Allium tuberosum) Uptake and Dissipation of Thiamethoxam in an Agricultural Soil. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 390, 121749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Cao, J.; Mao, L.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, H.; Zheng, Y.; Liu, X. Effect of H3PO4-Modified Biochar on the Fate of Atrazine and Remediation of Bacterial Community in Atrazine-Contaminated Soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 851, 158278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.; Liu, X.; Wu, X.; Dong, F.; Xu, J.; Zheng, Y. Sorption, Degradation and Bioavailability of Oxyfluorfen in Biochar-Amended Soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 658, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hameed, R.; Li, G.; Son, Y.; Fang, H.; Kim, T.; Zhu, C.; Feng, Y.; Zhang, L.; Abbas, A.; Zhao, X.; et al. Structural Characteristics of Dissolved Black Carbon and Its Interactions with Organic and Inorganic Contaminants: A Critical Review. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 872, 162210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, K.; Siwal, S.S.; Sithole, T.; Singh, N.; Hart, P.; Thakur, V.K. Biorenewable Materials for Water Remediation: The Central Role of Cellulose in Achieving Sustainability. J. Bioresour. Bioprod. 2023, 9, 253–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ban, S.E.; Lee, E.J.; Yoon, J.; Lim, D.J.; Kim, I.S.; Lee, J.W. Role of Cellulose and Lignin on Biochar Characteristics and Removal of Diazinon from Biochar with a Controlled Chemical Composition. Ind. Crops Prod. 2023, 200, 116913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, R.; Hu, J.; Sun, Y.; Lu, P. Physicochemical and Adsorption Characteristics of Activated Carbons from Cellulose, Xylan and Lignin. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2023, 173, 106067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peter, Z. Order in Cellulosics: Historical Review of Crystal Structure Research on Cellulose. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 254, 117417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Gao, M.; Ding, W.; Huang, C.; Hu, C.; Shi, B.; Tsang, D.C.W. Selective Degradation and Oxidation of Hemicellulose in Corncob to Oligosaccharides: From Biomass into Masking Agent for Sustainable Leather Tanning. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 413, 125425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Zhou, H.; Hao, L.; Chen, H.; Zhou, X. Natural Rosin Modified Carboxymethyl Cellulose Delivery System with Lowered Toxicity for Long-Term Pest Control. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 259, 117749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, S.; Sharma, B.; Verma, A.; Chaudhary, J.; Tamulevicius, S.; Thakur, V.K. Recent Progress in Sodium Alginate Based Sustainable Hydrogels for Environmental Applications. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 198, 143–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Yu, P.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, P.; Yan, W.; Guo, B.; Huang, C.; Jiang, Q. Evaluating the Bio-Application of Biomacromolecule of Lignin-Carbohydrate Complexes (LCC) from Wheat Straw in Bone Metabolism via ROS Scavenging. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 176, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelhameed, R.M.; Abdel-Gawad, H.; Emam, H.E. Macroporous Cu-MOF@cellulose Acetate Membrane Serviceable in Selective Removal of Dimethoate Pesticide from Wastewater. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Saito, T.; Bergström, L.; Isogai, A. Acid-Free Preparation of Cellulose Nanocrystals by TEMPO Oxidation and Subsequent Cavitation. Biomacromolecules 2018, 19, 633–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Dong, H.; Zhang, Z.; Bian, H.; Yong, Q. Procuring the Nano-Scale Lignin in Prehydrolyzate as Ingredient to Prepare Cellulose Nanofibril Composite Film with Multiple Functions. Cellulose 2020, 27, 9355–9370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghali, A.E.; Baouab, M.H.V.; Roudesli, M.S. Aminated Cotton Fibers Loaded with Copper(II) Ions for Enhanced Pesticide Removal Performance from Water in a Laboratory Scale Batch. Ind. Crops Prod. 2012, 39, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelhameed, R.M.; El-Zawahry, M.; Emam, H.E. Efficient Removal of Organophosphorus Pesticides from Wastewater Using Polyethylenimine-Modified Fabrics. Polymer 2018, 155, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhir, B. Nanomaterials for Remediation of Pesticides. In New Frontiers of Nanomaterials in Environmental Science; Springer: Singapore, 2021; pp. 193–204. ISBN 9789811592393. [Google Scholar]
- Rani, M.; Shanker, U.; Jassal, V. Recent Strategies for Removal and Degradation of Persistent & Toxic Organochlorine Pesticides Using Nanoparticles: A Review. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 190, 208–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, P.; Liu, Y.; Guo, L.; Zeng, J.; Lu, H. Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes as Solid-Phase Extraction Adsorbent for the Preconcentration of Trace Metal Ions and Their Determination by Inductively Coupled Plasma Atomic Emission Spectrometry. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2004, 19, 1489–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savage, N.; Diallo, M.S. Nanomaterials and Water Purification: Opportunities and Challenges. J. Nanopart. Res. 2005, 7, 331–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Duan, L.; Zhu, D. Adsorption of Polar and Nonpolar Organic Chemicals to Carbon Nanotubes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 8295–8300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, S.C.; Rodrigues, D.F. Carbon-Based Nanomaterials for Removal of Chemical and Biological Contaminants from Water: A Review of Mechanisms and Applications. Carbon N. Y. 2015, 91, 122–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willner, M.R.; Vikesland, P.J. Nanomaterial Enabled Sensors for Environmental Contaminants. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2018, 16, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Biosorption Source | Biosorbent | Pollutant | Biosorption Capacity | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Agricultural wastes | Cucumber peels modified with ZnO nanoparticles | Metribuzin | 200 mg g−1 | [40] |
| cantaloupe seed shell powder | Butachlor | 142.857 mg g−1 | [41] | |
| Coffee residues | Dyes and heavy metals | 70 mg/g | [42] | |
| Wood sawdust, tree bark and wood chips | Dyes | [43] | ||
| Rice straw | Heavy metals | 0.1 g/35 ppm Zn (II); 0.1 g/70 ppm Cd (II) | [44] | |
| Agro-industrial | Wood charcoal, fly ash, coconut charcoal, saw dust, coconut fiber, bagasse charcoal | Atrazine | 5 g/0.05 or 0.1 ppm atrazine | [45] |
| Lignocellulosic substrate | Terbumeton, desethyl terbumeton, dimetomorph | 1- 8 g kg−1 | [46] | |
| Chitosan | chitosan-zinc oxide nanoparticles | Permethrin | 0.5 g per 0.1 mg L−1 permethrin | [47] |
| Industrial wastes | Oat bran, chitosan, alginate, tree bark, coconut fiber, and lignin | Heavy metals | [48] | |
| Coal fly ash | Metribuzin, metolachlor, atrazine | 0.20, 0.28, and 0.38 mg g−1 | [49] | |
| Microbial materials | Fungus Pleurotus mutilus | Metribuzin | 3 g per 200 mg L−1 | [50] |
| fungi, bacteria, yeasts | heavy metal | [51,52] | ||
| Activated sludge | Dyes | [53,54] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gad, M.F.; Todorova, T.I.; Mossa, A.-T.H. Eco-Friendly Adsorbents: Innovative Strategies for Pesticide Removal from Soil and Wastewater. Sustainability 2025, 17, 10477. https://doi.org/10.3390/su172310477
Gad MF, Todorova TI, Mossa A-TH. Eco-Friendly Adsorbents: Innovative Strategies for Pesticide Removal from Soil and Wastewater. Sustainability. 2025; 17(23):10477. https://doi.org/10.3390/su172310477
Chicago/Turabian StyleGad, Marwa F., Teodora I. Todorova, and Abdel-Tawab H. Mossa. 2025. "Eco-Friendly Adsorbents: Innovative Strategies for Pesticide Removal from Soil and Wastewater" Sustainability 17, no. 23: 10477. https://doi.org/10.3390/su172310477
APA StyleGad, M. F., Todorova, T. I., & Mossa, A.-T. H. (2025). Eco-Friendly Adsorbents: Innovative Strategies for Pesticide Removal from Soil and Wastewater. Sustainability, 17(23), 10477. https://doi.org/10.3390/su172310477








