A Review of the Characteristics and Mechanisms of Water Environment Evolution in Hulun Lake Under the Dual Drivers of Climate Warming-Drying and Human Activities
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Search Process Description
2.1. Review Questions
- (1)
- How have the hydrological dynamics (e.g., water level, water balance) of Hulun Lake evolved, and what are the relative roles of climate variability and anthropogenic factors in driving these changes?
- (2)
- What are the spatiotemporal patterns and trends of water quality degradation, particularly eutrophication, in Hulun Lake?
- (3)
- What are the key pathways and magnitudes of external nutrient loading and internal nutrient release from sediments?
- (4)
- How do specific human activities (e.g., overgrazing, land use change, water diversion) impact the lake’s water environment and ecosystem health?
2.2. Search Strategy and Keywords
- (1)
- Location: “Hulun Lake” OR “Hu Lun Hu” OR “Dalai Lake” OR “Hulun Nur”.
- (2)
- Theme: “water quality” OR “eutrophication” OR “hydrolog*” OR “water level” OR “nutrient” OR “pollution” OR “sediment” OR “climate change” OR “human activity” OR “grazing” OR “ecological effect”.
2.3. Information Sources and Search String
- (1)
- Web of Science Core Collection
- (2)
- China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI)
2.4. Eligibility Criteria
- (1)
- Studies focused on Hulun Lake or its basin.
- (2)
- Research articles, review articles, and conference proceedings that provided original data, analysis, or synthesis on the lake’s hydrology, water quality, sediment, biogeochemistry, ecology, or related driving mechanisms.
- (3)
- Publications within the timeframe of 1949–2025.
- (1)
- Studies not primarily focused on Hulun Lake.
- (2)
- Duplicate publications.
- (3)
- Articles for which the full text could not be retrieved.
2.5. Study Selection and Data Extraction
- (1)
- Bibliographic information (authors, year, title).
- (2)
- Study focus (e.g., hydrology, water quality, sediment, ecology).
- (3)
- Key methods used (e.g., field monitoring, remote sensing, modeling, geochemical analysis).
- (4)
- Temporal and spatial scale of the study.
- (5)
- Main findings related to the review questions (e.g., trends in water level, nutrient concentrations, identified driving factors, ecological impacts).
3. Evolution and Integration of Research Methods
3.1. Remote Sensing and Machine Learning Technologies
3.2. Geochemical and Sediment Analysis
3.3. Numerical Models and Driving Mechanism Analysis
3.4. Limitations and Challenges of Existing Research Methods
3.5. The Impact of Data and Artificial Intelligence on Research Paradigms
4. Hydrological Dynamics and Driving Mechanisms
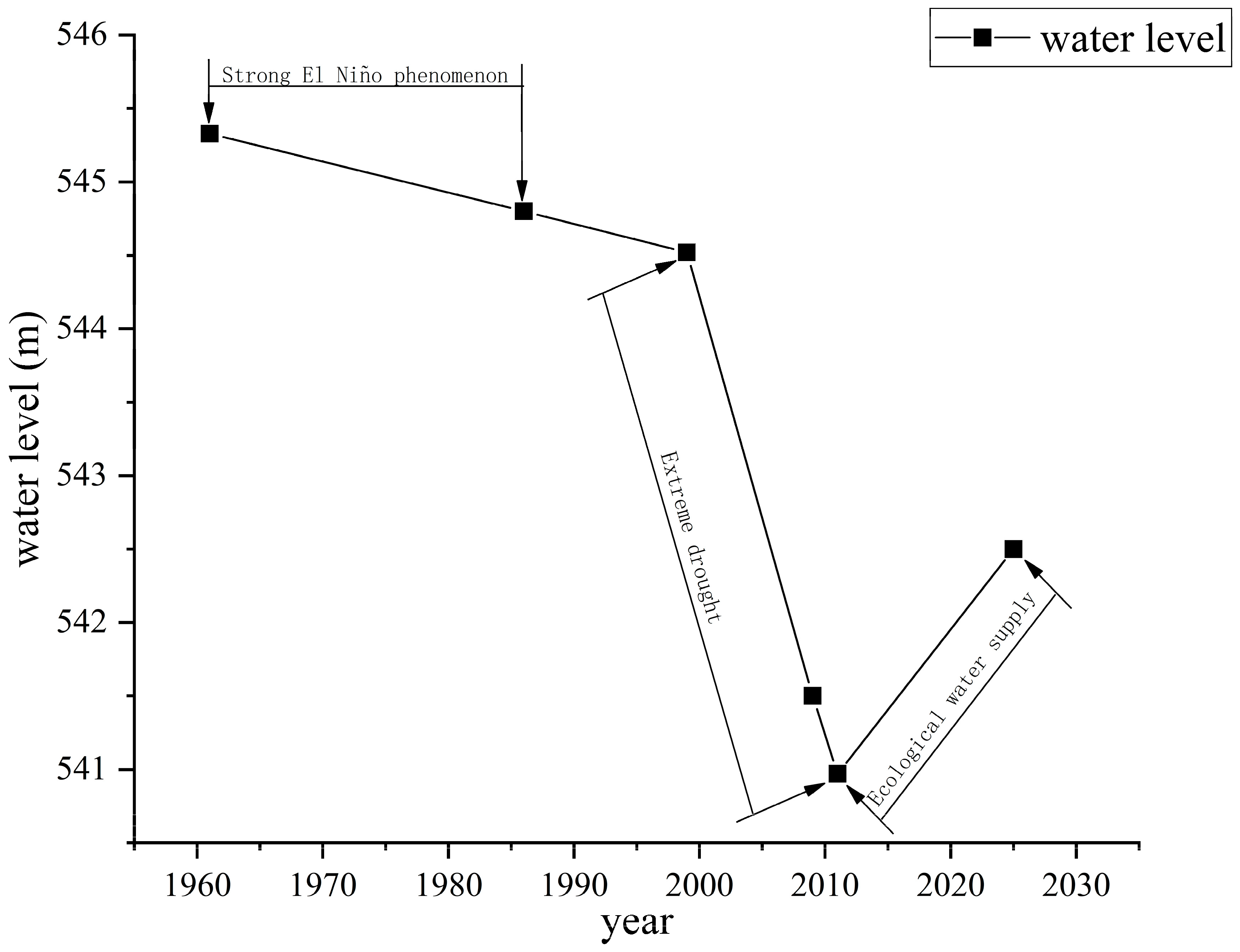
4.1. Phased Water Level Changes and Shift in Driving Mechanisms
4.2. Dual Pressures of Water Imbalance
4.3. Multi-Period Coupling Mechanism of Water Level Fluctuations
4.4. Spatially Heterogeneous Response
5. Water Quality Evolution and Eutrophication Process
5.1. Eutrophication Process
5.2. Spatiotemporal Heterogeneity of Water Quality
5.3. Sediment Pollution and Internal Release Mechanisms
5.4. External Drivers of Eutrophication
6. Watershed Human Activities and Water Environment Response
6.1. Hydrological and Ecological Effects of Land Use Change
6.2. Pollution Pathways and Ecological Impacts of Overgrazing
6.3. Ecological Security Assessment
7. Conclusions
- Implement Smart Water Resource Management Centered on Ecological Flow:
- 2.
- Enforce Precision Grazing Regulation Based on Watershed Carrying Capacity:
- 3.
- Construct an Integrated Watershed Management System Synergizing Water Quantity, Quality, and Ecology:
8. Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tao, S.L.; Fang, J.Y.; Zhao, X.; Zhao, S.Q.; Shen, H.H.; Hu, H.F.; Tang, Z.Y.; Wang, Z.H.; Guo, Q.H. Rapid loss of lakes on the Mongolian Plateau. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 2281–2286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, H.; Tang, J.P.; Cheng, L.; Li, M.C. Ensemble projections of climate and streamflow in a typical basin of semi-arid steppes in Mongolian Plateau of 2021–2100. Adv. Clim. Change Res. 2024, 15, 230–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williamson, C.E.; Saros, J.E.; Vincent, W.F.; Smol, J.P. Lakes and reservoirs as sentinels, integrators, and regulators of climate change. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2009, 54, 2273–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adrian, R.; O’Reilly, C.M.; Zagarese, H.; Baines, S.B.; Hessen, D.O.; Keller, W.; Livingstone, D.M.; Sommaruga, R.; Straile, D.; Donk, E.V. Lakes as sentinels of climate change. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2009, 54, 2283–2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maberly, S.C.; O’Donnell, R.A.; Woolway, R.I.; Cutler, M.E.J.; Tyler, A.N. Global lake thermal regions shift under climate change. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, X.Y.; Yang, J.; Hao, J.X.; Bu, T.G.; Liu, Z.G. The formation history and changes of Hulun Lake. Inn. Mong. Sci. Technol. Econ. 2015, 1, 43–47. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.K.; Wang, S.M. Comparison of Hulun Lake surface fluctuation, peat development, eolian sand paleosol sequence and its paleoclimatic significance since 13 ka. J. Arid Land Res. Environ. 2000, 3, 56–59. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, Z.S.; Jin, T.Y.; Li, C.Y.; Ofterdinger, U.; Zhang, S.; Ding, A.Z.; Li, J.C. Is China’s fifth-largest inland lake to dry-up? Incorporated hydrological and satellite-based methods for forecasting Hulun lake water levels. Adv. Water Resour. 2016, 94, 185–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.L.; Sun, B.; Shi, X.H.; Tao, Y.L.; Wang, Z.L.; Wang, S.H.; Ye, B.W. The Relationship Between Riparian Soil Nutrients and Water Quality in Inlet Sections of Lakes: A Case Study of the Kherlen River. Sustainability 2025, 17, 1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Yinglan, A.; Wang, Y.T.; Fang, Q.Q.; Tang, R. Study on remote sensing inversion and temporal-spatial variation of Hulun lake water quality based on machine learning. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2024, 260, 104282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Schuster, M.; Xin, S.W.; Zainescu, F.; Xue, X.Y.; Storms, J.; May, J.H.; Nutz, A.; van der Vegt, H.; Bozetti, G.; et al. Littoral landforms of Lake Hulun and Lake Buir (China and Mongolia): Wind-driven hydrosedimentary dynamics and resulting clastics distribution. J. Palaeogeogr. 2024, 13, 309–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.L.; A, Y.L.; Wang, L.B.; Xue, B.L.; Wang, Y.T.; Zhou, X.Y.; Ma, G.W.; Li, H.; Chen, H.; Liao, T.K.; et al. Review on the Collaborative Research of Water Resources-Water Environment-Water Ecology in Hulun Lake. Water 2024, 16, 2508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, S.Y.; Xu, W.J.; Zhang, B.; Yi, L.X.; Lu, X.Q. Geochemical Characteristics and Their Environmental Implications for the Water Regime of Hulun Lake, Inner Mongolia, China. Water 2022, 14, 3696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.N.; Zhang, F.J.; Ran, C.Q. Analysis of Climate Change in the Krulun River Basin in the Eastern Mongolian Plateau over the Past 50 Years. J. Dalian Natl. Univ. 2009, 11, 193–195. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, B.; Zhang, X.F.; Tong, Y.; Ao, W.; Wang, Z.L.; Zhu, S.L.; Wang, Y.P. Quantification of Nutrient Fluxes from Sediments of Lake Hulun, China: Implications for Plateau Lake Management. Sustainability 2023, 15, 8680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.Q.; Yao, B.; Li, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wang, S.R. Deciphering Hulun lake level dynamics and periodical response to climate change during 1961–2020. J. Hydrol.-Reg. Stud. 2023, 46, 101352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Zhang, Y.L.; Shi, X.H.; Sun, B.; Wu, L.J.; Wang, W. Driving Mechanisms of the Evolution and Ecological Water Demand of Hulun Lake in Inner Mongolia. Water 2022, 14, 3415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kravitz, J.; Matthews, M.; Bernard, S.; Griffith, D. Application of Sentinel 3 OLCI for chl-a retrieval over small inland water targets: Successes and challenges. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 237, 111562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.J.; Li, C.Y.; Li, W.P.; Zhang, S. Calculation and Analysis of Water Balance in Hulun Lake, Inner Mongolia. J. Lake Sci. 2012, 24, 273–281. [Google Scholar]
- Sagan, V.; Peterson, K.T.; Maimaitijiang, M.; Sidike, P.; Sloan, J.; Greeling, B.A.; Maalouf, S.; Adams, C. Monitoring inland water quality using remote sensing: Potential and limitations of spectral indices, bio-optical simulations, machine learning, and cloud computing. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2020, 205, 103187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.L.; Zhou, Q.; Li, T.; Wang, H.S.; Jiang, L.M.; Shen, X. Accurate estimation of lake levels by the spatio-temporal modeling of satellite altimetry data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2023, 295, 113681. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, H.; Fu, H.Y.; Chen, Z.; Liao, A.R.; Shen, M.Y.; Tao, Y.; Wu, Y.H.; Hu, H.Y. A multi-task deep neural network reveals inflowing river impacts for predictive lake management. Environ. Sci. Ecotechnol. 2025, 26, 100592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Yao, B.; Wang, S.R.; Huang, Y.Q. Understanding the changes of optically active substances (OACs) in Hulun Lake in the past 35 years and its indication to the degradation of aquatic ecology. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 377, 134286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.N.; Zhao, L.; Li, W.; Chen, J.Y.; Wang, S.H. Response mechanism of sediment organic matter of plateau lakes in cold and arid regions to climate change: A case study of Hulun Lake, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 26778–26790. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, Y.F.; Kong, X.Z.; Mao, Z.G.; Zhang, C.; Xue, B.; Shi, X.H.; Gu, X.H. Hydrological variation drives changes in food web structure and ecosystem function with potential hysteresis in a large temperate shallow lake. J. Hydrol. 2025, 650, 132463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.L.; Zhang, Y.R.; Kong, X.Z.; Zhang, S.; Xue, Y.F.; Ao, W.; Pang, B.; Dou, H.S.; Xue, B. Record-setting cyanobacterial bloom in the largest freshwater lake in northern China caused by joint effects of hydrological variations and nutrient enrichment. Environ. Res. 2025, 268, 120813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sayers, M.J.; Fahnenstiel, G.L.; Shuchman, R.A.; Bosse, K.R. A new method to estimate global freshwater phytoplankton carbon fixation using satellite remote sensing: Initial results. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2021, 42, 3708–3730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Fang, C.; Song, K.; Wang, X.; Wen, Z.; Shang, Y.; Tao, H.; Lyu, Y. Spatiotemporal variation in biomass abundance of different algal species in Lake Hulun using machine learning and Sentinel-3 images. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, A.B.G.; Teurlincx, S.; Beusen, A.H.W.; Huijbregts, M.A.J.; Rost, J.; Schipper, A.M.; Seelen, L.M.S.; Mooij, W.M.; Janse, J.H. PCLake plus: A process-based ecological model to assess the trophic state of stratified and non-stratified freshwater lakes worldwide. Ecol. Model. 2019, 396, 23–32. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Y.; Fu, C.S.; Wang, X.; Dong, L.Y.; Yao, S.C.; Xue, B.; Wu, H.W.; Wu, H.H. Decoding the dramatic hundred-year water level variations of a typical great lake in semi-arid region of northeastern Asia. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 770, 145353. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.L.; Leal, W.; Nagy, G.J.; Wang, J.; Ciani, A.; Sidsaph, H.; Fedoruk, M.; Yin, S.; Bao, Y.H.; Ayal, D.Y.; et al. Satellite imagery evidence for a multiannual water level decline in Hulun Lake, China, with suggestions to future policy making responses. Erde 2019, 150, 31–39. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, C.S.; Wu, H.W.; Zhu, Z.C.; Song, C.Q.; Xue, B.; Wu, H.H.; Ji, Z.M.; Dong, L.Y. Exploring the potential factors on the striking water level variation of the two largest semi-arid-region lakes in northeastern Asia. Catena 2021, 198, 105037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linderholm, H.W.; Ou, T.H.; Jeong, J.H.; Folland, C.K.; Gong, D.Y.; Liu, H.B.; Liu, Y.; Chen, D.L. Interannual teleconnections between the summer North Atlantic Oscillation and the East Asian summer monsoon. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2011, 116, 13107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.; Zhang, S.; Liu, Y.; Shi, X.H.; Zhao, S.N.; Kang, X.E.; Quan, D.; Sun, B.; Arvola, L.; Li, G.H. Spatiotemporal variation in water quality and identification and quantification of areas sensitive to water quality in Hulun lake, China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 149, 110176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, V.H. Eutrophication of freshwater and coastal marine ecosystems a global problem. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2003, 10, 126–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpenter, S.R.; Correll, D.L.; Howarth, R.W.; Sharpley, A.N.; Smith, V.H. Nonpoint pollution of surface waters with phosphorus and nitrogen. Ecol. Appl. 1998, 8, 559–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Wang, F.; Ma, Q.; Xiong, W.H. Water quality assessment and impact factor driving analysis of Hulun Lake in recent 40 years. Latit. Longit. Sky 2025, 1, 76–81. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, L.E.; Li, C.Y.; Shi, X.H.; Zhao, S.N.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, L.J. Eutrophication trend and analysis of Hulun Lake, Inner Mongolia, 2006–2015. J. Lake Sci. 2016, 28, 1265–1273. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, H.F.; Shi, X.H.; Sun, B.; Zhao, S.N.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, M.L. Analysis on water quality and eutrophication change of Hulun Lake from 2011 to 2020. Arid Zone Res. 2021, 38, 1534–1545. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Li, Y.; Yao, B.; Huang, Y.Q.; Wang, S.R.; Ni, S.Q. Untangling the coupling effect of water quality and quantity on lake algal blooms in Lake Hulun from a dual perspective of remote sensing and sediment cores. J. Hydrol. 2024, 645, 132141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.T.; Liu, Y.H.; Chen, Y.X.; Yao, Y.P.; Liu, H.Y.; Wang, Z.S. Water quality and pollution source apportionment responses to rainfall in steppe lake estuaries: A case study of Hulun Lake in northern China. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 168, 112791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Li, G.H.; Tao, Y.L.; Wang, S.H.; Yu, H.F.; Shi, X.H.; Zhao, S.N. Evolution Characteristics and Driving Factors of Cyanobacterial Blooms in Hulun Lake from 2018 to 2022. Water 2023, 15, 3765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, S.; Zhang, B.; Wang, P.F.; Li, H.; Jiang, X.; Wang, S.H. Evolution characteristics and influencing factors of fluoride in Hulun Lake. Environ. Sci. Res. 2021, 34, 841–848. [Google Scholar]
- Sondergaard, M.; Jensen, J.P.; Jeppesen, E. Role of sediment and internal loading of phosphorus in shallow lakes. Hydrobiologia 2003, 506, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.H.; Wen, Y.J.; Zhou, J.X.; Wu, Y.Y. Phosphorus release from lake sediments: Effects of pH, temperature and dissolved oxygen. Ksce J. Civ. Eng. 2014, 18, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.F.; Guo, Y.N.; Wang, G.X.; Jiang, X.; Wang, K. Distribution of phosphorus forms in Hulun Lake basin and traceability of particulate phosphorus. China Environ. Sci. 2023, 43, 4810–4818. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, W.; Yang, P.L.; Li, H.S.; Hu, G.W.; Liu, X.P. Characteristics of soil and water loss, nitrogen and phosphorus loss in three types of grassland use in Hulun Lake basin. Trans. CSAE 2011, 27, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, B.Q.; Gao, G.; Zhu, G.W.; Zhang, Y.L.; Song, Y.Z.; Tang, X.M.; Xu, H.; Deng, J.M. Lake eutrophication and its ecosystem response. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2013, 58, 961–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, C.Y.; Wang, C.Y.; Huang, L.; Gao, B.B.; Yin, W.J.; Wang, Q.T.; Chen, H.J.; Feng, Q.L.; Li, S.H.; Feng, A.P. Development of a 2022 Spatial Distribution Dataset for Surface Source Pollution Load in Grassland type Watersheds of the Krulun River Basin Integrated with Multi source Information. J. Agric. Big Data 2025, 7, 31–42. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.P.; Chen, A.H.; Yu, L.H.; Yang, W.H.; Yin, Z.Y.; Yang, P.F.; Jiao, L.Y. Pollutant flux of the main river flowing into Hulun Lake during the flood season (2010–2014). J. Lake Sci. 2016, 28, 281–286. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, W.H.; Chen, A.H.; Li, W.P.; Yu, L.H.; Yin, Z.Y.; Han, P.J.; Duan, H.J. Water quality assessment of the Klulun River and its impact on the water environment of Hulun Lake. Environ. Eng. 2015, 33, 113–116. [Google Scholar]
- Zuo, J.; Yang, S.Y.; Grossart, H.P.; Xiao, P.; Zhang, H.; Sun, R.; Li, G.Y.; Jiang, H.R.; Zhao, Q.H.; Jiao, M.; et al. Sequential decline in cyanobacterial, total prokaryotic, and eukaryotic responses to backward flow in a river connected to Lake Taihu. Water Res. 2025, 269, 122784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na, R.S.; Du, H.B.; Na, L.; Shan, Y.; He, H.S.; Wu, Z.F.; Zong, S.W.; Yang, Y.; Huang, L.R. Spatiotemporal changes in the Aeolian desertification of Hulunbuir Grassland and its driving factors in China during 1980–2015. Catena 2019, 182, 104123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, B.S.; Shan, N.; Gu, Y.Y.; Ao, W.; Pang, B.; Dou, H.S.; Wang, W.L.; Zou, C.X. Ecological security assessment and spatial-temporal distribution pattern change trend in Hulun Lake basin. Environ. Sci. Res. 2021, 34, 801–811. [Google Scholar]
- Foley, J.A. Global Consequences of Land Use. Science 2005, 309, 570–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, R.; Han, L.R.; Li, H. Study on the Change of Land Ecosystem Service Value in Hulun Lake National Nature Reserve. J. Hulunbeier Coll. 2023, 31, 86–92. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, Y.Y.; Lin, N.F.; Cao, B.S.; Ye, X.; Pang, B.; Du, W.; Dou, H.S.; Zou, C.X.; Xu, C.; Xu, D.L.; et al. Assessing the effectiveness of Ecological Conservation Red Line for mitigating anthropogenic habitat degradation in river corridors. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 154, 110742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.N.; Delgado-Baquerizo, M.; Li, G.Y.; Isbell, F.; Wang, Y.; Hautier, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xiao, Y.L.; Cai, J.T.; Pan, X.B.; et al. Experimental impacts of grazing on grassland biodiversity and function are explained by aridity. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 5040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, P.P.; Zhang, J.; Li, M.; Liu, Y.L.; Wang, X.; Yan, R.R.; Shen, B.B.; Zhang, X.; Shen, J.; Zhu, X.Y.; et al. Spatial and temporal variations in fractional vegetation cover and its driving factors in the Hulun Lake region. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 135, 108490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onda, Y.; Kato, H.; Tanaka, Y.; Tsujimura, M.; Davaa, G.; Oyunbaatar, D. Analysis of runoff generation and soil erosion processes by using environmental radionuclides in semiarid areas of Mongolia. J. Hydrol. 2007, 333, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.L.; Li, W.J.; Yan, Y.; Liu, B.; Wang, T.J.; Mao, S.C.; Song, L.H.; Dou, H.S.; Ao, W.; Zou, C.X. Organic Matter Pollution During the Spring Thaw in Hulun Lake Basin: Contribution of Multiform Human Activities. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2020, 105, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morain, A.; Nedd, R.; Poole, K.; Hawkins, L.; Jones, M.; Washington, B.; Anandhi, A. Artificial Intelligence Application in Nonpoint Source Pollution Management: A Status Update. Sustainability 2025, 17, 5810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Stage | Process Description | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Initial records identified through database searching (Web of Science, CNKI) | n = 348 records |
| 2 | Duplicates removed using reference management software and manual checking | n = 348 records |
| 3 | Records based on title and abstract against eligibility criteria | n = 98 records |
| 4 | Full-text articles assessed for eligibility | n = 63 records |
| 5 | Final number of studies included in the qualitative synthesis | n = 63 records |
| Research Method Category | Specific Techniques | Research Contents | Method Advantages and Applicability | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Remote Sensing & Machine Learning | Satellite Altimeters (TOPEX/Poseidon, Jason); Optical Sensors (Landsat, Sentinel-3); Machine Learning Algorithms (Random Forest, XGBoost) |
|
| |
| Geochemical & Sediment Analysis | Stable Isotopes (δD, δ18O); Fluorescence Spectroscopy (EEM-PARAFAC); Isotopic Dating (210Pb, 137Cs); High-Resolution Sediment Sampling |
|
| |
| Numerical Models & Driving Mechanism Analysis | Structural Equation Modeling; Watershed Hydrological Models (SWAT); Ecological Models (ECOPATH, PCLake); Hydrodynamic-Water Quality Models (GOTM-WET) |
|
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, B.; Liu, Y.; Chen, C.; Yao, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wang, L.; Wang, Z. A Review of the Characteristics and Mechanisms of Water Environment Evolution in Hulun Lake Under the Dual Drivers of Climate Warming-Drying and Human Activities. Sustainability 2025, 17, 10395. https://doi.org/10.3390/su172210395
Hu B, Liu Y, Chen C, Yao Y, Chen Y, Wang L, Wang Z. A Review of the Characteristics and Mechanisms of Water Environment Evolution in Hulun Lake Under the Dual Drivers of Climate Warming-Drying and Human Activities. Sustainability. 2025; 17(22):10395. https://doi.org/10.3390/su172210395
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Bingtao, Yuhong Liu, Cheng Chen, Yipeng Yao, Yixue Chen, Lixin Wang, and Zhongsheng Wang. 2025. "A Review of the Characteristics and Mechanisms of Water Environment Evolution in Hulun Lake Under the Dual Drivers of Climate Warming-Drying and Human Activities" Sustainability 17, no. 22: 10395. https://doi.org/10.3390/su172210395
APA StyleHu, B., Liu, Y., Chen, C., Yao, Y., Chen, Y., Wang, L., & Wang, Z. (2025). A Review of the Characteristics and Mechanisms of Water Environment Evolution in Hulun Lake Under the Dual Drivers of Climate Warming-Drying and Human Activities. Sustainability, 17(22), 10395. https://doi.org/10.3390/su172210395






