Research on the Spatiotemporal Evolution and Driving Mechanism of Urban Ecological Resilience in the Huaihe River Ecological Economic Belt
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review and Hypothesis Development
2.1. The Conceptual Evolution and Assessment of Urban Ecological Resilience
2.2. Identification of Spatial Pattern
2.3. Key Drivers and the Spatial Externality Mechanism
2.3.1. Effect of Economic Development on Urban Ecological Resilience
2.3.2. Effect of Industrial Upgrading on Urban Ecological Resilience
2.3.3. Effect of Urbanization on Urban Ecological Resilience
2.3.4. Effect of Environmental Regulations on Urban Ecological Resilience
2.3.5. Effect of Technological Innovation on Urban Ecological Resilience
2.3.6. Spatial Spillover Effects
3. Data Sources and Methodology
3.1. Research Area
3.2. Variable Selection
3.2.1. Dependent Variable: Comprehensive Urban Ecological Resilience Index
3.2.2. Core Explanatory and Control Variables
3.3. Data Sources
3.4. Methodology
3.4.1. Urban Resilience Evaluation Model
3.4.2. Kernel Density Estimation
3.4.3. Exploratory Spatial Data Analysis
- (1)
- Global Spatial Autocorrelation (Moran’s I)
- (2)
- Local Spatial Autocorrelation
- (3)
- Construction of an Improved Spatial Weight Matrix
3.4.4. Dynamic Spatial Durbin Model
4. Empirical Results and Analysis
4.1. Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Urban Ecological Resilience
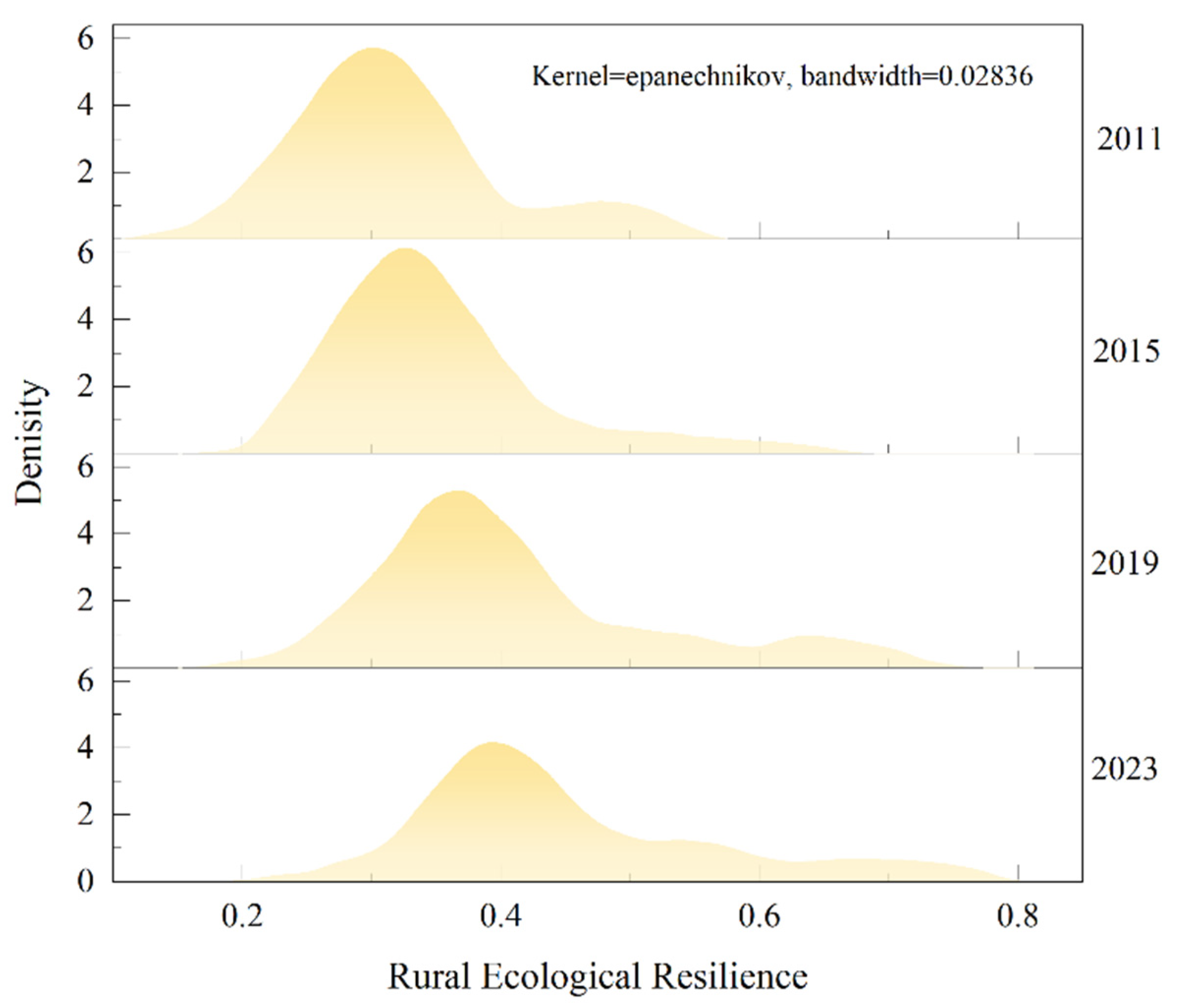
4.1.1. Temporal Patterns of Urban Ecological Resilience
4.1.2. Spatial Patterns of Urban Ecological Resilience
4.2. Spatial Evolution of Urban Ecological Resilience
4.2.1. Global Spatial Patterns
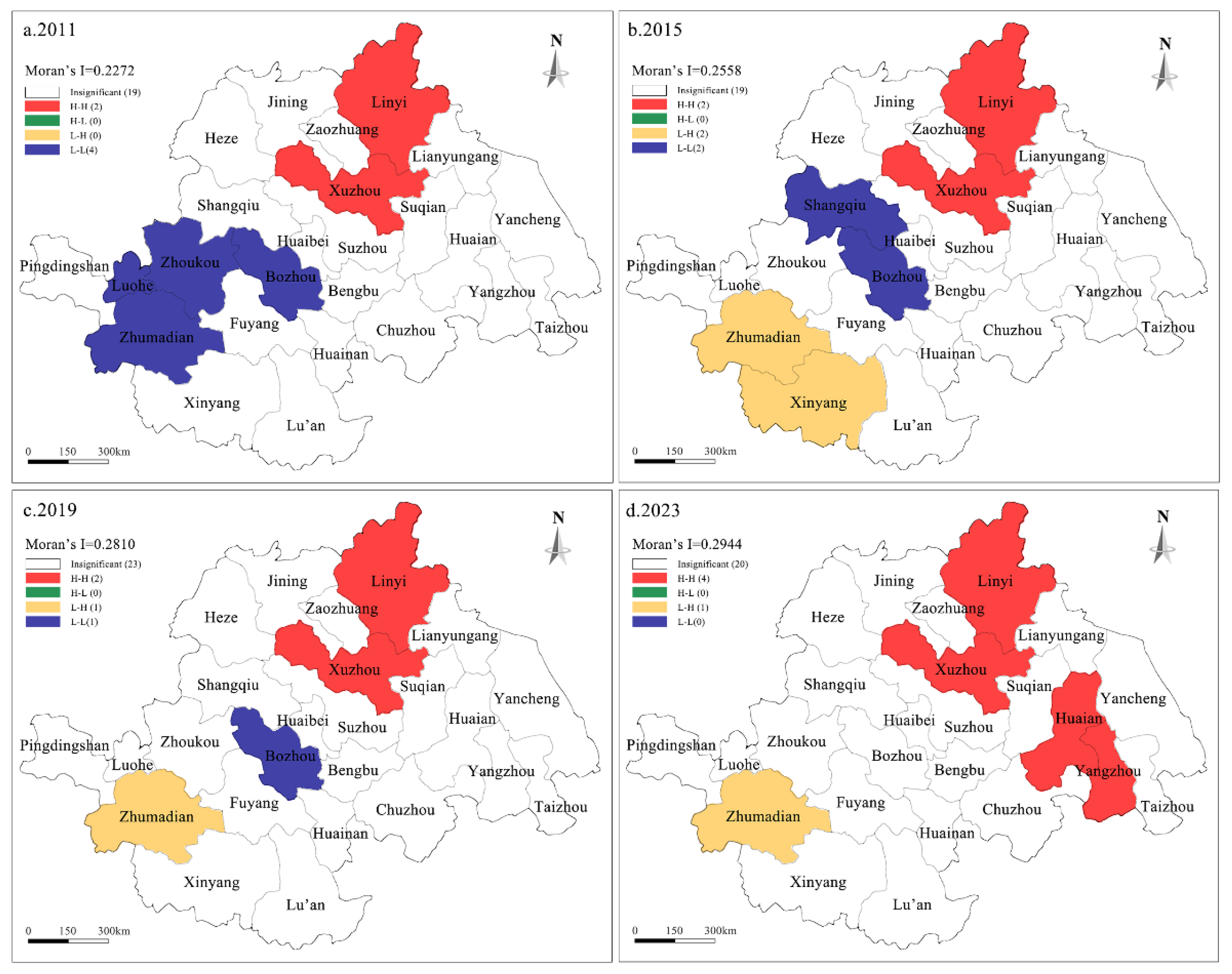
4.2.2. Local Spatial Patterns
4.3. Drivers of Urban Ecological Resilience and Spatial Interactions
4.3.1. Model Selection and Diagnostics
- (1)
- Multicollinearity Test
- (2)
- Spatial Dependence and Model Selection
- (3)
- Residual Distribution Diagnostics
- (4)
- Residual Spatial Autocorrelation Test
4.3.2. Estimation Results of the Spatial Econometric Model
4.3.3. Decomposition of Direct and Spillover Effects
4.3.4. Robustness Tests
5. Discussion
5.1. The Coexistence of Growth and Polarization in Resilience
5.2. Path Dependence and the Lock-In of Spatial Hierarchies
5.3. Direct Effects of Driving Factors
5.4. Synergy and Competition in Spatial Interactions
6. Conclusions and Police Implication
6.1. Conclusions
6.2. Policy Recommendations
- (1)
- Differentiated and Targeted Regional Governance
- (2)
- A Coordinated Governance Framework with Specific Institutions
- (3)
- Integrating Ecology and Industry through Specific Technologies
7. Limitations and Future Research Directions
7.1. Data Constraints
7.2. Potential Endogeneity Issues
7.3. Generalizability to Other Basin Regions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Indicators | Number of Missing Values | Percentage of Missing Data (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Per capita park green space area | 2 | 0.616 |
| Built-up area green coverage rate | 0 | 0.000 |
| Water area ratio | 5 | 1.538 |
| Proportion of protected areas to total land area | 2 | 0.616 |
| Comprehensive utilization rate of general industrial solid waste | 0 | 0 |
| Urban sewage treatment rate | 0 | 0 |
| Harmless treatment rate of domestic waste | 0 | 0 |
| Proportion of environmental protection expenditure to public fiscal expenditure | 0 | 0 |
| Number of green patents | 2 | 0.616 |
| Number of college students per 10,000 people | 0 | 0 |
| Proportion of high-tech enterprises to total enterprises | 6 | 1.846 |
| per capita GDP | 0 | 0 |
| the ratio of value added in the tertiary to the secondary sector | 0 | 0 |
| the proportion of built-up land area relative to total municipal land area | 0 | 0 |
| the share of environmental pollution control investment in local public expenditure | 0 | 0 |
| the number of invention patents granted per 10,000 residents | 3 | 0.923 |
| the normalized difference vegetation index | 0 | 0 |
| per capita urban road area. | 0 | 0 |
| Variables | Delete Missing Data | Using Interpolated Data | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| β | T Statistics | p-Value | β | T Statistics | p-Value | |
| LnUERt−1 | 0.268 | 3.255 | 0.001 | 0.266 | 3.291 | 0.001 |
| lnGDP | −0.301 | −3.539 | 0.001 | −0.301 | −3.547 | 0.000 |
| ln(GDP) 2 | 0.222 | 4.021 | 0.005 | 0.224 | 4.037 | 0.005 |
| lnIU | −0.110 | −1.866 | 0.030 | −0.105 | −1.887 | 0.032 |
| lnUL | −0.295 | −3.844 | 0.005 | −0.296 | −3.838 | 0.006 |
| lnER | −0.190 | −2.917 | 0.002 | −0.191 | −2.914 | 0.001 |
| lnTI | 0.229 | 3.094 | 0.007 | 0.239 | 3.287 | 0.005 |
| lnEE | 0.143 | 3.901 | 0.001 | 0.143 | 3.920 | 0.000 |
| lnIL | 0.092 | 3.004 | 0.001 | 0.095 | 3.175 | 0.001 |
| lnOP | 0.088 | 2.658 | 0.017 | 0.084 | 2.926 | 0.016 |
| lnPD | −0.095 | −2.470 | 0.002 | −0.098 | −2.466 | 0.002 |
| W × lnGDP | −0.149 | −3.355 | 0.004 | −0.147 | −3.681 | 0.003 |
| W × lnIU | 0.236 | 2.760 | 0.001 | 0.236 | 2.794 | 0.001 |
| W × lnUL | 0.086 | 3.158 | 0.000 | 0.085 | 3.495 | 0.001 |
| W × lnER | −0.059 | −1.602 | 0.025 | −0.054 | −1.588 | 0.029 |
| W × lnTI | 0.201 | 3.385 | 0.000 | 0.166 | 3.085 | 0.002 |
| ρ | 0.300 | 2.994 | 0.002 | 0.304 | 3.227 | 0.001 |
| R2 | 0.802 | 0.811 | ||||
| N | 325 | 325 | ||||
| Variables | Static SDM | Dynamic SDM | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model I (Geographic Distance Matrix) | Model II (Economic Distance Matrix) | Model IV (Geographic Distance Matrix) | Model V (Economic Distance Matrix) | |||||
| β | p-Value | β | p-Value | β | p-Value | β | p-Value | |
| LnUERt−1 | 0.353 | 0.014 | 0.192 | 0.001 | ||||
| lnGDP | −0.372 | 0.022 | −0.465 | 0.001 | −0.264 | 0.001 | −0.240 | 0.001 |
| ln(GDP) 2 | 0.134 | 0.016 | 0.222 | 0.016 | 0.150 | 0.009 | 0.212 | 0.005 |
| lnIU | −0.180 | 0.028 | −0.315 | 0.024 | −0.088 | 0.033 | −0.255 | 0.011 |
| lnUL | −0.289 | 0.003 | −0.077 | 0.019 | −0.161 | 0.007 | −0.152 | 0.002 |
| lnER | −0.082 | 0.059 | −0.176 | 0.033 | −0.147 | 0.016 | −0.380 | 0.000 |
| lnTI | 0.104 | 0.018 | 0.280 | 0.000 | 0.163 | 0.055 | 0.272 | 0.028 |
| lnEE | 0.255 | 0.000 | 0.106 | 0.005 | 0.227 | 0.001 | 0.219 | 0.009 |
| lnIL | 0.261 | 0.001 | 0.133 | 0.002 | 0.183 | 0.003 | 0.112 | 0.002 |
| lnOP | 0.112 | 0.377 | 0.062 | 0.206 | 0.045 | 0.100 | 0.099 | 0.017 |
| W × lnGDP | 0.108 | 0.011 | −0.210 | 0.020 | 0.238 | 0.013 | −0.179 | 0.011 |
| W × lnIU | 0.340 | 0.003 | 0.259 | 0.015 | 0.265 | 0.024 | 0.274 | 0.003 |
| W × lnUL | 0.062 | 0.005 | 0.216 | 0.002 | 0.114 | 0.005 | 0.135 | 0.006 |
| W × lnER | 0.044 | 0.281 | −0.122 | 0.168 | 0.088 | 0.299 | −0.068 | 0.185 |
| W × lnTI | 0.207 | 0.000 | 0.153 | 0.000 | 0.090 | 0.004 | 0.148 | 0.002 |
| ρ | 0.345 | 0.001 | 0.297 | 0.002 | 0.311 | 0.000 | 0.292 | 0.001 |
| R2 | 0.725 | 0.782 | 0.749 | 0.736 | ||||
| N | 325 | 325 | 325 | 325 | ||||
References
- Wang, H.; Feng, R.; Li, X.; Yang, Y.; Pan, Y. Land use change and its impact on ecological risk in the Huaihe River Eco-Economic Belt. Land 2023, 12, 1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; He, G.; Zhang, G.; Wang, X.; Yang, C. Research on Spatio-Temporal Characteristics and Obstacle Diagnosis of Ecosystem Security in Huaihe River Economic Belt. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2021, 30, 5377–5389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunderson, L.H. Ecological resilience—In theory and application. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 2000, 31, 425–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickett, S.T.; McGrath, B.; Cadenasso, M.L.; Felson, A.J. Ecological resilience and resilient cities. Build. Res. Inf. 2014, 42, 143–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaker, R.R.; Mackay, B.R. Hidden patterns of sustainable development in Asia with underlying global change correlations. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 131, 108227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.; Chen, Y.; Zheng, X.; Li, H.; Chen, Y.; Kong, L.; Ou, C. Spatiotemporal characteristics and influential factors of coupling coordination degree of urbanization and ecological environment in the Huaihe River ecological economic belt. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 12287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holling, C.S. Resilience and stability of ecological systems. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 1973, 4, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozza, A.; Asprone, D.; Fabbrocino, F. Urban resilience: A civil engineering perspective. Sustainability 2017, 9, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Wu, T. Ecological resilience as a foundation for urban design and sustainability. In Resilience in Ecology and Urban Design: Linking Theory and Practice for Sustainable Cities; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2012; pp. 211–229. [Google Scholar]
- Nunes, D.M.; Pinheiro, M.D.; Tomé, A. Does a review of urban resilience allow for the support of an evolutionary concept? J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 244, 422–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bautista-Puig, N.; Benayas, J.; Manana-Rodríguez, J.; Suárez, M.; Sanz-Casado, E. The role of urban resilience in research and its contribution to sustainability. Cities 2022, 126, 103715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.M.; Niu, J.L. Spatio-temporal evolution and influencing factors of urban ecological resilience in the Yellow River Basin. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2023, 43, 8309–8320. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yu, X.; Liu, Y.; He, H.; Yang, B. Revealing the Spatial Effects of New-Type Urbanization on Urban Ecological Resilience: Evidence from 281 Prefecture-Level Cities in China. Land 2025, 14, 1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, W. A comparative study of urban ecological resilience in the Yangtze River Economic Belt and the Yellow River Basin. Humanit. Soc. Sci. Commun. 2024, 11, 1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wu, Y. Spatiotemporal Evolution and Influencing Factors of Urban Ecological Resilience: Evidence from the Yellow River Basin, China. Sustainability 2025, 17, 7114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Niu, J. Dynamic evolution and obstacle factors of urban ecological resilience in Shandong Peninsula urban agglomeration. Econ. Geogr. 2022, 42, 51–61. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liao, Z.; Zhang, L. Spatio-temporal pattern evolution and dynamic simulation of urban ecological resilience in Guangdong Province, China. Heliyon 2024, 10, e25127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Wang, L. Study of regional variations and convergence in ecological resilience of Chinese cities. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 154, 110667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberti, M.; Marzluff, J.M. Ecological resilience in urban ecosystems: Linking urban patterns to human and ecological functions. Urban Ecosyst. 2004, 7, 241–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Wang, X.; Li, X.; Zhu, X.; Li, L.; Chen, L. Spatio-Temporal Differentiation and Influencing Factors of Urban Ecological Resilience in Xuzhou City. Land 2025, 14, 1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Chang, J.; Li, C.; Gu, S. Ecological restoration and protection of national land space in coal resource-based cities from the perspective of ecological security pattern: A case study in Huaibei City, China. Land 2023, 12, 442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamazian, A.; Rao, B.B. Do economic, financial and institutional developments matter for environmental degradation? Evidence from transitional economies. Energy Econ. 2010, 32, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Lin, B. Ecological total-factor energy efficiency of China’s heavy and light industries: Which performs better? Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 72, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahzad, U.; Ferraz, D.; Nguyen, H.H.; Cui, L. Investigating the spill overs and connectedness between financial globalization, high-tech industries and environmental footprints: Fresh evidence in context of China. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2022, 174, 121205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Štrbac, S.; Kašanin-Grubin, M.; Pezo, L.; Stojić, N.; Lončar, B.; Ćurčić, L.; Pucarević, M. Green infrastructure designed through nature-based solutions for sustainable urban development. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, D.; Xia, Q. Does environmental regulation promote environmental innovation? An empirical study of cities in China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 19, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, K.C.; Wang, D.; Lu, Y.; Chang, W.; Ren, G.; Liu, L.; Zhou, X. Environmental regulation, promotion pressure of officials, and enterprise environmental protection investment. Front. Public Health 2021, 9, 724351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.; Liang, K. The role of technological innovation in enhancing resource sustainability to achieve green recovery. Resour. Policy 2024, 89, 104659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; He, Z. The Impact of Agricultural Total Factor Productivity and Green Finance Development on Ecological Resilience. Financ. Res. Lett. 2025, 84, 107829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cumming, G.S.; Allen, C.R. Protected areas as social-ecological systems: Perspectives from resilience and social-ecological systems theory. Ecol. Appl. 2017, 27, 1709–1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Wang, Y. Impact of digital economy on ecological resilience of resource-based cities: Spatial spillover and mechanism. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 41299–41318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Kong, Y.; Sha, J.; Wang, H. The role of industrial structure upgrades in eco-efficiency evolution: Spatial correlation and spillover effects. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 687, 1327–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, W.; Liu, J. Nonlinear and spatial spillover effects of urbanization on air pollution and ecological resilience in the Yellow River Basin. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 43229–43244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Ren, Y. Impact of environmental regulation on ecological resilience a perspective of “Local-neighborhood” effect. J. Beijing Inst. Technol. (Soc. Sci. Ed.) 2022, 24, 16–29. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Radmehr, R.; Shayanmehr, S.; Baba, E.A.; Samour, A.; Adebayo, T.S. Spatial spillover effects of green technology innovation and renewable energy on ecological sustainability: New evidence and analysis. Sustain. Dev. 2024, 32, 1743–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Yang, H.; Zhao, X.; Yang, Y. Study on urban resilience from the perspective of the complex adaptive system theory: A case study of the Lanzhou-Xining urban agglomeration. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 13667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apostu, S.A.; Vasile, V.; Vasile, R.; Rosak-Szyrocka, J. Do smart cities represent the key to urban resilience? Rethinking urban resilience. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 15410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Zhao, Y.; Mo, D. Coordinated development and convergence of urban ecological resilience and land use intensity in the Yellow River Basin. J. Nat. Resour. 2025, 40, 2479–2496. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Z.; Zhang, L. Spatiotemporal interaction characteristics and transition mechanism of tourism environmental efficiency in China. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 14196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Gao, J.; Li, Y. Does Low-Carbon Transition Promote Regional Sustainable Development? Evidence from the Huaihe River Ecological Economic Belt. Sustainability 2024, 16, 9107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, I.; Nahar, K.; Morshed, M.M. Measuring urban expansion pattern using spatial matrices in Khulna City, Bangladesh. Heliyon 2023, 9, e13193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Guo, X.; Wu, G.; Zhu, Y. Investigating the effects of environmental regulation on industrial ecological efficiency in China using a panel smooth transition regression model. Sustainability 2023, 15, 15408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, K.H.; Liao, Y.C. Innovation capacity and the implementation of eco-innovation: Toward a contingency perspective. Bus. Strategy Environ. 2017, 26, 1000–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Xia, B. A significant increase in the normalized difference vegetation index during the rapid economic development in the Pearl River Delta of China. Land Degrad. Dev. 2019, 30, 359–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Gao, Q.; Hu, X.; Lei, J. The impact of digital transformation of infrastructure on carbon emissions: Based on a “local-neighborhood” perspective. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0307399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Xie, C.; Liu, J.B. The impact of population agglomeration on ecological resilience: Evidence from China. Math. Biosci. Eng. 2023, 20, 15898–15917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niako, N.; Melgarejo, J.D.; Maestre, G.E.; Vatcheva, K.P. Effects of missing data imputation methods on univariate blood pressure time series data analysis and forecasting with ARIMA and LSTM. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2024, 24, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medrano, J.; Kheddar, A.; Lesne, A.; Ramdani, S. Radius selection using kernel density estimation for the computation of nonlinear measures. Chaos Interdiscip. J. Nonlinear Sci. 2021, 31, 83131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bofa, A.; Zewotir, T. Key predictors of food security and nutrition in Africa: A spatio-temporal model-based study. BMC Public Health 2024, 24, 885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wang, W. Pattern evolution and spatial spillover effect of urban resilience in the Yangtze River Delta. Geogr. Geo-Inf. Sci. 2024, 40, 57–66. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Li, J. The influence mechanism and spatial effect of carbon emission intensity in the agricultural sustainable supply: Evidence from china’s grain production. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 44442–44460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeSage, J.P.; Dominguez, M. The importance of modeling spatial spillovers in public choice analysis. Public Choice 2012, 150, 525–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elhorst, J.P. Specification and estimation of spatial panel data models. Int. Reg. Sci. Rev. 2003, 26, 244–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baltagi, B.H.; Liu, L. Random effects, fixed effects and Hausman’s test for the generalized mixed regressive spatial autoregressive panel data model. Econom. Rev. 2016, 35, 638–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lind, J.T.; Halvor, M. With or without U? The appropriate test for a U-shaped relationship. Oxf. Bull. Econ. Stat. 2010, 72, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayaraman, A.; Sudhir, C.R.; Palaniappan, R. Food system resilience: Unraveling power relations and the Matthew effect in farmers networks. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2024, 200, 123144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, M.E. Location, competition, and economic development: Local clusters in a global economy. Econ. Dev. Q. 2000, 14, 15–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oteng-Abayie, E.F.; Duodu, E.; Oduro, S.; Tawiah, B.S. Greening the future: Unveiling the link between industrial structure upgrading and pollution emission in sub-Saharan Africa. Cogent Econ. Financ. 2023, 11, 2257069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Peng, G.; Du, H. Digital economy development boosts urban resilience—Evidence from China. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 2925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, S.; Chen, H.; Han, J. Green Innovation Quality in Center Cities and Economic Growth in Peripheral Cities: Evidence from the Yangtze River Delta Urban Agglomeration. Systems 2025, 13, 642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Primary Indicators | Secondary Indicators | Units | Combined Weight | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Urban Ecological Resilience | Resistance Capacity | Per capita park green space area | m2 (+) | 0.109 |
| Built-up area green coverage rate | % (+) | 0.087 | ||
| Water area ratio | % (+) | 0.091 | ||
| Proportion of protected areas to total land area | % (+) | 0.133 | ||
| Response Capacity | Comprehensive utilization rate of general industrial solid waste | % (+) | 055 | |
| Urban sewage treatment rate | % (+) | 0.093 | ||
| Harmless treatment rate of domestic waste | % (+) | 0.045 | ||
| Proportion of environmental protection expenditure to public fiscal expenditure | % (+) | 0.104 | ||
| Transformation Capacity | Number of green patents | % (+) | 0.071 | |
| Number of college students per 10,000 people | person (+) | 0.099 | ||
| Proportion of high-tech enterprises to total enterprises | % (+) | 0.113 |
| Category | Variables | Notation | Indicators | Units |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Explained Variable | Urban Ecological Resilience | UER | — | |
| Explanatory Variables | Economic Development | GDP | per capita GDP | Yuan/person |
| Industrial Upgrading | IU | the ratio of value added in the tertiary to the secondary sector | % | |
| Urbanization Level | UL | the proportion of built-up land area relative to total municipal land area | % | |
| Environmental Regulation | ER | the share of environmental pollution control investment in local public expenditure | 103 yuan | |
| Technological Innovation | TI | the number of invention patents granted per 10,000 residents | — | |
| Control variables | Ecological Endowment | EE | the normalized difference vegetation index | % |
| Infrastructure Level | IL | per capita urban road area. | m2/person | |
| Openness | OP | the ratio of total imports and exports to GDP. | % | |
| Population Density | PD | the number of permanent residents per square kilometer of the built-up area. | Person/km2 |
| Year | Global Moran’s I | z-Value | p-Value | Year | Global Moran’s I | z-Value | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2011 | 0.227 | 2.536 | 0.011 | 2018 | 0.266 | 2.619 | 0.003 |
| 2012 | 0.241 | 2.011 | 0.044 | 2019 | 0.281 | 2.296 | 0.009 |
| 2013 | 0.233 | 2.727 | 0.006 | 2020 | 0.282 | 2.803 | 0.005 |
| 2014 | 0.233 | 3.119 | 0.000 | 2021 | 0.282 | 2.491 | 0.013 |
| 2015 | 0.256 | 2.321 | 0.020 | 2022 | 0.285 | 2.776 | 0.004 |
| 2016 | 0.251 | 2.339 | 0.007 | 2023 | 0.294 | 3.115 | 0.002 |
| 2017 | 0.252 | 2.804 | 0.019 |
| Variables | VIF | Variables | VIF |
|---|---|---|---|
| lnGDP | 2.452 | lnTI | 2.594 |
| ln(GDP) 2 | 3.101 | lnEE | 1.666 |
| lnIU | 2.806 | lnIL | 2.195 |
| lnUL | 1.955 | lnOP | 1.438 |
| lnER | 2.650 | lnPD | 1.562 |
| Test | Static SDM | Dynamic SDM | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| β | p-Value | β | p-Value | |
| LM-lag test | 16.845 | 0.001 | 20.749 | 0.004 |
| Robust LM-lag test | 15.946 | 0.000 | 15.001 | 0.000 |
| LM-error test | 23.460 | 0.000 | 26.458 | 0.000 |
| Robust LM-error test | 19.412 | 0.001 | 21.464 | 0.001 |
| Wald-spatial lag test | 35.022 | 0.000 | 47.783 | 0.005 |
| LR-spatial lag test | 42.129 | 0.000 | 44.255 | 0.001 |
| Wald-spatial error test | 39.555 | 0.003 | 50.128 | 0.001 |
| LR-spatial error test | 35.911 | 0.001 | 54.774 | 0.001 |
| Hausman test | 53.458 | 0.000 | 106.440 | 0.003 |
| Variables | Static SDM | Dynamic SDM | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| β | T Statistics | p-Value | β | T Statistics | p-Value | |
| LnUERt−1 | 0.266 | 3.291 | 0.001 | |||
| lnGDP | −0.252 | −4.169 | 0.000 | −0.301 | −3.547 | 0.000 |
| ln(GDP) 2 | 0.246 | 4.568 | 0.014 | 0.224 | 4.037 | 0.005 |
| lnIU | −0.146 | −2.655 | 0.004 | −0.105 | −1.887 | 0.032 |
| lnUL | −0.184 | −2.937 | 0.022 | −0.296 | −3.838 | 0.006 |
| lnER | −0.105 | −2.742 | 0.012 | −0.191 | −2.914 | 0.001 |
| lnTI | 0.269 | 3.629 | 0.000 | 0.239 | 3.287 | 0.005 |
| lnEE | 0.188 | 3.280 | 0.000 | 0.143 | 3.920 | 0.000 |
| lnIL | 0.164 | 4.299 | 0.001 | 0.095 | 3.175 | 0.001 |
| lnOP | 0.055 | 2.636 | 0.229 | 0.084 | 2.926 | 0.016 |
| lnPD | −0.117 | −3.742 | 0.009 | −0.098 | −2.466 | 0.002 |
| W × lnGDP | −0.244 | −2.758 | 0.020 | −0.147 | −3.681 | 0.003 |
| W × lnIU | 0.219 | 4.544 | 0.000 | 0.236 | 2.794 | 0.001 |
| W × lnUL | 0.071 | 3.176 | 0.011 | 0.085 | 3.495 | 0.001 |
| W × lnER | 0.082 | 1.037 | 0.036 | −0.054 | −1.588 | 0.029 |
| W × lnTI | 0.111 | 3.974 | 0.004 | 0.166 | 3.085 | 0.002 |
| ρ | 0.331 | 3.584 | 0.012 | 0.304 | 3.227 | 0.001 |
| R2 | 0.792 | 0.811 | ||||
| N | 325 | 325 | ||||
| Variables | Direct Effect | Spillover Effect | Total Effect | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| β | T Statistics | p-Value | β | T Statistics | p-Value | β | T Statistics | p-Value | |
| lnGDP | −0.214 | −2.977 | 0.006 | −0.194 | 2.852 | 0.014 | −0.408 | 3.568 | 0.001 |
| lnIU | −0.135 | −1.994 | 0.061 | 0.220 | 2.757 | 0.009 | 0.085 | 2.055 | 0.027 |
| lnER | −0.130 | −2.588 | 0.011 | −0.096 | −1.118 | 0.177 | −0.224 | −0.611 | 0.311 |
| lnUL | −0.196 | −2.872 | 0.004 | 0.315 | 2.845 | 0.003 | 0.119 | 2.640 | 0.015 |
| lnTI | 0.159 | 2.799 | 0.009 | 0.069 | 2.688 | 0.001 | 0.228 | 2.935 | 0.006 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, G. Research on the Spatiotemporal Evolution and Driving Mechanism of Urban Ecological Resilience in the Huaihe River Ecological Economic Belt. Sustainability 2025, 17, 10363. https://doi.org/10.3390/su172210363
Wang G. Research on the Spatiotemporal Evolution and Driving Mechanism of Urban Ecological Resilience in the Huaihe River Ecological Economic Belt. Sustainability. 2025; 17(22):10363. https://doi.org/10.3390/su172210363
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Guokui. 2025. "Research on the Spatiotemporal Evolution and Driving Mechanism of Urban Ecological Resilience in the Huaihe River Ecological Economic Belt" Sustainability 17, no. 22: 10363. https://doi.org/10.3390/su172210363
APA StyleWang, G. (2025). Research on the Spatiotemporal Evolution and Driving Mechanism of Urban Ecological Resilience in the Huaihe River Ecological Economic Belt. Sustainability, 17(22), 10363. https://doi.org/10.3390/su172210363






