Environmental DNA Reveals the Influence of Human Activities on Fish Community Variation Across a Large River and Its Connected Lakes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
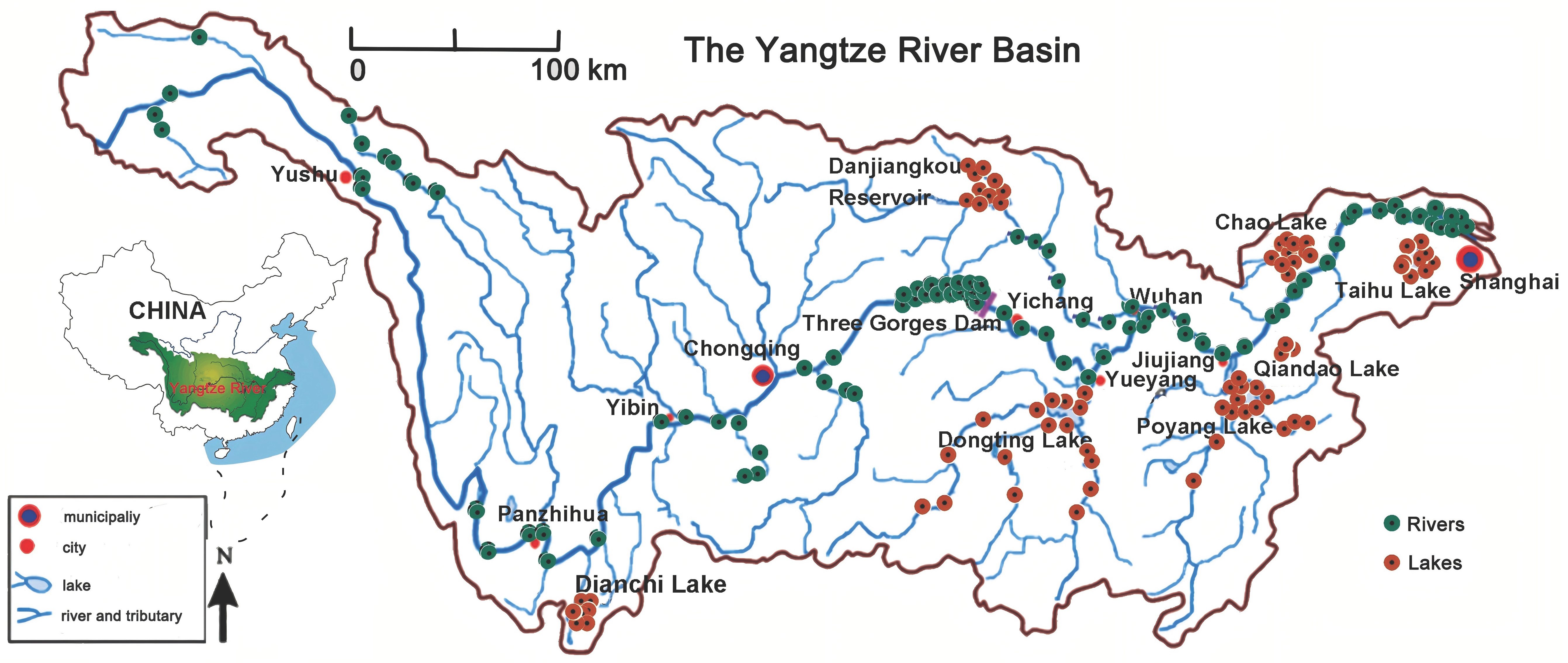
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. eDNA Processing and Sequencing
2.3. The Construction of a Local Barcoding Database
2.4. Bioinformatics Processing
2.5. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Fish Diversity in the YR Basin
3.2. Comparison of Lake and River Fish Communities
3.3. Lake and River Fish Diversity Response to Environmental Variables
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Allen, G.H.; Pavelsky, T.M. Global extent of rivers and streams. Science 2018, 361, 585–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, A.J.; Carlson, A.K.; Creed, I.F.; Eliason, E.J.; Gell, P.A.; Johnson, P.T.J.; Kidd, K.A.; MacCormack, T.J.; Olden, J.D.; Ormerod, S.J.; et al. Emerging threats and persistent conservation challenges for freshwater biodiversity. Biol. Rev. Camb. Philos. Soc. 2019, 94, 849–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, G.; Logez, M.; Xu, J.; Tao, S.; Villeger, S.; Brosse, S. Human impacts on global freshwater fish biodiversity. Science 2021, 371, 835–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, B.; Jiang, Z.; Wang, C.; Matsuzaki, S.-I.S.; Zhou, L. Abundance-based dissimilarity measurements reveal higher heterogeneity of fish communities in the lotic habitats of the Yangtze-Caizi transitional floodplain. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 112, 106122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashworth, P.J.; Lewin, J. How do big rivers come to be different? Earth-Sci. Rev. 2012, 114, 84–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zheng, Y.T.; Zhan, A.B.; Dong, C.; Zhao, J.; Yao, M. Environmental DNA captures native and non-native fish community variations across the lentic and lotic systems of a megacity. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eabk0097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, S.W.; Li, Z.J.; Zhang, T.L.; Liu, J.; Xie, S.; Ye, S.; Li, Z.; Zhang, T.; Liu, J.; Xie, S. Assessing fish distribution and threats to fish biodiversity in the Yangtze River Basin, China. Ichthyol. Res. 2014, 61, 183–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudgeon, D. The ecology of tropical Asian rivers and streamsin relation to biodiversity conservation. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 2000, 31, 239–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.; Chang, J.; Lek, S.; Cao, W.; Brosse, S. Conservation strategies for endemic fish species threatened by the ThreeGorges Dam. Conserv. Biol. 2003, 17, 1748–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.W.; Wang, D.Q.; Tian, H.W.; Pu, Y.; Yu, L.; Duan, X.; Liu, S.; Chen, D. Genetic structure of two sympatric gudgeon fishes (Xenophysogobio boulengeri and X. nudicorpa) in the upper reaches of Yangtze River Basin. PeerJ 2019, 7, e7393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.D.; Wang, D.Q.; Gao, L.; Tian, H.W.; Liu, S.P.; Chen, D.Q.; Duan, X.B. Species diversity of drifting fish eggs in the Yangtze River using molecular identification. PeerJ 2018, 6, e5807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, T.M.; He, J.Y.; Yang, D.Y.; Ma, Z.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Q.; Deng, F.; Ye, L.; Pu, Y.; Zhang, M.; et al. Fish community structure and biomass particle-size spectrum in the upper reaches of the Jinsha river (China). Animals 2022, 12, 3412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.L.; Wang, C.Y.; Liu, Y.Z.; Zhang, X.Y.; Jian, S.Q. Fish species composition, distribution and community structure in the lower reaches of Ganjiang River, Jiangxi, China. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 10100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.J.; Qin, J.J.; Xu, Y.; Zhou, M.; Wu, X.P.; Ouyang, S. Biodiversity pattern of fish assemblages in Poyang Lake basin: Threat and conservation. Evol. Ecol. 2019, 9, 11672–11683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohmann, K.; Evans, A.; Gilbert, M.T.P.; Carvalho, G.R.; Creer, S.; Knapp, M.; Yu, D.W.; Bruyn, M. Environmental DNA for wildlife biology and biodiversity monitoring. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2014, 29, 358–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ficetola, G.F.; Miaud, C.; Pompanon, F.; Taberlet, P. Species detection using environmental DNA from water samples. Biol. Lett. 2008, 4, 423–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Yan, Z.; Hanfling, B.; Zheng, X.; Wang, P.; Fan, J.; Li, J. Methodology of fish eDNA and its applications in ecology and environment. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 755, 142622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanfling, B.; Handley, L.L.; Read, D.S.; Hahn, C.; Li, J.; Nichols, P.; Blackman, R.C.; Oliver, A.; Winfield, I.J. Environmental DNA metabarcoding of lake fish communities reflects long-term data from established survey methods. Mol. Ecol. 2016, 25, 3101–3119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valentini, A.; Taberlet, P.; Miaud, C.; Civade, R.; Herder, J.; Thomsen, P.F.; Bellemain, E.; Besnard, A.; Coissac, E.; Boyer, F.; et al. Next-generation monitoring of aquatic biodiversity using environmental DNA metabarcoding. Mol. Ecol. 2016, 25, 929–942. [Google Scholar]
- Hering, D.; Borja, A.; Jones, J.I.; Pont, D.; Boets, P.; Bouchez, A.; Bruce, K.; Drakare, S.; Hanfling, B.; Kahlert, M.; et al. Implementation options for DNA-based identification into ecological status assessment under the European Water Framework Directive. Water Res. 2018, 138, 192–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laramie, M.B.; Pilliod, D.S.; Goldberg, C.S. Characterizing the distribution of an endangered salmonid using environmental DNA analysis. Biol. Conserv. 2015, 183, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Yoshizawa, S.; Iwasaki, W.; Xian, W. Seasonal fish Assem. structure using environmental DNA in the Yangtze Estuary and its adjacent waters. Front. Mar. Sci. 2019, 6, 515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, M.M.; Wang, Z.Y.; Zhou, Q.; Wang, J.; Shao, Y.; Qiao, Q.; Fan, J.T.; Yan, Z.G. Environmental DNA unveiling the fish community structure and diversity features in the Yangtze River basin. Environ. Res. 2023, 239, 117198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, L.; Ludwig, A.; Peng, Z.G. Standards for Methods Utilizing Environmental DNA for Detection of Fish Species. Genes 2020, 11, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, H.; Shen, W.; Du, X.; Li, S.; Wei, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Feng, K.; Deng, Y. The large-scale spatial patterns of ecological networks between phytoplankton and zooplankton in coastal marine ecosystems. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 827, 154285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miya, M.; Sato, Y.; Fukunaga, T.; Poulsen, J.Y.; Sato, K.; Minamoto, T.; Yamamoto, S.; Yamanaka, H.; Araki, H.; Kondoh, M.; et al. MiFish, a set of universal PCR primers for metabarcoding environmental DNA from fishes: Detection of more than 230 subtropical marine species. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2015, 2, 150088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, F.; Shu, L.; Zeng, H.; Gan, X.; He, S.; Peng, Z. Methodology for fish biodiversity monitoring with environmental DNA metabarcoding: The primers, databases and bioinformatic pipelines. Water Biol. Secur. 2022, 1, 100007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Lu, Q.; Wang, Y.; Yao, M. Assessment of fish communities using environmental DNA: Effect of spatial sampling design in lentic systems of different sizes. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2020, 20, 242–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gold, Z.; Curd, E.E.; Goodwin, K.D.; Choi, E.S.; Frable, B.W.; Thompson, A.R.; Walker, H.J.; Burton, R.S.; Kacev, D.; Martz, L.D.; et al. Improving metabarcoding taxonomic assignment: A case study of fishes in a large marine ecosystem. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2021, 21, 2546–2564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.J.; Hubert, N.; Huang, Y.; Wang, X.; Gan, X.; Peng, Z.; He, S. DNA barcoding the ichthyofauna of the Yangtze River: Insights from the molecular inventory of a mega-diverse temperate fauna. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2019, 19, 1278–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Froese, R. FishBase. World Wide Web Electron Publication. Available online: https://www.fishbase.org (accessed on 1 May 2024).
- Kimura, M.A. Simple method for estimating evolutionary rates of base substitutions through comparative studies of nucleotidesequences. J. Mol. Evol. 1980, 16, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paradis, E.; Claude, J.; Strimmer, K. APE: Analyses of phylogenetics and evolution in R language. Bioinformatics 2004, 20, 289–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, S.D.J.; Collins, R.A.; Boyer, S.; Lefort, M.C.; Malumbres-Olarte, J.; Vink, C.J.; Cruickshank, R.H. Spider: An R package for the analysis of species identity and evolution, with particular reference to DNA barcoding. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2012, 12, 562–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, M. Cutadapt removes adapter sequences from high-throughput sequencing reads. EMBnet. J. 2011, 17, 10–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.A.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, J.; Zhou, Y.; Peres-Neto, P.R. Generalizing hierarchical and variation partitioning in multiple regression and canonical analyses using the rdacca.hp R package. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2022, 13, 782–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Hatton-Ellis, T.W.; Lawson, H.L.J.; Kimbell, H.S.; Benucci, M.; Peirson, G.; Hnfling, B. Ground-truthing of a fish-based environmental DNA metabarcoding method for assessing the quality of lakes. J. Appl. Ecol. 2019, 56, 1232–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawlowski, J.; Apotheloz, P.G.L.; Altermatt, F. Environmental DNA: What’s behind the term? Clarifying the terminology and recommendations for its future use in biomonitoring. Mol. Ecol. 2020, 29, 4258–4264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pont, D.; Rocle, M.; Valentini, A.; Civade, R.; Jean, P.; Maire, A.; Roset, N.; Schabuss, M.; Zoring, H.; Dejean, T. Environmental DNA reveals quantitative patterns of fish biodiversity in large rivers despite its downstream transportation. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 82–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czegledi, I.; Saly, P.; Specziar, A.; Preiszner, B.; Szaloky, Z.; Maroda, A.; Pont, D.; Meulenbroek, P.; Valentini, A.; Eros, T. Congruency between two traditional and eDNA-based sampling methods in characterising taxonomic and trait-based structure of fish communities and community-environment relationships in lentic environment. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 129, 107952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goutte, A.; Molbert, N.; Guerin, S.; Richoux, R.; Rocher, V. Monitoring freshwater fish communities in large rivers using environmental DNA metabarcoding and a long-termelectrofishing survey. J. Fish Biol. 2020, 97, 444–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McColl-GausdenLiu, X.; Zeng, H.; Wang, C.; Bo, J.; Gan, X.; Fang, C. Improved genome assembly of Chinese sucker (Myxocyprinus asiaticus) provides insights into the identification and characterization of pharyngeal teeth related maker genes in Cyprinoidei. Water Biol. Secur. 2022, 1, 100049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDevitt, A.D.; Sales, N.G.; Browett, S.S.; Sparnenn, A.O.; Mariani, S.; Wangensteen, O.S.; Coscia, I.; Benvenuto, C. Environmental DNA metabarcoding as an effective and rapid tool for fish monitoring in canals. J. Fish Biol. 2019, 95, 679–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deiner, K.; Fronhofer, E.A.; Machler, E.; Walser, J.C.; Altermatt, F. Environmental DNA reveals that rivers are conveyer belts of biodiversity information. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pont, D.; Valentini, A.; Rocle, M.; Maire, A.; Delaigue, O.; Jean, P.; Dejean, T. The future of fish-based ecological assessment of European rivers: From traditional EU Water Framework Directive compliant methods to eDNA metabarcoding-based approaches. J. Fish Biol. 2021, 98, 354–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Shen, L.; He, Y.; Tian, H.; Gao, L.; Wu, J.; Mei, Z.; Wei, N.; Wang, L.; Zhu, T.; et al. Status of aquatic organisms resources and their environments in Yangtze river system (2017–2021). J. Fish. China 2023, 2, 3–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, S.; Li, Z.; Liu, J.; Zhang, T.; Xie, S. Distribution, endemism and conservation status of fishes in the Yangtze River basin, China. Ecosyst. Biodivers. 2011, 1, 41–66. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Xue, D.; Zhang, B.; Liu, J. Population Genomic Signatures of Genetic Structure and Environmental Selection in the Catadromous Roughskin Sculpin Trachidermus fasciatus. Genome Biol. Evol. 2019, 11, 1751–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waters, T.; Langlois, K.; Gold, Z.; Theroux, S.; Eagle, R.A. Hidden in plain sight: The invasive macroalga Caulerpa prolifera evades detection by environmental DNA methods. Environ. DNA 2023, 6, e496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roblet, S.; Priouzeau, F.; Gambini, G.; Cottalorda, J.M.; Gastaldi, J.M.; Pey, A.; Raybaud, V.; Romero, S.G.; Serre, C.; Sabourault, C.; et al. From sight to sequence: Underwater visual census vs environmental DNA metabarcoding for the monitoring of taxonomic and functional fish diversity. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 956, 177250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boussarie, G.; Bakker, J.; Wangensteen, O.S.; Mariani, S.; Bonnin, L.; Juhel, J.-B.; Kiszka, J.J.; Kulbicki, M.; Manel, S.; Robbins, W.D.; et al. Environmental DNA illuminates the dark diversity of sharks. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, eaap9661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maggio, T.; Cattapan, F.; Falautano, M.; Julian, D.; Malinverni, R.; Poloni, E.; Sanseverino, W.; Todesco, S.; Castriota, L. eDNA metabarcoding analysis as tool to assess the presence of Non-Indigenous Species (NIS): A case study in the Bilge Water. Diversity 2023, 15, 1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rey, A.; Viard, F.; Lizé, A.; Corre, E.; Valentini, A.; Thiriet, P. Coastal rocky reef fish monitoring in the context of the Marine Strategy Framework Directive: Environmental DNA metabarcoding complements underwater visual census. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2023, 241, 106625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xanthopoulou, P.; Katsanevakis, S.; Ragkousis, M.; Papadakis, O.; Zotou, M.; Kamidis, N.; Wangensteen, O.S.; Papathanasiou, V.; Karampetsis, D.; Mazaris, A.D.; et al. Complementing underwater visual surveys with eDNA metabarcoding to detect Mediterranean non-indigenous fishes. Mediterr. Mar. Sci. 2025, 26, 216–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xiong, F.; Fang, C.; Jing, Z.; Hu, S.; Bing, H.; Wang, C.; Lu, Y.; Zeng, H.; Hu, Y.; Wang, Y.; et al. Environmental DNA Reveals the Influence of Human Activities on Fish Community Variation Across a Large River and Its Connected Lakes. Sustainability 2025, 17, 10353. https://doi.org/10.3390/su172210353
Xiong F, Fang C, Jing Z, Hu S, Bing H, Wang C, Lu Y, Zeng H, Hu Y, Wang Y, et al. Environmental DNA Reveals the Influence of Human Activities on Fish Community Variation Across a Large River and Its Connected Lakes. Sustainability. 2025; 17(22):10353. https://doi.org/10.3390/su172210353
Chicago/Turabian StyleXiong, Fan, Chengchi Fang, Zhang Jing, Sheng Hu, Houhua Bing, Cheng Wang, Yongrui Lu, Honghui Zeng, Yuxin Hu, Yingcai Wang, and et al. 2025. "Environmental DNA Reveals the Influence of Human Activities on Fish Community Variation Across a Large River and Its Connected Lakes" Sustainability 17, no. 22: 10353. https://doi.org/10.3390/su172210353
APA StyleXiong, F., Fang, C., Jing, Z., Hu, S., Bing, H., Wang, C., Lu, Y., Zeng, H., Hu, Y., Wang, Y., & He, S. (2025). Environmental DNA Reveals the Influence of Human Activities on Fish Community Variation Across a Large River and Its Connected Lakes. Sustainability, 17(22), 10353. https://doi.org/10.3390/su172210353






