Hydrogeochemical Characteristics and Formation Mechanisms of Groundwater Around Ji’an City, Southern China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
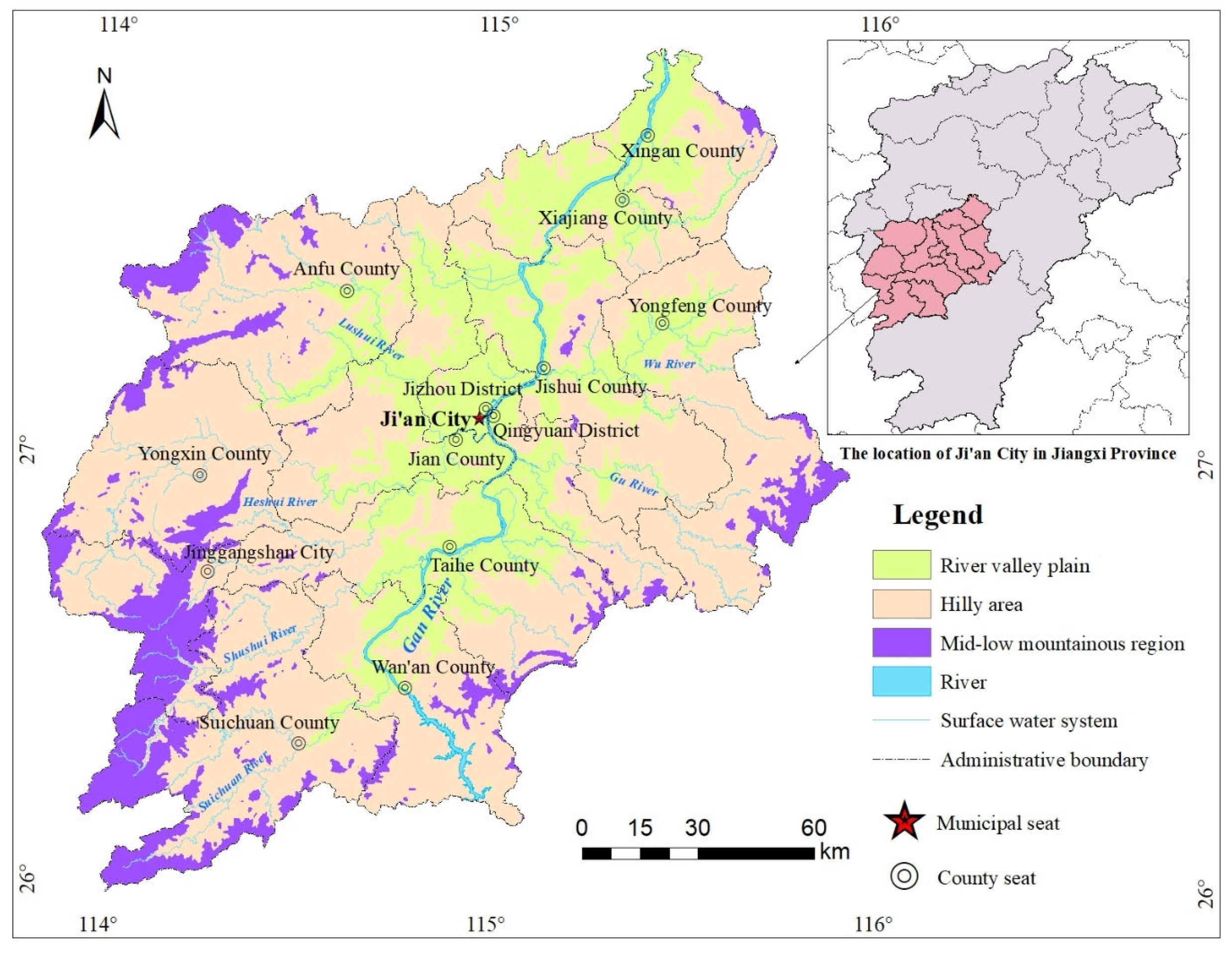
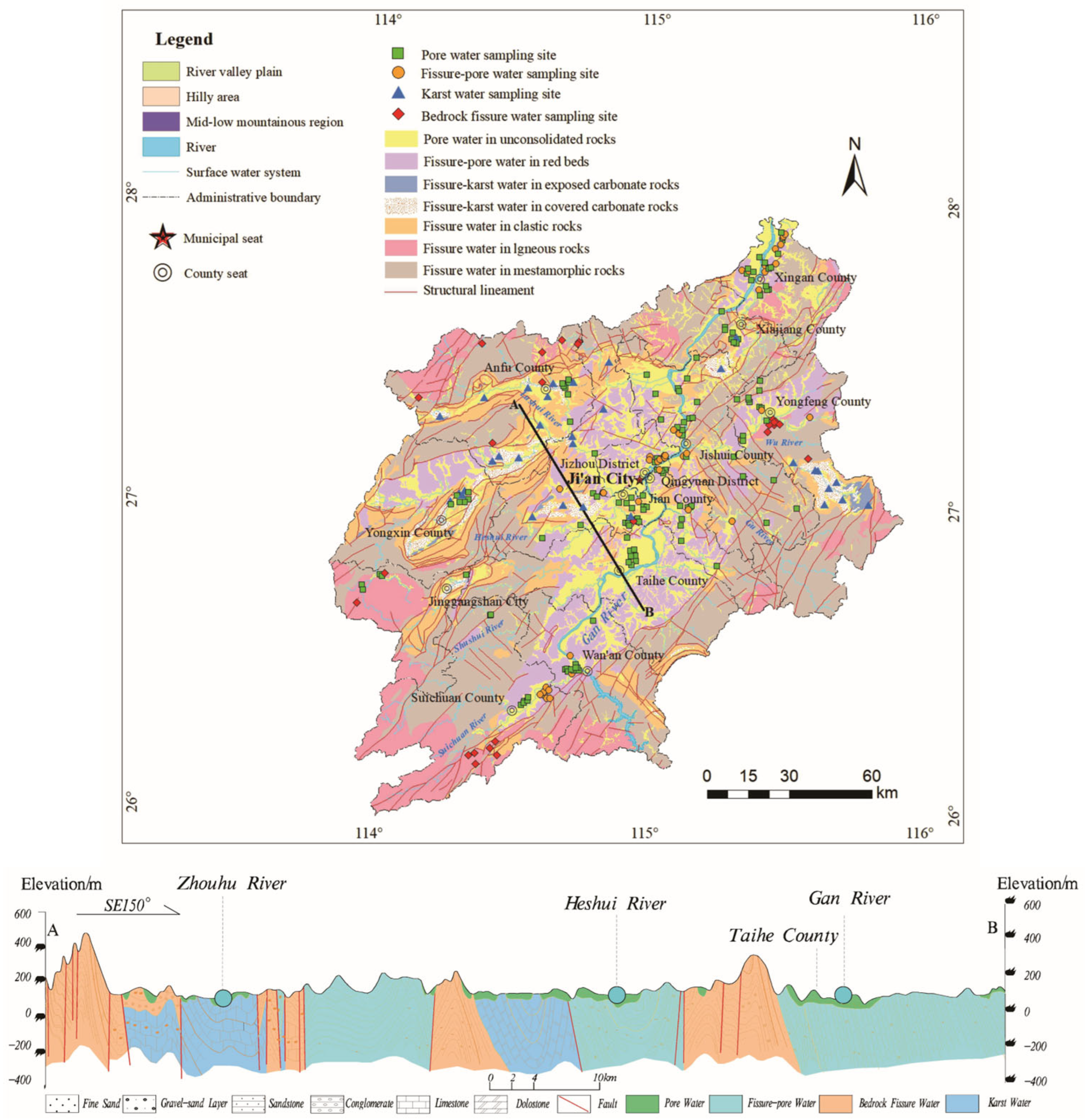
2.1. Regional Settings
2.2. Sample Collection and Analysis
2.3. Data Processing
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Hydrochemical Characteristics
3.1.1. General Hydrochemistry
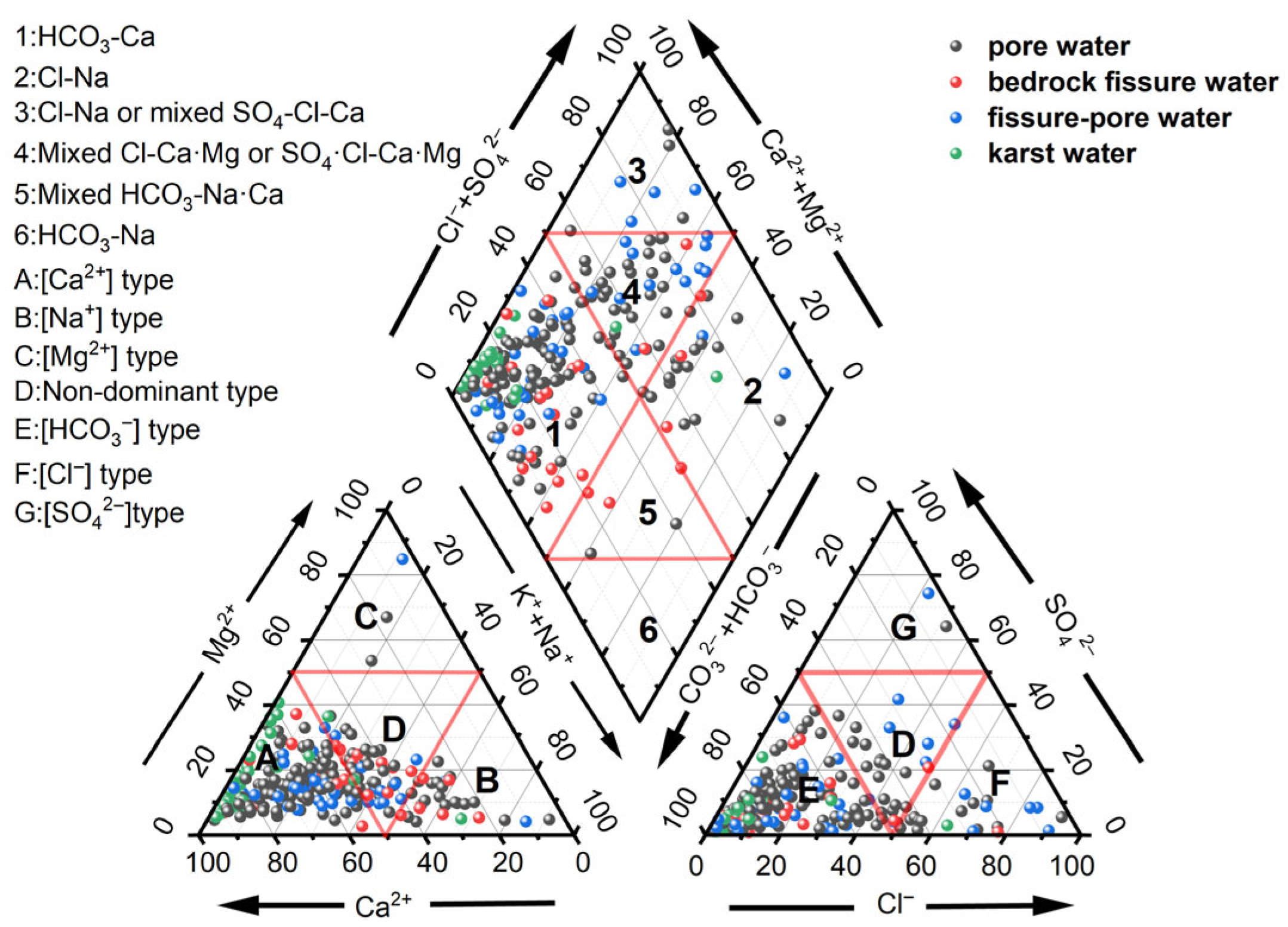
3.1.2. Water Type
3.2. Formation Mechanism of Groundwater Chemistry
3.2.1. Correlation Analysis
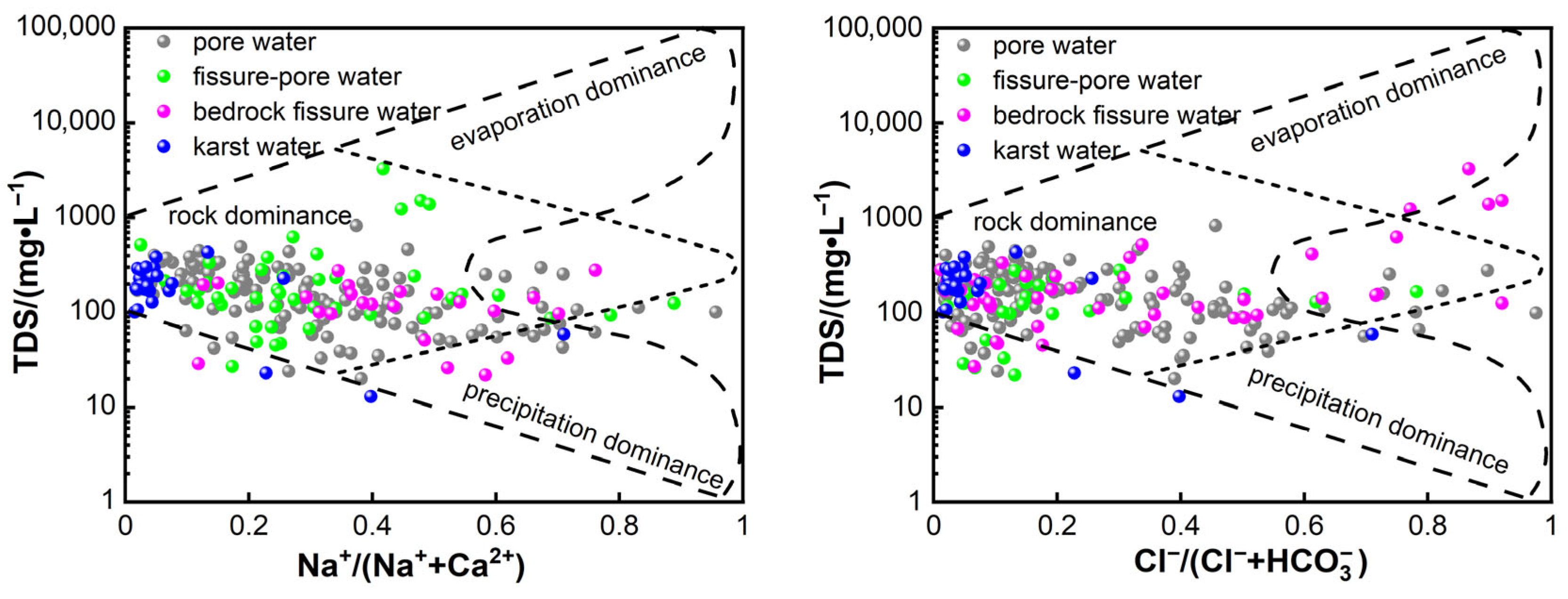
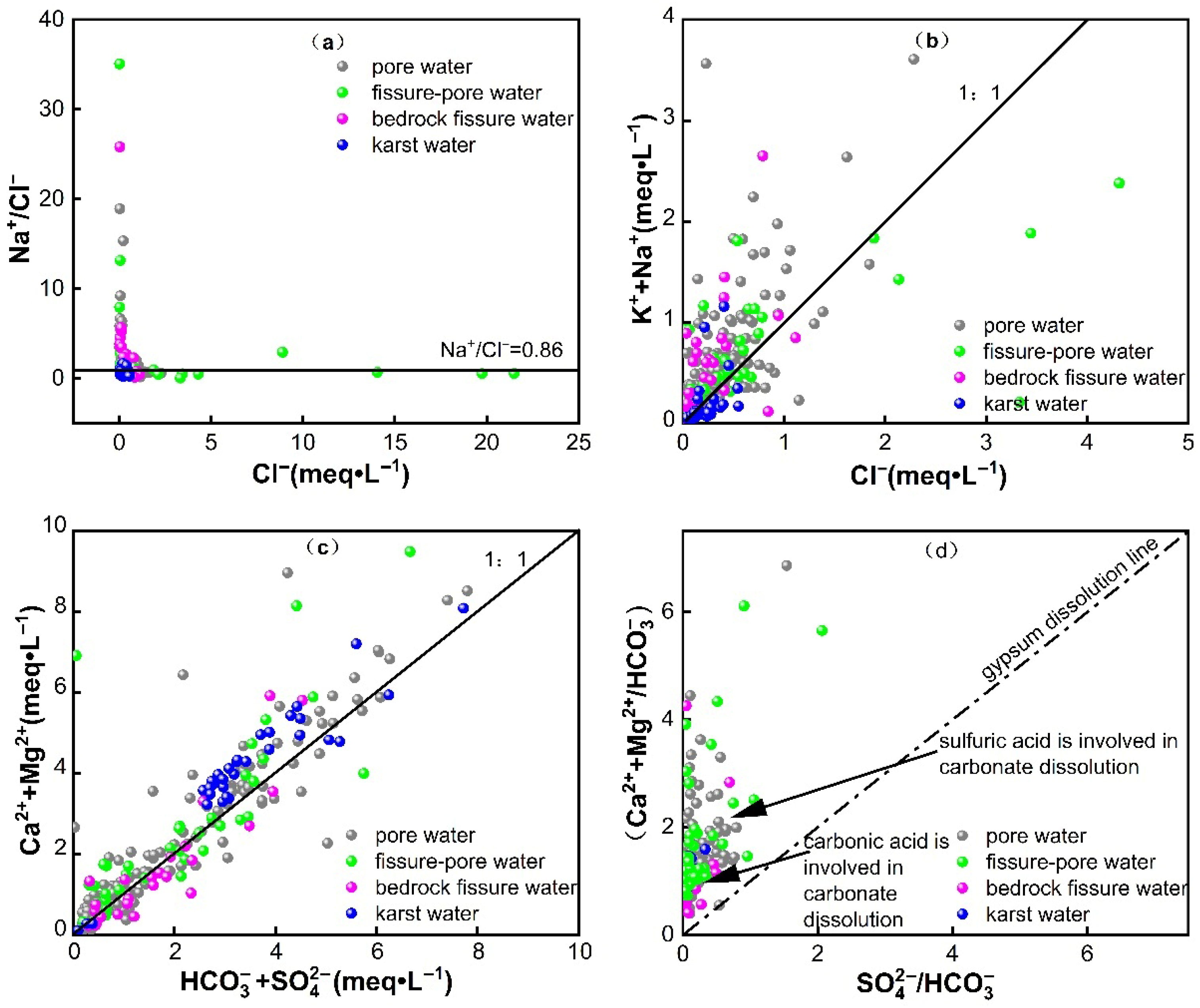
3.2.2. Leaching Process
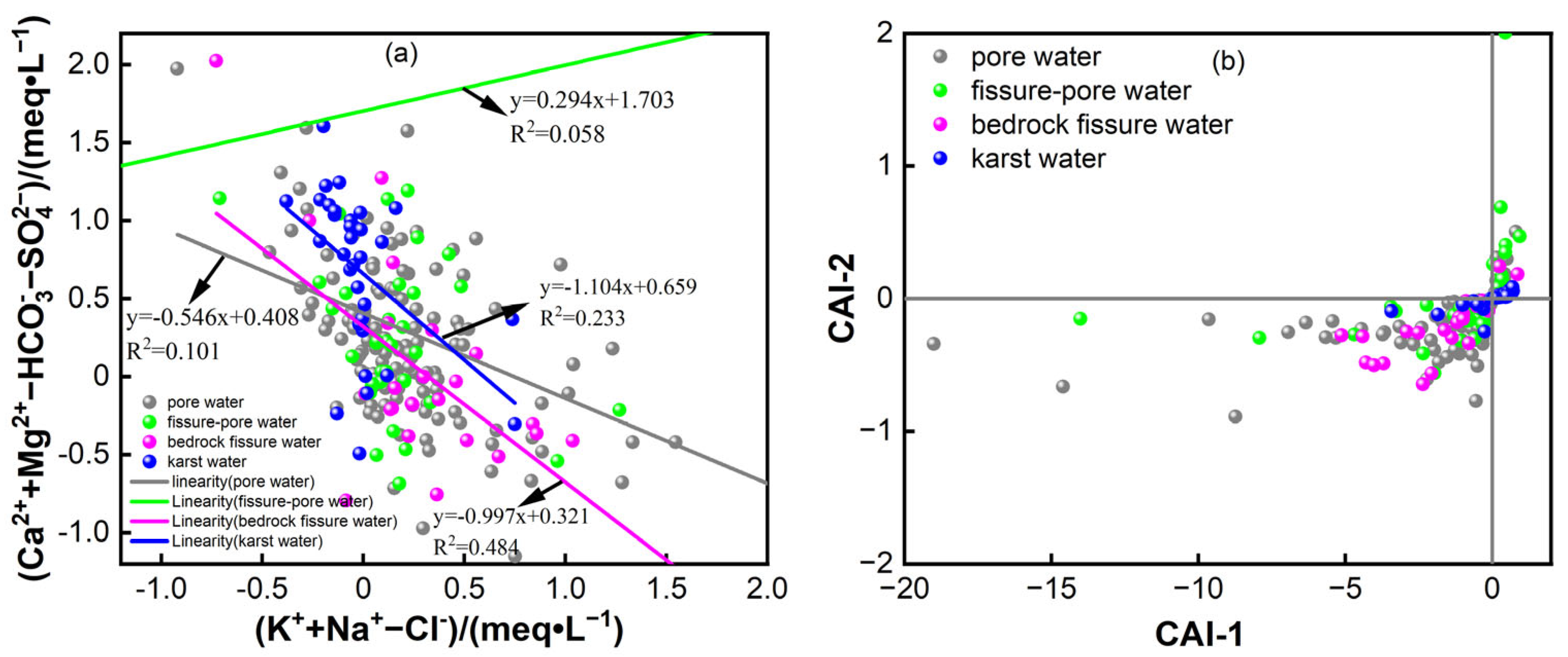
3.2.3. Cation Exchange
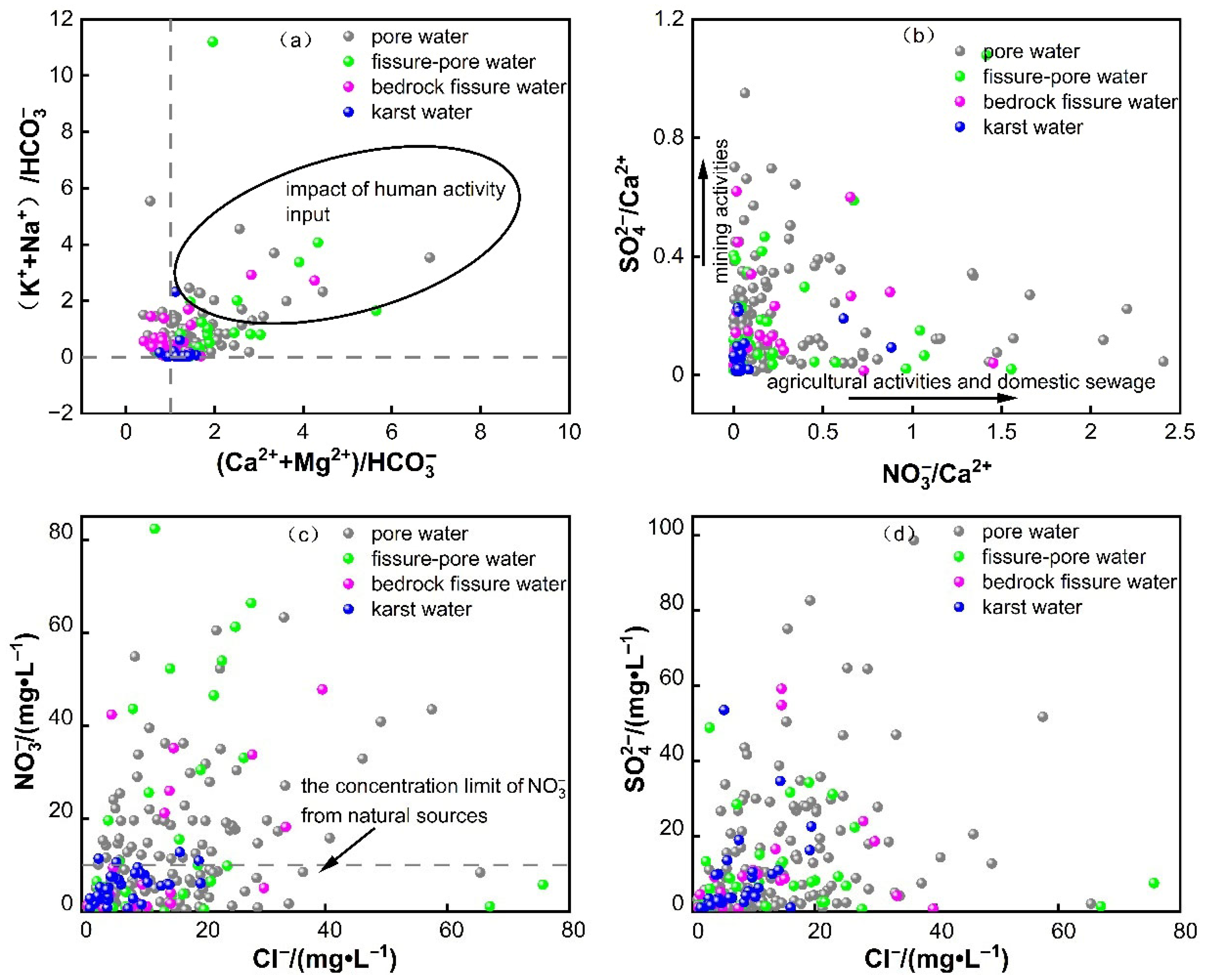
3.2.4. Anthropogenic Impact
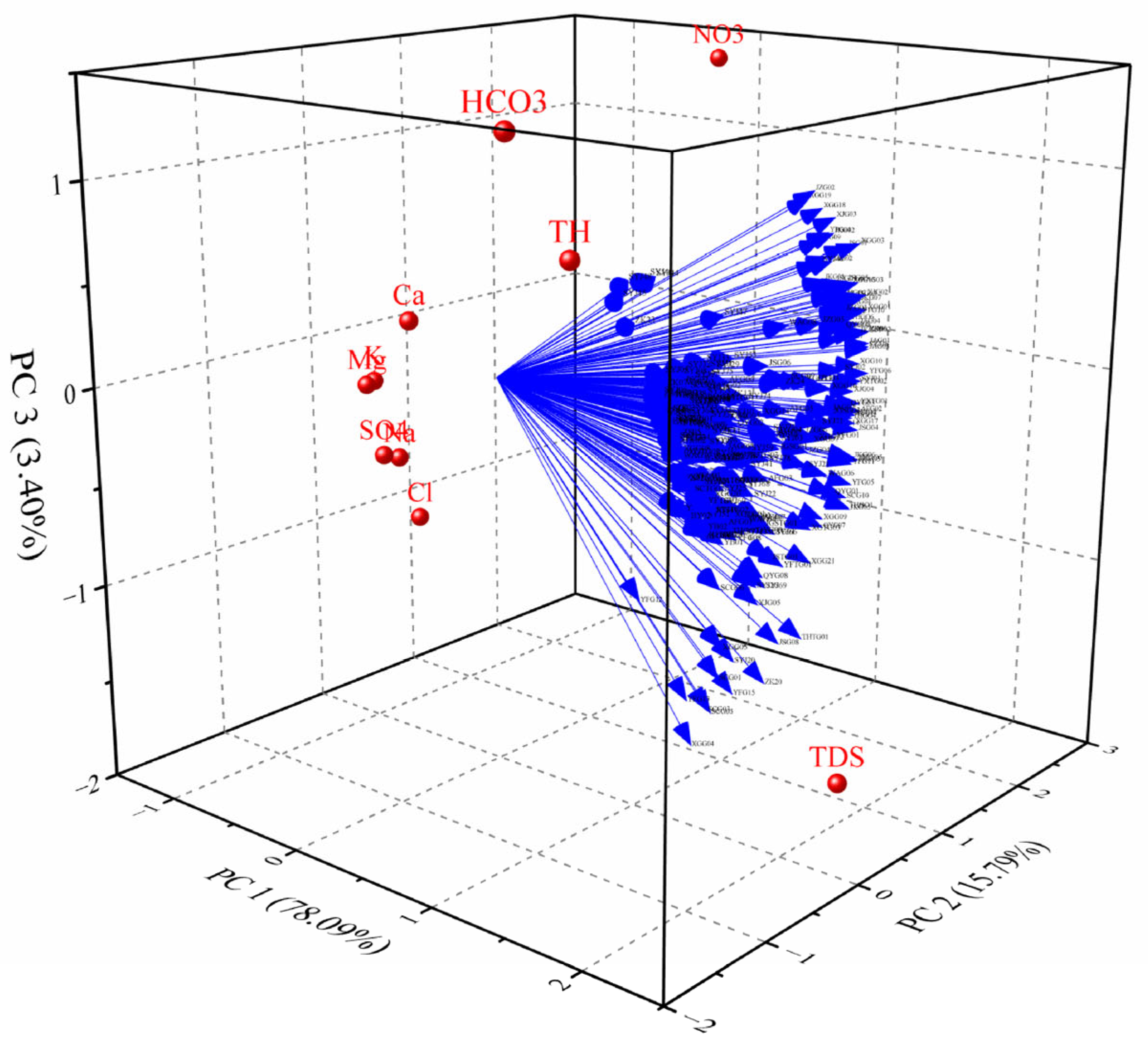
3.3. Factor Analysis
3.4. Implication for Groundwater Sustainable Management
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- UNESCO. Groundwater: Making the Invisible Visible. The United Nations World Water Development Report. 2022; 246p, Available online: https://unesdoc.unesco.org/ark:/48223/pf0000380721 (accessed on 15 October 2025).
- Wang, Y.X.; Deng, Y.M.; Zhang, J.W.; Yan, B.; Xiao, Z.Y.; Fan, R.Y.; Xie, X.J. Advances in groundwater quality and health studies: A comprehensive review. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2025, 68, 2753–2766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karandish, F.; Liu, S.; de Graaf, I. Global groundwater sustainability: A critical review of strategies and future pathways. J. Hydrol. 2025, 657, 133060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choubisa, S.L.; Choubisa, D.; Choubisa, A. Fluoride contamination of groundwater and its threat to health of villagers and their domestic animals and agriculture crops in rural Rajasthan, India. Environ. Geochem. Health 2023, 45, 607–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Udokpoh, U.U.; Ndem, U.A.; Abubakar, Z.S.; Yakasi, A.B.; Saleh, D. Comparative assessment of groundwater and surface water quality for domestic water supply in rural areas surrounding crude oil exploration facilities. J. Environ. Pollut. Hum. Health 2021, 9, 80–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marwaha, N.; Kourakos, G.; Levintal, E.; Dahlke, H.E. Identifying agricultural managed aquifer recharge locations to benefit drinking water supply in rural communities. Water Res. Res. 2021, 57, e2020WR028811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Kang, F.; Guo, Y.; Li, Z.; Liu, B.; Bu, H.; Xia, C.; He, Q. Evolution of hydrochemistry and water quality of karst groundwater under the effects of intense anthropogenic activities. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 371, 123059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Bian, J.; Li, Y.; Wu, J.; Sun, X.; Wang, Y. Characteristics of fluoride migration and enrichment in groundwater under the influence of natural background and anthropogenic activities. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 314, 120208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, F.; Wang, G.; Shi, Z.; Huang, X.; Xu, F.; Xu, Q.; Guo, L. Distributions, sources, and species of heavy metals/trace elements in shallow groundwater around the Poyang Lake, East China. Expo. Health 2018, 10, 211–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Xiao, P.; Song, W.; Li, Y.; Liu, Q. Hydrochemical characteristics and genetic analysis of groundwater in the red bed area of southern Jiangxi Province. Sci. Technol. Eng. 2023, 23, 14112–14122, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Mao, H.; Wang, G.; Liao, F.; Shi, Z.; Huang, X.; Li, B.; Yan, X. Geochemical evolution of groundwater under the influence of human activities: A case study in the southwest of Poyang Lake Basin. Appl. Geochem. 2022, 140, 105299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Hou, B.; Ye, L.; Xu, S.; Xin, H.; Zhang, S. Groundwater chemical evolution characteristics and human health risk assessment in Shicheng County, Jiangxi Province. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 37337–37355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Wang, T.; Bai, X.; Chen, G.; Wan, P.; Chen, S.; Chen, Q.; Wan, H.; Deng, F. Hydrochemical characteristics and formation mechanisms of groundwater in the Nanmiao emergency groundwater source area, Yichun, western Jiangxi, China. Water 2025, 17, 2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubang, J.; Liu, H.; Chen, R. Combined application of hydrogeological and geoelectrical study in groundwater exploration in karst-granite areas, Jiangxi Province. Water 2023, 15, 865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, X.; Wang, D.; Wang, P.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, D. Evaluation of water quality in surface water and shallow groundwater: A case study of a rare earth mining area in southern Jiangxi Province, China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2016, 188, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.Y.; Guo, H.M.; Pourret, O.; Wang, Z.; Liu, M.H.; Zhang, W.M.; Li, Z.B.; Gao, B.; Sun, Z.X.; Laine, P. Geochemical signatures of rare earth elements and yttrium exploited by acid solution mining around an ion-adsorption type deposit: Role of source control and potential for recovery. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 804, 150241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Guo, X.; Zhao, L.; Wang, J. Characteristics and influencing factors of karst groundwater in southern Jiangxi in Poyang Lake Basin. Shaanxi Water Res. 2023, 2, 97–100, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.T.; Wang, H.; Hu, H.J.; Fang, Y.H. Analysis of climate change characteristics in Ji’an City from 1960 to 2020. South-Central Agric. Sci. Technol. 2024, 45, 120–124. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xie, X.D.; Gu, Y.Y.; Lin, T.H. Regional Hydrogeological Survey Report of Ji’an Area; Unpublished Report; Hydrogeological Team of Jiangxi Geological Bureau: Nanchang, China, 1981. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Appelo, C.A.J.; Postma, D. Geochemistry, Groundwater and Pollution, 2nd ed.; A.A. Balkema: Leiden, The Netherlands, 2005; ISBN 9780415364287. [Google Scholar]
- Edmunds, W.M.; Shand, P. Natural Groundwater Quality; Blackwell Publishing: Oxford, UK, 2008; pp. 1–20. ISBN 9781405156752. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, J.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, Y.; Ta, M.; Wang, Y. Occurrence and hydrochemical characteristics of saline and salty springs in the Sichuan Basin of China. Geofluids 2019, 2019, 8671973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O Dochartaigh, B.E.; MacDonald, A.M.; Fitzsimons, V.; Ward, R. Scotland’s Aquifers and Groundwater Bodies; British Geological Survey: Nottingham, UK, 2015; 63p. [Google Scholar]
- Foster, S.S.D.; Chilton, P.J. Groundwater: The processes and global significance of aquifer degradation. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. B. 2003, 358, 1957–1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, H.; Wang, G.; Liao, F.; Shi, Z.; Rao, Z.; Zhang, H.; Qiao, Z.; Bai, Y.; Chen, X.; Yan, X.; et al. Spatiotemporal variation of groundwater nitrate concentration controlled by groundwater flow in a large basin: Evidence from multi-isotopes (15N, 11B, 18O, and 2H). Water Resour. Res. 2024, 60, e2023WR035299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, G.; Liu, B.; Sun, F.; Wang, R. Experimental investigation of the fracture evolution and fracture criterion of jointed sandstone subject to dry-wet cycling. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2023, 82, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.L.; Zhang, T.Y.; Zhang, L. The law of strength damage and deterioration of jointed sandstone after dry-wet cycles. J. Mt. Sci. 2023, 20, 1170–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, G.; Chen, J.; Zhang, Z.; Zeng, Y.; Yin, C.; Yu, J.; Wu, D.; Yuan, H.; Cen, M. Cyanobacterial dominance under CO2(aq)-limited conditions increases ecological risks in karst reservoirs. Water Res. 2025, 285, 124060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, K.; Dai, Z.; Meng, Y.; Yu, F.; Yao, J.; Zhang, W.; Chi, Z.; Chen, S. Mechanical behavior and fracture mechanism of red-bed mudstone under varied dry-wet cycling and prefabricated fracture planes with different loading angles. Theor. Appl. Fract. Mech. 2023, 127, 104094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbs, R.J. Mechanisms controlling world water chemistry. Science 1970, 170, 1088–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.T.; Wang, W.; Li, J.L.; Fang, Y.H. Hydrochemical characteristics and health risk assessment of groundwater in Dingbian county of the Chinese Loess Plateau, northwest China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2022, 81, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Y. Hydrochemical evolution of shallow and deep groundwater in Tongchuan city, China. J. Coastal Res. 2015, 73, 436–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Xu, Z.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Q. Geochemistry of the upper Han River basin, China: 3: Anthropogenic inputs and chemical weathering to the dissolved load. Chem. Geol. 2009, 264, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.L.; Peng, W.H.; Gui, H.R. Hydrochemical characteristics and quality assessment of deep groundwater from the coal-bearing aquifer of the Linhuan Coal-mining District, northern Anhui Province, China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2016, 188, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barzegar, R.; Moghaddam, A.A.; Tziritis, E.; Fakhri, M.S.; Soltani, S. Identification of hydrogeochemical processes and pollution sources of groundwater resources in the Marand Plain, northwest of Iran. Environ. Earth Sci. 2017, 76, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, J.; Li, S.; Chen, J.; Li, Y. Origin and hydrochemical evolution of confined groundwater in Shanghai, China. Front. Earth Sci. 2024, 11, 1117132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Zhang, L.; Pei, L.; Li, X.; Yang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Liang, L. Chemical characteristics and controlling factors of shallow groundwater in the lower reaches of Changhua River basin, Hainan Island, China. Water 2023, 15, 3508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houatmia, F.; Azouzi, R.; Charef, A.; Bédir, M. Assessment of groundwater quality for irrigation and drinking purposes and identification of hydrogeochemical mechanisms evolution in Northeastern, Tunisia. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhang, G.; Guo, H.; Wang, Z.; Ge, Q. Occurrences of nitrate-contaminated groundwater in the piedmont aquifers: Hydrogeochemical characteristics and health risks. Environ. Geochem. Health 2024, 46, 366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.Q.; Wei, S.C.; Liang, H.Y.; Zheng, W.B.; Li, X.X.; Hu, C.S.; Currell, M.J.; Zhou, F.; Min, L.L. Nitrogen stock and leaching rates in a thick vadose zone below areas of long-term nitrogen fertilizer application in the North China Plain: A future groundwater quality threat. J. Hydrol. 2019, 576, 28–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zazouli, M.A.; Yousefi, Z.; Babanezhad, E.; Ala, A. Evaluation of combined efficiency of conventional coagulation-flocculation process with advanced oxidation process (sulfate-hydroxyl radical) in leachate treatment. Environ. Eng. Res. 2024, 29, 230548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, A.; Gad, A.; Ahmed, A.; Arman, H.; Farhat, H.I. Groundwater hydrochemical characteristics and water quality in Egypt’s central eastern desert. Water 2023, 15, 971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amer, R.; Ripperdan, R.; Wang, T.; Encarnación, J. Groundwater quality and management in arid and semi-arid regions: Case study, Central Eastern Desert of Egypt. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2012, 69, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.; Xiao, Y.; Yin, S.; Pan, X.; Niu, Y.; Shao, J.; Cui, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Hao, Q. Natural and anthropogenic factors affecting the shallow groundwater quality in a typical irrigation area with reclaimed water, North China Plain. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2017, 189, 514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raheja, H.; Goel, A.; Pal, M. Groundwater quality appraisal using IWQI and PCA for irrigation uses. ISH J. Hydraul. Eng. 2023, 29 (Suppl. 1), 264–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huneau, F.; Jaunat, J.; Kavouri, K.; Plagnes, V.; Rey, F.; Dörfliger, N. Intrinsic vulnerability mapping for small mountainous karst aquifers, implementation of the new PaPRIKa method to Western Pyrenees (France). Eng. Geol. 2013, 161, 81–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pochon, A.; Tripet, J.P.; Kozel, R.; Meylan, B.; Sinreich, M.; Zwahlen, F. Groundwater protection in fractured media: A vulnerability-based approach for delineating protection zones in Switzerland. Hydrogeol. J. 2008, 16, 1267–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoker, P.; Albrecht, T.; Follingstad, G.; Carlson, E. Integrating land use planning and water management in US cities: A literature review. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2022, 58, 321–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Category | pH | Concentration (mg/L) | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K+ | Na+ | Ca2+ | Mg2+ | SO42− | NO3− | Cl− | HCO3− | TH | TDS | |||
| pore water (n = 133) | Max. | 8.50 | 88.30 | 80.60 | 146.00 | 52.00 | 98.70 | 320.00 | 81.00 | 446.00 | 449.00 | 820.00 |
| Min. | 4.70 | 0.23 | 0.67 | 1.17 | 0.50 | 0.33 | 0.09 | 0.83 | 0.55 | 6.30 | 20.00 | |
| Avg. | 6.66 | 7.45 | 10.87 | 38.95 | 6.37 | 15.32 | 15.41 | 14.90 | 114.35 | 122.60 | 180.03 | |
| Std. | 0.74 | 12.67 | 9.82 | 33.47 | 7.07 | 18.45 | 30.47 | 13.01 | 99.34 | 100.82 | 119.75 | |
| Vc. | 0.11 | 1.70 | 0.90 | 0.86 | 1.11 | 1.20 | 1.98 | 0.87 | 0.87 | 0.82 | 0.67 | |
| fissure–pore water (n = 44) | Max. | 8.10 | 39.70 | 597.00 | 737.00 | 202.00 | 1427.00 | 82.40 | 762.00 | 399.00 | 1868.0 | 3282.0 |
| Min. | 5.20 | 0.32 | 0.59 | 4.62 | 0.46 | 0.65 | 0.04 | 0.91 | 1.42 | 16.00 | 27.00 | |
| Avg. | 6.84 | 5.60 | 41.79 | 68.38 | 13.90 | 52.45 | 16.28 | 73.07 | 109.30 | 204.60 | 329.66 | |
| Std. | 0.73 | 7.29 | 104.91 | 120.27 | 32.04 | 214.44 | 22.60 | 170.68 | 91.53 | 316.85 | 562.81 | |
| Vc. | 0.11 | 1.30 | 2.51 | 1.76 | 2.30 | 4.09 | 1.39 | 2.34 | 0.84 | 1.55 | 1.71 | |
| karst water (n = 33) | Max. | 8.20 | 23.40 | 13.30 | 132.00 | 31.40 | 53.60 | 12.80 | 19.50 | 447.00 | 405.00 | 432.00 |
| Min. | 6.60 | 0.22 | 0.56 | 1.49 | 0.31 | 0.68 | 0.60 | 1.34 | 5.00 | 5.50 | 13.00 | |
| Avg. | 7.35 | 2.54 | 2.93 | 65.42 | 10.11 | 8.50 | 5.54 | 7.41 | 197.79 | 206.46 | 202.48 | |
| Std. | 0.40 | 5.45 | 2.85 | 27.92 | 7.64 | 10.95 | 3.24 | 5.00 | 87.89 | 82.92 | 88.26 | |
| Vc. | 0.05 | 2.14 | 0.97 | 0.43 | 0.76 | 1.29 | 0.59 | 0.67 | 0.44 | 0.40 | 0.44 | |
| bedrock fissure water (n = 25) | Max. | 7.50 | 32.70 | 41.70 | 108.00 | 17.00 | 59.20 | 47.80 | 39.50 | 265.00 | 301.00 | 296.00 |
| Min. | 5.40 | 0.43 | 0.56 | 2.83 | 0.70 | 0.71 | 0.10 | 0.94 | 16.00 | 11.20 | 22.00 | |
| Avg. | 6.68 | 6.71 | 11.23 | 26.01 | 4.47 | 10.46 | 10.72 | 11.21 | 89.68 | 87.88 | 139.92 | |
| Std. | 0.54 | 8.67 | 8.89 | 26.55 | 3.79 | 15.31 | 14.79 | 10.81 | 63.92 | 78.42 | 78.73 | |
| Vc. | 0.08 | 1.29 | 0.79 | 1.02 | 0.85 | 1.46 | 1.38 | 0.96 | 0.71 | 0.89 | 0.56 | |
| Pore Water | Fissure–Pore Water | Karst Water | Bedrock Fissure Water | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water Type | Percentage | Water Type | Percentage | Water Type | Percentage | Water Type | Percentage |
| HCO3-Ca | 34.59% | HCO3-Ca | 38.64% | HCO3-Ca | 69.70% | HCO3-Na·Ca | 40% |
| HCO3·Cl-Na·Ca | 19.55% | HCO3-Na·Ca | 11.36% | HCO3-Ca·Mg | 24.24% | HCO3-Ca | 16% |
| HCO3-Na·Ca | 11.28% | HCO3·Cl-Na·Ca | 9.09% | HCO3·Cl-Na·Ca | 6.06% | HCO3·Cl-Na·Ca | 12% |
| HCO3-Ca·Mg | 6.77% | HCO3·Cl-Ca | 9.09% | HCO3-Ca·Mg | 12% | ||
| HCO3·Cl-Ca | 6.77% | Cl-Na·Ca | 9.09% | ||||
| K+ | Na+ | Ca2+ | Mg2+ | SO42− | NO3− | Cl− | HCO3− | TH | TDS | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K+ | 1 | 0.623 * | 0.172 * | 0.251 * | 0.491 * | 0.324 * | 0.546 * | 0.081 | 0.184 * | 0.351 * |
| Na+ | 0.623 * | 1 | 0.104 | 0.220 * | 0.423 * | 0.341 * | 0.657 * | 0.015 | 0.129 ** | 0.366 * |
| Ca2+ | 0.172 * | 0.104 | 1 | 0.759 * | 0.628 * | −0.039 | 0.324 * | 0.899 * | 0.983 * | 0.891 * |
| Mg2+ | 0.251 * | 0.220 * | 0.759 * | 1 | 0.578 * | 0.012 | 0.408 * | 0.687 * | 0.826 * | 0.752 * |
| SO42− | 0.491 * | 0.423 * | 0.628 * | 0.578 * | 1 | 0.094 | 0.517 * | 0.514 * | 0.639 * | 0.728 * |
| NO3− | 0.324 * | 0.341 * | −0.039 | 0.012 | 0.094 | 1 | 0.481 * | −0.226 | −0.038 | 0.105 |
| Cl− | 0.546 * | 0.657 * | 0.324 * | 0.408 * | 0.517 * | 0.481 * | 1 | 0.110 | 0.338 * | 0.491 * |
| HCO3− | 0.081 | 0.015 | 0.899 * | 0.687 * | 0.514 * | −0.226 * | 0.110 | 1 | 0.908 * | 0.801 * |
| TH | 0.184 * | 0.129 ** | 0.983 * | 0.826 * | 0.639 * | −0.038 | 0.338 * | 0.908 * | 1 | 0.902 * |
| TDS | 0.351 * | 0.366 * | 0.891 * | 0.752 * | 0.728 * | 0.105 | 0.491 * | 0.801 * | 0.902 * | 1 |
| Parameter | PC1 | PC2 | PC3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 78.09% | 15.79% | 3.40% | |
| K+ | −0.823 | −0.180 | −0.114 |
| Na+ | −0.729 | −0.060 | −0.519 |
| Ca2+ | −0.313 | −0.455 | 0.297 |
| Mg2+ | −0.818 | −0.262 | −0.122 |
| SO42− | −0.712 | −0.235 | −0.476 |
| NO3- | 0.005 | 2.473 | 1.394 |
| Cl− | −0.654 | 0.044 | −0.841 |
| HCO3- | 0.989 | −1.238 | 1.384 |
| TH | 1.057 | −0.743 | 0.787 |
| TDS | 1.999 | 0.656 | −1.789 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, C.; Xia, B.; Dong, L.; Bai, X.; Wang, X.; Xie, Y.; Yu, S.; Liu, H. Hydrogeochemical Characteristics and Formation Mechanisms of Groundwater Around Ji’an City, Southern China. Sustainability 2025, 17, 10306. https://doi.org/10.3390/su172210306
Xu C, Xia B, Dong L, Bai X, Wang X, Xie Y, Yu S, Liu H. Hydrogeochemical Characteristics and Formation Mechanisms of Groundwater Around Ji’an City, Southern China. Sustainability. 2025; 17(22):10306. https://doi.org/10.3390/su172210306
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Chao, Bing Xia, Linming Dong, Ximin Bai, Xiaoyun Wang, Yingying Xie, Shengpin Yu, and Haiyan Liu. 2025. "Hydrogeochemical Characteristics and Formation Mechanisms of Groundwater Around Ji’an City, Southern China" Sustainability 17, no. 22: 10306. https://doi.org/10.3390/su172210306
APA StyleXu, C., Xia, B., Dong, L., Bai, X., Wang, X., Xie, Y., Yu, S., & Liu, H. (2025). Hydrogeochemical Characteristics and Formation Mechanisms of Groundwater Around Ji’an City, Southern China. Sustainability, 17(22), 10306. https://doi.org/10.3390/su172210306






