Sediment Quality in an Anthropogenically Disturbed Shallow Lake: A Case Study of Baiyangdian Lake
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Overview of Baiyangdian Lake and Sample Collection
2.2. Sample Analysis
2.3. Evaluation Methods
- (1)
- Comprehensive Pollution Index
- (2)
- Organic index and organic nitrogen evaluation
2.4. Data Processing
3. Results and Discussion
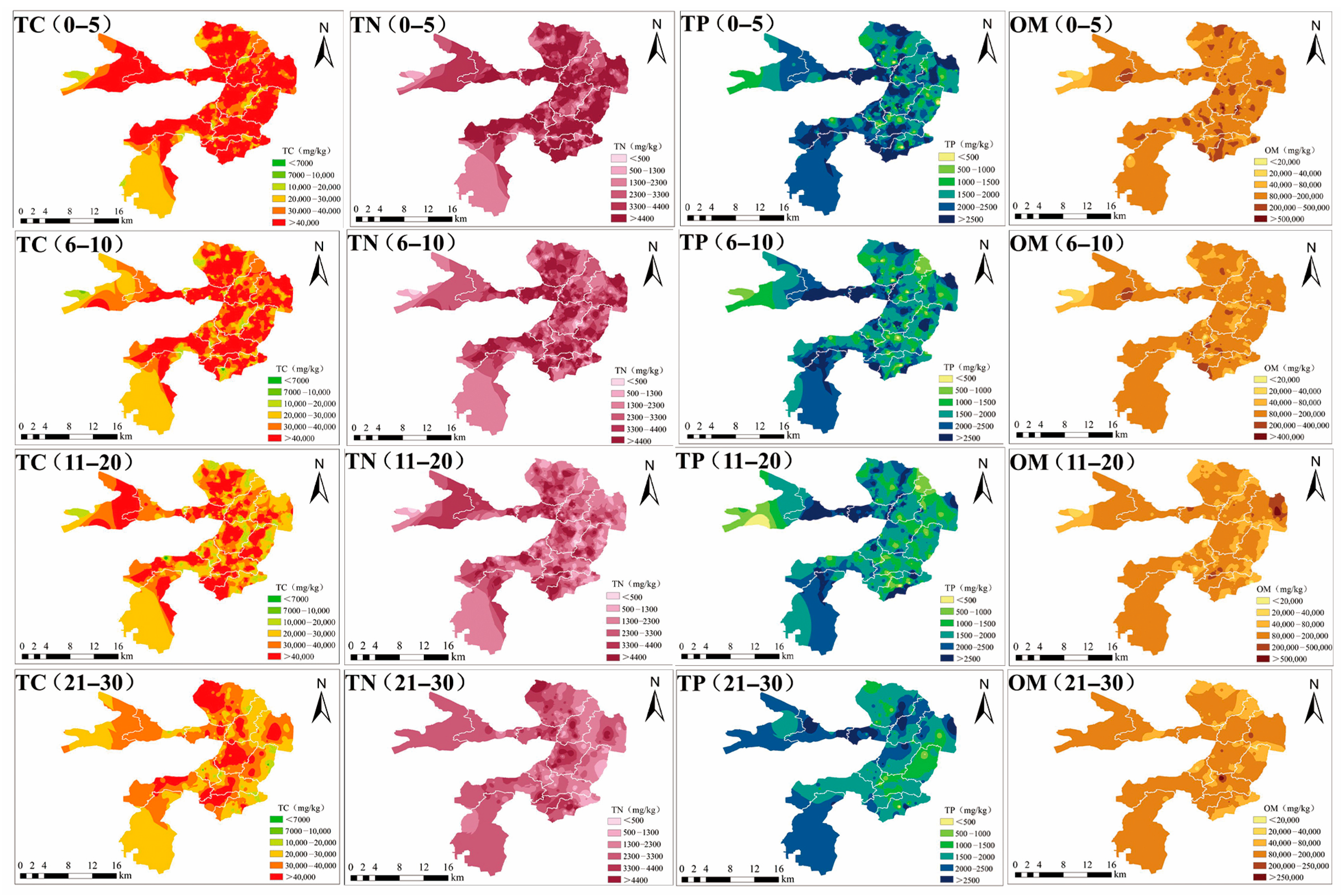
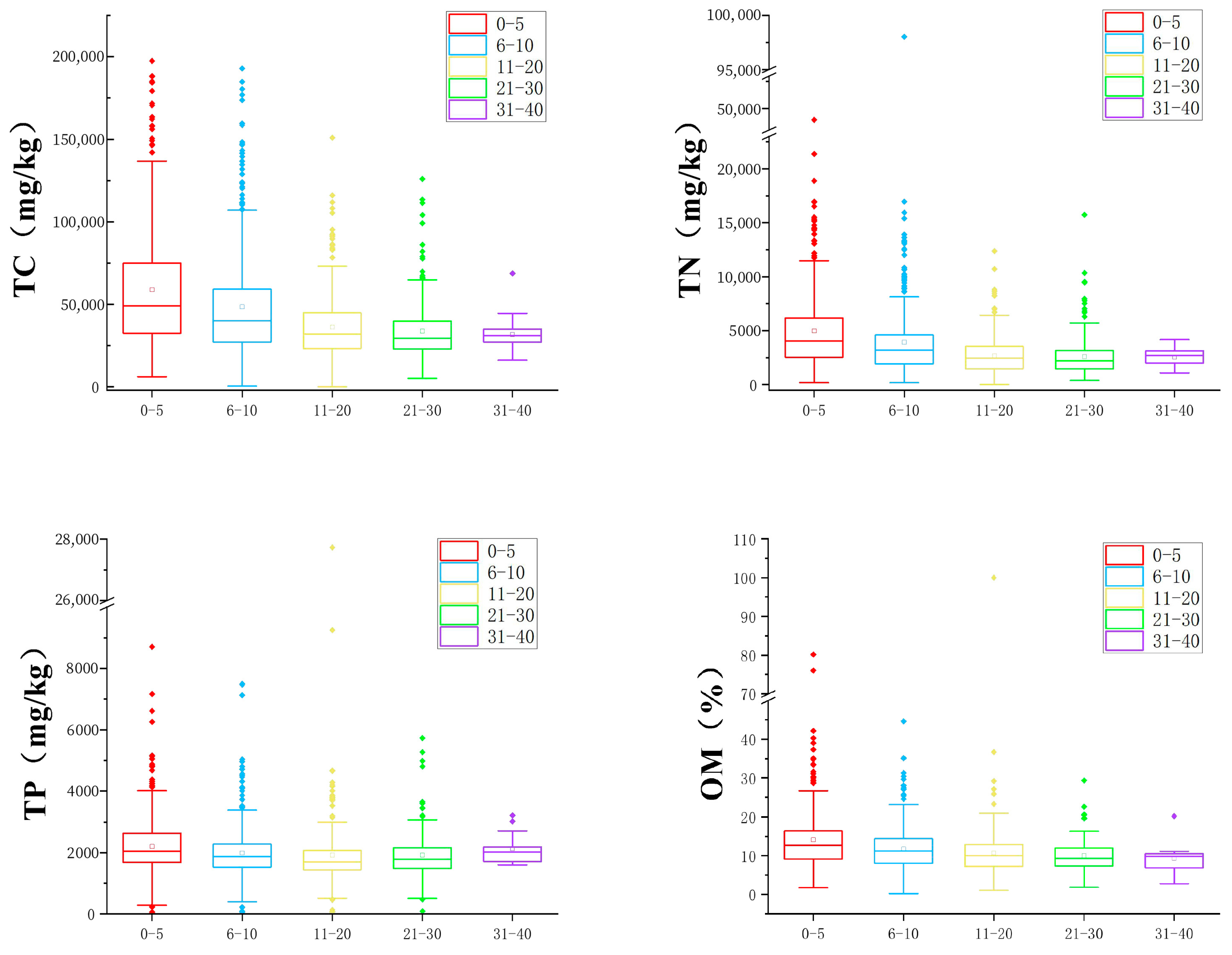
3.1. Spatial Distribution of Nutrients in Sediments
3.2. Evaluation of Nutrient Pollution in Surface Sediments
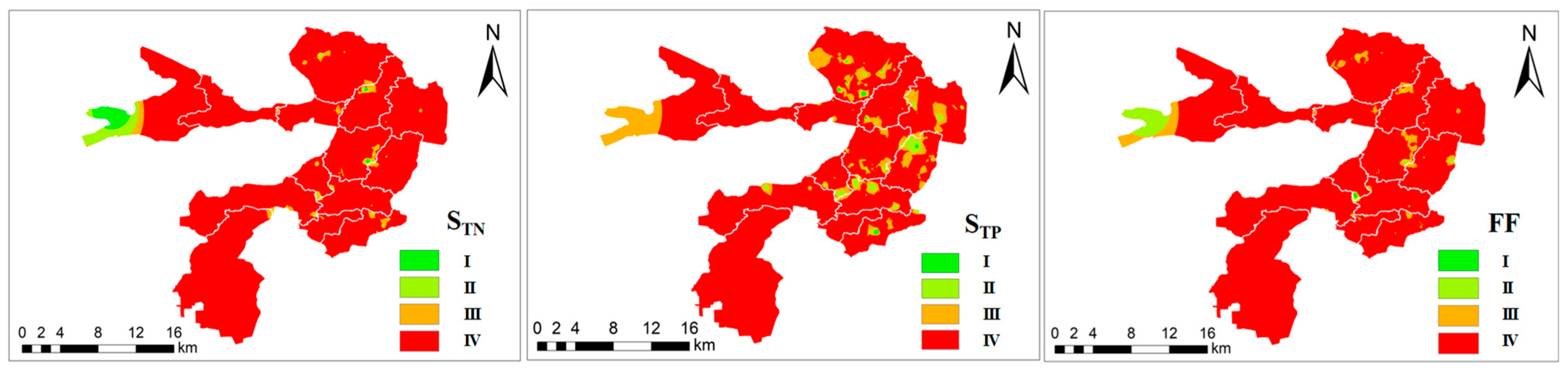
3.2.1. Comprehensive Pollution Index
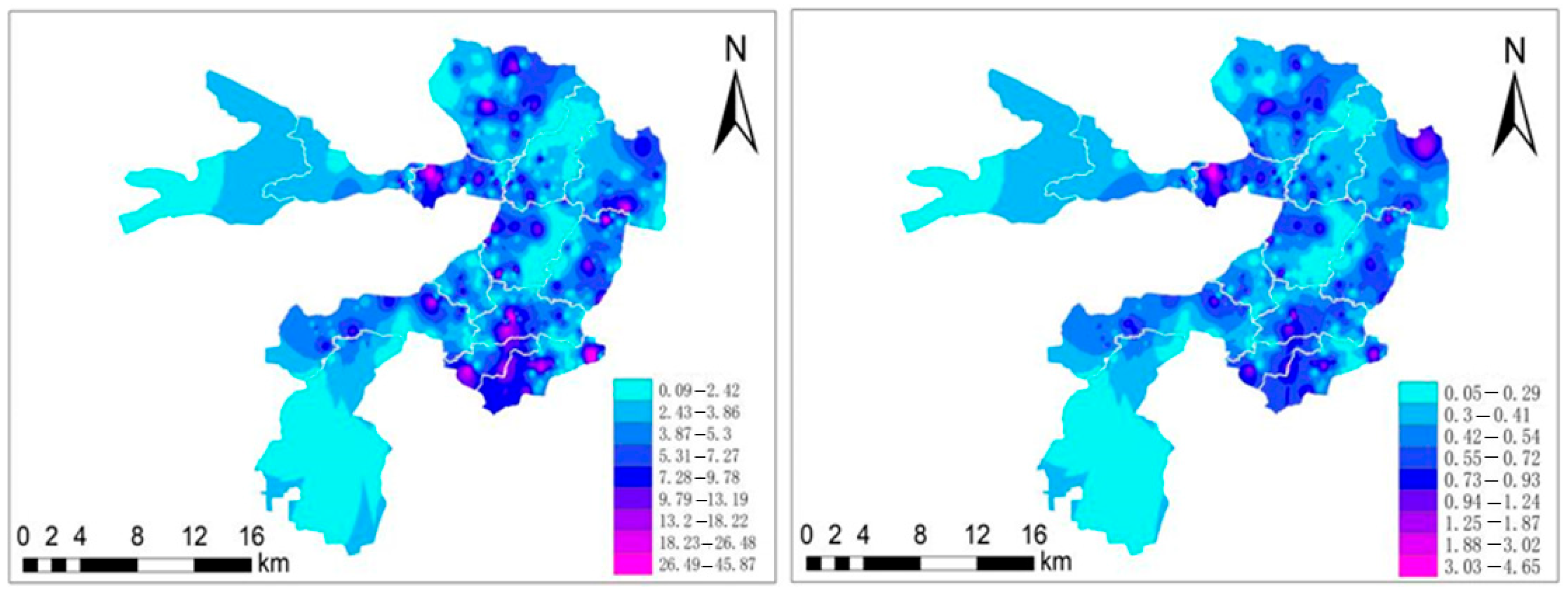
3.2.2. Characteristics of the OPI and ONI
3.3. Sediment Nutrient Source Analysis
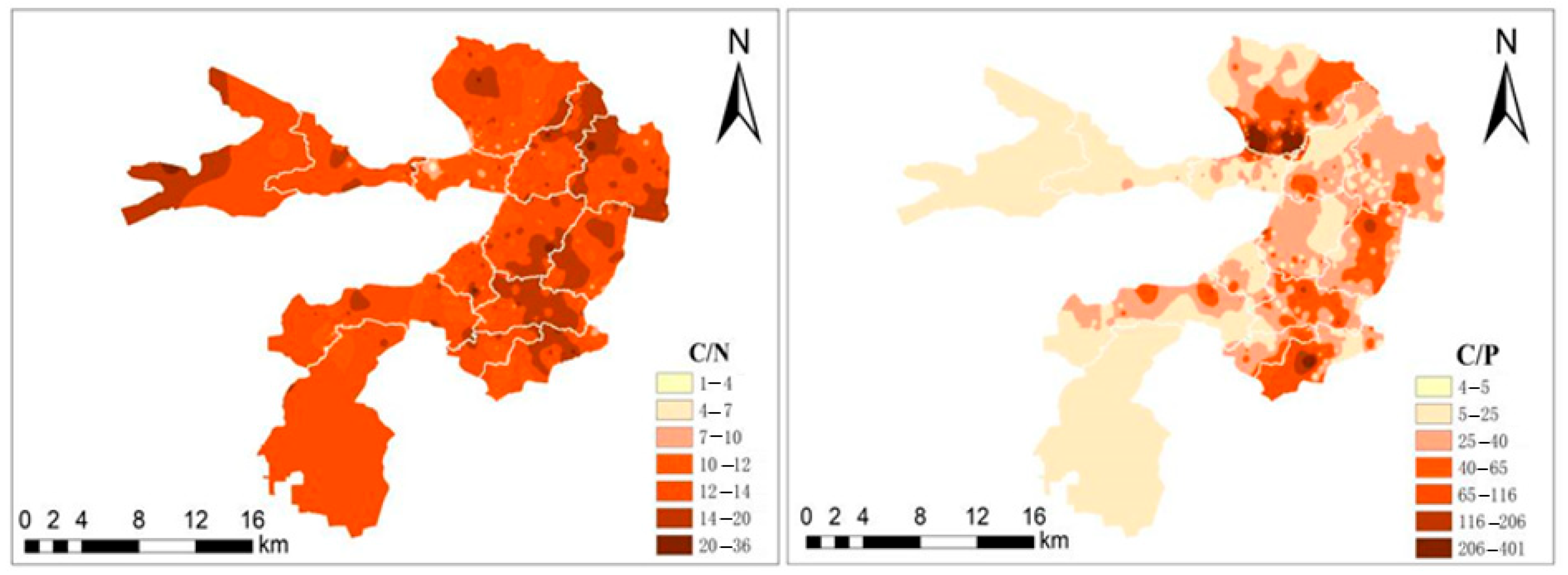
3.3.1. Characterization of the Sediment C/N and C/P
3.3.2. Sediment Nutrient Correlation Analysis
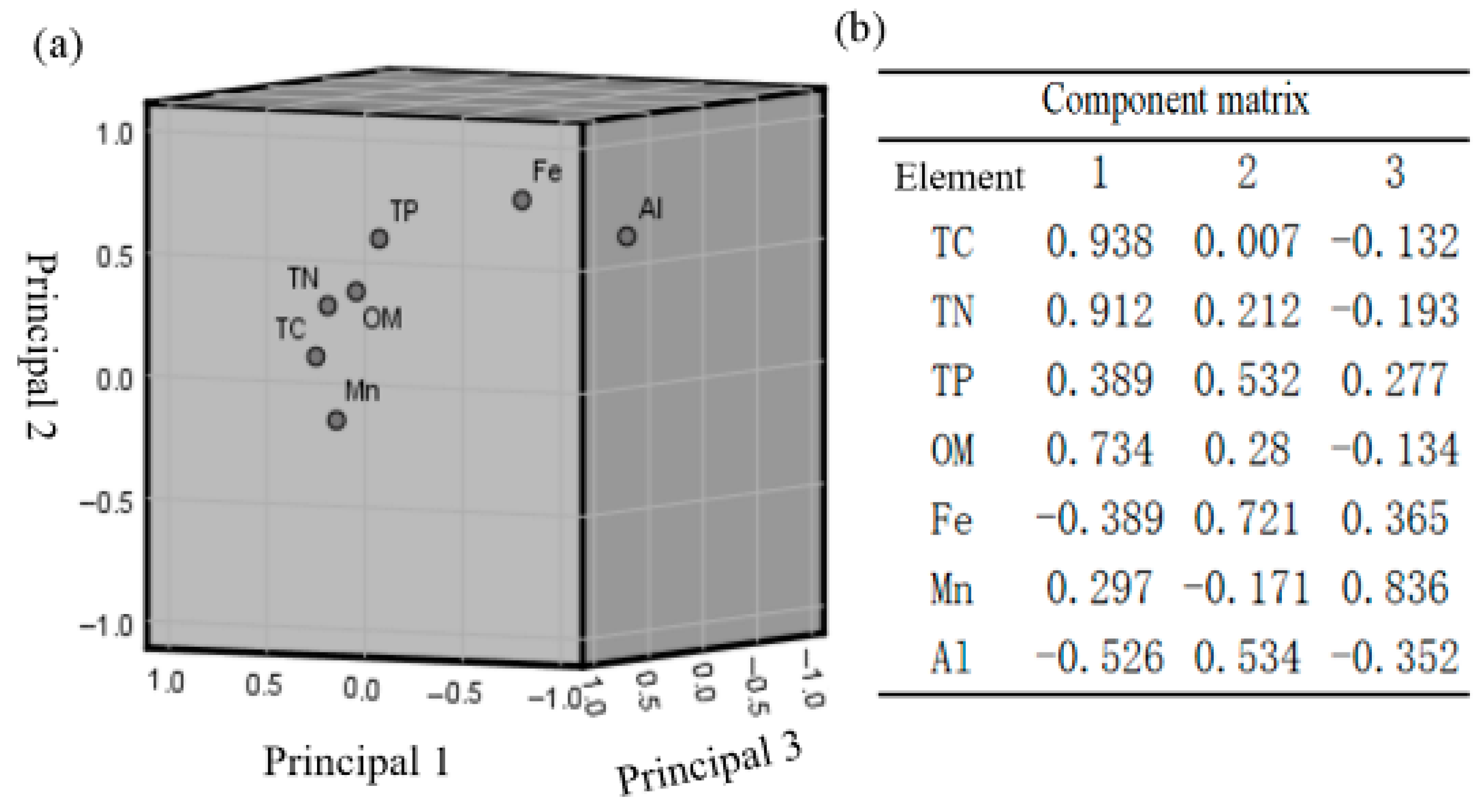
3.3.3. Principal Component Analysis
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- The OM and TN concentrations in the BYDL sediments were high and showed spatial variation, and the pollutant concentrations were particularly high in the marsh area. Overall, the concentrations were ranked as follows: marsh > ditch > open precipitation surface > watercourse or pond. Also, the TN, TP and OM concentrations were higher in the surface sediments (0–10 cm) than in the deeper sediments.
- (2)
- The STN, STP, and FF indices showed that more than 99.73% of the surface sediments in the BYDL were severely polluted. The ONI and OPI of the BYDL had similar spatial distributions and indicated higher pollution in the Nanliuzhuang, Caiputai, and Julongdian areas than in the other areas of the lake.
- (3)
- The C/N ratio and correlation analysis of the sediment properties showed that the OM and TN pollution of the BYDL bottom sediment were related to the natural decay of aquatic plants in the same region. These results show that it would be useful to harvest aquatic plants and reeds from transitional growth areas (e.g., Nanliuzhuang, Caiputai, and Julongdian) before the rainy season and at the end of the growth cycle (e.g., September–October) to capture nutrients before senescence and decomposition. This balanced harvesting approach would help to avoid further enrichment of N, P, and OM in sediments caused by decaying aquatic plants. At the same time, it would be useful to dredge the sediments from the heavily polluted areas of the BYDL watershed during the dry season (e.g., November–March) to minimize resuspension and ecological impact. A sustainable dredging strategy should prioritize localized hotspots while preserving benthic habitats and ecological functions. A long-term monitoring program (e.g., seasonal sampling of sediment and water quality) is recommended to evaluate the effectiveness of these interventions and track the recovery of the ecosystem.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhuo, Y.; Zeng, W.; Ma, B.; Cui, D.; Xie, Y.; Wang, J. Spatiotemporal variation and influencing factors of nitrogen and phosphorus in lake sediments in China since 1850. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 368, 133170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Yang, P.; Geng, J.; Yin, H.; Chen, K. Sediment internal nutrient loading in the most polluted area of a shallow eutrophic lake (Lake Chaohu, China) and its contribution to lake eutrophication. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 262, 114292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Li, J.; Yin, H. Phosphorus internal loading and sediment diagenesis in a large eutrophic lake (Lake Chaohu, China). Environ. Pollut. 2022, 292, 118471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Du, Y.; Chen, K.; Ma, S.; Chen, B.; Lan, Y. Contrasting exchanges of nitrogen and phosphorus across the sediment–water interface during the drying and re-inundation of littoral eutrophic sediment. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 255, 113356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, J.; Wen, S.; Zhang, L.; Wang, J.; Liu, C.; Yu, J.; Zhang, L.; Fan, C. Nitrogen budget at sediment–water interface altered by sediment dredging and settling particles: Benefits and drawbacks in managing eutrophication. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 406, 124691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abell, J.M.; Özkundakci, D.; Hamilton, D.P.; Reeves, P. Restoring shallow lakes impaired by eutrophication: Approaches, outcomes, and challenges. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 52, 1199–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Socohou, A.A.; Djihouessi, M.B.; Tigo, B.A.; Viainon, V.M.; Adandedji, F.M.; Adounpke, J.; Aina, M.P. Spatio-temporal dynamics of nutrients at the water-sediment interface: Case of the Nokoue lagoon in Southern Benin. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2024, 196, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horppila, J. Sediment nutrients, ecological status and restoration of lakes. Water Res. 2019, 160, 206–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, M.; Dai, Y.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, S. Health and ecotoxicological risk assessment for human and aquatic organism exposure to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the Baiyangdian Lake. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 574–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Yang, Z.; Liu, X. Phosphorus fractions, sorption characteristics, and its release in the sediments of Baiyangdian Lake, China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2011, 179, 335–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Xia, X.; Yang, Z.; Xia, N. Temporal and spatial variations of nutrients in Baiyangdian Lake, North China. J. Environ. Inform. 2011, 17, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Shan, B.; Zhao, Y.; Song, Z.; Tang, W. Spatial distribution, fractionation, toxicity and risk assessment of surface sediments from the Baiyangdian Lake in northern China. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 90, 633–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HJ 632-2011; Soil-Determination of Total Phosphorus by Alkali Fusion–Mo-Sb Anti Spectrophotometric Method. Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2012.
- Zhang, J.-W.; Wei, J.; Liu, L.; Wang, J.; Zhu, Y.-R.; Duan, L. Distribution characteristics and pollution assessment of nutrients in Hengshui Lake sediments. Huanjing Kexue 2020, 41, 5389–5399. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, W.; Fan, Y.; Lu, J.; Zhu, S. Nutrient Distribution and Interrelationships in Chaohu Lake, China: Insights from Sedimentary Records. Expo. Health 2025, 17, 863–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wei, H.; Liang, Z.; Zhan, S.; Jia, H.; Guo, S.; Ge, P. Contamination, risk and quantitative identification of nutrients and potentially toxic elements in the surface sediments of Baiyangdian Lake, North China. Ecotoxicology 2022, 31, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, W.; Wang, L.G.; Zhang, H.Z.; Wang, J.F.; Tian, Z.F.; Chen, X.Y. Study on phosphorus pollution load of aquaculture in Baiyangdian Lake. Adv. Mater. Res. 2012, 518, 1406–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.; Ao, L.; Zhang, S. Sedimentary phosphorus fractions in typical lacustrine wetland of Changshou Lake flowing into the Three-Gorges Reservoir. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2022, 109, 706–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Chu, E.; Xu, M.; Guo, J.; Zhang, Y. Temporal and spatial variation analysis on nutritive salt of Hongze Lake. Environ. Eng. Res. 2015, 20, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Liang, T. Distribution characteristics of phosphorus in the sediments and overlying water of Poyang Lake. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0125859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Yuan, H.; Liu, E.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y. Spatial distribution and stratigraphic characteristics of surface sediments in Taihu Lake, China. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2011, 56, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Huang, J.; Zeng, G.; Yuan, X.; Li, X.; Liang, J.; Wang, X.; Tang, X.; Bai, B. Spatial risk assessment and sources identification of heavy metals in surface sediments from the Dongting Lake, Middle China. J. Geochem. Explor. 2013, 132, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Ma, L.; Yu, H.; Zeng, H.; Liu, W.; Abuduwaili, J. Sediment geochemical records of environmental change in Lake Wuliangsu, Yellow River Basin, north China. J. Paleolimnol. 2013, 50, 245–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Zhao, H.; Wang, S.; Zhang, L.; Qiao, Z. Coupling characteristics and environmental significance of nitrogen, phosphorus and organic carbon in the sediments of Erhai Lake. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 19901–19914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lone, A.M.; Shah, R.A.; Achyuthan, H.; Rafiq, M. Source identification of organic matter using C/N ratio in freshwater lakes of Kashmir Valley, Western Himalaya, India. Himal Geol 2018, 39, 101–114. [Google Scholar]
- Amor, R.B.; Jerbi, H.; Abidi, M.; Gueddari, M. Assessment of trace metal contamination, total organic carbon and nutrient accumulation in surface sediments of Monastir Bay (Eastern Tunisia, Mediterranean Sea). Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2020, 34, 101089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Qiu, J.; Hong, Q.; Chen, L. Simulation of spatial and temporal distributions of non-point source pollution load in the Three Gorges Reservoir Region. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 493, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Yu, R.; Chen, J.; Leng, X.; Zhao, D.; Jia, H.; An, S. Ecological risk of heavy metals in lake sediments of China: A national-scale integrated analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 334, 130206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Bai, Z.-L.; Liu, W.-X.; Kong, X.-Z.; Yang, B.; Yang, C.; Jørgensen, S.E.; Xu, F.-L. Occurrence, spatial distribution, sources, and risks of polychlorinated biphenyls and heavy metals in surface sediments from a large eutrophic Chinese lake (Lake Chaohu). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 10335–10348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.-H.; Cui, B.-S.; Yang, Z.-F. Influence of hydrological characteristic change of Baiyangdian on the ecological environment in wetland. J. Nat. Resour. 2004, 19, 62–68. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, W.; Yan, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, B.-T.; Wang, H. Seasonal variation of aquatic macrophytes and its relationship with environmental factors in Baiyangdian Lake, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 708, 135112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuo, H.-H.; Qiu, G.-S.; Zhai, W.-Y.; Liu, Y.-B.; Lan, J.J.H.J.k.X.H.K. Evaluation of temporal and spatial variation characteristics of nutrients in surface sediment in the Three Gorges Reservoir area. Huanjing Kexue 2017, 38, 5020–5031. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Z.; Huang, T.; Li, Y.; Ma, W.; Zhou, S.; Long, S. Sediment pollution characteristics and in situ control in a deep drinking water reservoir. J. Environ. Sci. 2017, 52, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Chen, X.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, W.; Wang, D.; Wang, H. The spatial variations of water quality and effects of water landscape in Baiyangdian Lake, North China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 16716–16726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, N.; Sheng, Y.; Tang, Q.; Liu, X. Mechanisms of nitrogen and phosphorus release from heavily polluted coastal sediments and identification of influencing factor. Environ. Res. Commun. 2025, 7, 025005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Zhang, W.; Shan, B. Distribution of nitrogen and phosphorus and estimation of nutrient fluxes in the water and sediments of Liangzi Lake, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 7096–7104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Lv, C.; Gu, C.; Yu, Y.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Tang, C. Pollutants Source Assessment and Load Calculation in Baiyangdian Lake Using Multi-Model Statistical Analysis. Water 2022, 14, 3386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.-Y.; Cao, P.-P.; Xu, C.; Liu, M.-S. Effects of aquatic plants during their decay and decomposition on water quality. Shengtai Xuebao 2013, 24, 83–89. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, T.; Qin, B.; Brookes, J.D.; Yan, W.; Ji, X.; Feng, J. Spatial distribution of sediment nitrogen and phosphorus in Lake Taihu from a hydrodynamics-induced transport perspective. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 650, 1554–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Gong, J.; Zeng, Q.; Yang, M.; Wang, Y. Landscape pattern evolution processes and the driving forces in the wetlands of lake Baiyangdian. Sustainability 2021, 13, 9747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Evaluation Methodology-Classification of Integrated Pollution Levels of Baiyangdian Sediments | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Classification | STN | STP | FF |
| Clean | <1.0 | <0.5 | <1.0 |
| Slightly polluted | 1.0–1.5 | 0.5–1.0 | 1.0–1.5 |
| Moderately polluted | 1.5–2.0 | 1.0–1.5 | 1.5–2.0 |
| Heavily polluted | >2.0 | >1.5 | >2.0 |
| Organic pollution index (OPI) | Organic nitrogen index (ONI) | ||
| Threshold interval | Pollution level | Threshold interval | Pollution level |
| <0.05 | Clean | <0.033 | Clean |
| ≥0.05–<0.20 | Subclean | ≥0.033–<0.066 | Subclean |
| ≥0.20–<0.50 | Fairly clean | ≥0.066–<0.133 | Fairly clean |
| ≥0.50 | Organic Contamination | ≥0.133 | Organic Contamination |
| Lakes | Provinces | Organic Matter (mg/kg) | TN (mg/kg) | TP (mg/kg) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Poyang Lake | Jiangxi | 15,900 | 1340 | 460 | [19] |
| Taihu Lake | Jiangsu | 12,800 | 860 | 560 | [20] |
| Chaohu Lake | Anhui | 64,800 | 1794 | 792 | [14] |
| Dongting Lake | Hunan | 20,600 | 1340 | 294 | [21] |
| Wuliangsu Sea | Inner Mongolia | 3050 | 1570 | 410 | [22] |
| Hengshui Lake | Hebei | 93,226 | 1850 | 1020 | [13] |
| Baiyangdian | Hebei | 120,500 | 3677 | 2038 | This work |
| Index | All Waters | Open Precipitation | Watercourses | Ditches | Fishponds | Marshes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OPI | ||||||
| Clean (I) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Subclean (II) | 1.10 | 0.28 | 0.83 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Fairly Clean (III) | 6.08 | 2.20 | 3.04 | 0.28 | 0.28 | 0.28 |
| Organic Contamination (IV) | 92.82 | 26.24 | 39.5 | 15.48 | 8.56 | 3.04 |
| ONI | ||||||
| Clean (I) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Subclean (II) | 0.83 | 0.28 | 0.55 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Fairly Clean (III) | 5.52 | 1.93 | 2.48 | 0.28 | 0.55 | 0.28 |
| Organic Contamination (IV) | 93.65 | 26.52 | 40.33 | 15.47 | 8.29 | 3.04 |
| Nutrient | TC | TN | TP | OM | C/N |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TC | 1 | ||||
| TN | 0.943 * | 1 | |||
| TP | 0.314 ** | 0.353 ** | 1 | ||
| OM | 0.659 ** | 0.696 ** | 0.225 * | 1 | |
| C/N | −0.189 * | −0.424 * | −0.228 ** | −0.343 ** | 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qu, W.; Fu, D.; Xi, Y.; Wang, S. Sediment Quality in an Anthropogenically Disturbed Shallow Lake: A Case Study of Baiyangdian Lake. Sustainability 2025, 17, 10184. https://doi.org/10.3390/su172210184
Qu W, Fu D, Xi Y, Wang S. Sediment Quality in an Anthropogenically Disturbed Shallow Lake: A Case Study of Baiyangdian Lake. Sustainability. 2025; 17(22):10184. https://doi.org/10.3390/su172210184
Chicago/Turabian StyleQu, Wenfeng, Deyu Fu, Yin Xi, and Shengrui Wang. 2025. "Sediment Quality in an Anthropogenically Disturbed Shallow Lake: A Case Study of Baiyangdian Lake" Sustainability 17, no. 22: 10184. https://doi.org/10.3390/su172210184
APA StyleQu, W., Fu, D., Xi, Y., & Wang, S. (2025). Sediment Quality in an Anthropogenically Disturbed Shallow Lake: A Case Study of Baiyangdian Lake. Sustainability, 17(22), 10184. https://doi.org/10.3390/su172210184






