Abstract
Against the backdrop of global warming and intensified anthropogenic activities, groundwater reserves are rapidly depleting and facing unprecedented threats to their long-term sustainability. Consequently, investigating groundwater reserves is of critical importance for ensuring water security and promoting sustainable development. This study takes the Heilongjiang (Amur) River Basin as the research area. Groundwater storage was estimated using data from the Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment (GRACE) satellite and the Global Land Data Assimilation System (GLDAS) covering the period from 2002 to 2024. A combination of Random Forest (RF), SHapley Additive exPlanation (SHAP) models, and Pearson partial correlation coefficients was employed to analyze the spatiotemporal evolution characteristics, driving mechanisms, and spatial linear correlations of the primary influencing factors. The results indicate that the basin’s groundwater storage anomaly (GWSA) exhibits an overall declining trend. GWSA is influenced by multiple factors, including climatic and anthropogenic drivers, with temperature (TEM) and precipitation (PRE) identified as the primary controlling variables. Spatiotemporal analysis reveals significant spatial heterogeneity in the relationship between GWSA evolution and its primary drivers. This study adopts a “retrieval–attribution–spatial analysis” framework to provide a scientific basis for enhancing regional groundwater security and supporting sustainable development goals.
1. Introduction
Water resources constitute essential natural assets that sustain ecosystem stability and underpin human societal development [1,2]. Owing to groundwater’s extensive distribution, high quality, and significant potential for sustainable utilization, its dynamic variations exert a direct influence on regional water security, agricultural irrigation, ecological integrity, and sustainable development [3,4]. In recent years, under the dual pressures of global warming and anthropogenic disturbances, the Heilongjiang (Amur) River Basin has exhibited pronounced spatial heterogeneity in groundwater storage. However, aquifers have received insufficient attention [5], thereby placing the sustainability of groundwater resources under severe threat. The Heilongjiang (Amur) River Basin is characterized by pronounced temperature gradients across latitudes, precipitation patterns modulated by longitude, and complex topographic conditions. These climatic and topographic factors amplify local variations, making the basin a prototypical study area for large-scale and long-term groundwater storage monitoring, attribution analysis, and spatial heterogeneity investigations in transboundary river basins [6].
With the advancement of remote sensing technology, measuring variations in the Earth’s gravity field to derive changes in global terrestrial water storage (TWSA) has provided unprecedented data support for monitoring TWS at global and regional scales [7], compensating for the spatial continuity and temporal consistency limitations of ground-based observations. The Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment (GRACE) satellite and its follow-on mission GRACE-FO, combined with land surface model data such as the Global Land Data Assimilation System (GLDAS), can further isolate components like soil water, snow water equivalent, and canopy water, thereby enabling the calculation of groundwater storage anomalies (GWSA) [8,9]. For example, Famiglietti et al. [10] and Scanlon et al. [11] used GRACE data to invert groundwater storage changes in California’s Central Valley, yielding results broadly consistent with measured groundwater levels in the study area; Arega et al. [12] estimated the spatiotemporal characteristics of groundwater storage changes in Ethiopia using GRACE satellite data, revealing significant spatial influences of precipitation, temperature, and evapotranspiration on GWSA, with precipitation exerting the strongest impact on GWSA after a two-month lag. Wang et al. [13] combined GRACE satellite and GNSS data to derive monthly groundwater storage changes in North America from 2002 to 2017. The results from 13 regions aligned with observation well data, providing high-precision dynamic assessment support for sustainable groundwater management in North America. Massoud et al. [14] constructed a groundwater storage model for California’s Central Valley using supply/demand data from the California Department of Water Resources, calibrated against historical data from the USGS Central Valley Hydrological Model (USGSCVHM) and NASA GRACE. Past studies using GRACE satellite data to invert groundwater storage in various regions not only validated the effectiveness and applicability of GRACE data for groundwater monitoring but also advanced the field from mechanistic analysis to management applications, supporting quantitative assessment and sustainable management of global groundwater resources.
Remote sensing and machine learning have been widely applied across multiple fields. Su et al. [15] employed traditional statistical methods like geographic detectors and correlation analysis to identify drivers of soil salinization, revealing that coastal groundwater aquifers are primarily affected by seawater intrusion. Cao et al. [16] used correlation analysis to uncover the complex interaction mechanisms between extreme climate and human activities on vegetation ecological traits in the Yellow River Basin, finding that climate change in the study area exhibits stronger correlations with vegetation ecology than human activities. Mei et al. [17] identified ecosystem service bundles and their drivers in Anhui Province using clustering and Shapley Additive Explanation (SHAP), revealing complex interactions between natural and socioeconomic factors. Other scholars [18,19] leveraged SHAP to provide insights into each feature’s contribution to specific predictions, making it universally applicable across machine learning and deep learning models. To examine the spatial linear correlation between primary driver trends and GWSA trends, the Pearson correlation coefficient was introduced. Its advantages and limitations have been explored through applications and refinements by multiple scholars. Yu et al. [20] reviewed the research history of Pearson correlation coefficients and experimentally demonstrated that error control often fails in practical applications due to hypothesis violations. They also identified theoretical flaws and applicability limitations in its null hypothesis testing, proposing more effective and accurate hypothesis testing methods based on these deficiencies. Papageorgiou [21] conducted statistical analyses using Pearson correlation with an arbitrarily set 5% significance level, emphasizing that the interpretation of correlation coefficients should be discipline-specific. Liu et al. [22] employed Pearson correlation to analyze propagation relationships among drought types, revealing the lagged effects from meteorological drought to groundwater drought and elucidating the dynamic relationships between different drought types. Thurstone [23] proposed calculating Pearson’s correlation coefficient without considering the sign involved in the computation, thereby avoiding biased calculation. Lee Rodgers et al. [24] presented 13 distinct formulas, each representing different computational approaches and conceptual definitions of r.
Although previous studies have successfully used GRACE data to invert groundwater reserves and machine learning to identify driving factors, these studies have mainly focused on the national scale or have only analyzed the entire river basin. There is still a gap in the visual assessment of spatial heterogeneity within large cross-border river basins. Therefore, to fill the above research gap, a research framework of “inversion—attribution—spatial analysis” is constructed for the study of groundwater reserves based on the coupling of remote sensing and machine learning. Innovations and Contributions of This Study: First, in the Heilongjiang (Amur) River Basin, long-term groundwater storage was inverted using GRACE and GLDAS data. Combining RF–SHAP enabled quantitative analysis of each driver’s contribution to GWSA, thereby more accurately identifying dominant factors. Second, unlike previous studies that predominantly focused on regional-level analysis, this research emphasizes the spatial differentiation patterns of correlations between GWSA and primary drivers. By introducing Pearson partial correlation coefficients for pixel-by-pixel analysis, it reveals the differential impacts of climate and human activities across distinct sub-basins, achieving a shift from “overall attribution” to “spatial differentiation of causes.”
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
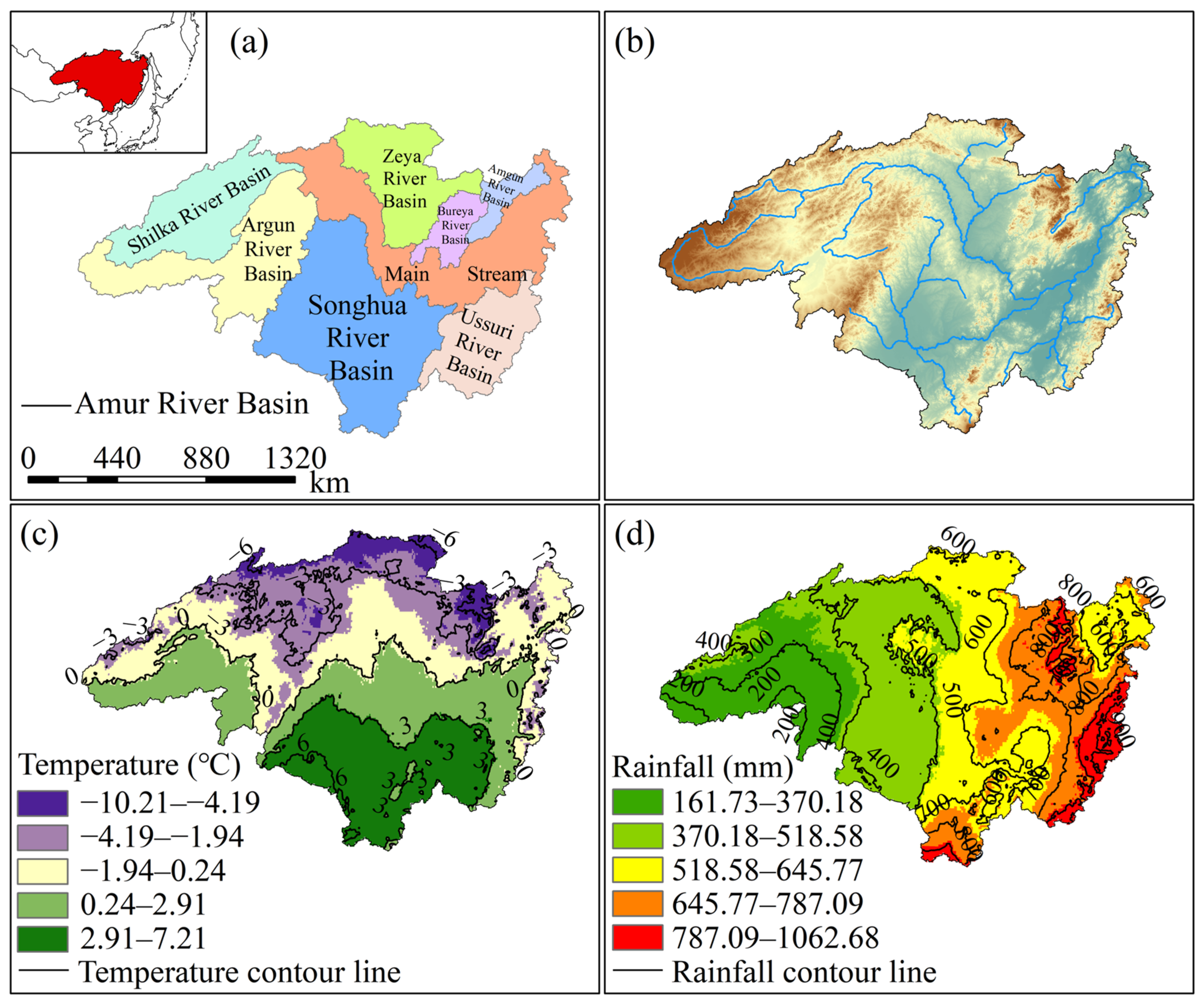
The Heilongjiang (Amur) River Basin is the world’s sixth-longest river, spanning Mongolia, China, and Russia. The Chinese section accounts for approximately 48% of the basin’s total area. The basin lies between 41°42′ and 55°56′ north latitude and 107°31′ and 141°14′ east longitude, covering a total area of approximately 185.5 × 104 km2. It is primarily composed of the MainStream and seven major tributaries (Amgun River, Bureya River, Argun River, Zeya River, Shilka River, Ussuri River, and Songhua River) (Figure 1a), with over 200 tributaries in total [25]. The basin exhibits a general topographic gradient from higher elevations in the west to lower elevations in the east, with higher elevations in the north and south and lower elevations in the central region. Significant variations in elevation distribution have formed a complex and diverse terrain pattern (Figure 1b). The northern and western areas consist of mountainous regions and plateaus with significant topographic undulations, including mountain ranges such as the Greater Khingan and Outer Khingan, where elevations generally exceed 500 m. The central and eastern regions are primarily plains, with elevations mostly below 200 m. This pronounced topographic differentiation not only influences the development of the basin’s hydrological systems and runoff formation but also exerts significant control over precipitation distribution, surface runoff convergence, and groundwater recharge, constituting the unique natural geographical background of the Heilongjiang (Amur) River Basin [26].
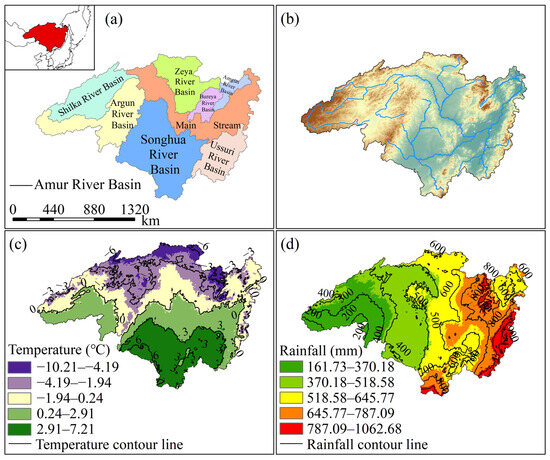
Figure 1.
Overview of the Heilongjiang (Amur) River Basin. (a) Location of the Heilongjiang (Amur) River Basin and sub-basin divisions, The red area in the upper left corner represents the location of the Heilongjiang (Amur) River Basin within the world; (b) Elevation distribution and major rivers within the Heilongjiang (Amur) River Basin; (c) Spatial distribution of average temperature isohypses in the Heilongjiang (Amur) River Basin from 2003 to 2024; (d) Spatial distribution of average precipitation isohypses in the Heilongjiang (Amur) River Basin from 2003 to 2024.
The spatial distribution of the multi-year average temperature in the Heilongjiang (Amur) River Basin shows significant zonal and topographic influence characteristics in the zonal direction (Figure 1c). According to the contour line distribution, the multi-year average temperature span ranges from −10.21 °C to 7.21 °C, and the overall temperature within the basin shows a gradually decreasing pattern from south to north [27]. Permafrost and seasonal permafrost are widely developed in the low-temperature area in the north, which affects the infiltration of surface runoff and the recharge mode of groundwater. In the southern regions with higher temperatures, evapotranspiration and human activities have a significant impact, increasing the pressure on water resource consumption. The spatial distribution of the multi-year average rainfall shows a distinct meridional differentiation pattern, generally characterized by a significant decreasing trend from east to west (Figure 1d) [28]. According to the contour distribution, the rainfall in the basin varies greatly, ranging from 161.73 mm to 1062.68 mm. The southeastern region has the most abundant rainfall due to the influence of the Pacific monsoon, while the inland areas in the southwest have relatively less rainfall, making it a relatively arid area in the basin. This pattern of rainfall distribution shapes the complex water cycle characteristics of the Heilongjiang (Amur) River Basin.
2.2. Data Sources
GRACE data are primarily processed and released by three research institutions: the Center for Space Research (CSR) at the University of Texas at Austin, the Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) of NASA, and the German Research Center for Geosciences (GFZ) in Potsdam. This study jointly utilizes GRACE and its successor mission GRACE-FO (Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment Follow-On), adopting the RL06 Mascon solution released by CSR (https://www2.csr.utexas.edu/grace/RL06_mascons.html, accessed on 12 August 2025). Compared with traditional spherical harmonic solutions, the Mascon product has the distinct advantage of requiring no post-processing, as it directly provides gridded datasets. The dataset is referenced to the terrestrial water storage equivalent water height for the baseline period of 2004–2009, with a spatial resolution of 0.25° × 0.25° and a temporal resolution of one month. The dataset has global coverage. For this study, GRACE data from April 2002 to June 2016 and GRACE-FO data from June 2018 to December 2024 were selected for the Heilongjiang (Amur) River Basin. Missing data were interpolated using Singular Spectrum Analysis (SSA) [29,30], and the results were expressed as equivalent water height.
The Global Land Data Assimilation System (GLDAS) was jointly developed by NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA). This study utilizes Noah model data from April 2002 to December 2024 (https://disc.gsfc.nasa.gov/, accessed on 12 August 2025), featuring a spatial resolution of 0.25° × 0.25° and a temporal resolution of 1 month, consistent with the CSRGRACE/GRACE-FO RL06.2 Mascon product data. Soil moisture (SMS), total canopy water (CWS), and snow water equivalent (SWE) data were extracted. SMS represents the sum of soil moisture content across four layers (0–10 cm, 10–40 cm, 40–100 cm, 100–200 cm). The temporal duration and spatial resolution are consistent with GRACE data.
The meteorological data are sourced from the TerraClimate (TC) dataset (http://www.climatologylab.org/, accessed on 14 August 2025). TerraClimate integrates the high spatial resolution advantage of WorldClim with the long-term observational records of datasets such as CRU TS4.0 and the Japanese reanalysis (JRA-55), generated through interpolation and correction methods [31]. Compared to traditional meteorological station data, the TC dataset offers significant advantages in spatial coverage and continuity, making it particularly suitable for large-scale hydrometeorological studies in river basins. With global coverage, this study selected temperature (TEM), precipitation (PRE), precipitation-to-evapotranspiration ratio (PDSI), evapotranspiration (PET), snow water equivalent (SWE), and soil moisture (SM) data from the Heilongjiang (Amur) River Basin from January 2003 to December 2024. This provides a basis for investigating the influence of meteorological factors on groundwater storage anomalies (GWSA).
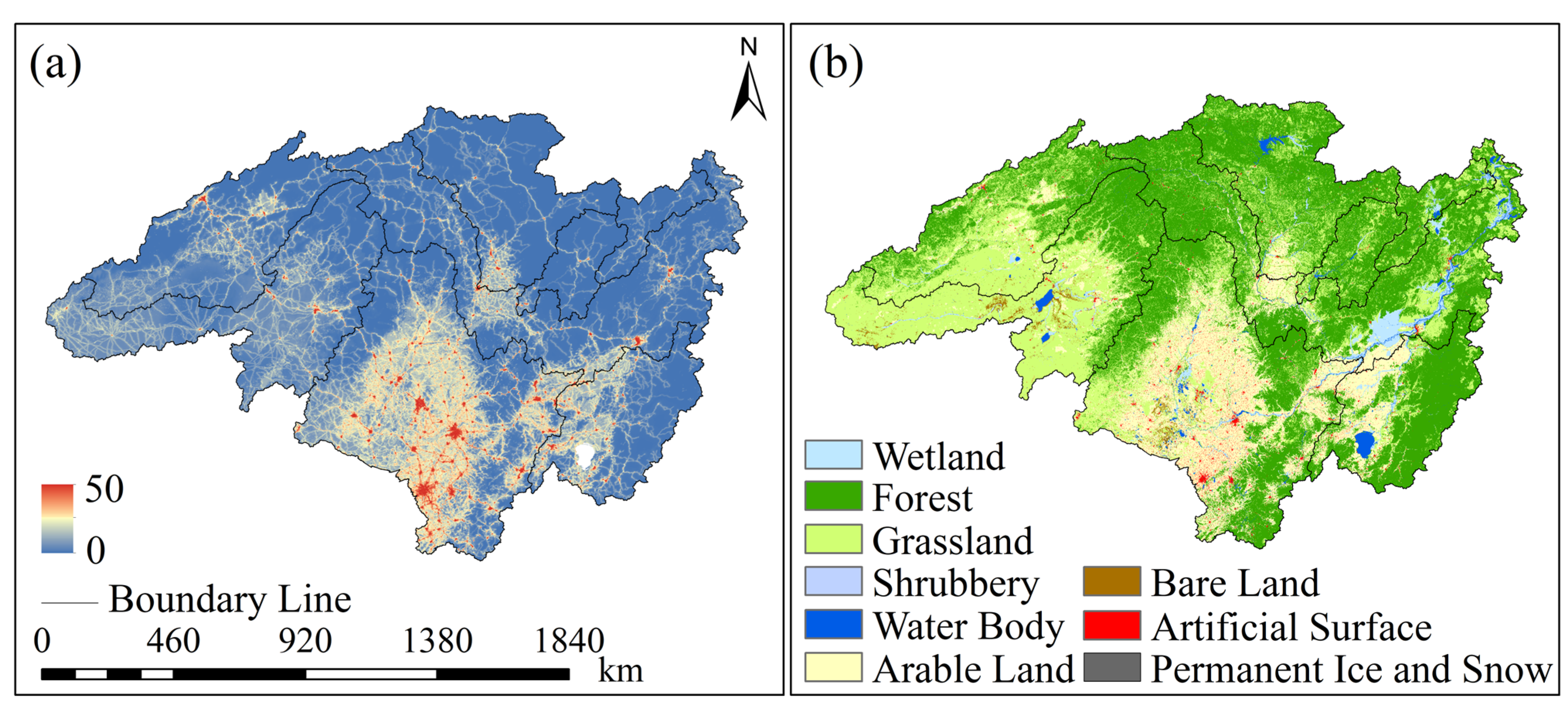
Land use data utilized the Global 30 m Land Use and Land Cover (LUCC) Dynamic Monitoring Product (GLC_FCS30-2020) developed by the team led by Researcher Liu Liangyun at the Institute of Aerospace Engineering (https://data.casearth.cn/dataset/, accessed on 16 August 2025) [32]. This product is generated using a combination of change detection and dynamic updating methods based on Landsat TM/ETM+/OLI imagery from 1985 to 2020. It includes 29 detailed land cover types with a five-year update cycle. Covering the entire globe, this study utilizes the 2020 land use data for the Heilongjiang (Amur) River Basin to provide a basis for investigating the impact of LUCC on GWSA changes.
Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) data were obtained from the MODIS Terra Vegetation Index product (https://developers.google.com/earth-engine/datasets/catalog/MODIS_061_MOD13Q1, accessed on 16 August 2025). This dataset is provided by NASA, with a spatial resolution of 250 m and a temporal resolution of 16 days, and has global coverage. The MOD13Q1 V6.1 product is derived from bidirectional surface reflectance data acquired by the MODIS sensor. The dataset undergoes rigorous atmospheric correction and removes the effects of clouds, cloud shadows, aerosols, and snow cover. The product employs a Best Pixel Compositing algorithm, which selects the optimal observation within each 16-day period (e.g., lowest cloud cover, minimum view angle, and highest NDVI value) to generate high-quality NDVI data, ensuring temporal continuity and reliability. The dataset provides global coverage. In this study, NDVI data for the Heilongjiang (Amur) River Basin in 2020 were used to support the analysis of the impact of vegetation cover change on GWSA.
Human Footprint (HFP) serves as a crucial metric for quantifying the degree of disturbance caused by human activities to ecosystems. It reflects the comprehensive environmental pressure exerted by humans by assessing the extent of anthropogenic alterations to ecological processes and natural landscapes (Data source: https://doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.16571064, accessed on 16 August 2025). This metric is widely applied in ecohydrological research to characterize human activity patterns [33,34]. The global HFP dataset (2000–2020, spatial resolution 1000 m) developed by Mu et al. [35] integrates seven key pressure factors based on methodologies proposed by Sanderson [34] and Venter [36]: population density, nighttime light intensity, cropland distribution, pasture extent, road networks, rail systems, and navigable waterways. These indicators reflect the comprehensive human impact on groundwater resources from multiple dimensions. The dataset covers the entire globe. This study utilizes the 2020 HFP data for the Heilongjiang (Amur) River Basin to investigate the influence of HFP on GWSA.
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. Interpolation Method
Referencing the SSA interpolation method and formula proposed by Yi [29], data spanning 267 months was extracted from the CSR Mascon database. Interpolation was performed on the 33 missing data points within this dataset. An iterative selection of the optimal window width M and number of reconstruction components K was conducted, ultimately setting M = 48 for the window width and K = 8 for the number of RC. The SSA interpolation process is as follows:
Convert time series into the trajectory matrix [29]:
In the formula: the number of columns L = N + 1 − M, where N is the length of the time series and M is the window Width.
Singular Value Decomposition. Let matrix S = XXT. Find the eigenvalues of S and arrange them in descending order ). The corresponding eigenvectors are U1, …, UM. Let d = rank (X). Then the delay matrix X can be expressed as [37]:
Consequently, the diagonal averaging reconstruction of the original sequence G for Y is to be performed, as illustrated below [38]:
Since the physical processes in the GLDAS model typically do not account for dynamic changes in large static water bodies, the surface water storage variables output by GLDAS do not include water volume changes in lakes and reservoirs. After interpolation, a total of 267 months of valid data were obtained [39].
2.3.2. Calculation of Groundwater Reserve Changes
Estimation of Groundwater Reserve Variations Terrestrial water reserves encompass surface water, groundwater, soil water, biological water, ice and snow, and vegetation canopy water. Among these components, the multi-year variation in surface water and biological water is negligible compared to other constituents [40]. Therefore, changes in terrestrial water reserves can be expressed as:
This allows us to calculate the change in groundwater reserves [40]:
In the equation: represents groundwater storage change (mm); represents terrestrial water storage change (mm); represents soil moisture change (mm); represents snow water equivalent change (mm); represents canopy water change (mm). Terrestrial water storage change is derived from GRACE gravity satellite data, while soil moisture, snow water equivalent, and vegetation canopy water changes are calculated using GLDAS data.
2.3.3. Trend and Correlation Analysis
The Theil-Sen slope, as a robust nonparametric statistical technique, offers the advantage of high tolerance for missing values and outliers in time series data. This robustness to anomalies makes it more suitable than traditional linear regression methods for certain data analyses [41]. The Mann–Kendall test is employed to assess the statistical significance of trends. Its robustness to measurement errors and outliers has led to its widespread application in time series analysis [42]. This study combines Theil-Sen slope estimation with the Mann–Kendall test to analyze the trend of GWSA in the Amur River Basin from 2002 to 2024 at a 0.05 significance level.
For time series data, the slope β is calculated using the median method [42]:
Here, and represent the GWSA values for the and months, respectively. If , an upward trend is indicated; if , a downward trend is indicated; otherwise, no trend is present.
Define the test statistic as [42]:
In the formula, denotes the defined test statistic, represents the length of the time series, and is the sign function, defined as follows [42]:
When , approximately follows a normal distribution with variance.
The standardized statistic is calculated using the following formula [42]:
If (=1.96 at = 0.05), reject the null hypothesis and conclude that the time series exhibits a significant trend.
2.3.4. GWSA-Driven Mechanism Based on RF–SHAP Methods
This study employs an RF–SHAP model to quantitatively analyze the driving mechanisms of groundwater salinization (GWSA) in the Heilongjiang (Amur) River Basin. Based on the RF model, nonlinear contribution assessments of GWSA influencing factors were achieved by calculating SHAP values for nine environmental factors (TEM, PRE, PDSI, PET, LUCC, SWE, SM, NDVI, HFP) [17,18,19]. To achieve optimal model performance, grid search was employed for systematic hyperparameter tuning. The finalized model parameters were: number of trees = 100, maximum tree depth = 15, minimum leaf node size = 5, and minimum split size = 2. Internal validation was conducted using out-of-bag (OOB) error. During model training and evaluation, 70% of the data served as the training set and 30% as the test set. Ten-fold cross-validation ensured model stability and generalization capability, revealing the relative importance of key factors such as TEM and PRE. The model successfully highlighted the significance of these critical factors. The calculation formula is as follows [43]:
In the formula, is the SHAP value of feature , Indicates the contribution of feature to the prediction result, is the feature set, Indicates all subsets of feature in other features . is the set of all features. is the prediction result of the model on the feature subset .
2.3.5. Pearson Correlation Coefficient Method
Both natural factors and human activities exert varying degrees of influence on groundwater storage fluctuations. Investigating the correlation between primary driving factors and groundwater storage changes holds significant implications for water resource management, conservation, and sustainable development. This study employs Pearson’s correlation coefficient to analyze the relationship between groundwater storage changes and key drivers [22]. Based on contribution shares derived from SHAP analysis, we examine the impact or correlation of factors with higher contribution shares on groundwater storage changes, temporarily disregarding the influence of other elements. The formula for Pearson’s correlation coefficient is as follows [23,24]:
In the formula: denotes the Pearson correlation coefficient; represents the number of samples; is the i-th observed value of variable x; is the i-th observed value of variable y; and denote the mean values of samples x and y, respectively.
The test for partial correlation coefficients typically employs the t-test method. The calculation formula is as follows [44]:
In the formula: denotes the t-statistic; denotes the sample size; denotes the Pearson correlation coefficient; denotes the coefficient of determination.
3. Results
3.1. Spatio-Temporal Variation Characteristics of Groundwater Reserves
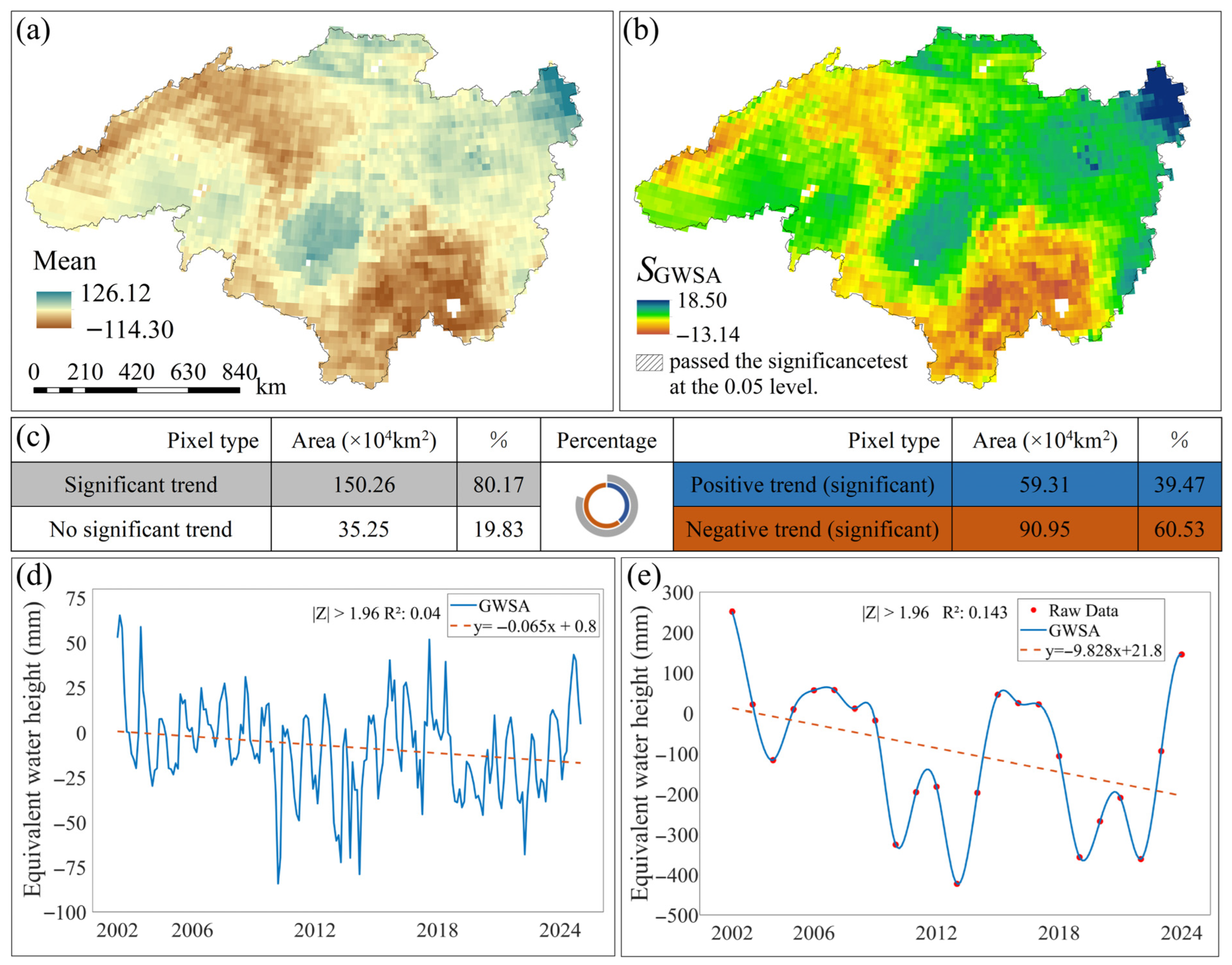
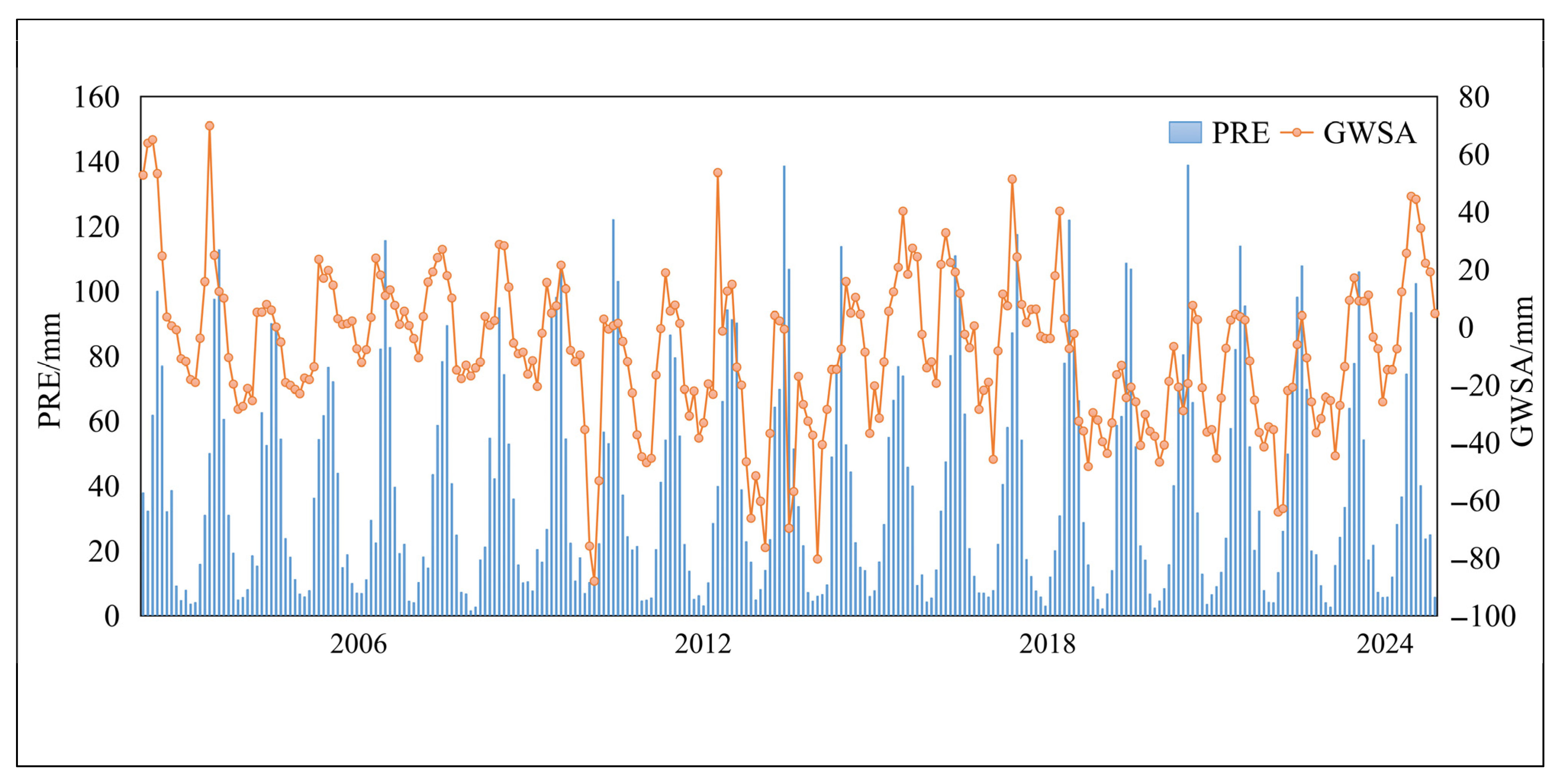
From 2002 to 2024, the spatially averaged monthly GWSA in the Heilongjiang (Amur) River Basin ranged from –114.3 to 126.12 mm (Figure 2a). Areas exhibiting significant groundwater storage depletion were primarily located in the northeastern and southern parts of the basin, whereas positive anomalies were concentrated in the northwest. Trend analysis using Sen’s slope estimation and the Mann–Kendall test revealed pronounced spatial variability in groundwater storage across the basin during 2002–2024. Approximately 80% of the basin exhibited statistically significant trends (|Z| ≥ 1.96) (Figure 2b,c), whereas the remaining 20% showed no significant change (|Z| ≤ 1.96). Among these areas, around 40% exhibited a significant upward trend (|Z| ≥ 1.96 and > 0), whereas 60% showed a significant downward trend (|Z| ≥ 1.96 and < 0). The temporal variation in monthly GWSA exhibited a significant downward trend at a rate of 0.065 mm/month (Figure 2d), beginning in 2002 and reaching its lowest value in 2010. The maximum value was recorded in March 2002 (65.4 mm), whereas the minimum occurred in May 2010 (−84.2 mm). Similarly, the annual GWSA demonstrated a decreasing trend at a rate of 9.8 mm/year (Figure 2e). This decline began in 2002 and reached its minimum in 2013. The maximum annual value was observed in 2002 (251.53 mm), whereas the minimum occurred in 2013 (−424.01 mm).
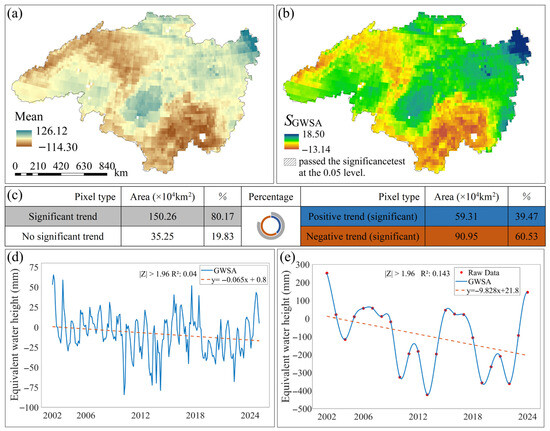
Figure 2.
Changes in GWSA in the Heilongjiang (Amur) River Basin from 2002 to 2024. (a) Monthly average GWSA values in the Heilongjiang (Amur) River Basin from 2002 to 2024; (b) Spatial trend results and significance analysis of monthly GWSA changes in the Heilongjiang (Amur) River Basin from 2002 to 2024; (c) Statistical analysis of spatial GWSA trends, with circles representing the percentage area for different GWSA trends. Inner ring colors correspond to right-side color and statistics; outer ring colors correspond to left-side color and statistics. (d) Monthly temporal trend results of GWSA in the Heilongjiang (Amur) River Basin from 2002 to 2024. (e) Annual temporal trend results of GWSA in the Heilongjiang (Amur) River Basin from 2002 to 2024.
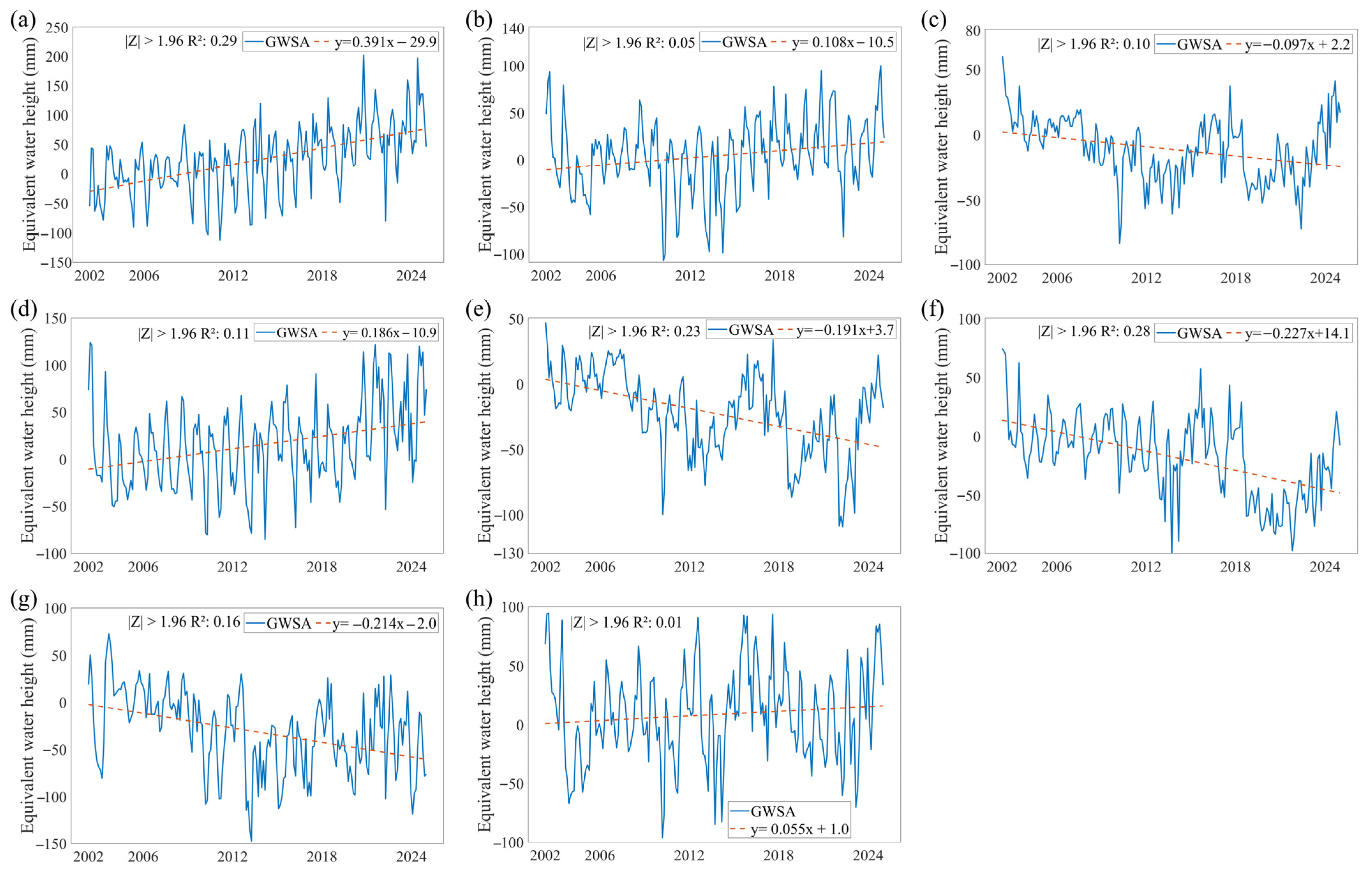
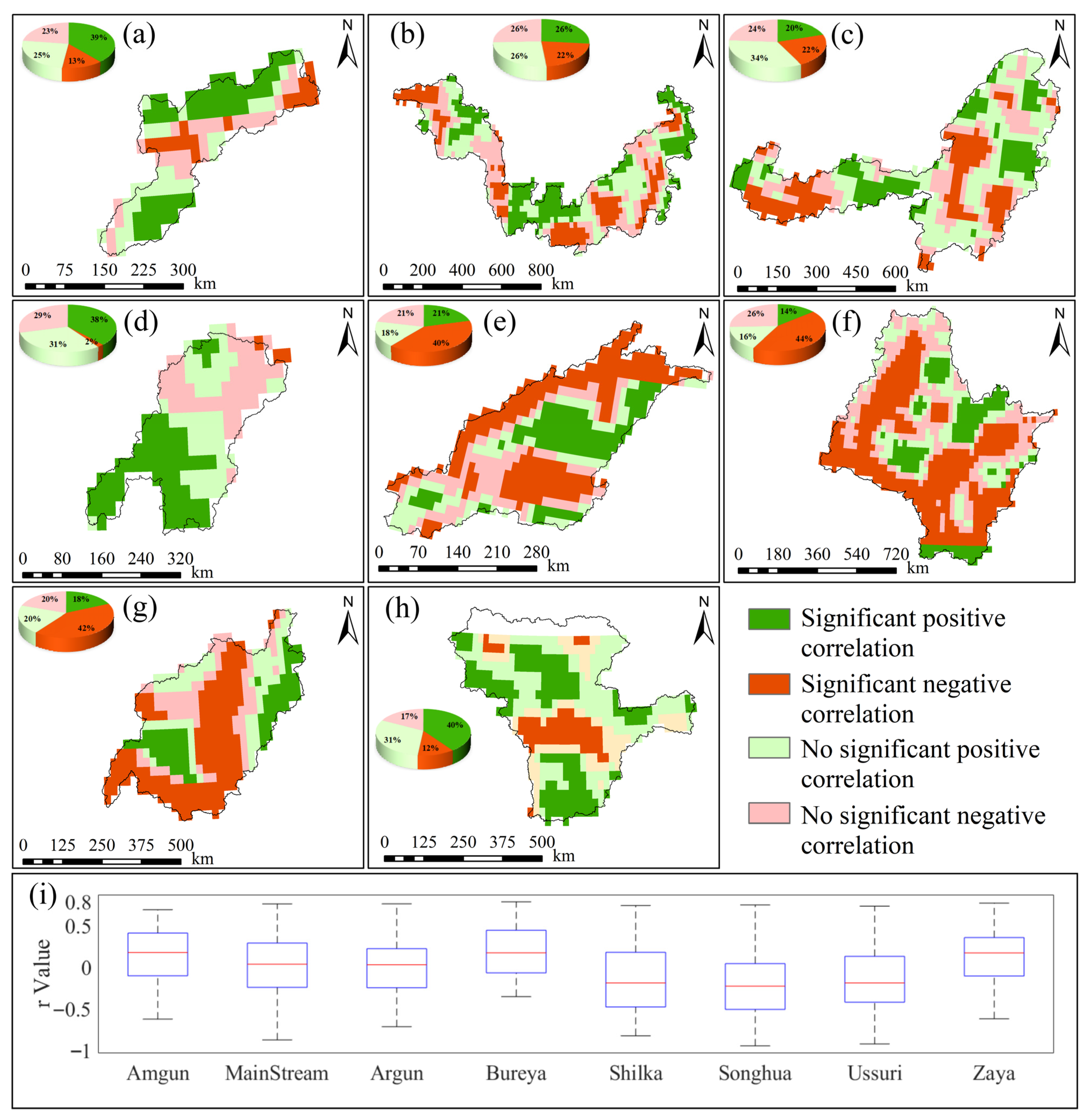
A comparative analysis of monthly GWSA changes across sub-basins within the Heilongjiang (Amur) River Basin (Figure 3) reveals that GWSA declined in most sub-basins over the study period. The Amgun River Basin exhibited a monthly average recharge rate of 0.39 mm, with a maximum of 201.97 mm in September 2020 and a minimum of −112.54 mm in February 2011 (Figure 3a). The MainStream Domain recorded a monthly average increase of 0.11 mm, with the highest value of 99.82 mm in August 2024 and the lowest of −106.73 mm in February 2010 (Figure 3b). The Argun River Basin showed a monthly average decrease of 0.10 mm, with a maximum of 60.27 mm in April 2024 and a minimum of −83.07 mm in February 2010 (Figure 3c). The Bureya River Basin exhibited a monthly average increase of 0.19 mm, with a maximum of 123.96 mm in May 2002 and a minimum of −85.15 mm in February 2014 (Figure 3d). The Shilka River Basin exhibited a monthly average increase of 0.19 mm, with the highest value of 47.35 mm in April 2002 and the lowest of −109.08 mm in April 2022 (Figure 3e). The Songhua River Basin experienced a monthly average drawdown of 0.23 mm, with a maximum of 74.6 mm in April 2002 and a minimum of –102.89 mm in September 2013 (Figure 3f). The Ussuri River Basin exhibited a monthly average drawdown of 0.21 mm, with a maximum of 72.88 mm in September 2003 and a minimum of −147.44 mm in September 2013 (Figure 3g). The Zeya River Basin showed a monthly average increase of 0.06 mm, with a maximum of 94.12 mm in July 2002 and a minimum of −96.03 mm in February 2010 (Figure 3h). Overall, the Amgun River Basin, MainStream Domain, Bureya River Basin, and Zeya River Basin exhibited rising trends, with increases in the MainStream Domain concentrated primarily in its middle and lower reaches. Conversely, the Argun River Basin, Shilka River Basin, Songhua River Basin, and Ussuri River Basin demonstrated declining trends. Between 2002 and 2024, the Songhua River Basin experienced the most rapid decline in groundwater reserves, whereas the Amgun River Basin showed the most rapid increase. In contrast, the Zeya River Basin exhibited the most stable GWSA trend.
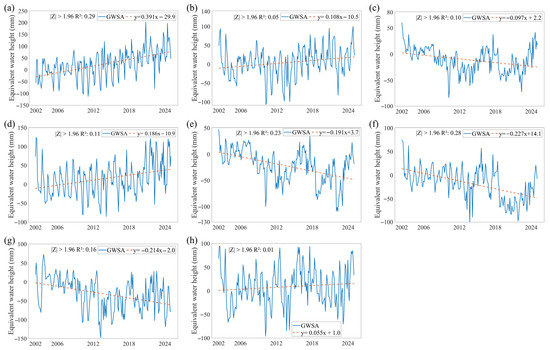
Figure 3.
Changes in GWSA of Amur River Basin Sub-basins from 1992 to 2024. (a–h) represent the monthly time trend results for Amgun River Basin, MainStream Domain, Argun River Basin, Bureya River Basin, Shilka River Basin, Songhua River Basin, Ussuri River Basin, and Zeya River Basin, respectively.
Overall, GWSA in the Heilongjiang (Amur) River Basin exhibited pronounced spatial heterogeneity during 2002–2024. Across the entire basin, GWSA declined significantly at an average rate of 0.065 mm per month and 9.8 mm per year. Spatially, GWSA exhibited continuous declines in the northwestern and southern regions, whereas the northeastern region showed a clear increasing trend. At the sub-basin scale, GWSA increased in the MainStream Domain, Amgun River Basin, Bureya River Basin, and Zeya River Basin, with the Amgun sub-basin exhibiting the highest rate of increase. Conversely, the Argun River Basin, Shilka River Basin, Songhua River Basin, and Ussuri River Basin experienced overall declines, with the Songhua sub-basin showing the most pronounced decrease. This pronounced spatial heterogeneity underscores the varying degrees of pressure on groundwater sustainability across different regions of the basin.
3.2. Correlation Analysis of Groundwater Reserve Variations
Through SHAP analysis of GWSA drivers across the Heilongjiang (Amur) River Basin (model accuracy: R2 = 0.87, RMSE = 10.47) (Table 1), TEM was identified as the primary driver, with a SHAP mean value of 1.3902 and a contribution rate of 44.37%, indicating that warming exerts a significant positive influence on groundwater dynamics. PRE was identified as the second most influential factor, with a SHAP mean of −1.0826 and a contribution rate of 37.17%. This negative contribution suggests that increased precipitation is, to some extent, associated with reduced groundwater storage, potentially reflecting the lagging effect and limited infiltration capacity in certain regions.

Table 1.
SHAP Analysis Results 1.
Among the remaining drivers, the PDSI ranked third in importance, its contribution was markedly lower than that of TEM and PRE. LUCC exerted a negative influence, suggesting that anthropogenic activities such as urbanization and agricultural expansion exacerbate groundwater depletion [45]. PET and SWE contributed 3.94% and 3.20%, respectively, both exerting positive effects and reflecting the role of evapotranspiration demand and snowmelt in groundwater recharge. The impacts of SM, NDVI, and HFP were relatively weak, indicating their limited explanatory power for groundwater variations in the Heilongjiang (Amur) River Basin [46].
3.3. Correlation Analysis of GWSA with Key Driving Factors
3.3.1. Correlation Analysis with TEM
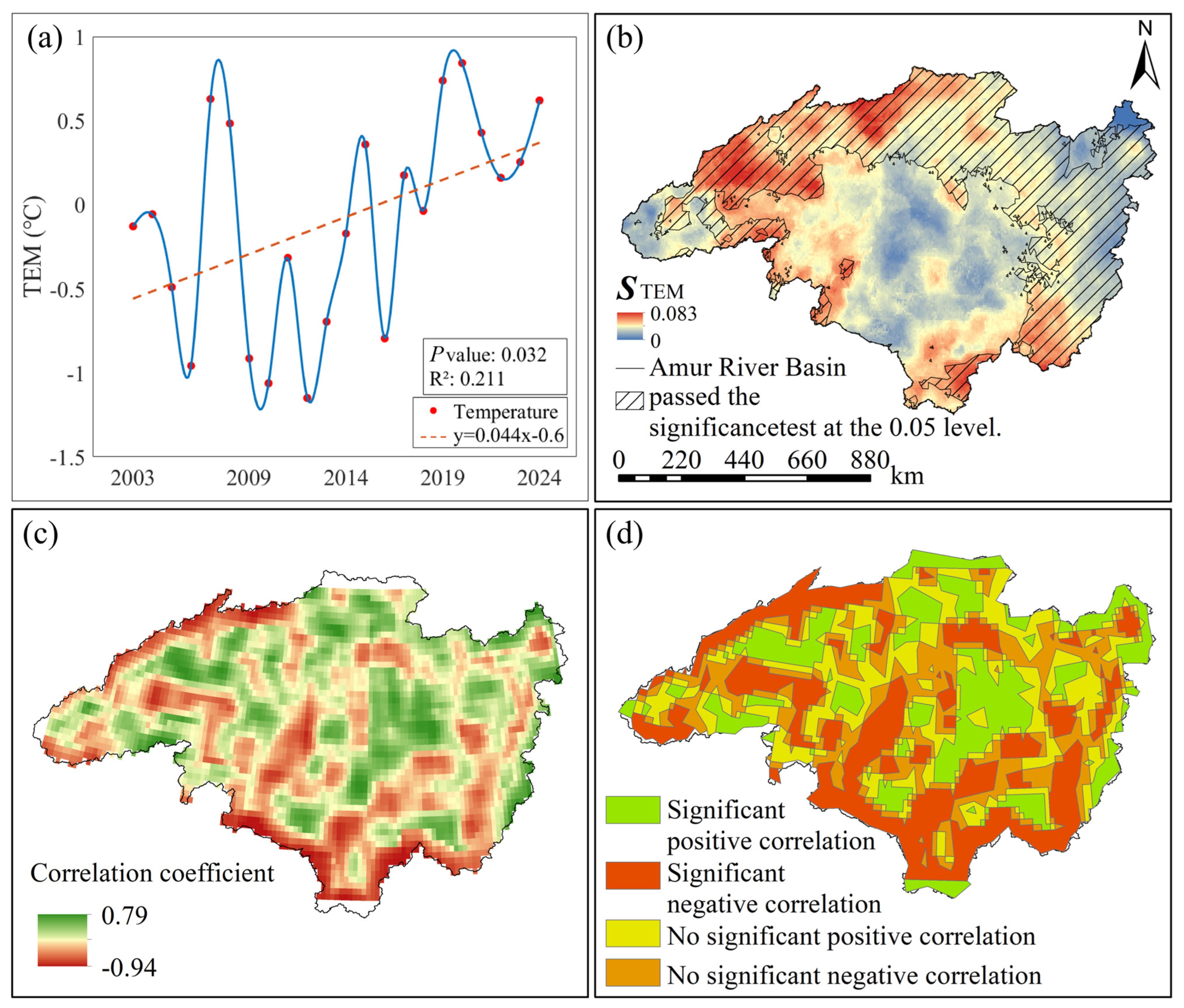
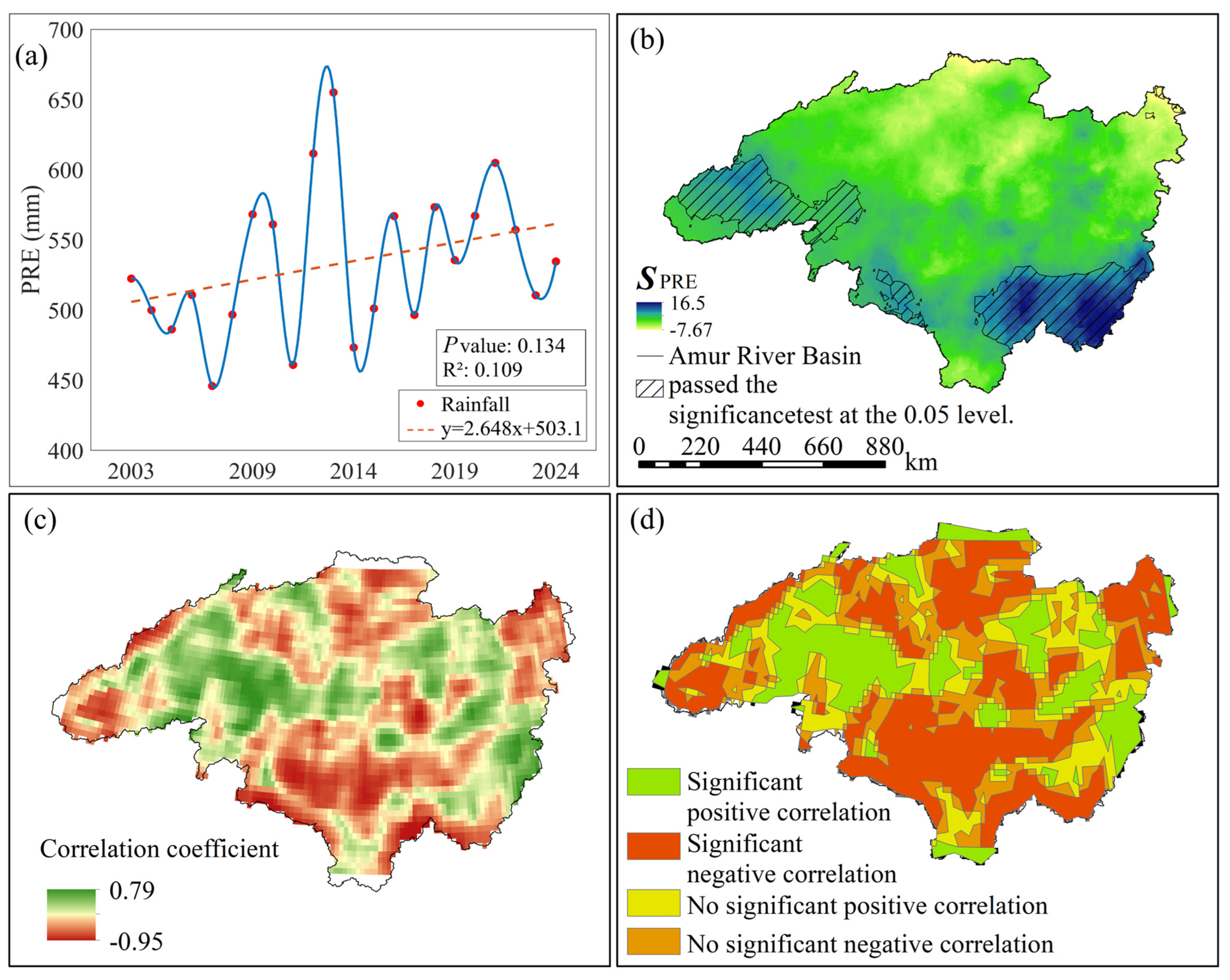
From a temporal perspective, the annual mean temperature in the Heilongjiang (Amur) River Basin exhibited an overall fluctuating upward trend from 2003 to 2024 (Figure 4a), with an average increase rate of 0.04 °C/a. The lowest annual increase occurred in 2012 at −1.14 °C, while the highest was recorded in 2020 at 0.64 °C. Spatially and temporally (Figure 1c), the basin’s annual mean temperature exhibits a north-to-south gradient influenced by latitude and topography, with lower values concentrated in the north and higher values in the south. Spatially and temporally (Figure 4b), no negative values were recorded within the study area. Significant increases occurred in the northwest and southeast, while the northeastern coastal region showed a gradual rise.
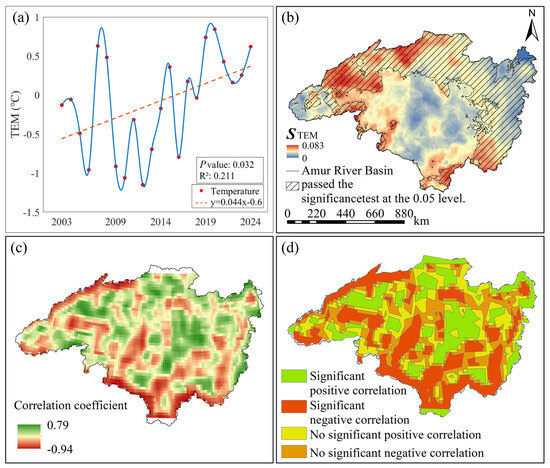
Figure 4.
Correlation analysis between GWSA and TEM in the Heilongjiang (Amur) River Basin from 2003 to 2024. (a) Annual trend of TEM from 2002 to 2024, red dots represent raw data points for annual average temperature, the blue wavy line represents a smoothed curve fitted to the raw data, the red dashed line represents the trend in annual average temperature; (b) Annual spatial trends and significance analysis results of TEM from 2002 to 2024; (c) Spatial results of GWSA-TEM correlation coefficients; (d) Spatial results of GWSA-TEM correlation significance.
In the spatial distribution maps of partial correlation coefficients between GWSA and TEM in the Heilongjiang (Amur) River Basin from 2003 to 2024, along with the significance tests for these coefficients (Figure 4c,d), the partial correlation coefficients between GWSA and TEM in the Heilongjiang (Amur) River Basin ranged from −0.94 to 0.79. Areas exhibiting positive correlation accounted for 56% of the basin, while negative correlation covered 44%. Significant positive correlation was observed in 50% of the area, and significant negative correlation in 23%. The remaining 27% showed no significant relationship between the two variables. To visually represent the correlation between groundwater storage variations and surface temperature, pixel-by-pixel partial correlation analysis was performed on GWSA and TEM raster data from 2003 to 2024 using Matlab 2021b software. Results indicate that |Z| > 1.96, confirming a significant positive correlation between GWSA and TEM, with an overall average correlation coefficient of 0.27.
3.3.2. Correlation Analysis with PRE
From a temporal perspective, the annual average precipitation in the Heilongjiang (Amur) River Basin exhibited an overall fluctuating upward trend from 2003 to 2024 (Figure 5a), with an average increase rate of 2.65 mm/a. The lowest value occurred in 2007 at 445.65 mm, while the highest was recorded in 2013 at 651.93 mm. Spatially and temporally (Figure 1d), the basin’s annual precipitation is influenced by latitude, with lower values concentrated in the west and higher values in the east, showing a gradual increase from west to east. Spatiotemporal trends (Figure 4b) indicate a significant increase primarily in the southeastern part of the basin, while the northern region experienced a marked decrease.
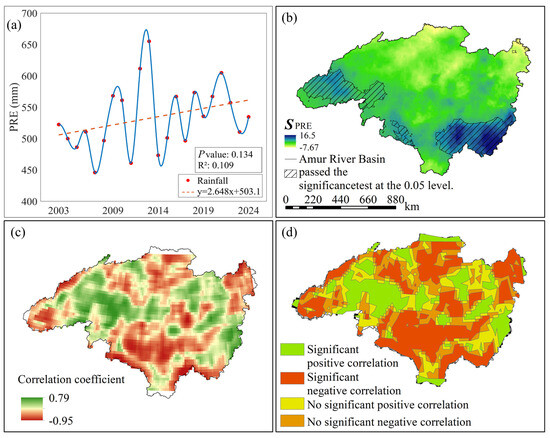
Figure 5.
Correlation analysis between GWSA and PRE in the Heilongjiang (Amur) River Basin from 2003 to 2024. (a) Annual average PRE trend from 2002 to 2024, red dots represent raw data points for annual average precipitation, the blue wavy line represents a smoothed fitting curve for the raw data, the red dashed line represents the trend in annual average precipitation; (b) Spatial trend and significance analysis of annual average PRE from 2002 to 2024; (c) Spatial results of GWSA-PRE correlation coefficients; (d) Spatial distribution of GWSA-PRE correlation significance.
In the spatial distribution maps of partial correlation coefficients between GWSA and TEM in the Heilongjiang (Amur) River Basin from 2003 to 2024, along with the significance tests for these coefficients (Figure 5c,d), the partial correlation coefficients between GWSA and TEM in the Heilongjiang (Amur) River Basin ranged from −0.95 to 0.79. Areas exhibiting positive correlations between GWSA and PRE accounted for 44% of the total area, while those showing negative correlations covered 56%. Specifically, 24% of the area demonstrated significant positive correlations, and 34% exhibited significant negative correlations. The remaining 42% of the area showed no significant relationship between the two variables. To more intuitively represent the correlation between GWSA and TEM, pixel-by-pixel partial correlation analysis was performed on the GWSA and PRE raster data from 2003 to 2024 using Matlab software. The analysis results showed that GWSA and PRE exhibited a significant negative correlation, with an overall average correlation coefficient of −0.43.
3.4. Spatial Heterogeneity Analysis of GWSA and Dominant Factors
3.4.1. Spatial Heterogeneity Analysis of GWSA and TEM
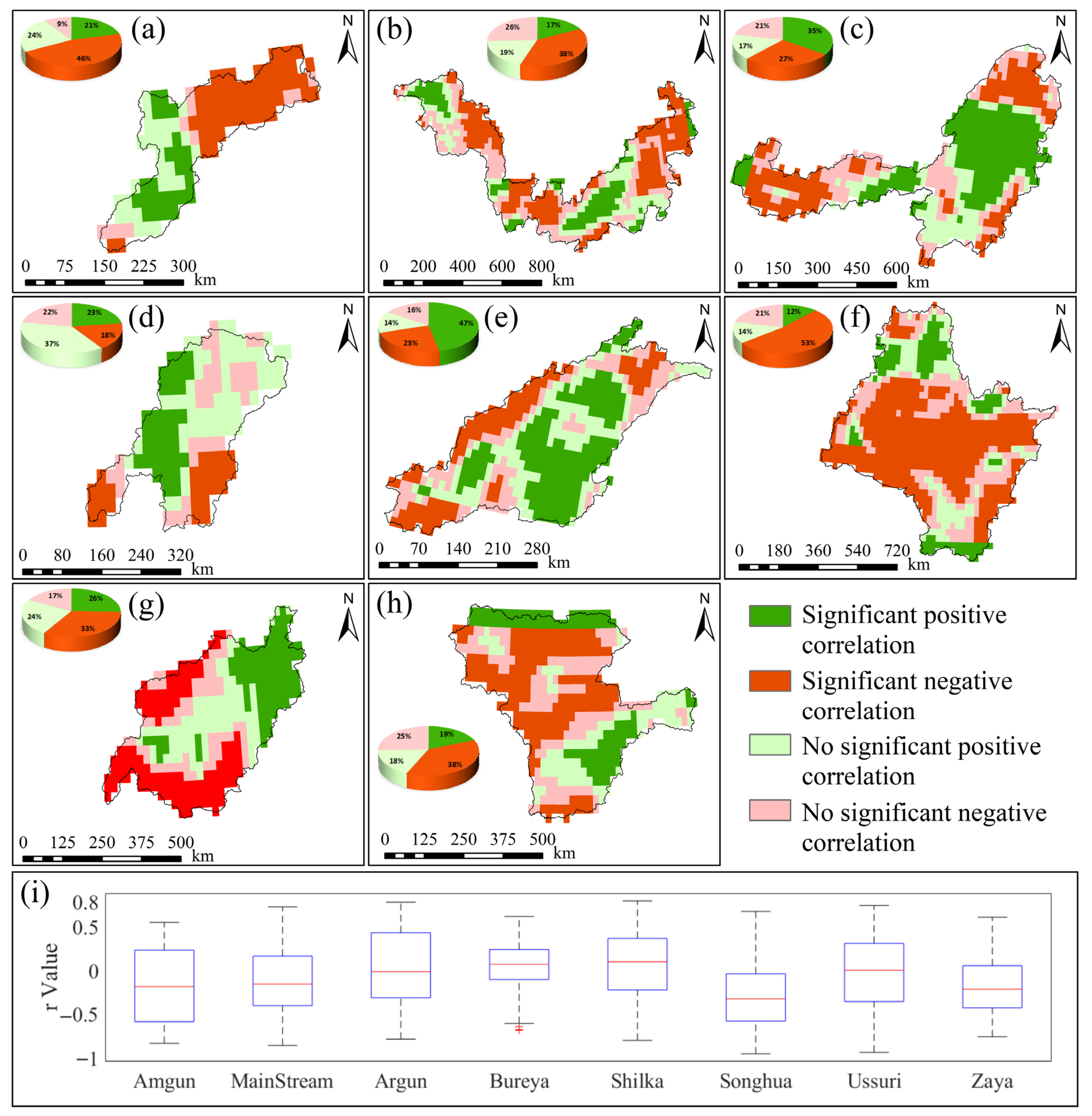
The spatial distribution of significant GWSA and TEM interactions in the Amgun River Basin (Figure 6a) shows: 39% of areas exhibit significant positive correlations, 13% exhibit significant negative correlations, and the remaining 48% show no significant relationship. The spatial distribution of significant MainStream Domain GWSA and TEM interactions (Figure 6b) shows: 26% of areas exhibit significant positive correlations, 22% exhibit significant negative correlations, and the remaining 52% show no significant relationship. The spatial distribution of significant GWSA and TEM relationships in the Argun River Basin (Figure 6c): 20% of areas showed significant positive correlation, 22% showed significant negative correlation, and the remaining 58% showed no significant relationship. The spatial distribution of significant GWSA and TEM relationships in the Bureya River Basin (Figure 6d): 38% of areas showed significant positive correlation, 2% showed significant negative correlation, and the remaining 60% showed no significant relationship. The spatial distribution of significant GWSA-TEM relationships in the Shilka River Basin (Figure 6e) shows: 21% of areas exhibit significant positive correlations, 40% exhibit significant negative correlations, and the remaining 39% show no significant relationship. The spatial distribution of significant GWSA and TEM relationships in the Songhua River Basin (Figure 6f) shows: 14% of areas exhibit significant positive correlations, 44% exhibit significant negative correlations, and the remaining 42% show no significant relationship. The spatial distribution of significant GWSA and TEM relationships in the Ussuri River Basin (Figure 6g) shows: 18% of areas exhibit significant positive correlations, 42% exhibit significant negative correlations, and the remaining 40% show no significant relationship. The spatial distribution of significant GWSA and TEM relationships in the Zeya River Basin (Figure 6h) shows: 40% of areas exhibit significant positive correlations, 12% exhibit significant negative correlations, and the remaining 48% show no significant relationship.
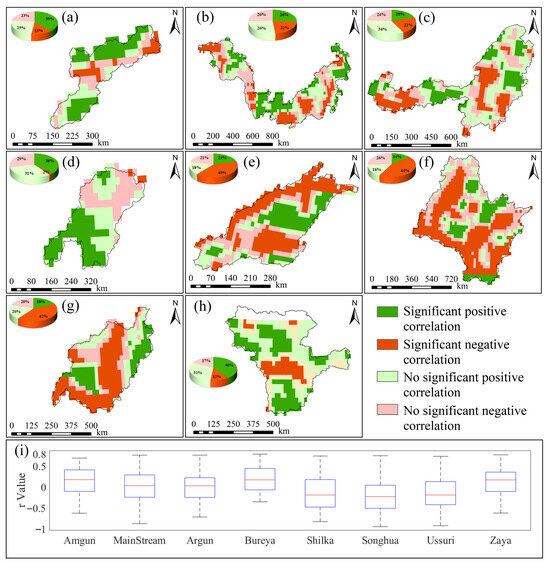
Figure 6.
Significant spatial correlation results between GWSA and TEM for sub-basins in the Heilongjiang (Amur) River Basin from 2002 to 2024. (a–h) represent the spatial correlation significance results between annual GWSA changes and annual TEM changes for the Amgun River Basin, MainStream Domain, Argun River Basin, Bureya River Basin, Shilka River Basin, Songhua River Basin, Ussuri River Basin, Zeya River Basin, respectively; (i) shows box plots of the spatial distribution of r values for each sub-basin.
Box plots of the spatial distribution of partial correlation coefficients (r) between GWSA and TEM in each sub-basin (Figure 6i) reveal basin-specific correlation patterns. In the Amgun River Basin (−0.62 to 0.68, , |Z| > 1.96), a weak overall positive correlation is observed. The MainStream Domain (−0.87 to 0.76, , |Z| < 1.96) and Argun River Basin (−0.71 to 0.76, , |Z| < 1.96) display symmetrical distributions centered near zero, indicating predominantly weak correlations without statistical significance. In the Bureya River Basin (−0.35 to 0.79, , |Z| < 1.96), positive correlations predominate spatially, though statistical significance is weak. The Shilka River Basin (−0.82 to 0.74, , |Z| > 1.96), Songhua River Basin (−0.94 to 0.75, , |Z| < 1.96), and Ussuri River Basin (−0.92 to 0.73, , |Z| > 1.96) exhibit a wide negative range, with the Shilka River Basin and Ussuri River Basin showing significant negative correlations. In the Zeya River Basin (−0.62 to 0.77, , |Z| > 1.96), the box plots show concentrated r-value distributions with distinctly elevated boxes, indicating small spatial fluctuations and an overall significant positive correlation. The spatial distribution of GWSA–TEM correlations exhibits pronounced heterogeneity in both direction and strength. Most sub-basins display significant positive correlations, with the Zeya River Basin showing the highest proportion of significantly positively correlated pixels, while the central region exhibits a predominance of negative correlations. The Songhua River Basin contains the largest proportion of negative correlations, which are distributed in a continuous spatial band. The MainStream Domain and Argun River Basin exhibit symmetrical distributions around zero, with no statistically significant correlations. The Songhua River Basin exhibits a wide range of correlation coefficients, reflecting high spatial heterogeneity among pixels within the basin. In contrast, the Amgun River Basin and Bureya River Basin display shorter boxplots, suggesting more concentrated correlation distributions and stronger spatial consistency.
3.4.2. Spatial Heterogeneity Analysis of GWSA and PRE
The spatial distribution of significant GWSA and PRE interactions in the Amgun River Basin (Figure 7a): 21% of the area showed a significant positive correlation, 46% showed a significant negative correlation, and the remaining 33% showed no significant relationship. The spatial distribution of significant MainStream Domain GWSA and PRE interactions (Figure 7b): 17% of the area showed a significant positive correlation, 38% showed a significant negative correlation, and the remaining 45% showed no significant relationship. The spatial distribution of significant GWSA and PRE relationships in the Argun River Basin (Figure 7c): 35% of areas showed a significant positive correlation, 27% showed a significant negative correlation, and the remaining 48% showed no significant relationship. The spatial distribution of significant GWSA and PRE relationships in the Bureya River Basin (Figure 7d): 23% of areas showed a significant positive correlation, 18% showed a significant negative correlation, and the remaining 59% showed no significant relationship. The spatial distribution of significant GWSA and PRE relationships in the Shilka River Basin (Figure 7e) shows: 47% of areas exhibit significant positive correlations, 23% exhibit significant negative correlations, and the remaining 30% show no significant relationship. The spatial distribution of significant GWSA and PRE relationships in the Songhua River Basin (Figure 7f) shows: 23% of areas exhibit significant positive correlations, 32% exhibit significant negative correlations, and the remaining 45% show no significant relationship. The spatial distribution of significant GWSA and PRE relationships in the Ussuri River Basin (Figure 7g) shows: 26% of areas exhibit significant positive correlations, 33% exhibit significant negative correlations, and the remaining 41% show no significant relationship. The spatial distribution of significant GWSA and PRE relationships in the Zeya River Basin (Figure 7h) shows: 19% of areas exhibit significant positive correlations, 38% exhibit significant negative correlations, and the remaining 43% show no significant relationship.
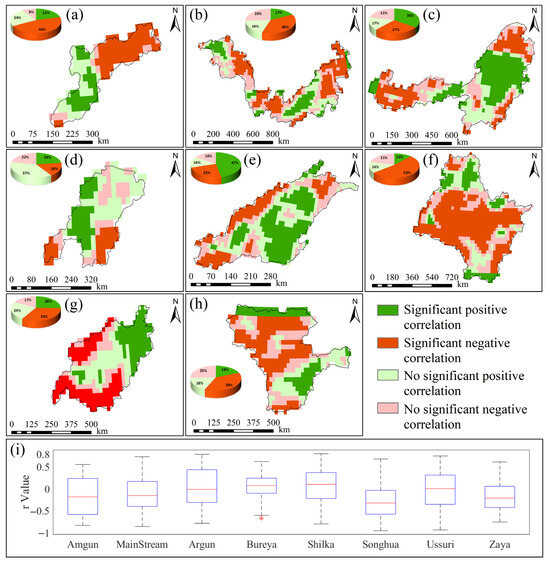
Figure 7.
Significant spatial correlation results between GWSA and PRE for sub-basins in the Heilongjiang (Amur) River Basin from 2002 to 2024. (a–h) represent the spatial correlation significance results between annual GWSA changes and annual PRE changes for the Amgun River Basin, MainStream Domain, Argun River Basin, Bureya River Basin, Shilka River Basin, Songhua River Basin, Ussuri River Basin, Zeya River Basin, respectively; (i) Box plots showing the spatial distribution of r values for each sub-basin.
Box plots of the spatial distribution of partial correlation coefficients (r) between GWSA and PRE across sub-basins (Figure 7i) reveal clear basin-specific correlation patterns. In the Amgun River Basin (−0.84 to 0.5,, |Z| > 1.96), a significant overall negative correlation trend is observed. The MainStream Domain (−0.86 to 0.73, , |Z| > 1.96) exhibits a significant overall negative trend, whereas the Argun River Basin (−0.79 to 0.78, , |Z| > 1.96) shows a significant overall positive correlation. The Bureya River Basin (−0.69 to 0.62, , |Z| < 1.96) shows no statistically significant correlation. In contrast, the Shilka River Basin (−0.8 to 0.79, , |Z| > 1.96) exhibits a significant overall positive correlation trend. The Songhua River Basin (−0.95 to 0.67, , |Z| > 1.96) demonstrates a strong negative correlation trend, while the Ussuri River Basin (−0.94 to 0.74, , |Z| > 1.96) and Zeya River Basin (−0.76 to 0.61, , |Z| > 1.96) both exhibit significant overall negative correlations. The spatial distribution of GWSA and PRE correlations exhibits pronounced heterogeneity in both direction and strength. Most sub-basins display significant negative correlations, with the Songhua River Basin showing the highest proportion of significantly negatively correlated pixels, concentrated mainly in its central region. The Shilka River Basin shows the highest proportion of significantly positively correlated pixels, located primarily in its southeastern part. The Bureya River Basin contains few significant pixels, and the overall correlations fail to pass significance tests. The distribution range and boxplot morphology of r-values across sub-basins also reflect the degree of internal spatial heterogeneity. For example, the MainStream Domain and Ussuri River Basin exhibit a wide range of correlation coefficients, indicating high spatial heterogeneity among pixels within these basins. Conversely, the Zeya River Basin and Bureya River Basin display shorter boxplots, suggesting more concentrated correlation distributions and stronger spatial consistency.
4. Discussion
4.1. Uncertainty Analysis of the Inversion Results
Due to its limited temporal resolution and signal gaps, GRACE satellite data often require interpolation and gap-filling in large-scale hydrological studies [47]. Previous interpolation approaches have typically addressed missing months by replacing them with long-term mean values [48], linear interpolation [49], cubic spline interpolation [50], or kriging interpolation [51]. To better account for temporal dependency and overcome the main limitations of these conventional methods (Table 2), this study applies Singular Spectrum Analysis (SSA) interpolation to fill the missing months [52,53,54]. The advantage of applying SSA to the Heilongjiang (Amur) River Basin with its long time series and extensive spatial coverage lies in its ability to decompose and reconstruct the series from a global perspective, accurately capturing long-term trends and key periodic signals embedded in GRACE data. This method preserves interannual variability and long-term trends more effectively [29], thereby improving data continuity and reliability and providing a robust foundation for subsequent driving mechanism analyses and correlation studies.

Table 2.
Comparison of GRACE Data Interpolation Methods.
After successfully interpolating using SSA, the next critical step is to compute it to obtain GWSA. In groundwater storage change calculations, surface water and biotic water storage are negligible, and their variations are typically ignored [39]. However, in systems with large rivers and reservoirs, the impact of surface water changes requires careful consideration. This study did not explicitly subtract surface water variations in the Heilongjiang (Amur) River Basin calculations, primarily due to: (1) Considering large-scale averaging effects, the GRACE/GRACE-FO signal reflects mass-weighted averages over hundreds of square kilometers. Compared to the widely distributed and massive reserves of soil water, groundwater, and snow water equivalent, the water bodies in rivers and reservoirs constitute a relatively small proportion within their coverage area. Their strong local signals are smoothed and attenuated in satellite observations [55,56]; (2) To ensure the applicability of long-term trends, this study focuses on long-term trends. Although surface water (especially reservoirs) may exhibit significant seasonal fluctuations, these fluctuations largely cancel each other out in multi-year analyses, making it difficult to establish stable long-term trends. Consequently, their impact on revealing the long-term evolution patterns of GWSA is relatively limited [57].
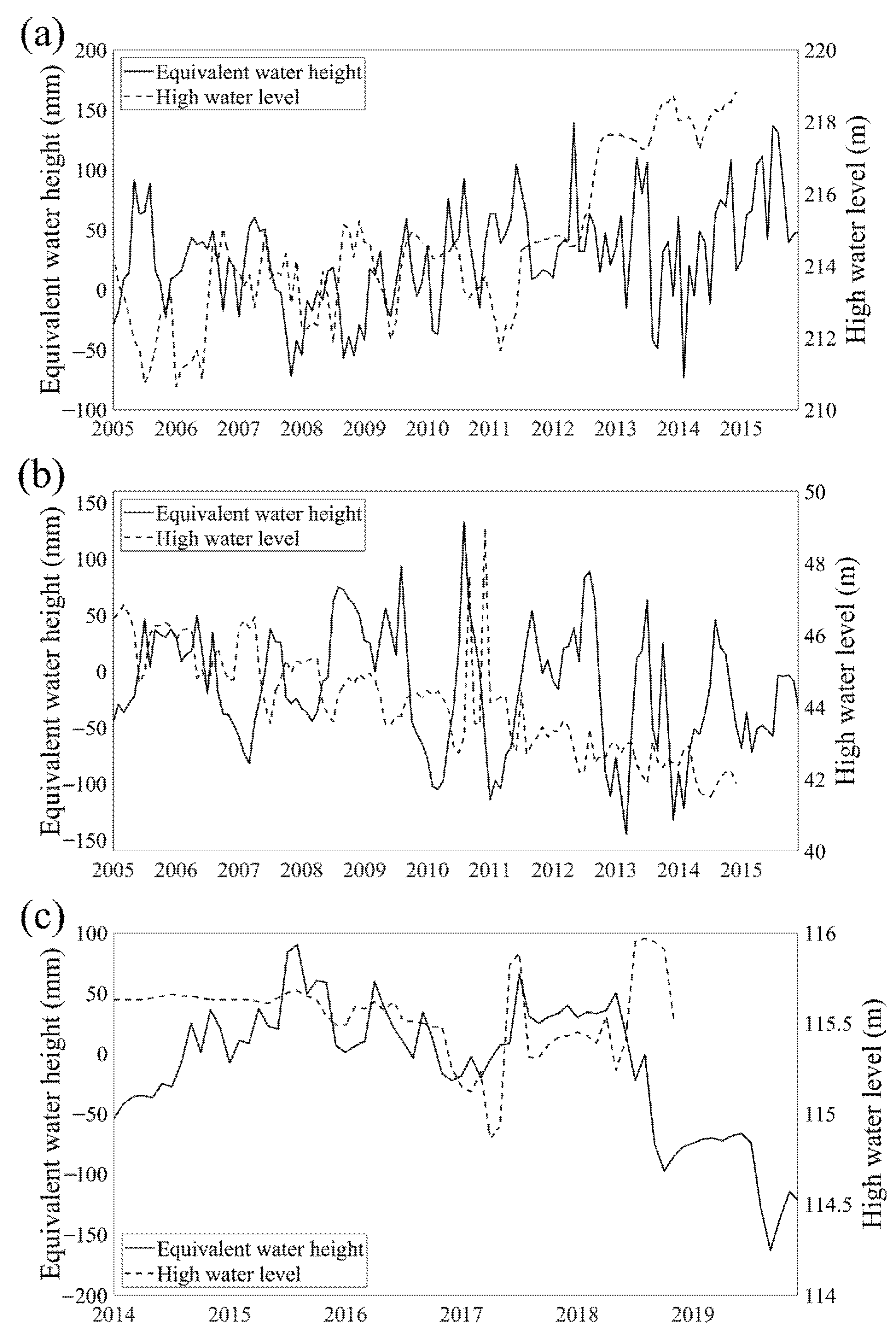
Order evaluate the overall reliability of the data processing assumptions, this study further validated the results using groundwater observation well data. However, due to the uneven spatial distribution of observation wells and the limited duration of monitoring records, long-term groundwater level observations are scarce across the study area. Therefore, representative wells were selected based on the availability of long and continuous time series to minimize potential errors introduced by data interpolation. Continuous groundwater table depth data for January 2005 to December 2014 (120 months) are available at the Hailun and Sanjiang stations from the Chinese Ecosystem Research Network (CERN) (https://cstr.cn/31253.11.sciencedb.293, accessed on 16 October 2025) [58]. In addition, the monitoring well at Youyi Palace in Daoli District, Harbin, provides 60 months of continuous groundwater level data from 2014 to 2018 [59]. A comparison of the GRACE-derived groundwater storage anomalies with in situ groundwater levels revealed a clear lagged correlation between the two time series (Figure 8): (1) When the lag time of the Hailun station inversion results was adjusted to 8 months, the correlation coefficient with the observed groundwater level reached its maximum (r = 0.65, p < 0.05), indicating an 8-month lag between the GRACE-derived and observed data. A comparison of the temporal trends (Figure 8a) shows that during the overlapping period, both datasets exhibited a stable rising trend, with the inversion results increasing at a rate of 0.50 mm/month and the observed water level rising at 0.05 m/month; (2) When the lag time at the Sanjiang station was set to 5 months, the correlation coefficient peaked (r = 0.54, p < 0.05), indicating a 5-month lag between the inversion and observed groundwater levels. Trend comparison (Figure 8b) shows that both datasets display a declining trend during the overlapping period, with the inversion results decreasing at a rate of –0.45 mm/month and the observed water level decreasing at –0.03 m/month; (3) When the lag time for the Youyi Palace monitoring well in Harbin was adjusted to 9 months, the correlation coefficient reached its maximum (r = 0.52, p < 0.05), indicating a 9-month lag between inversion and observation. A trend comparison (Figure 8c) shows that both datasets display a declining trend during the overlapping period, with the inversion results decreasing at a rate of –2.09 mm/month and the observed water level decreasing at –0.002 m/month.
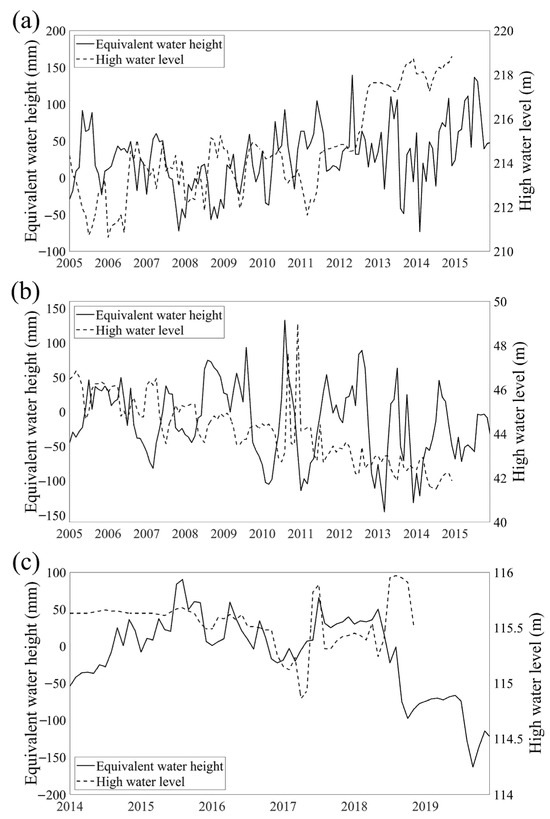
Figure 8.
Comparison of Groundwater Inversion Results with Logged Water Levels. (a) Comparison of Groundwater Inversion Results with Logged Water Levels at Helen Station; (b) Comparison of Groundwater Inversion Results with Logged Water Levels at Sanjiang Station; (c) Comparison of Groundwater Inversion Results and Logged Water Levels at the Monitoring Well in Youyi Palace, Daoli District, Harbin City.
4.2. Spatial Analysis of Driving Mechanisms
The transition from nonlinear SHAP analysis to linear Pearson correlation analysis establishes a research framework that shifts from “overall attribution” to “spatial differentiation.” To investigate the linear spatial relationship between dominant factors and GWSA under multiple driving influences, the RF–SHAP modeling approach was employed to rank the relative importance of different factors within the study area [18,19]. At the individual pixel scale, the true relationship between dominant driving factors and GWSA inherently contains nonlinear components. However, Pearson correlation analysis is sufficient to reveal the spatial heterogeneity in the strength and direction of the linear associations between dominant driving factors and GWSA [24].
Based on the above methodology, this study clearly identifies the dominant role of climatic factors in controlling GWSA variations in the Heilongjiang (Amur) River Basin. Results from the RF–SHAP model indicate that under the influence of climate change, natural climatic factors predominantly govern GWSA variations in the Heilongjiang (Amur) River Basin [45]. Regarding the dominant driving factors: (1) Rising TEM enhances snowmelt and permafrost degradation, which alters the hydrogeological conditions of cold regions, increasing soil moisture and thereby effectively recharging groundwater storage [60,61]. However, in the southern parts of the basin, land use and human activities also exert significant influence. (2) Increasing PRE contributes to groundwater recharge through surface water infiltration; however, in some regions, the rate of groundwater decline exceeds the recharge rate from precipitation. Moreover, due to the lag effect of precipitation on groundwater replenishment, short-term increases in rainfall cannot effectively reverse the declining groundwater trend [62].
4.2.1. Focusing Specifically on the Impact of TEM on GWSA
The correlation between TEM and GWSA exhibits a distinct spatial differentiation pattern characterized by positive correlations in the north and negative correlations in the south. In the northern high-latitude sub-basins (Amgun River Basin and Zeya River Basin), which are underlain by permafrost, Evans [61] analyzed groundwater discharge under projected warming scenarios from the IPCC and found that in high-latitude and high-altitude regions, permafrost degradation and the deepening of the active layer lead to increased groundwater flow, resulting in a pronounced positive correlation between TEM and GWSA. This process generates two primary hydrological effects: (1) the release of previously frozen water, which is converted into liquid groundwater; and (2) the thickening of the active layer, which enhances surface infiltration and storage capacity. In contrast, the southern and central–western sub-basins (Shilka River Basin, Songhua River Basin, and Ussuri River Basin) exhibit strong negative correlations, particularly in the Songhua River Basin, where climatic aridity combined with intensive human activities has led to groundwater overexploitation [63]. These sub-basins are characterized by intensive agricultural activities, dense populations, and a high degree of urbanization. In these areas, rising temperatures significantly increase evapotranspiration and intensify agricultural water demand. To meet crop water requirements, intensive groundwater extraction is carried out [64,65], which is the direct driver of declining groundwater storage [66]. These results suggest that under global warming, different regions of the Heilongjiang (Amur) River Basin will face contrasting groundwater challenges and opportunities [67]. The northern regions may benefit from enhanced meltwater recharge, whereas the southern regions must be particularly vigilant regarding the compounded impacts of rising temperatures and intensified human activities [68].
4.2.2. Focusing Specifically on the Impact of PRE on GWSA
As the second most influential driving factor, PRE exhibits a similarly complex mechanism, and the linear correlation between GWSA and PRE demonstrates pronounced spatial heterogeneity across sub-basins. In sub-basins where natural conditions are relatively well preserved and human disturbance is minimal (e.g., the Shilka River Basin), precipitation shows a positive correlation with GWSA, indicating that in these regions, rainfall can still effectively infiltrate and recharge the aquifers [69]. However, in the Amgun River Basin, Songhua River Basin, Ussuri River Basin, and Zeya River Basin, despite increasing annual precipitation, a negative correlation between precipitation and GWSA was observed. This seemingly counterintuitive pattern is primarily driven by the lag effect of precipitation on groundwater recharge and the strong anthropogenic disturbances to natural hydrological processes [70].
The RF–SHAP model used in this study reveals that PRE is the second most important driving factor influencing groundwater storage. However, its mean SHAP value is negative. This finding does not imply that precipitation itself is not a source of groundwater recharge. GRACE provides groundwater storage estimates at a monthly scale, whereas the recharge effect of precipitation on groundwater exhibits a distinct temporal lag (Figure 9) [54], particularly in regions with deep water tables or thick vadose zones [62]. Consequently, the relationship between PRE and GWSA yields negative SHAP values, which manifests as a negative correlation.
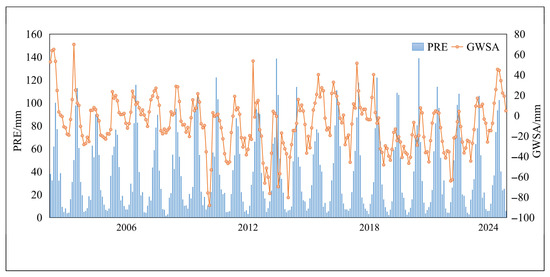
Figure 9.
Changes in GWSA and PRE from 2002 to 2022.
4.2.3. In-Depth Analysis of the Impact of Human Activities on GWSA
Although the RF–SHAP model indicates that HFP and LUCC have relatively low global contributions, this does not imply that human activities are unimportant. The rapid decline of GWSA in the Songhua River Basin, along with its negative correlations with TEM and PRE, suggests the need to further investigate the role of human activities.
Within the basin, the HFP exhibits a pronounced spatial gradient, with significantly higher values in the south and lower values in the north (Figure 10a). The areas with high HFP values spatially coincide with regions experiencing rapid GWSA decline (e.g., the Songhua River Basin). This spatial coupling indicates that human activities are the dominant driver of localized groundwater depletion and help explain the counterintuitive relationship between PRE and GWSA: (1) Amplification of warming-induced negative effects: In agricultural regions, increasing TEM enhances evapotranspiration. Human activities exacerbate this water deficit by extracting groundwater to meet water demands, thereby amplifying the negative impact of TEM on GWSA [71]. (2) Disruption of the recharge effect of precipitation: Human activities act as an indirect driver of groundwater depletion by disrupting the recharge efficiency of precipitation to groundwater, thereby contributing to the observed negative correlation between PRE and GWSA [70].
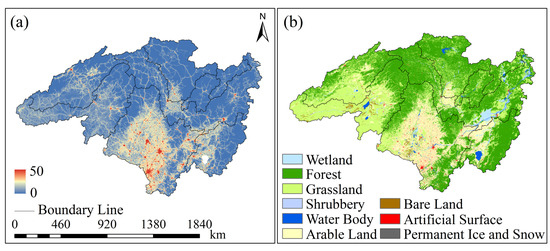
Figure 10.
Distribution of HFP and LUCC in the Heilongjiang (Amur) River Basin in 2020. (a) Distribution of HFP in the Heilongjiang (Amur) River Basin in 2020. Higher values from 0 to 50 indicate greater human activity impact; (b) Land Use and Land Cover Distribution in the Heilongjiang (Amur) River Basin in 2020.
The spatial distribution of LUCC (Figure 10b) further reveals the specific pathways through which human activities impact groundwater resources. In the Songhua River Basin, where GWSA depletion is most severe, extensive Arable Land and Artificial Surfaces dominate the landscape, exerting substantial pressure on groundwater systems: (1) Urban expansion transforms natural surfaces with infiltration capabilities into impervious surfaces, thereby reducing the effective recharge capacity of precipitation to groundwater [72]. (2) A well-developed drainage network system quickly drains away rainwater, further reducing the replenishment opportunities in this area [73].
4.3. Comparison with Other Cross-Border River Basins and Methods Within the Same River Basin
Comparing groundwater storage drivers across transboundary river basins: (1) The Indus River Basin is widely recognized as a global hotspot for groundwater depletion, with its rapid decline primarily attributed to human activities—particularly intensive groundwater over-exploitation driven by agricultural irrigation [74]. Asoka [75] findings indicate that groundwater storage changes in Northwest India (including the Indus River) are primarily influenced by fluctuations in irrigation water withdrawals, which are in turn indirectly affected by temperature and precipitation; (2) Groundwater changes in the upper Mekong River Basin are mainly climate-driven, while the lower basin is increasingly impacted by intensifying human activities [76]. Compared with studies in the Indus and Mekong basins, this research not only reveals the universal pattern of GWSA variations being driven by both climate and human activities but also highlights the unique characteristics of the Heilongjiang (Amur) River Basin’s unique climate-dominated dynamics at high latitudes. This deepens our understanding of the differentiated challenges facing global transboundary groundwater systems. In transboundary water resource assessment and management, differentiated strategies should be developed based on the dominant driving mechanisms within each basin.
This study’s progress is validated by comparison with existing research within the Heilongjiang (Amur) River Basin. Most studies identify precipitation as the primary driver of groundwater dynamics. Yue [77] employed Pearson correlation analysis using precipitation, temperature, and evapotranspiration factors for GWSA, similarly finding that TEM contributed slightly more to GWSA than PRE in the Heilongjiang (Amur) River Basin. This aligns with the findings from the RF-SHAP model in this study. However, by integrating multi-source drivers from climate and human activities, this research not only rigorously identifies key drivers but also accounts for spatial heterogeneity. This represents significant progress over previous studies, deepening our understanding of the response mechanisms within the groundwater system of the Heilongjiang (Amur) River Basin.
4.4. Limitations of This Study and Future Prospects
Although this study establishes a “Inversion–attribution–spatial analysis” framework and advances the understanding of the spatiotemporal evolution and driving mechanisms of groundwater storage in the Heilongjiang (Amur) River Basin, several limitations remain, which also point to directions for future research: (1) Insufficient spatial resolution of the data. The relatively low spatial resolution of GRACE data, approximately 300 km, inevitably smooths out locally intense groundwater signals, leading to an underestimation of regional changes in human activity areas. (2) Uncertainty in inversion result validation. The difficulty in obtaining publicly available, long-term, and uniformly distributed groundwater measurement data within the study area limits the ability to conduct more comprehensive and precise validation of the inversion results. (3) There exists a gap between statistical associations and causal mechanisms. The correlation analysis employed in this study essentially reveals statistical associations rather than definitive causal relationships. (4) Static representation of human activities. This study utilized LUCC and HFP data from 2020, failing to capture the dynamic changes in land use and human activity intensity during the study period. Consequently, the assessment of long-term human activity impacts is subject to bias. (5) Potential critical omitted variables. Specific key management information, such as actual agricultural irrigation water usage, reservoir scheduling data, and groundwater extraction policies, is missing due to data availability constraints, limiting the model’s ability to analyze the specific impacts of human activities.
Looking ahead, research could be deepened in the following directions: (1) Utilizing higher-resolution GRACE-FO satellites [78] and integrating satellite altimetry, InSAR, and densified ground observation data [79,80] to establish a multi-source data validation system, thereby enhancing the accuracy and reliability of inversion results; (2) Employing time-series remote sensing data to represent human activity evolution [35] and exploring the integration of statistical data to supplement critical water use and management information; (3) Combining causal discovery algorithms with physical mechanism models [81,82] to identify causal relationships and lag effects between driving factors and GWSA. This in-depth research provides a scientific basis for rational water resource development and management, as well as urbanization planning, ultimately achieving sustainable development of groundwater resources, socio-economic conditions, and ecological environments across diverse regions.
5. Conclusions
Global warming and intensified human activities have significantly impacted GWSA in the Heilongjiang (Amur) River Basin. Notably, the study area’s vast geographical span and substantial elevation variations make it an ideal representative region for GWSA analysis. This study employs GRACE satellite data and the GLDAS to reconstruct groundwater storage changes. By integrating Sen-MK trend analysis, a Random Forest-SHAP machine learning model, and Pearson spatial correlation analysis, it examines the evolution characteristics, dominant drivers, and spatial heterogeneity of GWSA in the Heilongjiang (Amur) River Basin from 2002 to 2024. The following conclusions were drawn: (1) The basin GWSA exhibits an overall declining trend, with spatially variable patterns—relatively stable or increasing in the northeast, while other regions show divergent trends. The Songhua sub-basin experienced the fastest degradation, and the Amgun sub-basin showed the most significant increase; (2) Temperature and precipitation are the primary drivers of GWSA changes, highlighting the dominant role of climate; (3) GWSA shows a positive correlation with temperature overall, particularly in the northern permafrost zone, reflecting the potential positive effect of climate warming on groundwater recharge through snowmelt and permafrost degradation; (4) GWSA shows an overall negative correlation with precipitation, indicating a lag effect of precipitation on groundwater recharge. Simultaneously, under conditions of intense human activity and surface constraints, the recharge efficiency of increased precipitation is severely diminished, sometimes accompanied by even greater groundwater depletion.
Against the backdrop of global warming and intensified human activities, mitigating the declining trend of groundwater storage in the Heilongjiang (Amur) River Basin is essential for ensuring long-term regional sustainability. Future strategies should integrate multi-source datasets to coordinate groundwater resource management with economic development and ecological protection, promoting synergistic development among groundwater resources, socio-economic systems, and ecological environments across different subregions.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, T.S.; methodology, T.S.; software, T.S.; validation, Y.L. and K.Z.; formal analysis, T.S.; investigation, Y.L.; resources, K.Z.; data curation, C.D.; writing—original draft preparation, T.S.; writing—review and editing, T.S., Y.L. and K.Z.; visualization, T.S.; supervision, K.Z. and C.D.; project administration, C.D.; funding acquisition, C.D. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by the National-level Scientific Research Project: Study on the Physical and Mechanical Properties of Reservoir Ice in Ice Engineering and Their Trends Affected by Global Climate Change (51079021) and Strategic Priority Research Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (Xda28100105).
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to express their sincere gratitude to the valuable support given by the Chinese Academy of Sciences and the Heilongjiang University. We also thank our classmates and teachers for their help, their insightful discussions and technical support. Special thanks to the institutions and individuals who provided important data and resources for this research. Their support played an important role in the successful completion of this research.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors have no competing interests to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
References
- Zuo, Q.T. Research on sustainable utilization of water resources and its contribution to modern water control in China. Adv. Earth Sci. 2023, 38, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez-Márquez, C.; Posadas-Paredes, T.; Raya-Tapia, A.Y.; Ponce-Ortega, J.M. Natural Resource Optimization and Sustainability in Society 5.0: A Comprehensive Review. Resources 2024, 13, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Li, K.; Li, H.J.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Fu, T.L.; Sun, L.C.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.X. Water resource utilization and future supply–demand scenarios in energy cities of semi-arid regions. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 5005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.P.; Bantilan, C.; Byjesh, K. Vulnerability and policy relevance to drought in the semi-arid tropics of Asia—A retrospective analysis. Weather Clim. Extrem. 2014, 3, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.S.; Jayakumar, R.; Liu, K.; Wang, H.; Chai, R. Review on transboundary aquifers in People’s Republic of China with case study of Heilongjiang-Heilongjiang (Amur) River Basin. Environ. Geol. 2008, 54, 1411–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.Y.; Xu, C.C.; Gao, X.; Lu, C.Y.; Cao, B.; Guo, H.; Yan, L.J.; Wu, C.; He, X. Response of groundwater to different water resource allocation patterns in the Sanjiang Plain, Northeast China. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2022, 42, 101156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frappart, F.; Ramillien, G. Monitoring Groundwater Storage Changes Using the Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment (GRACE) Satellite Mission: A Review. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Nan, Z.; Cheng, G. GRACE Gravity Satellite Observations of Terrestrial Water Storage Changes for Drought Characterization in the Arid Land of Northwestern China. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 1021–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Li, G.; Zhu, Z.; Hao, Y.; Hao, H.; Yao, J.; Bao, T.; Liu, Q.; Yeh, T.-C.J. Analysis of the spatiotemporal variation of groundwater storage in Ordos Basin based on GRACE gravity satellite data. J. Hydrol. 2024, 632, 130931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Famiglietti, J.S.; Lo, M.; Ho, S.L.; Bethune, J.; Anderson, K.; Syed, T.H.; Swenson, S.C.; de Linage, C.R.; Rodell, M. Satellites measure recent rates of groundwater depletion in California’s Central Valley. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2011, 38, L03403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scanlon, B.R.; Longuevergne, L.; Long, D. Ground referencing GRACE satellite estimates of groundwater storage changes in the California Central Valley, USA. Water Resour. Res. 2012, 48, W04520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arega, K.A.; Birhanu, B.; Ali, S.; Hailu, B.T.; Tariq, M.A.U.R.; Adane, Z.; Nedaw, D. Analysis of spatio-temporal variability of groundwater storage in Ethiopia using Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment (GRACE) data. Environ. Earth Sci. 2024, 83, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Xiang, L.; Steffen, H.; Wu, P.; Jiang, L.; Shen, Q.; Li, Z.; Hayashi, M. GRACE-based estimates of groundwater variations over North America from 2002 to 2017. Geod. Geodyn. 2022, 13, 11–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massoud, E.C.; Purdy, A.J.; Miro, M.E.; Famiglietti, J.S. Projecting groundwater storage changes in California’s Central Valley. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 12917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Li, T.; Cheng, S.; Wang, X. Spatial Distribution Exploration and Driving Factor Identification for Soil Salinisation Based on Geodetector Models in Coastal Area. Ecol. Eng. 2020, 156, 105961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Sun, Y.; Chen, Z.; Yan, H.; Qian, S. Dynamic Changes of Vegetation Ecological Quality in the Yellow River Basin and Its Response to Extreme Climate During 2000–2020. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2022, 42, 4524–4535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, Z.; Li, C.; Zhao, J.; Li, Z.; Chen, K.; Huang, X.; Zhao, Z. The Temporal and Spatial Evolution Characteristics and Driving Factors of Ecosystem Service Bundles in Anhui Province, China. Land 2024, 13, 736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Liang, Q.; Hancock, J.T.; Khoshgoftaar, T.M. Feature selection strategies: A comparative analysis of SHAP-value and importance-based methods. J. Big Data 2024, 11, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Broeck, G.; Lykov, A.; Schleich, M.; Suciu, D. On the tractability of SHAP explanations. J. Artif. Intell. Res. 2022, 74, 851–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Hutson, A.D. A robust Spearman correlation coefficient permutation test. Commun. Stat.-Theory Methods 2024, 53, 2141–2153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papageorgiou, S.N. On correlation coefficients and their interpretation. J. Orthod. 2022, 49, 359–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Shan, F.; Yue, H.; Wang, X.; Fan, Y. Global analysis of the correlation and propagation among meteorological, agricultural, surface water, and groundwater droughts. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 333, 117460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thurstone, L.L. A method of calculating the Pearson correlation coefficient without the use of deviations. Psychol. Bull. 1917, 14, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee Rodgers, J.; Nicewander, W.A. Thirteen ways to look at the correlation coefficient. Am. Stat. 1988, 42, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, C.; Li, M.; Zhang, Z. Study on hydrogeological regionalization of Heilongjiang (Amur River) Basin. Eng. J. Heilongjiang Univ. 2021, 12, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.L.; Xia, Z.Q.; Cai, T.; Guo, L.D. Variations of temperature, precipitation, and extreme events in Heilongjiang River. Procedia Eng. 2012, 28, 326–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yue, Q.; Yu, G.; Miao, Y.; Zhou, Y. Analysis of Meteorological Element Variation Characteristics in the Heilongjiang (Amur) River Basin. Water 2024, 16, 521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, R.; Huang, Q.; Xia, J.; Wang, P.; Fang, Y.; Shamov, V.V.; Frolova, N.L.; She, D. Climate Warming-Induced Hydrological Regime Shifts in Cold Northeast Asia: Insights from the Heilongjiang-Heilongjiang (Amur) River Basin. Land 2025, 14, 980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, S.; Sneeuw, N. Filling the data gaps within GRACE missions using singular spectrum analysis. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2021, 126, e2020JB021227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; van Dam, T.; Sneeuw, N.; Collilieux, X.; Weigelt, M.; Rebischung, P. Singular spectrum analysis for modeling seasonal signals from GPS time series. J. Geodyn. 2013, 72, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abatzoglou, J.T.; Dobrowski, S.Z.; Parks, S.A.; Hegewisch, K.C. TerraClimate, a High–Resolution Global Dataset of Monthly Climate and Climatic Water Balance from 1958–2015. Sci. Data 2018, 5, 170191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, L.; Zhao, T.; Chen, X.; Lin, S.; Wang, J.; Mi, J.; Liu, W. GWL_FCS30: A Global 30 m Wetland Map with a Fine Classification System Using Multi–Sourced and Time–Series Remote Sensing Imagery in 2020. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2023, 15, 265–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Liu, Y.; Li, J.; Tian, P.; Zhang, H. Surface Water Changes in China’s Yangtze River Delta over the Past Forty Years. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2023, 91, 104458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanderson, E.W.; Jaiteh, M.; Levy, M.A.; Redford, K.H.; Wannebo, A.V.; Woolmer, G. The Human Footprint and the Last of the Wild: The Human Footprint Is a Global Map of Human Influence on the Land Surface, Which Suggests That Human Beings Are Stewards of Nature, Whether We Like It or Not. BioScience 2002, 52, 891–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, H.; Li, X.; Wen, Y.; Huang, J.; Du, P.; Su, W.; Miao, S.; Geng, M. A Global Record of Annual Terrestrial Human Footprint Dataset from 2000 to 2018. Sci. Data 2022, 9, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venter, O.; Sanderson, E.W.; Magrach, A.; Allan, J.R.; Beher, J.; Jones, K.R.; Possingham, H.P.; Laurance, W.F.; Wood, P.; Fekete, B.M.; et al. Sixteen Years of Change in the Global Terrestrial Human Footprint and Implications for Biodiversity Conservation. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Gong, H.; Chen, B.; Zhang, Q.; Li, Z. Long-term and seasonal variation in groundwater storage in the North China Plain based on GRACE. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2021, 104, 102560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, T.Y.; Li, X.L.; Shum, C.K.; Ding, H.; Xu, X.Y. The Balance and Abnormal Increase of Global Ocean Mass Change from Land Using GRACE. Earth Space Sci. 2020, 7, e2020EA001104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houser, P.; Gottschalck, J.; Meng, C.-J.; Cosgrove, B.; Radakovich, J.; Bosilovich, M. The global land data assimilation system. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2004, 85, 381–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Zuo, D.; Xu, Z.; Wang, G.; Peng, D.; Pang, B.; Yang, H. Attributing the Imp acts of Vegetation and Climate Changes on the Spatial Heterogeneity of Terrestrial Water Storage over the Tibetan Plateau. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohlson, J.A.; Kim, S. Linear Valuation Without OLS: The Theil–Sen Estimation Approach. Rev. Account. Stud. 2015, 20, 395–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanan, P.; Basistha, A.; Sarkar, S.; Sachdeva, K. Trend Analysis and ARIMA Modelling of Pre–Monsoon Rainfall Data for Western India. Comptes Rendus Geosci. 2013, 345, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alomari, Y.; Andó, M. SHAP-based insights for aerospace PHM: Temporal feature importance, dependencies, robustness, and interaction analysis. Results Eng. 2024, 21, 101834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Wang, L. t-Test and ANOVA for data with ceiling and/or floor effects. Behav. Res. Methods 2021, 53, 264–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asadollahi, A.; VB, M.K.; Ghimire, A.B.; Poudel, B.; Shin, S. The impact of climate change and urbanization on groundwater levels: A system dynamics model analysis. Environ. Prot. Res. 2024, 4, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, G.; Jin, H. Permafrost and groundwater on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau and in northeast China. Hydrogeol. J. 2013, 21, 5–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, D.; Pan, Y.; Zhou, J.; Chen, Y.; Hou, X.; Hong, Y.; Scanlon, B.R.; Longuevergne, L. Global analysis of spatiotemporal variability in merged total water storage changes using multiple GRACE products and global hydrological models. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 192, 198–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Xin, Z.; Cheng, Y. Groundwater storage changes and influencing factors in the Mongolian Plateau. J. Desert Res. 2025, 45, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhai, L.; Qiao, Q.; Liu, J. Changes of groundwater storage and their influencing factors in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region based on GRACE and GLDAS data. Sci. Surv. Mapp. 2023, 48, 94–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Wang, Z. Detect Songhua River Basin Groundwater Spatiotemporal Variation Characteristics by GRACE and Multi-source Hydrological Data. Geomat. Inf. Sci. Wuhan Univ. 2023, 48, 1409–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, M.A.; Webster, R. Kriging: A method of interpolation for geographical information systems. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Syst. 1990, 4, 313–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Fang, S.; Han, J.; Yu, Y.; Wu, D. Analysis of groundwater storage anomaly and multisource influencing factors in the North China Plain. Natl. Remote Sens. Bull. 2025, 29, 677–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Peng, Y.; Liu, J.; Hao, C. Study on groundwater storage changes in Henan province during 2003–2022 derived from GRACE and GLDAS. Bull. Surv. Mapp. 2024, 10, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Dai, C.; Jing, Y.; Ru, Q.; Yan, F.; Zhang, Y. GRACE/GRACE-FO Satellite Assessment of Sown Area Expansion Impacts on Groundwater Sustainability in Jilin Province. Sustainability 2025, 17, 7731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahr, J.; Swenson, S.; Zlotnicki, V.; Velicogna, I. Time-variable gravity from GRACE: First results. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004, 31, L11501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swenson, S.; Wahr, J. Post-processing removal of correlated errors in GRACE data. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33, L08402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longuevergne, L.; Scanlon, B.R.; Wilson, C.R. GRACE Hydrological estimates for small basins: Evaluating processing approaches on the High Plains Aquifer, USA. Water Resour. Res. 2010, 46, W11517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Tang, X.; Yuan, G.; Zhang, X.; Sun, X. Chinese Ecosystem Research Network 2005–2014 Groundwater Data Set; Science Data Bank: Beijing, China, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y. Simulation and Dynamic Analysis of Groundwater Depression Funnel Control Following Reservoir Impoundment at Dadingzi Mountain Reservoir, Harbin. Master’s Thesis, Heilongjiang University, Harbin, China, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walvoord, M.A.; Kurylyk, B.L. Hydrologic impacts of thawing permafrost—A review. Vadose Zone J. 2016, 15, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, S.G.; Ge, S. Contrasting hydrogeologic responses to warming in permafrost and seasonally frozen ground hillslopes. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2017, 44, 1803–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Dai, C.; Jing, J.; Liu, G.; Ru, Q.; Li, J.; Liu, P. Study on the relationship between surface water and groundwater transformation in the middle and lower reaches of Songhua river basin. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 8088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, D.; Yang, W.; Scanlon, B.R.; Zhao, J.; Liu, D.; Burek, P.; Pan, Y.; You, L.; Wada, Y. South-to-North Water Diversion stabilizing Beijing’s groundwater levels. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, G.; Liu, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, S.; Qu, X.; Wang, L.; Tong, S.; Zhang, M.; Li, X.; Zhang, W. Impacts of groundwater storage variability on soil salinization in a semi-arid agricultural plain. Geoderma 2025, 454, 117162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, S.; Cui, G.; Yan, L.; Tong, S. Hydro-salinity dynamics in a semi-arid agricultural plain: Implications for sustainable land management. Ecol. Indic. 2025, 178, 114100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Cui, G.; Li, X.; Liu, Y.; Li, X.; Tong, S.; Zhang, M. GRACE Satellite-based analysis of spatiotemporal evolution and driving factors of groundwater storage in the black soil region of Northeast China. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Famiglietti, J.S. The global groundwater crisis. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2014, 4, 945–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuthbert, M.; Gleeson, T.; Moosdorf, N.; Befus, K.M.; Schneider, A.; Hartmann, J.; Lehner, B. Global patterns and dynamics of climate–groundwater interactions. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2019, 9, 137–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Li, B.; Li, Z.; Li, W. Water resource formation and conversion and water security in arid region of Northwest China. J. Geogr. Sci. 2016, 26, 939–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wada, Y.; Van Beek, L.P.; Van Kempen, C.M.; Reckman, J.W.; Vasak, S.; Bierkens, M.F. Global depletion of groundwater resources. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2010, 37, L20402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanshan, W.; Tong, J.; Xiucang, L.; Tengfei, W.; Yanjun, W.; Fischer, T. Changes of actual evapotranspiration over the Songhua River Basin from 1961 to 2010. Adv. Clim. Chang. Res. 2014, 10, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diadin, D.; Shandyba, D.; Drozd, O.; Yakovlev, V. Assessment of anthropogenic transformation of groundwater recharge conditions in urban areas. Ecol. Saf. Balanc. Use Resour. 2025, 16, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiflay, E.; Schirmer, M.; Foppen, J.W.; Moeck, C. Impact of urbanization on groundwater recharge: Altered recharge rates and water cycle dynamics for Arusha, Tanzania. Hydrogeol. J. 2025, 33, 33–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodell, M.; Velicogna, I.; Famiglietti, J.S. Satellite-based estimates of groundwater depletion in India. Nature 2009, 460, 999–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asoka, A.; Gleeson, T.; Wada, Y.; Mishra, V. Relative contribution of monsoon precipitation and pumping to changes in groundwater storage in India. Nat. Geosci. 2017, 10, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Duy, N.; Nguyen, T.V.K.; Nguyen, D.V.; Tran, A.T.; Nguyen, H.T.; Heidbüchel, I.; Merz, B.; Apel, H. Groundwater dynamics in the Vietnamese Mekong Delta: Trends, memory effects, and response times. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2021, 33, 100746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Z. Study on Terrestrial Water Storage Changes in the Heilongjiang (Amur) River Basin Based on GRACE Satellite Data. Master’s Thesis, Heilongjiang University, Harbin, China, 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, W.; Wang, C.-Q.; Mu, D.-P.; Zhong, M.; Zhong, Y.-L.; Xu, H.-Z. Groundwater storage variations in the North China Plain from GRACE with spatial constraints. Chin. J. Geophys. 2017, 60, 1630–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellazzi, P.; Longuevergne, L.; Martel, R.; Rivera, A.; Brouard, C.; Chaussard, E. Quantitative mapping of groundwater depletion at the water management scale using a combined GRACE/InSAR approach. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 205, 408–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Béjar-Pizarro, M.; Ezquerro, P.; Herrera, G.; Tomás, R.; Guardiola-Albert, C.; Hernández, J.M.R.; Merodo, J.A.F.; Marchamalo, M.; Martínez, R. Mapping groundwater level and aquifer storage variations from InSAR measurements in the Madrid aquifer, Central Spain. J. Hydrol. 2017, 547, 678–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonotto, G.; Peterson, T.J.; Fowler, K.; Western, A.W. Identifying causal interactions between groundwater and streamflow using convergent cross-mapping. Water Resour. Res. 2022, 58, e2021WR030231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Runge, J.; Bathiany, S.; Bollt, E.; Camps-Valls, G.; Coumou, D.; Deyle, E.; Glymour, C.; Kretschmer, M.; Mahecha, M.D.; Muñoz-Marí, J. Inferring causation from time series in Earth system sciences. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).