Pollution and Carbon Emission Reduction Effects of Transit Metropolis Construction: Evidence from China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Policy Background
3. Research Hypotheses
4. Methods and Data
4.1. Model Specification
4.2. Main Variables and Data Sources
4.2.1. Dependent Variable
4.2.2. Independent Variables
4.2.3. Control Variables
5. Empirical Results and Analysis
5.1. Baseline Regression Results
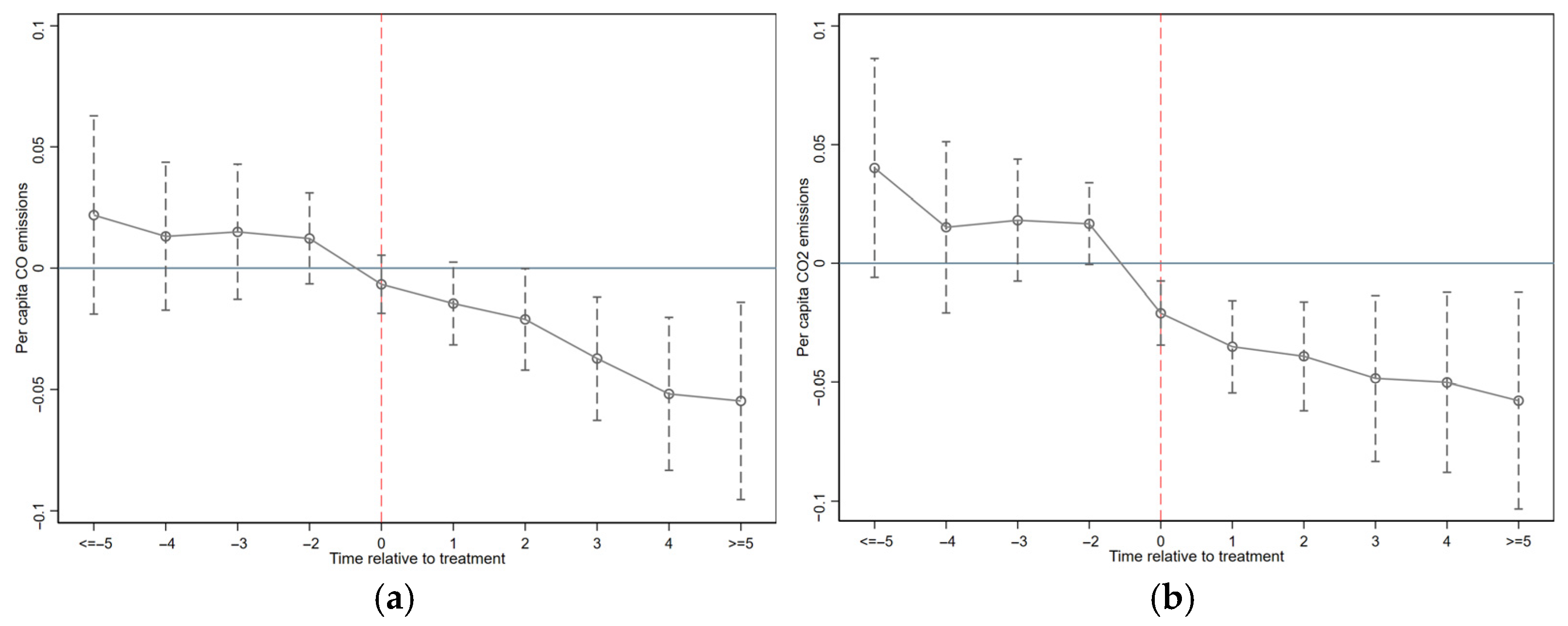
5.2. Parallel Trend Assumption
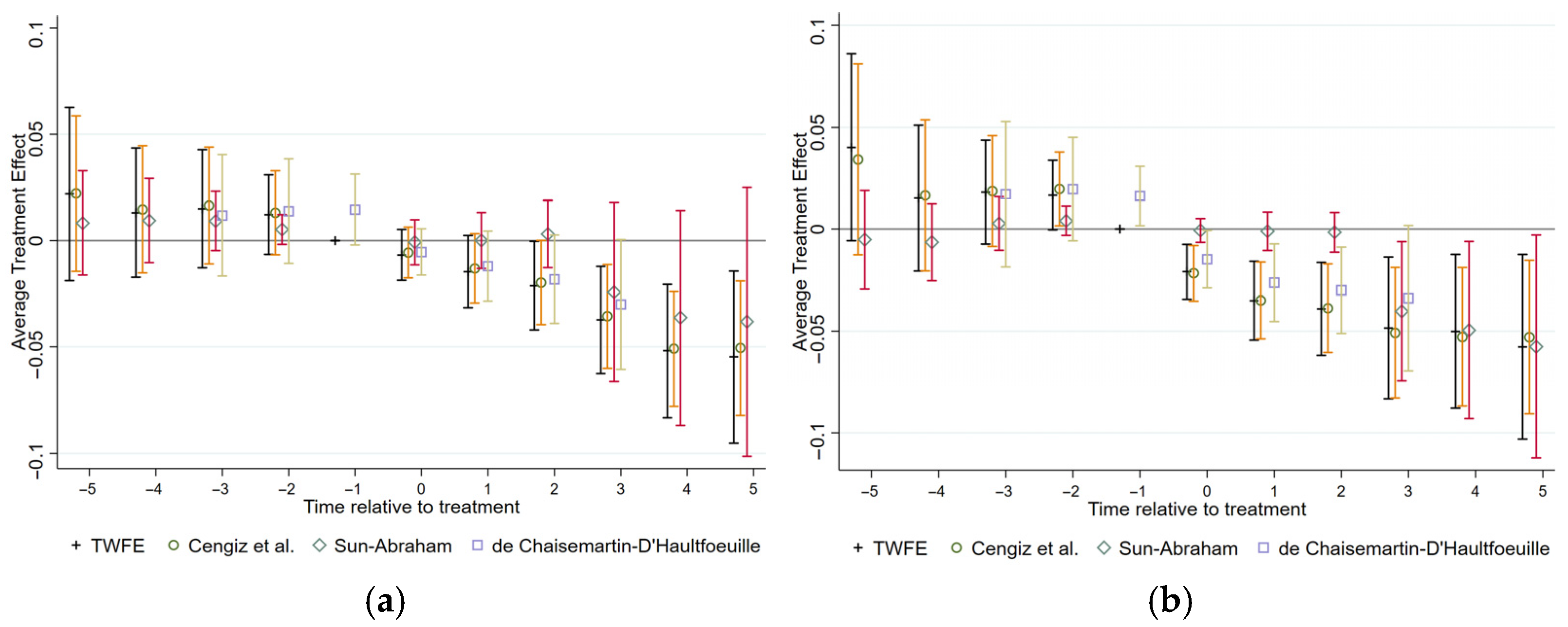
5.3. Robustness Checks
5.3.1. PSM-DID Estimation
5.3.2. Other Related Policies
5.3.3. Alternative Measures of the Dependent Variable
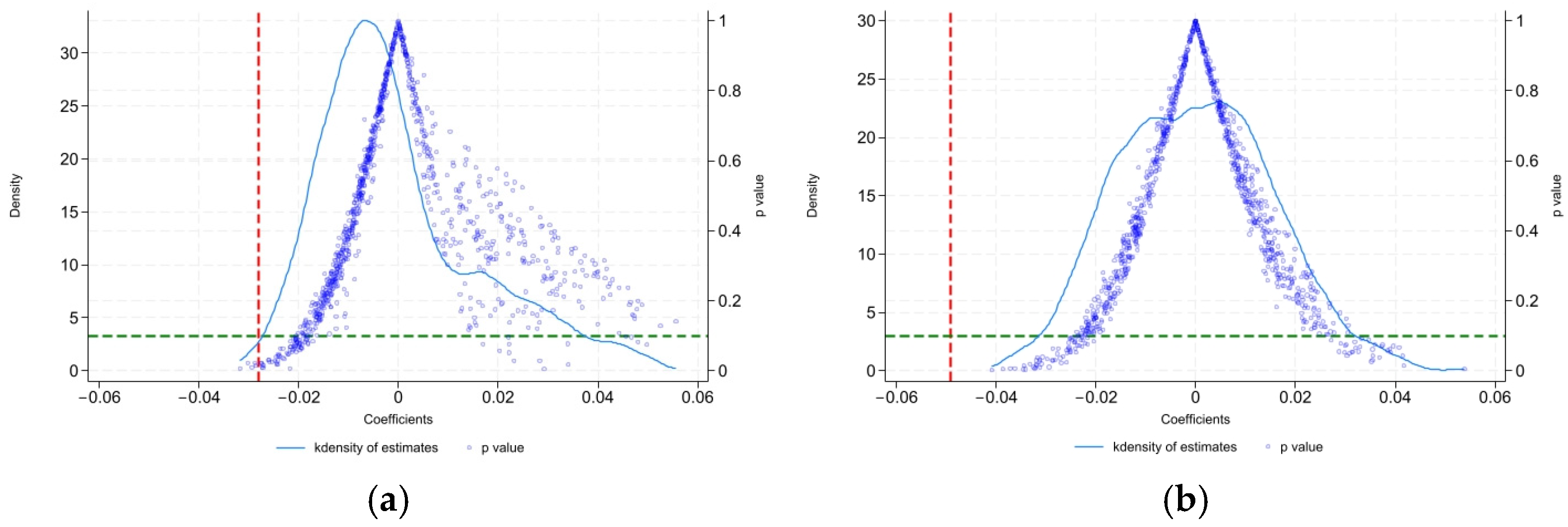
5.3.4. Placebo Test
5.3.5. Treatment Effects Heterogeneity
5.3.6. Double Machine Learning Estimation
5.4. Underlying Mechanisms
5.5. Heterogeneity Analysis
6. Conclusions and Policy Implications
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| TMCP | Transit Metropolis Construction Pilot |
| CO | Carbon monoxide |
| CO2 | Carbon dioxide |
| PM | Particulate matter |
| DID | Difference-in-differences |
| PSM | Propensity score matching |
| TWFE | Two-way fixed effects |
| GDP | Gross domestic product |
References
- Cai, W.; Li, K.; Liao, H.; Wang, H.; Wu, L. Weather conditions conducive to Beijing severe haze more frequent under climate change. Nat. Clim. Change 2017, 7, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xianning News Network. China’s first “Green and Low-Carbon Development Report on Mobile Sources (Blue Book)” Has Been Released, Exploring the Scientific Pathway for Green and Low-Carbon Development. Available online: https://tech.chinadaily.com.cn/a/202408/01/WS66ab037aa310054d254eafad.html (accessed on 1 August 2024).
- Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China. China Mobile Source Environmental Management Annual Report. Available online: https://www.mee.gov.cn/hjzl/sthjzk/ydyhjgl/202503/W020250326518388591055.pdf (accessed on 1 March 2025).
- Ding, P.; Feng, S.; Pojani, D. Nationwide diffusion of China’s Transit Metropolis Pilot Program. Util. Policy 2025, 95, 101958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, K.; Guo, J. The impact of institutional openness on the synergistic effect of air pollution reduction and carbon reduction in China. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 22575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, Z.; Bai, Y.; Jian, K.; Chalermkiat, W. The Spatial Spillover Effect and Mechanism of Carbon Emission Trading Policy on Pollution Reduction and Carbon Reduction: Evidence from the Pearl River–West River Economic Belt in China. Sustainability 2024, 16, 10279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Yue, S. Impact of digital economy on co-benefits of air pollution reduction and carbon reduction: Evidence from Chinese cities. Urban Clim. 2024, 58, 102189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Qiu, Z.; Hu, L.; Hu, D.; Nai, Y. How digital transformation facilitate synergy for pollution and carbon reduction: Evidence from China. Environ. Res. 2024, 251, 118639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Cai, X.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, D. Can green technology innovations achieve the collaborative management of pollution reduction and carbon emissions reduction? Evidence from the Chinese industrial sector. Environ. Res. 2025, 264, 120400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Fu, M.; Wang, L.; Liang, Y.; Tang, F.; Li, S.; Wu, C. Impact of Urban Shrinkage on Pollution Reduction and Carbon Mitigation Synergy: Spatial Heterogeneity and Interaction Effects in Chinese Cities. Land 2025, 14, 537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang-Tung, N.; Linh, H.T.; Tan, N.V.; Kato, H. Traffic congestion and ride-hailing booking: Evidence from Hanoi, Vietnam. J. Transp. Geogr. 2025, 129, 104422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, W.-L.; Ling, Y.; Ochieng, W.; Yang, L.; Gao, X.; Ren, Q.; Chen, Y.; Cao, M. Driving forces of CO2 emissions from the transport, storage and postal sectors: A pathway to achieving carbon neutrality. Appl. Energy 2024, 365, 123226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, W.-L.; Song, X.; Xiang, Q.; Chen, H.; Elhajj, M.; Bi, H.; Wang, K.; Ochieng, W. The impact of deep reinforcement learning-based traffic signal control on Emission reduction in urban Road networks empowered by cooperative vehicle-infrastructure systems. Appl. Energy 2025, 390, 125884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bel, G.; Holst, M. Evaluation of the impact of Bus Rapid Transit on air pollution in Mexico City. Transp. Policy 2018, 63, 209–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, C.; Pan, T.; Dong, X. The Impact of Urban Form on Carbon Emission Efficiency Under Public Transit-Oriented Development: Spatial Heterogeneity and Driving Forces. Land 2025, 14, 1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topalovic, P.; Carter, J.; Topalovic, M.; Krantzberg, G. Light Rail Transit in Hamilton: Health, Environmental and Economic Impact Analysis. Soc. Indic. Res. 2012, 108, 329–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Yu, T.; Huang, J. Subway Openings and Urban Air Pollution Mitigation: Pathways to Sustainable Development in China. Sustainability 2025, 17, 4782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, S.; Huang, Y.; Sun, T. Urban sprawl, public transportation efficiency and carbon emissions. J. Clean. Prod. 2025, 489, 144652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Sial, M.S.; Deng, D.; Saxunova, D.; Haider, A.; Khan, M.A. The Significance of Urban Rail Transit Systems in Mitigating Air Pollution Effects: The Case of China. Sustainability 2022, 14, 13944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, S.; Hu, J.; Shao, L.; Feng, T.; Appolloni, A. Can public transportation development improve urban air quality? Evidence from China. Urban Clim. 2024, 54, 101825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J. The transit metropolis of Chinese characteristics? Literature review, interviews, surveys and case studies. Transp. Policy 2016, 51, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Huang, Y.; Ji, A.; Liu, H.; Li, J.; Ni, A.; Lu, W. Policy implications of the transit metropolis project: A quasi-natural experiment from China. Transp. Policy 2025, 162, 155–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhejiang Online. National Model! Hangzhou Has Been Designated as a National Demonstration City for the Transit Metropolis Construction Pilot Program. Available online: https://hangzhou.zjol.com.cn/jrsd/bwzg/201812/t20181214_8988109.shtml (accessed on 14 December 2018).
- Pang, J.; An, L.; Shen, S. Gasoline prices, traffic congestion, and carbon emissions. Resour. Energy Econ. 2023, 75, 101407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, F.; Cheng, X.; Lei, Z.; Xu, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Q. Heterogeneous impacts of local traffic congestion on local air pollution within a city: Utilizing taxi trajectory data. J. Environ. Econ. Manag. 2023, 122, 102896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Luo, Y.; Li, J. Urban traffic infrastructure investment and air pollution: Evidence from the 83 cities in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 172, 488–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daily Qingdao. The Average Daily Passenger Volume of Public Transportation in Qingdao is 3.26 Million. The City Is Making Every Effort to Become a Pilot City for Transit Metropolis Construction. Available online: https://www.dailyqd.com/makers/2019-08/12/content_480857.htm (accessed on 12 August 2019).
- Wuhu Municipal People’s Government. Wuhu’s “National Transit Metropolis Construction Pilot City” Initiative Has Been Successfully Completed. Available online: https://www.wuhu.gov.cn/xwzx/zwyw/36362651.html (accessed on 23 December 2022).
- Open Platform For Government Information of Shangrao. Good News! Shangrao City Has Been Successfully Designated as a National Demonstration City for the Transit Metropolis Construction Pilot Program. Available online: https://www.zgsr.gov.cn/jtj/gzdt/202308/07d130b08dda40f481c23ae1e8faed9e.shtml (accessed on 30 August 2023).
- Daily Taiyuan. The “Taiyuan Model” of Transit Metropolis Construction Pilot City: Green Travel Becomes a Trend, and Quality Service Takes Root in People’s Hearts. Available online: https://sx.cri.cn/2021-08-12/cf94a555-25d8-ca0f-1d8f-db26b8cb102c.html (accessed on 12 August 2021).
- Zhang, H.; Di Maria, C.; Ghezelayagh, B.; Shan, Y. Climate policy in emerging economies: Evidence from China’s Low-Carbon City Pilot. J. Environ. Econ. Manag. 2024, 124, 102943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodman-Bacon, A. Difference-in-differences with variation in treatment timing. J. Econom. 2021, 225, 254–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Abraham, S. Estimating dynamic treatment effects in event studies with heterogeneous treatment effects. J. Econom. 2021, 225, 175–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cengiz, D.; Dube, A.; Lindner, A.; Zipperer, B. The Effect of Minimum Wages on Low-Wage Jobs. Q. J. Econ. 2019, 134, 1405–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Chaisemartin, C.; D’Haultfœuille, X. Two-Way Fixed Effects Estimators with Heterogeneous Treatment Effects. Am. Econ. Rev. 2020, 110, 2964–2996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Yao, D. How does public transport development contribute to carbon emission reduction? Transp. Res. Part A Policy Pract. 2025, 191, 104327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Kang, C.; Zhang, H. China’s efforts towards carbon neutrality: Does energy-saving and emission-reduction policy mitigate carbon emissions? J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 316, 115286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.; Gu, G.; Zhou, H. Assessing the low-carbon city pilot policy on carbon emission from consumption and production in China: How underlying mechanism and spatial spillover effect? Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 71958–71977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.; Wang, F. Does urban agglomeration reduce carbon emissions in Chinese cities? New perspective on factor mobility. Energy Econ. 2025, 143, 108297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Shen, D. Contribution of shared bikes to carbon dioxide emission reduction and the economy in Beijing. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2019, 51, 101749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, M.; Chen, D.; Wu, T.; Tao, M.; Sheng, M.S.; Zhang, Y. Intelligence and carbon emissions: The impact of smart infrastructure on carbon emission intensity in cities of China. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2024, 112, 105602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernozhukov, V.; Chetverikov, D.; Demirer, M.; Duflo, E.; Hansen, C.; Newey, W.; Robins, J. Double/debiased machine learning for treatment and structural parameters. Econom. J. 2018, 21, C1–C68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.H.; Wang, X.Y.; Tong, X.C. From the Sharing Economy to the Low Carbon Economy: Evidence from the Entry of Bicycle Sharing Platforms. J. Quant. Technol. Econ. 2024, 41, 111–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Central People’s Government of the People’s Republic of China. Notice from the State Council on Issuing the 11th Five-Year Plan for National Environmental Protection. Available online: https://www.gov.cn/zwgk/2007-11/26/content_815498.htm (accessed on 26 November 2007).
| Batch | Cities | Date |
|---|---|---|
| First batch (15 cities total) | Beijing, Shenzhen, Chongqing, Nanjing, Jinan, Zhengzhou, Wuhan, Xi’an, Changsha, Shijiazhuang, Taiyuan, Dalian, Harbin, Kunming, Urumqi. | 2012 |
| Second batch (22 cities total) | Shanghai, Tianjin, Guangzhou, Hangzhou, Ningbo, Hefei, Fuzhou, Nanchang, Qingdao, Shenyang, Changchun, Suzhou, Xinxiang, Zhuzhou, Liuzhou, Haikou, Guiyang, Lanzhou, Xining, Yinchuan, Baoding, Hohhot. | 2013 |
| Third batch (50 cities total) | Zhangjiakou, Linfen, Wuhai, Anshan, Panjin, Tonghua, Mudanjiang, Changzhou, Yangzhou, Kunshan, Huzhou, Jinhua, Suzhou, Fuyang, Bengbu, Wuhu, Shangrao, Zaozhuang, Yantai, Weifang, Weihai, Luoyang, Xuchang, Nanyang, Zhumadian, Xiangyang, Yichang, Changde, Zhangjiajie, Loudi, Foshan, Nanning, Guilin, Guigang, Sanya, Chengdu, Zigong, Luzhou, Meishan, Fuling, Zunyi, Kaili, Yuxi, Baoshan, Baoji, Xianyang, Tianshui, Guyuan, Kashgar, Yining. | 2017 |
| Fourth batch (30 cities total) | Tangshan, Cangzhou, Xingtai, Yangquan, Jinzhou, Baicheng, Wuxi, Xuzhou, Yancheng, Shaoxing, Taizhou, Yiwu, Jiujiang, Yichun, Jining, Rizhao, Hebi, Puyang, Luohe, Shiyan, Jingzhou, Xianning, Yueyang, Yongzhou, Duyun, Lijiang, Jiuquan, Wuzhong, Bole, Korla. | 2023 |
| Variables | Definitions | Mean | S.D. | Min | Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| lnPCO | Per capita CO emissions (kg) | 4.210 | 0.786 | 2.652 | 9.201 |
| lnPCO2 | Per capita CO2 emissions (kg) | 8.746 | 0.849 | 6.274 | 11.650 |
| TMCP | Binary indicator of TMCP policy implementation | 0.159 | 0.366 | 0 | 1 |
| lnPGDP | Per capita GDP (Yuan) | 10.691 | 0.569 | 9.394 | 12.051 |
| lnPD | Population density (people per square kilometer) | 5.407 | 0.956 | 2.659 | 7.716 |
| lnEI | Energy intensity (tons of standard coal per million yuan) | 4.139 | 0.484 | 3.044 | 5.383 |
| IS | Industrial structure (%) | 46.716 | 10.521 | 19.25 | 72.83 |
| IC | Innovation capability | 0.194 | 0.041 | 0.094 | 0.291 |
| FFD | Financial freedom degree | 0.462 | 0.221 | 0.102 | 1.007 |
| Variables | lnPCO | lnPCO2 | lnPCO | lnPCO2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | |
| TMCP | −0.055 *** | −0.073 *** | −0.028 ** | −0.049 *** |
| (0.014) | (0.013) | (0.013) | (0.012) | |
| lnPGDP | 0.051 * | 0.034 | ||
| (0.029) | (0.031) | |||
| lnPD | −1.022 *** | −0.904 *** | ||
| (0.069) | (0.080) | |||
| lnEI | 0.025 | 0.055 ** | ||
| (0.022) | (0.023) | |||
| IS | −0.001 | 0.002 | ||
| (0.001) | (0.001) | |||
| IC | 0.053 | −0.209 | ||
| (0.123) | (0.199) | |||
| FFD | 0.056 | 0.075 | ||
| (0.050) | (0.064) | |||
| Constant | 4.218 *** | 8.757 *** | 9.088 *** | 12.964 *** |
| (0.002) | (0.002) | (0.349) | (0.542) | |
| Observations | 2574 | 2574 | 2574 | 2574 |
| R-squared | 0.986 | 0.987 | 0.987 | 0.988 |
| Date FE | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| City FE | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| Control | NO | NO | YES | YES |
| Variables | PSM-DID | Other Related Policies | Alternative Measures | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| lnPCO | lnPCO2 | lnPCO | lnPCO2 | lnCOI | lnCEI | |
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | |
| TMCP | −0.027 ** | −0.040 *** | −0.026 ** | −0.048 *** | −0.039 ** | −0.051 *** |
| (0.013) | (0.012) | (0.013) | (0.013) | (0.015) | (0.014) | |
| Constant | 9.008 *** | 12.927 *** | 9.099 *** | 13.070 *** | 11.504 *** | 15.581 *** |
| (0.362) | (0.562) | (0.356) | (0.538) | (0.616) | (0.759) | |
| Observations | 2385 | 2385 | 2574 | 2574 | 2574 | 2574 |
| R-squared | 0.987 | 0.988 | 0.988 | 0.988 | 0.982 | 0.981 |
| Date FE | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| City FE | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| Control | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| Comparison Groups | Coefficient | Weight |
|---|---|---|
| Panel A Dependent variable: lnPCO | ||
| Treatment vs. Never Treated | −0.028 | 0.876 |
| Earlier Group Control vs. Later Group Treatment | −0.003 | 0.040 |
| Later Group Control vs. Earlier Groups Treatment | 0.001 | 0.084 |
| Panel B Dependent variable: lnPCO2 | ||
| Treatment vs. Never Treated | −0.049 | 0.876 |
| Earlier Group Control vs. Later Group Treatment | −0.004 | 0.040 |
| Later Group Control vs. Earlier Groups Treatment | −0.001 | 0.084 |
| Panel A Dependent Variable: lnPCO | ||||
| Variables | LASSO | GB | NN | RF |
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | |
| TMCP | −0.047 *** | −0.081 * | −0.058 *** | −0.108 ** |
| (0.008) | (0.042) | (0.018) | (0.045) | |
| Constant | −0.000 | 0.003 | 0.015 *** | 0.010 |
| (0.002) | (0.013) | (0.002) | (0.013) | |
| Observations | 2574 | 2574 | 2574 | 2574 |
| Date FE | YSE | YSE | YSE | YSE |
| City FE | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| Control | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| Panel B Dependent variable: lnPCO2 | ||||
| Variables | LASSO | GB | NN | RF |
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | |
| TMCP | −0.063 *** | −0.108 *** | −0.154 *** | −0.169 *** |
| (0.008) | (0.041) | (0.021) | (0.042) | |
| Constant | 0.001 | 0.000 | −0.005 | −0.000 |
| (0.002) | (0.014) | (0.003) | (0.013) | |
| Observations | 2574 | 2574 | 2574 | 2574 |
| Date FE | YSE | YSE | YSE | YSE |
| City FE | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| Control | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| Variables | PTR | CDI | SMOG-Search | EP-Search |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | |
| TMCP | 0.390 ** | −0.032 ** | 3.061 *** | 8.619 *** |
| (0.166) | (0.016) | (0.461) | (1.346) | |
| Constant | −4.023 | 7.574 | −102.972 *** | −196.122 *** |
| (3.888) | (5.623) | (15.000) | (36.357) | |
| Observations | 2527 | 268 | 2544 | 2562 |
| R-squared | 0.990 | 0.837 | 0.860 | 0.940 |
| Date FE | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| City FE | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| Control | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| Panel A | High Transit Availability | Low Transit Availability | ||
| Variables | lnPCO | lnPCO2 | lnPCO | lnPCO2 |
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | |
| TMCP | −0.021 | −0.032 * | −0.047 * | −0.074 *** |
| (0.013) | (0.018) | (0.027) | (0.020) | |
| Constant | 9.134 *** | 12.896 *** | 9.219 *** | 12.995 *** |
| (0.514) | (0.676) | (0.453) | (0.890) | |
| Observations | 1305 | 1305 | 1305 | 1305 |
| R-squared | 0.996 | 0.989 | 0.980 | 0.988 |
| Date FE | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| City FE | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| Control | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| Panel B | High regulation intensity | Low regulation intensity | ||
| Variables | lnPCO | lnPCO2 | lnPCO | lnPCO2 |
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | |
| TMCP | −0.027 * | −0.010 | −0.065 *** | −0.038 * |
| (0.014) | (0.014) | (0.020) | (0.020) | |
| Constant | 13.374 *** | 10.285 *** | 11.928 *** | 8.523 *** |
| (0.725) | (0.523) | (0.906) | (0.455) | |
| Observations | 972 | 972 | 1602 | 1602 |
| R-squared | 0.989 | 0.996 | 0.987 | 0.982 |
| Date FE | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| City FE | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| Control | YES | YES | YES | YES |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, S.; Huang, G. Pollution and Carbon Emission Reduction Effects of Transit Metropolis Construction: Evidence from China. Sustainability 2025, 17, 9695. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17219695
Chen S, Huang G. Pollution and Carbon Emission Reduction Effects of Transit Metropolis Construction: Evidence from China. Sustainability. 2025; 17(21):9695. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17219695
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Shiwen, and Ganxiang Huang. 2025. "Pollution and Carbon Emission Reduction Effects of Transit Metropolis Construction: Evidence from China" Sustainability 17, no. 21: 9695. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17219695
APA StyleChen, S., & Huang, G. (2025). Pollution and Carbon Emission Reduction Effects of Transit Metropolis Construction: Evidence from China. Sustainability, 17(21), 9695. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17219695







