Key Drivers of Green Logistics: A Systematic Literature Review and Conceptual Framework
Abstract
1. Introduction
- RQ1: What is the publication trend and who are the major contributors to green logistics and supply chain literature?
- RQ2: Which theories and methodologies are most applied in this field?
- RQ3: What are the key antecedents of GLPs, and how do they influence adoption?
- RQ4: What gaps exist, and what directions should future research take?
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Planning
2.2. Conducting
- (i)
- Quality filtering: To ensure the robustness of findings and relevance for future research, this study applied a journal quality filter during the initial screening stage. This is consistent with the approach adopted in prior reviews [28,29,30]. Articles published in A and B-ranked journals in the ABDC Journal Quality List and Q1–Q2 journals in the Scimago Journal Rank (SJR) were retained. A limited number of C-ranked journals were included only if they were classified within the Q1–Q2 quartiles in SJR.
- (ii)
- Abstract screening: The abstracts of the remaining papers were reviewed to confirm their focus on critical success factors, drivers, antecedents, enablers or pressures influencing the adoption and implementation of GLPs.
- (iii)
- Full-text assessment: Eligible full-text articles were then reviewed in detail. Studies were excluded if they focused solely on barriers and addressed green supply chain management (GSCM) without discussing at least one logistics-related component (e.g., transportation, reverse logistics, warehousing, and distribution).
2.3. Documentation
- Bibliographic details: authors, publication year, journal, country of study, and keywords.
- Methodological characteristics: research approach, method, and analytical techniques.
- Theoretical foundations.
- Research focus: objectives, key drivers of green logistics adoption, main findings, and industry context.
3. Results
3.1. Bibliometric Analysis
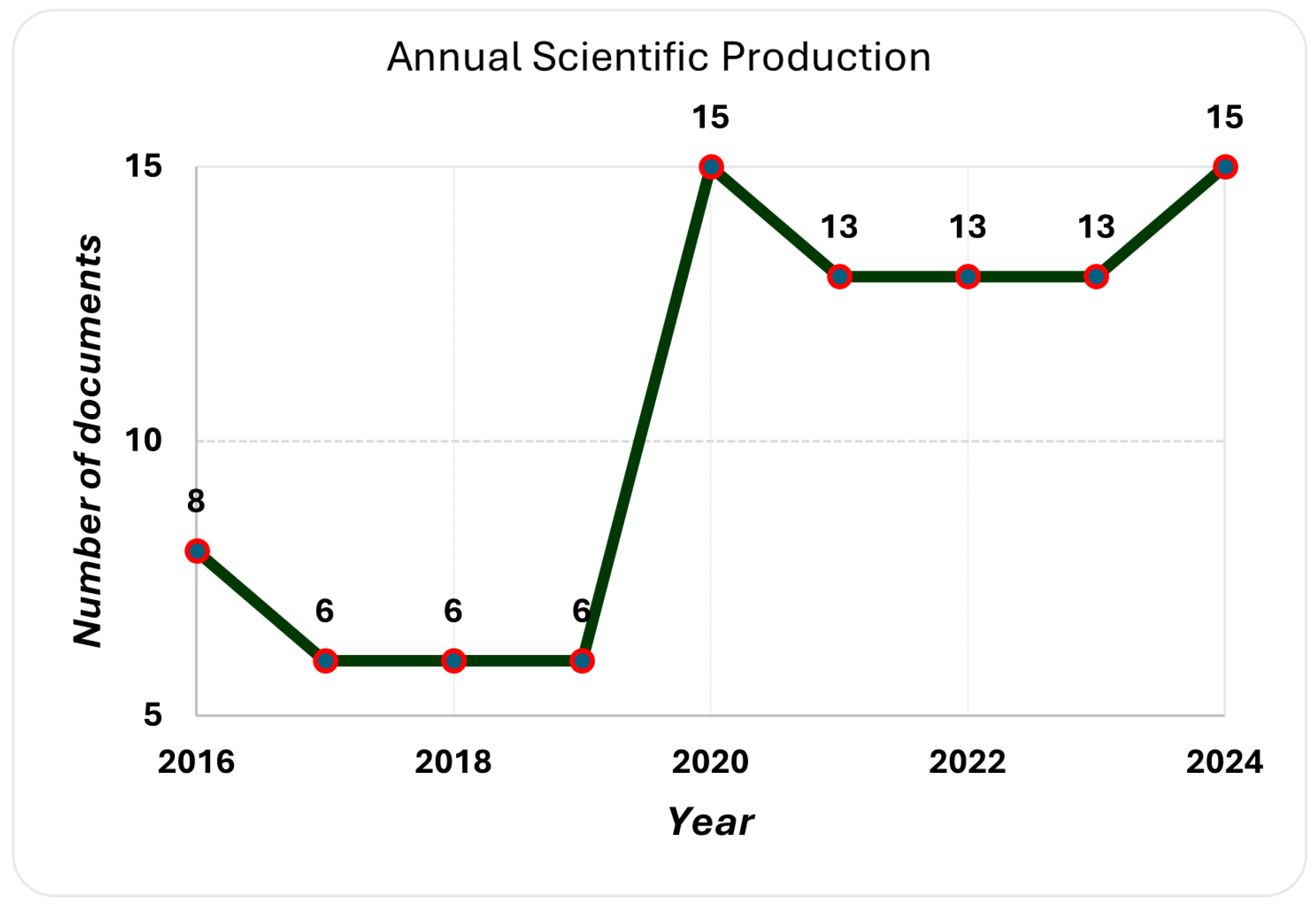
3.1.1. Publication Trends
3.1.2. Key Journals
3.1.3. Most Cited Documents
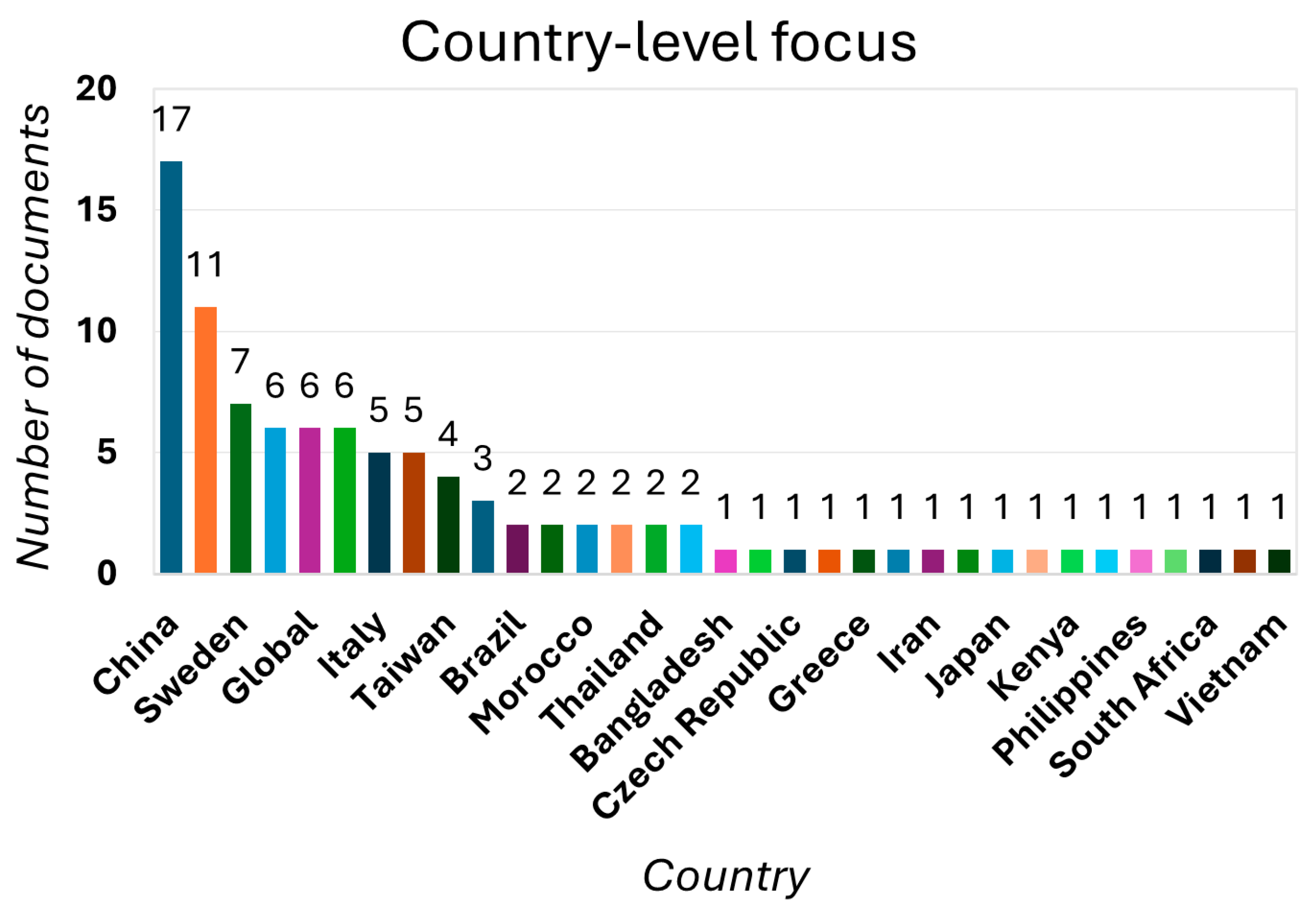
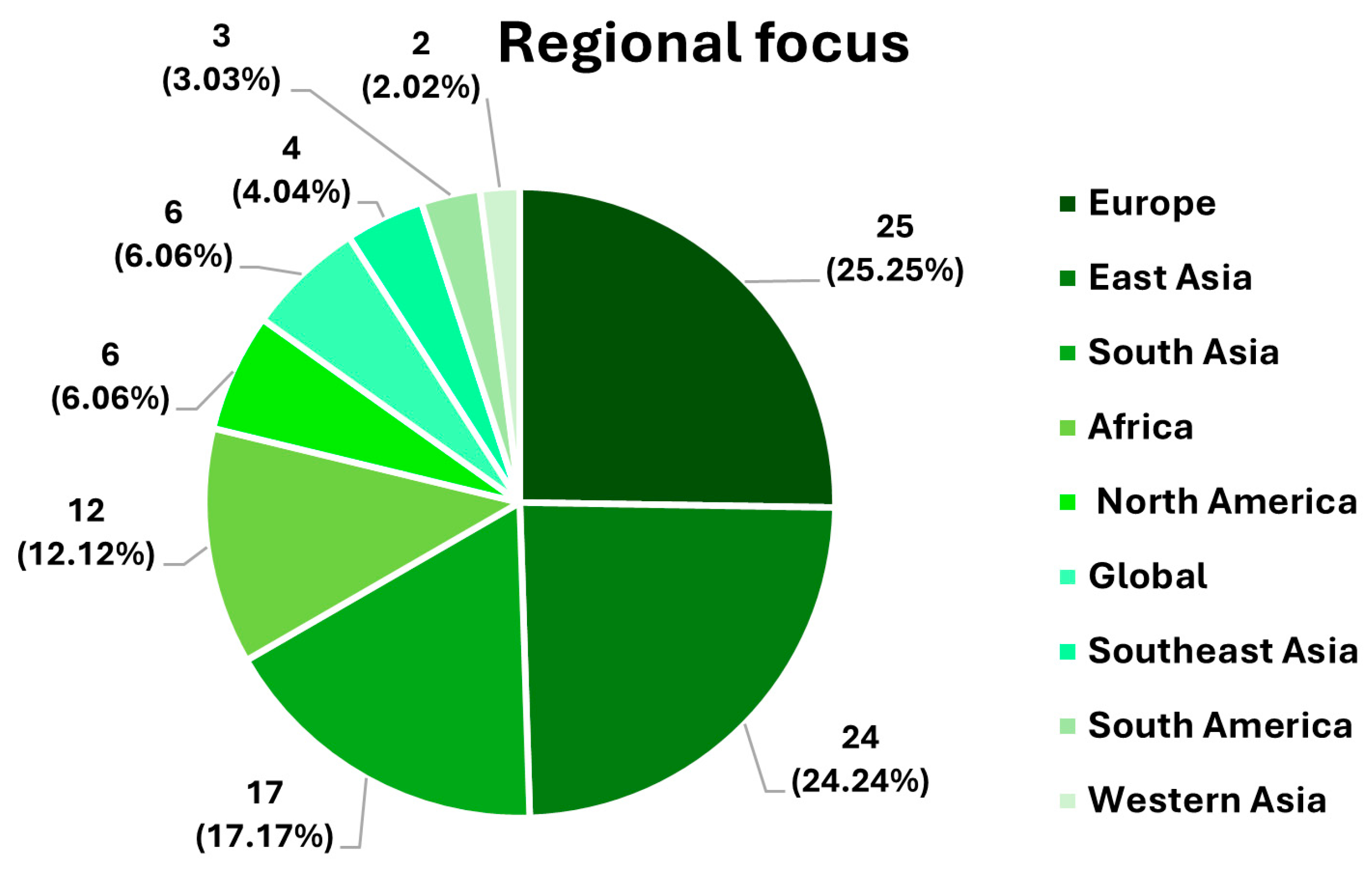
3.1.4. Geographical Focus
3.1.5. Research Method Employed
3.1.6. Theoretical Framework
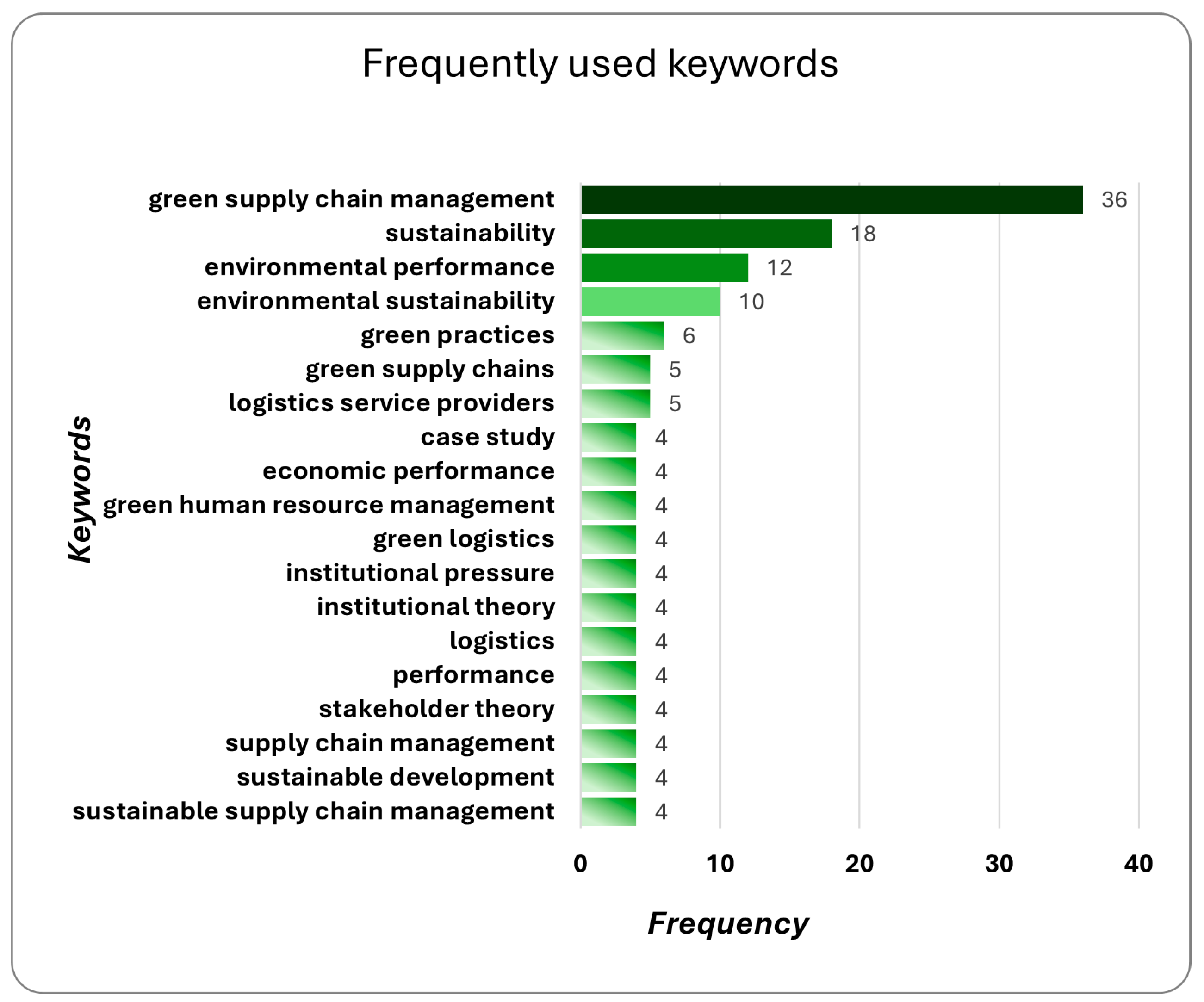
3.1.7. Common Keywords
3.2. Content Analysis
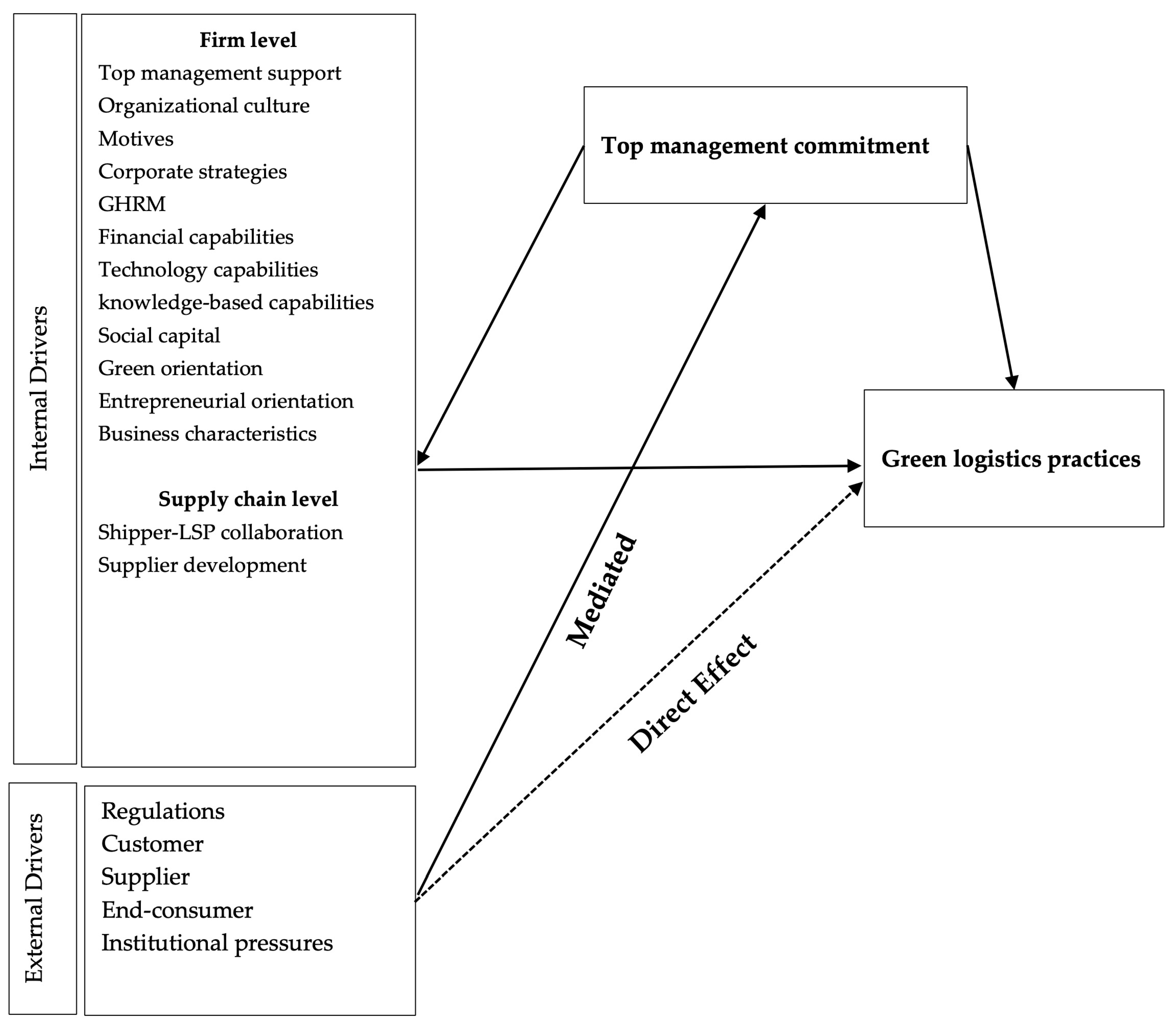
3.2.1. Internal Drivers
Firm Level
Supply Chain-Level
3.2.2. External Drivers
4. Discussion
Future Research
5. Conclusions
5.1. Implications for Managers
5.2. Implications for Policymakers
5.3. Limitations
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| GLPs | Green Logistics Practices |
| GL | Green Logistics |
| GSCM | Green Supply Chain Management |
| DTs | Digital Technologies |
| GHRM | Green Human Resource Management |
References
- Pathak, M.; Slade, R.; Shukla, P.R.; Skea, J.; Pichs-Madruga, R.; Ürge-Vorsatz, D. Technical Summary. Climate Change 2022: Mitigation of Climate Change. Contribution of Working Group III to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2022; pp. 1–102. [Google Scholar]
- Fox, K.; Rohloff, K. NASA Analysis Confirms 2023 as Warmest Year on Record; Headquarters: Washington, DC, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- IPCC. Climate Change 2023; IPCC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2023.
- Mckinnon, A.; Browne, M.; Piecyk, M.; Whiteing, A. Green Logistics: Improving the Environmental Sustainability of Logistics, 3rd ed.; Kogan Page: London, UK; Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2015; ISBN 9780749471859, 0749471859. [Google Scholar]
- Tinnes, E.; Kandel, M.; Probst, T. Decarbonizing Logistics Charting the Path Ahead. 2024. Available online: https://www.mckinsey.com/capabilities/operations/our-insights/decarbonizing-logistics-charting-the-path-ahead (accessed on 24 October 2025).
- Mackinsey & Company. What Are Scope 1, 2, and 3 Emissions? 2024. Available online: https://www.mckinsey.com/featured-insights/mckinsey-explainers/what-are-scope-1-2-and-3-emissions (accessed on 24 October 2025).
- Wang, J.; Lim, M.K.; Wang, C.; Tseng, M.L. Comprehensive Analysis of Sustainable Logistics and Supply Chain Based on Bibliometrics: Overview, Trends, Challenges, and Opportunities. Int. J. Logist. Res. Appl. 2023, 26, 1285–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKinnon, A.C. Logistics and Climate: An Assessment of Logistics’ Multiple Roles in the Climate Crisis. Int. J. Logist. Res. Appl. 2024, 27, 2556–2570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Z.; Wang, L.; Lai, F. Customer Pressure and Green Innovations at Third Party Logistics Providers in China: The Moderation Effect of Organizational Culture. Int. J. Logist. Manag. 2019, 30, 57–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.C.; Huang, C.H.; Yang, M.L. Drivers of Green Supply Chain Initiatives and Performance: Evidence from the Electrical and Electronics Industries in Taiwan. Int. J. Phys. Distrib. Logist. Manag. 2017, 47, 796–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaman, A.S.; Ellili, N.O.D.; Uyar, A. Do Sustainable Supply Chain Practices Mitigate Carbon Emissions? The Role of Supplier Environmental, Social and Governance Training. Bus. Strategy Environ. 2024, 33, 8126–8148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creazza, A.; Colicchia, C.; Evangelista, P. Leveraging Shippers-Logistics Providers Relationships for Better Sustainability in Logistics: The Perspective of SMEs. Int. J. Logist. Manag. 2024, 35, 1009–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huge-Brodin, M.; Sweeney, E.; Evangelista, P. Environmental Alignment between Logistics Service Providers and Shippers—A Supply Chain Perspective. Int. J. Logist. Manag. 2020, 31, 575–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jazairy, A.; von Haartman, R. Analysing the Institutional Pressures on Shippers and Logistics Service Providers to Implement Green Supply Chain Management Practices. Int. J. Logist. Res. Appl. 2020, 23, 44–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ocko, I.B.; Hamburg, S.P.; Jacob, D.J.; Keith, D.W.; Keohane, N.O.; Oppenheimer, M.; Roy-Mayhew, J.D.; Schrag, D.P.; Pacala, S.W. Unmask Temporal Trade-Offs in Climate Policy Debates. Science 2017, 356, 492–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tambo, E.; Duo-quan, W.; Zhou, X.N. Tackling Air Pollution and Extreme Climate Changes in China: Implementing the Paris Climate Change Agreement. Environ. Int. 2016, 95, 152–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jazairy, A.; Pohjosenperä, T.; Prataviera, L.B.; Juntunen, J. Innovators and Transformers Revisiting the Gap between Academia and Practice: Insights from the Green Logistics Phenomenon. Int. J. Phys. Distrib. Logist. Manag. 2024, 55, 341–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, R.; Singh, R.; Govindan, K. Net-Zero Economy Research in the Field of Supply Chain Management: A Systematic Literature Review and Future Research Agenda. Int. J. Logist. Manag. 2023, 34, 1352–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaharudin, M.S.; Fernando, Y.; Chiappetta Jabbour, C.J.; Sroufe, R.; Jasmi, M.F.A. Past, Present, and Future Low Carbon Supply Chain Management: A Content Review Using Social Network Analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 218, 629–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tetteh, F.K.; Owusu Kwateng, K.; Mensah, J. Green Logistics Practices: A Bibliometric and Systematic Methodological Review and Future Research Opportunities. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 476, 143735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.S.; Moeinzadeh, S.; Tseng, M.L.; Tan, K. A Literature Review on Environmental Concerns in Logistics: Trends and Future Challenges. Int. J. Logist. Res. Appl. 2021, 24, 126–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, W.M. Systematic Literature Reviews: Reflections, Recommendations, and Robustness Check. J. Consum. Behav. 2025, 24, 1498–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spanaki, K.; Sivarajah, U.; Fakhimi, M.; Despoudi, S.; Irani, Z. Disruptive Technologies in Agricultural Operations: A Systematic Review of AI-Driven AgriTech Research. Ann. Oper. Res. 2022, 308, 491–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tranfield, D.; Denyer, D.; Smart, P. Towards a Methodology for Developing Evidence-Informed Management Knowledge by Means of Systematic Review. Br. J. Manag. 2003, 14, 207–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahran, K.; Elamer, A.A. Chief Executive Officer (CEO) and Corporate Environmental Sustainability: A Systematic Literature Review and Avenues for Future Research. Bus. Strategy Environ. 2024, 33, 1977–2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tucker, J.C. Database Support for Research in Public Administration. Behav. Soc. Sci. Libr. 2005, 24, 47–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crippa, M.; Guizzardi, D.; Pagani, F.; Banja, M.; Muntean, M.; Schaaf, E.; Becker, W.E.; Monforti-Ferrario, F.; Quadrelli, R.; Risquez, M.A.; et al. GHG Emissions of All World Countries; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Fatima, T.; Elbanna, S. Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) Implementation: A Review and a Research Agenda Towards an Integrative Framework. J. Bus. Ethics 2023, 183, 105–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoque, Z. 20 Years of Studies on the Balanced Scorecard: Trends, Accomplishments, Gaps and Opportunities for Future Research. Br. Account. Rev. 2014, 46, 33–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Ntim, C.G.; Zhang, Q.; Li, P. Board of Directors’ Attributes and Corporate Outcomes: A Systematic Literature Review and Future Research Agenda. Int. Rev. Financ. Anal. 2022, 84, 102424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaur, A.; Kumar, M. A Systematic Approach to Conducting Review Studies: An Assessment of Content Analysis in 25 Years of IB Research. J. World Bus. 2018, 53, 280–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nejati, M.; Rabiei, S.; Chiappetta Jabbour, C.J. Envisioning the Invisible: Understanding the Synergy between Green Human Resource Management and Green Supply Chain Management in Manufacturing Firms in Iran in Light of the Moderating Effect of Employees’ Resistance to Change. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 168, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luthra, S.; Garg, D.; Haleem, A. The Impacts of Critical Success Factors for Implementing Green Supply Chain Management towards Sustainability: An Empirical Investigation of Indian Automobile Industry. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 121, 142–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandhi, S.; Mangla, S.K.; Kumar, P.; Kumar, D. A Combined Approach Using AHP and DEMATEL for Evaluating Success Factors in Implementation of Green Supply Chain Management in Indian Manufacturing Industries. Int. J. Logist. Res. Appl. 2016, 19, 537–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bag, S.; Dhamija, P.; Bryde, D.J.; Singh, R.K. Effect of Eco-Innovation on Green Supply Chain Management, Circular Economy Capability, and Performance of Small and Medium Enterprises. J. Bus. Res. 2022, 141, 60–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baah, C.; Jin, Z.; Tang, L. Organizational and Regulatory Stakeholder Pressures Friends or Foes to Green Logistics Practices and Financial Performance: Investigating Corporate Reputation as a Missing Link. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 247, 119125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adusei, E.; Demah, E.; Boso, R.K. Top Management Commitment in Greening Supply Chain Operations: Post-COVID-19 Perspectives from an Emerging Economy. J. Glob. Oper. Strateg. Sourc. 2023, 16, 773–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, A.; Giraud-Carrier, F.C.; Li, Y. A Mediation Model of Green Supply Chain Management Adoption: The Role of Internal Impetus. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2018, 205, 342–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, V.; Mohanty, R.P.; Agarwal, S.; Dixit, J.K.; Agrawal, A.M. Analyzing Critical Success Factors for Sustainable Green Supply Chain Management. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2023, 25, 8233–8258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Bentley, Y.; Cao, G.; Habib, F. Green Supply Chain Management–Food for Thought? Int. J. Logist. Res. Appl. 2017, 20, 22–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banik, A.; Taqi, H.M.M.; Ali, S.M.; Ahmed, S.; Garshasbi, M.; Kabir, G. Critical Success Factors for Implementing Green Supply Chain Management in the Electronics Industry: An Emerging Economy Case. Int. J. Logist. Res. Appl. 2022, 25, 493–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitsis, A.M.; Chen, I.J. Do Stakeholder Pressures Influence Green Supply Chain Practices?Exploring the Mediating Role of Top Management Commitment. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 316, 128258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, K.H.; Feng, Y.; Zhu, Q. Digital Transformation for Green Supply Chain Innovation in Manufacturing Operations. Transp. Res. E Logist. Transp. Rev. 2023, 175, 103145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muduli, K.K.; Luthra, S.; Kumar Mangla, S.; Jabbour, C.J.C.; Aich, S.; de Guimarães, J.C.F. Environmental Management and the “Soft Side” of Organisations: Discovering the Most Relevant Behavioural Factors in Green Supply Chains. Bus. Strategy Environ. 2020, 29, 1647–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nureen, N.; Liu, D.; Ahmad, B.; Irfan, M. Exploring the Technical and Behavioral Dimensions of Green Supply Chain Management: A Roadmap toward Environmental Sustainability. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 63444–63457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.K.; Rastogi, S.; Aggarwal, M. Analyzing the Factors for Implementation of Green Supply Chain Management. Compet. Rev. 2016, 26, 246–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sureeyatanapas, P.; Poophiukhok, P.; Pathumnakul, S. Green Initiatives for Logistics Service Providers: An Investigation of Antecedent Factors and the Contributions to Corporate Goals. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 191, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preuss, L.; Fearne, A. Cognitive Frames Held by Supply Chain Managers: Implications for the Management of Sustainability in Supply Chains. Supply Chain Manag. 2022, 27, 681–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellram, L.M.; Tate, W.L.; Saunders, L.W. A Legitimacy Theory Perspective on Scope 3 Freight Transportation Emissions. J. Bus. Logist. 2022, 43, 472–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitsis, A.M.; Chen, I.J. Do Motives Matter? Examining the Relationships between Motives, SSCM Practices and TBL Performance. Supply Chain Manag. 2020, 25, 325–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lintukangas, K.; Arminen, H.; Kähkönen, A.K.; Karttunen, E. Determinants of Supply Chain Engagement in Carbon Management. J. Bus. Ethics 2023, 186, 87–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youngswaing, W.; Jomnonkwao, S.; Cheunkamon, E.; Ratanavaraha, V. Key Factors Shaping Green Logistics in Thailand’s Auto Industry: An Application of Structural Equation Modeling. Logistics 2024, 8, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, S.M.; Shiah, Y.A. Associating the Motivation with the Practices of Firms Going Green: The Moderator Role of Environmental Uncertainty. Supply Chain Manag. 2016, 21, 485–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, C.; Liu, Y.Q.; Shan, M. Drivers of Low-Carbon Practices in Green Supply Chain Management in Construction Industry: An Empirical Study in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 428, 139497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iddik, S. The Role of Cultural Factors in Green Supply Chain Management Practices: A Conceptual Framework and an Empirical Investigation. RAUSP Manag. J. 2024, 59, 96–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzi, F.; Gigliotti, M.; Annunziata, E. Exploring the Nexus between GSCM and Organisational Culture: Insights on the Role of Supply Chain Integration. Supply Chain Manag. 2023, 28, 300–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prataviera, L.B.; Creazza, A.; Perotti, S.; Rodrigues, V.S. How to Align Logistics Environmental Sustainability with Corporate Strategy? An Italian Perspective. Int. J. Logist. Res. Appl. 2023, 28, 931–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laari, S.; Töyli, J.; Ojala, L. The Effect of a Competitive Strategy and Green Supply Chain Management on the Financial and Environmental Performance of Logistics Service Providers. Bus. Strategy Environ. 2018, 27, 872–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, S.; Cadden, T.; Treacy, R. Examining the Influence of Employee Engagement in Supporting the Implementation of Green Supply Chain Management Practices: A Green Human Resource Management Perspective. Bus. Strategy Environ. 2023, 32, 4750–4766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acquah, I.S.K.; Agyabeng-Mensah, Y.; Afum, E. Examining the Link among Green Human Resource Management Practices, Green Supply Chain Management Practices and Performance. Benchmarking 2021, 28, 267–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trujillo-Gallego, M.; Sarache, W.; Sousa Jabbour, A.B.L.d. Digital Technologies and Green Human Resource Management: Capabilities for GSCM Adoption and Enhanced Performance. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2022, 249, 108531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Fang, W.; Feng, T.; Gao, N. Bolstering Green Supply Chain Integration via Big Data Analytics Capability: The Moderating Role of Data-Driven Decision Culture. Ind. Manag. Data Syst. 2022, 122, 2558–2582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umar, M.; Khan, S.A.R.; Zia-ul-haq, H.M.; Yusliza, M.Y.; Farooq, K. The Role of Emerging Technologies in Implementing Green Practices to Achieve Sustainable Operations. TQM J. 2022, 34, 232–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chung, H.F.L.; Mi, L. Fostering Sustainable Logistics Businesses: The Role of Innovation Ecosystems and Institutional Contexts for Logistics Firms in China. Asia Pac. J. Mark. Logist. 2023, 35, 35–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorini, P.C.; Jabbour, C.J.C.; Latan, H.; De Sousa Jabbour, A.B.L.; Mariano, E.B. Green Emerging Digital Technologies, Green Supply Chains, and the Performance of Environmentally Friendly Firms: The Underpinning Role of Human Resources. IEEE Trans. Eng. Manag. 2024, 71, 13134–13148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Luu, T.; Chromjaková, F.; Nguyen, H.Q. A Model of Industry 4.0 and a Circular Economy for Green Logistics and a Sustainable Supply Chain. Bus. Strategy Dev. 2023, 6, 897–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prataviera, L.B.; Creazza, A.; Perotti, S. A Call to Action: A Stakeholder Analysis of Green Logistics Practices. Int. J. Logist. Manag. 2024, 35, 979–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Susanty, A.; Sari, D.P.; Rinawati, D.I.; Setiawan, L. The Role of Internal and External Drivers for Successful Implementation of GSCM Practices. J. Manuf. Technol. Manag. 2019, 30, 391–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dube, A.S.; Gawande, R.S. Analysis of Green Supply Chain Barriers Using Integrated ISM-Fuzzy MICMAC Approach. Benchmarking 2016, 23, 1558–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, Q. How Does Knowledge Seeking and Knowledge Generation Promote Green Supply Chain Management? An Empirical Study from China. Int. J. Logist. Res. Appl. 2023, 26, 37–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, H.S.; Grant, D.B. Investigating Effects of Organisational Culture and Learning on Environmental Collaboration and Performance of Korean Exporting Firms. Int. J. Logist. Res. Appl. 2018, 21, 614–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acquah, I.N. Antecedents and Consequences of Green Supply Chain Management Practices in Ghana’s Manufacturing Sector. J. Manuf. Technol. Manag. 2024, 35, 524–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, W.; Najmi, A.; Arif, M.; Younus, M. Exploring Firm Performance by Institutional Pressures Driven Green Supply Chain Management Practices. Smart Sustain. Built Environ. 2019, 8, 415–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borazon, E.Q.; Huang, Y.C.; Liu, J.M. Green Market Orientation and Organizational Performance in Taiwan’s Electric and Electronic Industry: The Mediating Role of Green Supply Chain Management Capability. J. Bus. Ind. Mark. 2022, 37, 1475–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maaz, M.A.M.; Ahmad, R.; Abad, A. Antecedents and Consequences of Green Supply Chain Management Practices: A Study of Indian Food Processing Industry. Benchmarking 2022, 29, 2045–2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, G.M.; Gomes, P.J.; Carvalho, H.; Geraldes, V. Sustainable Development in Small and Medium Enterprises: The Role of Entrepreneurial Orientation in Supply Chain Management. Bus. Strategy Environ. 2021, 30, 3804–3820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhu, Q.; Sarkis, J. Heterogeneity in Corporate Green Supply Chain Practice Adoption: Insights from Institutional Fields. Bus. Strategy Environ. 2024, 33, 389–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thanh Ha, L. Is It a Good Idea to Select Green Logistics to Enhance Environmental Sustainability? Insights from Global Sample. Int. J. Logist. Res. Appl. 2024, 28, 558–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahlmann, F.; Roehrich, J.K. Sustainable Supply Chain Management and Partner Engagement to Manage Climate Change Information. Bus. Strategy Environ. 2019, 28, 1632–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jazairy, A.; von Haartman, R.; Björklund, M. Unravelling Collaboration Mechanisms for Green Logistics: The Perspectives of Shippers and Logistics Service Providers. Int. J. Phys. Distrib. Logist. Manag. 2021, 51, 423–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Qian, C.; Wang, S. When Do 3PLs Initiate Low-Carbon Supply Chain Integration? Int. J. Oper. Prod. Manag. 2020, 40, 1367–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Björklund, M.; Forslund, H.; Ülgen, V.S. The Paradoxical Nature of Greening Transportation: An Analysis of Tensions in Buyer–Supplier Dyads. Int. J. Phys. Distrib. Logist. Manag. 2024, 54, 532–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sallnäs, U.; Huge-Brodin, M. De-Greening of Logistics?—Why Environmental Practices Flourish and Fade in Provider-Shipper Relationships and Networks. Ind. Mark. Manag. 2018, 74, 276–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Foerstl, K.; Schmidt, C.G.; Wagner, S.M. Adoption of Green Supply Chain Management Practices in Multi-Tier Supply Chains: Examining the Differences between Higher and Lower Tier Firms. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2022, 60, 6451–6468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nkrumah, S.K.; Asamoah, D.; Annan, J.; Agyei-Owusu, B. Examining Green Capabilities as Drivers of Green Supply Chain Management Adoption. Manag. Res. Rev. 2021, 44, 94–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wamalwa, L.S.; Nang’ole Meyer, P. Green Supplier Development and Sustainable Supply Chain Management. Bus. Strategy Dev. 2024, 7, e357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eggert, J.; Hartmann, J. Purchasing’s Contribution to Supply Chain Emission Reduction. J. Purch. Supply Manag. 2021, 27, 100685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, E.L.; Zhou, L.; Wu, A. The Supply-Side of Environmental Sustainability and Export Performance: The Role of Knowledge Integration and International Buyer Involvement. Int. Bus. Rev. 2017, 26, 724–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, W.; Ashraf, M.S.; Khan, S.A.; Kusi-Sarpong, S.; Arhin, F.K.; Kusi-Sarpong, H.; Najmi, A. Analyzing the Impact of Environmental Collaboration among Supply Chain Stakeholders on a Firm’s Sustainable Performance. Oper. Manag. Res. 2020, 13, 4–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, J.; Li, S.; Capaldo, A. Why and How Do Suppliers Develop Environmental Management Capabilities in Response to Buyer-Led Development Initiatives? Supply Chain Manag. 2024, 29, 112–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asif, M.S.; Lau, H.; Nakandala, D.; Fan, Y.; Hurriyet, H. Adoption of Green Supply Chain Management Practices through Collaboration Approach in Developing Countries—From Literature Review to Conceptual Framework. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 276, 124191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; He, S.; Wang, Y.; An, J. Green Pharmaceutical Supply Chain Coordination Considering Green Investment, Green Logistics, and Government Intervention. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 63321–63343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, B.; Wang, Z. Environmental Regulation, Green Technology Innovation and Green Logistics Development Level of Fresh Agricultural Products. Int. J. Logist. Res. Appl. 2024, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Chen, Y.; Wang, D. An Empirical Study of the Factors Influencing the Willingness to Implement Green Coal Logistics in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 245, 118932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, T.C.H.; Guan, J.; Lau, Y.Y. Exploring Environmental Sustainability and Green Management Practices: Evidence from Logistics Service Providers. Sustain. Account. Manag. Policy J. 2023, 14, 461–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.C.; Borazon, E.Q.; Liu, J.M. Antecedents and Consequences of Green Supply Chain Management in Taiwan’s Electric and Electronic Industry. J. Manuf. Technol. Manag. 2021, 32, 1066–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Misra, S.C. Ordering Drivers of Green Supply Chain Management Practices in Indian Construction Industry: An Impact Assessment Framework. Int. J. Qual. Reliab. Manag. 2022, 39, 1869–1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Baz, J.; Laguir, I. Third-Party Logistics Providers (TPLs) and Environmental Sustainability Practices in Developing Countries: The Case of Morocco. Int. J. Oper. Prod. Manag. 2017, 37, 1451–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, J.; Inkpen, A.; Ramaswamy, K. An FsQCA Exploration of Multiple Paths to Ecological Innovation Adoption in European Transportation. J. World Bus. 2022, 57, 101327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jum’a, L.; Ikram, M.; Alkalha, Z.; Alaraj, M. Factors Affecting Managers’ Intention to Adopt Green Supply Chain Management Practices: Evidence from Manufacturing Firms in Jordan. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 5605–5621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Berg, R.; De Langen, P.W. Environmental Sustainability in Container Transport: The Attitudes of Shippers and Forwarders. Int. J. Logist. Res. Appl. 2017, 20, 146–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jazairy, A. Aligning the Purchase of Green Logistics Practices between Shippers and Logistics Service Providers. Transp. Res. D Transp. Environ. 2020, 82, 102305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tetteh, F.K.; Owusu Kwateng, K.; Mensah, J. Enhancing Carbon Neutral Supply Chain Performance: Can Green Logistics and Pressure from Supply Chain Stakeholders Make Any Differences? Sustain. Account. Manag. Policy J. 2024, 16, 521–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sallnäs, U.; Björklund, M. Consumers’ Influence on the Greening of Distribution—Exploring the Communication between Logistics Service Providers, e-Tailers and Consumers. Int. J. Retail. Distrib. Manag. 2020, 48, 1177–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, F.; Huang, G.; Zhan, Y.; Li, Y. Factors Mediating and Moderating the Relationships Between Green Practice and Environmental Performance: Buyer-Supplier Relation and Institutional Context. IEEE Trans. Eng. Manag. 2023, 70, 142–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, X.; Cheah, J.H.; Lim, X.J.; Ramachandran, S. Why Does “Green” Matter in Supply Chain Management? Exploring Institutional Pressures, Green Practices, Green Innovation, and Economic Performance in the Chinese Chemical Sector. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 427, 139182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Layaoen, H.D.; Abareshi, A.; Abdulrahman, M.D.A.; Abbasi, B. Impacts of Institutional Pressures and Internal Abilities on Green Performance of Transport and Logistics Companies. Int. J. Logist. Manag. 2024, 35, 2087–2113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seles, B.M.R.P.; de Sousa Jabbour, A.B.L.; Jabbour, C.J.C.; Dangelico, R.M. The Green Bullwhip Effect, the Diffusion of Green Supply Chain Practices, and Institutional Pressures: Evidence from the Automotive Sector. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2016, 182, 342–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabat, K.C.; Krishnamoorthy, B.; Bhattacharyya, S.S. Green Drivers and Green Enablers in Pharmaceuticals Supply Chain: In the Context of an Emerging Economy. TQM J. 2023, 35, 1349–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, K.; Sangwan, K.S. Adoption of Green Practices throughout the Supply Chain: An Empirical Investigation. Benchmarking 2019, 26, 1650–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, R.B.; Onwuegbuzie, A.J. Toward a Definition of Mixed Methods Research. J. Mix. Methods Res. 2007, 1, 112–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, R.; Lin, S.; Dai, J. Examining Customer Pressure and Green Supply Chain Management in Emerging Market: An Institutional Logics Perspective. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2024, 278, 109431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. bmj 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
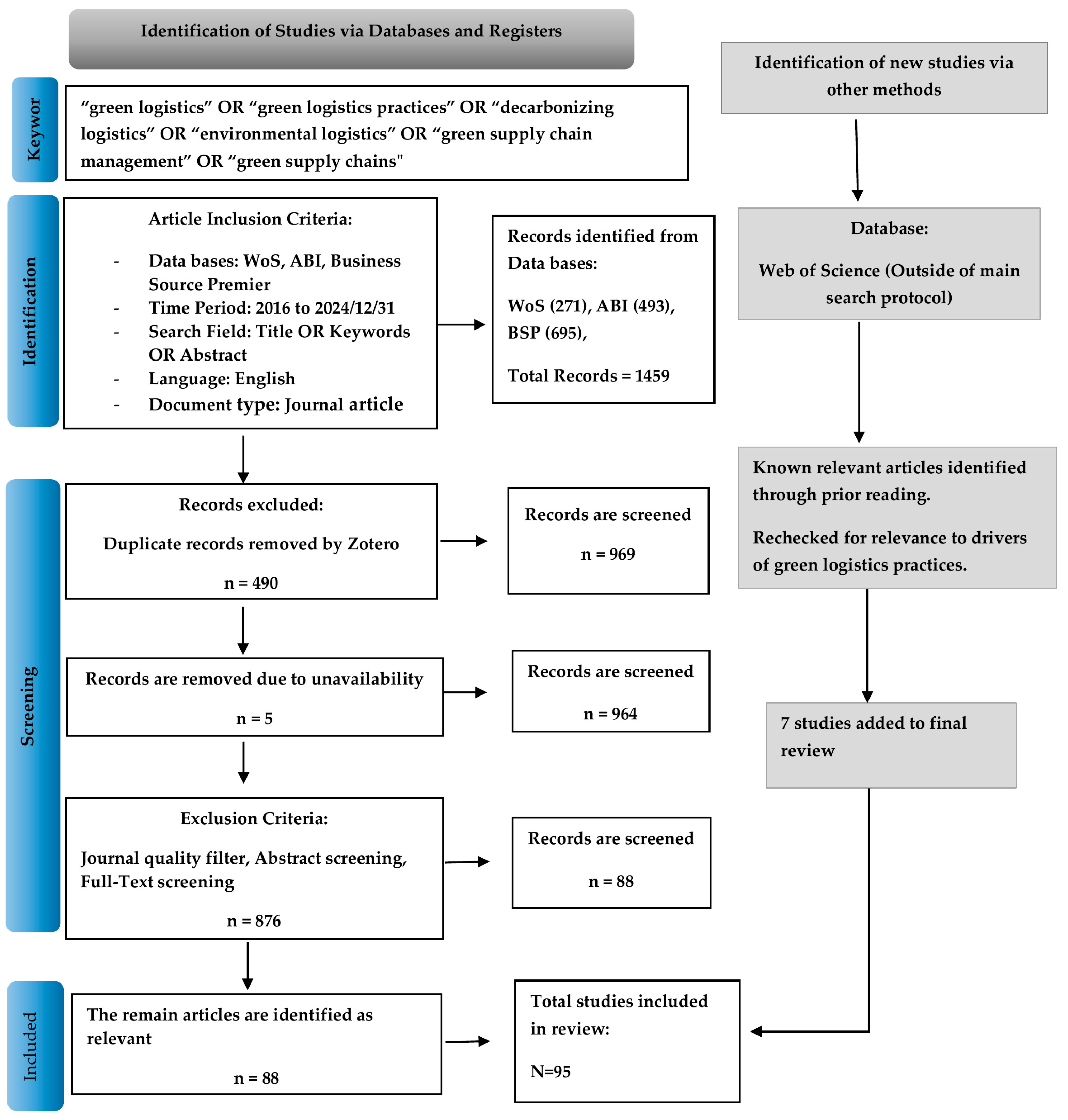


| Inclusion | Exclusion |
|---|---|
| Papers published 2016–2024 | Written in any language other than English |
| Full text available | Working papers, conference papers, thesis, book, book chapter |
| Written in English | |
| Articles from peer-reviewed journals by a reading committee | Not clearly focused on the drivers of green logistics adoption, focusing on barriers |
| Articles from the A and B category of ABDC ranking or from Q1 and Q2 of SJR | |
| Clearly focused on drivers of green logistics adoption. |
| Venue | Documents |
|---|---|
| International Journal of Logistics: Research & Application | 9 |
| Journal of Cleaner Production | 9 |
| Business Strategy and the Environment | 8 |
| Benchmarking: An International Journal | 5 |
| The International Journal of Logistics Management | 5 |
| Title | Author(s) | Citation |
|---|---|---|
| Envisioning the invisible: Understanding the synergy between green human resource management and green supply chain management in manufacturing firms in Iran in light of the moderating effect of employees’ resistance to change | [32] | 294 |
| The impacts of critical success factors for implementing green supply chain management towards sustainability: an empirical investigation of Indian automobile industry | [33] | 293 |
| success factors, implementation, green supply chain management, Indian manufacturing industries | [34] | 185 |
| Effect of eco-innovation on green supply chain management, circular economy capability, and performance of small and medium enterprises | [35] | 180 |
| Organizational and regulatory stakeholder pressures friends or foes to green logistics practices and financial performance: Investigating corporate reputation as a missing link | [36] | 133 |
| Approach | Number of Documents |
|---|---|
| Quantitative | 70 |
| Qualitative | 19 |
| Mixed method | 5 |
| Semi-qualitative | 1 |
| Total | 95 |
| Theory | Frequency |
|---|---|
| Institutional pressure | 23 |
| Resource-based view (RBV) | 16 |
| Natural resource-based view (NRBV) | 8 |
| Dynamic capability | 7 |
| Stakeholder theory | 7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rastegardehbidi, P.; Su, Z. Key Drivers of Green Logistics: A Systematic Literature Review and Conceptual Framework. Sustainability 2025, 17, 9604. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17219604
Rastegardehbidi P, Su Z. Key Drivers of Green Logistics: A Systematic Literature Review and Conceptual Framework. Sustainability. 2025; 17(21):9604. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17219604
Chicago/Turabian StyleRastegardehbidi, Parvaneh, and Zhan Su. 2025. "Key Drivers of Green Logistics: A Systematic Literature Review and Conceptual Framework" Sustainability 17, no. 21: 9604. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17219604
APA StyleRastegardehbidi, P., & Su, Z. (2025). Key Drivers of Green Logistics: A Systematic Literature Review and Conceptual Framework. Sustainability, 17(21), 9604. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17219604






