Abstract
Effective carbon emission control at the provincial level is essential for advancing the high-quality development of the national economy under the “dual carbon” targets. Although Hubei Province is endowed with abundant natural resources and significant potential for sustainable growth, it still faces considerable challenges in industrial and energy restructuring. Therefore, improving carbon emission efficiency (CEE) is imperative. This study thoroughly analyzes the spatial and temporal characteristics of CEE in Hubei Province. Furthermore, the spatial Durbin model (SDM) and geographically and temporally weighted regression (GTWR) were applied to analyze the determinants of changes in CEE. The results indicate that significant disparities in CEE exist across Hubei Province, with the eastern region exhibiting the highest efficiency and the central region the lowest. The year 2016 represented a turning point, as Moran’s I increased from −0.0006 in 2016 to 0.5134 in 2017, indicating a shift in the spatial pattern of CEE from a weak and insignificant spatial autocorrelation to a strong positive spatial autocorrelation. In addition, the CEE in Hubei Province demonstrated a “siphon effect” and exhibited pronounced polarization. Based on these findings, region-specific policies are proposed. The eastern region should optimize its industrial structure and strengthen urban governance. The western region should leverage its clean energy advantage and enhance carbon sink capacity. The central region should advance low-carbon industrial transformation and coordinated governance to prevent core cities from transferring resources and pollution to surrounding areas.
1. Introduction
Recently, global warming has induced extreme weather events such as heat waves, droughts, excessive rainfall, and flooding. These events have severely challenged ecosystem stability and sustainable development [1]. Excessive greenhouse gas emissions, particularly carbon dioxide, are the primary drivers of climate change, significantly disrupting the balance of the natural carbon cycle [2]. China is the world’s largest emitter of greenhouse gases and has the second-largest economy globally [3]. In 2023, China’s carbon dioxide emissions increased by 565 million tons, accounting for 35% of global emissions [4]. Rapid economic growth has, to some extent, been achieved at the expense of environmental degradation. International organizations have since implemented policies to reduce carbon emissions and address climate change [5]. China has responded proactively by proposing the “dual carbon” targets, which aim to achieve carbon peaking by 2030 and carbon neutrality by 2060 [6]. Provincial-level units serve as an essential link between the state and cities. They implement specific emission reduction measures that translate national carbon targets into regional actions and ensure effective policy execution [7,8]. Most existing research has focused on the national level or economically developed provinces, with relatively little attention paid to central regions. Therefore, strengthening provincial-level carbon emission management has become crucial for advancing the country’s low-carbon transition.
Hubei is a moderately developed province and one of the first national low-carbon pilot regions [9]. Although Hubei has abundant hydroelectric resources, its dominant industries remain agriculture and heavy industries. Hydropower generation in Hubei shows strong seasonal variation. It is dominant during the wet season but relies heavily on coal-fired power during the dry season. In 2022, a severe drought in the Yangtze River basin led to water shortages in Wuhan, Yichang, and other cities. As a result, thermal power plants had to be activated to meet peak electricity demand. Consequently, monthly carbon emissions rose sharply [10]. Interregional hydropower transmission is crucial for achieving net-zero emissions [11]. Therefore, tailored strategies are required in Hubei to reduce carbon emission efficiency (CEE). As one of the founding members of the APCC, Wuhan is the only megacity in central China. The government has implemented policies to support Wuhan’s development as a “Green Economic Engine”, including the “Wuhan Urban Circle” and “Central China Revitalization” programs [12]. The rising standard of living and economic growth in Hubei have contributed to increasing urban carbon emissions [13]. Given the high baseline of emissions and the substantial costs of a low-carbon transition, significant challenges have emerged for the province [14]. However, existing research has primarily examined carbon emission efficiency at national or regional levels, while intra-provincial disparities and spatial interactions remain underexplored.
This study employs panel data from 12 prefecture-level cities in Hubei, covering 2006–2022. The analysis aims to support the province’s low-carbon transition and to address the significant regional disparities and unclear determinants identified in its CEE sector. The primary research objectives are: (1) examining the spatiotemporal evolution characteristics and regional disparities of CEE; and (2) clarifying the mechanisms underlying carbon emission efficiency. Based on the analytical results of spatiotemporal characteristics, regional disparities, and determinants, this study proposes more nuanced regional low-carbon trans-formation strategies. These findings provide useful references for other provinces facing the challenge of balancing economic growth with carbon emissions.
2. Literature Review
With technological progress, methods for calculating CEE have continued to evolve, and therefore, appropriate approaches should be selected for different research contexts [15,16]. Chen et al. (2021) employed the non-radial distance function (NDDF) and the global DEA model to evaluate the CEE of Chinese cities [17]. According to Maziotis et al. (2024), technological lag is one of the main obstacles to improving CEE. They applied the SFA model to evaluate CEE in the water sector of England and Wales [18]. However, traditional measurement methods display inherent limitations in practice, often overlooking undesirable outputs and external environmental factors during model construction, thereby reducing the precision of the results. Advanced methodologies such as the Super-SBM, Super-EBM, and Super-DEA models have been developed to address these shortcomings. Dong et al. (2022) applied the Super-SBM model to measure CEE in 143 countries worldwide, thereby addressing the limitations of conventional DEA models in identifying efficient decision-making units [19]. Furthermore, Zheng et al. (2024) combined the Super-EBM and Tobit models to quantify urban energy eco-efficiency (UEEE), analyzing both the technical gap rate and the composite impact of urbanization on UEEE [20]. Additionally, Cui et al. (2024) employed the Super-DEA model to evaluate the green efficiency of China’s coastal ports, emphasizing the substantial influence of external environmental factors and stochastic errors on the efficiency assessment [21].
Research on the spatiotemporal aspects of CEE has primarily focused on spatiotemporal regularity [22], heterogeneity [23], and regional differences [24]. Li et al. (2022) found that disparities in CEE among Chinese regions are likely to widen due to increasing technological inequalities. However, developed regions may mitigate this efficiency gap by optimizing their production structures [25]. Wei et al. (2025) employed standard deviation ellipses (SDE) to identify spatial directional features, examined the drivers of CEE migration in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region, and observed that regional disparities intensified with the advancement of marketization [26]. According to existing studies, the primary methods for examining the spatiotemporal evolution of carbon emissions include kernel density estimation (KDE) [27], exploratory spatial data analysis [28], and Markov chains [29]. To effectively promote low-carbon development at the provincial level, a comprehensive investigation of the factors influencing carbon emission efficiency is required [30].
Enhancing carbon emission control at the provincial level is critical for substantially reducing national carbon emissions. The combined use of the spatial Durbin model (SDM) and geographically and temporally weighted regression (GTWR) to analyze influencing factors can complementarily capture spatial correlation and spatio-temporal heterogeneity, enabling more comprehensive analysis [31,32]. Zeng et al. rigorously validated via the GTWR that energy consumption structure, industrial upgrading, economic development, and population agglomeration exert significant impacts on carbon emission efficiency in the transport sector of the Yangtze River Economic Belt [33]. Zhang et al. applied GTWR to evaluate the spatiotemporal heterogeneity of carbon emission efficiency’s influencing factors, uncovering pronounced disparities in both the intensity and directional effects of each factor across northern, central, and southern Chinese cities [34]. Energy-abundant western provinces export high-carbon products to the developed eastern regions; however, the east, in seeking to reduce its carbon emissions, has relocated high-carbon industries to other regions for production [35]. Using a dynamic panel model, Song et al. (2023) found that such industrial transfer has produced a notable “centrifugal effect”, whereby carbon emissions are displaced to less-developed areas through industrial outsourcing from developed regions [36]. Moreover, it is essential to assess the influence of technological advancement on regional low-carbon transformation [37]. Developing clean technologies can enhance local CEE and facilitate emissions reductions in adjacent regions through spillover effects [38]. In central and western regions, where industrialization remains incomplete, excessively constraining traditional sectors may hinder economic development. Therefore, Tian and Pang (2024) advocate using technological advancement to reduce emissions during development [39].
Extensive research has been conducted on CEE measurement, spatiotemporal evolution, and determinants at both national and global levels. However, two deficiencies persist: (1) most studies concentrate on developed or resource-rich regions, with insufficient analysis of complex energy-dependent provinces; (2) research has seldom addressed the unique challenges faced by provinces reliant on diverse energy structures.
This study is motivated by three main objectives. First, to clarify the necessity and urgency of the regional low-carbon transition and to quantify CEE using the Super-SBM model with panel data from 12 prefecture-level cities in Hubei Province from 2006 to 2022. Second, to investigate the spatial patterns and regional variations in CEE using kernel density estimation (KDE) and exploratory spatial data analysis (ESDA), and to analyze its dynamic evolution and long-term transfer trends with the standard deviation ellipse (SDE) and spatial Markov chain. Third, to apply the spatial Durbin model (SDM) and geographically and temporally weighted regression (GTWR) to analyze the determinants behind variations in CEE and to inform the development of differentiated emission reduction strategies.
3. Study Area and Methods
3.1. Study Area
Hubei Province is located in central China, within the middle reaches of the Yangtze River. The province administers 12 prefecture-level cities, one autonomous prefecture, three county-level cities, and one forest region. As one of China’s first low-carbon pilot regions, Hubei is a core hub of the Yangtze River Economic Belt and the Rise of Central China Strategy. In 2024, Hubei ranked seventh in national GDP, with a growth rate surpassing that of central China. Hubei is a major industrial province, with heavy chemicals comprising most of its industrial structure. Traditional sectors such as steel and automobile manufacturing also contribute substantially. Its energy consumption per unit of GDP is approximately 10% higher than the national average, reflecting the characteristics of a high-carbon economy. Therefore, by examining the spatiotemporal evolution of Hubei’s CEE and its determinants, we can identify opportunities for effective emission reductions.
Based on differences in geographic features, economic levels, and functional roles, the province is divided into three major regions—eastern, western, and central—as shown in Note: The maps are produced based on the standard map GS (2024)0650 from the National Platform for Common Geospatial Information Services, with no modification to the base map.
As shown in Figure 1, the eastern region centers on Wuhan, the hub of industry, as well as scientific and technological development. The western region is rich in biological resources and focuses on a green economy. The central region is characterized by the synergistic development of industry and agriculture. This study excludes Xiantao, Tianmen, Qianjiang, Enshi, and Shennongjia. The analysis focuses on prefecture-level cities in Hubei Province; however, these five cities have distinct administrative classifications and contain substantial data gaps in the statistical yearbook. The data used in this study are primarily derived from the China National Bureau of Statistics and municipal statistical yearbooks, the China Power and Municipal Statistical Yearbooks, and CEADs. This study analyzes 12 prefecture-level cities characterized by industrial dominance, all of which exhibit high carbon emissions and face considerable pressure to reduce them.
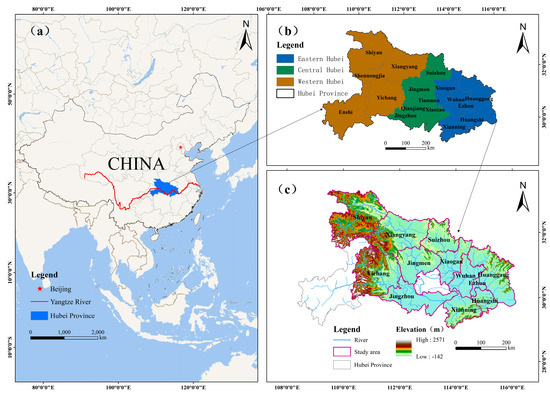
Figure 1.
Study area and regional classification. (a) Location of Hubei Province in China; (b) Regional division of Hubei Province into eastern, central, and western Hubei; (c) The study area in Hubei Province. Note: The maps are produced based on the standard map GS (2024)0650 from the National Platform for Common Geospatial Information Services, with no modification to the base map.
3.2. Research Methods
3.2.1. Super-SBM Model
The Super-SBM model is an efficiency evaluation approach developed from the traditional DEA and SBM models. This model not only retains the advantages of the SBM model in handling slack variables and undesirable outputs but also allows efficiency values to exceed 1, thereby enabling a complete ranking and comparison of the efficiency of all decision-making units [19,40]. The Super-SBM model was employed to calculate the carbon emission efficiency of 12 prefecture-level cities in Hubei based on previous research. The specifics of each variable are shown in Table 1. The number of people employed at the end of the year mainly reflects formal employment and does not fully capture informal or casual work. Nevertheless, since this underreporting remains relatively stable over time and across cities, its impact on the comparative analysis of carbon emission efficiency is likely limited. Electricity-related emissions are allocated based on consumption, ensuring that each unit of electricity is assigned to exactly one consuming city, thereby avoiding double counting or omission. In this study, each prefecture-level city is regarded as a production decision-making unit. This study adopts the methods of Song et al. [41], employing a super-SBM model that accounts for undesirable outputs to measure CEE. For the detailed derivation, refer to Appendix A.1.

Table 1.
Carbon Emission Efficiency Indicators and Calculation Guidelines.
3.2.2. Standard Deviation Ellipse
The Standard Deviation Ellipse (SDE) method systematically analyzes the spatial distribution characteristics of regional elements. By constructing a spatial ellipse model, the method quantitatively characterizes three core features of geographical distribution: agglomeration, centrality, and directionality [45]. Its core parameters include the spatial centroid, azimuth, major axis, and minor axis. Among them, the spatial centroid indicates the central location of the distribution; the azimuth reveals the dominant orientation; and the major and minor axes represent the maximum and minimum degrees of dispersion, respectively. For the detailed derivation, refer to the Appendix A.2.
3.2.3. Kernel Density Estimation
Kernel density estimation (KDE) is a fundamental method in nonparametric density estimation. In spatial analysis, this method transforms discrete spatial point elements into a continuous density surface, which facilitates the visualization of spatial distribution patterns and accurately identifies statistically significant spatial clusters [46]. The formula is as follows:
In the formula, represents the kernel density value; represents the distance from the estimated point to ; is the bandwidth; is the number of observations, is the kernel function.
3.2.4. Spatial Markov Chain
The traditional Markov chain method is a Markov process characterized by discrete time and discrete states, primarily used to analyze the transfer patterns of spatial distributions through the construction of weight matrices [47]. This study adopts the quartile method for classification, CEE is categorized into four types: 0–25% as low efficiency (I), 25–50% as medium-low efficiency (II), 50–75% as medium-high efficiency (III), and 75–100% as high efficiency (IV). The corresponding formulas are as follows:
where represents the probability of carbon emission efficiency in each prefecture-level city in Hubei Province transitioning from type at time to type at time ; denotes the sum of the number of cities that transitioned from type at time to type at time during the study period; represents the sum of the number of cities with type during the study period.
Spatial Markov chains extend traditional Markov chains by incorporating spatial lag effects, such that the state transition of the current region depends not only on its own previous state but also on the spatial influence of neighboring regions [48]. This approach not only compensates for the traditional Markov chain’s neglect of regional interactions but also enables a more accurate grasp of its dynamic evolutionary trends. This paper constructs the spatial Markov chains’ state transition probability matrix under different lag conditions, decomposing the traditional Markov chain into the transition probability matrix . represents the probability that, when a city is of type in the period , the type of the city transitions from in the period to in the period .
3.2.5. Exploratory Spatial Data Analysis
Exploratory Spatial Data Analysis (ESDA) is an essential approach for examining spatial distribution patterns, consisting primarily of two levels: global spatial autocorrelation and local spatial autocorrelation. Global Moran’s I quantifies the overall degree of spatial correlation within a study area and effectively identifies trends of agglomeration or dispersion of observed values. Global Moran’s I quantifies the overall degree of spatial correlation within a study area and effectively identifies trends of agglomeration or dispersion of observed values [49]. The corresponding formulas are as follows:
where is the global Moran index; is the local form of ; is the number of samples; and are the CEE of prefecture-level cities and , respectively, is the mean of CEE; is the spatial weight matrix. When the index value approaches 1, it indicates a significant positive correlation characteristic. When it approaches −1, it reflects a significant negative correlation characteristic. If it fluctuates around 0, there is a random distribution pattern in space, with no significant spatial autocorrelation.
3.2.6. Spatial Durbin Model
The spatial Durbin model (SDM) examines global spatial effects, capturing both temporal and spatial dynamics of the study object, thereby providing a more comprehensive account of the spatial associations between independent and dependent variables [50]. This study employs the SDM to investigate the factors influencing CEE in Hubei. The corresponding formula is as follows:
In the formula, represents the CEE index of Hubei Province for year ; denotes the influencing factors; refers to the spatial adjacency weight matrix; is the spatial correlation coefficient of the dependent variable, reflecting the mutual influence between adjacent regions; is the coefficient of the spatial lag term of the independent variable, reflecting the spatial impact of the independent variable, and is the random error term.
3.2.7. Geographically and Temporally Weighted Regression
Geographically and temporally weighted regression (GTWR) is a local spatial regression analysis method. Compared with traditional GWR, GTWR incorporates temporal variables into the weight function, enabling simultaneous representation of spatial dependence and temporal evolution characteristics [51]. This model more effectively captures the geographical characteristics of CEE, facilitating the identification of spatial dependence among determinants. The corresponding formula is as follows:
In the formula, is the spatiotemporal coordinate of the city; represents the observation time; and are the explanatory variables and the explained variable, respectively; is the number of explanatory variables; is the regression coefficient of the city; is the regression coefficient of the explanatory variable of the city; is the residual of the model.
4. Results
4.1. Spatiotemporal Characteristics of CEE in Hubei
This study employs a CEE analysis to examine the temporal and spatial trends in 12 prefecture-level cities in Hubei over the study period. Figure 2 presents the average CEE of Hubei and its three regions from 2006 to 2022. As illustrated in the figure, the CEE of Hubei followed a three-stage pattern: ascension, decline, and stabilization. Eastern Hubei exhibits the highest overall CEE, followed by western Hubei, whereas central Hubei remains the least efficient. Between 2011 and 2016, eastern Hubei experienced rapid growth, increasing from 0.37 to 0.46, but subsequently witnessed a steep decline after 2016. The CEE in western Hubei consistently outperformed the provincial average, peaking between 2006 and 2011, and while it fluctuated thereafter, it remained relatively high. The CEE in central Hubei fluctuated considerably, remaining below the provincial average for an extended period, with the lowest value approaching 0.2, indicating relatively low energy utilization efficiency. Between 2010 and 2014, a minor improvement occurred, followed by a further decline, before a rebound in 2017. Although the central region will be the primary focus of future low-carbon development, the eastern and western regions have generally driven the province’s CEE improvements.
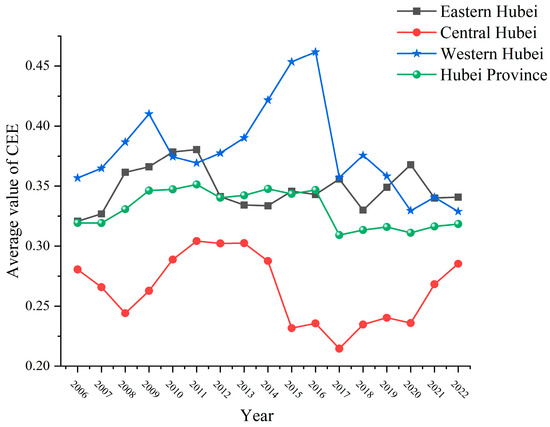
Figure 2.
Average value of CEE in Hubei and three regions from 2006 to 2022.
In this study, the average CEE of Hubei Province ranged from 0.309 to 0.346. As shown in Table 2, Hubei’s CEE is comparable to the national average but remains substantially lower than that of the economically developed coastal regions. Within the province, CEE varies considerably, ranging from a minimum of 0.215 to a maximum of 0.462. Compared with Shandong Province, which is also an industrial region, the intra-provincial disparities in Hubei are relatively less pronounced. The CEE of Hubei Province underwent significant fluctuations in 2016. During this period, the province established a binding target to reduce carbon emissions per unit of GDP by 19.5% and initiated 28,000 major technological transformation projects. Although these measures laid the foundation for long-term change, the initial stage of technological transformation involved the rapid elimination of outdated production capacity. By contrast, new capacity had not yet been successfully established. This resulted in a decline in CEE in areas dependent on traditional industries, followed by subsequent fluctuations in the province’s overall CEE.

Table 2.
Summary of representative studies on CEE.
This study selects 2006, 2011, 2016, and 2022 as the observation years. According to Figure 3, the CEE of each city exhibits a spatial pattern of being high in the west, low in the center, and moderate in the east. The eastern region exhibited considerable internal variation: Wuhan, Huangshi, and Xianning experienced consistent improvements in CEE, whereas Xiaogan, Huanggang, and Ezhou maintained medium-to-low performance levels. While the central portion of Hubei Province remained within the medium-to-low CEE range, the western portion consistently maintained a medium-to-high CEE level, leading the province.
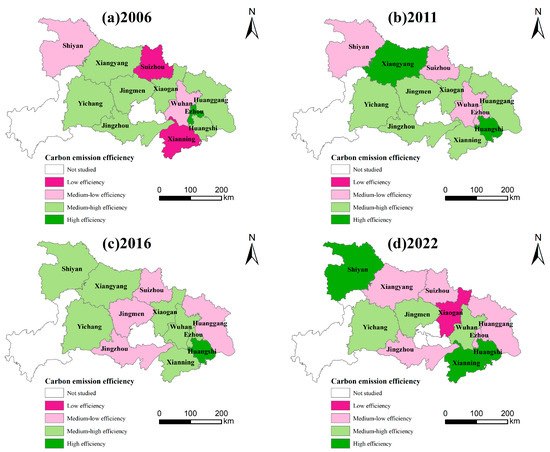
Figure 3.
Spatial pattern of CEE in prefecture-level cities in Hubei from 2006 to 2022. (a) CEE distribution in 2006; (b) CEE distribution in 2011; (c) CEE distribution in 2016; (d) CEE distribution in 2022.
Over time, the number of high-efficiency zones increased. Huangshi consistently exhibited high CEE, while Wuhan’s CEE gradually increased, and Xianning achieved substantial growth. Huangshi functioned as the high-CEE nucleus of eastern Hubei, contributing to improvements in Ezhou’s CEE before 2016. After 2016, Shiyan, a resource-based city, underwent a successful transformation and emerged as the new high-CEE center of western Hubei. Low-CEE regions were primarily located along provincial boundaries. Suizhou consistently exhibited low CEE, whereas adjacent areas maintained medium-to-low CEE levels. By 2022, the CEE of Wuhan and its surrounding cities had increased significantly, with the radiating effect of the provincial capital becoming evident.
The general pattern can be summarized as follows. First, core cities possessed a significant CEE advantage: between 2006 and 2022, Shiyan’s CEE increased by 64.9% and Wuhan’s by 27.2%, while Xiaogan experienced remarkable progress. Second, path dependence on conventional sectors persists, and notable CEE disparities remain in peripheral cities. Cities such as Huanggang and Suizhou continue to exhibit persistent inefficiency.
4.2. Evolution Trend of Hubei’s City-Level CEE
4.2.1. The Dynamic Evolution of CEE in Prefecture-Level Cities of Hubei
To analyze the dynamic evolutionary characteristics of CEE among prefecture-level cities in Hubei Province, the kernel density estimation (KDE) method is employed to plot kernel density curves from 2006 to 2022, illustrating the distribution of CEE across different periods and efficiency levels. The dynamic evolution of CEE during the study period exhibited distinct stages, as shown in Figure 4. Between 2006 and 2010, the kernel density curves exhibited dispersion without distinct peaks. During this period, the CEE of Hubei Province remained generally low, accompanied by significant regional disparities. Between 2011 and 2016, Hubei Province’s CEE increased, and the kernel density curve exhibited multiple peaks. This phenomenon suggests potential polarization, with some cities improving their CEE through green transformation while others remain at low CEE levels. From 2017 to 2022, the peak of the curve increased, indicating that Hubei Province’s low-carbon transition had entered a more mature stage. However, the tail of the curve continued to display low value, indicating that regional differences in CEE remained significant and reflected an unbalanced development pattern.
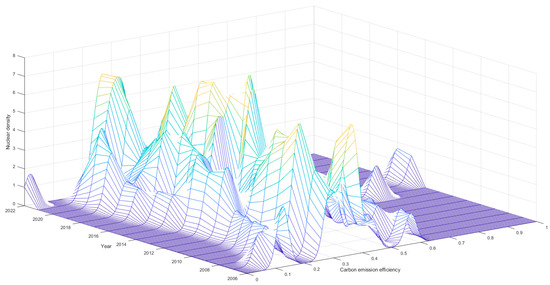
Figure 4.
Kernel density curve of CEE in prefecture-level cities of Hubei from 2006 to 2022.
The CEE of the cities exhibited an upward trend throughout the study period. The kernel density curves further indicated that the polarization of CEE among cities in the province had intensified. Therefore, deploying more location-specific emission reduction strategies is essential for advancing the low-carbon transition.
4.2.2. The Long-Term Transfer Trend of CEE in Prefecture-Level Cities of Hubei
This study uses ArcGIS 10.8 to examine the spatial distribution characteristics of CEE in different cities. The spatial pattern evolution and migration characteristics of CEE in Hubei Province are analyzed through the migration path of the gravity center and the evolutionary trends of key parameters, as presented in Table 3 and Figure 5. The latitude and longitude coordinates of the gravity center reveal the dynamic shifts in the spatial center of CEE in Hubei Province. In 2006, the gravity center was located in the central-eastern region of the province. By 2011, it had shifted slightly westward, indicating enhanced CEE in the western region. In 2016, it moved northeastward, reflecting the consolidation of favorable regions around the Wuhan and Xiaogan urban agglomerations in northeastern Hubei. By 2022, the gravity center shifted slightly southwestward, although it remained within the central-eastern part of the province.

Table 3.
Migration of the CEE centroid and variations in SDE parameters in Hubei Province from 2006 to 2022.
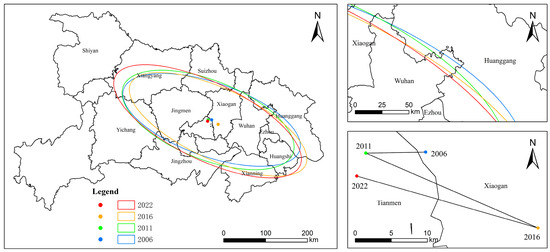
Figure 5.
The SDE changes of CEE in prefecture-level cities of Hubei from 2006 to 2022.
The standard deviations of the major and minor axes, along with the azimuth angle, indicate spatial distribution patterns and directional tendencies. In 2006, the major axis measured 222.2218 km, the minor axis 87.5147 km, and the azimuth angle 109.1531 degrees, indicating stretching and aggregation in the southwest–northeast direction. In 2011, the major axis was slightly shortened, the minor axis increased, and the azimuth angle reached 111.5364 degrees, suggesting a more compact spatial distribution and stronger aggregation. In 2016, the major axis significantly increased, the minor axis slightly decreased, and the azimuth angle rose to 114.7495 degrees, indicating more pronounced regional disparities and intensified polarization along the southwest–northeast direction. In 2022, the major axis further expanded, the minor axis slightly increased, and the azimuth angle increased to 115.6474 degrees, indicating an expansion of elliptical coverage and a continued widening of regional disparities. This reflects a growing imbalance in spatial efficiency across the province.
Between 2006 and 2022, the CEE gravity center in Hubei Province exhibited a southwest–northeast trajectory, highly consistent with the province’s core economic belts. This migration path not only illustrates the interdependent and mutually supportive dynamics among Hubei’s cities in promoting energy system upgrades, industrial structure optimization, and regional coordination, but also reflects the evolving roles of these cities in balancing CEE improvements with emission reduction obligations.
The traditional and spatial Markov transition probability matrices are shown in Table 4. The results of the traditional Markov chain analysis show three features: first, there was significant path dependence, with the self-maintenance probabilities of the four types of CEE being 79.17%, 67.39%, 60%, and 77.08%, respectively; transition probabilities between types were low, indicating strong path dependence within provinces; second, neighboring transitions dominated the evolution paths, with cross-level transition probabilities were lower than neighboring transition probabilities, such as the transition probability from Type I to Types III and IV being 0% and the transition probability from Type III to Type IV was 22%; and third, there was an upward trend in CEE overall, which meant that cities with lower CEE were more likely to transition to higher CEE types.

Table 4.
The Markov transfer probability matrix of CEE in prefecture-level cities of Hubei from 2006 to 2022.
In contrast, under the spatial Markov model, low-CEE Type I regions had a 50.00% probability of transitioning to the medium-low CEE state and a 0% probability of advancing to higher efficiency when the spatial lag type was Type I. When the spatial lag type was Type II, Type I regions had a 69.23% probability of staying unchanged and a 30.77% probability of upgrading to Type II, a figure higher than the 20.83% in the traditional model. Type III regions exhibited a 26.67% probability of transitioning to Type IV. When the spatial lag type was Type III, Type I regions exhibited a 93.33% probability of maintaining their original state, compared to 79.17% in the traditional model. Type III regions had a 42.86% probability of remaining unchanged and a 35.71% probability of upgrading to Type IV, demonstrating an apparent spatial spillover effect. When the spatial lag type was Type IV, Type II regions exhibited a 12.50% probability of advancing to Type III. In comparison, Type III regions demonstrated a 33.33% probability of progressing to Type IV. Furthermore, Type IV regions had a 62.50% probability of maintaining stability.
Analysis of the Markov transition probability matrix indicates that the transition process of CEE among cities in Hubei exhibits a substantial “siphon effect” under spatial lag conditions. Moreover, while low CEE in neighboring regions may exacerbate local CEE losses, high CEE in neighboring regions may foster improvements in local CEE.
4.3. Temporal Features of CEE in Prefecture-Level Cities of Hubei
During the study period, the CEE of Hubei exhibited notable temporal variation trends. As shown in Table 5, between 2006 and 2015, Moran’s I index was primarily negative and statistically insignificant, indicating that the CEE of cities was characterized mainly by random distribution. Significant negative spatial autocorrelation emerged in 2010, 2011, and 2013, suggesting that the distribution of high-CEE and low-CEE cities alternated, thereby intensifying regional disparities and potentially indicating the presence of a “carbon transfer” phenomenon. By 2016, the intensity of spatial autocorrelation had declined to its lowest level. From 2017 onward, the spatial pattern of CEE in Hubei Province transitioned from nearly insignificant to exhibiting strong positive spatial autocorrelation, thereby displaying an evident spatial clustering trend.

Table 5.
Moran’s I of CEE in prefecture-level cities of Hubei from 2006 to 2022.
As shown in Figure 6, the Moran scatter plot further confirms this spatial pattern shift. In 2006, the spatial distribution of CEE was highly dispersed. By 2022, the spatial pattern had clearly shifted toward a more concentrated configuration, exhibiting significant positive spatial autocorrelation. This confirms the occurrence of spatial spillover effects and the presence of agglomeration processes. This study examines the spatiotemporal characteristics and evolutionary dynamics of CEE in Hubei Province. The findings indicate that 2016 represented a crucial turning point in the evolution of Hubei’s CEE. During this year, the average CEE values of the entire province and its three major regions underwent abrupt changes, while the spatial correlation of CEE shifted from a dispersed pattern to a significant spatial agglomeration. The introduction of multiple regulatory measures by the national and provincial governments in 2016 suggests that policy interventions significantly influenced CEE.
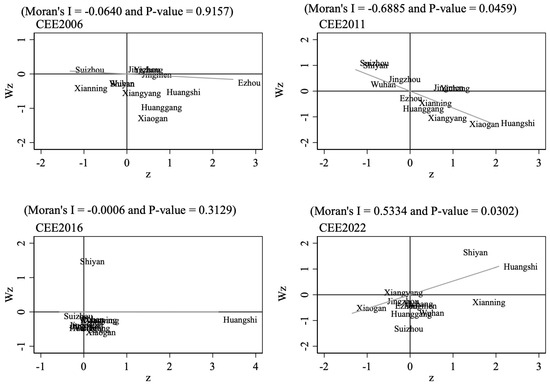
Figure 6.
Moran scatter plot of CEE in prefecture-level cities of Hubei from 2006 to 2022.
4.4. CEE Determinants Analysis
4.4.1. Overall Average Impact of Determinants
This study focuses on seven determinants influencing CEE, considering available prefecture-level data and prior research: (1) economic development level [57], measured by GDP per capita; (2) population scale [58], measured by resident population at year-end and population density; (3) urbanization level [59], measured by urbanization rate; (4) industrial structure, measured by the share of the secondary sector; (5) energy structure [60], measured by energy consumption per unit of GDP and the share of hydropower, defined as the proportion of hydropower consumption in total final energy consumption. For details of the data dictionary table, refer to Table A1. In this study, the relevant variables were transformed using logarithms. To rule out the potential issue of multicollinearity among the variables, the variance inflation factor (VIF) was further employed for analysis, and the results are presented in Table 6. As shown in Table 6, all VIF values are less than 10, with an average of 2.88, indicating that multicollinearity is unlikely to be a serious concern among the variables.

Table 6.
Variance inflation factor test results.
As shown in Table 7, Wald and LR tests indicated that the SDM model was more appropriate for the present data analysis. In this model, the dependent variable is CEE, while explanatory variables include energy intensity, hydropower proportion, per capita GDP, share of the secondary sector, resident population, population density, and urbanization rate. The Hausman test further confirmed that a fixed-effects specification was more suitable for this study. The model includes both city-fixed effects and time-fixed effects. The time-fixed effects are used to control for all province-wide or nation-wide common shocks that vary over time but are invariant across cities, such as unified macro-policies, macroeconomic fluctuations, global energy price changes, and widespread climate events. Therefore, the coefficient estimates for the variables in the model are primarily identified from the relative differences in city characteristics, after netting out these common trends. Besides, the inclusion of the lag term does not change the direction and significance of the main spatial spillover effects, indicating robustness of the results; for detailed results, refer to Table A2.

Table 7.
Direct, indirect, and total effects of the SDM on CEE in 12 prefecture-level cities of Hubei from 2006 to 2022.
Regarding energy, energy intensity exerts a significant positive direct effect on local CEE. This result suggests that an increase in CEE is associated with an increase in GDP per capita. However, its spatial spillover effect is relatively weak. The proportion of hydropower has little impact on CEE.
Regarding economic growth and industrial structure, per capita GDP and the share of the secondary sector exert distinct influences on CEE. The coefficient of per capita GDP is significantly positive, suggesting that more developed economies exhibit higher CEE. The direct effect coefficient of the secondary sector share is significantly positive. By contrast, its spatial spillover effect is significantly negative, suggesting that expanding the secondary industry in neighboring regions may intensify resource competition and exacerbate pollution transfer between cities.
Concerning population and urbanization, the coefficients of resident population, population density, and urbanization rate are all significantly positive. This suggests that larger populations can generate economies of scale, improving resource-use efficiency. In addition, higher population density results in more concentrated urban infrastructure and resources, thereby reducing energy consumption per unit of output. The results reveal that the spatial spillover effect of population density is negative. This may be because high-density core cities tend to externalize environmental costs through cross-regional commuting and industrial linkages. For example, residents may choose to live in low-cost peripheral cities while working in the core, causing commuting-related carbon emissions to be attributed to the residential areas rather than the workplaces. In addition, during industrial upgrading, core cities may relocate energy-intensive manufacturing or logistics activities to surrounding cities. However, cross-border freight generated to meet the demands of core cities further increases the carbon emission burden of neighboring regions. CEE can also be considerably enhanced by increasing the urbanization rate.
Overall, changes in CEE across Hubei Province are influenced by a variety of determinants. From a total-effect perspective, per capita GDP, permanent resident population, population density, and urbanization rate continue to exert significant impacts on CEE. However, the significantly negative indirect effect of the secondary sector share largely offsets its direct effect, rendering its overall impact insignificant. This suggests that industrial optimization at the local level may contribute little to improving overall environmental outcomes unless accompanied by inter-city collaboration.
Table 7 reports the direct, indirect, and total effects implied by SDM. All covariates are log-transformed, so the reported effects can be approximately interpreted as elasticities. A positive direct effect indicates that an increase in the variable improves local CEE, whereas a negative effect reduces it. Indirect effects capture how changes in one city influence the CEE of neighboring cities through spatial spillovers. The total effect is the sum of both, and thus more suitable for policy interpretation. In this study, standardized beta coefficients were calculated, with the detailed results presented in Table A3.
The results are directionally consistent with the main conclusions derived from the SDM, thereby reinforcing the internal consistency of the results and providing additional support for the validity of the study’s conclusions.
4.4.2. Spatiotemporal Heterogeneity in the Effects of Determinants
The GTWR model results indicate that the determinants of CEE across the three major regions of Hubei Province exhibit distinct characteristics, as shown in Figure 7. Among them, the most complex mechanism is observed in eastern Hubei. In eastern Hubei, energy intensity generally negatively influences CEE, particularly in Huangshi, where traditional industries dominate. The proportion of hydropower exerts a significant positive influence on CEE in most cities. CEE is typically negatively associated with per capita GDP. The impact of the secondary sector share on CEE varies considerably across eastern Hubei: while most cities exhibit a positive correlation, Wuhan and Xianning display negative correlations. Owing to dense populations, Wuhan, Ezhou, and Xianning exhibit lower CEE. Furthermore, urbanization rates positively influence CEE in eastern Hubei, except Wuhan.
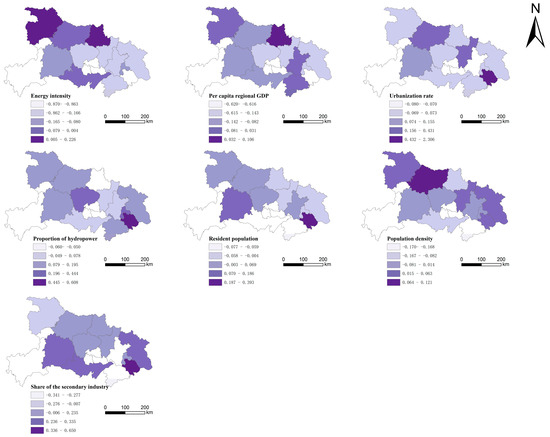
Figure 7.
Spatial distribution pattern of regression coefficients of determinants in prefecture-level cities of Hubei from 2006 to 2022.
The western Hubei region, endowed with abundant hydropower resources, exhibits a distinctive CEE determinant. Only Shiyan displays a positive association between energy intensity and per capita GDP, suggesting that the city has achieved notable success in green transformation. The abundance of hydropower resources in western Hubei has driven improvements in CEE. The secondary sector share positively correlates with CEE in Xiangyang and Yichang but exerts no significant effect in Shiyan. Population density and permanent resident numbers positively influence CEE in western Hubei. Urbanization positively influences CEE in western Hubei, with the most substantial impact observed in Xiangyang.
In central Hubei, Suizhou exhibits a strong positive association with energy intensity, whereas Jingmen shows a negative correlation. Only Suizhou is negatively associated with the hydropower proportion, in contrast to the general provincial trend. Suizhou is positively associated with per capita GDP, whereas Jingmen and Jingzhou exhibit negative correlations. Growth of the secondary industry generally exerts a positive impact on CEE in central Hubei, with the strongest effect observed in Jingzhou. Population-related factors primarily exert negative effects on CEE, while urbanization primarily exerts positive effects.
The GTWR results reveal significant spatial heterogeneity in the estimated coefficients. Energy intensity shows positive effects in Suizhou (+0.226) and Shiyan (+0.108), suggesting that, as an automobile manufacturing hub and an old industrial city. Respectively, their industrial upgrading and low-carbon transition contribute to improved production efficiency and reduced carbon emissions per unit of output. The share of the secondary industry exerts a positive influence in Jingzhou (+0.335) and Huangshi (+0.650) during the stage of industrial deepening but turns negative in Wuhan (−0.277) and Xianning (−0.341), which are at the post-industrialization and green transition stages. Per capita GDP exhibits positive correlations only in Shiyan (+0.031), Suizhou (+0.106), and Xianning (+0.006), indicating that economic development in these regions plays a limited yet positive role in enhancing carbon emission efficiency. GTWR
Despite notable regional differences, clean energy and urbanization generally exert positive influences on CEE. By contrast, the effects of energy intensity, per capita GDP, and secondary sector share depend on region-specific conditions. These differences are shaped by the long-term interaction of economic development paths, resource endowments, policy orientations, and related factors.
5. Discussion
5.1. Trends in Regional Differentiation
From the perspective of temporal evolution, the CEE of Hubei Province shows a clear phased pattern. The results demonstrate that Hubei’s CEE experienced three distinct stages: initial improvement, subsequent decline, and eventual stabilization. The year 2016 served as a critical turning point, marked by evident fluctuations in the average efficiency of the province and its subregions. After 2016, the spatial distribution of CEE also underwent a transformation from a random and discrete pattern to a positively correlated agglomeration, suggesting that the province’s low-carbon transition has entered a new phase characterized by spatial differentiation and intercity linkage. This evolution is consistent with the transitional dynamics observed in other rapidly industrializing regions of China, reflecting the coupling between economic restructuring and environmental governance [55].
Spatially, the CEE of Hubei exhibits persistent regional disparities, with high efficiency in the west, moderate in the east, and low in the central region. Core cities such as Wuhan, Shiyan, and Huangshi have maintained strong upward trajectories. While peripheral cities like Huanggang and Suizhou remain at relatively low levels. According to the SDE analysis, the ellipse consistently extends along the southwest–northeast axis, aligning with the province’s main economic belt. The continuous elongation of the major axis reflects the widening regional disparities and increasing polarization along this direction. This suggests that the observed pattern is not merely a geographic shift but also a deeper manifestation of strategic low-carbon development, which has become increasingly concentrated along the province’s most dynamic economic axes [36].
5.2. Characterization of Influencing Factors
A key finding of the SDM analysis is the significantly negative spatial autoregressive coefficient, revealing a “siphon effect”. This finding indicates that improvements in CEE within core cities may suppress efficiency growth in surrounding regions, as advanced urban centers attract green investments, talent, and infrastructure resources. In contrast, peripheral regions may become passive recipients of relocated high-carbon industries, thus reinforcing structural dependence and spatial inequity. Such spatial polarization suggests that deeper marketization and policy interventions could further exacerbate regional disparities in low-carbon development [61,62].
Regarding influencing factors, there is a significant positive correlation between per capita GDP and CEE, with a direct effect of 0.1048, indicating that higher levels of economic development contribute to improved CEE. However, the share of the secondary sector exerts a dual effect. A positive direct effect (0.0950) within the region but a negative spatial spillover effect on neighboring areas. This duality implies that industrial expansion may improve local CEE while simultaneously inducing resource competition and pollution transfer externally. The comparison between SDM and GTWR results reveals that the share of hydropower exerts an insignificant effect in SDM but a positive effect on GTWR. This discrepancy is largely attributed to Hubei’s seasonal hydrological variability, which the global SDM cannot fully capture. By incorporating localized temporal variations, GTWR more accurately reflects the role of clean energy in improving regional CEE. Both models consistently indicate that clean energy utilization and urbanization are key positive drivers of CEE, while energy intensity, per capita GDP, and industrial structure exhibit spatial heterogeneity. These results underline the importance of local resource endowments and development trajectories in shaping low-CEE outcomes.
Overall, the results emphasize the need for differentiated regional strategies. Promoting clean energy, guiding urbanization toward ecological and intensive development, and coordinating industrial restructuring across regions are essential for improving CEE and achieving sustainable growth in Hubei Province. Without effective mechanisms for ecological compensation and coordinated governance, regional development may continue to polarize, resulting in a polarized pattern of the strong becoming stronger and the weak becoming weaker [14,63].
5.3. Limitations and Future Research Directions
This study has several limitations that should be acknowledged. Potential bidirectional causality between CEE and explanatory variables such as urbanization and industrial structure, may bias coefficient estimates. Limited city-level data coverage and inconsistent definitions across municipalities reduce the robustness of results. Five cities were excluded, potentially constraining the generalizability of findings for the province. Indicators such as the share of hydropower generation and year-end resident population may suffer from inconsistencies in statistical definitions across cities, reducing data accuracy. Additionally, the study lacks a full dynamic model and a consumption-based carbon accounting framework, limiting the ability to capture temporal and spatial dynamics and interpret emission patterns. Moreover, the failure to distinguish between locally generated and imported electricity may further introduce attribution errors.
Future research should integrate inter-city trade and electricity flow data to mitigate embodied emission misallocation and develop dynamic spatial models. In addition, future studies that integrate CEE forecasting models account for factors such as technological innovation and carbon market mechanisms and broaden the analytical scope to include the Yangtze River Midstream Urban Agglomeration for cross-regional comparison would substantially enhance the comprehensiveness and policy relevance of the findings. Furthermore, although the local hydropower share variable effectively reflects intercity differences in energy structures and demonstrates significant spatial heterogeneity, future research should employ more granular datasets, such as grid-level real-time dispatch records for renewable energy and high-resolution climatic drought indicators, to rigorously validate the multiscale relationship between clean energy utilization and CEE.
6. Conclusions and Policy Implications
6.1. Conclusions
This study systematically investigates spatiotemporal evolution, regional disparities, and driving factors of CEE in 12 prefecture-level cities across Hubei Province from 2006 to 2022. The year 2016 marks a critical turning point in the evolution of CEE in Hubei Province, manifested in two primary dimensions: (1) temporally, CEE experienced a sharp decline after 2016; (2) spatially, the distribution pattern shifted from an early-stage random and discrete state to a distinct positive spatial autocorrelation. The analysis of determinants indicates that economic development, population size, and the process of urbanization exert significant positive effects on improving CEE. However, the results of the SDM reveal a significant “siphon effect”. Specifically, the proportion of secondary industry positively influences local CEE, but its spatial spillover effect is negative, suggesting that industrial expansion may intensify cross-regional resource competition and pollution transfer. By integrating the SDM and GTWR models, this study reveals not only the global spatial determinants of CEE but also captures the spatial–temporal heterogeneity of these effects across regions. The results underscore the necessity of differentiated yet regionally coordinated emission-reduction policies to foster high-quality, sustainable development.
6.2. Policy Implications
Based on the results, the following region-specific policy recommendations are proposed to improve CEE and foster a green economy across Hubei Province. It should be noted that the quantified effects of the proposed policy are based on model estimates and may be influenced by data inconsistencies, sample range limitations, and the complexity of spatial spillover effects. Therefore, these values should be interpreted as indicative trends rather than precise forecasts. In practice, policy design should also account for local energy structures, industrial characteristics, and environmental carrying capacity. In eastern Hubei, Huangshi exhibits the lowest coefficient of energy intensity on carbon emission efficiency (−0.863). It indicates that its energy consumption problem is particularly severe and that priority should be given to energy efficiency improvement programs. In addition, the secondary sector share shows significant negative coefficients in Wuhan (−0.277) and Xianning (−0.341), reflecting prominent structural contradictions in these cities. To mitigate such adverse effects, efforts should focus on increasing the proportion of advanced manufacturing and modern service industries, while simultaneously supporting green transportation and sustainable building development. In this region, introducing low-carbon is essential, alongside promoting advanced energy-saving technologies and clean production processes to achieve a coordinated improvement in economic development and CEE. Urban governance should also be strengthened, emphasizing optimizing spatial layouts, developing green buildings, and transportation systems.
In western Hubei, abundant hydropower and natural resources provide ecological advantages, but CEE remains constrained by reliance on energy intensity and population factors. This region needs to consolidate clean energy advantages, expand non-fossil sources, and strengthen carbon sink capacity. Thereby promoting the synergistic development of ecology and economy. The western region of Hubei Province enjoys abundant natural resource endowments, providing a solid foundation for ecological development. However, CEE remains constrained by energy intensity and demographic factors. To fully leverage its ecological advantages, Shiyan City aims to achieve an installed capacity of 8.8 million kW of clean energy by 2030 [64], while Xianning City plans to exceed 10,000 MW of clean energy capacity by 2035 [65]. Considering these clean energy development targets, the region needs to consolidate its advantages in renewable energy, accelerate the green transformation and upgrading of industries, expand the share of non-fossil energy, and further explore the carbon sink potential of ecosystems, thereby promoting the coordinated development of ecology and economy.
Central Hubei faces persistent challenges in industrial transformation. In Suizhou, the coefficient of energy intensity (0.226) is the highest in the province. Meanwhile, the secondary sector share shows a negative spillover effect. Green retrofitting should be prioritized. Therefore, establishing green manufacturing demonstration zones in these cities would not only promote the greening of local industrial chains but also help mitigate the risk of cross-regional pollution spillovers. Enhancing green infrastructure and implementing measures to control agricultural non-point source pollution.
At the provincial level, cross-regional coordination is crucial to overcoming development limitations in any single region. Efforts should promote joint progress by leveraging the green growth of core cities to drive surrounding areas, avoiding one-way transfers of resources or pollution. Establishing ecological compensation mechanisms and carbon trading markets would provide incentives for high-efficiency, low-carbon regions through technical and financial support, thereby facilitating responsibility-sharing for emission reduction. The fundamental path is continuously optimizing the energy structure and advancing ecological urbanization, thereby improving energy efficiency and ultimately fostering a resilient, sustainable development model for Hubei Province.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.L.; methodology, M.Y.; formal analysis, M.L. and X.H.; resources, J.Z.; data curation, M.H.; investigation, X.H.; writing—original draft, X.H.; writing—review and editing, M.L.; visualization, X.H.; supervision, M.L.; software, W.Z.; project administration, M.H.; funding acquisition, M.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research is partially funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant: no. 51778065).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Appendix A
Appendix A.1
Assuming that each prefecture-level city has types of inputs that can produce kinds of desirable outputs and types of undesirable outputs . represents a feasible production technology set at year . The equation for the production technology containing desirable and undesirable outputs for each prefecture in the year is as follows:
Assuming variable returns to scale, the non-radial, non-oriented SBM model that incorporates desirable outputs and undesirable outputs for the city in the year is denoted as follows:
where the objective function represents the average distance of inputs and outputs from the production frontier, denotes input excess, represents desirable output shortfall, and indicates desirable output shortfall, while is the weight vector.
Appendix A.2
Appendix A.3
For details of the data dictionary table, refer to Table A1.

Table A1.
Data dictionary.
Table A1.
Data dictionary.
| Variable | Unit | Source |
|---|---|---|
| Per capita regional GDP | 10,000 CNY/person | Hubei Statistical Yearbook |
| Energy intensity | tonne of SCE/10,000 CNY | China City Statistical Yearbook |
| Population Density | person/km2 | China City Statistical Yearbook |
| Share of the secondary sector | % | Hubei Statistical Yearbook |
| Urbanization Rate | % | China City Statistical Yearbook |
| Resident population | 10,000 persons | Hubei Statistical Yearbook |
For details of the lagged dependent variable into the SDM, refer to Table A2.

Table A2.
Include the lagged dependent variable in SDM.
Table A2.
Include the lagged dependent variable in SDM.
| Variable | Direct Effect | Indirect Effect | Total Effect |
|---|---|---|---|
| Energy intensity | 0.1276 *** | −0.0037 | 0.1238 *** |
| (0.0020) | (0.0031) | (0.0032) | |
| Proportion of hydropower | 0.6165 | −1.0279 | −0.4114 |
| (0.5986) | (0.8828) | (0.8297) | |
| Per capita regional GDP | 0.1029 *** | 0.0006 | 0.1034 *** |
| (0.0029) | (0.0039) | (0.0035) | |
| Share of the secondary sector | 0.1002 *** | −0.0789 *** | 0.0213 |
| (0.0079) | (0.0119) | (0.0148) | |
| Resident population | 0.1003 *** | 0.0006 | 0.1010 *** |
| (0.0013) | (0.0024) | (0.0027) | |
| Population density | 0.1013 *** | −0.0119 *** | 0.0894 *** |
| (0.0018) | (0.0026) | (0.0029) | |
| Urbanization rate | 0.0978 *** | −0.0108 | 0.0870 *** |
| (0.0039) | (0.0093) | (0.0089) | |
| Regional fixed effect | Yes | Time fixed effect | Yes |
| R2 | 0.939 |
Note: *** indicate significance at the 0.01 levels.
For details of the standardized beta, refer to Table A3.

Table A3.
Standardized beta of determinants.
Table A3.
Standardized beta of determinants.
| Variable | Standardized Beta |
|---|---|
| Energy intensity | −0.178 |
| Proportion of hydropower | 0.298 |
| Per capita regional GDP | −0.575 |
| Share of the secondary sector | 0.859 |
| Resident population | 0.102 |
| Population density | −1.103 |
| Urbanization rate | 0.083 |
References
- Huang, L.; Kelly, S.; Lv, K.; Giurco, D. A systematic review of empirical methods for modeling sectoral carbon emissions in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 215, 1382–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Gao, W.; Su, Y.; Wang, T. Carbon emissions trajectory and driving force from the construction industry with a city-scale: A case study of Hangzhou, China. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2023, 88, 104283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Yang, H.N.; Xiao, Y.; Tang, P.Y.; Liu, S.Y.; Chang, M.; Huang, H. Exploring spatial pattern optimization path of urban building carbon emission based on low-carbon cities analytical framework: A case study of Xi’an, China. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2024, 111, 105551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IEA. CO2 Total Emissions by Region, 2000–2023; IEA: Paris, France, 2024; Available online: https://www.iea.org/data-and-statistics/charts/co2-total-emissions-by-region-2000-2023 (accessed on 27 February 2024).
- Yang, B.; Jahanger, A.; Usman, M.; Khan, M.A. The dynamic linkage between globalization, financial development, energy utilization, and environmental sustainability in GCC countries. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 16568–16588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Development and Reform Commission. Introduction to the “1+N” Planning Policy System for the Development of the Yangtze River Economic Belt During the 14th Five-Year Plan Period (I). 2021. Available online: https://www.ndrc.gov.cn/fggz/fgzy/shgqhy/202111/t20211122_1304650.html (accessed on 6 November 2021).
- Wen, W.; Wang, Q. Re-examining the realization of provincial carbon dioxide emission intensity reduction targets in China from a consumption-based accounting. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 244, 118488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Guo, S.; Xu, H.; Tian, M.; Pan, X.; Chu, J. China’s carbon intensity factor decomposition and carbon emission decoupling analysis. Energy 2022, 239, 122175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Development and Reform Commission. Notice on Launching Pilot Programs for Low-Carbon Provinces and Low-Carbon Cities. 2010. Available online: https://www.ndrc.gov.cn/xxgk/zcfb/tz/201008/t20100810_964674.html (accessed on 8 August 2010).
- Wuhan Water Authority. Floods and Droughts Are Not Constant, and Rivers Are Safe—CKRC Actively Responds to the Rare Drought in the Yangtze River Basin in 2022. Available online: https://swj.wuhan.gov.cn/tzdt/jcss/202211/t20221125_2102612.html (accessed on 25 November 2022).
- Wang, W.; Wang, H.; Sun, D.; Liu, G.; Fang, Z.; He, W. Carbon emission reduction or biodiversity conservation? Insights gained from interregional hydropower transmission. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2025, 212, 108014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- General Office of Wuhan Municipal People’s Government. Notice of the General Office of Wuhan Municipal People’s Government on Issuing the Work Plan for Promoting Carbon Reduction and Developing a Low-Carbon Industry in Wuhan (Document No. WZB [2021] 95). Available online: http://hbj.wuhan.gov.cn/hjsj/ztzl/hbcyzcqd/cygzlfz/202109/t20210914_1777522.html (accessed on 2 September 2021).
- Chen, H.; Chen, W. Carbon mitigation of China’s building sector at the city level: Pathways and policy implications based on a case study of a low-carbon province. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 224, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, N.; Lu, X.; Kuang, B.; Zhang, X. Regional disparities and evolution trend of city-level carbon emission intensity in China. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2023, 88, 104288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher-Vanden, K.; Jefferson, G.H.; Ma, J.; Xu, J. Technology development and energy productivity in China. Energy Econ. 2006, 28, 690–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Duan, F.; Ma, X.; He, L. Carbon emissions efficiency in China: Key facts from regional and industrial sector. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 206, 850–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Liu, Y.; Gao, Y.; Wang, J. Carbon emission trading policy and carbon emission efficiency: An empirical analysis of China’s prefecture-level cities. Front. Energy Res. 2021, 9, 793601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maziotis, A.; Sala-Garrido, R.; Mocholi-Arce, M.; Molinos-Senante, M. Evaluating carbon performance in the water industry: A longitudinal analysis of England and Wales. Results Eng. 2024, 24, 103580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, F.; Li, Y.; Gao, Y.; Zhu, J.; Qin, C.; Zhang, X. Energy transition and carbon neutrality: Exploring the non-linear impact of renewable energy development on carbon emission efficiency in developed countries. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2022, 177, 106002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Wu, Y.; He, H.; Delang, C.O.; Lu, J.; Yao, Z.; Dong, S. Urbanization and urban energy eco-efficiency: A meta-frontier super EBM analysis based on 271 cities of China. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2024, 101, 105089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.; Chen, L.; Yang, X. Evaluation and analysis of green efficiency of China’s coastal ports under the “double carbon” goal: Two improved DEA models with CO2 emissions. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2024, 26, 29099–29128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.; Wu, J.; Song, M.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, Y. Spatiotemporal regularity and spillover effects of carbon emission intensity in China’s Bohai Economic Rim. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 740, 140184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Y.; Khan, S.U.; Deng, Y.; Zhao, M. Spatiotemporal heterogeneity, convergence and its impact factors: Perspective of carbon emission intensity and carbon emission per capita considering carbon sink effect. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2022, 92, 106699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Gu, L.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X.; Song, Y. Research on carbon emission efficiency space relations and network structure of the Yellow River Basin City cluster. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 12235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Li, L.; Wang, Q. The impact of energy efficiency on carbon emissions: Evidence from the transportation sector in 30 Chinese provinces. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2022, 82, 103880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Q.; Xue, L.; Zhang, H.; Chen, P.; Yang, J.; Niu, B. Spatiotemporal analysis of carbon emission efficiency across economic development stages and synergistic emission reduction in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 377, 124609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuang, B.; Lu, X.; Zhou, M.; Chen, D. Provincial cultivated land use efficiency in China: Empirical analysis based on the SBM-DEA model with carbon emissions considered. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2020, 151, 119874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D. Exploratory study on the spatial relationship between emerging infectious diseases and urban characteristics: Cases from Korea. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 66, 102672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agovino, M.; Crociata, A.; Sacco, P.L. Proximity effects in obesity rates in the US: A spatial Markov chains approach. Soc. Sci. Med. 2019, 220, 301–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Chen, W.; Hu, T.; Yang, B.; Zeng, J. Regional carbon efficiency and corporate cash holdings: Evidence from China. Humanit. Soc. Sci. Commun. 2023, 10, 511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Liu, X.; Liu, X.; Li, X.; Liao, F.; Tang, H.; He, Q. Spatiotemporal evolution and influencing factors of carbon emission efficiency in China’s resource-based cities based on super-efficiency SBM–GML measurement and spatial econometric tests. Sustainability 2025, 17, 7540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Sun, Y.; Xu, D. Study on the spatial characteristics of the digital economy on urban carbon emissions. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 80261–80278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, G.; Sang, Y.; Gui, Q.; Li, J.; Yuan, J.; Zhu, K. Research on carbon emission efficiency and spatial-temporal factors in the transportation industry: Evidence from the Yangtze River Economic Belt. Glob. Nest J. 2024, 26, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, N.; Wang, S.; Dong, J.; Pan, X. Spatiotemporal evolution and influencing factors of carbon emission efficiency in western valley cities in China. Sustainability 2025, 17, 5025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Guo, R.; O’Connor, P.; Zhou, T.; Zhang, S.; Meng, H.; Ma, W. Embodied carbon transfers and employment-economic spillover effects in China’s inter-provincial trade. Front. Environ. Sci. 2023, 11, 1088997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, W.; Elshkaki, A. The spatial effect of industrial transfer on carbon emissions under firm location decision: A carbon neutrality perspective. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 330, 117139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhao, T.; Wang, J.; Guo, F.; Kan, X.; Yuan, R. Spatial analysis on carbon emission abatement capacity at provincial level in China from 1997 to 2014: An empirical study based on SDM model. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2019, 10, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Zeng, B. Urban technology transfer, spatial spillover effects, and carbon emissions in China. Sustainability 2024, 16, 9662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Pang, J. Promoting the achievement of carbon neutrality targets: Systematic review of research dimensions and measure methods on carbon equity in China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 58, 9912–9924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tone, K. Dealing with undesirable outputs in DEA: A slacks-based measure (SBM) approach. GRIPS Discuss. Pap. 2015, 1, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Song, C.; Liu, Q.; Song, J.; Jiang, Z.; Lu, Z.; Chen, Y. Land Use Efficiency in the Yellow River Basin in the Background of China’s Economic Transformation: Spatial-Temporal Characteristics and Influencing Factors. Land 2022, 11, 2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wu, G.; Zhang, J. The estimation of China’s provincial capital stock: 1952–2000. Econ. Res. J. 2004, 10, 35–44. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- GB/T 2589-2020; General Rules for Calculation of Comprehensive Energy Consumption. National Public Service Platform for Standards Information: Beijing, China, 2020. Available online: https://std.samr.gov.cn/gb/search/gbDetailed?id=B13990C15C2D5DDAE05397BE0A0A0D35 (accessed on 29 September 2020).
- Wu, J.; Guo, Z. Convergence analysis of China’s carbon emissions based on the continuous dynamic distribution approach. Stat. Res. 2016, 33, 54–60. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Wu, Q.; Wei, P.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, X.; Pang, C. Explore the mitigation mechanism of urban thermal environment by integrating geographic detector and standard deviation ellipse (SDE). Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katkovnik, V.; Shmulevich, I. Kernel density estimation with adaptive varying window size. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2002, 23, 1641–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phadkantha, R.; Tansuchat, R. Dynamic impacts of energy efficiency, economic growth, and renewable energy consumption on carbon emissions: Evidence from Markov Switching model. Energy Rep. 2023, 9, 332–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Gallo, J. Space-time analysis of GDP disparities among European regions: A Markov chains approach. Int. Reg. Sci. Rev. 2004, 27, 138–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, D.; Lei, Y.; Li, L.; Song, W. Carbon emission efficiency and spatial clustering analyses in China’s thermal power industry: Evidence from the provincial level. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 156, 518–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Xiao, H.; Lv, Y.; Zhang, N. The effect of new-type urbanization on energy consumption in China: A spatial econometric analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 163, S299–S305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Wu, B.; Barry, M. Geographically and temporally weighted regression for modeling spatio-temporal variation in house prices. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2010, 24, 383–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Wu, J.; Sun, J. Analysis of disequilibrium and driving factors of carbon emission efficiency: Evidence from five major urban agglomerations in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 478, 143908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Dong, F.; Ji, Z. Evaluation of carbon emission efficiency and reduction potential of 336 cities in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 428, 139372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Sun, W.; Li, P.; Zhang, L.; Li, M. Differential characteristics of carbon emission efficiency and coordinated emission reduction pathways under different stages of economic development: Evidence from the Yangtze River Delta, China. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 330, 117018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, H.; Guo, B.; Liu, X.; Deng, C.; Zhao, Z.; Jang, X.; Li, Y. Characteristics and formation mechanism of carbon emission efficiency spatial correlation network: Perspective from Shandong Province. Ecol. Indic. 2025, 170, 112996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.; Yin, J.; Huang, Z. Study on the Carbon Emission Efficiency of Pearl River Delta Ports Based on the Super-SBM-GML Index Model. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Neural Computing for Advanced Applications, Guilin, China, 5–7 July 2024; Springer Nature: Singapore; pp. 263–277. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Zhao, M.; Li, R.; Su, M. Decomposition and decoupling analysis of carbon emissions from economic growth: A comparative study of China and the United States. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 197, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Chen, B.; Deng, H.; Du, H.; Yang, R.; Ju, L.; Liu, S. Analysis on the evolution law and influencing factors of Beijing’s power generation carbon emissions. Energy Rep. 2022, 8, 1689–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, E.; Qi, Q.; Chen, L.; Wu, X. The spatial-temporal patterns and multiple driving mechanisms of carbon emissions in the process of urbanization: A case study in Zhejiang, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 358, 131954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, L.; Jia, J.; Hu, W.; Zeng, H.; Chen, C.; Wu, B. Decomposition and decoupling analysis of CO2 emissions based on LMDI and two-dimensional decoupling model in Gansu Province, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 6013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Pan, X.; Li, C.; Song, J.; Zhang, J. Effects of China’s environmental policy on carbon emission efficiency. Int. J. Clim. Change Strateg. Manag. 2019, 11, 326–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Li, H. Have regional coordinated development policies promoted urban carbon emission efficiency? —Evidence from the urban agglomerations in the middle reaches of the Yangtze River. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 39618–39636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Dong, S.; Li, F.; Cheng, H.; Chi, Y.; Li, Z.; Li, Y. Interregional polarized and trickling-down effect of carbon emission space and the optimization policies: Case studies of the Jing-Jin-Ji region. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 370, 133426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiyan Municipal People’s Government. Notice on Issuing the Implementation Plan for the National Carbon Peaking Pilot (Shiyan). Available online: http://www.yrdcpcn.org.cn/c55951/20240807/i116369.phtml (accessed on 2 August 2024).
- Xianning Municipal Development and Reform Commission. The First Announcement of Environmental Impact Assessment for the Clean Energy Development Plan of Xianning City (2023–2035). Available online: http://fgw.xianning.gov.cn/zwdt/tzgg/202404/t20240425_3560508.shtml (accessed on 25 April 2024).
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).