Pedagogical Strategies for Teaching Environmental Literacy in Secondary School Education: A Systematic Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Theoretical Framework
2.1. Environmental Education (EE) and Environmental Literacy
2.2. Models of Teaching and Pedagogical Approaches
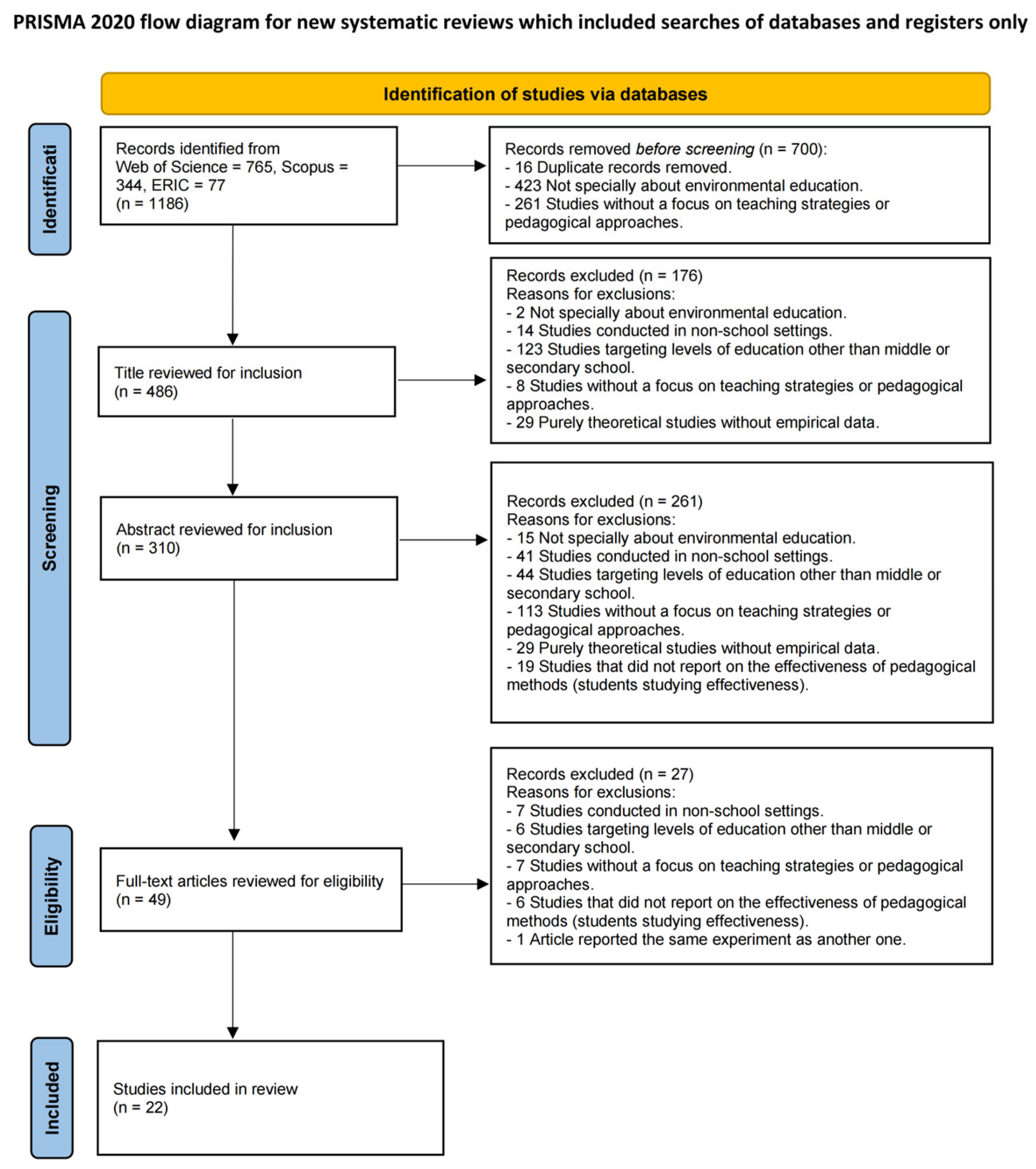
3. Research Methods
3.1. Research Design
3.2. Search Strategy
3.3. Data Analysis
4. Results
4.1. Characteristics of Studies
4.1.1. Geographical Distribution of Studies
4.1.2. Sample Characteristic
4.1.3. Research Methods and Instruments Used
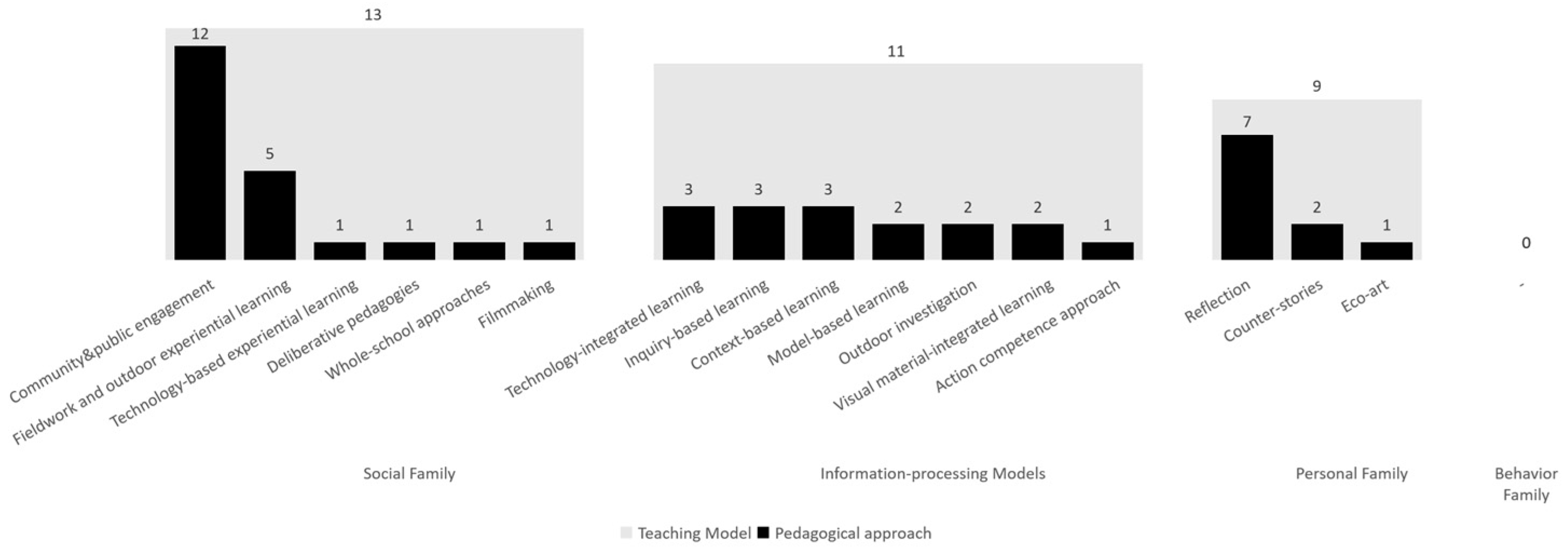
4.2. What Pedagogical Approaches Were Used to Foster Environmental Literacy in Secondary School Settings?
4.2.1. The Implementation of Social Family of Teaching Models in Classroom
4.2.2. The Implementation of Information-Processing Models of Teaching in Classroom
4.2.3. The Implementation of Personal Family of Teaching Models in Classroom
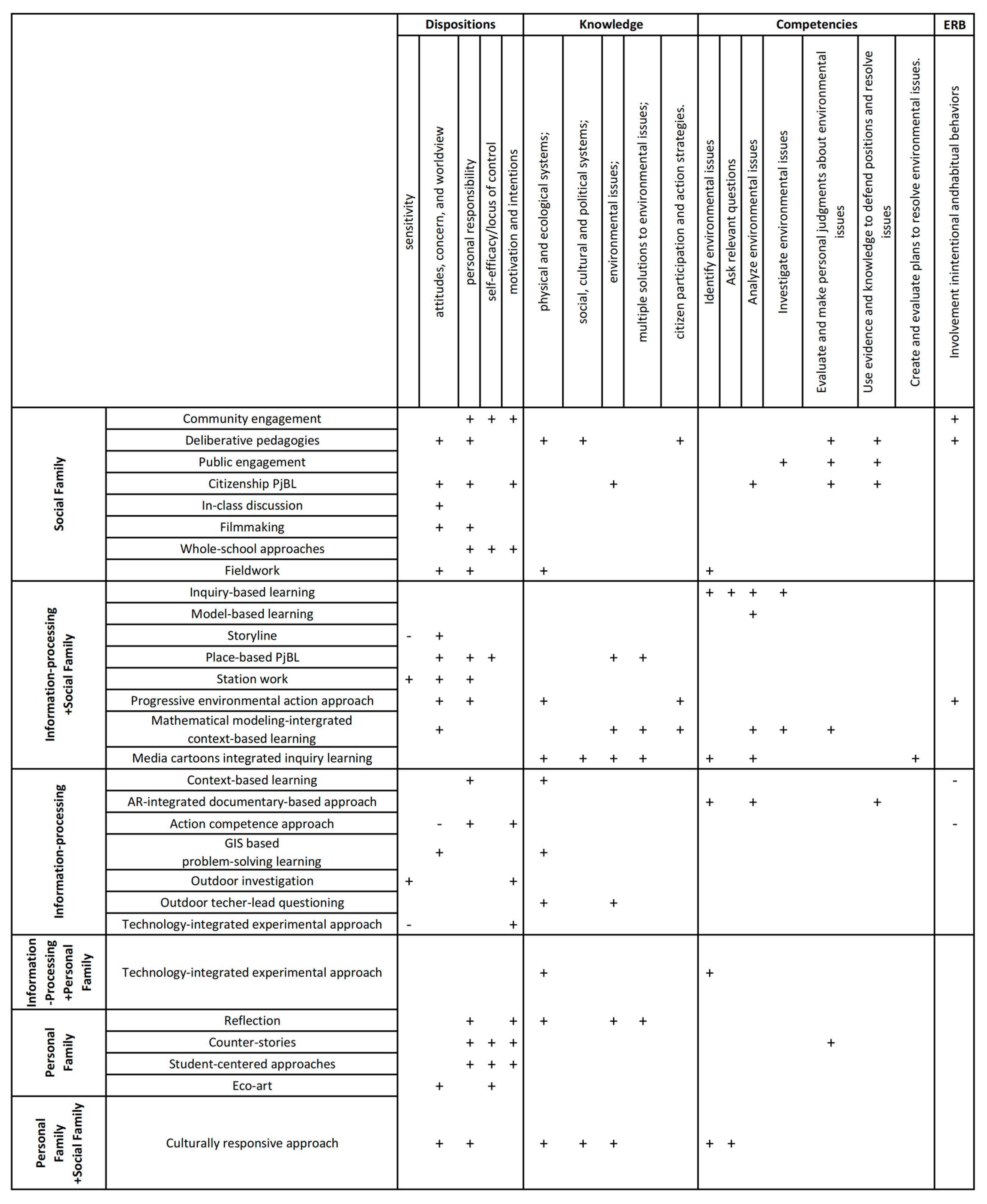
4.3. How Did Different Pedagogical Approaches Contribute to the Development of Students’ Environmental Literacy?
4.3.1. Pedagogical Approaches and the Knowledge Dimension of Environmental Literacy
4.3.2. Pedagogical Approaches and the Dispositional Dimension of Environmental Literacy
4.3.3. Pedagogical Approaches in Fostering Students’ Competencies Dimensions of Environmental Literacy
4.3.4. Pedagogical Approaches in Fostering Students’ ERB
5. Discussion
5.1. Pedagogical Orientation in Teaching EE During Secondary Education
5.2. Contributions of Different Pedagogical Models to Students’ Environmental Literacy
6. Recommendation
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| A-B | Attitude-Behavior |
| ESD | Education for Sustainable Development |
| EE | Environmental education |
| ERB | Environmentally responsible behavior |
| GIS | Geographic information systems |
| GAP | Global Action Programme |
| ICT | Information and communication technologies |
| NAAEE | North American Association for Environmental Education |
| PRISMA | Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses |
| PISA | Programme for International Student Assessment |
| UNESCO | United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization |
| VR | Virtual reality |
| WSA | Whole-school approach |
References
- United Nations. Declaration of the United Nations Conference on the Human Environment; United Nations Environment Programme: Nairobi, Kenya, 1972; Available online: https://climatepositions.com/wp-content/uploads/2014/03/stockholm_declaration.pdf (accessed on 27 August 2025).
- Sterling, S. Living in the earth: Towards an education for our times. J. Educ. Sustain. Dev. 2010, 4, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNESCO. The Belgrade Charter: A Global Framework for Environmental Education; UNESCO: Paris, France, 1975; Available online: https://unesdoc.unesco.org/ark:/48223/pf0000017772 (accessed on 27 August 2025).
- UNESCO. Intergovernmental Conference on Environmental Education: Final Report; UNESCO: Paris, France, 1978; Available online: https://unesdoc.unesco.org/ark:/48223/pf0000032763 (accessed on 27 August 2025).
- United Nations. Agenda 21: Programme of Action for Sustainable Development; United Nations Conference on Environment & Development (UNCED): Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 1992; Available online: https://sustainabledevelopment.un.org/content/documents/Agenda21.pdf (accessed on 27 August 2025).
- UNESCO. Education 2030: Incheon Declaration and Framework for Action for the Implementation of Sustainable Development Goal 4; UNESCO: Paris, France, 2016; Available online: https://unesdoc.unesco.org/ark:/48223/pf0000245656 (accessed on 27 August 2025).
- Bianchi, G.; Pisiotis, U.; Cabrera Giraldez, M. GreenComp: The European Sustainability Competence Framework; European Union: Luxembourg, 2022; Available online: https://publications.jrc.ec.europa.eu/repository/handle/JRC128040 (accessed on 27 August 2025).
- Stern, M.J.; Powell, R.B.; Hill, D. Environmental education program evaluation in the new millennium: What do we measure and what have we learned? Environ. Educ. Res. 2013, 20, 581–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heimlich, J.E.; Ardoin, N.M. Understanding behavior to understand behavior change: A literature review. Environ. Educ. Res. 2008, 14, 215–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chawla, L. Significant Life Experiences Revisited: A Review of Research on Sources of Environmental Sensitivity. J. Environ. Educ. 1998, 29, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, N.M.; Lekies, K.S. Nature and the Life Course: Pathways from Childhood Nature Experiences to Adult Environmentalism. Child. Youth Environ. 2006, 16, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barker, M.; Rogers, L. “In, about and for”: Exploring the foundations of environmental education. Set Res. Inf. Teach. 2004, 2, 15–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevenson, R.B. Schooling and environmental education: Contradictions in purpose and practice. Environ. Educ. Res. 2007, 13, 139–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vesterinen, M.; Ratinen, I. Sustainability competences in primary school education–a systematic literature review. Environ. Educ. Res. 2024, 30, 56–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiek, A.; Withycombe, L.; Redman, C.L. Key competencies in sustainability: A reference framework for academic program development. Sustain. Sci. 2011, 6, 203–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acosta Castellanos, P.M.; Queiruga-Dios, A. From environmental education to education for sustainable development in higher education: A systematic review. Int. J. Sustain. High. Educ. 2022, 23, 622–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strife, S. Reflecting on Environmental Education: Where Is Our Place in the Green Movement? J. Environ. Educ. 2010, 41, 179–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swarts, P. Humanising life orientation pedagogy through environmental education. S. Afr. J. Educ. 2023, 43, 1–12. Available online: https://scielo.org.za/pdf/saje/v43n1/10.pdf (accessed on 27 August 2025). [CrossRef]
- Ardoin, N.M.; Bowers, A.W.; Roth, N.W.; Holthuis, N. Environmental education and K-12 student outcomes: A review and analysis of research. J. Environ. Educ. 2017, 49, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNESCO. Education for Sustainable Development: A Roadmap; UNESCO: Paris, France, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalla, M.; Jerowsky, M.; Howes, B.; Borda, A. Expanding Formal School Curricula to Foster Action Competence in Sustainable Development: A Proposed Free-Choice Project-Based Learning Curriculum. Sustainability 2022, 14, 16315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jickling, B.; Wals, A.E. Globalization and environmental education: Looking beyond sustainable development. In Curriculum and Environmental Education; Routledge: London, UK, 2018; pp. 221–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopnina, H. Education for sustainable development (ESD): The turn away from ‘environment’ in environmental education? In Environmental and Sustainability Education Policy; Routledge: London, UK, 2018; pp. 135–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pihkala, P. Eco-Anxiety and Environmental Education. Sustainability 2020, 12, 10149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McBride, B.B.; Brewer, C.A.; Berkowitz, A.R.; Borrie, W.T. Environmental literacy, ecological literacy, ecoliteracy: What do we mean and how did we get here? Ecosphere 2013, 4, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD. PISA 2025 Science Framework; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2023; Available online: https://pisa-framework.oecd.org/science-2025/assets/docs/PISA_2025_Science_Framework.pdf (accessed on 27 August 2025).
- Hollweg, K.S.; Taylor, J.R.; Bybee, R.W.; Marcinkowski, T.J.; McBeth, W.C.; Zoido, P. Developing a Framework for Assessing Environmental Literacy; North American Association for Environmental Education: Washington, DC, USA, 2011; p. 122. Available online: https://cdn.naaee.org/sites/default/files/inline-files/devframewkassessenvlitonlineed.pdf (accessed on 27 August 2025).
- OECD. Trends Shaping Education 2025; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2025; Available online: https://www.oecd.org/en/publications/trends-shaping-education-2025_ee6587fd-en.html (accessed on 27 August 2025).
- Joyce, B.; Calhoun, E. Models of Teaching; Routledge: London, UK, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; Moher, D.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; McKenzie, J.E. PRISMA 2020 Explanation and Elaboration: Updated Guidance and Exemplars for Reporting Systematic Reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landis, J.R.; Koch, G.G. The Measurement of Observer Agreement for Categorical Data. Biometrics 1977, 33, 159–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tayne, K. Buds of Collectivity: Student Collaborative and System-Oriented Action towards Greater Socioenvironmental Sustainability. Environ. Educ. Res. 2022, 28, 216–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, K.D.; Burke, C.J.F.; Askari, E. Change Day: How a High School Environmental Justice Class Inspired Student Agency and Prompted Civic Action. Race Ethn. Educ. 2022, 27, 970–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, Y.W. Developing Youth toward Pluralistic Environmental Citizenship: A Taiwanese Place-Based Curriculum Case Study. Environ. Educ. Res. 2022, 29, 121–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basche, A.; Genareo, V.; Leshem, A.; Kissell, A.; Pauley, J. Engaging Middle School Students through Locally Focused Environmental Science Project-Based Learning. Nat. Sci. Educ. 2016, 45, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergman, B.G. Assessing Impacts of Locally Designed Environmental Education Projects on Students’ Environmental Attitudes, Awareness, and Intention to Act. Environ. Educ. Res. 2015, 22, 480–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindgren, S.; Morris, K.; Price, A. Designing Environmental Storylines to Achieve the Complementary Aims of Environmental and Science Education through Science and Engineering Practices. J. Environ. Educ. 2021, 52, 239–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yucel, E.O.; Ozkan, M. Development and Implementation of an Instructional Design for Effective Teaching of Ecosystem, Biodiversity, and Environmental Issues. Educ. Sci. Theory Pract. 2015, 15, 1051–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadjichambis, A.C.; Paraskeva-Hadjichambi, D.; Georgiou, Y. Evaluating a Novel Learning Intervention Grounded in the Education for Environmental Citizenship Pedagogical Approach: A Case Study from Cyprus. Sustainability 2022, 14, 1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harness, H.; Drossman, H. The Environmental Education through Filmmaking Project. Environ. Educ. Res. 2011, 17, 829–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Youssfi, S.; Ben Filali, I.; El Hammoumi, M.M. Teaching for a Sustainable Future: Implementing Education for Sustainability in a Moroccan High School. Int. Rev. Educ. 2024, 70, 979–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, D.; Ginns, I. Implementing a Context-Based Environmental Science Unit in the Middle Years: Teaching and Learning at the Creek. Teach. Sci. 2015, 61, 26–36. Available online: https://search.informit.org/doi/10.3316/informit.493423842304125 (accessed on 27 August 2025).
- Torsdottir, A.E.; Olsson, D.; Sinnes, A.T.; Wals, A. The Relationship between Student Participation and Students’ Self-Perceived Action Competence for Sustainability in a Whole School Approach. Environ. Educ. Res. 2024, 30, 1308–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schönfelder, M.L.; Bogner, F.X. How to Sustainably Increase Students’ Willingness to Protect Pollinators. Environ. Educ. Res. 2017, 24, 461–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Loinaz, G.; Ametzaga-Arregi, I.; Palacios-Agundez, I. ICT Tools and Citizen Science: A Pathway to Promote Science Learning and Education for Sustainable Development in Schools. J. Biol. Educ. 2022, 58, 609–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vygotsky, L.S. Thought and Language; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2012; Volume 29. [Google Scholar]
- Bruner, J. Acts of Meaning: Four Lectures on Mind and Culture; Harvard University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1990; Volume 3. [Google Scholar]
- Çakirlar-Altuntaş, E.; Levent Turan, S. Effectiveness of Documentary-Based Augmented Reality Application in Teaching Environmental Problems. J. Biol. Educ. 2023, 59, 4–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurniawan, E.; Syifauddin, M.; Sholeh, M.; Sriyanto; Sari, S.N. Environmental Problem-Solving Learning Model with Geographic Information System-Based Learning Media. Int. J. Environ. Impacts 2024, 7, 381–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmäing, T.; Grotjohann, N. Environmental Education in Teaching Science on the Wadden Sea Ecosystem: What Are the Effects on Environmental Psychological Constructs? Environ. Educ. Res. 2022, 29, 232–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gürbüz, R.; Çalik, M. Intertwining Mathematical Modeling with Environmental Issues. Probl. Educ. 21st Cent. 2021, 79, 412–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toledo, M.; Yangco, R.; Espınosa, A. Media Cartoons: Effects on Issue Resolution in Environmental Education. Int. Electron. J. Environ. Educ. 2014, 4, 19–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottlieb, D.; Vigoda-Gadot, E.; Haim, A. Encouraging Ecological Behaviors among Students by Using the Ecological Footprint as an Educational Tool: A Quasi-Experimental Design in a Public High School in the City of Haifa. Environ. Educ. Res. 2013, 19, 844–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cermak, M.J. Hip-Hop, Social Justice, and Environmental Education: Toward a Critical Ecological Literacy. J. Environ. Educ. 2012, 43, 192–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsekoleng, T.K.; Tomé Awshar, M. Improved Attitudes towards Littering through Progressive Action Research Activities in an Environmental Education Context. Asia-Pac. J. Teach. Educ. 2020, 50, 51–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbah, M.F.; Ezegwu, C. The Decolonisation of Climate Change and Environmental Education in Africa. Sustainability 2024, 16, 3744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourn, D.; Tarozzi, M. Pedagogy of Hope for Global Social Justice: Sustainable Futures for People and the Planet; Bloomsbury Academic: London, UK, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, H.; Krishna, K. Climate Change Education in Indian Schooling: Examining the Perspectives of Environmental Educators. Int. Res. Geogr. Environ. Educ. 2025, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevenson, R.B.; Brody, M.; Dillon, J.; Wals, A.E.J. International Handbook of Research on Environmental Education, 1st ed.; Routledge: London, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wals, A.E.J. Transgressive Learning, Resistance Pedagogy and Disruptive Capacity Building as Levers for Sustainability. New Visions for Higher Education Towards 2030—Part 2: Transitions: Key Topics, Key Voices [Online Report]; GUNI Global University Network for Innovation: Barcelona, Spain, 2023; Available online: https://www.guni-call2action.org/wp-content/uploads/2023/05/Arjen-E.J.-Wals.pdf (accessed on 27 August 2025).
- De Young, R. Changing Behavior and Making it Stick. Environ. Behav. 1993, 25, 485–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burn, S.M.; Oskamp, S. Increasing Community Recycling with Persuasive Communication and Public Commitment. J. Appl. Soc. Psychol. 1986, 16, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monroe, M.C.; Plate, R.R.; Oxarart, A.; Bowers, A.; Chaves, W.A. Identifying Effective Climate Change Education Strategies: A Systematic Review of the Research. Environ. Educ. Res. 2017, 25, 791–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Z.; Wang, Q.; Normand, R.; Zhang, X. Using Global Competence as a Pedagogical Approach to Teach Sustainable Development Goals in Higher Education. Int. J. Sustain. High. Educ. 2025, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisk, E.; Larson, K.L. Educating for sustainability: Competencies & practices for transformative action. J. Sustain. Educ. 2011, 2, 1–20. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/228620687 (accessed on 27 August 2025).
- Shepardson, D.P.; Choi, S.; Niyogi, D.; Charusombat, U. Seventh grade students’ mental models of the greenhouse effect. Environ. Educ. Res. 2011, 17, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, T.; Dierkes, P. Connecting Students to Nature—How Intensity of Nature Experience and Student Age Influence the Success of Outdoor Education Programs. Environ. Educ. Res. 2016, 23, 937–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chawla, L. Childhood Nature Connection and Constructive Hope: A Review of Research on Connecting with Nature and Coping with Environmental Loss. People Nat. 2020, 2, 619–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Dimension | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Knowledge | What you know about: physical and ecological systems; social, cultural and political systems; environmental issues; multiple solutions to environmental issues; citizen participation and action strategies. |
| Dispositions | How you respond to environmental issues: sensitivity; attitudes, concern, and worldview; personal responsibility; self-efficacy/locus of control; motivation and intentions. |
| Competencies | What skills and abilities you may call upon and express for specific purposes: identify environmental issues; ask relevant questions; analyze environmental issues; investigate environmental issues; evaluate and make personal judgments about environmental issues; use evidence and knowledge to defend positions and resolve issues; create and evaluate plans to resolve environmental issues. |
| Environmentally responsible behavior (ERB) | How you act, individually and collectively, to solve and prevent environmental problems: the point at which competencies, knowledge, and dispositions are brought to bear within a particular context. |
| Teaching Models | Description | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Information-processing models | Models designed to enhance learners’ capacity to acquire, organize, and retrieve information through structured cognitive operations. | Inductive learning Scientific inquiry Concept attainment |
| The social family of models | Models that utilize social interaction as the primary mechanism for constructing shared understanding and collective knowledge. | Group investigation Cooperative inquiry Role playing |
| The personal family of models | Models that prioritize the individual’s affective development and self-actualization through personalized learning experiences. | Non-directive teaching Inquiry training |
| The behavioral family of models | Models based on behavior modification principles that shape learning through systematic reinforcement and task analysis. | Explicit teaching of comprehension Mastery learning Direct instruction |
| Domain | Inclusion Criteria |
|---|---|
| Publication type | Peer-reviewed empirical studies (qualitative, quantitative, or mixed methods). |
| Language & Date | Published in English between 2010–2024. |
| Educational level | Focused on secondary education (lower or/and high secondary education). |
| Focus of study | Addressed environmental education (EE) or education for sustainable development (ESD). |
| Intervention | Investigated teaching strategies, pedagogical approaches, or instructional models. |
| Outcomes | Reported outcomes related to environmental literacy. |
| Domain | Exclusion Criteria |
|---|---|
| Educational context | Studies outside formal school contexts (community programs, workshops, corporate training). |
| Focus of study | Articles not addressing pedagogy (e.g., purely curriculum design without teaching strategies). |
| Intervention | Theoretical papers with no empirical data. |
| Outcomes | Studies not reporting outcomes linked to environmental literacy. |
| Screening Stage | Agreement % | Cohen’s κ |
|---|---|---|
| Title | 88% | 0.82 |
| Abstract | 88% | 0.82 |
| Full-Text | 94% | 0.91 |
| Category | Subcategory | No. of Studies | Percentage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Region | United States | 7 | 31.8% |
| Asia | 7 | 31.8% | |
| Europe | 5 | 22.7% | |
| Africa | 2 | 9.1% | |
| Australia | 1 | 4.5% | |
| Sample Size | <100 | 13 | 59.1% |
| ≥100 | 9 | 40.9% | |
| Methods | Mixed methods | 10 | 45.5% |
| Qualitative | 7 | 31.8% | |
| Quantitative | 5 | 22.7% | |
| Instruments | Questionnaires | 13 | 59.1% |
| Assessments | 6 | 27.3% | |
| Interviews | 6 | 27.3% | |
| Student work/products | 5 | 22.7% | |
| Field notes | 3 | 13.6% | |
| Participant observation | 3 | 13.6% | |
| Audio/video recordings | 3 | 13.6% | |
| Curricular artifacts produced by students | 2 | 9.1% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xiong, Z.; Song, Y.; Zhu, R. Pedagogical Strategies for Teaching Environmental Literacy in Secondary School Education: A Systematic Review. Sustainability 2025, 17, 9104. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17209104
Xiong Z, Song Y, Zhu R. Pedagogical Strategies for Teaching Environmental Literacy in Secondary School Education: A Systematic Review. Sustainability. 2025; 17(20):9104. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17209104
Chicago/Turabian StyleXiong, Ziyin, Yuye Song, and Ruizhi Zhu. 2025. "Pedagogical Strategies for Teaching Environmental Literacy in Secondary School Education: A Systematic Review" Sustainability 17, no. 20: 9104. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17209104
APA StyleXiong, Z., Song, Y., & Zhu, R. (2025). Pedagogical Strategies for Teaching Environmental Literacy in Secondary School Education: A Systematic Review. Sustainability, 17(20), 9104. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17209104








