Performance of Electrocoagulation Process with Copper Electrodes for Tannery Wastewater Treatment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Wastewater Characteristics
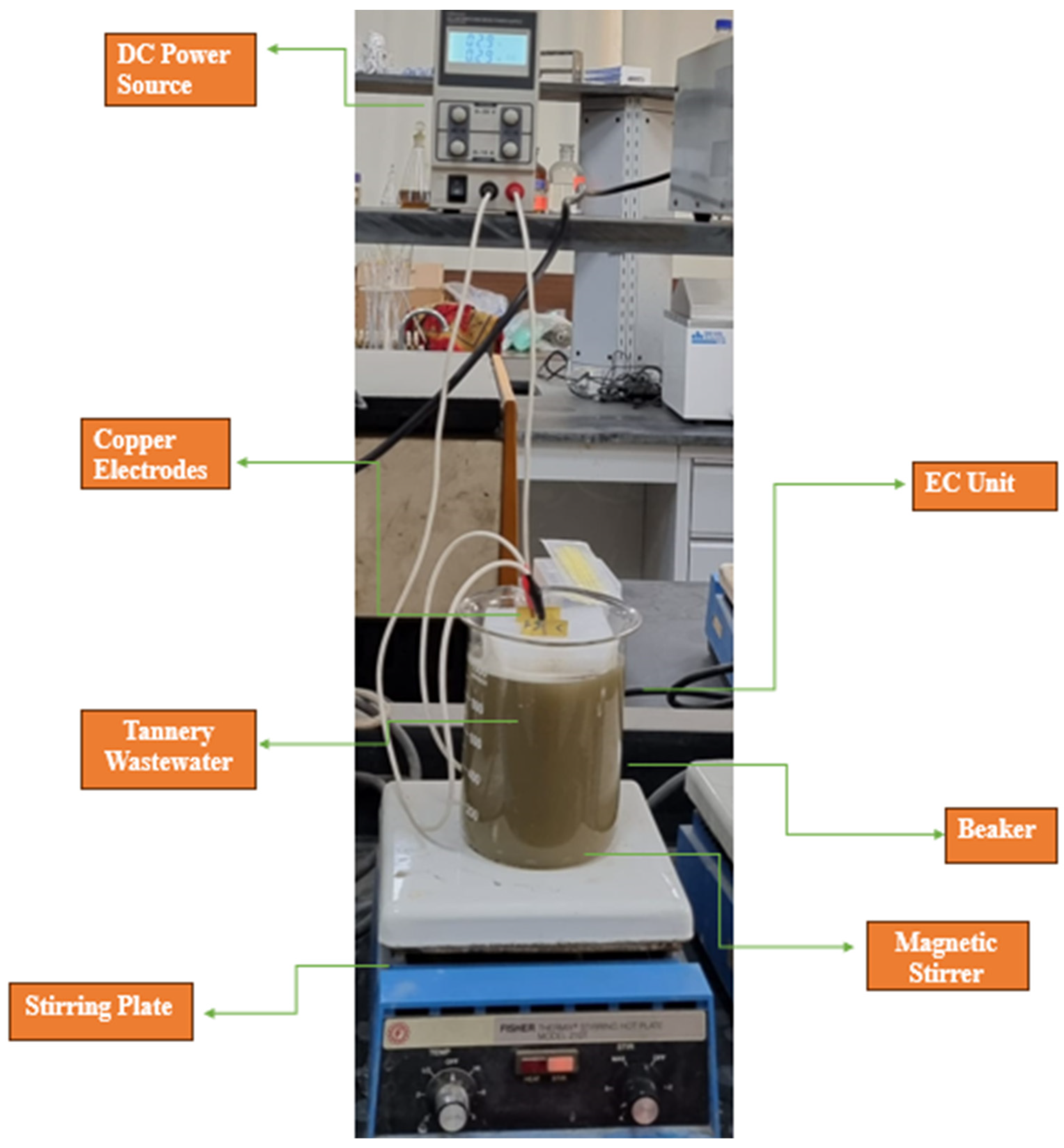
2.2. Setup and Operation of Cu-EC
2.3. Analysis of Samples and Calculations
3. Results
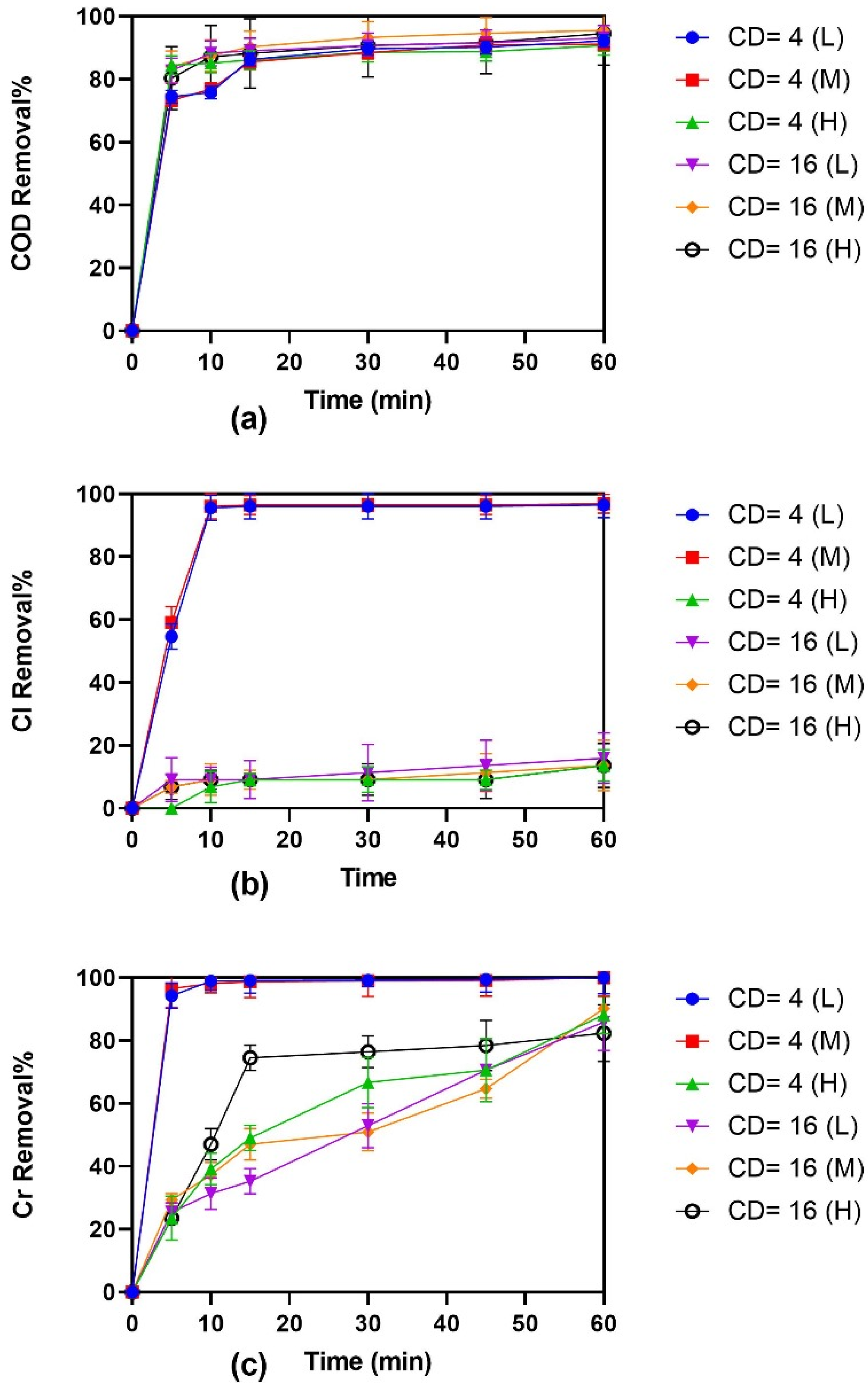
3.1. Effects of Stirring Speeds on EC for Treatment of Tannery Wastewater
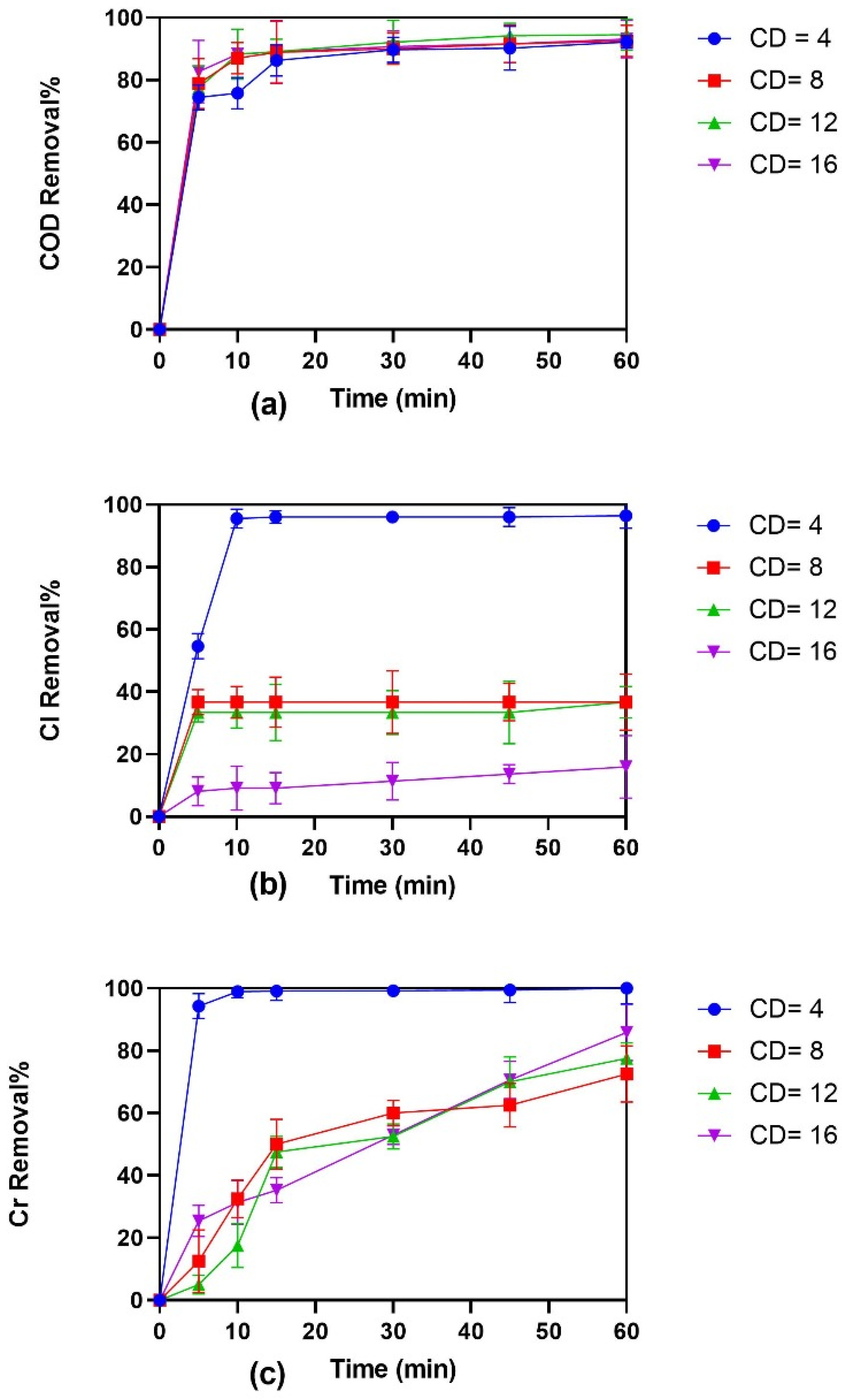
3.2. Effect of CD on EC for Treatment of Tannery Wastewater
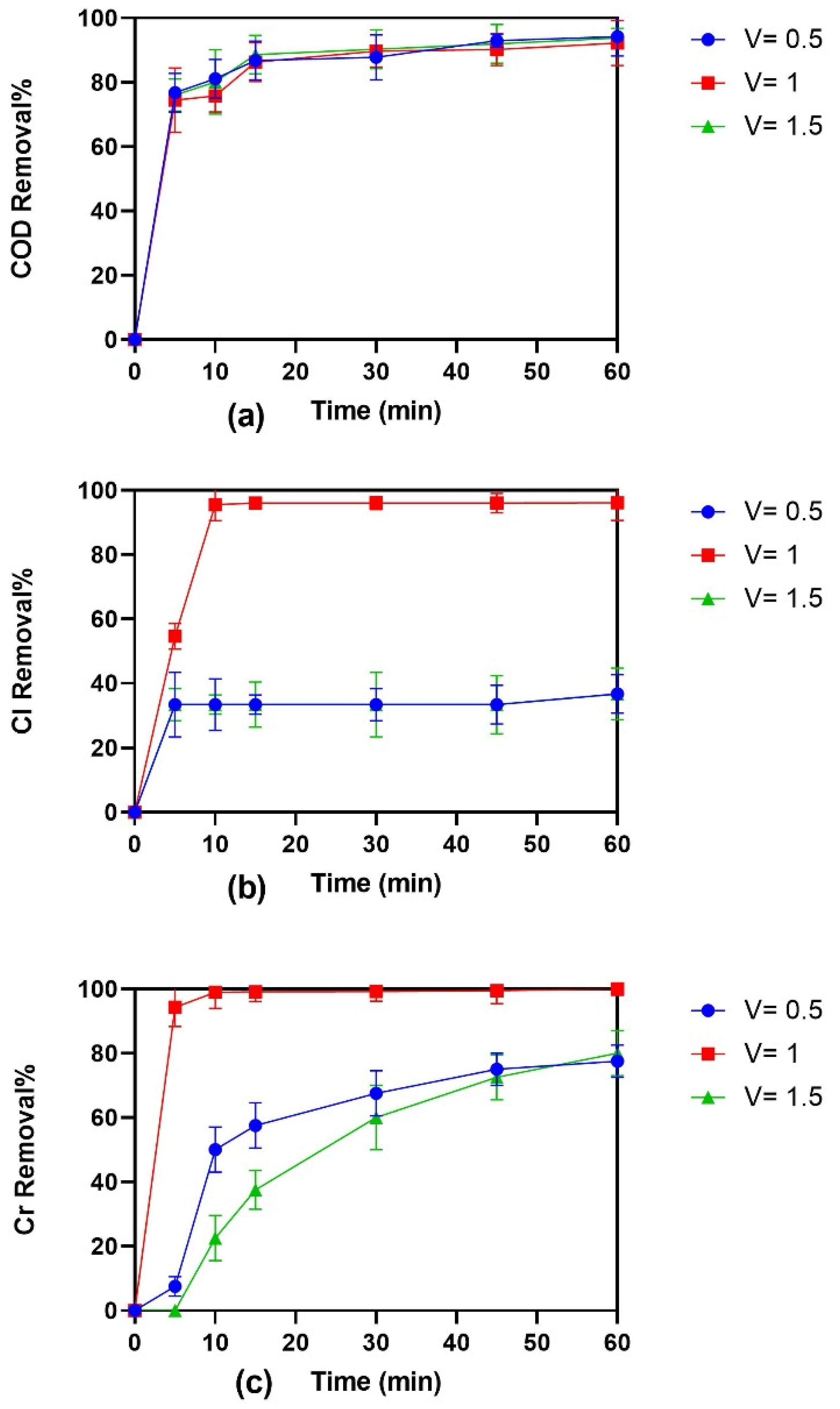
3.3. Effect of Volume on EC for Treatment of Tannery Wastewater
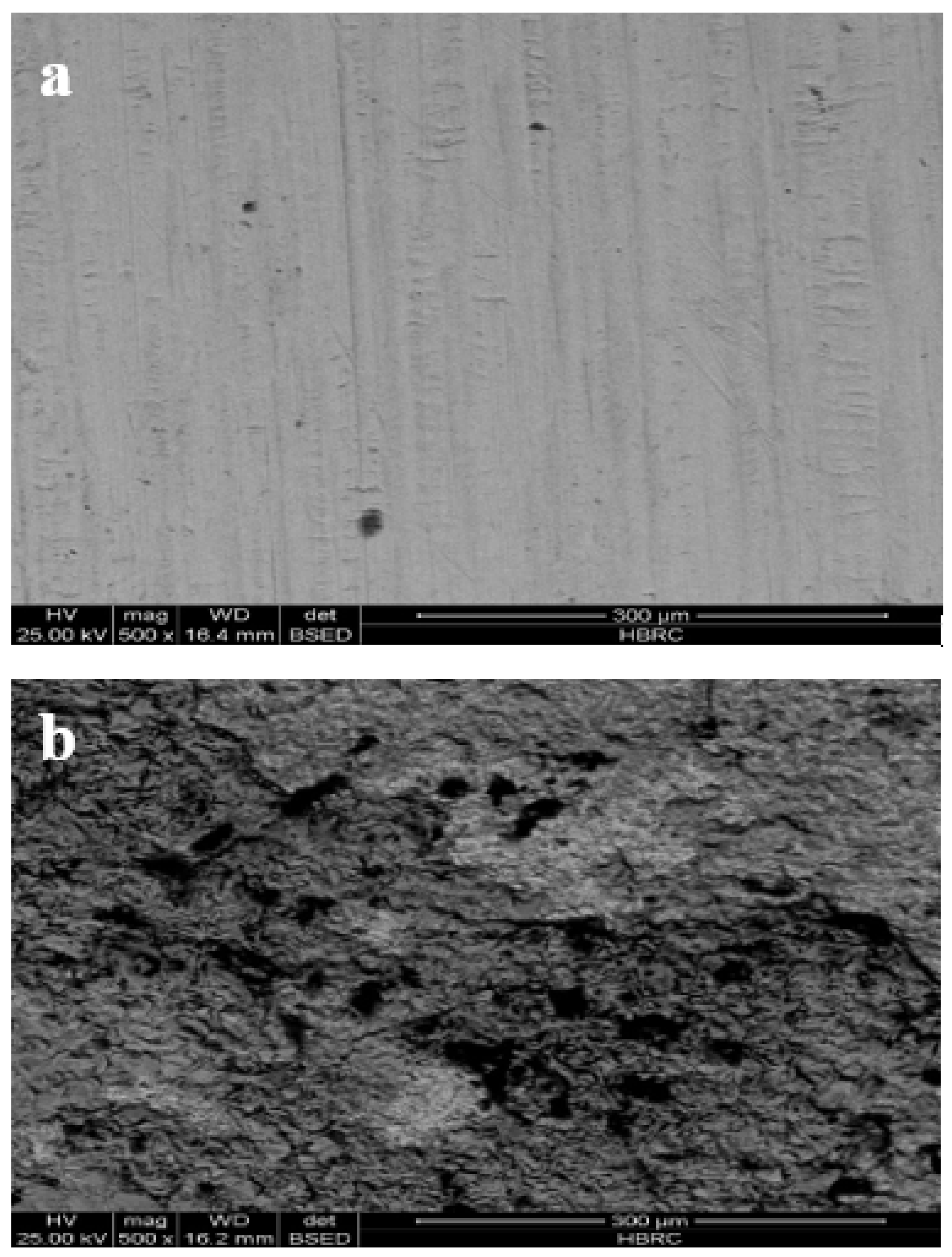
3.4. Electrode Morphology
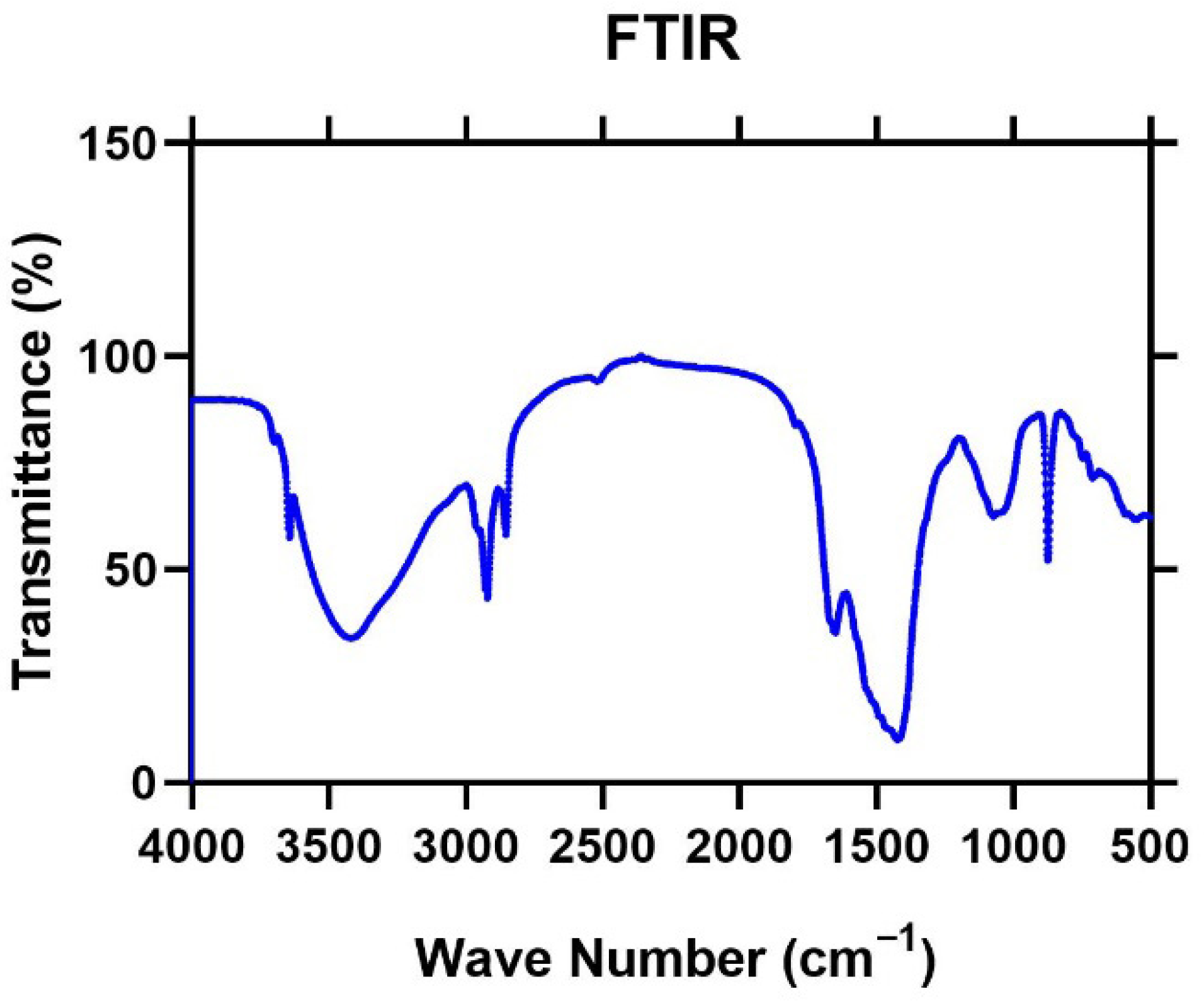
3.5. Characterization of the Generated By-Products
3.6. Electrical Energy Consumption and Cost Analysis
3.7. Kinetic Study
3.8. Comparison of the Results with the Literature
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bhardwaj, A.; Kumar, S.; Singh, D. Tannery effluent treatment and its environmental impact: A review of current practices and emerging technologies. Water Qual. Res. J. 2023, 58, 128–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusif, B.B.; Bichi, K.A.; Oyekunle, O.A.; Girei, A.I.; Garba, P.Y.; Garba, F.H. A Review of Tannery Effluent Treatment. Int. J. Appl. Sci. Math. Theory 2016, 2, 29–43. [Google Scholar]
- Nigam, M.; Mishra, P.; Kumar, P.; Rajoriya, S.; Pathak, P.; Singh, S.R.; Kumar, S.; Singh, L. Comprehensive technological assessment for different treatment methods of leather tannery wastewater. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 124686–124703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suman, H.; Sangal, V.K.; Vashishtha, M. Treatment of tannery industry effluent by electrochemical methods: A review. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 47, 1438–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irimia, O.; Gaspar, E.; Stanciu, M.; Moșneguțu, E.; Bârsan, N. Optimizing Nitrogen and Phosphorus Removal from Wastewater in the Context of a Sustainable Economy. Water 2024, 16, 1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jallouli, S.; Wali, A.; Buonerba, A.; Zarra, T.; Belgiorno, V.; Naddeo, V.; Ksibi, M. Efficient and sustainable treatment of tannery wastewater by a sequential electrocoagulation-UV photolytic process. J. Water Process Eng. 2020, 38, 101642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaspar, E.; Irimia, O.; Stanciu, M.; Barsan, N.; Mosnegutu, E. Strategies for a Sustainable Economy: Optimizing Processes for BOD, COD and TSS Removal from Wastewater. Water 2025, 17, 318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bingul, Z.; Irdemez, S.; Yildiz, Y.; Demircioglu, N. Organic and inorganic matter removal from tannery wastewater using the electrocoagulation process. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 20, 2171–2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaspar, E.; Munteanu, I.; Sintea, S. Removal of N and P in a Rotating Biological Contactor Plant: Case Study Agnita, Romania. Water 2022, 14, 3670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadaf, S.; Roy, H.; Fariha, A.; Rahman, T.U.; Tasnim, N.; Jahan, N.; Sokan-Adeaga, A.A.; Safwat, S.M.; Islam, M.S. Electrocoagulation-based wastewater treatment process and significance of anode materials for the overall improvement of the process: A critical review. J. Water Process Eng. 2024, 62, 105409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, P.; Yang, Z.; Zeng, G.; Yang, X.; Xu, H.; Wang, L.; Xu, R.; Xiong, W.; Ahmad, K. Electrocoagulation treatment of arsenic in wastewaters: A comprehensive review. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 317, 707–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moussa, D.T.; El-Naas, M.H.; Nasser, M.; Al-Marri, M.J. A comprehensive review of electrocoagulation for water treatment: Potentials and challenges. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 186, 24–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genawi, N.M.; Ibrahim, M.H.; El-Naas, M.H.; Alshaik, A.E. Chromium removal from tannery wastewater by electrocoagulation: Optimization and sludge characterization. Water 2020, 12, 1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahreen, A.; Jami, M.S.; Ali, F. Role of electrocoagulation in wastewater treatment: A developmental review. J. Water Process Eng. 2020, 37, 101440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naje, A.S.; Abbas, S.A. Electrocoagulation technology in wastewater treatment: A review of methods and applications. Civ. Environ. Res. 2013, 3, 29–42. [Google Scholar]
- Bazrafshan, E.; Mohammadi, L.; Ansari-Moghaddam, A.; Mahvi, A.H. Heavy metals removal from aqueous environments by electrocoagulation process—A systematic review. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2015, 13, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishna B, R.; Bhuvaneshwari, S.; Majeed, F.; P, A.S. Development and applicability of Aluminium—Copper alloy electrodes for dairy wastewater treatment. J. Water Process Eng. 2022, 48, 102915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mia, M.A.S.; Nur-E-Alam, M.; Ahmad, F.; Alam, M.Z.; Rahman, M.M. Treatment of tannery wastewater by electrocoagulation technology. J. Sci. Innov. Res. 2017, 6, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarei, A.; Biglari, H.; Mobini, M.; Dargahi, A.; Ebrahimzadeh, G.; Narooie, M.R.; Mehrizi, E.A.; Yari, A.R.; Mohammadi, M.J.; Baneshi, M.M.; et al. Disinfecting poultry slaughterhouse wastewater using copper electrodes in the electrocoagulation process. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2018, 27, 1907–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayar, S.; Yildiz, Y.S.; Yilmaz, A.E.; Irdemez, S. The effect of stirring speed and current density on removal efficiency of poultry slaughterhouse wastewater by electrocoagulation method. Desalination 2011, 280, 103–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.R.; Parikh, S.P.; Prajapati, A.K. Copper electrode for the removal of chromium from dyestuff industries effluent by electrocoagulation: Kinetic study and operating cost. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2022, 43, 1652–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaled, B.; Wided, B.; Béchir, H.; Elimame, E.; Mouna, L.; Zied, T. Investigation of electrocoagulation reactor design parameters effect on the removal of cadmium from synthetic and phosphate industrial wastewater. Arab. J. Chem. 2019, 12, 1848–1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, M.S.; Garg, A. Performance of electro-Fenton process for the treatment of synthetic sulphidic spent caustic waste stream generated from petroleum refineries. Chemosphere 2024, 346, 140572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Li, H.; Yang, G. Configuration, anion-specific effects, diffusion, and impact on counterions for adsorption of salt anions at the interfaces of clay minerals. J. Phys. Chem. C 2016, 120, 14621–14630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Qodah, Z.; AL-Rajabi, M.M.; Da’na, E.; Al-Shannag, M.; Bani-Melhem, K.; Assirey, E. Continuous Electrocoagulation Processes for Industrial Inorganic Pollutants Removal: A Critical Review of Performance and Applications. Water 2025, 17, 2639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.Y.; Raharjo, A.; Hsu, L.H.; Shih, Y.J.; Huang, Y.H. Electrocoagulation of tetrafluoroborate (BF4−) and the derived boron and fluorine using aluminum electrodes. Water Res. 2019, 155, 362–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prajapati, A.K.; Chaudhari, P.K.; Pal, D.; Chandrakar, A.; Choudhary, R. Electrocoagulation treatment of rice grain based distillery effluent using copper electrode. J. Water Process Eng. 2016, 11, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suhan, M.B.K.; Shuchi, S.B.; Anis, A.; Haque, Z.; Islam, M.S. Comparative degradation study of remazol black B dye using electro-coagulation and electro-Fenton process: Kinetics and cost analysis. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2020, 14, 100335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akter, S.; Suhan, M.B.K.; Islam, M.S. Recent advances and perspective of electrocoagulation in the treatment of wastewater: A review. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2022, 17, 100643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanafy, R.; Mohamed, N.Y.; Zaher, K.; Safwat, S.M. Techno-economic feasibility of real tannery wastewater treatment using electrocoagulation and electro-Fenton like processes with titanium electrodes. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2025, 60, 1805–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawarkar, C.J.; Salkar, V.D. Solar powered Electrocoagulation system for municipal wastewater treatment. Fuel 2019, 237, 222–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, D.; Nandi, B.K. Removal of Hexavalent Chromium from Wastewater by Electrocoagulation (EC): Parametric Evaluation, Kinetic Study and Operating Cost. Trans. Indian Inst. Met. 2020, 73, 2053–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| pH | 8 ± 0.5 |
| COD (mg·L−1) | 786 ± 50 |
| Cr (mg·L−1) | 51 ± 10 |
| Cl (mg·L−1) | 1099 ± 70 |
| TDS (mg·L−1) | 1801 |
| Conductivity (μS/cm) | 2686 |
| Unit | EC After 10 Min | EC After 60 Min | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Energy Consumption | (kWh/m3) | 0.147 | 1.659 |
| Electrode Consumption | (kg/m3) | 0.057 | 0.341 |
| Sludge Production | (kg sludge/m3) | 0.371 | 1.045 |
| Total Operating Cost | (US$/m3) | 0.463 | 2.622 |
| COD Removal | % | 75.8 | 92.2 |
| Cr Removal | % | 98.9 | >99 |
| Cl Removal | % | 95.5 | 96.5 |
| Current Density | qe (mg L−1) | k2 (L mg−1 min−1) | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 4 mA cm−2 | 50.96 | 0.284 | 0.999 |
| 8 mA cm−2 | 36.90 | 0.018 | 0.994 |
| 12 mA cm−2 | 39.53 | 0.015 | 0.992 |
| 16 mA cm−2 | 43.80 | 0.012 | 0.988 |
| Current Density | k1 (min−1) | R2 |
|---|---|---|
| 4 mA cm−2 | 0.0512 | 0.989 |
| 8 mA cm−2 | 0.0184 | 0.976 |
| 12 mA cm−2 | 0.0161 | 0.972 |
| 16 mA cm−2 | 0.0095 | 0.965 |
| Pollutants Removed | Wastewater Type | Type of Treatment | Electrode Material (Anode/Cathode) | Operating Conditions | Removal Efficiency (%) and Power | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| COD | Rice grain-based distillery effluent | EC | Copper/Copper | pH = 3.5 CD = 89.3 A/m2 | COD = 80% EEC = 11.42 Wh/L | [27] |
| COD–Color–Dye– Turbidity | Textile wastewater | EC | Stainless steel | pH = 3 CD = 10 mA/cm2 Time = 50 min | COD = 76% Color = 94% Dye = 95% Turbidity = 95% | [28] |
| Diclofenac (DCF)–Carbamazepine (CBZ)–Amoxicillin (AMX) | Pharmaceutical wastewater | EC | Aluminum/Stainless steel | pH = 7.24 CD = 0.3 mA/cm2 Time = 3 h | DCF = 45% CBZ = 40% AMX = 46% | [29] |
| COD–Chlorides (Cl)–Chromium (Cr) | Tannery | EC | Titanium/Titanium | pH = 8 CD = 12 mA/cm2 Mixing Speed = 780 rpm (M) Volume Reactor = 1.5 L Time = 60 min | COD = 97.96% Cl = 15.92% Cr = 98.23% EEC = 8.05 kWh/m3 OPEX = 5.91 US$/m3 | [30] |
| COD–Chromium–Total nitrogen–Phosphate–Sulfate | Tannery | EC | Aluminum/Aluminum | CD = 1.2 mA/cm2 Time = 25 min Stirring speed = 150 rpm | COD = 84% Chromium = 98% Total nitrogen = 68% Phosphate = 100% Sulfate = 79% EEC = 2.37 kWh/m3 | [8] |
| COD–Turbidity–TDS | Municipal wastewater | EC | Aluminum/Aluminum | pH = 7 COD = 260 mg·L−1 Turbidity (NTU) = 60 Conductivity = 2.4 ms/cm TDS = 1300 mg·L−1 | COD = 92.01% Turbidity = 93.97% TDS = 49.78% | [31] |
| Chromium | Synthetic | EC | Iron/Iron | pH = 4 COD = 43.103 mg·L−1 Cr concentration = 40 mg·L−1 Time = 60 mi | Cr = 99.4% EEC = 1.78 kWh/m3 | [32] |
| COD–Chlorides (Cl)–Chromium (Cr) | Tannery | EC | Copper/Copper | pH = 8 CD = 4 mA/cm2 Mixing Speed = 60 rpm (L) Volume Reactor = 1 L Time = 60 min | COD = 92.24% Cl = 96.45% Cr > 99% EEC = 1.66 kWh/m3 OPEX = 2.62 US$/m3 | This study |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hanafy, R.; Mohamed, N.Y.; Zaher, K.; Islam, M.S.; Safwat, S.M. Performance of Electrocoagulation Process with Copper Electrodes for Tannery Wastewater Treatment. Sustainability 2025, 17, 9031. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17209031
Hanafy R, Mohamed NY, Zaher K, Islam MS, Safwat SM. Performance of Electrocoagulation Process with Copper Electrodes for Tannery Wastewater Treatment. Sustainability. 2025; 17(20):9031. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17209031
Chicago/Turabian StyleHanafy, Radwa, Nouran Y. Mohamed, Khaled Zaher, Md. Shahinoor Islam, and Safwat M. Safwat. 2025. "Performance of Electrocoagulation Process with Copper Electrodes for Tannery Wastewater Treatment" Sustainability 17, no. 20: 9031. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17209031
APA StyleHanafy, R., Mohamed, N. Y., Zaher, K., Islam, M. S., & Safwat, S. M. (2025). Performance of Electrocoagulation Process with Copper Electrodes for Tannery Wastewater Treatment. Sustainability, 17(20), 9031. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17209031







