Abstract
This work presents an innovative approach to enhancing the performance of concrete with reclaimed asphalt pavement (RAP) aggregates using titanium dioxide (TiO2) nanoparticles. Traditional limestone coarse aggregates were partially replaced with 30% and 50% RAP aggregates; a subset of mixtures containing RAP aggregates was treated with TiO2 nanoparticles. The rheological, mechanical, and long-term properties of concrete, along with changes in its chemical composition following the addition of RAP and TiO2, were evaluated. Results revealed that using 30% and 50% RAP in concrete mixtures reduced their compressive strength by 18% and 27%, respectively. However, using TiO2 in those mixtures enhanced their compressive strength by 8.7% and 6.3%. Moreover, concrete with 50% RAP exhibited an 85% increase in water absorption (the highest among all mixtures) compared to the control. TiO2 treatment was most beneficial in the 30% RAP mixture, reducing its water absorption by 32.5% compared to its untreated counterpart. Additionally, the 30% RAP mixture treated with TiO2 showed the highest resistance to sulfates among modified mixtures, as its compressive strength decreased by 10.4% compared to a decrease of 23% in the strength of the untreated 30% RAP mixture. Statistical analysis using single-factor ANOVA showed that integrating RAP aggregates with or without the presence of TiO2 particles would significantly affect the concrete properties in terms of their population means. The t-test analysis, on the other hand, proved sufficient evidence that the mean values of the 30% RAP mixture treated with TiO2 would not differ significantly from the control in terms of its slump and water absorption properties. The chemical structure analysis revealed an increase in the Si-O-Si and Si-O functional groups when using TiO2 in RAP mixtures, suggesting improved hydration activity and accelerated C-S-H formation in the treated RAP mixtures. Moreover, distinct C-H peaks were witnessed in concrete with untreated RAP aggregates, resulting from the aged asphalt coating on the RAP, which weakened the bond between the RAP and the cementitious matrix.
1. Introduction
In recent years, sustainable construction has become the primary focus of researchers due to the escalating environmental concerns and the depletion of natural resources [1,2]. Natural aggregates, such as sand and gravel, which constitute the major components of concrete mixtures, are being depleted at an alarming rate due to excessive extraction [1,3]. Therefore, there is an urgent need to adopt alternative construction materials, particularly those derived from waste streams like construction and demolition waste (CDW), to conserve natural resources and reduce environmental pollution [4]. Among CDW, reclaimed asphalt pavement (RAP), generated during pavement rehabilitation and reconstruction, has significant potential as an aggregate replacement in concrete production [5]. RAP consists of aggregates coated with aged bitumen and has traditionally been reused in new asphalt mixtures [6]. In 2021 alone, approximately 94.6 million tons of RAP in the United States were reused in pavement construction, repurposing nearly 89 million tons of traditional aggregate [7,8]. Moreover, the use of RAP in asphalt mixtures has been associated with a net decrease in CO2 emissions of 2.6 million metric tons [7]. Therefore, the integration of RAP into concrete can also decrease the demand for natural aggregates and contribute to significant reductions in CO2 emissions associated with the production and transportation of conventional aggregates [9]. Nevertheless, RAP’s characteristics differ significantly from those of natural aggregates due to the aged asphalt coating, which adversely affects the mechanical and durability properties of concrete [9]. Specifically, the presence of asphalt coating in RAP aggregates resulted in concrete mixtures with lower specific gravities, higher porosities, reduced compressive strengths, and reduced bonding with the cement paste [10,11,12,13]. Accordingly, few researchers have attempted to enhance the performance of RAP–concrete mixtures using various mineral admixtures, such as fly ash, silica fume, and bagasse ash extracted from sugarcane [14,15,16,17,18]. Moreover, silica fume was the most effective among all mineral admixtures in minimizing the reduction in the RAP–concrete’s strength. For instance, Singh et al. [15] demonstrated that using 5% silica fume in concrete with 100% coarse RAP aggregates resulted in a 5% decrease in the compressive strength. In contrast, a 19% decrease in strength (compared to the control) was noticed when using 10% silica fume in concrete with 50% fine and 50% coarse RAP aggregates, as reported by Debbarma et al. [14]. The same study demonstrated that the use of 10% silica fume successfully reduced the water absorption and porosity of concrete with 50% fine and 50% coarse RAP aggregates by 13% and 5.6%, respectively [14]. Moreover, Singh et al. [15] reported a reduction of 46% in water absorption of RAP–concrete containing 100% coarse RAP when using 10% silica fume. However, all RAP–concrete mixtures that were investigated in previous research still suffer from strength reduction despite the use of mineral admixtures. Moreover, all previous studies have focused on enhancing RAP–concrete performance by employing traditional secondary cementitious materials, and an extensive review of the existing literature did not reveal any studies that used other chemical compounds. This highlights a critical gap in the literature and emphasizes the need for innovative approaches to enhance the performance of such mixtures.
One innovative material with significant potential for this purpose is titanium dioxide (TiO2), which is widely recognized for its beneficial photocatalytic properties and chemical stability [19]. Moreover, previous research has demonstrated the efficacy of TiO2 in enhancing concrete performance, as the integration of TiO2 particles into concrete mixtures at varying ratios has resulted in increased strength and improved long-term performance. For instance, Qudoos et al. [20], Nazari and Riahi [21], and Bragança et al. [22] reported a reduction in the water absorption of concrete when replacing cement with TiO2 in various ratios, ranging from 1 to 12%. Additionally, it was found that TiO2 particles can help reduce chloride penetration through concrete, and their efficacy increases with increasing dosage up to 5% [23]. Moreover, most studies agreed on the positive effect of TiO2 particles in increasing the concrete’s compressive strength, where an 18% increase was observed when using 1% TiO2 [21], a 38% increase when using 3% TiO2 [24], a 24% increase when using 10% TiO2 [25], and a 42% increase when using 6% TiO2 [26]. On the other hand, TiO2 was also employed to improve the properties of concrete containing waste materials, such as rubber and glass. The findings of Abdullah et al. [27] demonstrated the ability of TiO2 to reduce the water absorption and drying shrinkage of concrete containing fine rubber aggregates, as it strengthened the interfacial transition zone (ITZ) between the rubber and cement paste. Additionally, Baikerikar et al. [28] highlighted the role of TiO2 in enhancing the mechanical performance, acid and chloride resistance, and impermeability of concrete containing glass powder due to its ability to fill pores and densify the concrete structure.
Given the demonstrated advantages of TiO2 in concrete applications and the current challenges associated with RAP aggregates, this research investigates the integration of TiO2-treated RAP particles in concrete mixtures to replace traditional limestone coarse aggregates. Specifically, the study assesses the impact of TiO2 treatment on physical, mechanical, and long-term properties, as well as synergistic characteristics of RAP–concrete.
2. Experimental Design
2.1. Materials and Mix Formulations
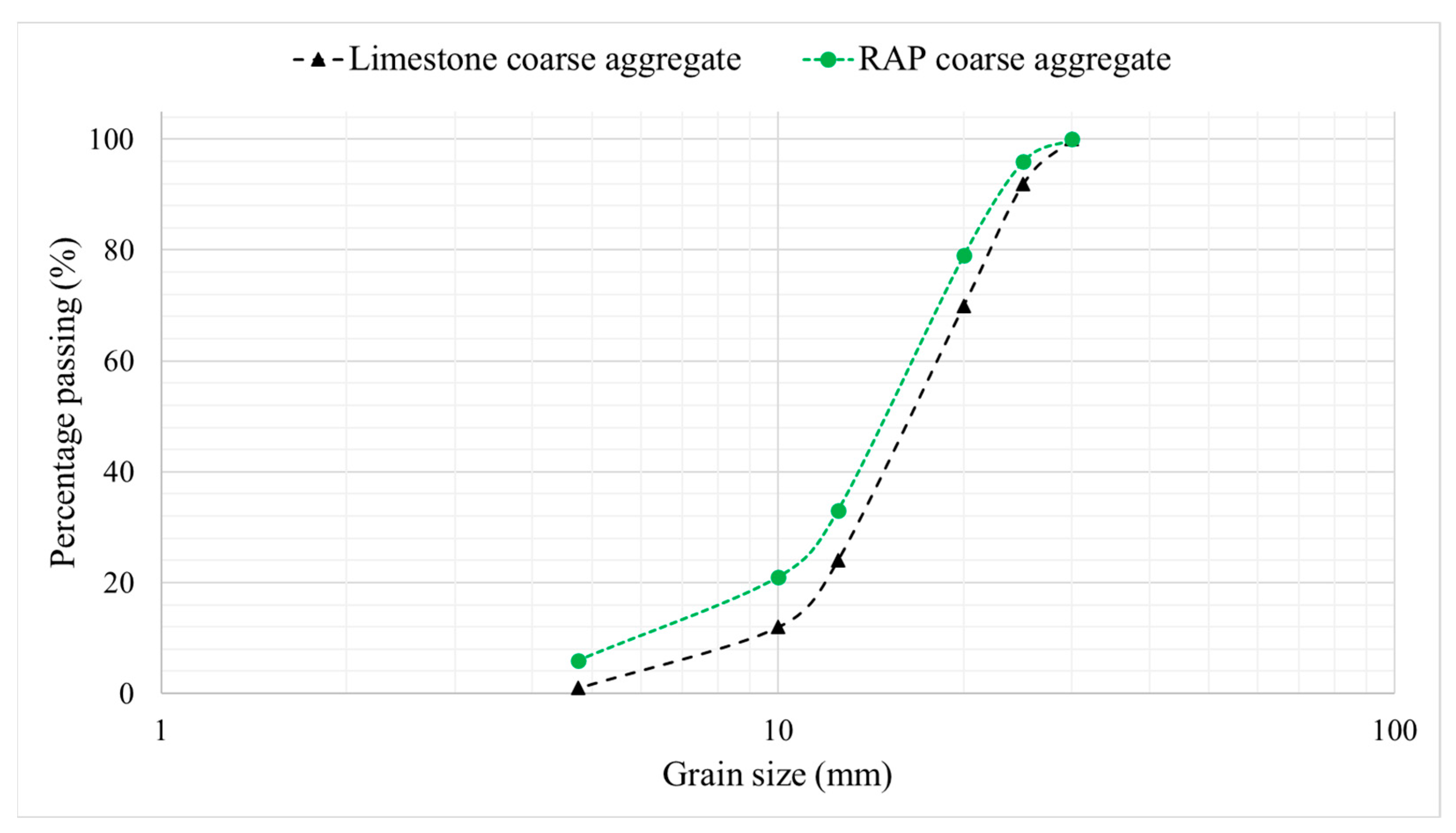
Ordinary Portland cement (CEM I 42.5 N), supplied by the Manaseer group, river sand fine aggregate with a maximum grain size of 2 mm, and limestone coarse aggregate with a maximum grain size of 20 mm were used to produce the concrete mixtures in this study. Moreover, the reclaimed asphalt pavement (RAP) was collected from a recently rehabilitated local road in Al-Karak, Jordan (Althanya-Alhawya road), which was milled to a depth of 50 mm. The collected RAP had an apparent specific gravity of 2.60, an SSD specific gravity of 2.46, a water absorption of 2.3%, and an asphalt content of 5.6% with a penetration of 28 dmm and a softening point of 60.3 °C. The pavement had approximately 12 years of aging under traffic and environmental exposure. The RAP was air-dried, crushed, and sieved to achieve the same gradation size as the used limestone coarse aggregate (Figure 1), conforming to ASTM C33 grading requirements, and it was incorporated into concrete at a 30% and 50% ratio of the weight of the coarse aggregate (replacing the limestone aggregate). Additionally, titanium dioxide (TiO2) nanoparticles with a size of 25 nm, supplied by Handan Yueci Advanced Materials Co., Ltd., China, were added into the concrete mixture by partially replacing cement at a dosage of 1% by weight. TiO2 nanoparticles were dry-mixed with the cement before their addition to the mixture. This is the optimal dosage of the material as recommended by previous research [27,28]. It is essential to note that, due to the associated toxicity risks of airborne nanoparticles, TiO2 powder was handled with the use of a fume hood, where researchers wore N95 respirators, nitrile gloves, and protective goggles. The entire dry mixing process was conducted in closed systems to minimize aerosolization. These procedures were carried out in accordance with the safety procedures outlined by Silva et al. [29] and Buzea and Pacheco [30], which focus on approaches to managing risks associated with the use of nanomaterials in construction laboratories.
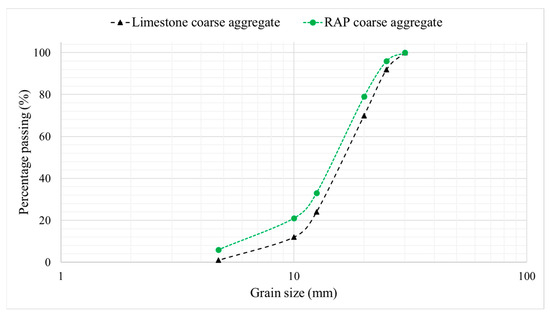
Figure 1.
Sieve analysis chart of the coarse limestone and RAP aggregates.
The physical characteristics and specifications of the used nano-TiO2 are illustrated in Table 1.

Table 1.
Specifications of the used TiO2.
Five concrete mixes were prepared, including a control mix (CL0) with 0% RAP, a mix containing 30% RAP (RAP30), a mix containing 50% RAP (RAP50), a mix containing 30% RAP and 1% TiO2 (RAPT30), and a mix containing 50% RAP and 1% TiO2 (RAPT50). After mixing, concrete was cast into 75 cube molds with a volume of 150 mm3. The tests were performed in triplicate, and the mean values were calculated to establish the reliability of the findings. After demolding, the mixes were cured in a water bath at a temperature of 22 ± 1 °C. The mix design and the quantities of used materials are illustrated in Table 2.

Table 2.
The adopted mix design.
2.2. Testing Methods
The slump cone test was utilized in this study to assess the workability of the designated concrete mixes following the guidelines of BS EN 12350-2 [31]. This test aimed to examine the consistency of mixtures in the presence of RAP and TiO2.
The mechanical properties of all the mixes were evaluated after 7 and 28 days using the compressive strength test, following the BS EN 12390-3 [32]. This test was accomplished using the Controls AUTOMAX 5 50-C4652 apparatus, where a loading rate of 1.2 MPa/min was applied to the test cubes.
Moreover, the permeability of concrete was assessed at 7 and 28 days, in accordance with the guidelines of BS 1881–122:2011 [33]. The concrete cubes were first dried in an oven at 110 ± 5 °C until a stable weight was reached. Afterwards, all cubes were submerged in a water bath, and their weights were taken at 24, 48, and 72 h intervals. The water absorption rate was determined using the following equation [34]:
where Md is the dry weight of the sample and Ms is the weight of the sample after soaking in water.
Furthermore, the resistance of concrete to acid attack was also evaluated as part of the durability testing program of the concrete mixtures, adhering to the procedure of ASTM C1898 [35]. The 28-day concrete cubes were immersed for 90 days in a 5% solution of sulfuric acid (H2SO4). Afterwards, all samples were dried at room temperature (23 ± 2 °C) for 3 days, followed by testing the loss in their compressive strength due to sulfate attack.
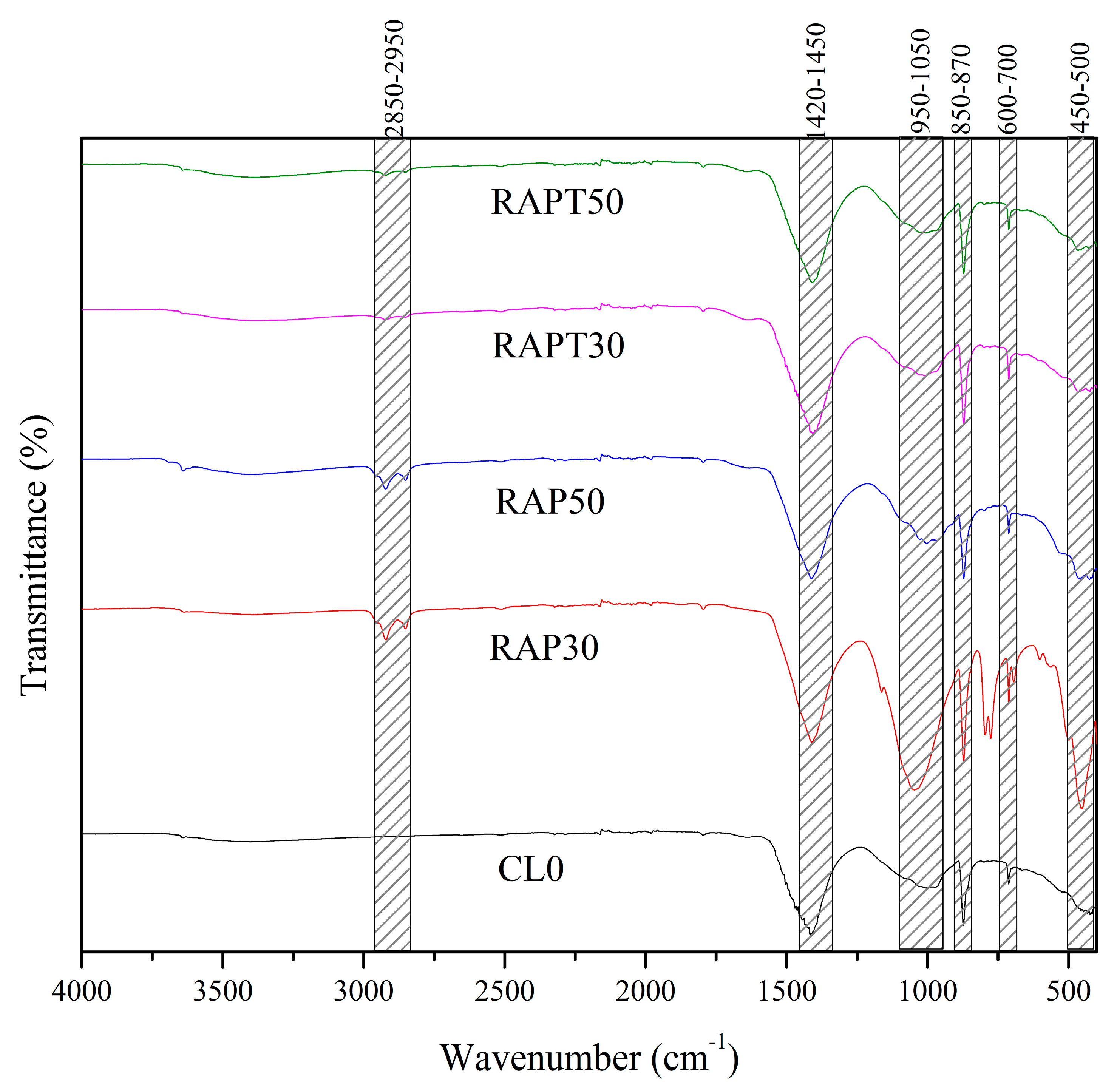
Attenuated total reflectance Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (ATR-FTIR) analysis was performed to investigate the synergistic effect of using RAP and TiO2 in the concrete mixes and their influence on the chemical structure of concrete. The test was performed using a PerkinElmer Spectrum Two FTIR apparatus equipped with a diamond/ZnSe ATR crystal across a wavenumber range of 4000 cm−1 to 400 cm−1. Concrete samples representing the five mixtures (CL0, RAP30, RAP50, RAPT30, and RAPT50) that were cured for 28 days were dried in an oven at 105 ± 5 °C for 48 h and then ground into a powder using an agate mortar (passing through a 75 μm sieve) to ensure suitable contact with the ATR crystal. All samples were analyzed using 32 scans at a 4 cm−1 resolution, followed by baseline correction of the spectra using SpectrumTM 10 software.
Statistically, the ANOVA single-factor was applied to investigate the significance among the concrete mixes at a 95% confidence level. The physical properties of all mixes were initially evaluated using this hypothesis in terms of their means, as follows:
The ANOVA analyses revealed that at least one concrete mix was statistically significant compared to the control mix. This observation was common for all measured properties of concrete (i.e., consistency, water absorption, compressive strength, and sulfate attack). A deep investigation was further performed through the “t-test of two population means” to assess the significance between each modified mix and the control. This was analyzed individually for each tested property.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Consistency of Concrete
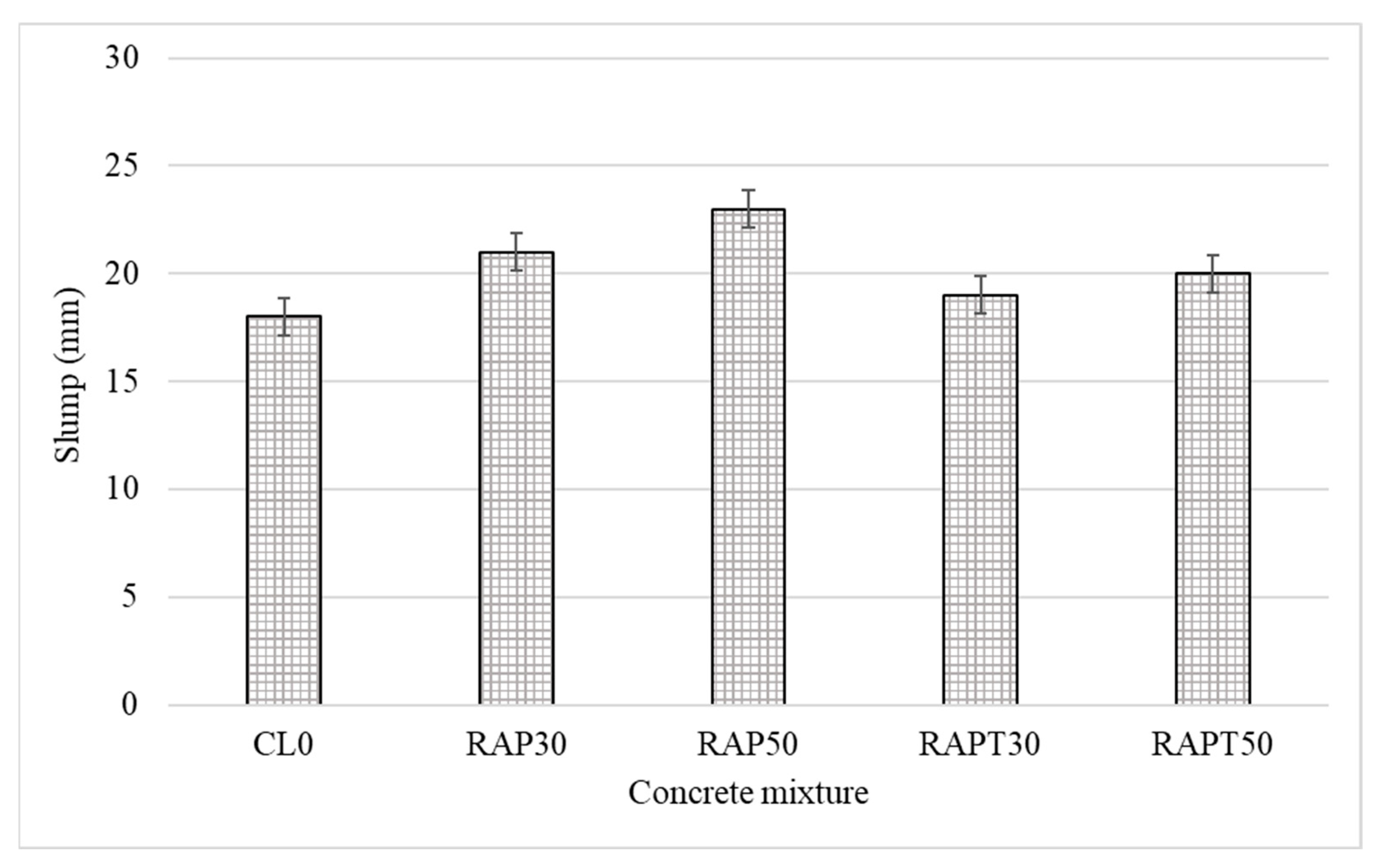
The slump cone test was performed to evaluate the effect of RAP and TiO2 on the workability of all concrete mixtures. As shown in Figure 2, replacing limestone coarse aggregates with RAP aggregates reduced the water demand of concrete, with the workability of the RAP30 and RAP50 mixtures increasing by 16.7% and 27.8%, respectively. This is due to the hydrophobic nature of the RAP aggregates resulting from the asphalt coating surrounding them [14,16,36,37]. However, the use of TiO2 particles in the RAP mixtures resulted in increases in the workability of the RAPT30 and RAPT50 mixtures of 5.6% and 11%, respectively, compared to the control, and reductions in it of 9.5% and 13%, respectively, compared to their untreated counterparts. It is clear that the water demand of concrete increases with the presence of TiO2, owing to the high surface area of TiO2 particles, which allows more water to be absorbed by the mixture [28]. Moreover, TiO2 particles may act as a filler in the mix, allowing for more structural packing and eliminating voids between the RAP aggregates and the cement matrix, which results in reduced workability.
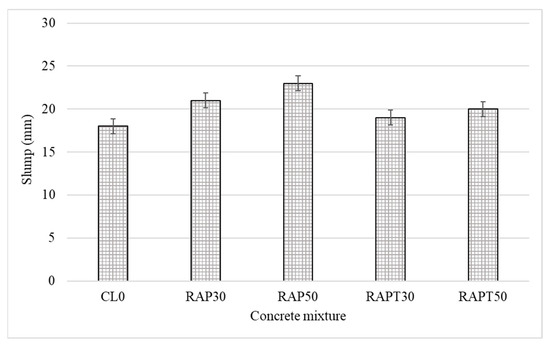
Figure 2.
The workability of fresh concrete mixtures.
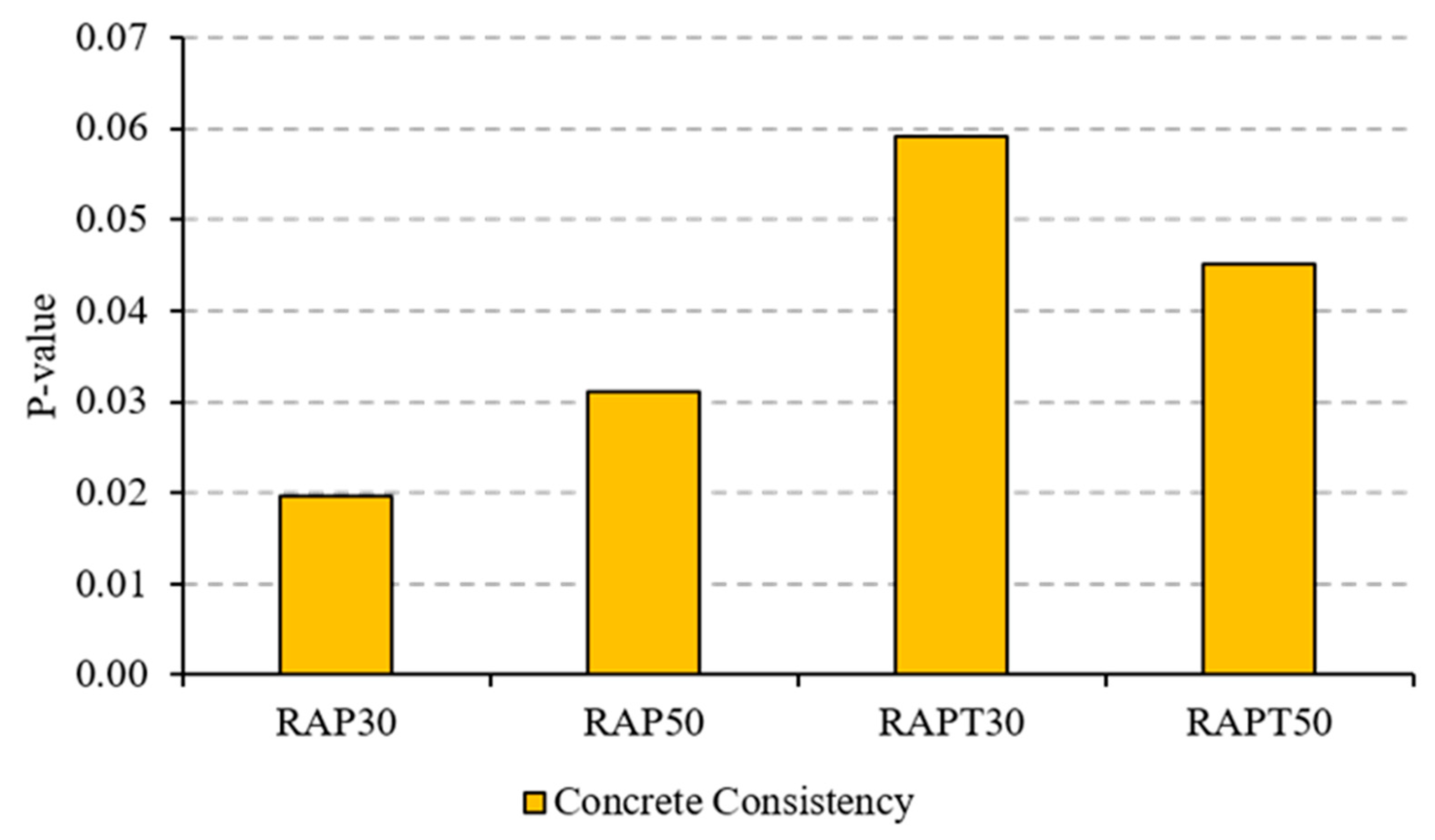
Figure 3 clarifies that the mean values of all mixes were statistically significant compared to the control mix, except for the RAPT30 mix, where its population mean was equal to the control (i.e., p-value > 0.05).
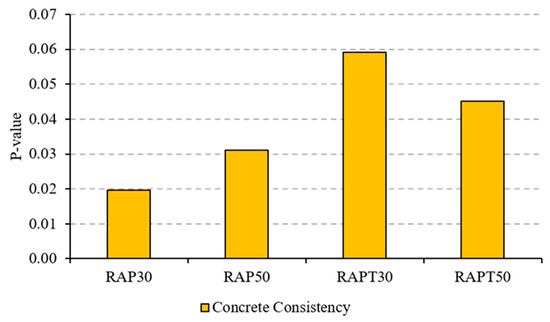
Figure 3.
“p-value” of concrete consistency.
3.2. Water Absorption of Concrete
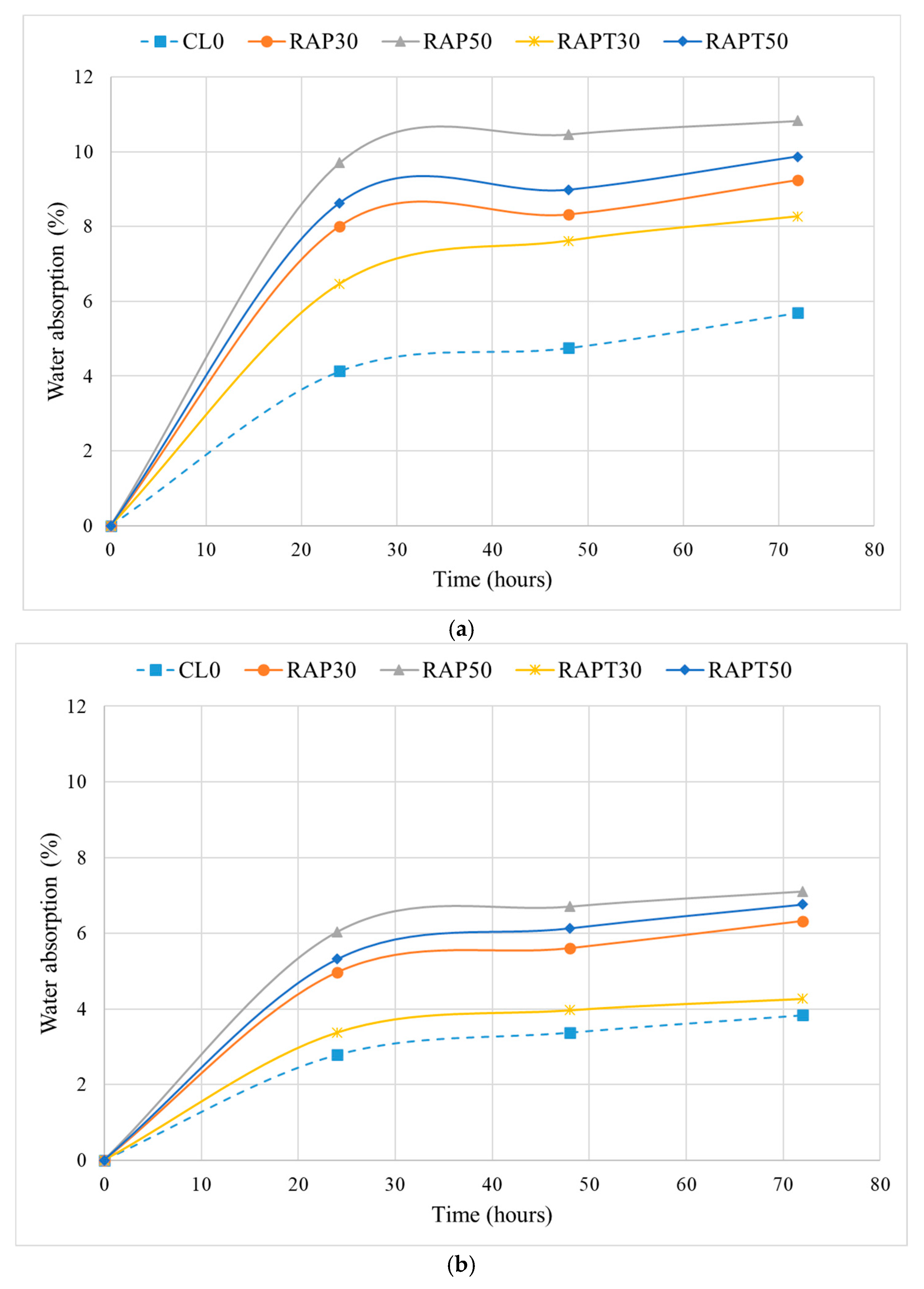
The water absorption results of concrete at 7 and 28 days are depicted in Figure 4. As illustrated in Figure 4a, all RAP concrete mixtures, either with or without TiO2, demonstrated higher absorption levels than the control at 7 days. Moreover, among the untreated mixtures, the RAP50 mixture achieved the highest absorption rate of 10.8%, followed by RAP30 with an absorption rate of 9.2%. This is attributed to the high porosity of these mixtures and the weak interfacial transition zone (ITZ) between the cement paste and RAP, which increases the concrete’s permeability [16]. Following the addition of TiO2 to the RAP mixtures, a reduction in water absorption of 10% and 9% was observed in the RAPT30 and RAPT50 mixtures, respectively, compared to their untreated counterparts. This can be attributed to the pore-refining influence of TiO2 particles, which densify the concrete microstructure and hinder water ingress through the pores [19].
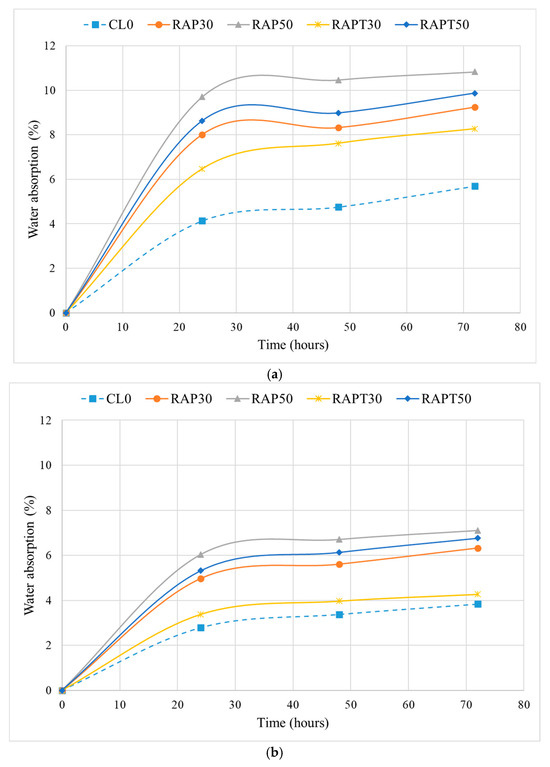
Figure 4.
Results of the water absorption test at (a) 7 and (b) 28 days.
Additionally, Figure 4b revealed an increase in water absorption rates at 28 days, with the RAP50 mixture attaining the highest value of 7%, the control achieving the lowest value of 3.8%, and the RAP30 mixture attaining a moderate rate of 6.3%. The increase in the water absorption levels of the RAP mixtures is attributed to the high porosity of RAP in the presence of the aged asphalt coating. This further confirms the results presented in earlier studies, which show that the use of RAP in concrete mixtures increases their water absorption due to the adverse effect of the asphalt coating on the bond strength between the RAP and the cementitious matrix [14,15,18].
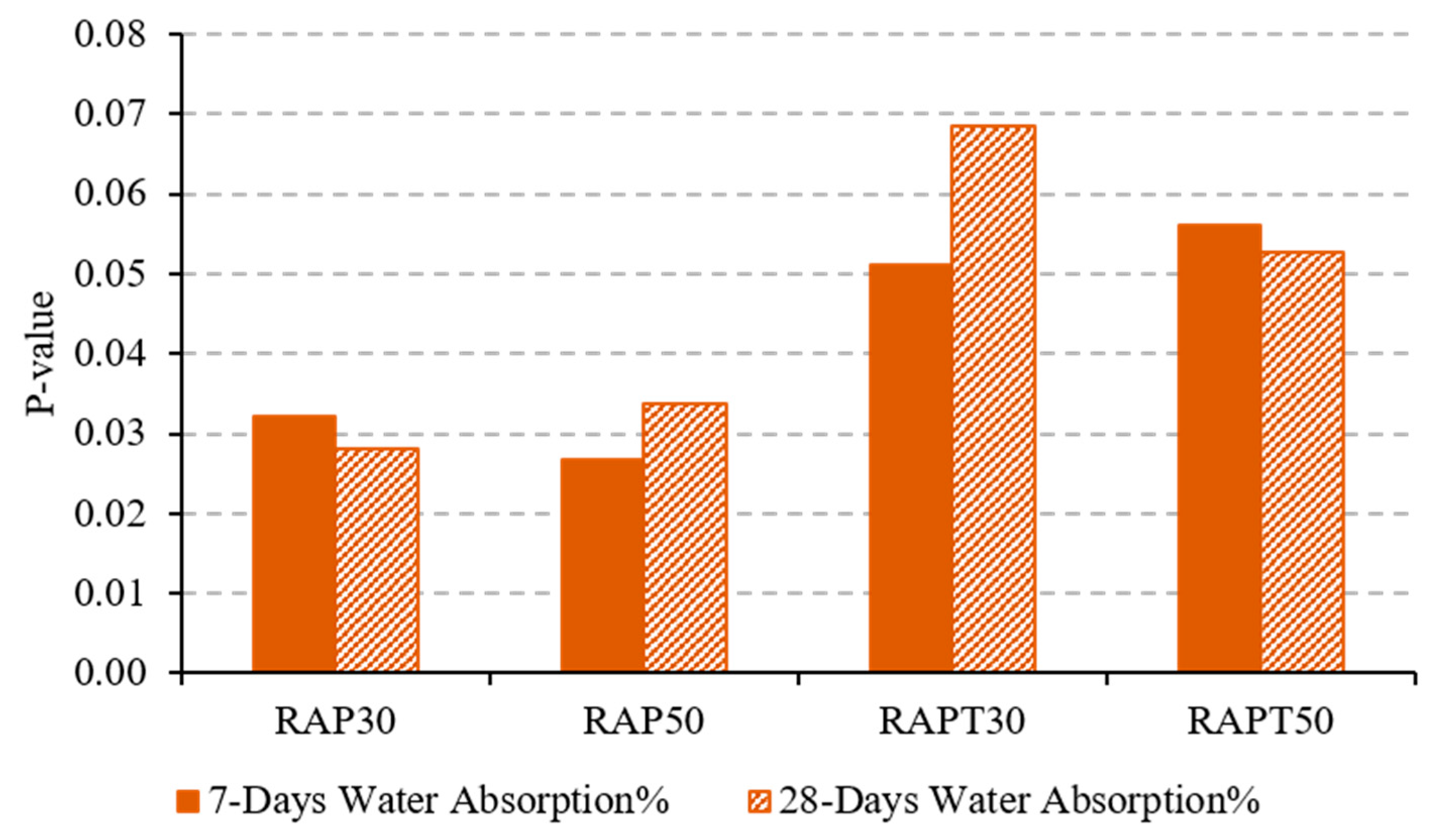
Interestingly, there was also an increase in the permeability of the RAP mixtures containing TiO2 at 28 days (Figure 4b). However, this increase was less pronounced than that in the RAP mixtures without TiO2, as TiO2 particles helped attenuate the adverse effect of incorporating RAP aggregates. The use of TiO2 particles in the RAPT30 and RAPT50 mixtures reduced their water absorption rate by 32.5% and 4.8%, respectively, compared to their untreated counterparts. This is due to the filling effect of TiO2 particles on the pore structure, resulting in a dense concrete that hinders water absorption [28]. Another reason for the improvement of the concrete’s impermeability is the nucleation effect of TiO2, which endorses the precipitation of calcium hydroxide (CH) and calcium silicate hydrates (C-S-H) and accelerates the hydration of cement, strengthening the ITZ between the RAP and the cement matrix [38]. The resulting “p-value” of the water absorption of concrete, shown in Figure 5, confirms these findings. It is evident that the population means of all mixes containing TiO2 at both ages were insignificant compared to the control mean. In contrast, the means of the other mixes exhibited differences.

Figure 5.
“p-value” of water absorption tests.
3.3. Compressive Strength of Concrete
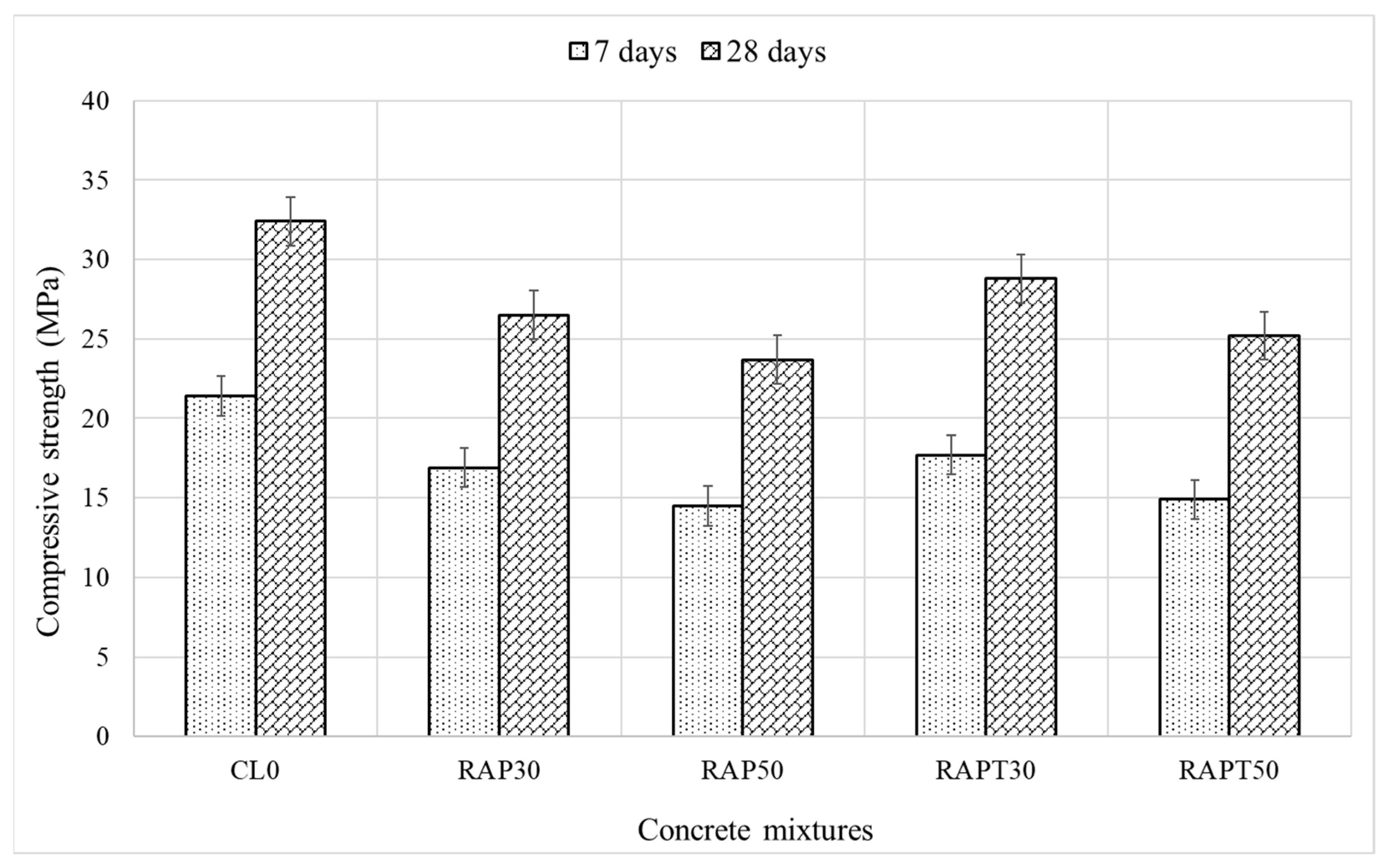
Figure 6 presents the results of the compressive strength test at 7 and 28 days. It is evident that the use of RAP as aggregates in concrete, regardless of its percentage, had a negative impact on the compressive strength of concrete. Furthermore, incorporating 30% and 50% RAP aggregates decreased the 7-day compressive strength of concrete by 21% and 32.2%, correspondingly, compared to the control. This is ascribed to the poor bond strength between the RAP aggregates and the other components of concrete, the inherent heterogeneity of RAP, and the lower stiffness of RAP compared to limestone, reducing the concrete’s resistance to compression [17]. On a positive note, employing TiO2 in RAP mixtures alleviated the adverse impact of RAP on the strength, as the compressive strength of the RAPT30 and RAPT50 mixtures was enhanced by 4.7% and 2.8%, respectively. Although TiO2 does not retain pozzolanic properties, it can increase the rate of the hydration activity owing to its nucleation effect, which facilitates the formation of CH and C-S-H gel, ultimately leading to higher early strength of the concrete [39,40].
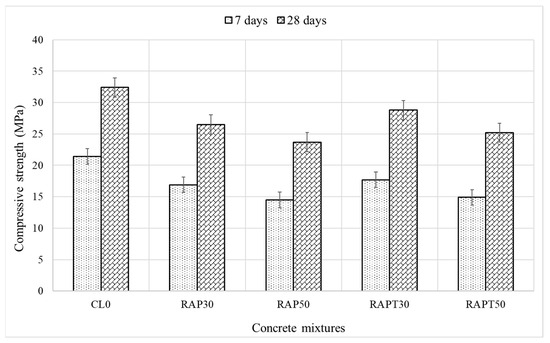
Figure 6.
Compressive strength results of concrete.
Remarkably, the 28-day compressive strength levels of the RAP mixtures, as shown in Figure 6, decreased, with the RAP30 and RAP50 mixtures exhibiting 18% and 27% drops, respectively, compared to the control. This could be due to the weak ITZ between the RAP and the cement paste, resulting from the presence of the hydrophobic asphalt coating on the RAP. Additionally, RAP aggregates have a lower elastic modulus than limestone aggregates, thereby reducing the concrete’s capacity to withstand compressive stresses [17]. Moreover, the old asphalt adhering to the surface of RAP may reduce the interlocking between the RAP aggregates and other components of concrete, including limestone aggregates, which in turn reduces load transfer in concrete and makes it less resistant to stresses.
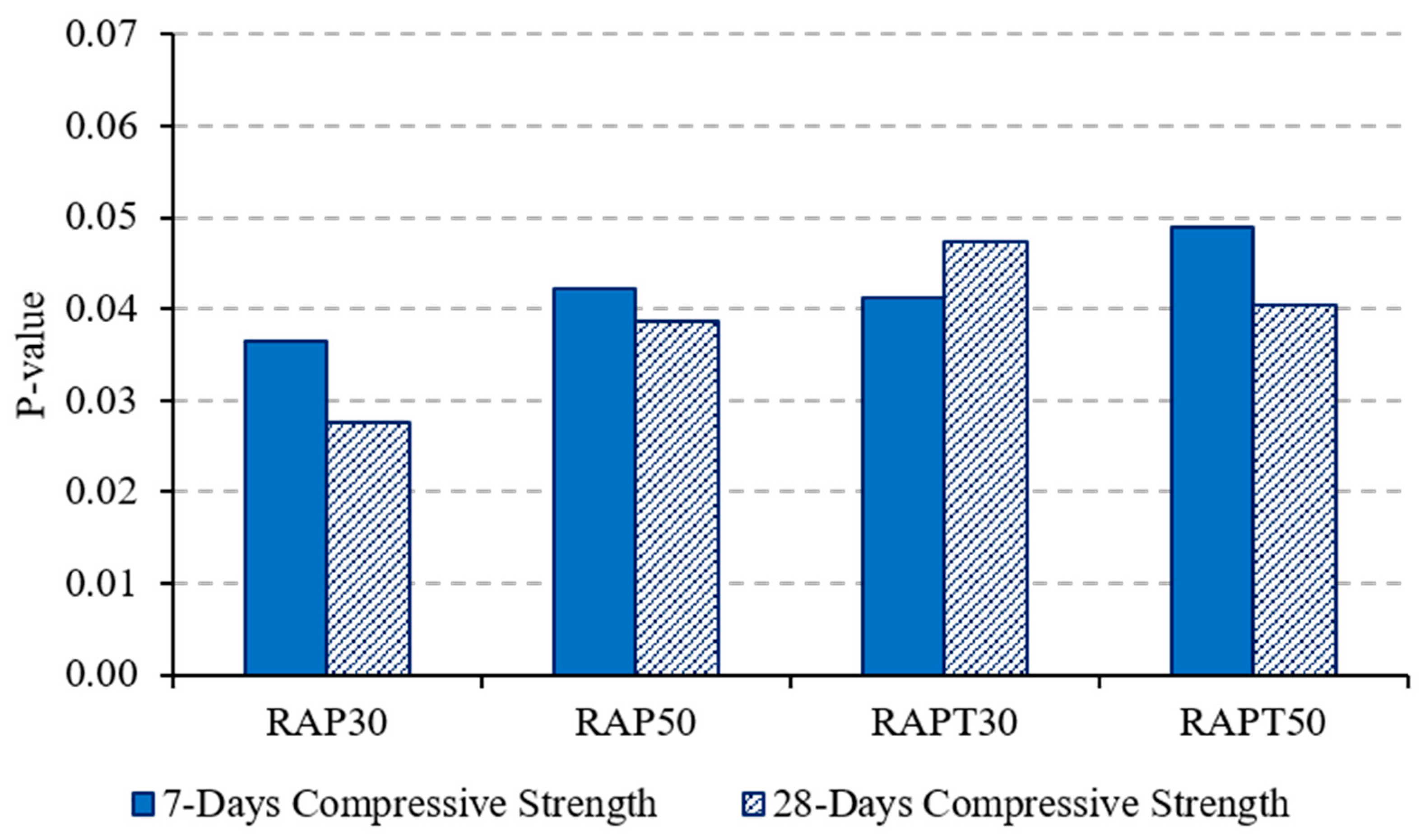
Notably, adding TiO2 to the RAP mixtures improved their compressive strength, as the RAPT30 and RAPT50 mixtures showed an increase of 8.7% and 6.3% in their strength, respectively, compared to the RAP30 and RAP50 mixtures. This can be attributed to the filling effect of TiO2 nanoparticles, which mitigates the interfacial defects and discontinuities at the ITZ caused by the presence of RAP. Additionally, the addition of TiO2 promotes the formation of hydration products, particularly CH and C-S-H, due to its nucleation effect, which in turn fills the voids and bridges microcracks at the ITZ [38,39,40]. Statistically, the population means of the compressive strength of all modified mixes were significantly different from the population mean of the control, as shown in Figure 7.
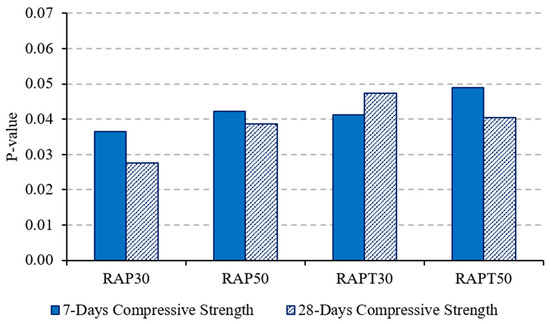
Figure 7.
“p-value” of concrete compressive strength.
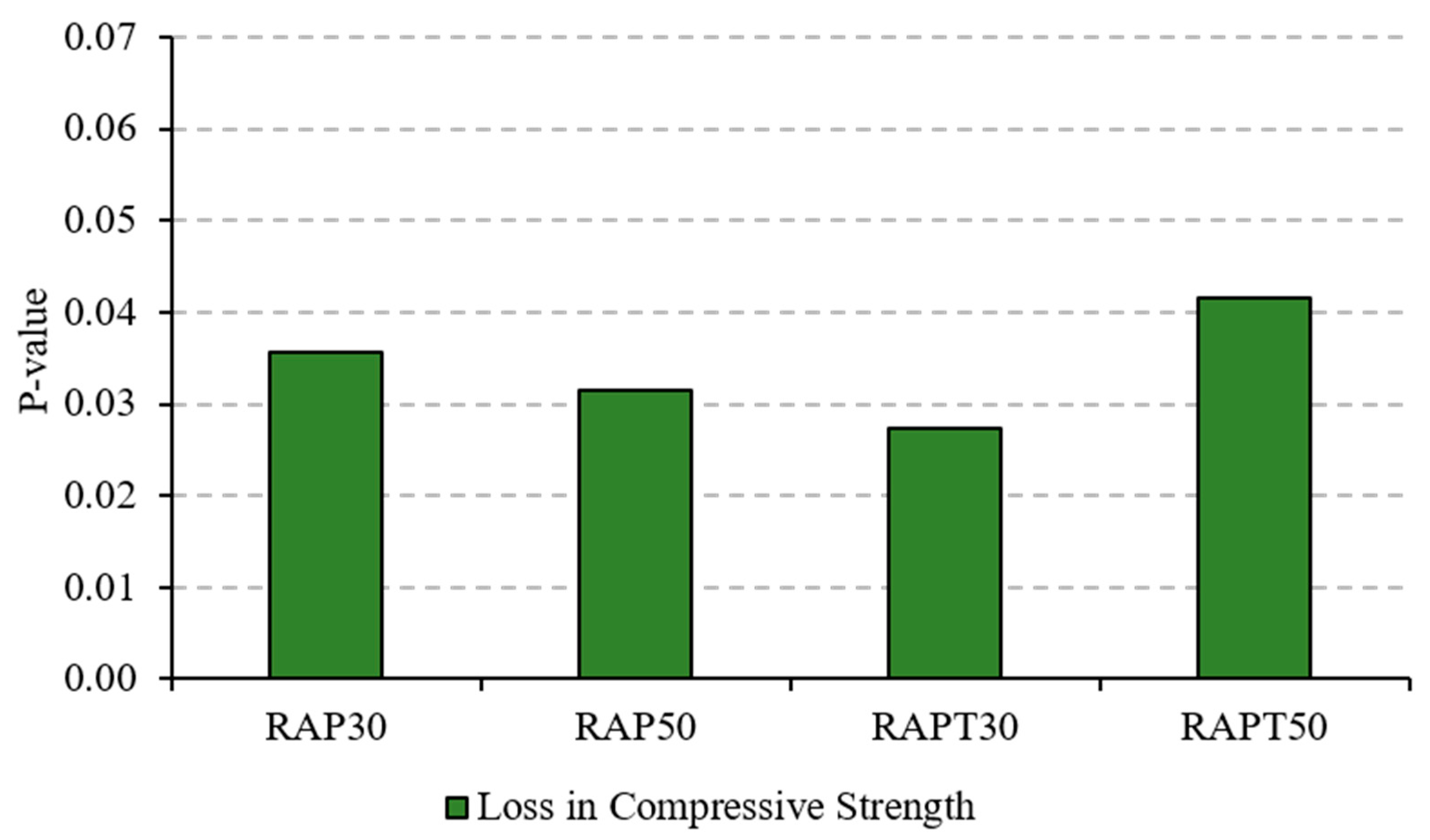
3.4. Sulfate Attack Assessment
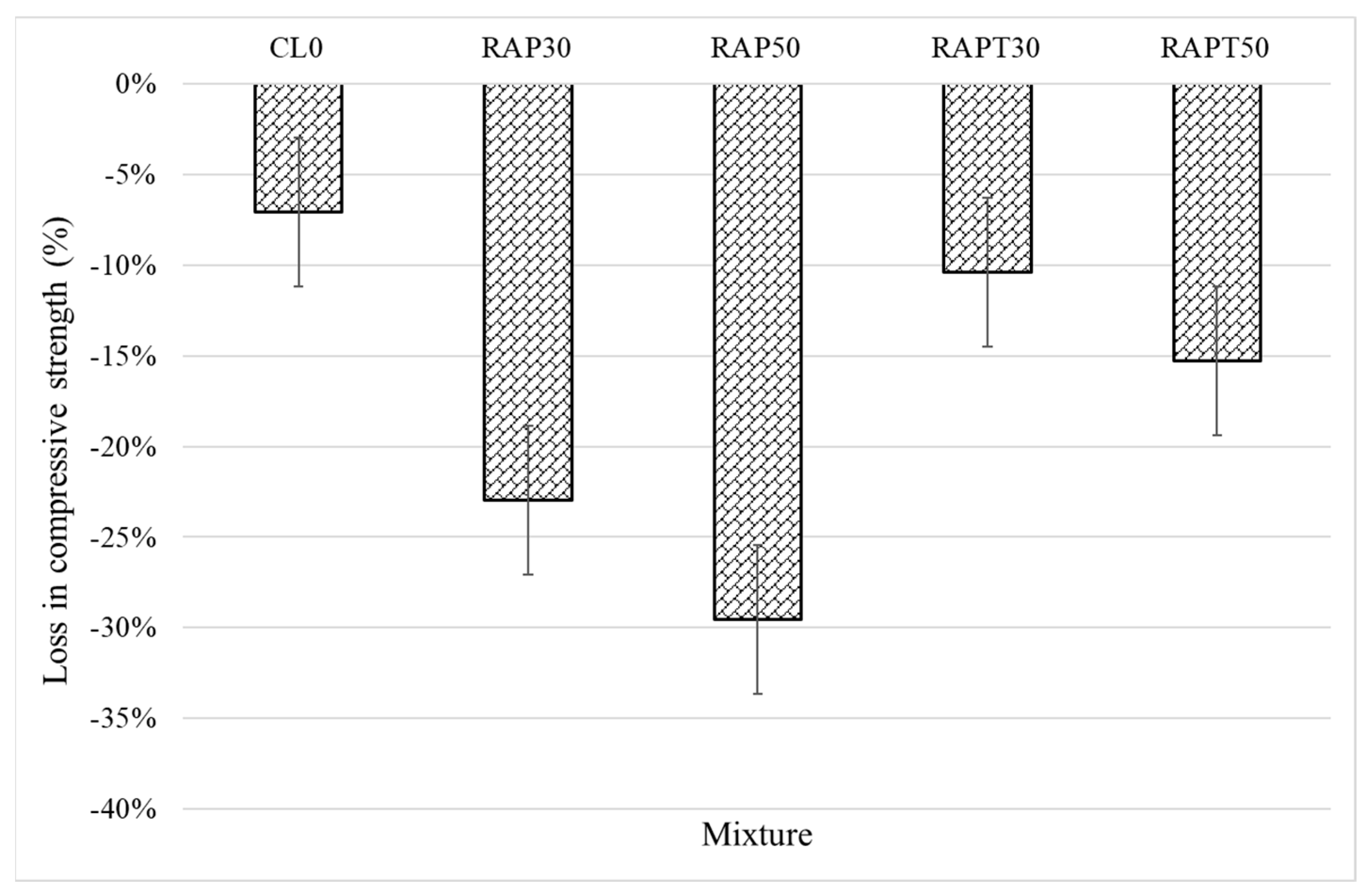
The resistance of the concrete mixtures to aggressive environments was evaluated using the sulfate attack test. Figure 8 shows that the control mixture exhibited the highest resistance to sulfates among all mixtures, experiencing a 7% drop in strength after exposure to the acid solution. Moreover, replacing limestone aggregates with RAP aggregates resulted in a 23% and 29.5% strength loss for the RAP30 and RAP50 mixtures, respectively. This could be credited to the higher porosity and weaker binder–aggregate interface in RAP concrete, where these voids and interfacial defects facilitate the intrusion of acid into the concrete. After the acid ingress through the pores, sulfates react easily with the alkaline components in cement, particularly CH and C-S-H, forming calcium salts that are promptly leached out of the concrete, resulting in the creation of large voids and a decrease in the concrete’s strength [41,42].
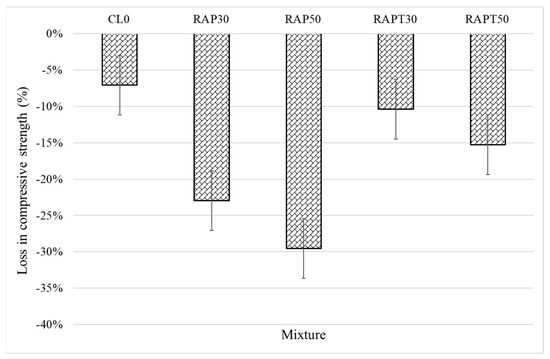
Figure 8.
Compressive strength reduction due to sulfate attack.
On the other hand, the addition of TiO2 to the RAP mixtures significantly attenuated the negative impact of RAP aggregates. The RAPT30 and RAPT50 mixtures experienced a 10.4% and 15% reduction in strength, respectively, after contact with sulfates. This might be due to the role of TiO2 particles in reducing the concrete’s permeability and refining pore structure, ultimately limiting acid ingress through the pores. Although the sulfate solution rapidly consumes CH and C–S–H hydrates towards the formation of microcracks and large voids, TiO2 particles compensate for the reduction in CH and C-S-H contents by promoting their formation in higher quantities, leading to the formation of concrete that is less susceptible to sulfate attack [20]. The statistical results of the loss in compressive strength reveal similar findings to those of the earlier compressive strength results; it appears that the population means of all RAP mixes, whether containing TiO2 particles or not, are statistically significant compared to the control, as shown in Figure 9.
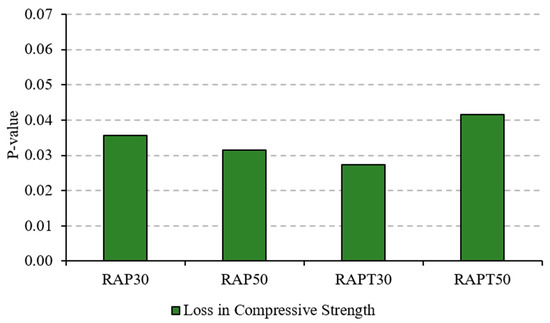
Figure 9.
“p-value” of loss in compressive strength of concrete.
3.5. Molecular Structure and Interactions
Figure 10 presents the results from the ATR-FTIR analysis showing the change in the chemical structure of the tested concrete mixtures because of the presence of RAP and TiO2. Moreover, the prominent peaks and their corresponding functional groups are illustrated in Table 3.
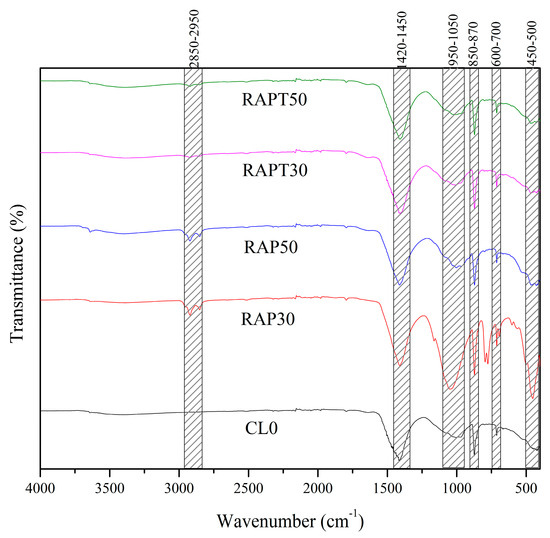
Figure 10.
Changes in the functional groups in the tested concrete mixtures.
As shown in Figure 10, distinct peaks of C-H stretching bonds (2850–2950 cm−1) can only be detected in the RAP30 and RAP50 mixes, which might result from the aged asphalt coating in the RAP aggregates. Those peaks disappear in the mixtures with TiO2 (RAPT30 and RAPT50), indicating the role of TiO2 in mitigating the adverse effect of the asphalt coating. Moreover, CO3−2 stretching (1420–1450 cm−1) and C-O vibration (850–870 cm−1) bonds were also more prominent in the RAP30 and RAP50 mixtures, indicating higher carbonation levels resulted from the higher void formation in those mixtures. Interestingly, the intensity of these peaks slightly decreased in the RAPT30 and RAPT50 mixtures, suggesting improved matrix densification. On the other hand, Si-O stretching (950–1050 cm−1 and 450–500 cm−1) and Si-O-Si bending vibration (600–700 cm−1) bonds, which are indicative of the presence of C-S-H gel in the mixes [43,44,45], decreased in the RAP30 and RAP50 mixes due to the aged asphalt coating of the RAP particles. However, those peaks demonstrated a recovery in their intensities in the RAPT30 and RAPT50 mixtures, which can be attributed to the nucleation effect of TiO2 that enhances hydration activity and the formation of C-S-H in these mixtures.

Table 3.
Main functional groups in the tested concrete.
Table 3.
Main functional groups in the tested concrete.
| Wavenumber (cm−1) | Functional Groups | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| 2850–2950 | C-H stretching | [46,47] |
| 1420–1450 | CO3−2 stretching | [46] |
| 950–1050 | Si-O stretching | [46] |
| 850–870 | C-O vibration | [47] |
| 600–700 | Si-O-Si bending vibration | [45] |
| 450–500 | Si-O stretching | [48] |
4. Real-World Implications
The integration of RAP in concrete as coarse aggregates has been proven to be a viable solution to the depletion of natural aggregates in various regions worldwide. This study contributes to the development of environmentally friendly concrete mixtures that can be used worldwide to achieve sustainable growth by demonstrating that up to 30% of RAP can be reused in structural concrete when modified with TiO2 nanoparticles. Additionally, it has been demonstrated that the introduction of TiO2 nanoparticles enhances durability performance, particularly in terms of resistance to moisture and acid ingress, which is crucial for increasing the service life of concrete infrastructure. This translates to less maintenance and repairs, reduced lifecycle environmental impact, and lower maintenance costs, which are of significant concern to both public agencies and private developers. In addition, 1% TiO2, which has been optimized based on the available literature, is a cost-effective dosage, as it achieves a balance between performance enhancement and cost-effectiveness. The materials employed in this research, such as RAP and commercially available TiO2, are readily available in most countries; therefore, the proposed mix design is not only technologically viable but can also be applied in large-scale civil engineering projects.
Overall, the research findings provide a scientifically proven and practically applicable approach to the two-fold task of sustainable material management and performance improvement in concrete construction.
5. Conclusions
This study presented an innovative approach to improve the properties of concrete containing RAP aggregates by adding TiO2 particles to the mixtures. Limestone coarse aggregates were partially replaced with 30% and 50% RAP aggregates, with the addition of TiO2 nanoparticles to a subset of the mixtures containing RAP aggregates to improve their performance. Moreover, the physical, mechanical, and long-term properties, as well as the synergistic characteristics of the developed mixes, were thoroughly assessed, yielding the following concluding remarks:
- The integration of 30% and 50% RAP aggregates in concrete increased its workability by 16.7% and 27.8%, respectively. In contrast, the addition of TiO2 in those mixtures reduced their workability by 9.5% and 13%.
- Concrete mixtures with 30% and 50% RAP aggregates exhibited water absorption levels of 6.3% and 7%, respectively, which are higher than the control at 3.8%. This is due to the high void content in those mixes resulting from the presence of aged asphalt coating around the RAP. However, using TiO2 particles in the 30% and 50% RAP mixtures reduced their water absorption by 32.5% and 4.8%, respectively, compared to their untreated counterparts. This is due to the filling effect of TiO2 particles, resulting in a dense concrete that hinders water absorption.
- The compressive strength of concrete declined with the increase in the replacement ratio of natural aggregates with RAP. Mixtures with 30% and 50% RAP aggregates exhibited a reduction of 18% and 27% in their 28-day strength, respectively, compared to the control, which is due to the weak ITZ between RAP aggregates and the cement matrix. The addition of TiO2 particles mitigated this decline in strength, as they contributed to increasing the strength of concrete with 30% and 50% RAP by 8.7% and 6.3%, correspondingly, due to the nucleation effect of TiO2 in improving the hydration process.
- The concrete mixture with 50% RAP aggregates showed the least resistance to sulfates, followed by the mixture with 30% RAP, as they experienced a loss of 23% and 29.5%, respectively, in their compressive strength. However, employing TiO2 particles in RAP mixtures enhanced their resistance to sulfates, where a 10.4% and 15% loss in strength was observed in the 30% and 50% RAP mixtures, respectively.
- Statistical analysis using single-factor ANOVA showed that either integrating RAP aggregates with TiO2 particles or not significantly affected the concrete properties in terms of their population means. The “t-test” analysis, on the other hand, provided sufficient evidence that the mean values of the RAPT30 mix did not differ significantly from the control in terms of its slump and water absorption properties. The RAPT50 mix also showed an insignificant difference compared to the control in terms of water absorption at 7 and 28 days. However, the population means of all mix combinations significantly differed from the control in terms of their compressive strength and their loss in compressive strength.
- ATR-FTIR analysis revealed the formation of distinct C-H stretching bonds in the mixtures with RAP aggregates due to the aged asphalt coating in the RAP aggregates. These bonds weaken when TiO2 is added to the mixtures due to its role in mitigating the adverse effects of the asphalt coating. Additionally, Si-O and Si-O-Si functional groups increased when using TiO2 in RAP mixtures, suggesting improved hydration activity and accelerated C-S-H formation in the mixes.
- Although the use of RAP and TiO2 in concrete offers a promising approach to improving performance and potentially increasing sustainability, this study lacked a formal life-cycle assessment (LCA). The environmental impact of TiO2 usage, particularly in terms of embodied energy and production emissions, requires further quantification. Future studies are necessary to determine the net environmental effects of the suggested mix designs using cradle-to-gate and service-life-based LCA models. Moreover, TiO2 nanoparticles are relatively expensive substances, but their use at low doses (1% of cement weight) and the possibility of using them as a partial cement replacement can present a relatively inexpensive solution, balancing performance, long-term benefits, and savings related to material costs in the implementation of RAPs. It is therefore suggested that a more comprehensive techno-economic analysis be carried out in future studies to substantiate the economic viability of these altered concrete systems.
Author Contributions
M.S.A.J.: Data curation, Investigation. M.M.A.-A.: Data curation, Investigation. A.K.A.-A.: Data curation, Investigation. M.J.A.-K.: Supervision, Project administration, Methodology, Formal analysis, Conceptualization, Resources, Writing—original draft, Writing—review and editing. Y.S.J.: Formal analysis, Investigation, Writing—original draft, Writing—review and editing. A.H.A.: Formal analysis, Methodology, Writing—review and editing. M.R.: Methodology, Data curation, Writing—review and editing. S.S.A.: Investigation, Data curation, Writing—review and editing. Y.A.A.-N.: Formal analysis, Methodology, Writing—original draft. S.H.G.: Visualization, Conceptualization, Writing—review and editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data will be available upon request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Bayaidah, R.H.; Habashneh, A.A.O.; Al-Ma’aitah, S.H.; Alfahajin, M.S.; Al-Kheetan, M.J.; Jweihan, Y.S.; Alrwashdeh, S.S.; Al-Hamaiedeh, H.; Ghaffar, S.H. Utilisation of raw oil shale as fine aggregate to replace natural sand in concrete: Microstructure, surface chemistry and macro properties. Results Eng. 2023, 19, 101265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Kheetan, M.J. Properties of lightweight pedestrian paving blocks incorporating wheat straw: Micro-to macro-scale investigation. Results Eng. 2022, 16, 100758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Awabdeh, F.W.; Al-Kheetan, M.J.; Jweihan, Y.S.; Al-Hamaiedeh, H.; Ghaffar, S.H. Comprehensive investigation of recycled waste glass in concrete using silane treatment for performance improvement. Results Eng. 2022, 16, 100790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Kheetan, M.J.; Jweihan, Y.S.; Rabi, M.; Ghaffar, S.H. Durability Enhancement of Concrete with Recycled Concrete Aggregate: The Role of Nano-ZnO. Buildings 2024, 14, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, B.B.; Singh, S. Evaluation of the failure planes in concrete containing reclaimed asphalt pavement (RAP) aggregates. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2024, 145, 105334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukhija, M.; Coleri, E. A systematic review on the role of reclaimed asphalt pavement materials: Insights into performance and sustainability. Clean. Mater. 2025, 16, 100316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, B.A.; Willis, J.R.; Shacat, J. Asphalt Pavement Industry Survey on Recycled Materials and Warm-Mix Asphalt Usage; National Asphalt Pavement Association: Greenbelt, MD, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhu, W.; Chu, X.; Shi, L.; Zhan, X.; Cheng, H.; Sun, L. The mechanical behavior of designing recycled hot-mix asphalt containing fine RAP particles with multiple parameters using orthogonal experimental approach. Constr. Build. Mater. 2025, 458, 139654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthikeyan, K.; Kothandaraman, S.; Sarang, G. Perspectives on the utilization of reclaimed asphalt pavement in concrete pavement construction: A critical review. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2023, 19, e02242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masi, G.; Michelacci, A.; Manzi, S.; Bignozzi, M.C. Assessment of reclaimed asphalt pavement (RAP) as recycled aggregate for concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 341, 127745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Shu, X.; Li, G. Laboratory investigation of portland cement concrete containing recycled asphalt pavements. Cem. Concr. Res. 2005, 35, 2008–2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansourian, A.; Hashemi, S.; Aliha, M.R.M. Evaluation of pure and mixed modes (I/III) fracture toughness of Portland cement concrete mixtures containing reclaimed asphalt pavement. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 178, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, K.E.; Brooks, J.J.; Erdman, M. The use of reclaimed asphalt pavement (RAP) aggregates in concrete. Waste Manag. Ser. 2000, 1, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debbarma, S.; Ransinchung, G.; Singh, S. Improving the Properties of RAP-RCCP Mixes by Incorporating Supplementary Cementitious Materials as Part Addition of Portland Cement. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2020, 32, 04020229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Ransinchung, G.D.; Kumar, P. Effect of mineral admixtures on fresh, mechanical and durability properties of RAP inclusive concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 156, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Shintre, D.; Ransinchung R.N., G.D.; Kumar, P. Performance of Fine RAP Concrete Containing Flyash, Silica Fume, and Bagasse Ash. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2018, 30, 04018233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alwathaf, A.H.; Jaber, M.A.; Hunaiti, Y.M. Enhancement and Optimization of the Mechanical Properties in Cement Concrete with Recycled Asphalt Pavement (RAP). Buildings 2024, 15, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Ransinchung R.N., G.D.; Kumar, P. Performance Evaluation of RAP Concrete in Aggressive Environment. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2018, 30, 04018231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunea, G.; Alexa-Stratulat, S.-M.; Mihai, P.; Toma, I.-O. Use of Clay and Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles in Mortar and Concrete—A State-of-the-Art Analysis. Coatings 2023, 13, 506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qudoos, A.; Kim, H.; Ryou, J.-S. Influence of Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles on the Sulfate Attack upon Ordinary Portland Cement and Slag-Blended Mortars. Materials 2018, 11, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazari, A.; Riahi, S. The effect of TiO2 nanoparticles on water permeability and thermal and mechanical properties of high strength self-compacting concrete. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2010, 528, 756–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bragança, M.D.G.P.; Portella, K.F.; Gobi, C.M.; de Mesquita Silva, E.; Alberti, E. The Use of 1% Nano-Fe3O4 and 1% Nano-TiO2 as Partial Replacement of Cement to Enhance the Chemical Performance of Reinforced Concrete Structures. Athens J. Technol. Eng. 2017, 4, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniyal, M.; Akhtar, S.; Azam, A. Effect of nano-TiO2 on the properties of cementitious composites under different exposure environments. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2019, 8, 6158–6172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, D.S.; Paul, S.C.; Anggraini, V.; Kong, S.Y.; Qureshi, T.S.; Rodriguez, C.R.; Liu, Q.; Šavija, B. Influence of SiO2, TiO2 and Fe2O3 nanoparticles on the properties of fly ash blended cement mortars. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 258, 119627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Kou, S.; Poon, C. Hydration and properties of nano-TiO2 blended cement composites. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2012, 34, 642–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikbin, I.M.; Mohebbi, R.; Dezhampanah, S.; Mehdipour, S.; Mohammadi, R.; Nejat, T. Gamma ray shielding properties of heavy-weight concrete containing Nano-TiO2. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2019, 162, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, G.M.S.; Chohan, I.M.; Ali, M.; Bheel, N.; Ahmad, M.; Najeh, T.; Gamil, Y.; Almujibah, H.R. Effect of titanium dioxide as nanomaterials on mechanical and durability properties of rubberised concrete by applying RSM modelling and optimizations. Front. Mater. 2024, 11, 1357094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baikerikar, A.V.; Ganachari, V.; Khed, V.C.; Bheel, N.; Alraeeini, A.S.; Almujibah, H. Synergistic effects of nano titanium dioxide and waste glass powder on the mechanical and durability properties of concrete. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 27573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, F.; Arezes, P.; Swuste, P. Risk management. In Nanotechnology in Eco-Efficient Construction; Elsevier: Cambridge, UK, 2019; pp. 755–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buzea, C.; Pacheco, I. Toxicity of nanoparticles. In Nanotechnology in Eco-Efficient Construction; Elsevier: Cambridge, UK, 2019; pp. 705–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BS EN 12350-2:2019—TC; Testing Fresh Concrete—Slump Test. BSI: London, UK, 2019.
- BS EN 12390-3:2019; Testing Hardened Concrete—Compressive Strength of Test Specimens. BSI: London, UK, 2019.
- BS 1881-122:2011+A1:2020; Testing Concrete—Method for Determination of Water Absorption. BSI: London, UK, 2020.
- Fang, H.; Yang, Q.; Ma, J.; Peng, X.; Xia, K. A Time-Variant Model for Chloride Ion Diffusion Coefficient in Concrete. Buildings 2025, 15, 2272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM C1898-20; Standard Test Methods for Determining the Chemical Resistance of Concrete Products to Acid Attack. ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2020.
- Singh, S.; Ransinchung, G.D.R.N.; Monu, K.; Kumar, P. Laboratory investigation of RAP aggregates for dry lean concrete mixes. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 166, 808–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brand, A.S.; Roesler, J.R. Ternary Concrete with Fractionated Reclaimed Asphalt Pavement. ACI Mater. J. 2015, 112, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Tian, L.; Yu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Li, C.; Hou, G.; Shen, X. Studies on the size effects of nano-TiO2 on Portland cement hydration with different water to solid ratios. Constr Build Mater 2020, 259, 120390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francioso, V.; Moro, C.; Martinez-Lage, I.; Velay-Lizancos, M. Curing temperature: A key factor that changes the effect of TiO2 nanoparticles on mechanical properties, calcium hydroxide formation and pore structure of cement mortars. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2019, 104, 103374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nochaiya, T.; Chaipanich, A. The effect of nano-TiO2 addition on Portland cement properties. In Proceedings of the 2010 3rd International Nanoelectronics Conference (INEC), Hong Kong, China, 3–8 January 2010; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2010; pp. 1479–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilbig, H.; Gutberlet, T.; Beddoe, R.E. Acid attack on hydrated cement: Effect of organic acids on the degradation process. Mater Struct. 2024, 57, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beddoe, R.E.; Dorner, H.W. Modelling acid attack on concrete: Part I. The essential mechanisms. Cem. Concr. Res. 2005, 35, 2333–2339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, N.A.; Chandana, P.S. Impact of nano-TiO2 on white Portland cement mortars: A combined XRD coupled rietveld, crystallographic and microstructural analysis. Discov. Civ. Eng. 2024, 1, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batista, G.D.S.; Takimi, A.S.; da Costa, E.M. Hardened oil well cement paste modified with TiO2@SiO2 nanoparticles: Physical and chemical properties. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 367, 130282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akono, A.-T. Effect of nano-TiO2 on C–S–H phase distribution within Portland cement paste. J. Mater. Sci. 2020, 55, 11106–11119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motevalizadeh, M.; Mollenhauer, K. Identification of chemical markers for blending phenomena in RAP mastics using FTIR spectroscopy and multivariate discriminant analysis. Constr. Build. Mater. 2025, 485, 141822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margaritis, A.; Tofani, G.; Jacobs, G.; Blom, J.; Tavernier, S.; Vuye, C.; Van den bergh, W. On the Applicability of ATR-FTIR Microscopy to Evaluate the Blending between Neat Bitumen and Bituminous Coating of Reclaimed Asphalt. Coatings 2019, 9, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, G.; Yao, W.; Zuo, J. Preparation and Characterization of Zeolite/TiO2 Cement-Based Composites with Excellent Photocatalytic Performance. Materials 2018, 11, 2485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).