Abstract
The surface temperature of grain piles is sensitive to environmental fluctuations and exhibits nonlinear, multi-scale temporal patterns, making accurate prediction crucial for grain storage risk early warning. This paper proposes a decomposition–reconstruction prediction method integrating Sample Entropy (SampEn), variational mode decomposition (VMD), and a variant Long Short-Term Memory network (vLSTM). SampEn determines the optimal decomposition parameters, VMD extracts intrinsic mode functions (IMFs), and vLSTM, with peephole connections and coupled gates, conducts synchronous multi-IMF prediction. To explicitly account for environmental influences, a support vector regression (SVR) model driven by dew point temperature and vapor pressure deficit is employed to estimate the surface temperature variation . This component enhances the adaptability of the framework to dynamic storage conditions. The environment-derived is then integrated with the VMD-SampEn-vLSTM output to obtain the final forecast. Experiments on real-granary data from Liaoning, China demonstrate that the proposed method reduces mean absolute error (MAE) and root mean square error (RMSE) by 25% and 14%, respectively, compared with baseline models, thus achieving a significant improvement in prediction performance. This integration of data-driven prediction with environmental adjustment significantly improves forecasting accuracy and robustness.
1. Introduction
Food security is fundamental to national stability and sustainable development. However, survey data indicate that post-harvest losses during grain storage remain substantial, typically ranging from 7% to 15% [1]. Such losses directly reduce the total available food supply and exacerbate the global food security crisis as highlighted by FAO data showing that approximately 9.8% of the global population experienced hunger in 2021. Therefore, more intelligent grain storage management and monitoring are of great significance for achieving sustainable development.
In grain storage management, temperature monitoring and prediction have become widely adopted and effective strategies to ensure safety [2]. Temperature monitoring enables the early identification of abnormal hot spots, thereby locating risk-prone areas within complex grain pile environments [3,4,5]. Figure 1 shows the grain condition in case of local high-temperature anomaly (the most common temperature anomaly). To mitigate such risks, dedicated drying devices [6] and Internet of Things-based sensor technologies [7,8,9] have been increasingly applied for monitoring temperature and humidity inside warehouses. As illustrated in Figure 2, the surface region of grain piles responds rapidly to external environmental fluctuations and often serves as the earliest indicator of abnormal conditions. Consequently, the accurate prediction of surface temperature plays a critical role in early warning systems for grain storage.
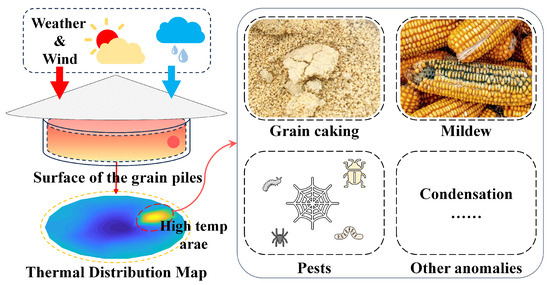
Figure 1.
Abnormal temperature of the grain piles and potential hazards.
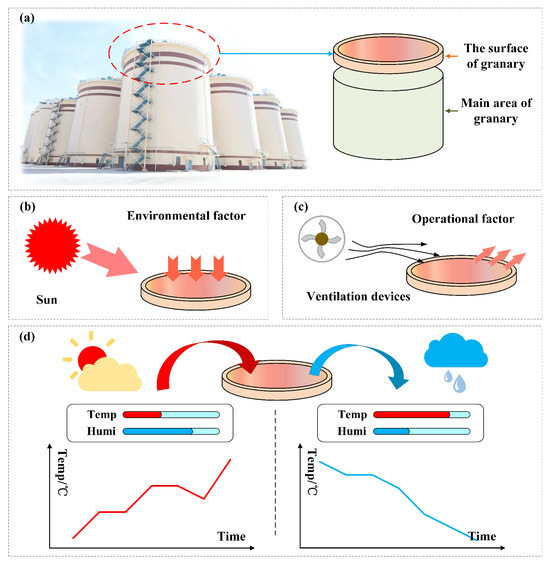
Figure 2.
Grain piles surface temperature variation: (a) Granary area division. (b) Environmental influence: solar radiation. (c) Operational influence: ventilation control. (d) Surface temperature trend under different weather conditions.
In the field of temperature prediction, the introduction of methods such as machine learning and deep learning [10], along with strategies like adaptive modeling [11] and noise suppression [12], has significantly improved time-series prediction accuracy [13,14,15]. These advancements have also driven methodological progress in grain pile temperature prediction. Research on grain pile temperature prediction can be divided into three distinct phases, each with its own characteristics and limitations:
Traditional physical/chemical models: These models are based on thermodynamics, heat conduction, or finite element methods [16], such as wheat cooling models [17,18] and sorghum temperature models [19]. While effective in simulating heat transfer processes, they are limited in scalability due to complex storage conditions and computational constraints.
Machine learning models: Hysteresis cycle models based on differential methods [20] and SVR [21] have been employed to predict grain pile temperatures using meteorological data. These approaches improve prediction accuracy and reduce reliance on physical/chemical parameters, but they exhibit limited generalization under extreme conditions, restricting broader applicability.
Deep learning models: Owing to their strong feature extraction capability, deep learning has become the mainstream approach [22], capable of capturing the nonlinear effects of environmental variation [23] and grain respiration [24]. Recurrent neural networks (RNNs) and Transformer-based models can effectively address temporal complexity [25,26]—with proven applications in finance [27,28]. Their use in grain storage includes graph convolution-Transformer networks (CGTNs) [29], LSTMs incorporating meteorological factors [30,31], bidirectional LSTMs [32], hybrid CNN-GRU models, and so on [33,34]. Nevertheless, these methods still struggle to capture the multi-scale dynamic patterns of grain surface temperatures and rarely incorporate explicit environmental correction mechanisms.
A common strategy for handling multi-scale time series is signal decomposition, which decomposes raw data into several sub-series with different characteristics [35]. Among the existing approaches, wavelet decomposition [36] relies on empirical wavelet basis selection; empirical mode decomposition [37] and ensemble empirical mode decomposition [38] suffer from mode mixing and component redundancy. Variational mode decomposition (VMD) [39], a variational framework-based approach, can effectively extract intrinsic mode functions (IMFs) of different frequencies and is suitable for non-stationary data. However, the performance of VMD depends on parameter settings (e.g., the optimal number of modes, K), and current adaptive approaches—such as entropy-based [35] and center-frequency-based methods [40,41,42]—lack customized optimization for grain pile temperature series.
In summary, building on existing grain pile temperature forecasting methods, this study addresses the core challenges of multi-scale and non-stationary dynamics in surface temperature prediction by proposing the VMD-SampEn-vLSTM-E framework, which integrates decomposition–reconstruction, data-driven modeling, and environmental correction. The main contributions are as follows:
- (1)
- Adaptive determination of VMD parameters: SampEn is introduced as a decomposition quality metric to automatically determine the optimal number of modes, thereby enhancing the physical interpretability and predictive reliability VMD.
- (2)
- Multivariate LSTM structure optimization: A variant LSTM architecture is developed by incorporating peephole connections and a coupled gating mechanism, which improves its capacity to model multiple decomposed components in parallel and enhances multivariate time-series forecasting performance.
- (3)
- Env-driven multiple regression for temperature variation: A multiple regression model based on SVR that incorporates specific environmental parameters as inputs is proposed to fuse and correct the VMD-SampEn-vLSTM predictions. This introduces environmental driving effects to ensure model robustness and generalizability.
The overall design of the grain pile surface temperature prediction proposed in this study is shown in Figure 3.
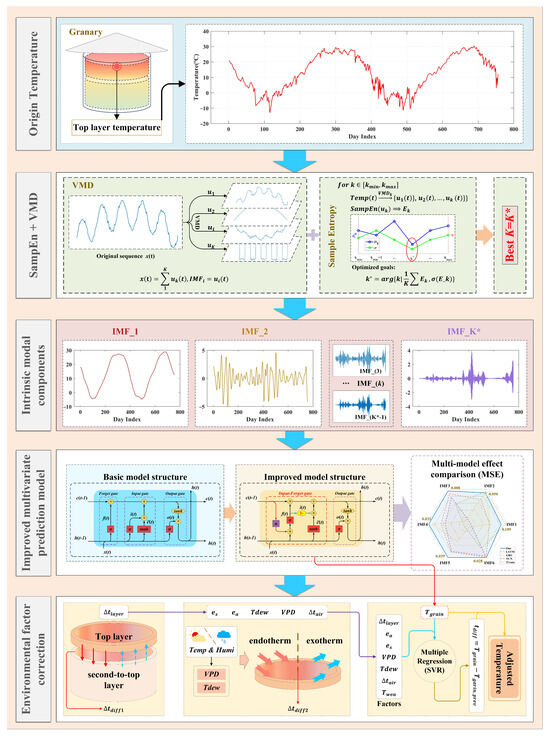
Figure 3.
Design diagram of grain piles surface temperature prediction scheme.
2. Database and Preprocessing
2.1. Database
The data used in this experiment comes from multiple granaries in Liaoning, China, with monitored temperature data collected by sensors deployed inside the granaries and transmitted to an external industrial control computer.
To ensure efficient data transmission and structural consistency, all raw data was stored in JSON format. By parsing the JSON file, surface temperature information of the grain piles and environmental factors were extracted as illustrated in Table 1.

Table 1.
Data collected: surface temperature of grain piles and environmental factors.
2.2. Preprocessing
In practical grain storage scenarios, the acquisition frequency of temperature and humidity sensors is dynamically adjusted in response to changing grain storage conditions. As a result, time-series data may contain missing values or anomalies, which can adversely affect model training and prediction accuracy. To address this, a series of preprocessing steps were carried out to improve data quality and usability based on the parsed data:
- (a)
- Time-series denoising: Temperature and humidity sequences were organized by timestamp and smoothed using techniques such as moving average filtering or Fourier transform-based denoising.
- (b)
- Missing value imputation: Discontinuities in time-series data were repaired using linear or Lagrange interpolation, depending on the context.
- (c)
- Outlier detection and correction: Abnormal values were identified and processed using statistical approaches including Z-score analysis and interquartile range (IQR)-based filtering.
After data collection and preprocessing, the core variables X and E were obtained in this study, where X represents the surface temperature of the grain piles, and E represents the environmental factors. The data spanned a period of 756 days, from 1 October 2022 to 25 October 2024.
where i is the time index, and jointly form the serial number of the temperature sensor, is the air temperature, and is the air humidity.
3. Methodology
The evolution of grain pile surface temperature is driven by internal dynamics and strongly modulated by external environments. Accordingly, this study develops a VMD-SampEn-vLSTM model based on historical temperature series, then incorporates environmental factors via multivariate regression to refine the prediction results.
3.1. VMD-SampEn-vLSTM
Owing to the multi-time-scale characteristics of grain pile surface temperature, the study proposes the VMD-SampEn-vLSTM model based on the decomposition–reconstruction concept to construct a predictor relying on the historical data of the grain pile itself.
3.1.1. VMD-SampEn
To effectively isolate and extract multi-scale characteristic information from non-stationary temperature sequences, this study employs the VMD method. VMD constructs a variational optimization model to decompose the original signal into multiple Intrinsic Mode Functions (IMFs) with adaptively determined center frequencies. Each IMF exhibits a compact spectral profile, enabling the precise separation of components across different frequency bands. The mathematical principles of VMD are as follows.
First, for the time-series signal , VMD decomposes it into K modal components , each of which has the property of narrow bandwidth and is concentrated around a center frequency . This process can be formulated as a constrained variational problem:
In this optimization objective: denotes the modal component; represents the corresponding center frequency; is the time derivative operator, used to measure the modal bandwidth; is the Dirac delta function; denotes the ; and represents the Hilbert transform of the modal component, forming the analytic signal. The objective function minimizes the bandwidth of each modal function after Hilbert transform and exponential modulation. The constraint ensures that the sum of all modal functions equals the original signal.
The optimization problem can be solved by introducing a penalty factor and Lagrange multipliers to construct a augmented Lagrangian function, thereby achieving the decomposition of the original temperature series.
The performance of VMD decomposition is significantly influenced by several parameters, including the number of modes K, the penalty factor , and so on. Among them, the selection of K plays a particularly critical role, as it directly determines the accuracy of multi-scale feature separation. If K is set too small, different frequency components may become entangled; conversely, an excessively large K may introduce spurious modes, thereby compromising the stability and interpretability of the results.
To address the empirical problem of selecting the mode number K in conventional VMD applications, this study introduces Sample Entropy (SampEn) as an evaluation metric for parameter optimization. SampEn can effectively quantify the complexity and irregularity of time series and demonstrates high sensitivity to nonlinear dynamic characteristics, thereby enabling the assessment of the physical validity of each set of VMD-derived components.
The principle of SampEn is based on the theory of phase space reconstruction. The mathematical principle is as follows:
- (1)
- Phase Space Embedding: Given a 1D sequence , construct m-dimensional embedding vectors:where , N is length of X.
- (2)
- Distance Measurement: Define the Chebyshev distance between two vectors and as
- (3)
- Probability Estimation: For a given threshold r and the standard deviation of the sequence itself, calculate the proportion of vector pairs within the threshold ():and calculate the average: .
- (4)
- Entropy Calculation: Repeat the process for embedding dimension , and compute SampEn as
By systematically comparing the SampEn values of decomposition results under different parameter configurations, the optimal set of VMD parameters can be identified, balancing both decomposition precision and physical interpretability. Accordingly, for the VMD decomposition of temperature time series, the specific procedure for determining the optimal number of modes based on SampEn is outlined as follows:
- (a)
- Parameter Initialization:Define a candidate range for the number of modes, . For each value of K, perform VMD decomposition to obtain a set of K IMFs, denoted as .
- (b)
- Evaluation Strategy:For each IMF component , calculate its corresponding SampEn value , where :For each candidate mode number K, compute the mean and standard deviation of the SampEn values across all IMF components, denoted as and , respectively:
The mean SampEn reflects the average complexity of the decomposed modes; a lower indicates smoother and more regular components with reduced noise. The standard deviation characterizes the variability in complexity among the IMFs; a larger may suggest the presence of outlier modes with abnormally high or low entropy, which could be a result of over-decomposition or mis-decomposition.
To comprehensively account for both decomposition stability and information redundancy, an evaluation metric is defined to assess the quality of each decomposition configuration:
where the optimal K satisfies: .
The VMD decomposition corresponding to exhibits the following characteristics: a more balanced distribution of complexity across IMFs, improved structural stability and regularity, and reduced redundancy and noise. This approach also helps to avoid excessive decomposition, which may otherwise increase computational cost and model complexity.
3.1.2. Variant LSTM
The prediction of each IMF after VMD essentially constitutes a multivariate time-series prediction task.
LSTM, a specialized variant of RNNs, introduces gated mechanisms to effectively mitigate the vanishing and exploding gradient problems commonly encountered in long sequence modeling [30]. The architecture of the LSTM cell is illustrated in Figure 4. Comprising a forget gate, an input gate, and an output gate, this architecture enables LSTM to selectively retain memory and discard information. Therefore, this study uses LSTM to perform parallel prediction on multiple modal sequences after VMD decomposition.
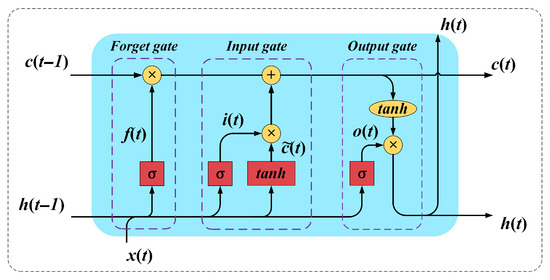
Figure 4.
Basic model structure.
The LSTM calculation formula is as follows:
where ⊙ represents the Hadamard product.
However, when the input to an LSTM model consists of multiple time-series variables, its original gating mechanism may exhibit limited coordination in handling inter-variable heterogeneity, making it difficult to effectively differentiate and adapt to the dynamic characteristics of each variable. This limitation stems from the fact that, in the standard LSTM architecture, the input gate and forget gate operate independently to regulate the writing of new information and the retention of past information, respectively. This lack of constraint and mutual regulation may lead to conflicts and redundancy during the information update process. Moreover, the gating operations in the original LSTM primarily rely on the previous hidden state , while the cell state can only be indirectly utilized via , which restricts the model’s ability to directly perceive and leverage historical context, ultimately affecting its modeling capacity for multimodal time-series data.
Therefore, in multivariate time-series forecasting tasks, optimizing the LSTM architecture to improve the efficiency of cell state information transmission and to enhance its capacity for modeling dynamic patterns across multiple time scales is a critical approach for achieving accurate prediction of the Intrinsic Mode Functions (IMFs) derived from VMD decomposition.
Previous studies have shown that the peephole connections mechanism proposed by Gers et al. allows the cell state to be directly incorporated into the gating unit computations, thereby alleviating the issue of delayed state updates [43,44]. Meanwhile, the GRU, as a simplified variant of LSTM, merges the input and forget gates into a single update gate, which reduces model complexity and improves training efficiency [45]. However, in most time-series forecasting applications, adopting such gated coupling mechanisms alone has not demonstrated significant advantages in modeling performance over the original LSTM architecture [46].
To address the aforementioned challenges, this study proposes an enhanced LSTM model (variant LSTM, vLSTM) that integrates the peephole connection mechanism with an input–forget gate coupling strategy. The goal is to improve the model’s capacity to capture complex multivariate dynamics and enhance the prediction accuracy of modal sequences derived from VMD decomposition. The optimized vLSTM architecture is illustrated in Figure 5.
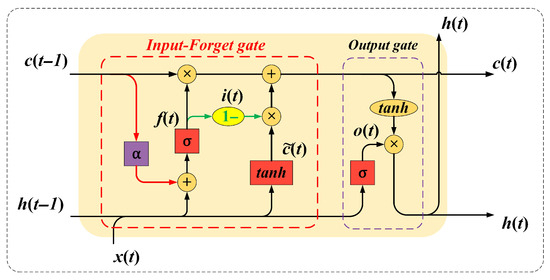
Figure 5.
Improved model structure (vLSTM).
The core of the proposed vLSTM lies in the following two structural improvements:
- (1)
- A coupled computation mechanism for the input and forget gates;
- (2)
- The introduction of a cell state via only one peephole connection exclusively within the input gate, enabling more direct access to historical information.
The corresponding computational structure of vLSTM is defined as follows:
Given the relative independence of each IMF component across different time scales, this study employs an element-wise Hadamard product in the peephole mechanism to better preserve the independence of dynamic features among the components. Consequently, this design not only reduces the overall parameter scale of the model but also mitigates the risk of overfitting that may arise from excessive coupling between components.
3.2. Multiple Regression Based on Environmental Conditions
To more precisely characterize the explicit contributions of environmental conditions (e.g., air temperature and humidity, and dew point temperature) on the surface temperature of the grain heap, this study introduces a multivariate regression model as an exogenous correction mechanism to refine the predictions generated by the VMD-SampEn-vLSTM framework. This secondary optimization aims to more accurately capture the actual daily variation trend of the grain heap surface temperature.
The relationship between the surface temperature change of grain piles caused by environmental factors and related parameters can be described as
where denotes the surface temperature variation of grain piles from environmental factors; is the air temperature; is the previous day’s surface temperature; represents the vapor pressure deficit; is the dew point temperature ( and can be calculated from air temperature and humidity); and is a constant term.
Accordingly, can be estimated based on , , , and . In this study, an SVR approach was employed to construct the multivariate regression function, enabling the integration of environmental variables with the grain heap’s intrinsic temperature data. This fusion-based correction markedly enhances the robustness and generalization capability of the predictive model under diverse environmental conditions.
The fitted combination is calibrated based on the prediction of VMD-SampEn-vLSTM, and the integrated prediction results are as follows:
where is the prediction result of VMD-SampEn-vLSTM (representing the temperature evolution result based on the characteristics of the grain pile itself).
In summary, this paper constructs a VMD-SampEn-vLSTM-E prediction framework based on the grain pile’s data-driven characteristics and external environmental effects. By integrating multi-time-scale feature modeling and environmental adaptability design, the framework aims to improve the accuracy and robustness of grain pile surface temperature prediction.
4. Experiment and Results
To address the prediction task of the complex grain pile surface temperature time series, which exhibits non-stationary and multi-time-scale characteristics, this section sequentially conducts experiments on VMD parameter optimization based on SampEn, analysis of the prediction performance of each IMF, and comparison of the overall prediction effects under various model combination strategies. Furthermore, a multivariate regression correction model incorporating environmental parameters is developed to enhance prediction accuracy under complex conditions. These efforts aim to systematically verify the effectiveness and advantages of the proposed VMD-SampEn-vLSTM-E method.
4.1. VMD Parameter Optimization Based on SampEn
In Section 4, this study proposes a VMD parameter selection method based on the Sample Entropy (SampEn) evaluation metric. Building upon this, the current section applies the method to the surface temperature series of a grain pile, aiming to extract dynamic features across multiple temporal scales and to establish a solid foundation for subsequent temperature prediction tasks.
The surface temperature data of grain piles were collected from 34 sensors deployed across the grain pile surface. The spatial distribution of these sensors is illustrated in Figure 6a, while Figure 6b presents the corresponding temperature variation curves recorded during the monitoring period. To quantitatively evaluate the consistency among the temperature variations at different locations, the Pearson correlation coefficient was employed, calculated as follows:
where r denotes the Pearson correlation coefficient, and represent the feature and target values of the i-th sample, respectively, and are the mean values of x and y, and n is the total number of samples.
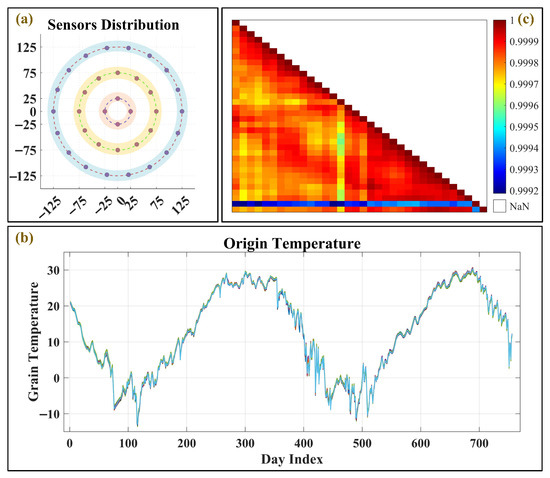
Figure 6.
(a) Sensors layout; (b) temperature curves; (c) correlation analysis at the grain surface layer.
As shown from the Pearson correlation heatmap in Figure 6c, the correlation coefficients between all temperature series are higher than 0.999, which indicates that under the dominance of external environmental factors, the temperatures at various measuring points on the grain piles surface show a highly synchronized variation trend. Based on this high synchronization, this study selects the average temperature series of the 34 measuring points on the grain pile surface as the representative sequence of the surface temperature, and all subsequent modeling and analysis are based on this sequence.
Given that the temperature variation process on the grain piles surface exhibits both non-stationarity and multi-time-scale characteristics, this study introduces VMD to decompose the original temperature into multiple IMFs with different frequency features. By predicting each IMF component separately and then reconstructing the temperature series, the difficulties in modeling and error propagation issues faced when directly modeling the original complex sequence can be effectively reduced.
To ensure the validity of VMD decomposition results and the rationality of modal distribution, this paper constructs an evaluation index based on Sample Entropy to assess the decomposition results under different numbers of decomposition modes (i.e., VMD parameter K). This index combines the mean and standard deviation of the Sample Entropy value of each mode, the optimization objective function defined as Formula (10).
In specific experiments, considering the physical characteristics and fluctuation cycle laws of grain pile temperature changes, this study determines the candidate range of the number of modes as . The setting of this range is mainly based on the physical mechanism by which the surface temperature of grain piles is affected by multi-scale factors: its variation process includes the superposition of multiple time-scale factors such as long-term trends caused by seasonal changes, medium-cycle fluctuations induced by day–night alternations, slow changes due to biological heat accumulation inside the grain pile, and random disturbances, thus exhibiting multiple significant time-scale features.
The calculated relationship curve is shown in Figure 7. It can be seen from the figure that when , both and reach their minimum values simultaneously, and their sum achieves the minimum value. This indicates that the internal structural components of each mode obtained by VMD decomposition at this point have the lowest degree of aliasing, with no significant redundant decomposition, and the information distribution among modes is the most balanced. Therefore, the optimal number of decomposition modes is finally determined as . The VMD decomposition results of the original grain pile surface temperature series are shown in Figure 8, which clearly reflect the dynamic structural characteristics of the grain pile surface temperature across different time scales.
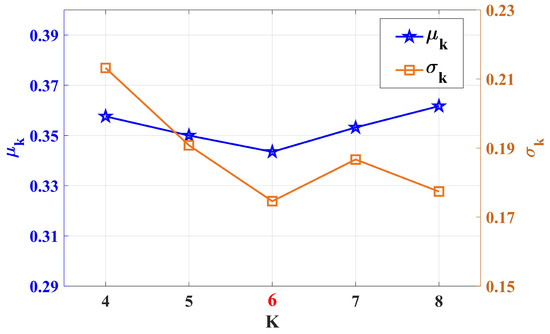
Figure 7.
SampEn-based evaluation of VMD mode number selection.
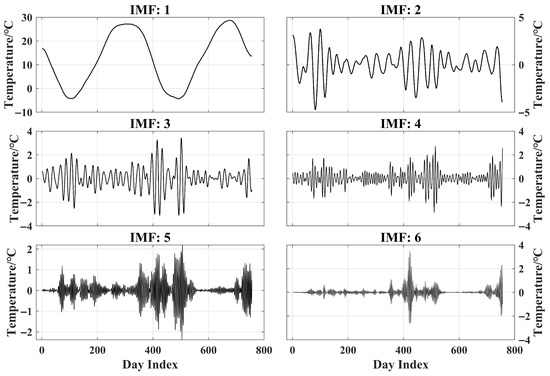
Figure 8.
IMFs obtained from VMD when .
4.2. Prediction of Decomposed IMFs
To evaluate the performance of the proposed improved vLSTM model in multivariate time-series prediction tasks, this study selects current mainstream time-series modeling methods as baseline comparison models for analysis. The selected models include the following:
- (1)
- Gated Recurrent Unit (GRU): A recurrent neural network with update and reset gates, effectively capturing temporal dependencies while mitigating gradient vanishing.
- (2)
- Temporal Convolutional Network (TCN): Based on causal convolution and dilated convolution, it can capture long-term temporal dependencies and support parallel computing, and avoid the gradient problem of recurrent networks.
- (3)
- iTransformer: An improved Transformer variant that optimizes the attention mechanism for time series, enhancing the ability to capture long sequences and being applicable to multivariate time-series prediction tasks.
In the experiment, the dataset is divided into training and testing sets at a ratio of 9:1. To provide an intuitive comparison of predictive performance across models, Figure 9 illustrates the predicted versus actual values of 6 IMF components over a 60-day period from the testing set.
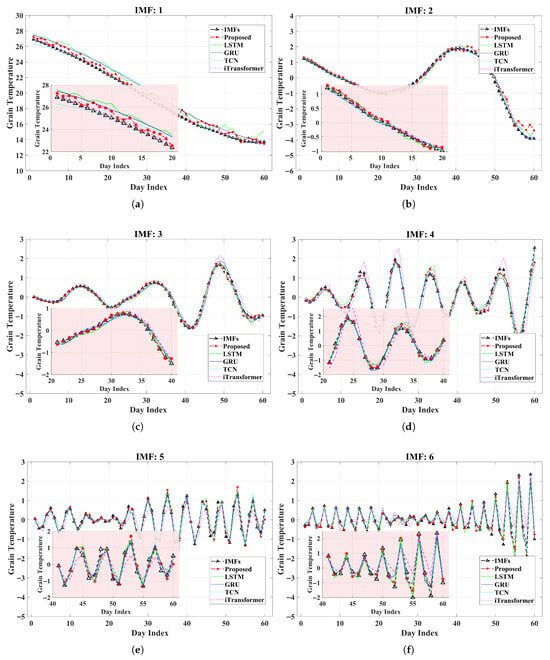
Figure 9.
Forecasting results for IMFs using different models: (a) IMF1. (b) IMF2. (c) IMF3. (d) IMF4. (e) IMF5. (f) IMF6.
Meanwhile, to comprehensively quantify the overall performance of each model in multi-component prediction tasks, this study concatenates all IMF components and calculates regression performance metrics including , , and coefficient of determination (). Their calculation formulas are as follows:
where n is the number of samples, is the actual value, is the predicted value, and is the mean of the actual values.
Specifically, is the average of absolute differences between the predicted values and actual values, with a smaller value indicating a smaller average error; is more sensitive to large errors and can reflect the degree of deviation between predicted values and actual values; represents the model’s ability to fit data fluctuations, and a value closer to 1 indicates the stronger explanatory power of the model.
As shown in the prediction results of each IMF in Figure 9, the proposed vLSTM model, while preserving the fundamental structural advantages of LSTM, effectively enhances the extraction capability of multi-input temporal features through the optimization of gating coupling and peephole connection mechanisms, leading to prediction results that are closer to the ground truth at most time points. Furthermore, the statistical results in Table 2 indicate that, compared with the original LSTM, the vLSTM achieves reductions of over 30% in both and , along with a significant improvement in the value; they also demonstrate superior overall performance compared with models such as GRU. In summary, the prediction comparison curves and quantitative metrics jointly confirm the effectiveness and applicability of the proposed vLSTM as a multivariate temperature prediction model following VMD decomposition.

Table 2.
Overall performance comparison of different models in multi-component IMFs prediction.
4.3. Performance Evaluation
4.3.1. Inter-Model Comparison
After completing the prediction of each IMF, this study leverages the signal reconstructability of the VMD method to superimpose the predicted results of each IMF component point-by-point, reconstructing the predicted surface temperature of grain piles. Subsequently, combined with the environmental factor model based on multiple regression, factors such as air temperature and humidity, and dew point temperature are explicitly integrated to generate the final surface temperature prediction results. Figure 10 presents the comparison between the final prediction results and the actual temperature curve.
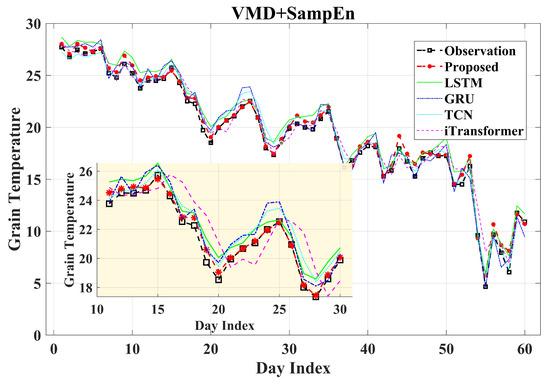
Figure 10.
Prediction results combining VMD and SampEn with various models.
From the visualization results, it can be observed that the proposed VMD-SampEn-vLSTM-E prediction framework exhibits excellent performance in three dimensions: overall trend tracking, local detail restoration, and response to temperature fluctuation amplitudes (specific details can be found in the enlarged subgraph). Compared with models such as GRU, original LSTM, and TCN, this method can effectively avoid the common smoothing distortion problem of traditional models when processing temperature changes in non-stationary periods, while significantly reducing prediction lag. The introduction of environmental factors directly highlights the higher fitting accuracy and stronger dynamic response capabilities of the proposed method.
To quantitatively evaluate the overall prediction effect, this study calculates three core performance metrics (, and ) based on the final prediction results, with specific results shown in Table 3. The data indicate that the proposed hybrid model outperforms the comparison models in all metrics: the MAE is as low as 0.4141, which is much lower than 0.8099 of the original LSTM model; the RMSE significantly decreases to 0.5653, indicating the smaller volatility of prediction errors. Further comparison reveals that this method achieves an average improvement of over 25% in the MAE and over 14% in the RMSE compared with other mainstream models, fully confirming its accuracy advantage in non-stationary time-series prediction.

Table 3.
Comparison of prediction performance metrics (, and ) among different models.
4.3.2. Ablation Experiment
To rigorously validate the rationality of the proposed VMD-SampEn-vLSTM-E framework for grain pile surface temperature prediction, ablation experiments are conducted to examine the necessity and contribution of each core component.
The first set of experiments aims to evaluate the necessity of the decomposition strategy. Specifically, the proposed VMD-SampEn decomposition is compared with the case where no decomposition is applied, in order to demonstrate the effectiveness of incorporating decomposition into the prediction framework.
Figure 11 presents a comparison between models with and without the decomposition. The results indicate that the direct modeling approach exhibits a clear prediction lag during the fitting stage and fails to effectively track rapid fluctuations, whereas the incorporation of VMD-SampEn decomposition significantly enhances both fitting accuracy and responsiveness to dynamic variations.
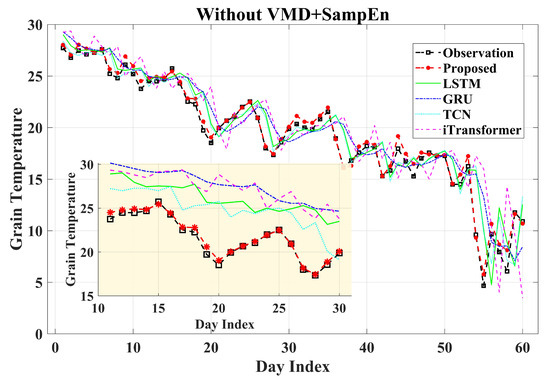
Figure 11.
Comparison of prediction results between the proposed method and conventional models.
The second set of experiments centers on the predictive modeling component. The proposed VMD-SampEn-vLSTM-E is compared with baseline models, including VMD-SampEn-LSTM and VMD-SampEn-vLSTM, to verify its superiority in capturing temporal dynamics and improving forecasting accuracy.
To further assess the long-term prediction capability, an additional experiment was conducted on a 300-day test dataset. Representative cases from April, July, October, and January were selected to reflect the four seasons under the granary’s climatic conditions. As shown in Figure 12, the vLSTM consistently outperforms the standard LSTM, delivering notably higher accuracy. More importantly, the proposed prediction framework achieves prediction accuracy improvements exceeding 50% over the baseline LSTM across all periods, thereby demonstrating strong robustness and stability under diverse seasonal conditions.
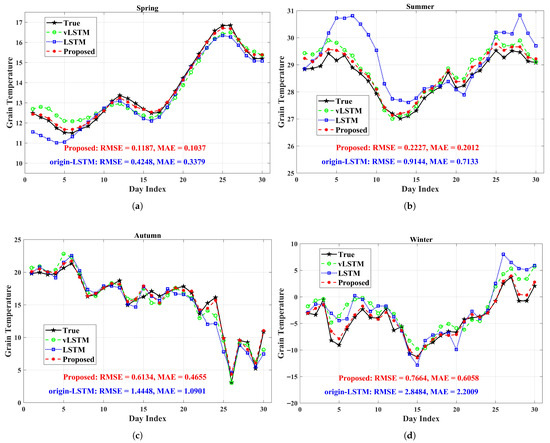
Figure 12.
Long-term prediction effect from typical four seasons perspective (Liaoning, China): (a) Spring (April). (b) Summer (July). (c) Autumn (October). (d) Winter (January).
In summary, the comparative results shown in Figure 11 and Figure 12 indicate that the proposed VMD-SampEn-vLSTM-E prediction framework, constructed under the hybrid strategy of “decomposition–prediction–reconstruction–environmental factor”, achieves superior performance through refined multi-scale feature modeling. It excels in both capturing dynamic variations and fitting overall trends, thereby effectively overcoming the limitations of single models in adapting to multi-scale temporal features.
4.4. Results and Discussion
The above experimental results demonstrate that the proposed VMD-SampEn-vLSTM-E method not only has accurate modeling capability in the prediction of multiple IMF components but also has significantly better temperature prediction results than traditional modeling methods in terms of overall accuracy, dynamic response speed, and generalization ability. This result fully verifies the feasibility and applicability of this method in complex non-stationary, multi-scale time-series prediction tasks, providing reliable technical support for the accurate prediction of grain pile surface temperature.
It should be noted that, as illustrated in Figure 9a, the prediction performance of vLSTM on the low-frequency component (IMF1) is slightly inferior to that of the iTransformer. Nevertheless, for the remaining high-frequency IMF components, the vLSTM model exhibits more stable and accurate prediction performance, thereby ensuring its superiority in overall predictive capability. This phenomenon is associated with the modeling characteristics of iTransformer’s attention mechanism: its attention mechanism tends to focus on modeling global relationships between variables (i.e., across different features) rather than emphasizing the feature of individual modalities. As a result, when processing high-frequency noise components, it easily introduces inter-modal interference, leading to a decline in prediction accuracy. In contrast, the proposed vLSTM model, with its optimized gating mechanism and direct cell state perception capability, exhibits better performance in modeling local and long-term dependencies of single sequences, thus demonstrating advantages in full-component modeling.
Based on these findings, it becomes possible to identify promising avenues for methodological advances, which are detailed below in the future work section.
5. Future Work
In the multi-IMF prediction experiments, it was observed that the iTransformer model outperforms the proposed vLSTM model in fitting low-frequency components (e.g., IMF1), but shows relatively weaker performance in modeling high-frequency disturbances. In contrast, the vLSTM model demonstrates distinct advantages in dynamic response to high-frequency variations and full-component prediction. Therefore, future work may focus on two aspects: first, developing multi-model fusion strategies that combine the strengths of iTransformer and vLSTM to collaboratively model features across different frequency bands; second, optimizing the input design and the application of the attention mechanism in iTransformer to fully leverage its capability to model relatively independent sequences in multi-time-series prediction tasks.
In addition, although the SampEn-based parameter selection strategy proposed in this study effectively enhances the balance and stability of the VMD decomposition, VMD behaves as a non-perfectly reversible process in practical applications due to limitations in numerical precision and optimization strategy. As a result, the decomposition and reconstruction processes inevitably introduce some degree of information loss, leading to slight deviations between the predicted results and the actual temperature signals. Thus, future research should aim to improve the decomposition efficiency and signal fidelity of VMD by optimizing its decomposition scheme and reconstruction algorithm. This would provide higher-quality input signals for temperature prediction models and further enhance the robustness and accuracy of forecasting outcomes.
6. Conclusions
The surface temperature of grain piles is highly sensitive to external environmental conditions and tends to exhibit more complex nonlinear and non-stationary fluctuations compared to internal grain temperatures. As such, it often serves as the earliest indicator of abnormal grain storage conditions. Considering the multi-scale temporal characteristics of surface temperature variations, this study proposes a decomposition–prediction–reconstruction framework that integrates environmental factors, Sample Entropy (SampEn), Variational Mode Decomposition (VMD), and an improved Long Short-Term Memory network (variant LSTM, vLSTM) to construct the VMD-SampEn-vLSTM-E prediction model, thereby reducing the difficulty of directly modeling the original temperature sequence.
Specifically, a SampEn-based evaluation criterion was first developed to guide the selection of optimal VMD decomposition parameters, enhancing the balance and physical interpretability of the resulting intrinsic mode functions (IMFs). Then, the original temperature sequence was decomposed into multiple IMFs, and the structure-optimized vLSTM model was used to perform multivariate time-series prediction on all components. Finally, by reconstructing all IMFs prediction results into a complete temperature series and using a multivariate regression model to correct the prediction results based on environmental factors, a high-precision prediction of the grain pile surface temperature was achieved. Experimental results show that compared with similar models, the proposed method improves MAE and RMSE by over 25% and 14%, respectively, significantly enhancing grain pile surface temperature prediction accuracy. Under non-standard storage conditions, the application of this method is expected to generate an economic benefit of over 10 CNY per ton of grain. Moreover, its low computational complexity facilitates practical application in grain storage, laying a technical foundation for food security and sustainable agricultural development.
In summary, this study provides a high-performance predictive modeling framework for surface temperature monitoring in grain storage, and also offers a transferable methodology for handling non-stationary, multi-scale time-series prediction tasks. Future research will focus on multi-model integration strategies and the optimization of VMD decomposition and reconstruction to further improve the modeling accuracy and robustness for complex, multi-scale temperature signals.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, B.L. and L.Q.; methodology, B.L. and P.L.; formal analysis, J.Q.; investigation, L.Q.; writing—original draft preparation, P.L.; visualization, P.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The author does not have the authority to publicly disclose all the data. However, interested researchers can contact the corresponding author via the provided email address to obtain a limited amount of experimental data for advancing research in this field.
Acknowledgments
During the preparation of this work the authors used ChatGPT (OpenAI, GPT-4.0, accessed in 2025) and DeepSeek (version 3) in order to improve the readability and language of the manuscript. After using this tool/service, the authors have reviewed and edited the output and take full responsibility for the content of this publication.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Kaushik, R.; Singhai, J. An approach for the development of a sensing system to monitor contamination in stored grain. In Proceedings of the 2019 6th International Conference on Signal Processing and Integrated Networks (SPIN), Noida, India, 7–8 March 2019; IEEE: Noida, India, 2019; pp. 880–884. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, W.; Cui, H.; Han, F.; Liu, Z.; Wu, X.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, Q. Digital monitoring of grain conditions in large-scale bulk storage facilities based on spatiotemporal distributions of grain temperature. Biosyst. Eng. 2021, 210, 247–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, C.; Sun, D.-W.; Cao, C. Computer simulation of temperature changes in a wheat storage bin. J. Stored Prod. Res. 2001, 37, 165–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.C.; Yang, K.M.; Zhang, Z.T.; Qi, W.; Yang, J. Natural convection heat and moisture transfer with thermal radiation in a cavity partially filled with hygroscopic porous medium. Dry. Technol. 2016, 34, 275–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, R.; Zhang, Q. A pore-scale model for predicting resistance to airflow in bulk grain. Biosyst. Eng. 2017, 155, 142–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estaquio, R.P.; Danao, L.A.; Lustro, J.R. A Numerical Study on Performance Enhancement of Locally Produced Axial-Flow Fans for Grain Drying. In ASME International Mechanical Engineering Congress and Exposition; American Society of Mechanical Engineers: Portland, OR, USA, 2020; p. V009T10A057. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, Y.-L.; Ma, X.-M.; Xi, L.; Yu, H.; Zhang, H.; Che, Y.-C. Research on a safe wheat storage monitoring and prediction system. N. Z. J. Agric. Res. 2007, 50, 673–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Wang, J.; Li, Z.; Hou, M.; Dong, G.; Liu, T.; Sun, T.; Grattan, K.T.V. Quasi-distributed fiber optic temperature and humidity sensor system for monitoring of grain storage in granaries. IEEE Sens. J. 2020, 20, 9226–9233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodali, R.K.; John, J.; Boppana, L. IoT monitoring system for grain storage. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Electronics, Computing and Communication Technologies (CONECCT), Bangalore, India, 2–4 July 2020; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Simin, W.; Yifei, K.; Yixuan, X.; Chunmiao, M.; Haitao, W.; Weiguo, W. Data center temperature prediction and management based on a Two-stage self-healing model. Simul. Model. Pract. Theory 2024, 132, 102883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Sun, K.; Yan, J.; Dong, C. The CNN-GRU model with frequency analysis module for sea surface temperature prediction. Soft Comput. 2023, 27, 8711–8720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, X.; Zhou, X.; Guo, D.; Li, S.; Liu, S.; Xu, C. Ocean temperature prediction based on stereo spatial and temporal 4-D convolution model. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2021, 19, 1003405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christian, R.A.; Patel, D.A. Potential of k-means clustering-based fuzzy logic for prediction of temperature in ambient atmosphere. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2015, 40, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Gao, P.; Sun, Z.; Wang, H.; Lu, M.; Liu, Y.; Hu, J. Multistep ahead prediction of temperature and humidity in solar greenhouse based on FAM-LSTM model. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2023, 213, 108261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Gao, J.; Wang, W.; Yan, Z. Physics-informed generative neural network: An application to troposphere temperature prediction. Environ. Res. Lett. 2021, 16, 065003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusinek, R.; Kobyłka, R. Experimental study and discrete element method modeling of temperature distributions in rapeseed stored in a model bin. J. Stored Prod. Res. 2014, 59, 254–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.-W.; Woods, J.L. Simulation of the heat and moisture transfer process during drying in deep grain beds. Dry. Technol. 1997, 15, 2479–2492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.-W.; Woods, J.L. Deep-bed simulation of the cooling of stored grain with ambient air: A test bed for ventilation control strategies. J. Stored Prod. Res. 1997, 33, 299–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quemada-Villagómez, L.I.; Molina-Herrera, F.I.; Carrera-Rodríguez, M.; Calderón-Ramírez, M.; Martínez-González, G.M.; Navarrete-Bolaños, J.L.; Jiménez-Islas, H. Numerical study to predict temperature and moisture profiles in unventilated grain silos at prolonged time periods. Int. J. Thermophys. 2020, 41, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Feng, J.; Han, F.; Wu, W.; Gao, S. Analysis and prediction of grain temperature from air temperature to ensure the safety of grain storage. Int. J. Food Prop. 2020, 23, 1200–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, S.; Yang, W.; Wang, X.; Mao, S.; Zhang, Y. Grain pile temperature forecasting from weather factors: A support vector regression approach. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CIC International Conference on Communications in China (ICCC), Changchun, China, 11–13 August 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 255–260. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, F.; Gong, C.; Lyu, Z. Grain storage temperature prediction based on chaos and enhanced RBF neural network. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 24015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrera-Rodríguez, M.; Martínez-González, G.M.; Navarrete-Bolaños, J.L.; Botello-Álvarez, J.E.; Rico-Martínez, R.; Jiménez-Islas, H. Transient numerical study of the effect of ambient temperature on 2-D cereal grain storage in cylindrical silos. J. Stored Prod. Res. 2011, 47, 106–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Z.; Chen, X.; Chen, Y. Research on the temperature field of grain piles in underground grain silos lined with plastic. J. Food Process Eng. 2022, 45, e13971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Si, X.; Hu, C.; Zhang, J. A review of recurrent neural networks: LSTM cells and network architectures. Neural Comput. 2019, 31, 1235–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Zhang, S.; Peng, J.; Zhang, S.; Li, J.; Xiong, H.; Zhang, W. Informer: Beyond efficient transformer for long sequence time-series forecasting. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Online, 2–9 February 2021; AAAI Press: Palo Alto, CA, USA; Volume 35, pp. 11106–11115. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, Q. Stock market index prediction using deep Transformer model. Expert Syst. Appl. 2022, 208, 118128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang, S.; Li, L. A novel variant of LSTM stock prediction method incorporating attention mechanism. Mathematics 2024, 12, 945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Hong, C.; Zhang, C.; Dai, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, X.; Jiang, X.; Qian, J.; Gu, Z. Temperature forecasting of grain in storage: A multi-output and spatiotemporal approach based on deep learning. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2023, 208, 107785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochreiter, S.; Schmidhuber, J. Long short-term memory. Neural Comput. 1997, 9, 1735–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, S.; Yang, W.; Wang, X.; Mao, S.; Zhang, Y. Temperature forecasting for stored grain: A deep spatiotemporal attention approach. IEEE Internet Things J. 2021, 8, 17147–17160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Yang, H.; Zhou, K.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, Y. Application of bidirectional LSTM neural network in grain stack temperature prediction. In International Conference on Bio-Inspired Computing: Theories and Applications; Springer: Huangshan, China, 2021; pp. 385–395. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, B.; Tao, S.; Li, B. Grain temperature prediction based on GRU deep fusion model. Int. J. Inf. Technol. Decis. Mak. 2025, 24, 797–815. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Liu, S.; Wang, Y.; Li, G.; Yu, L. Research on grain pile temperature prediction based on cnn-gru neural network. In The International Symposium on Computer Science, Digital Economy and Intelligent Systems; Springer: Tashkent, Uzbekistan, 2021; pp. 214–226. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Z.; Bai, Y.; Jin, X.; Wang, X.; Su, T.; Kong, J. Deep prediction model based on dual decomposition with entropy and frequency statistics for nonstationary time series. Entropy 2022, 24, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, W.; Tian, W.; Tian, Y.; Yang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J. The forecasting of PM2.5 using a hybrid model based on wavelet transform and an improved deep learning algorithm. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 142814–142825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, N.E.; Shen, Z.; Long, S.R.; Wu, M.C.; Shih, H.H.; Zheng, Q.; Yen, N.-C.; Tung, C.C.; Liu, H.H. The empirical mode decomposition and the Hilbert spectrum for nonlinear and non-stationary time series analysis. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A 1998, 454, 903–995. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.; Huang, N.E. Ensemble empirical mode decomposition: A noise-assisted data analysis method. Adv. Adapt. Data Anal. 2009, 1, 1–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragomiretskiy, K.; Zosso, D. Variational mode decomposition. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2013, 62, 531–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Z.; Wang, X.; Liu, J.; Fan, F. An adaptive spectrum segmentation-based optimized VMD method and its application in rolling bearing fault diagnosis. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2022, 33, 125107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, W.; Wang, K.; Li, C.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; Zhong, H. Vibration trend measurement for a hydropower generator based on optimal variational mode decomposition and an LSSVM improved with chaotic sine cosine algorithm optimization. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2018, 30, 015012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Z.; Wang, Z.; Shen, Y.; Huang, C.; Jiang, Y.; Li, P. Time-frequency information-based variational mode decomposition and its application in prediction models. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2025, 36, 036122. [Google Scholar]
- Gers, F.A.; Schmidhuber, J. Recurrent nets that time and count. In Proceedings of the IEEE-INNS-ENNS International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN 2000), Neural Computing: New Challenges and Perspectives for the New Millennium, Como, Italy, 27 July 2000; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2000; Volume 3, pp. 189–194. [Google Scholar]
- Li, P.; Zhang, Z.; Xiong, Q.; Ding, B.; Hou, J.; Luo, D.; Rong, Y.; Li, S. State-of-health estimation and remaining useful life prediction for the lithium-ion battery based on a variant long short term memory neural network. J. Power Sources 2020, 459, 228069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, K.; Van Merriënboer, B.; Gulcehre, C.; Bahdanau, D.; Bougares, F.; Schwenk, H.; Bengio, Y. Learning phrase representations using RNN encoder-decoder for statistical machine translation. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1406.1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greff, K.; Srivastava, R.K.; Koutník, J.; Steunebrink, B.R.; Schmidhuber, J. LSTM: A search space odyssey. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2016, 28, 2222–2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).