Are There Differences in the Response of Lake Areas at Different Altitudes in Xinjiang to Climate Change?
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Sources
2.3. Lake Selection and Mapping
2.4. Statistical Analysis
2.4.1. Trend Analysis
2.4.2. Partial Correlation Analysis
2.5. Accuracy Recognition
3. Results
3.1. Lake Water Extraction
3.2. Interannual Changes in Lake Area
3.2.1. Overall Change Trend of Lakes in Xinjiang
3.2.2. Interannual Variation in Plain Lakes Area
3.2.3. Interannual Variation in the Area of Alpine Lakes
3.2.4. Interannual Variation in the Area of Plateau Lakes
3.3. Background to Meteorological Factor Changes in Xinjiang
3.4. Changes in Human Activities
3.4.1. Changes in Urban Water Use
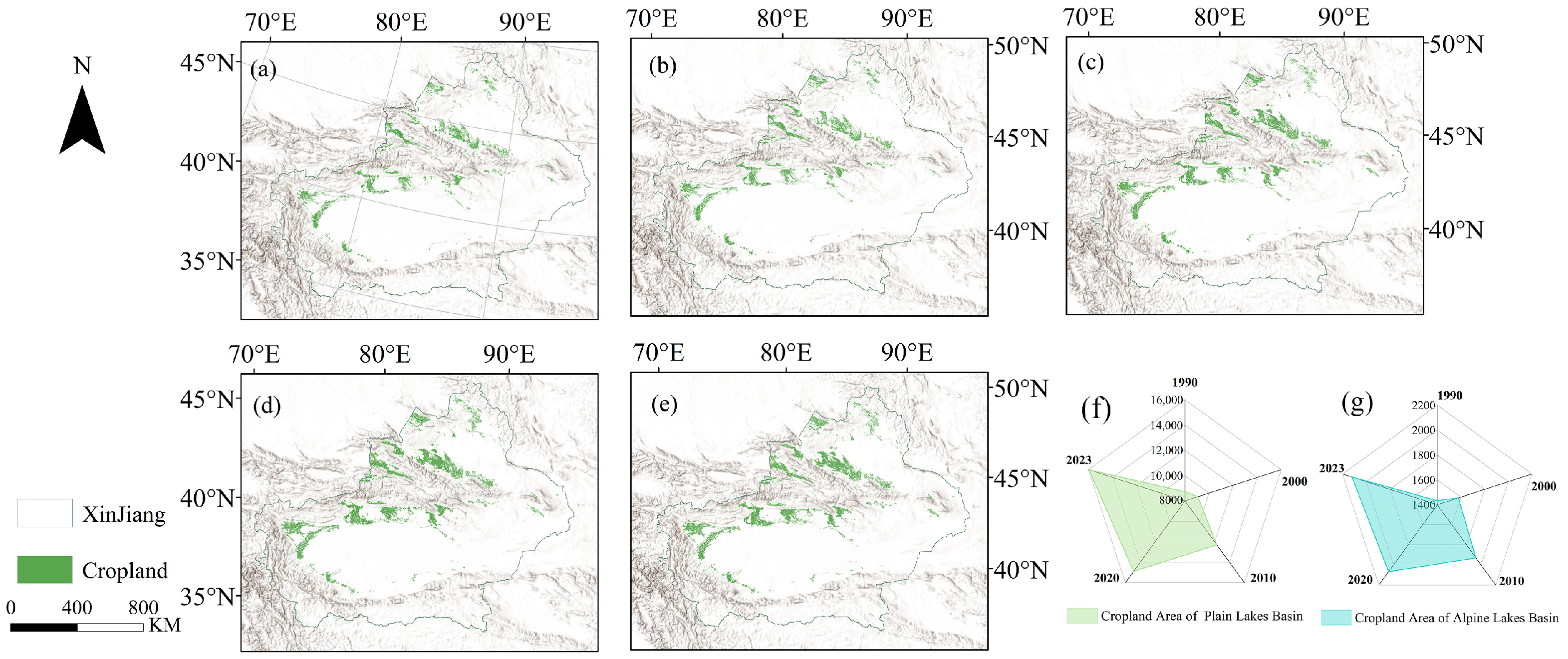
3.4.2. Changes in Agricultural Water Use
3.5. Statistical Analysis of the Relationship Between Changes in Lake Area and Influencing Factors
4. Discussion
4.1. Factors Affecting Plain Lakes
4.2. Factors Affecting Alpine Lakes
4.3. Factors Affecting Highland Lakes
4.4. Ecological Effects of Changes in Lake Area
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hu, R.; Jiang, F.; Wang, Y.; Sun, Z. On the importance of research on the lake in arid land of China. Arid Zone Res. 2007, 24, 137–140. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woolway, R.I.; Kraemer, B.M.; Lenters, J.D.; Merchant, C.J.; O’Reilly, C.M.; Sharma, S. Global Lake Responses to Climate Change. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2020, 1, 388–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Wang, N.; Chen, A.; He, J.; Hua, T.; Qie, Y. Changes in area and water volume of the Aral Sea in the arid Central Asia over the period of 1960–2018 and their causes. Catena 2020, 191, 104566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Yao, T.; Chen, W.; Zheng, G.; Shum, C.K.; Yang, K.; Piao, S.; Sheng, Y.; Yi, S.; Li, J.; et al. Regional differences of lake evolution across China during 1960s–2015 and its natural and anthropogenic causes. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 221, 386–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naeem, M.; Zhang, Y.; Vahid, N.; Tian, X.; Miao, P. Both climate and anthropogenic impacts on recent lake area change in the Erdos Plateau. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 373, 123443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Y.; Chen, R.; Yang, K.; Zhou, X.; Jia, T.; Shang, C.; Pei, X.; Wang, Q.; Li, D.; Peng, C.; et al. Response of changes in lake area to drought and land use change. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 947, 174638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wurtsbaugh, W.A.; Miller, C.; Null, S.E.; DeRose, R.J.; Wilcock, P.; Hahnenberger, M.; Howe, F.; Moore, J. Decline of the world’s saline lakes. Nat. Geosci. 2017, 10, 816–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinna, L.R.; Medhaug, I.; Schmid, M.; Bouffard, D. The vulnerability of lakes to climate change along an altitudinal gradient. Commun. Earth Environ 2021, 2, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Wang, W.; An, B.; Wei, L. Enhanced glacial lake activity threatens numerous communities and infrastructure in the Third Pole. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 8250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Yao, T.; Shum, C.K.; Yi, S.; Yang, K.; Xie, H.; Feng, W.; Bolch, T.; Wang, L.; Behrangi, A.; et al. Lake volume and groundwater storage variations in Tibetan Plateau’s endorheic basin. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2017, 44, 5550–5560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Ran, Y.; Zhang, G.; Li, X. Remotely sensed lake area changes in permafrost regions of the Arctic and the Tibetan Plateau between 1987 and 2017. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 880, 163355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dømgaard, M.; Kjeldsen, K.; How, P.; Bjørk, A. Altimetry-based ice-marginal lake water level changes in Greenland. Commun. Earth Environ. 2024, 5, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salerno, F.; Gambelli, S.; Viviano, G.; Thakuri, S.; Guyennon, N.; D’Agata, C.; Diolaiuti, G.; Smiraglia, C.; Stefani, F.; Bocchiola, D.; et al. High alpine ponds shift upwards as average temperatures increase: A case study of the Ortles-Cevedale mountain group (southern Alps, Italy) over the last 50 years. Glob. Planet. Change 2014, 120, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Yang, X.; Cui, Z.; Ren, L.; Jiang, S.; Liu, Y.; Yuan, S. The impact of human activities on blue-green water resources and quantification of water resource scarcity in the Yangtze River Basin. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 909, 168550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pekel, J.F.; Cottam, A.; Gorelick, N.; Belward, A.S. High-resolution mapping of global surface water and its long-term changes. Nature 2016, 540, 418–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, D. Remote sensing estimation of water volume changes of typical lakes in Xinjiang, China from 1990 to 2021. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2024, 35, 3141–3148. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wufu, A.; Wang, H.; Chen, Y.; Rusuli, Y.; Ma, L.; Yang, S.; Zhang, F.; Wang, D.; Li, Q.; Li, Y. Lake water volume fluctuations in response to climate change in Xinjiang, China from 2002 to 2018. PeerJ 2020, 8, e9683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Zheng, B.; Jia, H.; Peng, J.; Zhou, X. Influence of social and economic development on water quality in Dongting Lake. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 131, 108220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Li, Z.; Fan, Y.; Wang, H.; Fang, G. Research progress on the impact of climate change on water resources in the arid region of Northwest China. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2014, 69, 1295–1304. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B. The recent evolution of dune landforms and its environmental indications in the mid-latitude desert area (Hexi Corridor). J. Geogr. Sci. 2022, 32, 617–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, D.K.; O’Leary, D.S.; DiGirolamo, N.E.; Miller, W.; Kang, D.H. The role of declining snow cover in the desiccation of the Great Salt Lake, Utah, using MODIS data. Remote Sens. Env. 2021, 252, 112106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binh, P.D.; Florence, S.; Fabrice, P.; Frappart, F.; Bouchez, C.; Crétaux, J.F. The Lake Chad hydrology under current climate change. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 5498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Xu, W.; Bao, K.; Hou, W.; Su, J.; Li, H.; Miao, Z. A water body extraction methods comparison based on FengYun Satellite data: A case study of Poyang Lake Region, China. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tulbure, M.G.; Broich, M.; Stehman, S.V.; Kommareddy, A. Surface water extent dynamics from three decades of seasonally continuous Landsat time series at subcontinental scale in a semi-arid region. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 178, 142–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herath, H.M.P.I.K.; Halwatura, R.U.; Jayasinghe, G.Y. Evaluation of green infrastructure effects on tropical Sri Lankan urban context as an urban heat island adaptation strategy. Urban For. Urban Green. 2018, 29, 212–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Xie, G.; Deng, J.; Shao, K.; Hu, Y.; He, J.; Zhang, J.; Gao, G. Effects of climate change and anthropogenic activities on lake environmental dynamics: A case study in Lake Bosten Catchment, NW China. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 319, 115764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zhang, F.; Jim, C.Y.; Johnson, V.C.; Tan, M.L.; Shi, J.; Lin, X. Controlled and driving mechanism of the SPM variation of shallow Brackish Lakes in arid regions. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 878, 163127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, G.; Ji, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Fan, W. Climate and human-driven variations in lake area and number in North Xinjiang, China. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2021, 42, 469–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhai, P.; Qin, D. New perspectives on ‘warming–wetting’ trend in Xinjiang, China. Adv. Clim. Change Res. 2020, 11, 252–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Kang, S.; Wu, H.; Yuan, X. Detection of spatio-temporal variability of air temperature and precipitation based on long-term meteorological station observations over Tianshan Mountains, Central Asia. Atmos. Res. 2018, 203, 141–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Yang, Q.; Mao, W.; Zhao, Y.; Xu, X. Precipitation trend-Elevation relationship in arid regions of the China. Glob. Planet. Change 2016, 143, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, H.; Zhang, C.; Jin, X.; Ge, A.; Chen, M.; Ye, J.; Qiao, H.; Xiong, P.; Zhang, X.; Chen, J.; et al. A flagship species-based approach to efficient, cost-effective biodiversity conservation in the Qinling Mountains, China. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 305, 114388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Lei, X.; Chen, S.; Yu, T.; Hu, Z.; Zhang, M.; Jiang, L.; Bao, R.; Guan, X.; Ma, M.; et al. How Well Does the ERA5 Reanalysis Capture the Extreme Climate Events Over China? Part II: Extreme Temperature. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, e921659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorelick, N.; Hancher, M.; Dixon, M.; Ilyushchenko, S.; Thau, D.; Moore, R. Google earth engine: Planetary-scale geospatial analysis for everyone. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 202, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, J.; Yong, B. Automatic extraction of surface water based on lightweight convolutional neural network. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 256, 114843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H. Modification of normalised difference water index (NDWI) to enhance open water features in remotely sensed imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2006, 27, 3025–3033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, H.B. Nonparametric test against trend. Econometrica 1945, 13, 245–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, P. Estimates of the Regression Coefficient Based on Kendall’s Tau. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1968, 63, 1379–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Chen, X.; Disse, M.; Cyffka, B.; Lei, J.; Zhang, H.; Brieden, A.; Welp, M.; Abuduwaili, J.; Li, Y.; et al. Climate change in Central Asia: Sino-German cooperative research findings. Sci. Bull. 2020, 65, 689–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hugonnet, R.; McNabb, R.; Berthier, E.; Menounos, B.; Nuth, C.; Girod, L.; Farinotti, D.; Huss, M.; Dussaillant, I.; Brun, F.; et al. Accelerated global glacier mass loss in the early twenty-first century. Nature 2021, 592, 726–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huss, M.; Hock, R. Global-scale hydrological response to future glacier mass loss. Nat. Clim. Change 2018, 8, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Chen, J.; Huang, W.; Chen, S.; Huang, X.; Jin, L.; Jia, J.; Zhang, X.; An, C.; Zhang, J.; et al. Westerlies Asia and monsoonal Asia: Spatiotemporal differences in climate change and possible mechanisms on decadal to sub-orbital timescales. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2019, 192, 337–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Guan, X.; Mao, W.; Yang, L. Climatic and associated atmospheric water cycle changes over the Xinjiang, China. J. Hydrol. 2020, 585, 124823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, N.; Wang, Y.; Xu, H.; Fam, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Yao, J.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, Y. Differences in and driving forces of cultivated land expansion in the Manas River Basin oasis, Xinjiang. Chin. J. Eco-Agric. 2021, 29, 1008–1017. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, F.; Shi, J.; Chan, N.W.; Cai, Y.; Cheng, C.; An, C.; Wang, W.; Liu, C. Analysis of surface water area dynamics and driving forces in the Bosten Lake basin based on GEE and SEM for the period 2000 to 2021. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2024, 31, 9333–9346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, C.; Zhang, F.; Li, X.; Tan, M.L.; Kumar, P.; Johnson, B.A.; Shi, J.; Zhao, Q.; Liu, C. Variations in water storage of Bosten Lake, China, over the last two decades based on multi-source satellite data. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2023, 49, 101496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Yao, J.; He, Q.; Chen, J. Changes in precipitation amounts and extremes across Xinjiang (northwest China) and their connection to climate indices. PeerJ 2021, 9, e10792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Liu, Z.; Liu, J.; Yang, X.; Zhang, M.; Zhou, Y. Analysis of Convection-Symmetric Instability and Triggering Mechanism for Extreme Rainstorms on the Northern Slope of the Middle Kunlun Mountains. Chin. J. Atmos. Sci. 2024, 48, 987–1011. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, B.; Cai, X.; Zhou, T.; He, Q. Moisture transport and sources of an extreme rainfall event of June 2021 in southern Xinjiang, China. Adv. Clim. Change Res. 2022, 13, 843–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, N.; Yang, T.; Wu, T.; Hu, R.; He, X. Lake shrinkage-induced terrestrial ecological environmental quality degradation in a semiarid lake basin. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 120892–120902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Ding, J.; Ge, X.; Wang, J.; Qin, S.; Tan, J.; Han, L.; Zhang, Z. Impacts of climate change on the wetlands in the arid region of Northwestern China over the past 2 decades. Ecol. Indic. Indic. 2023, 149, 110168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Liu, Z.; Yao, H.; Chen, X.; Chen, X.; Zheng, Y.; He, Y. Impacts of reservoir operations on multi-scale correlations between hydrological drought and meteorological drought. J. Hydrol. 2018, 563, 726–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Zhou, X.; Li, J.; Wu, W.; Chen, Y. Assessment of the salinization processes in the largest inland freshwater lake of China. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2015, 29, 1823–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Woolway, R.I.; Yang, K.; Wada, Y.; Wang, J.; Crétaux, J.F. Widespread societal and ecological impacts from projected Tibetan Plateau lake expansion. Nat. Geosci. 2024, 17, 516–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Yao, T.; Xie, H.; Yang, K.; Zhu, L.; Shum, C.K.; Bolch, T.; Yi, S.; Allen, S.; Jiang, L.; et al. Response of Tibetan Plateau lakes to climate change: Trends, patterns, and mechanisms. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2020, 208, 103269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, B.; Wang, C.; Chen, J.; Chen, J.; Barry, D.A.; Wang, T.; Li, L. Missing water from the Qiangtang Basin on the Tibetan Plateau. Geology 2021, 49, 867–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Carling, P.A.; Hu, K.; Wang, H.; Zhou, Z.; Zhou, L.; Liu, D.; Lai, Z.; Zhang, X. Outburst floods in China: A review. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2019, 97, 102895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
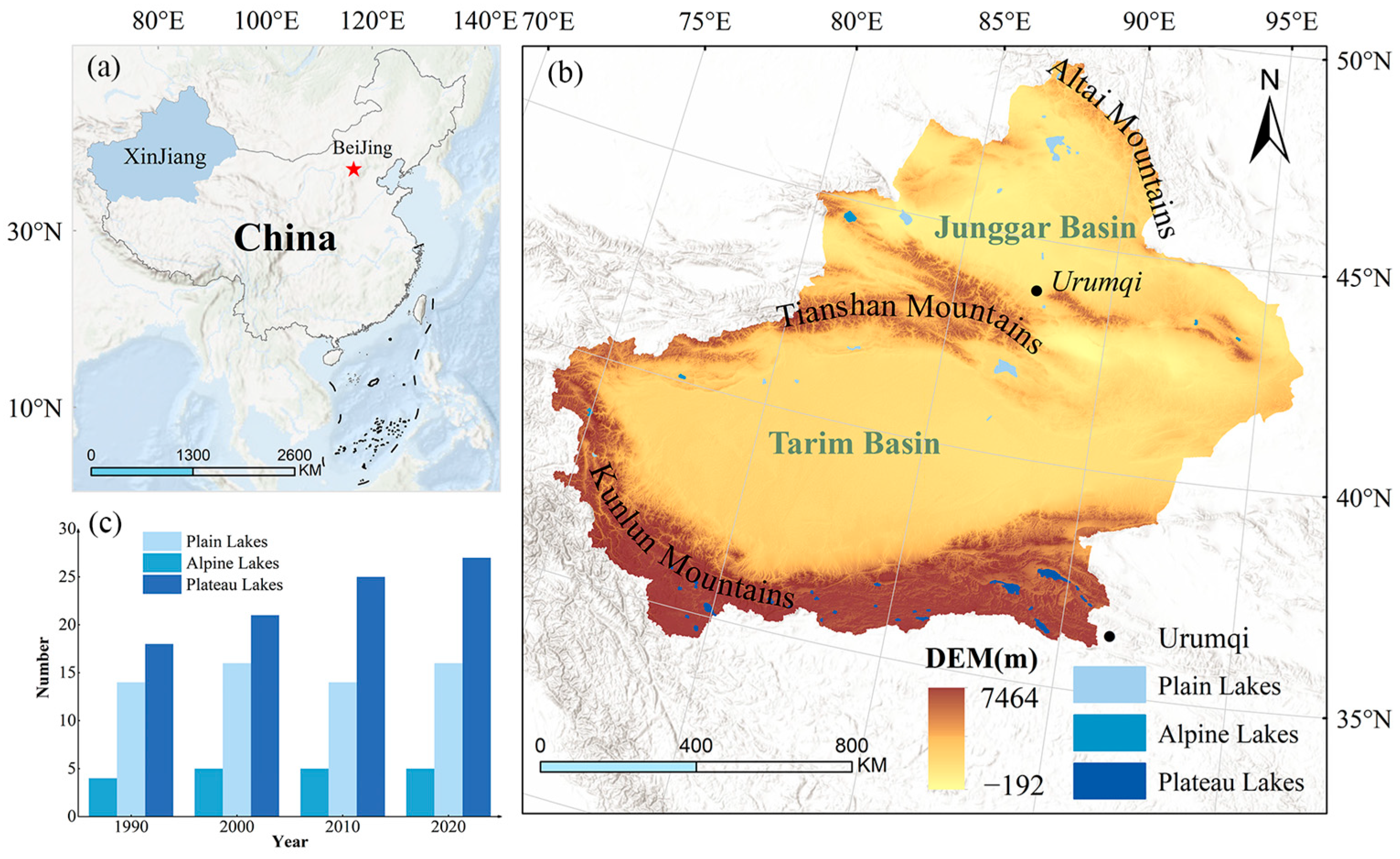


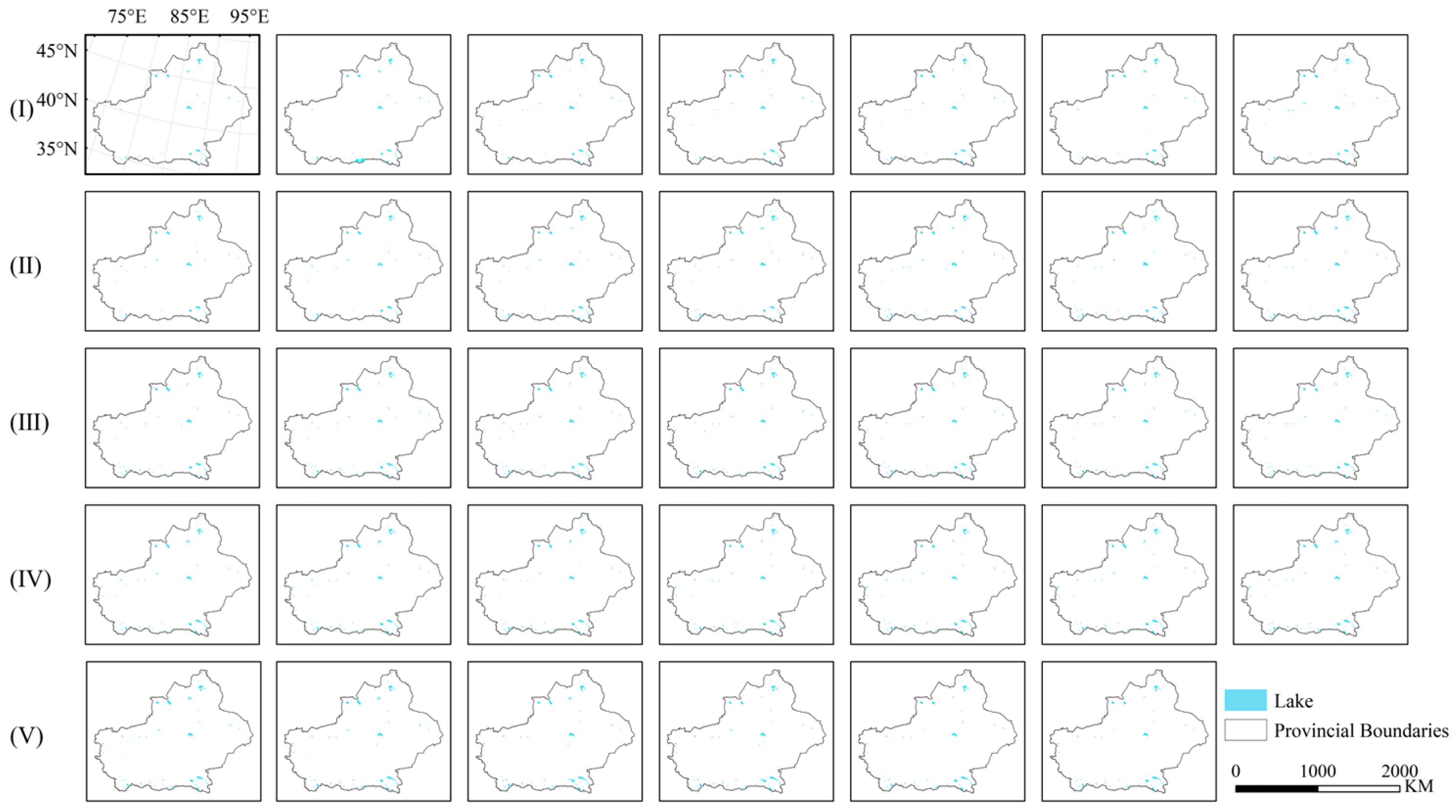


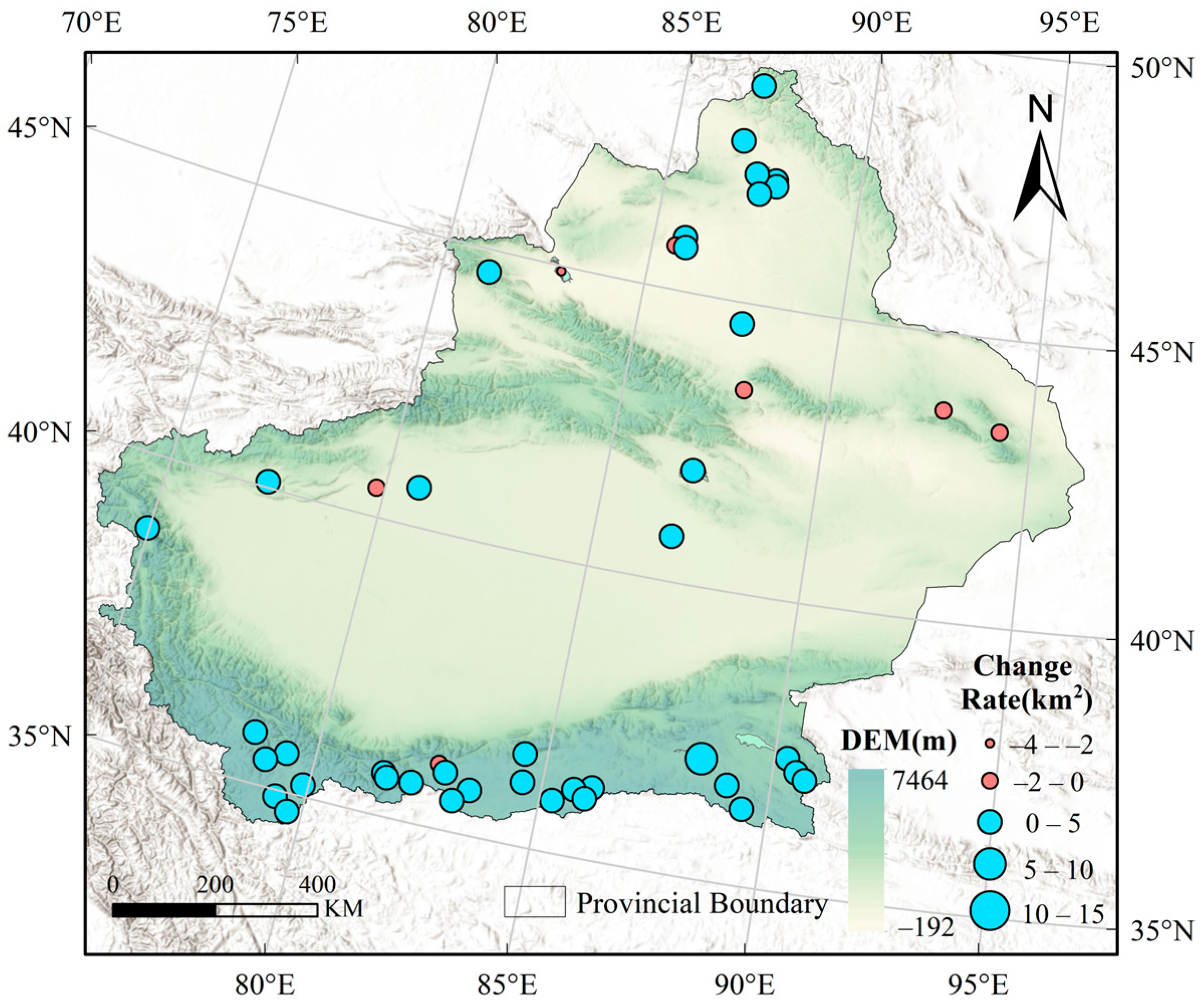

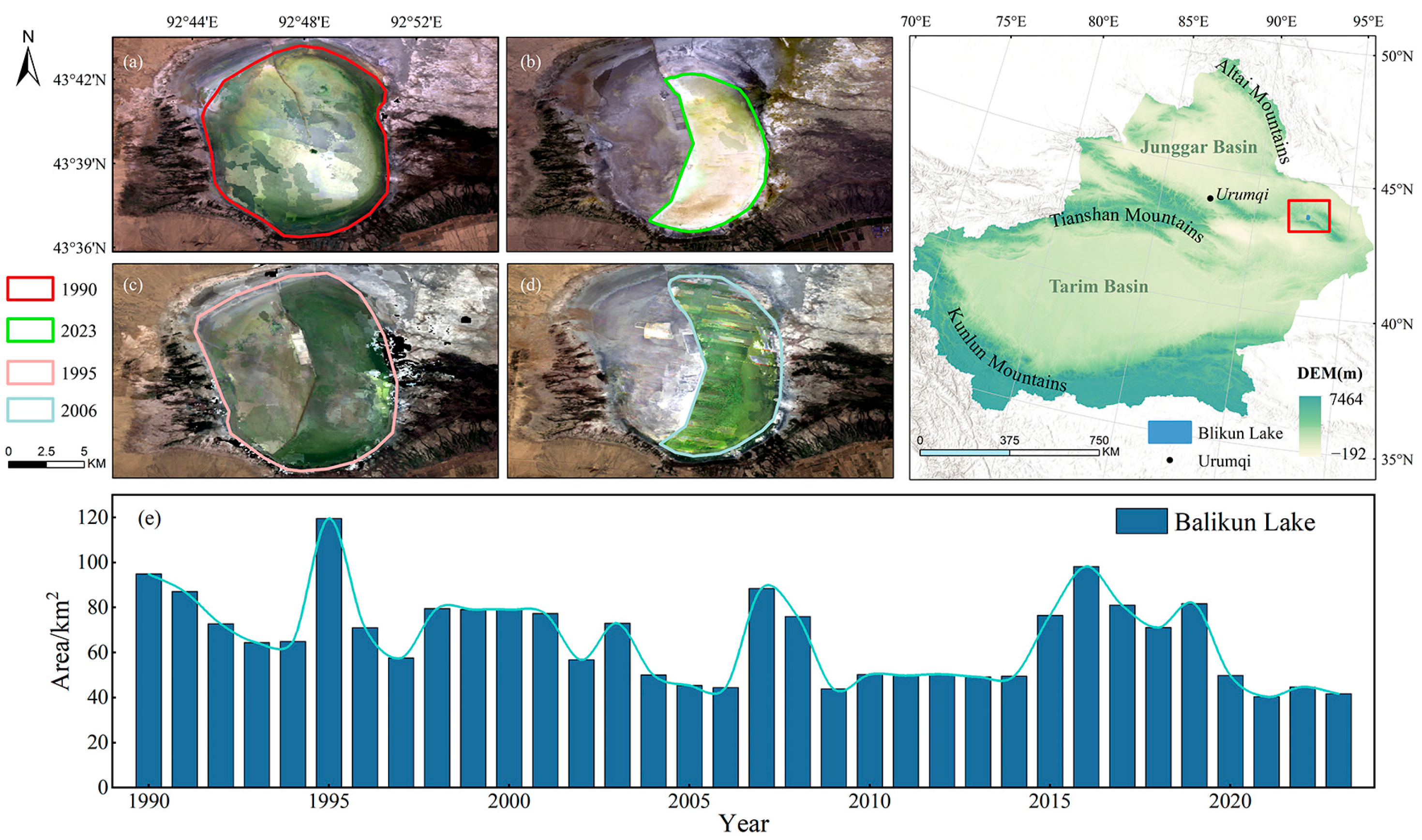



| Lake Type | Name | Depth (m) | Area (km2) | Elevation (m) | Latitude (°N) | Longitude (°E) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| plain lake | Bosten | 9.1 | 961.84 | 1050 | 41.83 | 86.75 |
| alpine lake | Balikun | 1.6 | 32.43 | 1577 | 43.66 | 92.78 |
| plateau lake | Ayakkum | 10 | 616.34 | 3876 | 37.56 | 89.43 |
| Data | Period | Data Sources | Resolution |
|---|---|---|---|
| Annual Average Temperature Data | 1990–2023 | ERA5-Land | 9 km |
| Precipitation Data | 1990–2023 | TerraClimate | 4638.3 m |
| Potential Evapotranspiration | 1990–2023 | National Earth System Science Data Center, National Science & Technology Infrastructure of China (http://www.geodata.cn, accessed on 18 April 2025) | 1 km |
| Nighttime Light Data | 1992–2023 | National Earth System Science Data Center, National Science & Technology Infrastructure of China (http://www.geodata.cn, accessed on 18 April 2025) | 1 km |
| Land Cover Data | 1990–2023 | The 30 m resolution land-use classification dataset developed by Professor Yang Jie’s team at Wuhan University | 30 m |
| DEM | - | Copernicus DEM (https://www.earthdata.nasa.gov/data/catalog/lpcloud-nasadem-hgt-001, accessed on 5 April 2025) | 90 m |
| Area Change Trend | Slope | Z Value | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Extremely significant expansion | Slope > 0 | Z > 2.58 | p < 0.01 |
| Significant expansion | Slope > 0 | 1.96 ≤ Z ≤ 2.58 | 0.01 ≤ p ≤ 0.05 |
| No obvious changes | Any value | −1.96 < Z < 1.96 | p > 0.05 |
| Significant shrinkage | Slope < 0 | −2.58 ≤ Z ≤ −1.96 | 0.01 ≤ p ≤ 0.05 |
| Extremely significant shrinkage | Slope < 0 | Z < −2.58 | p < 0.01 |
| Lakes Type | Meteorological Factors | Human Activities | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AAT (r) | AP (r) | PET (r) | NIL (r) | CA (r) | |
| Plain Lakes | 0.540 * | −0.042 | −0.556 * | −0.160 * | 0.491 ** |
| Alpine Lakes | 0.633 * | 0.195 * | −0.602 * | 0.150 | 0.193 * |
| Plateau Lakes | 0.723 * | 0.485 * | −0.281 | — | — |
| Lake | Meteorological Factors | Human Activities | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AAT (r) | AP (r) | PET (r) | NIL (r) | CA (r) | |
| Huancai Lake | −0.07 | −0.02225 | −0.13475 | −0.17686 | 0.08186 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhong, K.; Chen, C.; Xu, L.; Li, J.; Cui, L.; Wei, G. Are There Differences in the Response of Lake Areas at Different Altitudes in Xinjiang to Climate Change? Sustainability 2025, 17, 8705. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17198705
Zhong K, Chen C, Xu L, Li J, Cui L, Wei G. Are There Differences in the Response of Lake Areas at Different Altitudes in Xinjiang to Climate Change? Sustainability. 2025; 17(19):8705. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17198705
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhong, Kangzheng, Chunpeng Chen, Liping Xu, Jiang Li, Linlin Cui, and Guanghui Wei. 2025. "Are There Differences in the Response of Lake Areas at Different Altitudes in Xinjiang to Climate Change?" Sustainability 17, no. 19: 8705. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17198705
APA StyleZhong, K., Chen, C., Xu, L., Li, J., Cui, L., & Wei, G. (2025). Are There Differences in the Response of Lake Areas at Different Altitudes in Xinjiang to Climate Change? Sustainability, 17(19), 8705. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17198705








