An Integrated Strategy for Pre-Disposal of Spent Cation-Exchange Resins by Repurposing Industrial By-Products
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Fenton-like Wet Oxidation
2.3. Conditioning of the Residues
2.4. Testing of the Waste Forms
2.5. Characterization
2.6. Efficacy of the Management Strategy
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Fenton-like Wet Oxidation
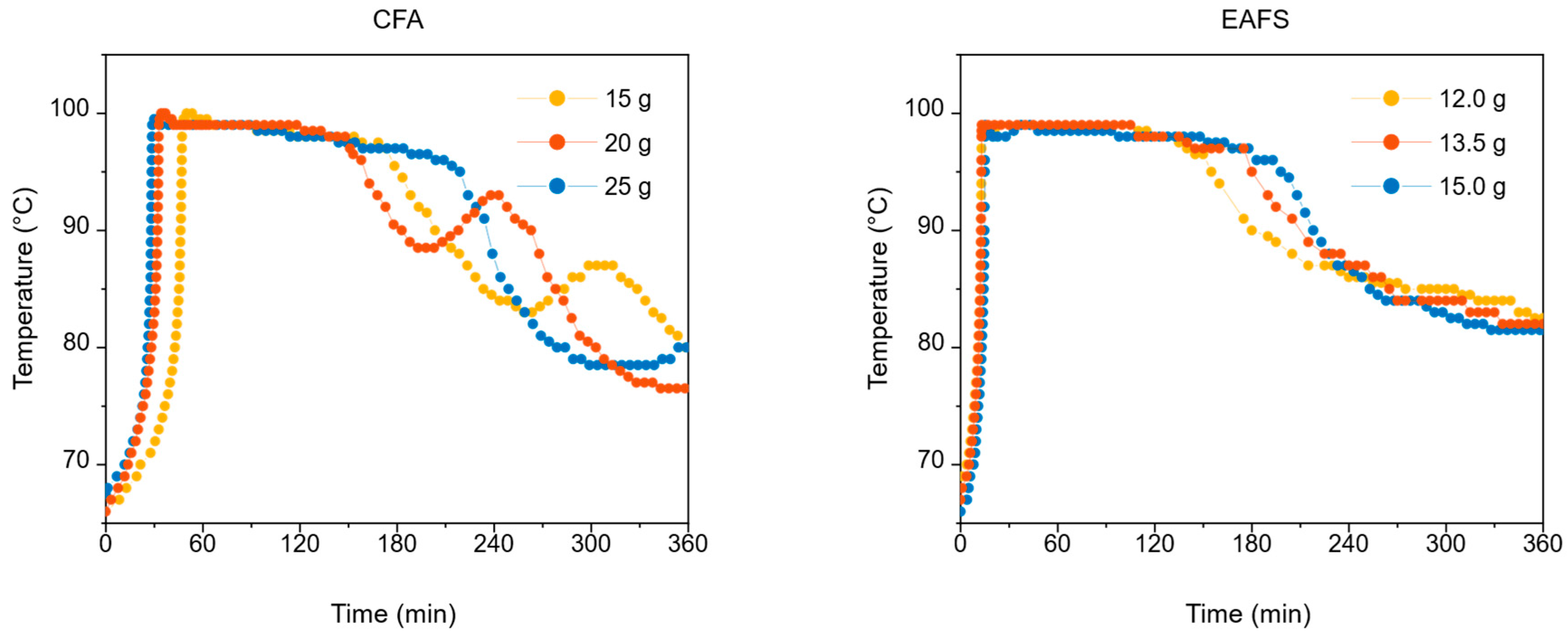
3.1.1. Oxidant Rate
3.1.2. Catalyst Mass
- ▪ ease of manipulation of the catalyst and availability;
- ▪ ease of peak control, by avoiding accumulation of unreacted H2O2;
- ▪ widening of the region at peak temperature, avoiding oscillating behavior of the process with multiple secondary peaks, thus allowing a complete mineralization of the resins;
- ▪ obtaining a residue easily workable and compatible with the conditioning matrix for encapsulation.
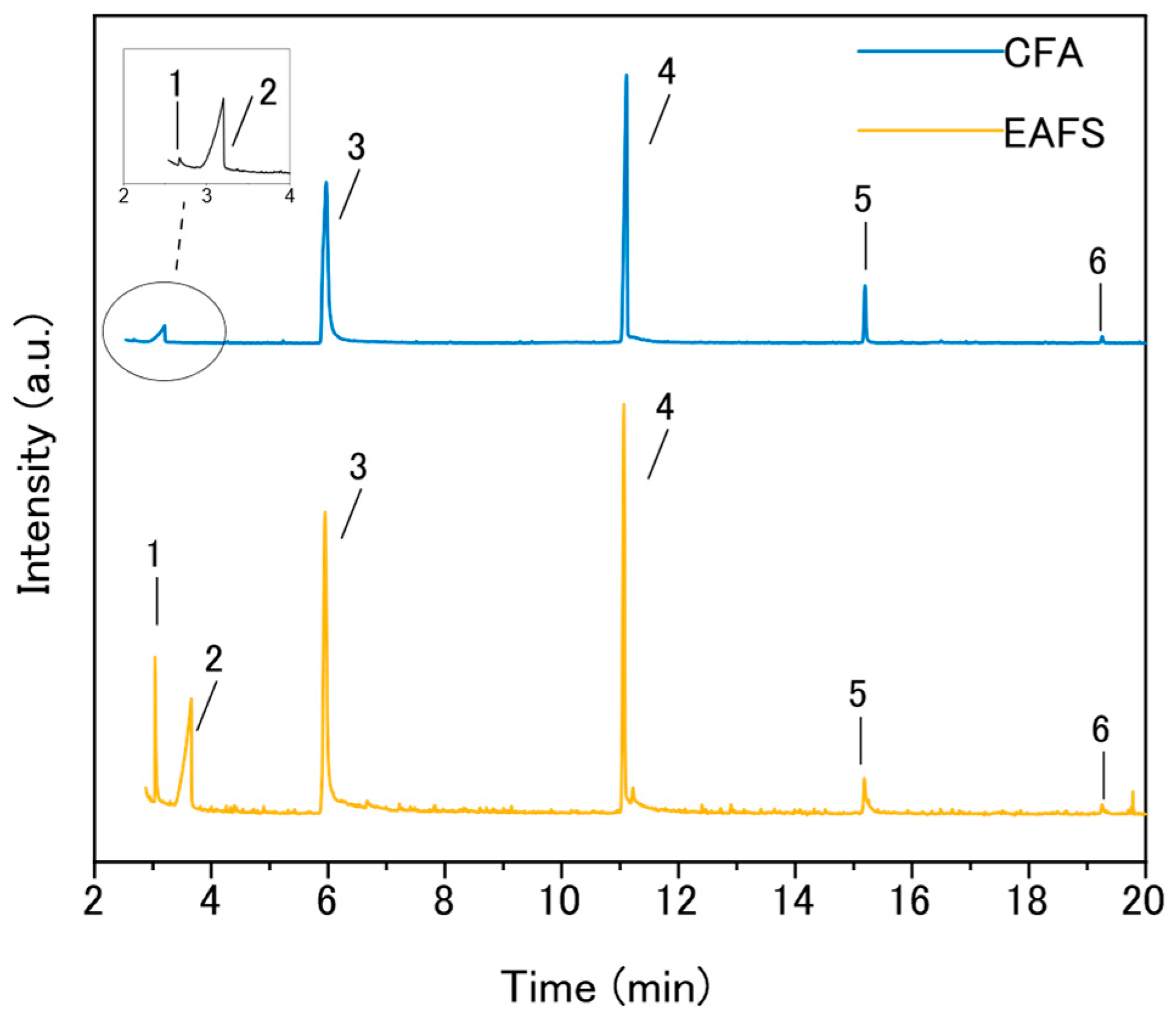
3.1.3. Characterization of the Fenton Liquors
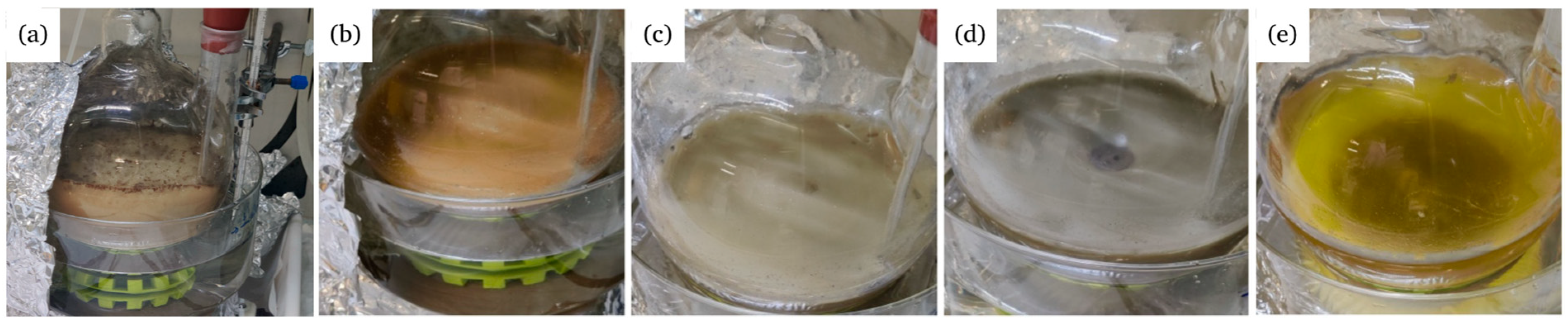
3.1.4. Characterization of the Fenton Residues
3.2. Conditioning in the Alkali-Activated Matrix
3.2.1. Conditioning and Preliminary Qualification
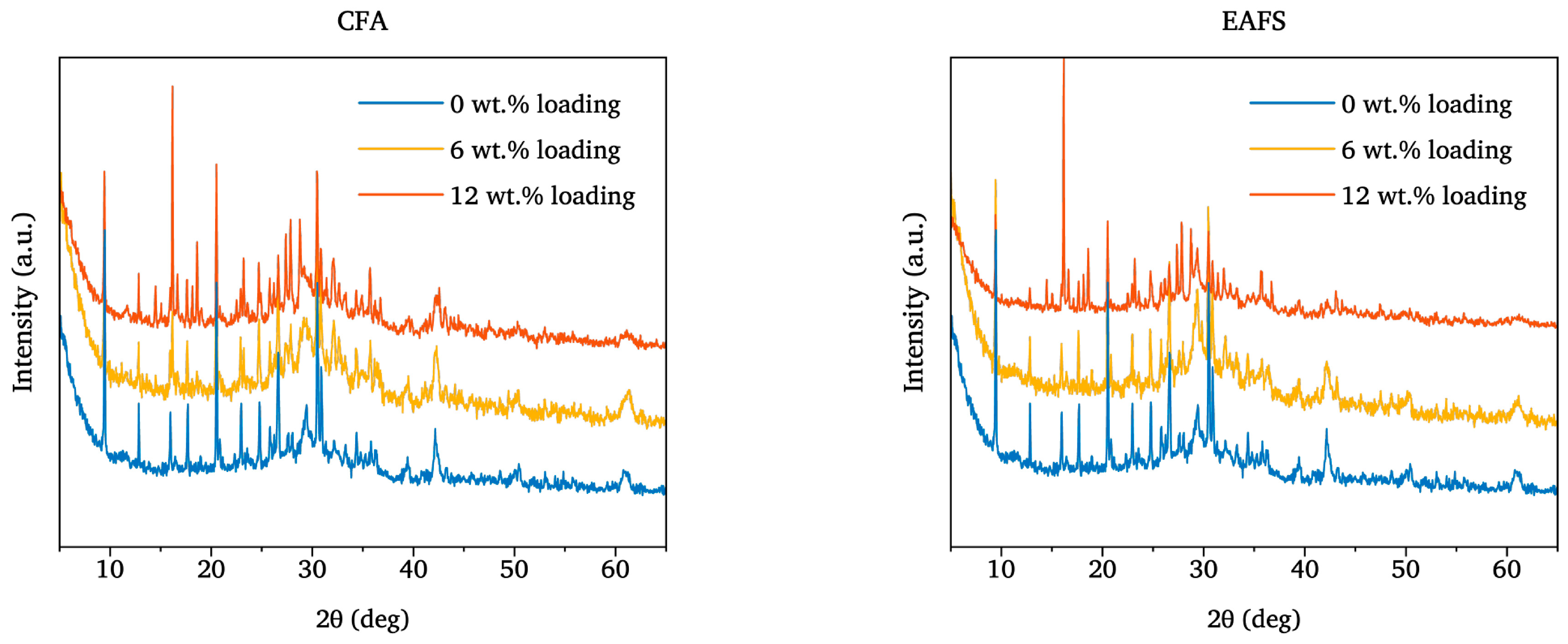
3.2.2. X-Ray Diffraction Patterns
3.2.3. Compressive Strength
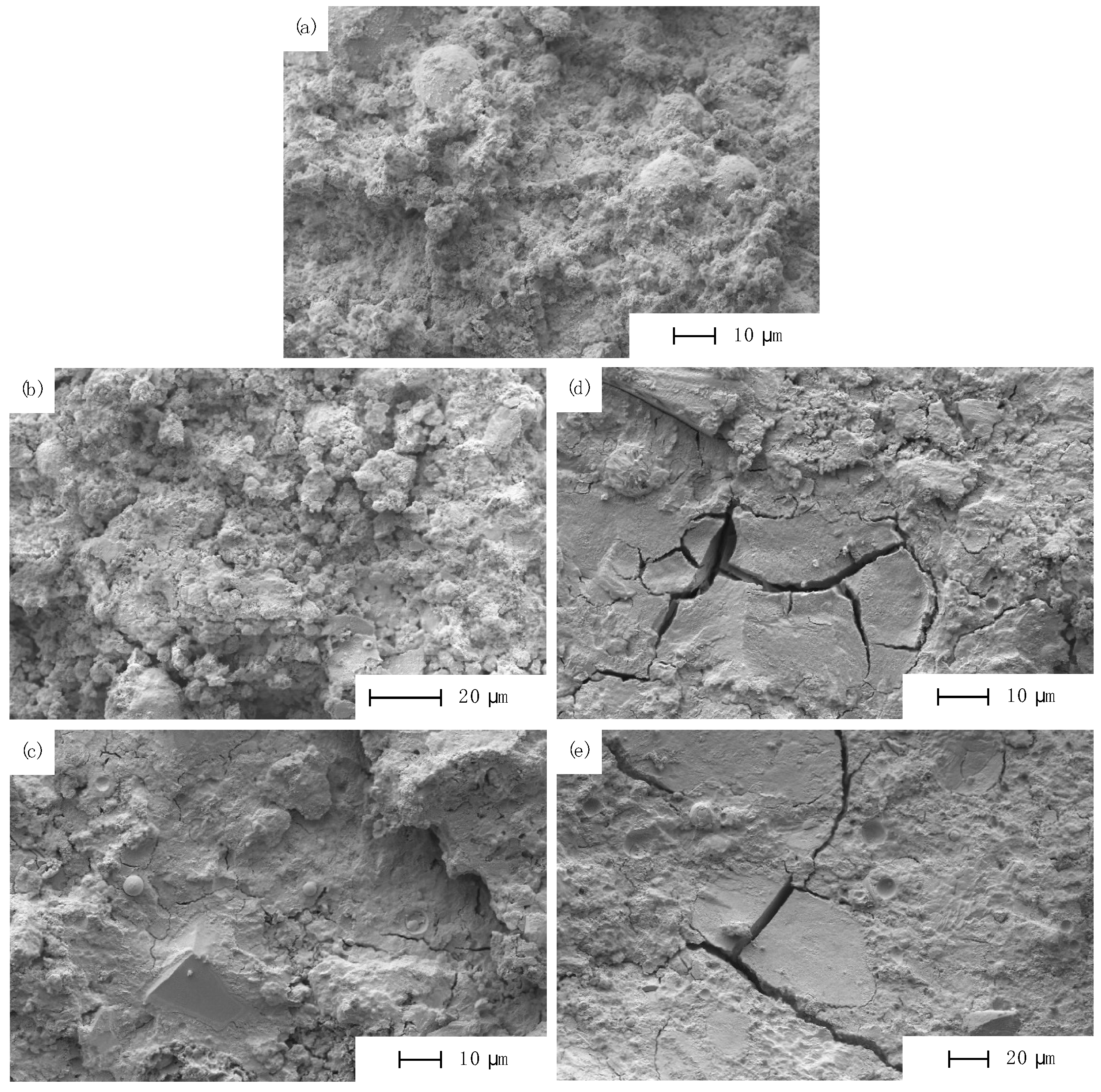
3.2.4. Microstructural Investigation by SEM
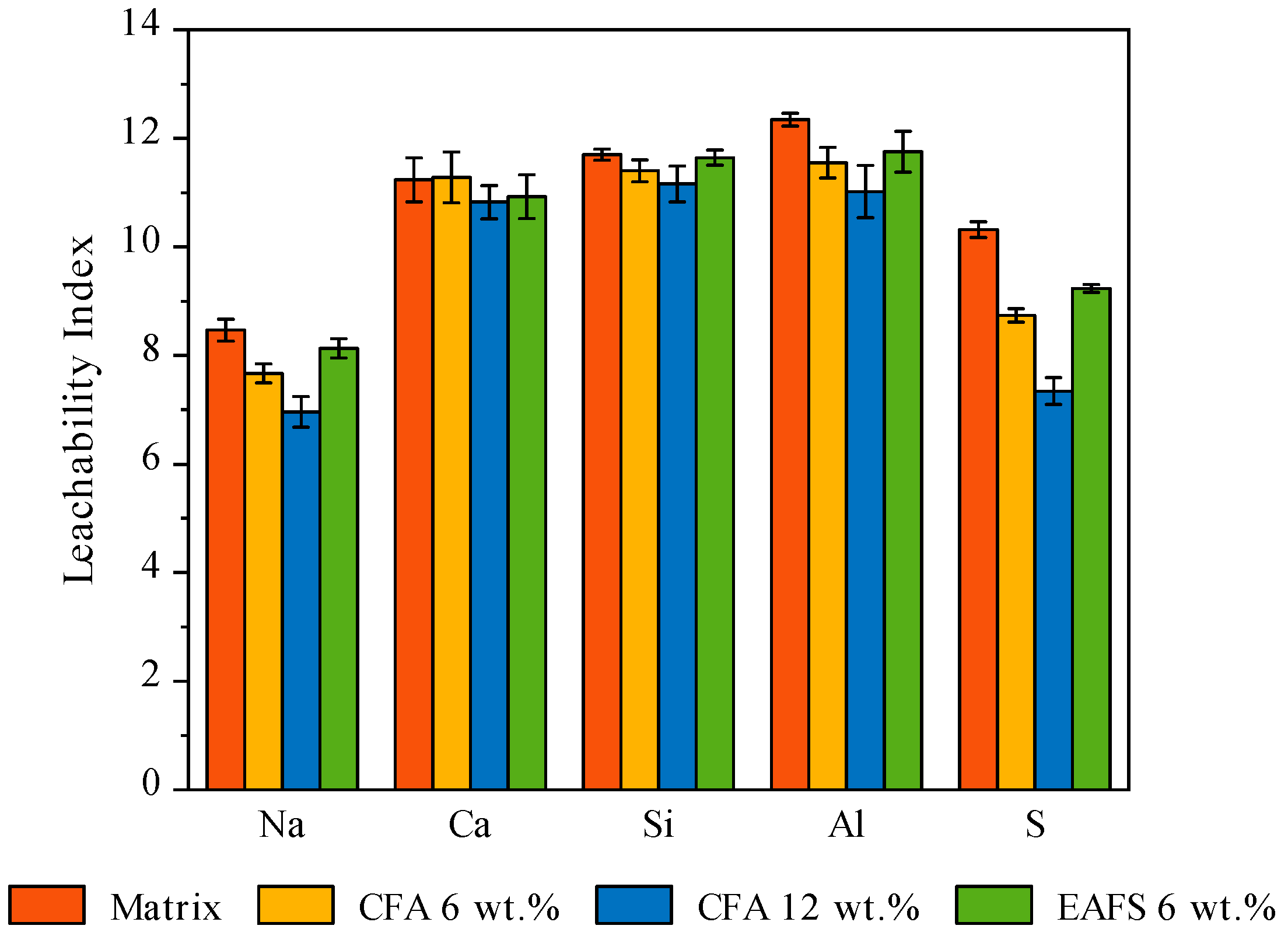
3.2.5. Leaching of the Waste Forms
3.3. Efficacy of the Management Strategy
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- International Atomic Energy Agency. Application of Ion Exchange Processes for Treatment of Radioactive Waste and Management of Spent Ion Exchangers. 2002, pp. 1–115. Available online: https://www.iaea.org/publications/6221/application-of-ion-exchange-processes-for-treatment-of-radioactive-waste-and-management-of-spent-ion-exchangers (accessed on 20 November 2024).
- International Atomic Energy Agency. Selection of Technical Solutions for the Management of Radioactive Waste. 2017, pp. 1–112. Available online: https://www.iaea.org/publications/12217/selection-of-technical-solutions-for-the-management-of-radioactive-waste (accessed on 20 November 2024).
- Castro, H.A.; Luca, V.; Bianchi, H.L. Study of plasma off-gas treatment from spent ion exchange resin pyrolysis. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 21403–21410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wan, Z. Treatment and disposal of spent radioactive ion-exchange resins produced in the nuclear industry. Prog. Nucl. Energy 2015, 78, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walling, S.A.; Um, W.; Corkhill, C.L.; Hyatt, N.C. Fenton and Fenton-like wet oxidation for degradation and destruction of organic radioactive wastes. npj Mater. Degrad. 2021, 5, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, S.; Onuaguluchi, O.; Banthia, N.; Troczynski, T. Advancements in immobilization of cesium and strontium radionuclides in cementitious wasteforms—A review. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2024, 108, e20131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vance, E.R.; Perera, D.S. Geopolymers for nuclear waste immobilisation. In Geopolymers: Structures, Processing, Properties and Industrial Applications; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2009; pp. 401–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantarel, V.; Motooka, T.; Yamagishi, I. Geopolymers and their potential applications in the nuclear waste management field—A bibliographical study. Jpn. JAEA 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.H.; Chen, H.Y.; Huang, C.P. Performance study of ion exchange resins solidification using metakaolin-based geopolymer binder. Prog. Nucl. Energy 2020, 129, 103508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nodehi, M.; Aguayo, F.; Madey, N.; Zhou, L. A Comparative Review of Polymer, Bacterial-based, and Alkali-Activated (also Geopolymer) Binders: Production, Mechanical, Durability, and Environmental impacts (life cycle assessment (LCA)). Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 422, 135816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.H.; Cheng, T.W.; Ding, Y.C.; Lin, K.L.; Tsao, S.W.; Huang, C.P. Geopolymer technology for the solidification of simulated ion exchange resins with radionuclides. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 235, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crivelli, F.; Cao, S.; Corrado, M.; Faccin, N.; Guerra, M.; Mascialino, C.; Ventura, G.; Savoldi, L. HYPEX®: A New Process for the Treatment and Conditioning of Radioactive Ion-Exchange Resins. 2024, pp. 1–14. Available online: https://iris.polito.it/handle/11583/2989388 (accessed on 26 November 2024).
- Galluccio, F.; Santi, A.; Mossini, E.; Magugliani, G.; Fattori, F.; Gatta, G.D.; Lotti, P.; Cori, D.; Macerata, E.; Bilancia, G.; et al. Pre-disposal management of spent ion-exchange resins by Fenton oxidation treatment and conditioning in an alkali-activated matrix. Nucl. Eng. Des. 2024, 429, 113621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galluccio, F.; Santi, A.; Mossini, E.; Magugliani, G.; Fattori, F.; Macerata, E.; Mariani, M. iRE-SOLVE Process for the Pre-Disposal Management of Spent Ion-Exchange Resins. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2025, 64, 10347–10351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, B.; Singh, A.K.; Kim, H.; Lichtfouse, E.; Sharma, V.K. Treatment of organic pollutants by homogeneous and heterogeneous Fenton reaction processes. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2018, 16, 947–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lama, G.; Meijide, J.; Sanromán, A.; Pazos, M. Heterogeneous Advanced Oxidation Processes: Current Approaches for Wastewater Treatment. Catalysts 2022, 12, 344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Meng, X.; Li, M.; Li, W.; Sui, Z.; Wang, J.; Yang, J. Dissolution and degradation of nuclear grade cationic exchange resin by Fenton oxidation combining experimental results and DFT calculations. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 361, 1511–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Wang, J.; Xu, L. Degradation of the mixed nuclear-grade cationic and anionic exchange resins using Fe2+/H+ homogeneous Fenton oxidation. Environ. Res. 2022, 212, 113400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adityosulindro, S.; Julcour, C.; Barthe, L. Heterogeneous Fenton oxidation using Fe-ZSM5 catalyst for removal of ibuprofen in wastewater. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 5920–5928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahorodna, M.; Oliveros, E.; Wörner, M.; Bogoczek, R.; Braun, A.M. Dissolution and mineralization of ion exchange resins: Differentiation between heterogeneous and homogeneous (photo-)Fenton processes. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2008, 7, 1480–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mushtaq, F.; Zahid, M.; Bhatti, I.A.; Nasir, S.; Hussain, T. Possible applications of coal fly ash in wastewater treatment. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 240, 27–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajput, H.; Verma, A.; Kaur, M.; Kaur, T.; Toor, A.P. Heterogeneous solar photo-fenton degradation of reactive Black 5 using foundry sand and fly ash: Value addition to waste. J. Environ. Eng. Landsc. Manag. 2016, 24, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Arzate-Salgado, S.Y.; Morales-Pérez, A.A.; Solís-López, M.; Ramírez-Zamora, R.M. Evaluation of metallurgical slag as a Fenton-type photocatalyst for the degradation of an emerging pollutant: Diclofenac. Catal. Today 2016, 266, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwar, R.; Ahmed, M.; Seats, P.; Huang, Q.; Lin, L.S. Prospect of utilizing coal mine drainage sludge as an iron source for value-creating applications. Rev. Environ. Sci. Biotechnol. 2021, 20, 679–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.E.M.; Gad-Allah, T.A.; Badawy, M.I. Heterogeneous Fenton process using steel industry wastes for methyl orange degradation. Appl. Water Sci. 2013, 3, 263–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Yang, X.; Men, B.; Wang, D. Interfacial mechanisms of heterogeneous Fenton reactions catalyzed by iron-based materials: A review. J. Environ. Sci. 2016, 39, 97–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S. Application of solid ash based catalysts in heterogeneous catalysis. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 7055–7063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathapati, M.; Amate, K.; Prasad, C.D.; Jayavardhana, M.L.; Raju, T.H. A review on fly ash utilization. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 50, 1535–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.H.; Du, D.Y. Degradation of n-butyl xanthate using fly ash as heterogeneous Fenton-like catalyst. J. Cent. South Univ. 2014, 21, 1448–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.; Wang, N.; Zhou, J.; Jiang, P.; Liu, G. Heterogeneous Fenton-like catalytic removal of p-nitrophenol in water using acid-activated fly ash. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 201–202, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pramanik, S.; Sur, B.; Dutta, B.K.; Chaudhuri, S.K. Fly ash—A cheap Catalyst in wet oxidation of an industrial pesticide effluent. Indian J. Eng. Mater. Sci. 1995, 2, 44–47. Available online: http://nopr.niscpr.res.in/handle/123456789/29826 (accessed on 22 November 2024).
- Chaudhuri, S.K.; Sur, B. Oxidative Decolorization of Reactive Dye Solution Using Fly Ash as Catalyst. J. Environ. Eng. 2000, 126, 583–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasuha, N.; Ismail, S.; Hameed, B.H. Activated electric arc furnace slag as an efficient and reusable heterogeneous Fenton-like catalyst for the degradation of Reactive Black 5. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2016, 67, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Luca, C.; Ivorra, F.; Massa, P.; Fenoglio, R. Alumina supported fenton-like systems for the catalytic wet peroxide oxidation of phenol solutions. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2012, 51, 8979–8984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liu, C.; Tong, L.; Li, J.; Luo, R.; Qi, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, L. Iron–copper bimetallic nanoparticles supported on hollow mesoporous silica spheres: An effective heterogeneous Fenton catalyst for orange II degradation. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 69593–69605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruipérez, F.; Mujika, J.I.; Ugalde, J.M.; Exley, C.; Lopez, X. Pro-oxidant activity of aluminum: Promoting the Fenton reaction by reducing Fe(III) to Fe(II). J. Inorg. Biochem. 2012, 117, 118–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pancotti, F.; Guerra, M.; Torres Alvarez, E.; Lodeiro, G.; Alonso, M.C.; Criado, M.; Phung, Q.T.; Banford, A.; Ellis, A. EURAD-2 WP6 Stream—Sustainable Treatment and Immobilisation of Challenging Waste. 2024. Available online: https://fisa-euradwaste2025.ncbj.gov.pl/sites/fisa-euradwaste2025.ncbj.gov.pl/files/2025-05/094%20Abstract.pdf (accessed on 8 September 2025).
- Prasad, S.P.; Eldridge, C. Thermal Treatment of Solid Radioactive Organic Wasteforms. 2024. Available online: https://www.ejp-eurad.eu/sites/default/files/2024-12/PREDIS_D6.4-Thermal-treatment-of-RSOW_vF-31.7.2024.pdf (accessed on 8 September 2025).
- Ispettorato Nazionale per la Sicurezza Nucleare e la Radioprotezione. Guida Tecnica n. 33 Criteri di sicurezza per la gestione dei rifiuti radioattivi. July 2022. Available online: https://www.isinucleare.it/sites/default/files/contenuto_redazione_isin/guida_tecnica_isin_n._33.pdf (accessed on 8 September 2025).
- ASTM C618-22; Specification for Coal Fly Ash and Raw or Calcined Natural Pozzolan for Use in Concrete. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2022. [CrossRef]
- Wan, Z.; Xu, L.; Wang, J. Disintegration and dissolution of spent radioactive cationic exchange resins using Fenton-like oxidation process. Nucl. Eng. Des. 2015, 291, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkhomchuk, E.V.; García-Aguilar, J.; Sashkina, K.A.; Berenguer-Murcia, A.; Cazorla-Amorós, D.; Dralyuk, R.I.; Shestakova, D.O.; Ayupov, A.B.; Danilova, I.G.; Parmon, V.N. Ferrosilicate-Based Heterogeneous Fenton Catalysts: Influence of Crystallinity, Porosity, and Iron Speciation. Catal. Letters 2018, 148, 3134–3146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahorodna, M.; Bogoczek, R.; Oliveros, E.; Braun, A.M. Application of the Fenton process to the dissolution and mineralization of ion exchange resins. Catal. Today 2007, 129, 200–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunale, T.L.; Mahajani, V.V.; Wattal, P.K.; Srinivas, C. Studies in liquid phase mineralization of cation exchange resin by a hybrid process of Fenton dissolution followed by wet oxidation. Chem. Eng. J. 2009, 148, 371–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mossini, E.; Santi, A.; Magugliani, G.; Galluccio, F.; Macerata, E.; Giola, M.; Vadivel, D.; Dondi, D.; Cori, D.; Lotti, P.; et al. Pre-impregnation approach to encapsulate radioactive liquid organic waste in geopolymer. J. Nucl. Mater. 2023, 585, 154608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santi, A.; Mossini, E.; Magugliani, G.; Galluccio, F.; Macerata, E.; Lotti, P.; Gatta, G.D.; Vadivel, D.; Dondi, D.; Cori, D.; et al. Design of sustainable geopolymeric matrices for encapsulation of treated radioactive solid organic waste. Front. Mater. 2022, 9, 1005864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EN 196-1:2016; Methods of Testing Cement—Part 1: Determination of Strength. UNI—Ente Italiano di Normazione: Milan, Italy, 2016. Available online: https://standards.iteh.ai/catalog/standards/cen/37b8816e-4085-4dcc-a642-a383d9bddd6c/en-196-1-2016?srsltid=AfmBOoqjTvhN5-siaU2Z0bdlDkmrkTYRkYchj1Amy-q32dE291VLKCgk (accessed on 25 May 2025).
- BS EN 12390-1-2021; Testing Hardened Concrete. Shape, Dimensions and Other Requirements for Specimens and Moulds. British Standard Institution: London, UK, 2021.
- BS EN 12390-3-2019; Testing Hardened Concrete. Compressive Strength of Test Specimens. British Standards Institution: London, UK, 2019. Available online: https://www.thenbs.com/PublicationIndex/documents/details?Pub=BSI&DocID=326874 (accessed on 27 November 2024).
- ANSI/ANS-16.1-2019; Measurement of the Leachability of Solidified Low-Level Radioactive Wastes by a Short-Term Test Procedure. American National Standard Institute: Washington, DC, USA; American Nuclear Society: Westmont, IL, USA, 2019.
- Wan, Z.; Wang, J. Optimization of spent radioactive resins degradation by Fenton-like oxidation using response surface methodology. Environ. Prog. Sustain. Energy 2016, 35, 1590–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNI EN 196-2:2013; UNI Ente Italiano di Normazione Metodi di Prova dei Cementi—Parte 2: Analisi Chimica dei Cementi. UNI Ente Italiano di Normazione: Milan, Italy.
- Rouquerol, J.; Llewellyn, P.; Rouquerol, F. Is the bet equation applicable to microporous adsorbents? Stud. Surf. Sci. Catal. 2007, 160, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leybros, A.; Roubaud, A.; Guichardon, P.; Boutin, O. Supercritical water oxidation of ion exchange resins: Degradation mechanisms. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2010, 88, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafeez, M.A.; Singh, B.K.; Yang, S.H.; Kim, J.; Kim, B.; Shin, Y.; Um, W. Recent advances in Fenton-like treatment of radioactive ion exchange resins. Chem. Eng. J. Adv. 2023, 14, 100461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inchaurrondo, N.S.; Bocero, F.; Ramos, C.P.; Freije, T.; Fasce, L.A. Enhanced mineralization of bisphenol A by electric arc furnace slag: Fenton-like oxidation. Appl. Catal. O Open 2024, 193, 206971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui-Teng, N.; Cheng-Yong, H.; Yun-Ming, L.; Abdullah, M.M.A.B.; Pakawanit, P.; Bayuaji, R.; Yong-Sing, N.; Zulkifly, K.B.; Wan-En, O.; Yong-Jie, H.; et al. Comparison of thermal performance between fly ash geopolymer and fly ash-ladle furnace slag geopolymer. JNCS 2022, 585, 121527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashad, A.M.; Khafaga, S.A.; Gharieb, M. Valorization of fly ash as an additive for electric arc furnace slag geopolymer cement. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 294, 123570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Liang, S.; Yang, J.; Chen, Y.; Ye, N.; Ke, Y.; Tao, S.; Xiao, K.; Hu, J.; Hou, H.; et al. Role of Fe species in geopolymer synthesized from alkali-thermal pretreated Fe-rich Bayer red mud. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 200, 398–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Noor-Ul-Amin; Ahmad, H.; Noor, S.; Sultana, S.; Umar, H.; Ahmad, H.; Awwad, F.A.; Ismail, E.A.A. Synthesis and characterization of novel iron-modified geopolymer cement from laterite clay as low energy material. AIP Adv. 2024, 14, 025209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Tan, X.; Si, R.; Luo, Z.; Yang, C. Characterization and performance evaluation of geopolymer prepared with thermal-mechanical activated aluminum sulfate residue. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 384, 131454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archer de Carvalho, T.; Gaspar, F.; Marques, A.C.; Mateus, A. Evaluation of the Potential of Metakaolin, Electric Arc Furnace Slag, and Biomass Fly Ash for Geopolymer Cement Compositions. Materials 2023, 16, 2741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Ruan, S.; Zeng, Q.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, M.; Tian, Y.; Yan, D. Pore structure of geopolymer materials and its correlations to engineering properties: A review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 328, 127064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Li, X.; Lu, Y.; Bai, X. Effects of Na/Al ratio on mechanical properties and microstructure of red mud-coal metakaolin geopolymer. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 263, 120653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, W.; Lv, Y.; Wang, S.; Qiao, J.; Zou, C.; Su, M.; Peng, H. Effects of Al/Na and Si/Na Molar Ratios on the Alkalinity of Metakaolin-Based Geopolymer Pore Solutions. Materials 2023, 16, 1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frederickx, L.; Nguyen, T.N.; Phung, Q.T. Strength and Microstructure Characteristics of Metakaolin-Based Geopolymer Mortars with High Water-to-Binder Ratios. Sustainability 2022, 14, 3141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Provis, J.L.; Walls, P.A.; van Deventer, J.S.J. Geopolymerisation kinetics. 3. Effects of Cs and Sr salts. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2008, 63, 4480–4489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desbats-Le Chequer, C.; Frizon, F. Impact of sulfate and nitrate incorporation on potassium- and sodium-based geopolymers: Geopolymerization and materials properties. J. Mater. Sci. 2011, 46, 5657–5664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahoti, M.; Wong, K.K.; Tan, K.H.; Yang, E.H. Effect of alkali cation type on strength endurance of fly ash geopolymers subject to high temperature exposure. Mater. Des. 2018, 154, 8–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahoti, M.; Narang, P.; Tan, K.H.; Yang, E.H. Mix design factors and strength prediction of metakaolin-based geopolymer. Ceram. Int. 2017, 43, 11433–11441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, S.; Zhu, Z.; Song, W.; Huo, W.; Zhang, C. A eco-friendly acid fly ash geopolymer with a higher strength. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 335, 127450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fattori, F.; Magugliani, G.; Santi, A.; Mossini, E.; Moschetti, I.; Galluccio, F.; Macerata, E.; de la Bernardie, X.; Abdelouas, A.; Cori, D.; et al. Radiation stability and durability of magnesium phosphate cement for radioactive reactive metals encapsulation. Prog. Nucl. Energy 2024, 177, 105463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barger, J.P.; Dillon, P.F. Near-membrane electric field calcium ion dehydration. Cell Calcium 2016, 60, 415–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amran, M.; Debbarma, S.; Ozbakkaloglu, T. Fly ash-based eco-friendly geopolymer concrete: A critical review of the long-term durability properties. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 270, 121857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Deng, P. Mechanical and fracture properties of slag/steel slag-based geopolymer fully recycled aggregate concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 413, 134533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoaei, P.; Ameri, F.; Karimzadeh, M.; Atabakhsh, E.; Zareei, S.A.; Behforouz, B. Difference between geopolymers and alkali-activated materials. In Handbook of Sustainable Concrete and Industrial Waste Management; Woodhead Publishing Series in Civil and Structural Engineering; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2022; pp. 335–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidovits, J. Geopolymers: Ceramic-Like Inorganic Polymers. J. Ceram. Sci. Technol. 2017, 8, 335–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izquierdo, M.; Querol, X.; Davidovits, J.; Antenucci, D.; Nugteren, H.; Fernández-Pereira, C. Coal fly ash-slag-based geopolymers: Microstructure and metal leaching. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 166, 561–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- International Atomic Energy. Agency Cost Considerations and Financing Mechanisms for the Disposal of Low and Intermediate Level Radioactive Waste. 2007, pp. 1–48. Available online: https://www.iaea.org/publications/7710/cost-considerations-and-financing-mechanisms-for-the-disposal-of-low-and-intermediate-level-radioactive-waste (accessed on 1 December 2024).
- International Atomic Energy. Agency Costing Methods and Funding Schemes for Radioactive Waste Disposal Programmes. 2020, pp. 1–75. Available online: https://www.iaea.org/publications/13508/costing-methods-and-funding-schemes-for-radioactive-waste-disposal-programmes (accessed on 1 December 2024).
- Deposito Nazionale: Scriviamo Insieme un Futuro Più Sicuro per Italia. Available online: https://www.depositonazionale.it/ (accessed on 2 December 2024).
- De Araujo, L.G.; Marumo, J.T. Reaction of Ion Exchange Resins with Fenton’s Reagent. Environments 2018, 5, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Material | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 wt.% | 6 wt.% | 12 wt.% | 18 wt.% | |
| Fenton residue | 0.0 | 6.0 | 12.0 | 18.0 |
| Volcanic tuff | 18.1 | 16.4 | 15.0 | 13.6 |
| Coal fly ash | 15.8 | 14.5 | 13.2 | 11.8 |
| Electric arc furnace slag | 15.8 | 14.5 | 13.2 | 11.8 |
| Blast furnace slag | 16.8 | 15.4 | 13.9 | 12.5 |
| Alumina | 2.2 | 2.0 | 1.8 | 1.6 |
| Sodium hydroxide | 4.0 | 6.1 | 8.1 | 10.2 |
| Water | 27.3 | 25.1 | 22.8 | 20.5 |
| Catalyst | Catalyst Mass | Oxidant Rate | MRR | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (g) | (mL/min) | (min) | (%) | (%) | |
| CFA | 20.0 | 1.5 | 30 ± 1 | 61 ± 1 | 93 ± 3 |
| 20.0 | 2.2 | 23 ± 1 | 64 ± 1 | 96 ± 3 | |
| EAFS | 15.0 | 1.5 | 12 ± 1 | 54 ± 2 | 72 ± 4 |
| 15.0 | 2.2 | 11 ± 1 | 68 ± 2 | 94 ± 4 |
| Catalyst | Catalyst Mass | Fe Content | MRR | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (g) | (g) | (min) | (%) | (%) | |
| CFA | 15.0 | 0.98 | 43 ± 1 | 65 ± 2 | 96 ± 3 |
| 20.0 | 1.30 | 32 ± 1 | 64 ± 2 | 96 ± 3 | |
| 25.0 | 1.63 | 28 ± 1 | 61± 2 | 96 ± 3 | |
| EAFS | 12.0 | 2.90 | 13 ± 1 | 66 ± 1 | 95 ± 2 |
| 13.5 | 3.26 | 13 ± 1 | 66 ± 1 | 95 ± 2 | |
| 15.0 | 3.63 | 14 ± 1 | 68 ± 1 | 94 ± 2 |
| Catalyst | Percentage Peak Area (%) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oxalic Acid + Formic Acid | Acetic Acid | Silox-3 | Silox-4 | Silox-5 | Silox-6 | |
| CFA | 0.1 | 4.6 | 46.2 | 42.5 | 5.9 | 0.6 |
| EAFS | 4.6 | 18.1 | 40.6 | 31.9 | 4.2 | 0.6 |
| Property | Catalyst | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Matrix Only | CFA | CFA | CFA | EAFS | EAFS | EAFS | |
| (wt.%) | 0.0 | 6.0 | 12.0 | 18.0 | 6.0 | 12.0 | 18.0 |
| (wt.%) | 0.0 | 15.4 | 30.8 | 46.2 | 18.8 | 37.5 | 56.3 |
| -- | 2.6 | 1.3 | 0.9 | 2.1 | 0.9 | 0.7 | |
| Compressive strength (MPa) | 17.2 ± 1.5 | 14.2 ± 1.4 | 11.1 ± 1.0 | -- | 12.1 ± 1.2 | 6.3 ± 0.8 | -- |
| Porosity (%) | 36.6 | 36.5 | 39.0 | -- | 37.4 | 39.7 | -- |
| Resistance toward static immersion | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | No | No |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Galluccio, F.; Santi, A.; Rizzi, E.; Fattori, F.; Magugliani, G.; Piazza, V.; Milanese, C.; Gatta, G.D.; Fornara, L.; Macerata, E.; et al. An Integrated Strategy for Pre-Disposal of Spent Cation-Exchange Resins by Repurposing Industrial By-Products. Sustainability 2025, 17, 8241. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17188241
Galluccio F, Santi A, Rizzi E, Fattori F, Magugliani G, Piazza V, Milanese C, Gatta GD, Fornara L, Macerata E, et al. An Integrated Strategy for Pre-Disposal of Spent Cation-Exchange Resins by Repurposing Industrial By-Products. Sustainability. 2025; 17(18):8241. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17188241
Chicago/Turabian StyleGalluccio, Francesco, Andrea Santi, Edoardo Rizzi, Fabio Fattori, Gabriele Magugliani, Veronica Piazza, Chiara Milanese, Giacomo Diego Gatta, Luca Fornara, Elena Macerata, and et al. 2025. "An Integrated Strategy for Pre-Disposal of Spent Cation-Exchange Resins by Repurposing Industrial By-Products" Sustainability 17, no. 18: 8241. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17188241
APA StyleGalluccio, F., Santi, A., Rizzi, E., Fattori, F., Magugliani, G., Piazza, V., Milanese, C., Gatta, G. D., Fornara, L., Macerata, E., Mariani, M., & Mossini, E. (2025). An Integrated Strategy for Pre-Disposal of Spent Cation-Exchange Resins by Repurposing Industrial By-Products. Sustainability, 17(18), 8241. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17188241








