Upcycling Anodic Sludge from Aluminum Anodizing: Leaching Efficiency and Thermal Conversion into Refractory Materials
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Collection of the AS from the Aluminum Plant
2.2. Determination of the Physical, Chemical, and Mineralogical Characteristics of the AS
2.3. Evaluation of the Recovery of Sodium Aluminate by Leaching with Sodium Hydroxide and Precipitation with H2O2
2.4. Thermal Transformation of AS at Different Temperatures and Granulometries
3. Results
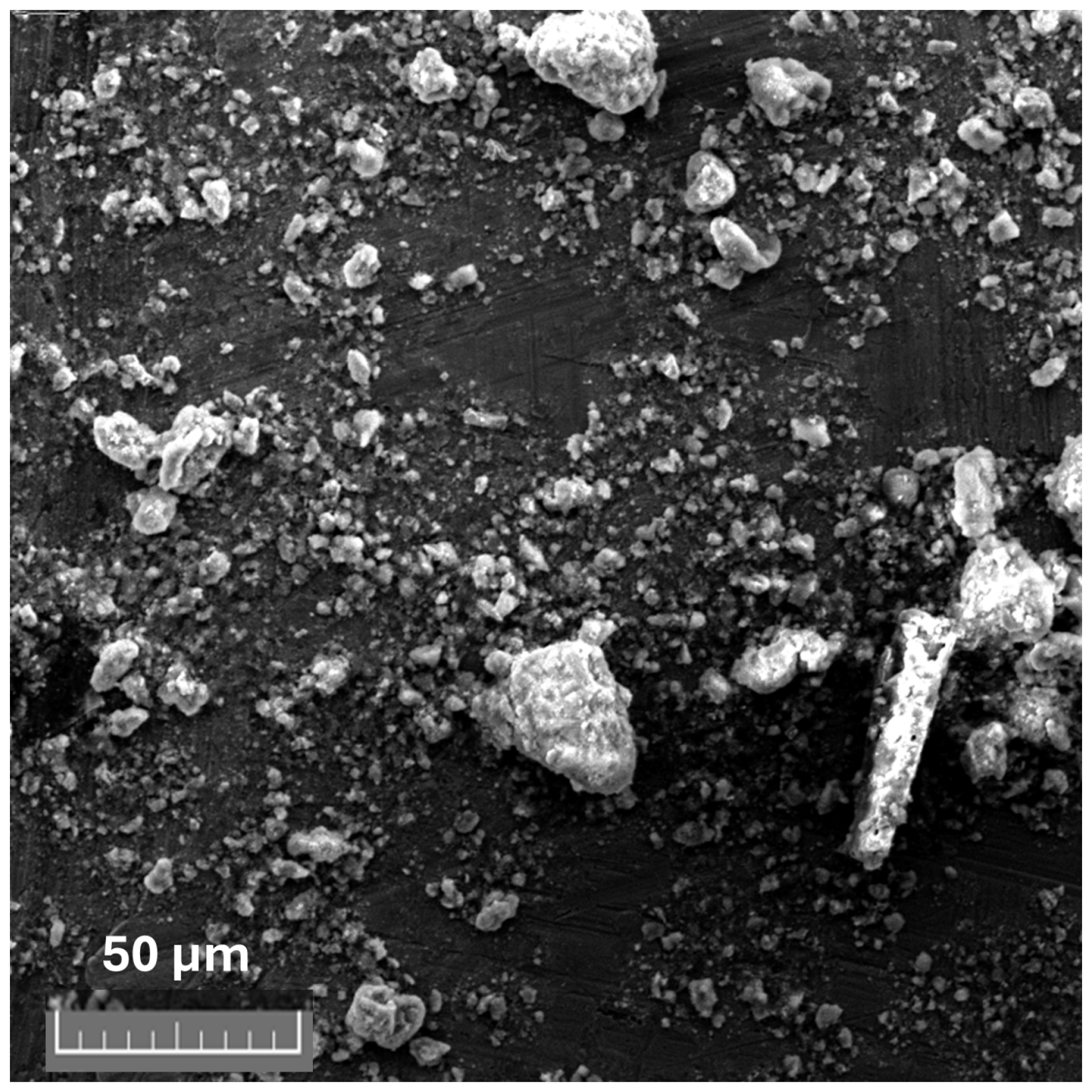
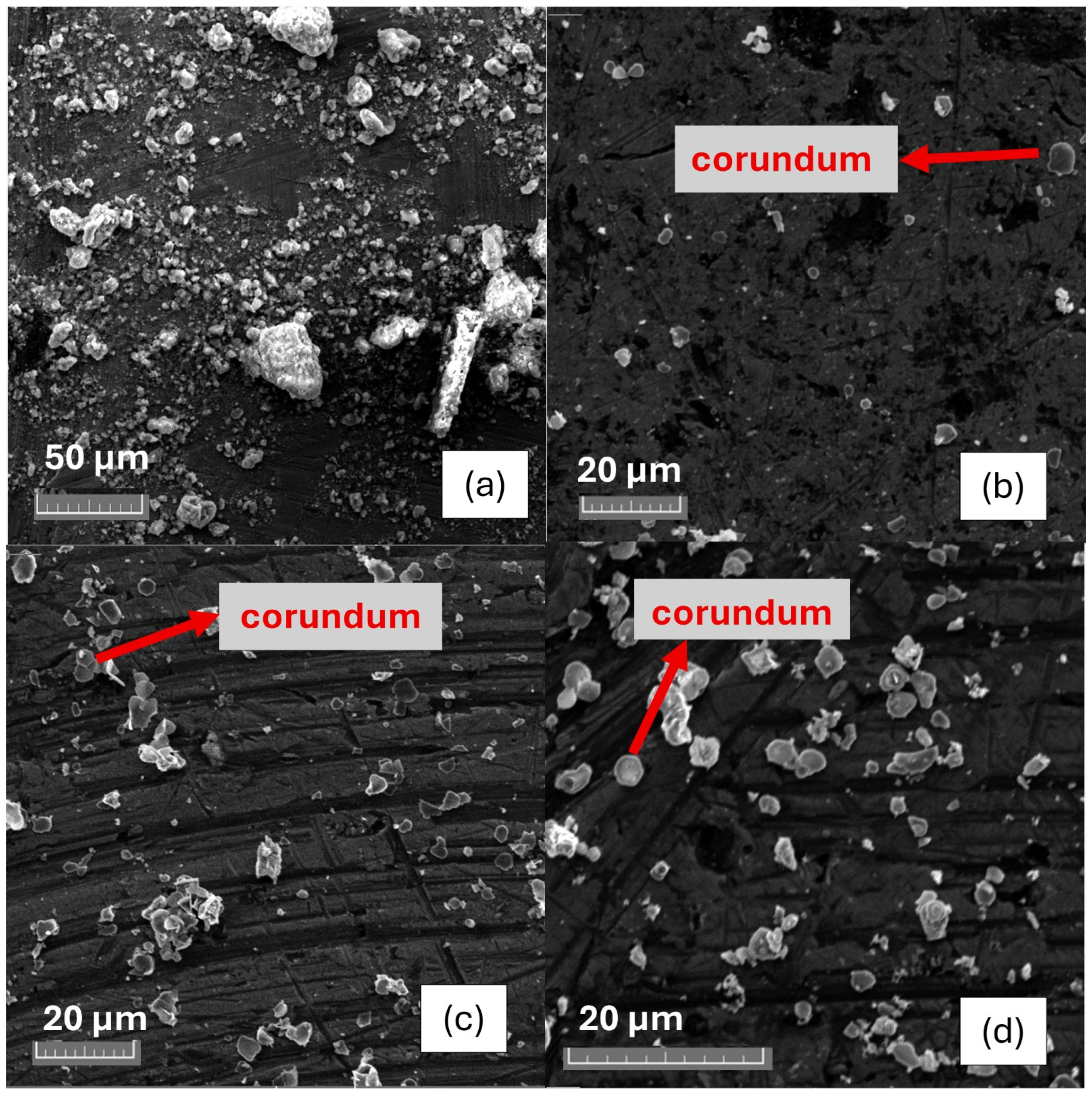
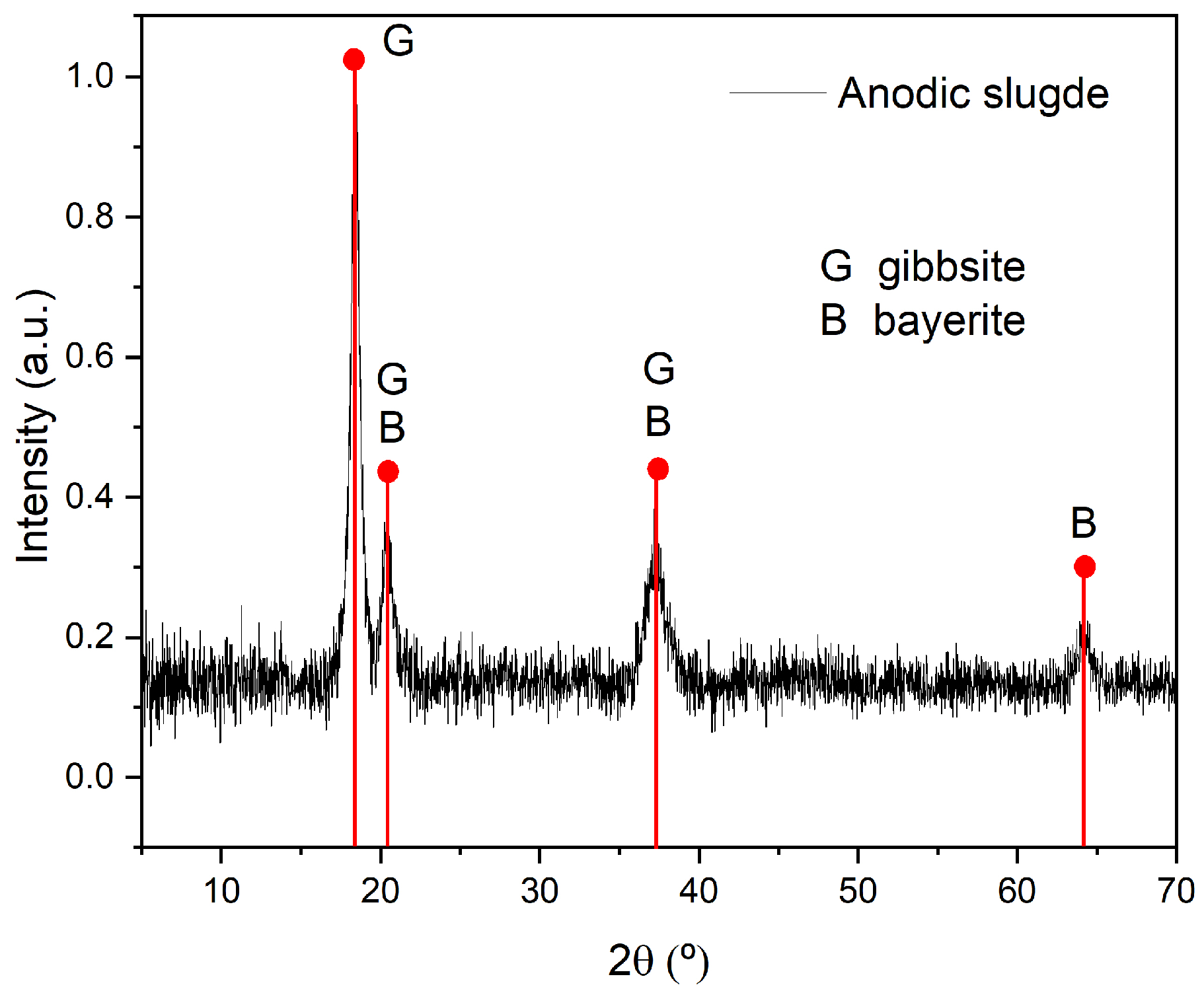
3.1. Physical, Chemical, and Mineralogical Characterization of the AS
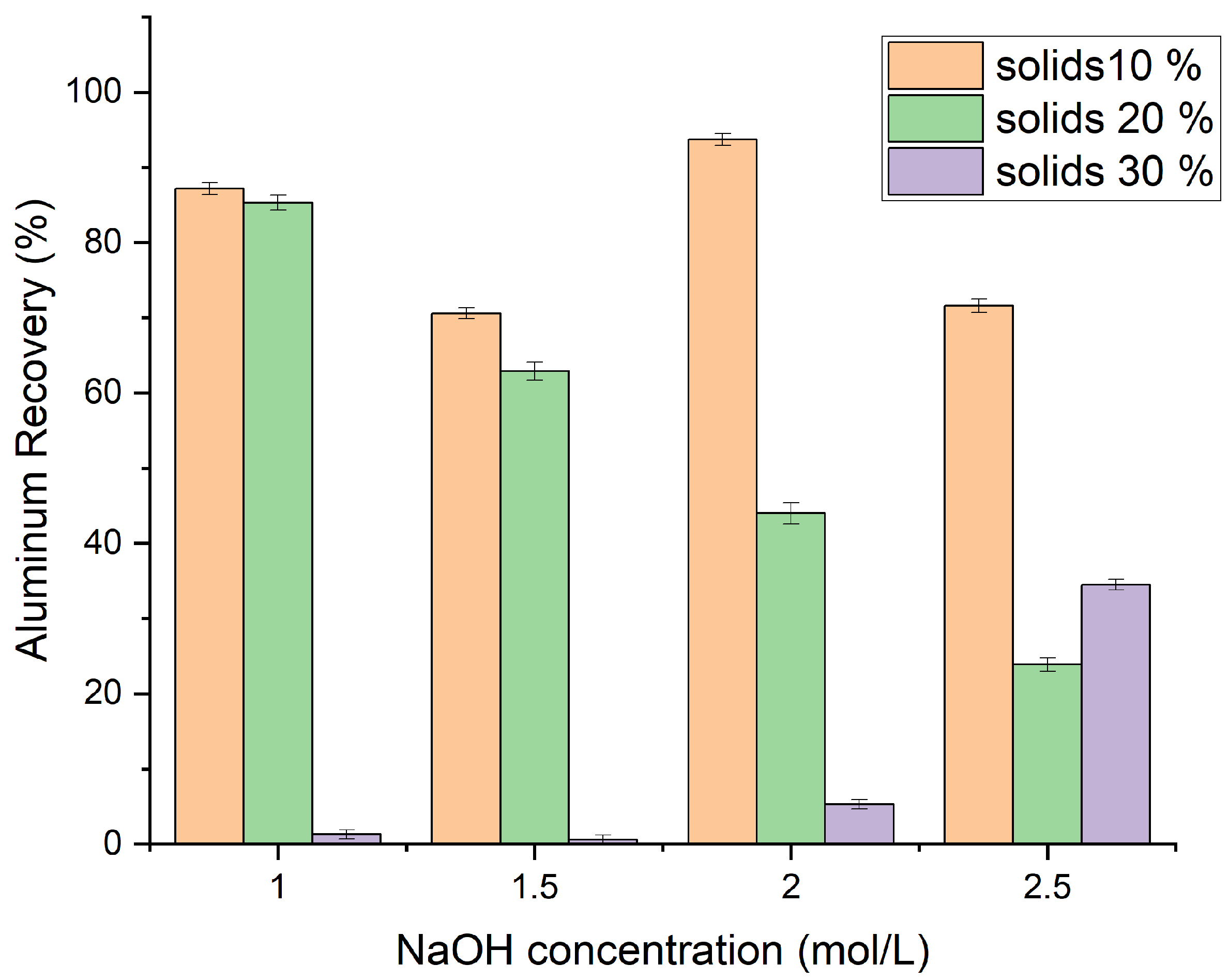
3.2. Hydrometallurgical Approaches for Recovering Value from AS
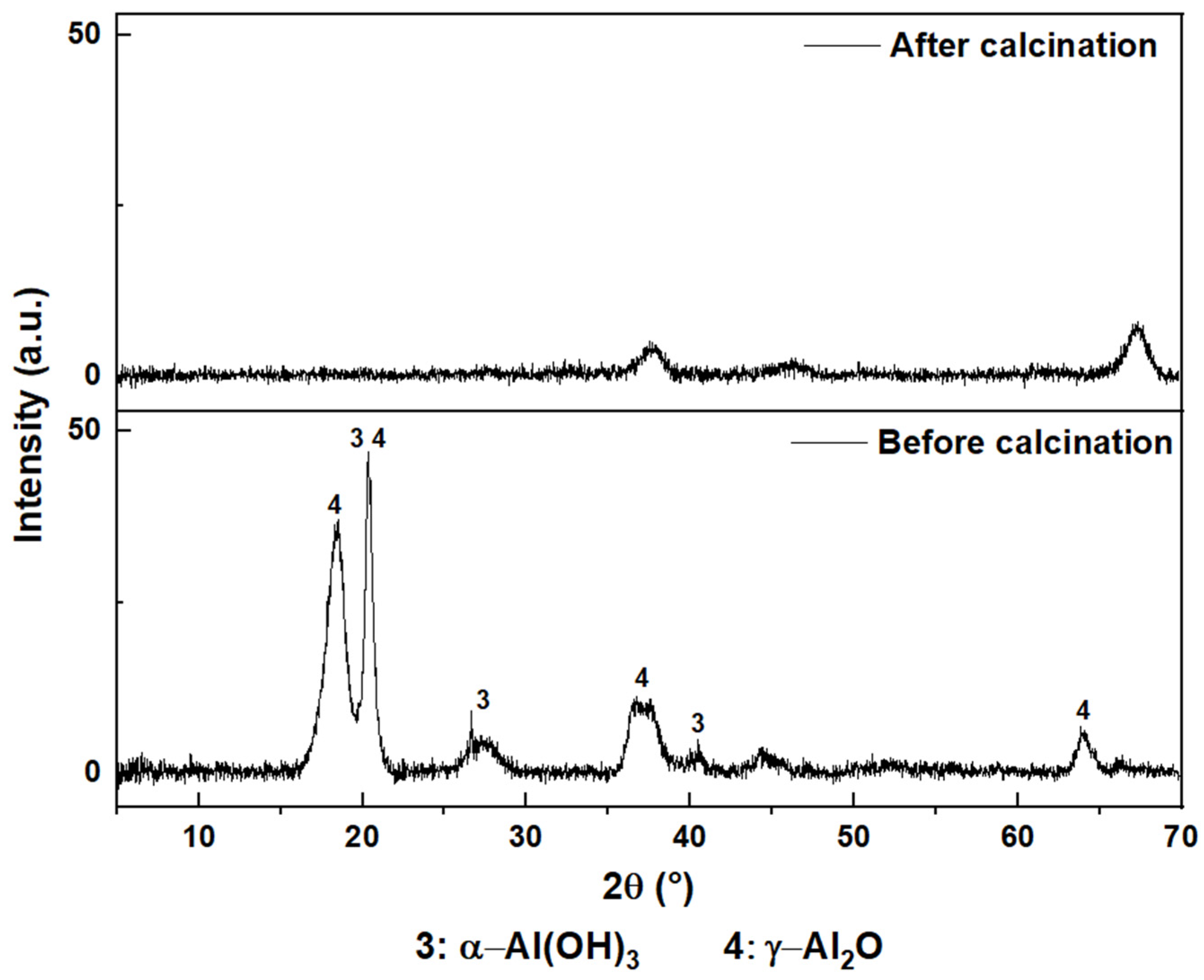
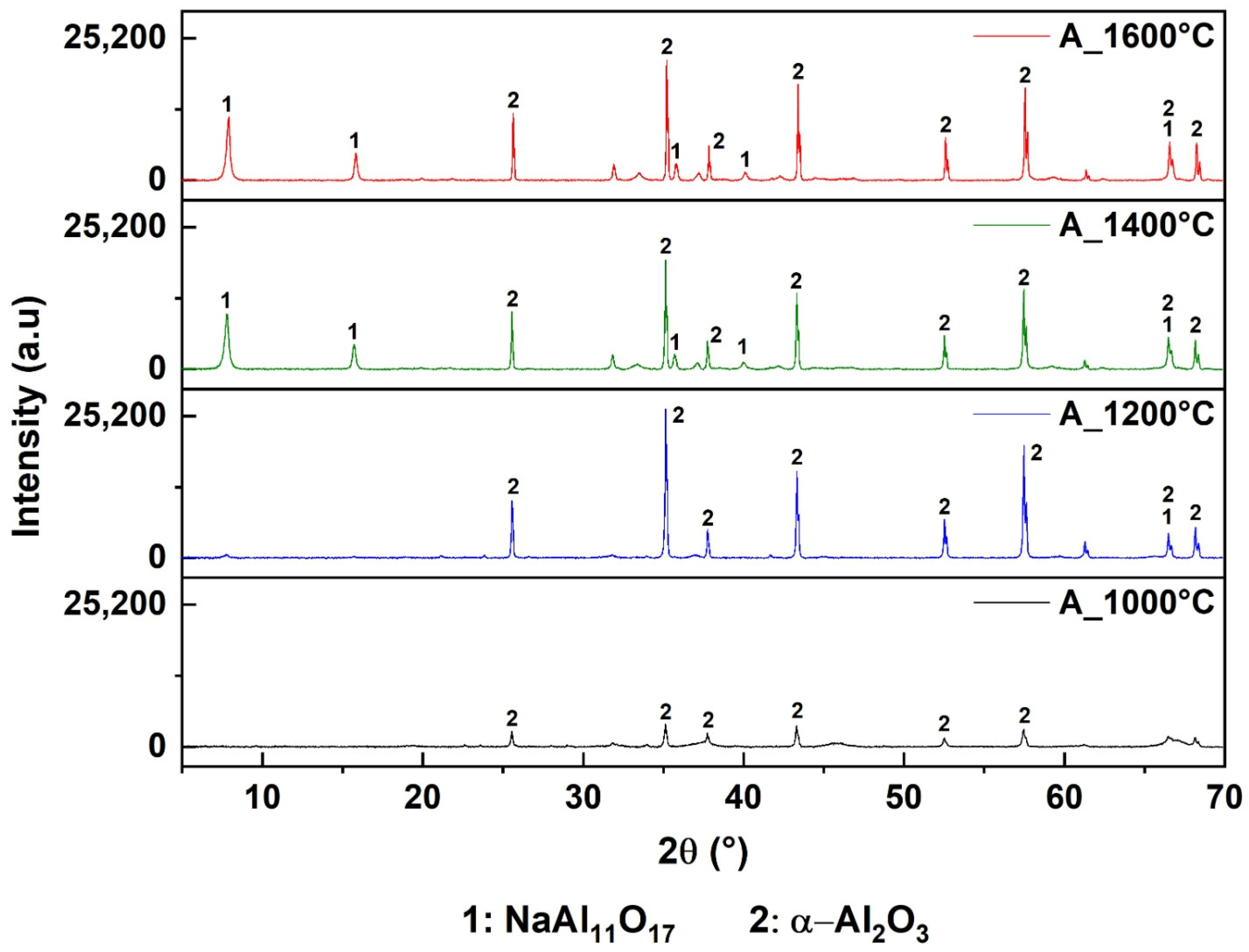
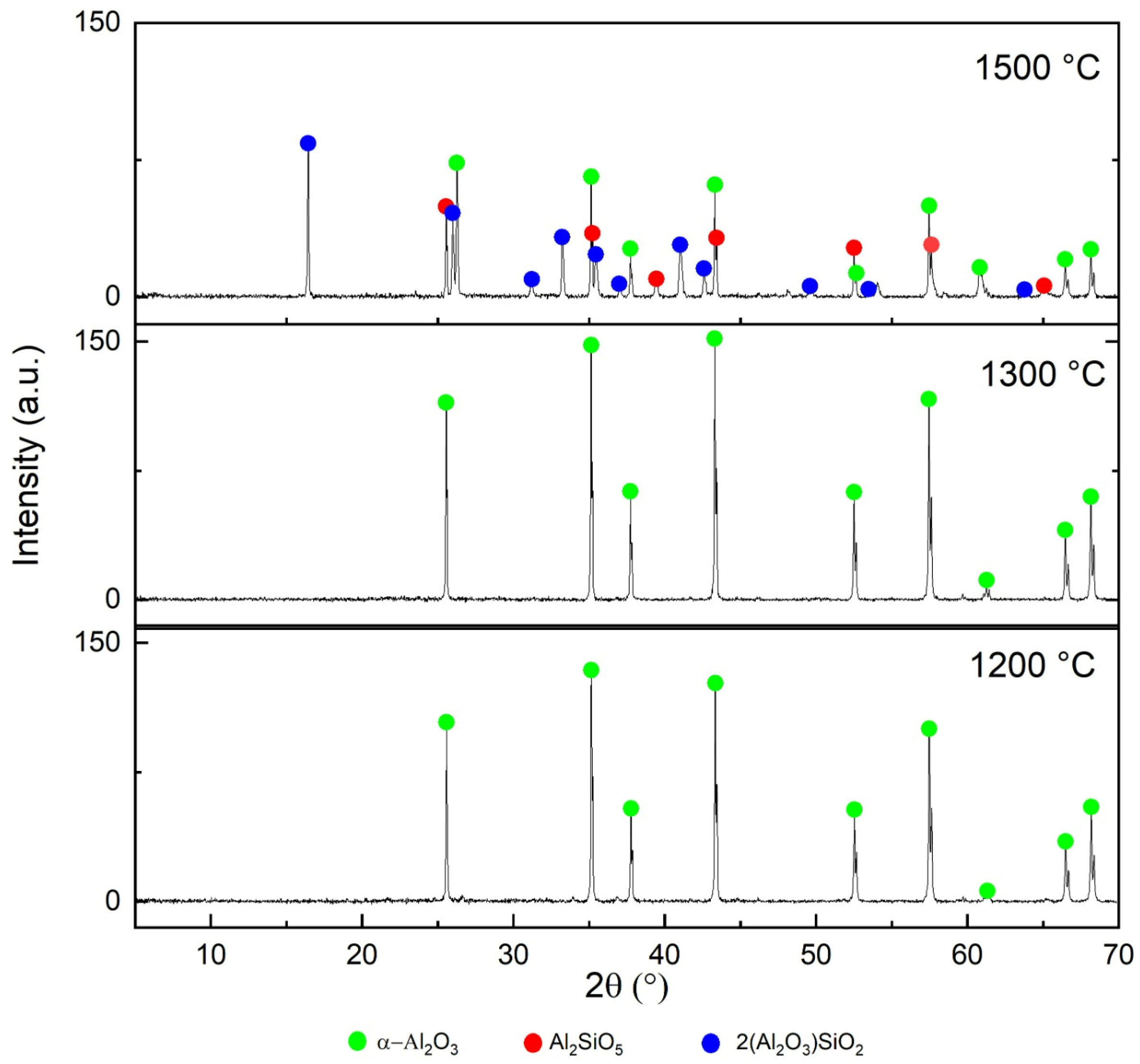
3.3. Pyrometallurgical Approaches for Value from AS
4. Discussion
4.1. Evaluation of the Hydrometallurgical Approaches for Recovering Value from AS
4.2. Pyrometallurgical Approaches for Recovering Value from AS
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AS | Anodic sludge |
References
- Ferreira, J.M.F.; Olhero, S.M. Al-rich sludge treatments towards recycling. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2002, 22, 2243–2249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitrakas, M.G.; Bakaloulis, A.K.; Gkinis, K.T. Studies on arsenic adsorption by the use of aluminum anodizing sludge. Desal. Water Treat. 2012, 39, 235–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Memon, N.A.; Ahmed, N.; Haq, T.; Ismail, S.; Rashid, U.; Begum, R. An Effective Use of Anodizing Mud for Treatment of Tannery Wastewater as a Coagulation Agent. Int. J. Sci. Res. Publ. 2018, 8, 418–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, X.; Peng, X.; Luo, L.; Shen, L. Comprehensive Recovery of Aluminum and Calcium from Aluminum-Anodizing Sludge by Physicochemical Process. J. Sustain. Metall. 2021, 7, 1343–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Magalhães, L.F.; Da Silva, G.R.; Henriques, A.B.; De Freitas, V.A.A.; Peres, A.E.C. Synthesis of Analcime Zeolite from Glass Powder Waste and Aluminium Anodizing Waste. Silicon 2024, 16, 4173–4185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdellatief, M.; Mortagi, M.; Hamouda, H.; Skrzypkowski, K.; Zagórski, K.; Zagórska, A. Influence of silicate modulus and eggshell powder on the expansion, mechanical properties, and thermal conductivity of lightweight geopolymer foam concrete. Materials 2025, 18, 2088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shackelford, J.F.; Doremus, R.H. Ceramic and Glass Materials: Structure, Properties and Processing; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busca, G. Structural, Surface, and Catalytic Properties of Aluminas. Adv. Catal. 2014, 57, 319–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruys, A. Processing, structure, and properties of alumina ceramics. Alum. Ceram. 2019, 4, 71–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novales, A.; Pereira, F.; Hotza, D.; Klegues, O. Aluminum rich sludge as raw material for the ceramic industry. Interceram 2003, 52, 44–46. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/269931045 (accessed on 15 May 2025).
- Álvarez-Ayuso, E. Approaches for the treatment of waste streams of the aluminium anodising industry. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 164, 409–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, X.; Chen, W.; Schollbach, K.; Brouwers, H.J.H. Valorization of biomass bottom ash in alkali-activated GGBFS-fly ash: Impact of biomass bottom ash characteristic, silicate modulus and aluminum-anodizing waste. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 428, 136408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, D.; Barcelos, R.L.; Parma, G.C.; Girotto, E.; Américo, J.; Pereira, N.C.; Magnago, R.F. Recycled polyethylene terephthalate and aluminum anodizing sludge-based boards with flame resistance. Waste Manag. 2019, 92, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silveira Júnior, J.G.; Sakata, R.D.; Onghero, L.; De Matos, P.R.; Rodríguez, E.D.; Simão, L.; De Oliveira, A.P.N.; De Araújo Moura, R.C.; De Campos, C.E.M.; De Castro Pessôa, J.R.; et al. Al-anodizing waste as a supplementary cementitious material for 3D-printed Portland cement. Waste Manag. Bull. 2025, 3, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, K.S.; Srinivas, J.; Ashokkumar, P.; Saravanan, R.; Aravind, V.; Bhat, S.S.; Raj, R.A.; Girimurugan, R. Utilization of Steelmaking By-Products and Aluminum sludges in Alkali-Activated Materials: A Sustainable approach for construction applications. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2025, 3045, 012002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajaniemi, K.; Tuomikoski, S.; Lassi, U. Electrocoagulation Sludge Valorization—A Review. Resources 2021, 10, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, E.; Kopac, J. Aluminum recovery as a product with high added value using aluminum hazardous waste. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 261, 316–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lecomte-Nana, G.; Hammas, A. Mullite: Structure and Properties. In Reference Module in Materials Science and Materials Engineering; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, L.K.S.; Silva, K.R.; Menezes, R.R.; Santana, L.N.L.; Lira, H.L. Microstructural characteristics, properties, synthesis and applications of mullite: A review. Cerâmica 2022, 68, 126–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dexpert, H.; Larue, J.F.; Mutin, I.; Moraweck, B.; Bertaud, Y.; Renouprez, A. Thermal Transformation of Transition Aluminas. JOM 1985, 37, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misra, C. Aluminum Oxide (Alumina), Hydrated; Kirk-Othmer Encyclopedia of Chemical Technology: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, F.A.C.; Livramento, V.; Delmas, F. Novel mullite-based ceramics manufactured from inorganic wastes: I. Densification behaviour. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2008, 196, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mymrin, V.; Pedroso, D.E.; Pedroso, C.; Alekseev, K.; Avanci, M.A.; Winter, E.; Cechin, L.; Rolim, P.H.B.; Iarozinski, A.; Catai, R.E. Environmentally clean composites with hazardous aluminum anodizing sludge, concrete waste, and lime production waste. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 174, 380–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carstens, S.; Meyer, R.; Enke, D. Towards Macroporous α-Al2O3—Routes, Possibilities and Limitations. Materials 2020, 13, 1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farinha, A.; Mendes, R.; Vieira, M. Production of Sintered α-Alumina by Explosive Compaction from Low Temperature Calcinated Aluminum-Rich Sludge. Waste Biomass Valor. 2013, 4, 627–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, M.J.; Abrantes, J.C.C.; Ferreira, J.M.; Labrincha, J.A. Predicting processing-sintering-related properties of mullite–alumina ceramic bodies based on Al-rich anodising sludge by impedance spectroscopy. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2004, 24, 3841–3848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, M.J.; Abrantes, J.C.C.; Labrincha, J.A. Electrical characterization of mullite bodies containing Al-rich anodizing sludge. Mater. Sci. Forum. 2006, 514–516 Pt 2, 1726–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, M.J.; Tulyaganov, D.U.; Ferreira, J.M.F.; Labrincha, J.A. Production of Al-rich sludge-containing ceramic bodies by different shaping techniques. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2004, 148, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, M.J.; Tulyaganov, D.U.; Ferreira, J.M.; Labrincha, J.A. Recycling of Al-rich industrial sludge in refractory ceramic pressed bodies. Ceram. Int. 2002, 28, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labrincha, J.A.; Albuquerque, C.M.; Ferreira, J.M.; Ribeiro, M.J. Electrical characterisation of cordierite bodies containing Al-rich anodising sludge. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2006, 26, 825–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labrincha, J.; Puertas, F.; Schroeyers, W.; Kovler, K.; Pontikes, Y.; Nuccetelli, C.; Krivenko, P.; Kovalchuk, O.; Petropavlovsky, O.; Komljenovic, M.; et al. From NORM by-products to building materials. In Naturally Occurring Radioactive Materials in Construction: Integrating Radiation Protection in Reuse (COST Action Tu1301 NORM4BUILDING); Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 183–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komarneni, S.; Schneider, H.; Okada, K. Mullite Synthesis and Processing. In Mullite; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2005; pp. 251–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badanoiu, A.-I.; Stoleriu, S.-P.; Carocea, A.-C.; Eftimie, M.-A.; Trusca, R. Influence of synthesis route on composition and main properties of mullite ceramics based on waste. Materials 2025, 18, 1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, E.; Barbadillo, P.; García, F.; Hernández, A.; Ayala, N. Utilización de los Lodos de Hidróxido de Aluminio Procedente de las Plantas de Anodizado. Patent No. 2130098, 1 March 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Sanga, P.; Iradukunda, Y.; Munyemana, J.C. Recycling of alum from water treatment residue and reuse it as a flocculating agent for raw water treatment. J. Geosci. Environ. Prot. 2018, 6, 216–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barakat, M.A.; El-Sheikh, S.M.; Farghly, F.E. Removing Al and regenerating caustic soda from the spent washing liquor of Al etching. JOM 2005, 57, 34–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, M.; Li, G.; Liang, J.; Liao, X.; Ren, J.; Fen, X.; Qian, W.; Li, L.; Sun, S. A high-efficiency process for the separation of chromium and aluminum from waste aluminum sludge with a high chromium content using a combined oxidation and dispersion process. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 258, 118083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miskufova, A.; Petranikova, M.; Kovacs, M.; Briancin, J.; Havlik, T.; Orac, D. Leaching of Aluminium Dross in Alkaline Solution. In Proceedings of the European Metallurgical Conference, Innsbruck, Austria, 28 June–1 July 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad Zauzi, N.S.; Zakaria, M.; Baini, R.; Rahman, M.; Mohamed Sutan, N.; Hamdan, S. Influence of alkali treatment on the surface area of aluminium dross. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2016, 2016, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahecha-Rivas, J.C.; Fuentes-Ordoñez, E.; Epelde, E.; Saldarriaga, J.F. Aluminum extraction from a metallurgical industry sludge and its application as adsorbent. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 310, 127374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Katatny, E.A.; Halawy, S.A.; Mohamed, M.A.; Zaki, M.I. Surface composition, charge and texture of active alumina powders recovered from aluminum dross tailings chemical waste. Powder Technol. 2003, 132, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathy, A.K.; Mahalika, S.; Sarangi, C.K.; Tripathy, B.C.; Sanjay, K.; Bhattacharya, I.N. A pyro-hydrometallurgical process for the recovery of alumina from waste aluminium dross. Minerals Eng. 2019, 137, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correia, A.; Chambino, T.; Gonçalves, L.; Franco, A.; Gonçalves, R.; Gonçalves, A.; Limpo, V.; Delmas, F.; Nogueira, C.; Bartolomeu, F. Municipal wastewater treatment with anodizing solid waste. Desalination 2005, 185, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, S.C.; Ramos, A.S.; Vieira, M.T. Mullitization kinetics from silica- and alumina-rich wastes. Ceram. Int. 2007, 33, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Peñafiel, F.; Martínez, R. Síntesis de zeolitas utilizando como materia prima lodos de los procesos de anodizado de aluminio. Tecnol. Marcha 2019, 32, 12–23. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Souza, M.T.; Simão, L.; Montedo, O.R.K.; Raupp Pereira, F.; de Oliveira, A.P.N. Aluminum anodizing waste and its uses: An overview of potential applications and market opportunities. Waste Manag. 2019, 84, 286–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Moraes, G.G.; Oliveira, B.G.; Siligardi, C.; Innocentini, M.D.M.; Oliveira, A.A.M., Jr.; Neto, J.B.R.; Hotza, D.; de Oliveira, A.P.N. Production of foundry filters using Al2O3 from the Al-anodizing process. Int. Ceram. Congr. Part 2010, 62, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghoniem, M.G.; Sami, T.M.; El-Reefy, S.A.; Mohamed, S.A. The production of high purity alumina from solid wastes obtained from aluminium factories. WIT Trans. Ecol. Environ. 2014, 180, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magalhães, J.M.; Silva, J.E.; Castro, F.P.; Labrincha, J.A. Physical and chemical characterisation of metal finishing industrial wastes. J. Environ. Manag. 2005, 75, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mymrin, V.; Pedroso, D.E.; Pedroso, C.L.; Avanci, M.A.; Rolim, P.H.B.; Carvalho, K.Q.; Catai, R.E. Physical-chemical processes of sustainable construction materials structure formation with iron ore processing tailings and aluminum anodizing sludge. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 298, 123698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corker, J.; Marques, I.; Resalati, S.; Okoroafor, T.; Maalouf, A.; Fu, Z.; Fan, M. Al-rich industrial waste as new alternative of fumed silica for the manufacture of vacuum insulation panels for building energy conservation. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 415, 137854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusta, I.; Castellano Calvo, A.; Aranburu, A.; Velasco Roldán, F. Los depósitos de Mn-Al-Fe de la cueva de Lazalday (Zarate, Alava): Composición química y mineralogía. Geogaceta 2009, 47, 31–34. [Google Scholar]
- Addai-Mensah, J. Surface and structural characteristics of gibbsite precipitated from pure, synthetic Bayer liquor. Miner. Eng. 1997, 10, 81–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thimmasandra, R. Mechanism of structural transformations during thermal decomposition studies of aluminium hydroxide polymorph. Inernational J. Sci. Res. 2013, 1, 514–518. [Google Scholar]
- Isobe, T.; Watanabe, T.; D’Espinose De La Caillerie, J.B.; Legrand, A.P.; Massiot, D. Solid-state 1H and 27Al NMR studies of amorphous aluminum hydroxides. J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2003, 261, 320–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercury, J.M.R.; Pena, P.; de Aza, A.H.; Sheptyakov, D.; Turrillas, X. On the decomposition of synthetic gibbsite studied by neutron thermodiffractometry. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2006, 89, 3728–3733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Shi, L.; Qizhen, H.; Hayat, W.; Shang, Z.; Ma, T.; Wang, M.; Yao, W.; Huang, H.; Chen, R. Extraction of alumina from aluminum dross by a non-hazardous alkaline sintering process: Dissolution kinetics of alumina and silica from calcined materials. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 777, 146123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, W.D.; Ahn, B.D.; Lee, M.S. Treatment of black dross with water and NaOH solution. J. Korean Inst. Resour. Recycl. 2017, 26, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y. Preparation of sodium aluminate from the leach liquor of diasporic bauxite in concentrated NaOH solution. Hydrometallurgy 2009, 98, 298–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayrapetyan, S.; Mangasaryan, L.; Tovmasyan, M.; Khachatryan, H. Precipitation of aluminum hydroxide from sodium aluminate, by treatment with formalin, and preparation of aluminum oxide. Acta Chromatogr. 2006, 16, 192. [Google Scholar]
- Chagas, L.H.; de Carvalho, G.S.G.; San Gil, R.A.S.; Chiaro, S.S.X.; Leitão, A.A.; Diniz, R. Obtaining aluminas from the thermal decomposition of their different precursors: An 27Al MAS NMR and X-ray powder diffraction studies. Mater. Res. Bull. 2014, 49, 216–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Páez, J.E.; Villaquirán, C.; Cobo, J. Estudio de la formación de los complejos intermedios durante la síntesis de alúmina. Mater. Res. 2001, 4, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, I.N.; Gochhayat, P.K.; Mukherjee, P.S.; Paul, S.; Mitra, P.K. Thermal decomposition of precipitated low bulk density basic aluminium sulfate. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2004, 88, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, B.R.; Dash, B.; Tripathy, B.C.; Bhattacharya, I.N.; Das, S.C. Production of η-alumina from waste aluminium dross. Miner. Eng. 2007, 20, 252–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matori, K.; Loy, C.; Hashim, M.; Ismail, I.; Mohd Zaid, M. Phase transformations of α-alumina made from waste aluminum via a precipitation technique. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 16812–16821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, V.; Rodriguez, J. The effect of the content of sodium in the obtaining of Na+ β-alúmina using the polymeric precursor. UNAL 2011, 78, 190–195. [Google Scholar]
- Kale, M.; Kale, S.; Joshi, C.; Moharil, S. Preparation of sodium beta-alumina using combustion synthesis. I-Manag. J. Mater. Sci. 2020, 7, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Chen, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, D.; Mao, Z. Synthesis and characterization of high ionic-conductive sodium beta-alumina solid electrolyte derived from boehmite. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2020, 31, 17670–17678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, A.; Kuo, C.K.; Nicholson, P.S. Formation and characterization of Na-β″-alumina single crystal films. Solid State Ion. 1993, 67, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Fang, M.; Huang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Yang, J.; Huang, S.; Xu, Y.; Chen, K.; Yi, S.; Zhang, S. Preparation, microstructure, and mechanical properties of spinel-corundum-sialon composite materials from waste fly ash and aluminum dross. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2014, 789867, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ligon, S.C.; Blugan, G.; Bay, M.C.; Battaglia, C.; Heinz, M.V.F.; Graule, T. Performance analysis of Na-β″-Al2O3/YSZ solid electrolytes produced by conventional sintering and by vapor conversion of α-Al2O3/YSZ. Solid State Ion. 2020, 345, 115169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadik, C.; El Amrani, I.; Albizane, A. Processing and characterization of alumina–mullite ceramics. J. Asian Ceram. Soc. 2014, 2, 310–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foo, C.T.; Salleh, M.A.M.; Ying, K.K.; Matori, K.A. Mineralogy and thermal expansion study of mullite-based ceramics synthesized from coal fly ash and aluminum dross industrial wastes. Ceram. Int. 2019, 45, 7488–7494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Shi, Z.; Wang, Z.; Wang, S. Phase transformation and properties of high-quality mullite ceramics synthesized using desert drift sands as raw materials. Mater. Lett. 2018, 221, 271–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Property | Value | Units |
|---|---|---|
| Humidity | 53.7 ± 0.5 | % |
| Bulk Density | 0.7 ± 0.1 | g cm−3 |
| True Density | 2.2 ± 0.1 | g cm−3 |
| Surface area | 13.7 ± 0.5 | m2 g−1 |
| Size particle (d80) | 4.5 ± 0.2 | mm |
| Element | wt (%) |
|---|---|
| Al | 26.6 ± 0.2 |
| Na | 1.5 ± 0.2 |
| Si | 0.6 ± 0.05 |
| Mg | 0.6 ± 0.05 |
| S | 2.0 ± 0.01 |
| Ca | 0.5 ± 0.05 |
| Fe | 0.4 ± 0.05 |
| P | 0.2 ± 0.02 |
| K | 0.04 ± 0.01 |
| Cr | 0.02 ± 0.01 |
| Ni | 0.1 ± 0.01 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Acosta, F.; Feijoo, C.; Sangurima-Cedillo, A.S.; Guevara, A.; Aragón-Tobar, C.F. Upcycling Anodic Sludge from Aluminum Anodizing: Leaching Efficiency and Thermal Conversion into Refractory Materials. Sustainability 2025, 17, 8491. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17188491
Acosta F, Feijoo C, Sangurima-Cedillo AS, Guevara A, Aragón-Tobar CF. Upcycling Anodic Sludge from Aluminum Anodizing: Leaching Efficiency and Thermal Conversion into Refractory Materials. Sustainability. 2025; 17(18):8491. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17188491
Chicago/Turabian StyleAcosta, Fausto, Cristhian Feijoo, Alfredo S. Sangurima-Cedillo, Alicia Guevara, and Carlos F. Aragón-Tobar. 2025. "Upcycling Anodic Sludge from Aluminum Anodizing: Leaching Efficiency and Thermal Conversion into Refractory Materials" Sustainability 17, no. 18: 8491. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17188491
APA StyleAcosta, F., Feijoo, C., Sangurima-Cedillo, A. S., Guevara, A., & Aragón-Tobar, C. F. (2025). Upcycling Anodic Sludge from Aluminum Anodizing: Leaching Efficiency and Thermal Conversion into Refractory Materials. Sustainability, 17(18), 8491. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17188491







