Toward Sustainable Wetland Management: A Literature Review of Global Wetland Vulnerability Assessment Techniques in the Context of Rising Pressures
Abstract
1. Introduction
- I.
- What methods are used to evaluate wetland vulnerability in various contexts, and what are their main attributes?
- II.
- How are wetland vulnerability indices formulated, and what environmental, ecological, and socio-economic parameters are typically considered in their development?
- III.
- What are the principal insights derived from the analysis of existing literature, and which knowledge gaps remain to be addressed?
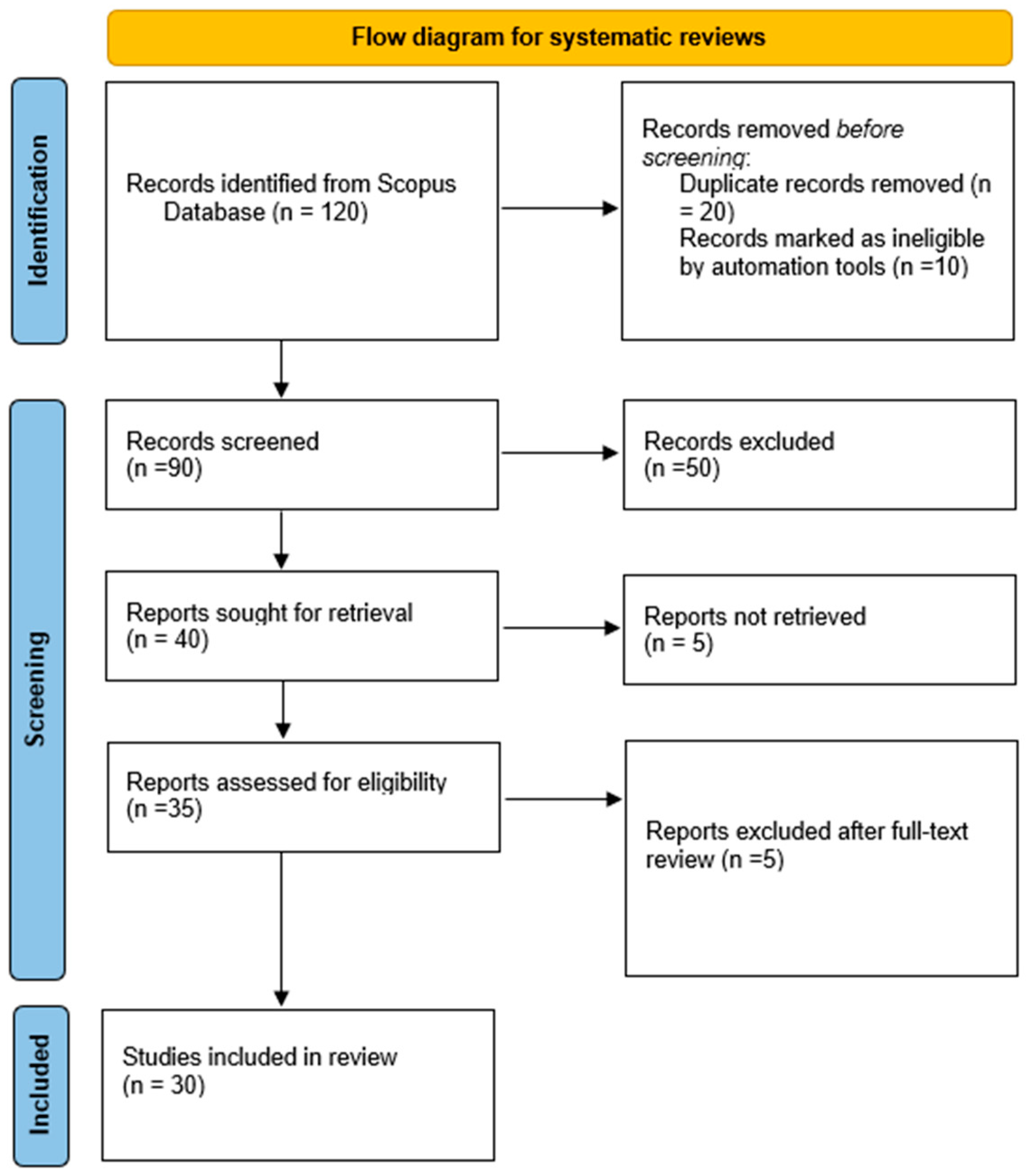
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Different Approaches Used to Assess Wetland Vulnerability
3.1.1. Integrating Multivariate Statistical Techniques in Wetland Vulnerability
3.1.2. Geospatial-Based Approaches for Assessing Wetland Vulnerability
3.1.3. The Importance of Artificial Intelligence in Assessing Wetland Vulnerability
3.1.4. The Use of Driver–Pressure–State–Impact–Response (DPSIR) Model for Wetland Vulnerability Assessment
3.2. Different Indices Developed to Assess Wetland Vulnerability
3.3. The Importance of Assessing Coastal Wetland Vulnerability
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Khatun, R.; Talukdar, S.; Pal, S.; Saha, T.K.; Mahato, S.; Debanshi, S.; Mandal, I. Integrating remote sensing with swarm intelligence and artificial intelligence for modelling wetland habitat vulnerability in pursuance of damming. Ecol. Inform. 2021, 64, 101349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramsar Convention Secretariat. The Ramsar Convention Manual: A Guide to the Convention on Wetlands, 6th ed.; Ramsar Convention Secretariat: Gland, Switzerland, 2013; Available online: https://www.ramsar.org/sites/default/files/documents/library/manual6-2013-e.pdf (accessed on 28 August 2025).
- Keddy, P.A. Wetland Ecology: Principles and Conservation; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Ballut-Dajud, G.A.; Sandoval Herazo, L.C.; Fernández-Lambert, G.; Marín-Muñiz, J.L.; López Méndez, M.C.; Betanzo-Torres, E.A. Factors affecting wetland loss: A review. Land 2022, 11, 434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finlayson, M.; Davidson, N. Global wetland outlook: Technical note on status and trends. Secretariat of the Ramsar Convention. Ramsar Convention on Wetlands, 2018. Global wetland outlook: State of the World’s wetlands and their services to people. Ramsar Conv. Wetl. 2018, 2018, 88. [Google Scholar]
- Mitra, S.; Wassmann, R.; Vlek, P.L. An appraisal of global wetland area and its organic carbon stock. Curr. Sci. 2005, 88, 25–35. [Google Scholar]
- Chiloane, C.; Dube, T.; Shoko, C. Impacts of groundwater and climate variability on terrestrial groundwater dependent ecosystems: A review of geospatial assessment approaches and challenges and possible future research directions. Geocarto Int. 2022, 37, 6755–6779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzurume, T.; Dube, T.; Shoko, C. Remotely sensed data for estimating chlorophyll-a concentration in wetlands located in the Limpopo Transboundary River Basin, South Africa. Phys. Chem. Earth Parts A/B/C 2022, 127, 103193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Das, A. Wetland conversion risk assessment of East Kolkata Wetland: A Ramsar site using random forest and support vector machine model. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 275, 123475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dube, T.; Dube, T.; Marambanyika, T. A review of wetland vulnerability assessment and monitoring in semi-arid environments of sub-Saharan Africa. Phys. Chem. Earth Parts A/B/C 2023, 132, 103473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finlayson, C.M.; van Dam, A.A. Climate change and wetlands: Vulnerability, adaptation, mitigation, resolutions, and scientific societies. In Ramsar Wetlands; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023; pp. 495–524. [Google Scholar]
- Davidson, N.C. How much wetland has the world lost? Long-term and recent trends in global wetland area. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2014, 65, 934–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, M.J.R.; Loh, J.; Davidson, N.C.; Beltrame, C.; Freeman, R.; Walpole, M. Tracking global change in ecosystem area: The Wetland Extent Trends index. Biol. Conserv. 2016, 193, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, N. Vulnerability, Risk and Adaptation: A Conceptual Framework; Tyndall Centre for Climate Change Research Working Paper 38, Tyndall Centre for Climate Change Research and Centre for Social and Economic Research on the Global Environment (CSERGE); School of Environmental Sciences, University of East Anglia: Norwich, UK, 2003; 16p. [Google Scholar]
- Nicholls, R.J.; PohPoh Wong Burkett, V.; Woodroffe, C.D.; Hay, J. Climate change and coastal vulnerability assessment: Scenarios for integrated assessment. Sustain. Sci. 2008, 3, 89–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, F.; Osbahr, H.; Boyd, E.; Thomalla, F.; Bharwani, S.; Zervogel, G.; Walker, B.; Birkmann, J.; van der Leeuw, S.; Rockstrom, J.; et al. Resilience and vulnerability: Complimentary or conflicting concepts. Ecol. Soc. 2010, 15, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Z.; Gao, G.; Fu, B. Spatiotemporal changes and driving forces of ecosystem vulnerability in the Yangtze River Basin, China: Quantification using habitat-structure-function framework. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 835, 155494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.; Fu, B.; Lü, Y.; Li, T.; Deng, L.; Wang, Y.; Lü, D.; Wang, Y.; Wu, X. Variable climatic conditions dominate decreased wetland vulnerability on the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau: Insights from the ecosystem pattern-process-function framework. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 458, 142496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moshiri, G.A. Constructed wetlands for water quality improvement. Environ. Int. 1994, 20, 551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gitay, H.; Finlayson, C.; Davidson, N.C. A Framework for Assessing the Vulnerability of Wetlands to Climate Change; Secretariat of the Ramsar Convention: Gland, Switzerland, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Alwang, J.; Siegel, P.B.; Jorgensen, S.L. Vulnerability: A View from Different Disciplines; Social Protection Discussion Paperseries; The World Bank: Washington DC, USA, 2001; Volume 115, p. 60. [Google Scholar]
- Bayliss, B.; Brennan, K.; Eliot, I.; Finlayson, M.; Hall, R.; House, T.; Pidgeon, B.; Walden, D.; Waterman, P. Vulnerability Assessment of Predicted Climate Change and Sea Level Rise in the Alligator Rivers Region, Northern Territory Australia; Supervising Scientist Report 123; Supervising Scientist: Barton, Australia, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Harvey, N.; Woodroffe, C.D. Australian approaches to coastal vulnerability assessment. Sustain. Sci. 2008, 3, 67–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acreman, M.C.; Blake, J.R.; Booker, D.J.; Harding, R.J.; Reynard, N.; Mountford, J.O.; Stratford, C.J. A simple framework for evaluating regional wetland ecohydrological response to climate change with case studies from Great Britain. Ecohydrology 2009, 2, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, S.; Xiao, H.; Peng, X.; Song, X. Hydroclimate-driven changes in the landscape structure of the terminal lakes and wetlands of the China’s Heihe River Basin. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2014, 187, 4091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, S.; Wang, Y.; Liu, J.; Cai, H.; Wu, P.; Geng, Q.; Xu, L. Sustainability assessment of regional water resources under the DPSIR framework. J. Hydrol. 2016, 532, 140–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khosravi, K.; Nohani, E.; Maroufinia, E.; Pourghasemi, H.R. A GIS-based flood susceptibility assessment and its mapping in Iran: A comparison between frequency ratio and weights-of-evidence bivariate statistical models with multi-criteria decision-making technique. Nat. Hazards 2016, 83, 947–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.M.; Ujiie, K.; Noguchi, R.; Ahamed, T. Flash flood-induced vulnerability and need assessment of wetlands using remote sensing, GIS, and econometric models. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2022, 25, 100692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Luo, J.; Bi, L.; Tong, K. Spatiotemporal heterogeneity and influencing factors of human activity intensity in the Guangxi Beibu Gulf Zone, China. Environ. Sustain. Indic. 2024, 22, 100372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Yan, Z.; Tong, X.; Han, Z.; Ma, M.; Yu, S.; Xia, J. Seasonal prediction of summer extreme precipitation over the Yangtze River based on random forest. Weather. Clim. Extrem. 2022, 37, 100477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhowmik, S. Ecological and economic importance of wetlands and their vulnerability: A review. In Research Anthology on Ecosystem Conservation and Preserving Biodiversity; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2022; pp. 11–27. [Google Scholar]
- Lamsal, P.; Kumar, L.; Atreya, K.; Pant, K.P. Vulnerability and impacts of climate change on forest and freshwater wetland ecosystems in Nepal: A review. Ambio 2017, 46, 915–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Defne, Z.; Aretxabaleta, A.L.; Ganju, N.K.; Kalra, T.S.; Jones, D.K.; Smith, K.E. A geospatially resolved wetland vulnerability index: Synthesis of physical drivers. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0228504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akumu, C.E.; Henry, J.; Gala, T.S.; Dennis, S.; Reddy, C.; Tegegne, F.; Haile, S.; Archer, R.S. Inland wetlands mapping and vulnerability assessment using an integrated geographic information system and remote sensing techniques. Glob. J. Environ. Sci. Manag. 2018, 4, 387–400. [Google Scholar]
- Abson, D.J.; Dougill, A.J.; Stringer, L.C. Using principal component analysis for information-rich socio-ecological vulnerability mapping in Southern Africa. Appl. Geogr. 2012, 35, 515–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PiraliZefrehei, A.R.; Hedayati, A.; Pourmanafi, S.; BeyraghdarKashkooli, O.; Ghorbani, R. Environmental vulnerability assessment of Choghakhor International Wetland during 1985 to 2018. Lakes Reserv. Res. Manag. 2020, 25, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veas-Ayala, N.; Alfaro-Córdoba, M.; Quesada-Román, A. Costa Rican wetlands vulnerability index. Prog. Phys. Geogr. Earth Environ. 2022, 47, 521–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haider, A.A.; Hassan, M.I.B.; Rasib, A.W.B. Geospatial Approach to Wetland Vulnerability Assessment for Northwest Bangladesh. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2023, 48, 139–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Liu, J. Wetland key habitat functional areas in China informed by flagship species. Sci. Adv. 2023, 9, eadd1234. [Google Scholar]
- Malekmohammadi, B.; Jahanishakib, F. Vulnerability assessment of wetland landscape ecosystem services using driver-pressure-state-impact-response (DPSIR) model. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 82, 293–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Liu, S.; Jia, C.; Liu, Y.; Yu, C. Vulnerability assessment and management planning for the ecological environment in urban wetlands. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 298, 113540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stratford, C.J.; Acreman, M.C.; Gwyn Rees, H. A simple method for assessing the vulnerability of wetland ecosystem services. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2011, 56, 1485–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslam, R.W.; Shu, H.; Naz, I.; Quddoos, A.; Yaseen, A.; Gulshad, K.; Alarifi, S.S. Machine Learning-Based Wetland Vulnerability Assessment in the Sindh Province Ramsar Site Using Remote Sensing Data. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagheri, M.; Farshforoush, N.; Bagheri, K.; Shemirani, A.I. Applications of Artificial Intelligence Technologies in Water Environments: From Basic Techniques to Novel Tiny Machine Learning Systems. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2023, 180, 10–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, S.; Paul, S. Assessing wetland habitat vulnerability in moribund Ganges delta using bivariate models and machine learning algorithms. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 119, 106866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, H.; Yu, X.; Zhang, L.; Xia, S.; Liu, Y.; Mao, D.; Zhang, G. An evaluating system for wetland ecological risk: Case study in coastal mainland China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 828, 154535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Cao, Z. How to measure wetland destruction and risk: Wetland damage index. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 141, 109126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez-González, C.; Fermán-Almada, J.L.; Moreno-Casasola, P.; Espejel, I. Scenarios of vulnerability in coastal municipalities of tropical Mexico: An analysis of wetland land use. Ocean. Coast. Manag. 2014, 89, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leberger, R.; Geijzendorffer, I.R.; Gaget, E.; Gwelmami, A.; Galewski, T.; Pereira, H.M.; Guerra, C.A. Mediterranean wetland conservation in the context of climate and land cover change. Reg. Environ. Change 2020, 20, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osland, M.J.; Enwright, N.M.; Day, R.H.; Gabler, C.A.; Stagg, C.L.; Grace, J.B. Beyond just sea-level rise: Considering macroclimatic drivers within coastal wetland vulnerability assessments to climate change. Glob. Change Biol. 2016, 22, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Webb, E.L.; Friess, D.A.; Krauss, K.W.; Cahoon, D.R.; Guntenspergen, G.R.; Phelps, J. A global standard for monitoring coastal wetland vulnerability to accelerated sea-level rise. Nat. Clim. Change 2013, 3, 458–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Das, A. Urban expansion induced vulnerability assessment of East Kolkata Wetland using Fuzzy MCDM method. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2019, 13, 191–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.; Ge, Z.; Yuan, L.; Zhang, L. Vulnerability assessment of the coastal wetlands in the Yangtze Estuary, China to sea-level rise. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2015, 156, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, G.; Xie, X.; Tan, C.; Liang, S.; Hu, X.; Wu, X. Assessment of vegetation vulnerability in floodplain wetlands: A perspective from carryover effect of seasonal growth under various extreme hydrological scenarios. J. Hydrol. 2025, 651, 132622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyden, J.; Wurm, P.; Joyce, K.E.; Boggs, G. A spatial vulnerability assessment of monsoonal wetland habitats to para grass invasion in Kakadu National Park, northern Australia. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2018, 71, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Mahfadi, A.S.; Dakki, M. Vulnerability of Al-hodidah wetlands in Yemen: Main socio-economic causes. Mater. Today Proc. 2019, 13, 515–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidalgo-Corrotea, C.; Alaniz, A.J.; Vergara, P.M.; Moreira-Arce, D.; Carvajal, M.A.; Pacheco-Cancino, P.; Espinosa, A. High vulnerability of coastal wetlands in Chile at multiple scales derived from climate change, urbanization, and exotic forest plantations. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 903, 166130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, T.K.; Pal, S. Exploring physical wetland vulnerability of Atreyee river basin in India and Bangladesh using logistic regression and fuzzy logic approaches. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 98, 251–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Lu, J.; Zheng, W.; Sun, J.; Li, J.; Guo, Z.; Huang, J.; Yu, S.; Yin, L.; Wang, Y.; et al. Evaluation system of coastal wetland ecological vulnerability under the synergetic influence of land and sea: A case study in the Yellow River Delta, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 161, 111735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Convention sur les Zones Humides. Perspectives Mondiales des Zones Humides: Édition Spéciale 2021; Secrétariat de la Convention sur les Zones Humides: Gland, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Abdi, H.; Williams, L.J. Principal component analysis. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Comput. Stat. 2010, 2, 433–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arias-Real, R.; Delgado-Baquerizo, M.; Sabater, S.; Gutiérrez-Cánovas, C.; Valencia, E.; Aragón, G.; Cantón, Y.; Datry, T.; Giordani, P.; Medina, N.G.; et al. Unfolding the dynamics of ecosystems undergoing alternating wet-dry transitional states. Ecol. Lett. 2024, 27, e14488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castello, L.; Macedo, M.N. Large-scale degradation of Amazonian freshwater ecosystems. Glob. Change Biol. 2016, 22, 990–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardisky, M.A.; Gross, M.F.; Klemas, V. Remote sensing of coastal wetlands. Bioscience 1986, 36, 453–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klemas, V. Remote sensing of emergent and submerged wetlands: An overview. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2013, 34, 6286–6320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkinson, C.; Horrigan, K.; Cane, T.; Gaborit, S.; McLernon, S.; Pennington, S.; Quon, S.; Woo, L.; Mulamoottil, G.; Jasinsky, P.; et al. An integrated approach to the planning and management of urban wetlands: The case of bechtel park wetland, Waterloo, Ontario. Can. Water Res. J. 1997, 22, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeda, T.; Kato, J.; Matsumura, T.; Murakami, T.; Abeynayaka, A. Governance of artificial intelligence in water and wastewater management: The case study of Japan. Hydrology 2021, 8, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghdam, E.; Mohandes, S.R.; Manu, P.; Cheung, C.; Yunusa-Kaltungo, A.; Zayed, T. Predicting quality parameters of wastewater treatment plants using artificial intelligence techniques. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 405, 137019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, J.F.; Saco, P.M.; Sandi, S.; Saintilan, N.; Riccardi, G. Potential increase in coastal wetland vulnerability to sea-level rise suggested by considering hydrodynamic attenuation effects. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 16094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabii, T. An Overview of African Wetlands; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Mandishona, E.; Knight, J. Inland wetlands in Africa: A review of their typologies and ecosystem services. Prog. Phys. Geogr. Earth Environ. 2022, 46, 547–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdenour, A.; Sinan, M.; Lekhlif, B.; Belloulid, O. A GIS based approach for assessing water body change in a mountain wetland: Case of Dayet Awwa, Morocco. In E3S Web of Conferences; EDP Sciences: Julius, France, 2024; Volume 489, p. 04001. [Google Scholar]
- Lefebvre, G.; Redmond, L.; Germain, C.; Palazzi, E.; Terzago, S.; Willm, L.; Poulin, B. Predicting the vulnerability of seasonally-flooded wetlands to climate change across the Mediterranean Basin. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 692, 546–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
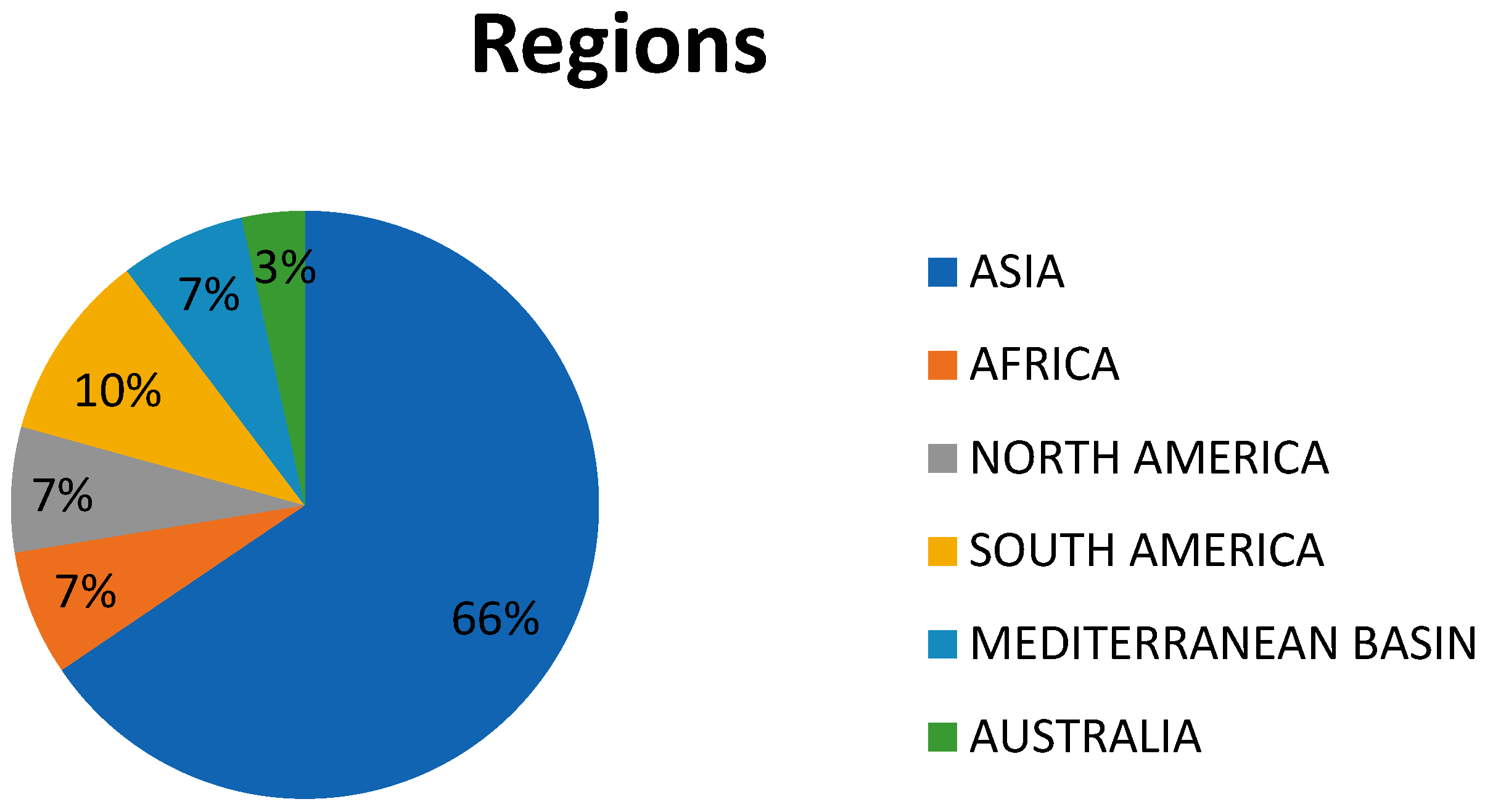
| Citation | Approach Used | Year | Region | Wetland Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [33] | GIS | 2020 | North America | Inland wetland |
| [34] | GIS + Remote sensing | 2018 | North America | Coastal wetland |
| [35] | PSA | 2012 | Africa | Inland wetland |
| [36] | GIS | 2020 | Asia | Inland wetland |
| [37] | Statistical techniques | 2023 | South America | Different types |
| [38] | GIS (MNDWI) | 2023 | Asia | Inland wetland |
| [39] | Hydrological and Climate models | 2019 | Mediterranean Basin | Seasonally flooded wetlands |
| [40] | DPSIR | 2017 | Asia | Inland wetland |
| [41] | FDAHP method | 2021 | Asia | Urban wetland |
| [42] | General Framework | 2011 | Asia | Mountain wetland |
| [43] | GIS + Remote sensing | 2024 | Asia | Inland wetland |
| [44] | AI | 2023 | Not specified | Different types |
| [45] | ML +Bivariate models | 2020 | Asia | Inland wetland |
| [1] | Remote sensing +AI | 2021 | Asia | River basin |
| [46] | WRI index | 2022 | Asia | Coastal wetland |
| [47] | WDI index | 2022 | Asia | Inland wetland |
| [48] | PSR approach | 2014 | South America | Coastal wetland |
| [49] | PTA | 2020 | Mediterranean Basin | Coastal wetland |
| [50] | Micro climatic drivers | 2016 | North America | Coastal wetland |
| [51] | RSET-MH method | 2013 | Not specified | Coastal wetland |
| [52] | Fuzzy MCDM method | 2019 | Asia | Urban wetland |
| [53] | SPRC model | 2015 | Asia | Coastal wetland |
| [54] | Statistical techniques | 2025 | Asia | Floodplain wetland |
| [18] | MGWR model | 2024 | Asia | Plateau wetland |
| [55] | GIS | 2018 | Australia | Monsoonal wetland |
| [56] | Socio-economicapproach | 2019 | Asia | Coastal wetland |
| [57] | Remote Sensing and statistical technique | 2023 | South America | Coastal wetland |
| [58] | Statistical methods | 2019 | Asia | Floodplain wetland |
| [59] | A comprehensive evaluation system | 2020 | Asia | Coastal wetland |
| [28] | Remote sensing +GIS+ econometric models | 2022 | Asia | Floodplain wetland |
| Criteria | Excluded | Included |
|---|---|---|
| Type of publication | Non-peer-reviewed publications (editorials, book chapters, meetings, conference posters and abstracts, etc.) | Peer-reviewed publications, which are highly relevant in applied conservation efforts. |
| Language | Non-English articles | English articles to ensure consistency and accessibility to widely recognized research. |
| Date of publication | Articles published prior to 2011 | Articles published prior to April 2025. |
| Methods used | Studies limited to general or foundational methods without the use of advanced techniques | Studies that utilize advanced, specialized, or technical methodologies, such as AI, GIS, remote sensing, statistical tools, etc. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abdenour, A.; Sinan, M.; Lekhlif, B. Toward Sustainable Wetland Management: A Literature Review of Global Wetland Vulnerability Assessment Techniques in the Context of Rising Pressures. Sustainability 2025, 17, 7962. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17177962
Abdenour A, Sinan M, Lekhlif B. Toward Sustainable Wetland Management: A Literature Review of Global Wetland Vulnerability Assessment Techniques in the Context of Rising Pressures. Sustainability. 2025; 17(17):7962. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17177962
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbdenour, Assia, Mohamed Sinan, and Brahim Lekhlif. 2025. "Toward Sustainable Wetland Management: A Literature Review of Global Wetland Vulnerability Assessment Techniques in the Context of Rising Pressures" Sustainability 17, no. 17: 7962. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17177962
APA StyleAbdenour, A., Sinan, M., & Lekhlif, B. (2025). Toward Sustainable Wetland Management: A Literature Review of Global Wetland Vulnerability Assessment Techniques in the Context of Rising Pressures. Sustainability, 17(17), 7962. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17177962






