A Study on the Associative Regulation Mechanism Based on the Water Environmental Carrying Capacity and Its Impact Indicators in the Songhua River Basin in Harbin City, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
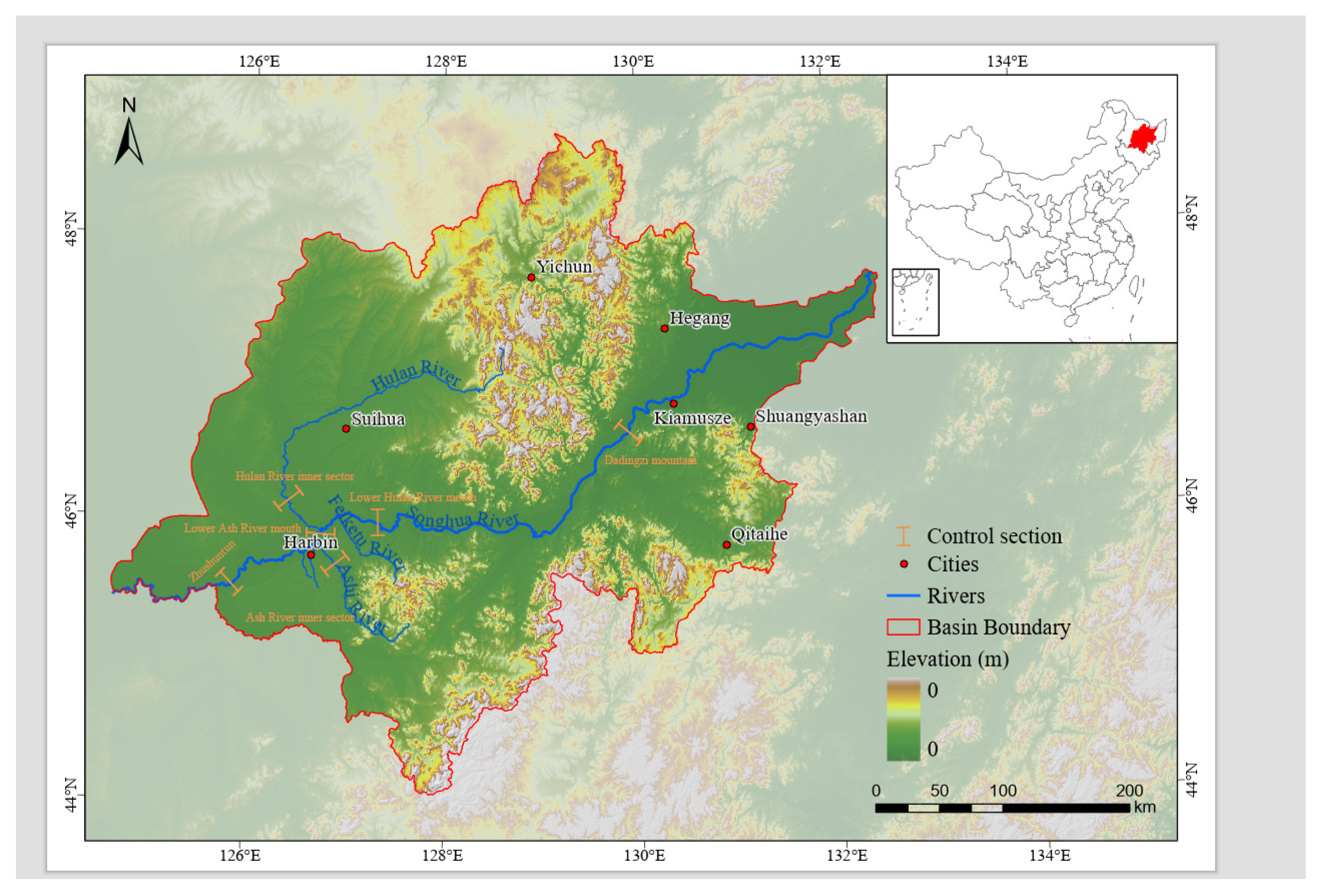
2.1. Overview of the Study Area
2.2. Data Sources
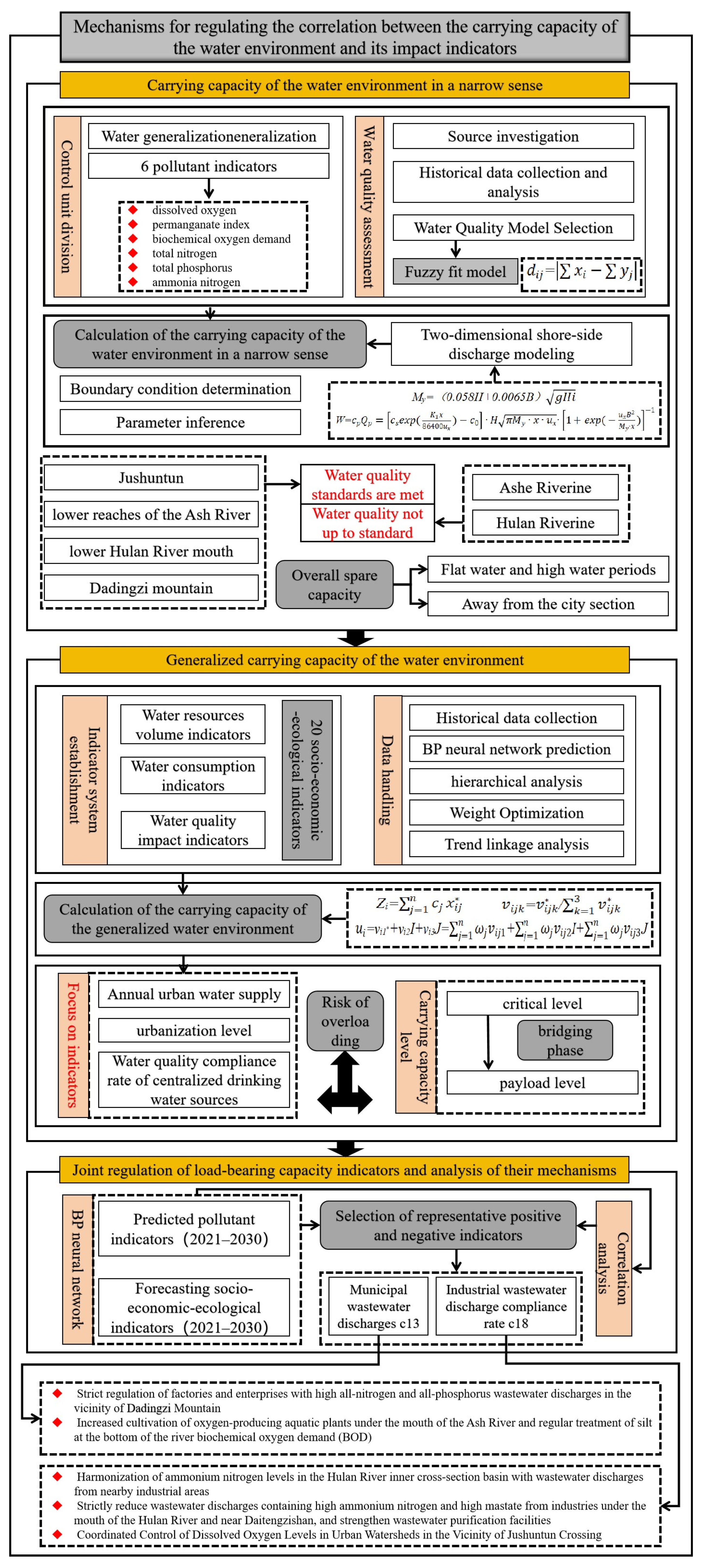
2.3. Selection of Indicators of the Carrying Capacity of a Water Environment in a Narrow Sense
2.4. Narrowly Defined Water Environment Carrying Capacity Calculations
2.4.1. Water Quality Fuzzy Closeness Modelling [50]
2.4.2. Two-Dimensional Riparian Discharge Modelling for the Carrying Capacity of the Water Environment in a Narrow Sense
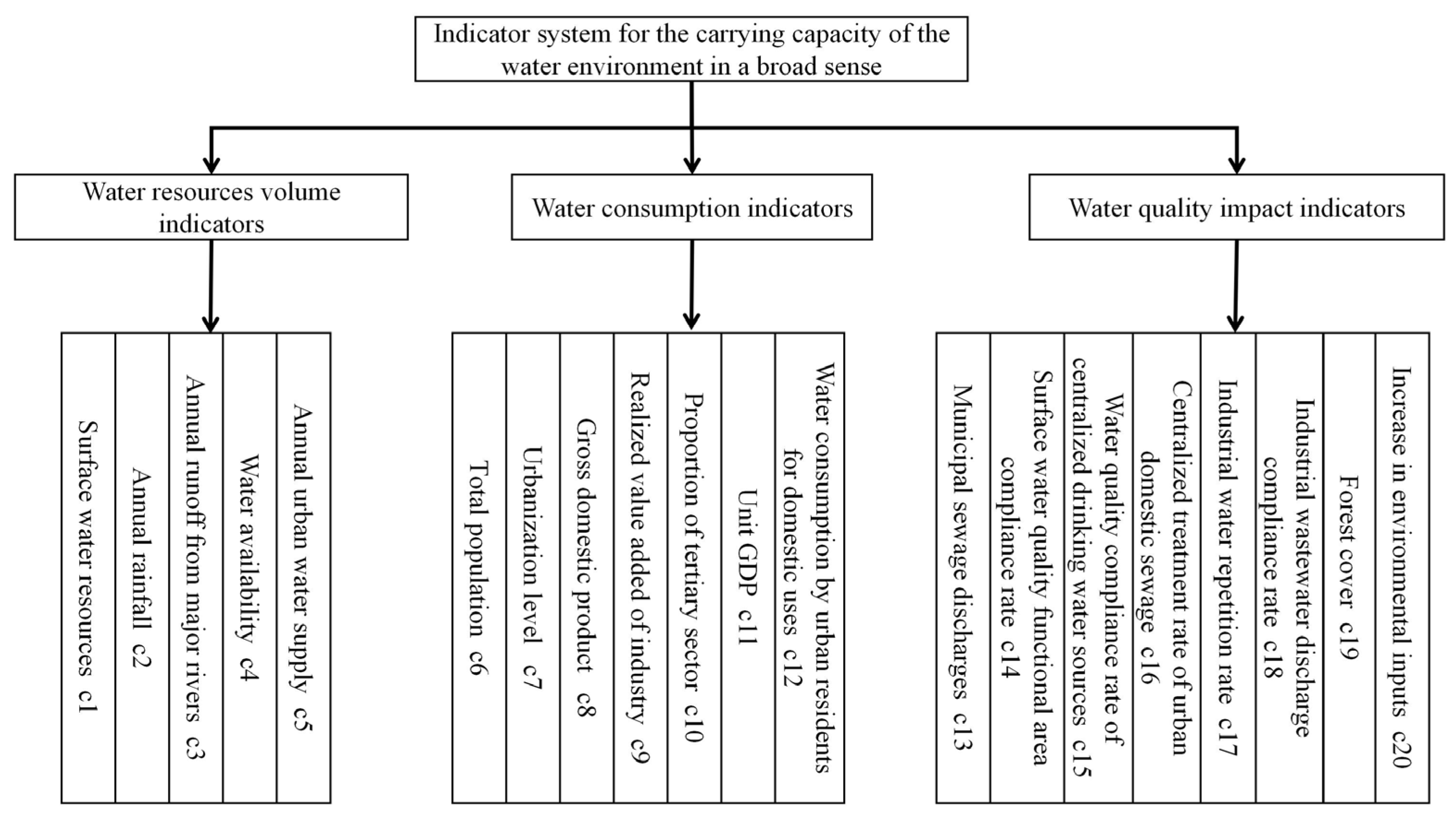
2.5. Establishment of a Generalized Water Environment Carrying Capacity Indicator System
2.6. Calculation of the Carrying Capacity of the Generalized Water Environment
2.7. BP Neural Network Prediction Model
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Narrowly Defined Water Environment Carrying Capacity Results
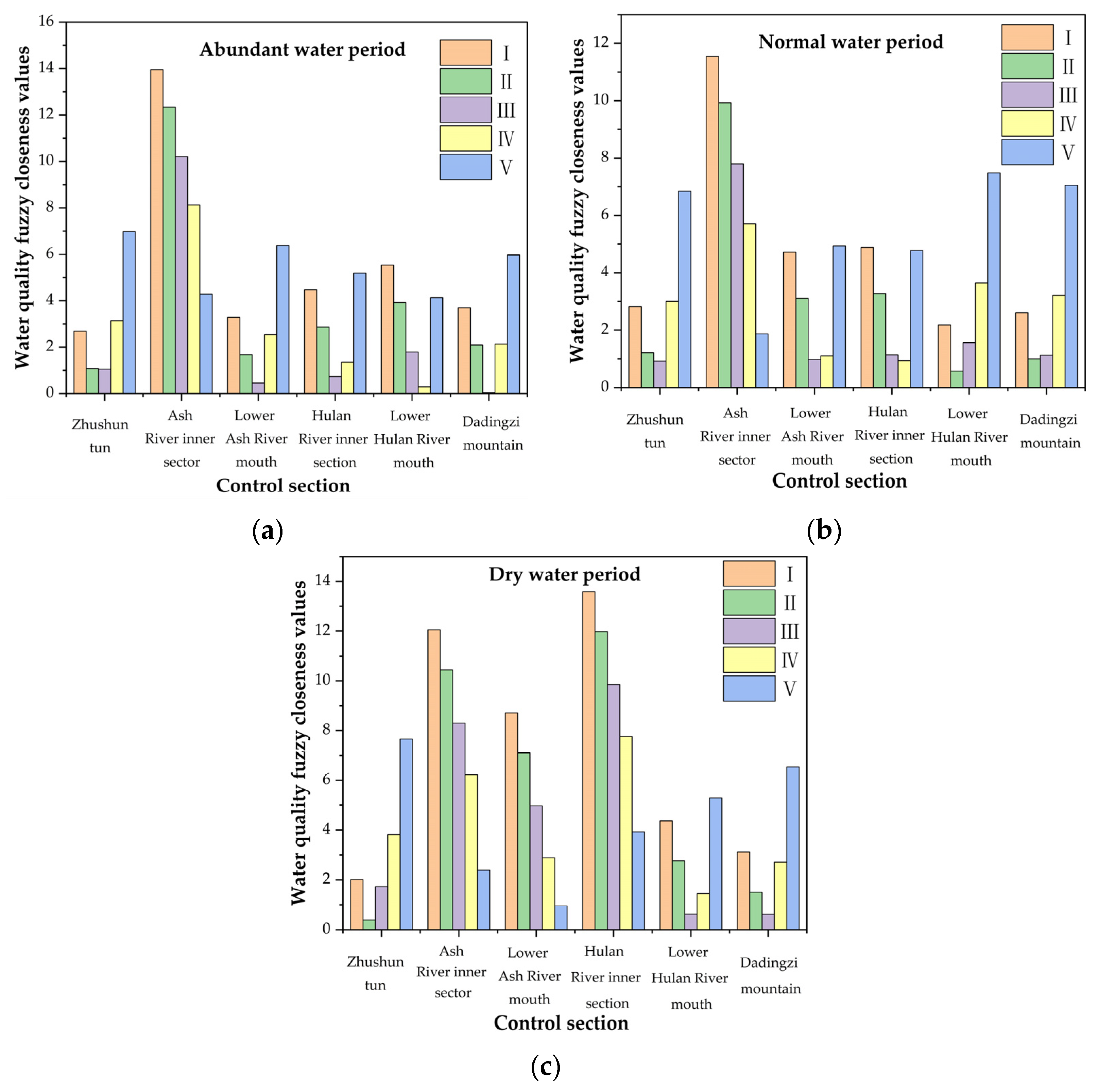
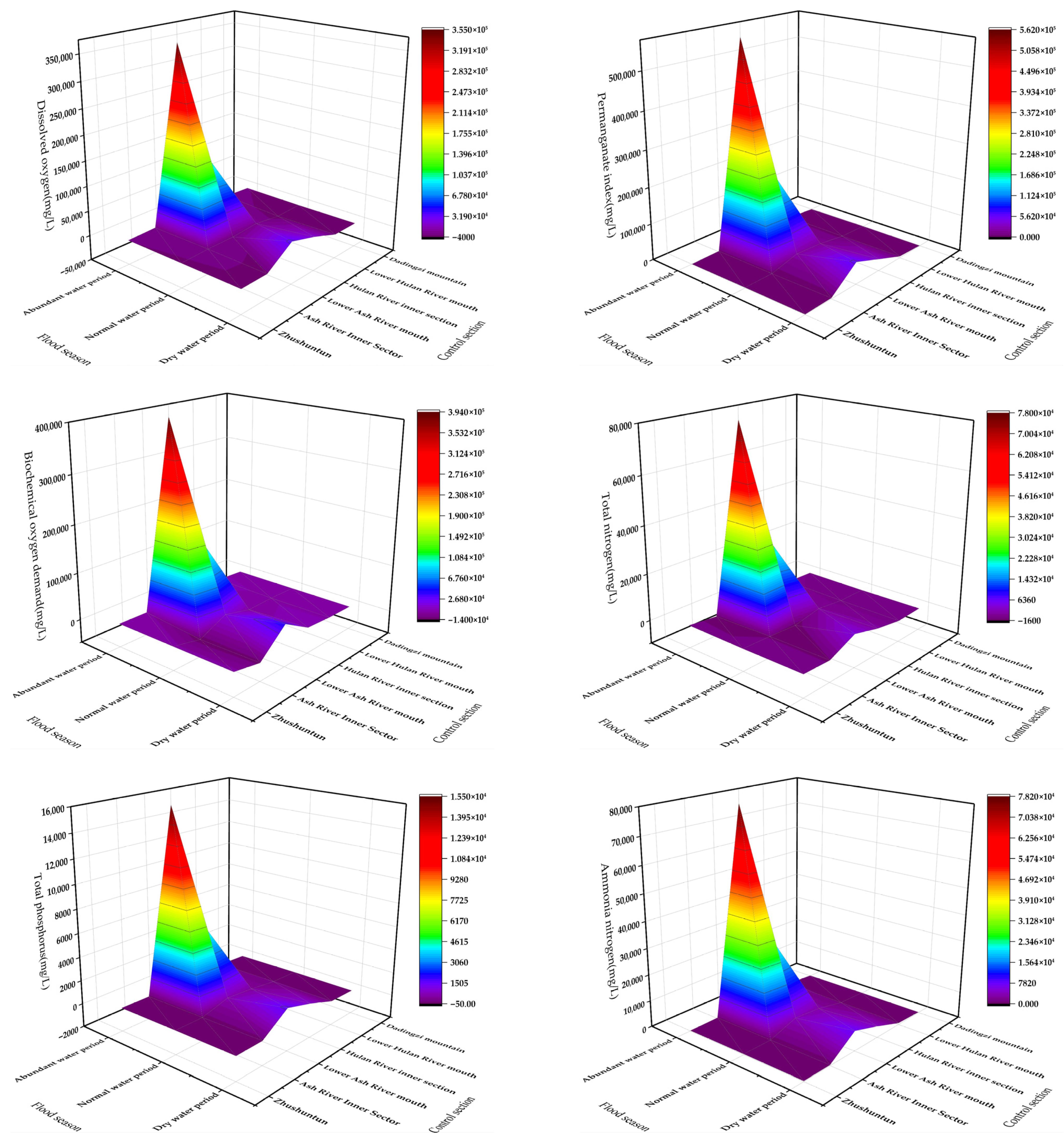
3.1.1. Water Quality Analysis of Different Cross-Sections During the Periods of Abundant Water, Flat Water, and Dry Water
3.1.2. Indicator Capacity Analysis of Pollutants in the Water Environment
3.2. Results of the Generalized Water Environment Carrying Capacity
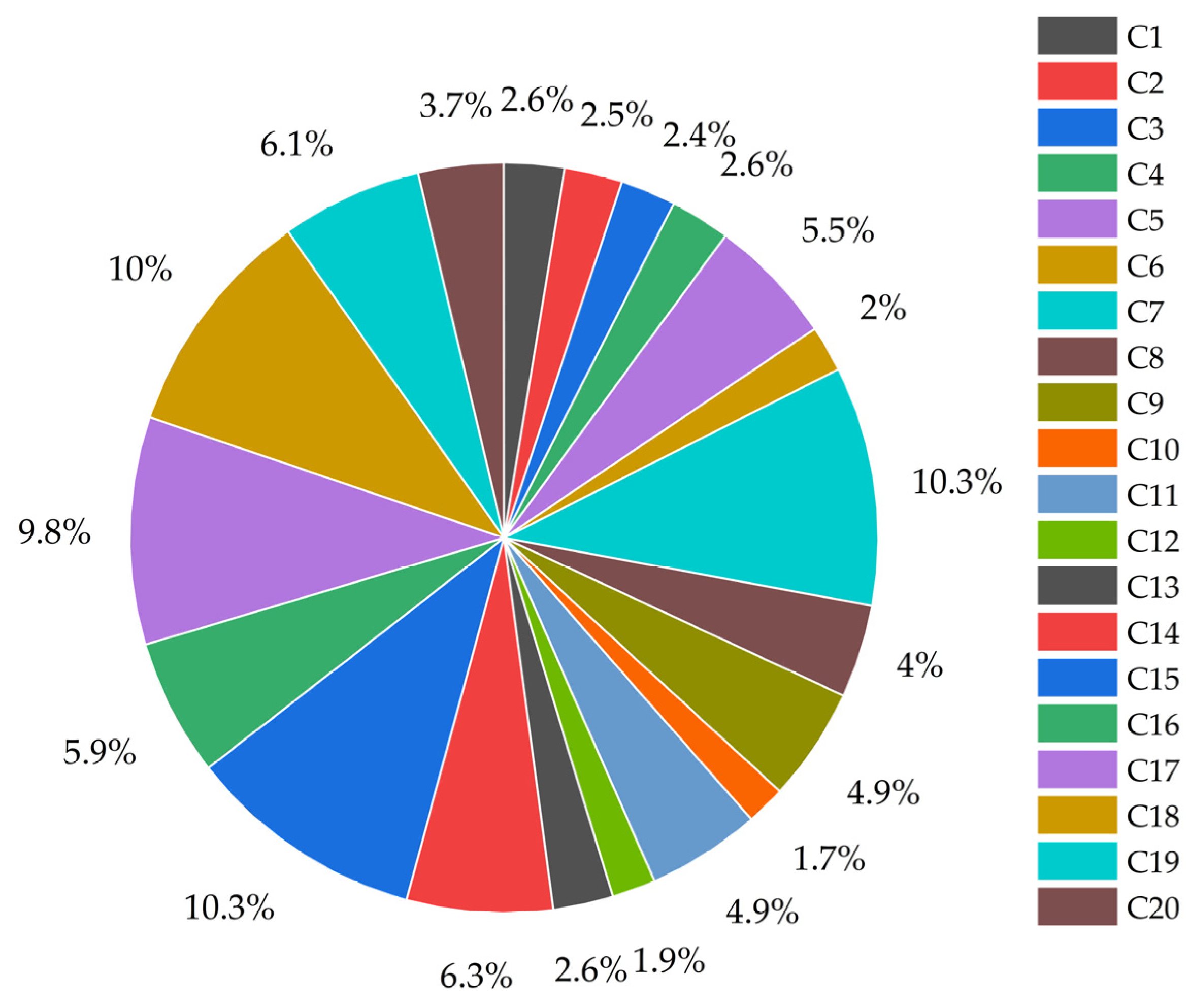
3.2.1. Determination of Evaluation Index Weights
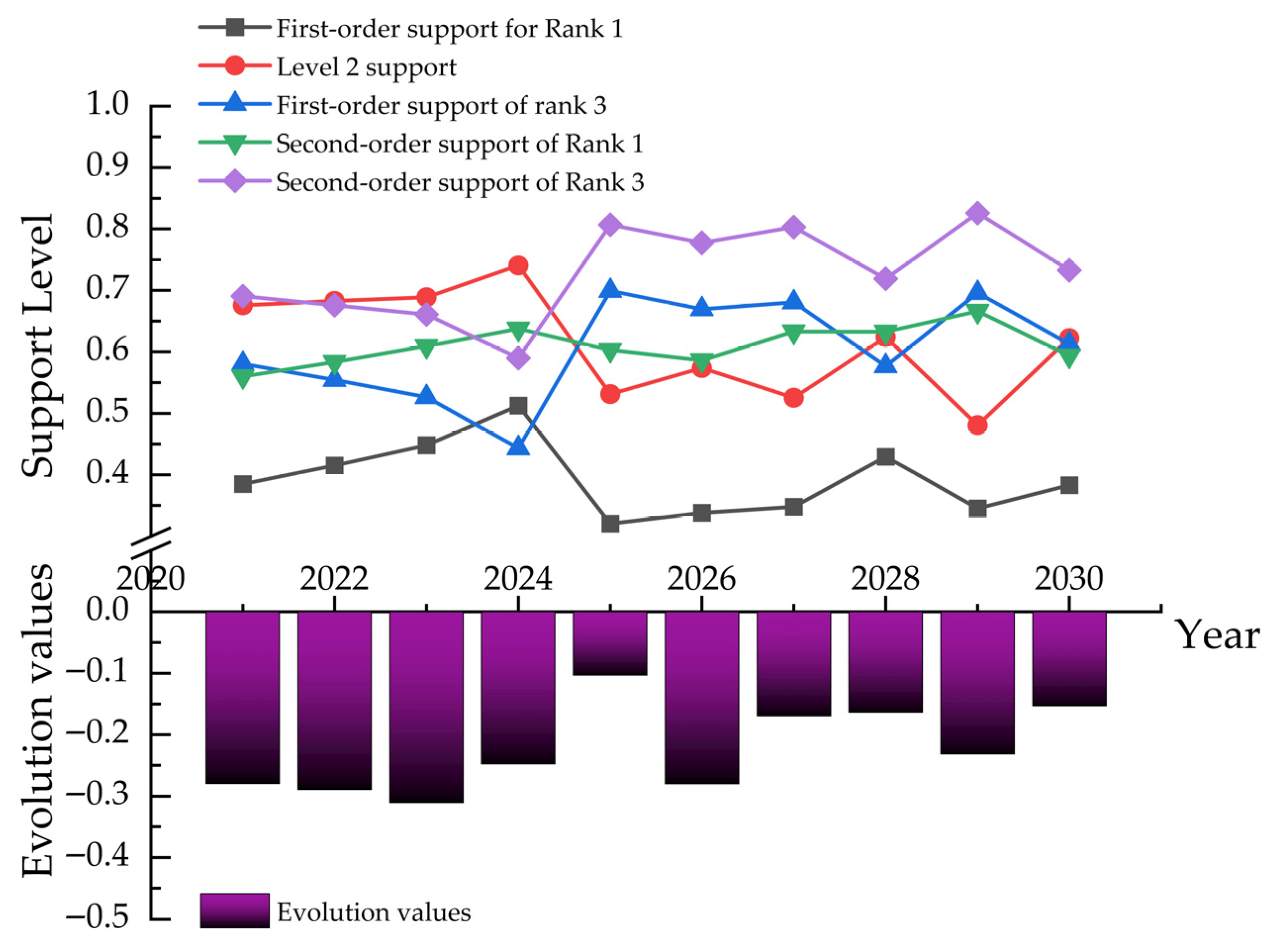
3.2.2. Analysis of Set-Pair Potential-Partial Linkage Number Results for PP-AHP Optimization
3.3. Joint Regulatory Mechanism of Broad and Narrow Water Environment Carrying Capacity Indicators
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, T.-Z.; Jian, S.-Q.; Wang, J.-Y.; Yan, D.-H. Dynamic interaction of water–economic–social–ecological environment complex system under the framework of water resources carrying capacity. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 368, 133132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jury, W.A.; Vaux, H.J. The Emerging Global Water Crisis: Managing Scarcity and Conflict Between Water Users. Adv. Agron. 2007, 95, 1–76. [Google Scholar]
- Song, W.-W.; Pang, Y. Research on narrow and generalized water environment carrying capacity, economic benefit of Lake Okeechobee, USA. Ecol. Eng. 2021, 173, 106420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.-T.; Zeng, W.-H.; Cao, R.-X.; Zhuo, Y.; Fu, J.; Wang, J.-P. Overloading risk assessment of water environment-water resources carrying capacity based on a novel Bayesian methodology. J. Hydrol. 2023, 622, 129697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, N.; Wang, T.-Y.; Qi, B.-W.; Yu, S.-J.; Yao, Z.-B.; Zhu, G.-L.; Fu, Q.; Li, C.-Y. Inhibiting release of phenanthrene from rice-crab coculture sediments to overlying water with rice stalk biochar: Performance and mechanisms. Sci. Total Env. 2024, 908, 168385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, P.; Li, M.; Zhang, Q.; Li, G.-L.; Song, L. Prediction model of drinking water source quality with potential industrial-agricultural pollution based on CNN-GRU-Attention. J. Hydrol. 2022, 610, 127934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.-X.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Fan, Y.-F. Differences in planktonic and benthic diatoms reflect water quality during a rainstorm event in the Songhua River Basin of northeast China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 144, 109547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.-Y.; Hörmann, G.; Huang, J.-L.; Fohrer, N. A grid-based interpretable machine learning method to understand the spatial relationships between watershed properties and water quality. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 154, 110627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.-T.; Barton, M.; Parker, M.; Sheng, Y.P. Estuarine water quality: One-dimensional model theory and its application to a riverine subtropical estuary in Florida. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2022, 277, 108058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bui, H.H.; Ha, N.H.; Nguyen, T.N.D.; Nguyen, A.T.; Pham, T.H.H.; Jaya, K.; Tien, V.N. Integration of SWAT and QUAL2K for water quality modeling in a data scarce basin of Cau River basin in Vietnam. Ecohydrol. Hydrobiol. 2019, 19, 210–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.-W.; Tan, K.; Zhu, C.-B.; Li, R.-N. Development and application of a two-dimensional water quality model for the Daqinghe River Mouth of the Dianchi Lake. J. Env. Sci. 2009, 21, 313–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, F.-F.; Lu, Z. Study on the interaction and relation of society, economy and environment based on PCA–VAR model: As a case study of the Bohai Rim region, China. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 48, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.-Y.; Chen, K.-L.; Chen, Z.-H.; Chen, Q.-H.; Qiu, Y.-P.; Wu, J.-C.; Zhang, J.-F. Evaluation for the ecological quality status of coastal waters in East China Sea using fuzzy integrated assessment method. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2012, 64, 546–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Z.-H.; Zhang, Y.; He, S.-S.; Wang, H.; Jiang, X.; Wang, S.-H. Multi-objective programming for economy–energy–environment system and policy mix with dual constraints of carbon emission and water consumption based on multi-scenario analysis. Energy Rep. 2012, 8, 7884–7891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.-Y.; Fu, X. Scheme simulation and predictive analysis of water environment carrying capacity in Shanxi Province based on system dynamics and DPSIR model. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 154, 110862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Wang, C.-X.; Ba, N.; Hao, Y. On the urban resource and environment carrying capacity in China: A sustainable development paradigm. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 342, 118212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, C.-L.; Shi, W.-L.; Fu, Y. Quantitative evaluation and optimized utilization of water resources-water environment carrying capacity based on nature-based solutions. J. Hydrol. 2019, 568, 96–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Xiao, C.-L.; Qi, Z.-W.; Meng, F.-N.; Liang, X.-J. Development tendency analysis for the water resource carrying capacity based on system dynamics model and the improved fuzzy comprehensive evaluation method in the Changchun city, China. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 122, 107232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.-B.; Wang, Y.-Y.; Wang, S.-L. Improved water pollution index for determining spatiotemporal water quality dynamics: Case study in the Erdao Songhua River Basin, China. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 129, 107931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, P.; Bai, Y.-J.; Tian, Z.-X.; Li, J.-W.; Shao, X.; Mustavich, L.F.; Li, B.L. Assessment of surface water quality via multivariate statistical techniques: A case study of the Songhua River Harbin region, China. J. Hydro Env. Res. 2013, 7, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.-Y.; Kang, C.-G.; Chi, Y.-P.; Wu, P.; Wei, Z.-Y.; Wang, J.-X.; Sun, L. Reversal of the middle-upper Songhua River in the late Early Pleistocene, Northeast China. Geomorphology 2020, 369, 107373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.-J.; Wang, Y.-J.; Ran, L.-S.; Su, T. Climatic and anthropogenic impacts on runoff changes in the Songhua River basin over the last 56years (1955–2010), Northeastern China. Catena 2015, 127, 258–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.-J.; Guo, R. The construction of green infrastructure network in the perspectives of ecosystem services and ecological sensitivity: The case of Harbin, China. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2021, 27, 101534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Z.; Bian, J.-M.; Wang, Y. Impacts of urban land use on the spatial distribution of groundwater pollution, Harbin City, Northeast China. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2018, 215, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escher, B.I.; Aït-Aïssa, S.; Behnisch, P.A.; Brack, W.; Brion, F.; Brouwer, A.; Buchinger, S.; Crawford, S.E.; Pasquier, D.D.; Hamers, T.; et al. Effect-based trigger values for in vitro and in vivo bioassays performed on surface water extracts supporting the environmental quality standards (EQS) of the European Water Framework Directive. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 628, 748–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Sun, W.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Q.-L.; Su, J.; Huang, G.-H.; Zhao, J. Inexact fuzzy-flexible left-hand-side chance-constrained programming for agricultural nonpoint-source water quality management. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 854, 158565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Yu, Z.-B.; Yi, P.; Frape, S.K.; Gong, M.; Zhang, Y.-T. Evaluation of surface water and groundwater interactions in the upstream of Kui river and Yunlong lake, Xuzhou, China. J. Hydrol. 2020, 583, 124549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamoon, A.A.; Keupink, E.; Rahman, M.M.; Eljack, Z.A.; Rahman, A. Sea outfall disposal of stormwater in Doha Bay: Risk assessment based on dispersion modelling. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 732, 139305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Liu, S.; Su, M.; Wang, C.; Ying, Z.-A.; Huo, M.-X.; Lin, Y.-Z.; Yang, W. Spatial distribution and potential sources of microplastics in the Songhua River flowing through urban centers in Northeast China. Env. Pollut. 2022, 292, 118384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Chen, S.S. Coupling coordination degree between social-economic development and water environment: A case study of Taihu lake basin, China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 148, 110118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.-Y.; Pu, X.; Wang, W.-M.; Dong, X.; Zhang, Y.-H.; Wang, J.-J.; Wang, Y.-F.; Meng, M.-X. Surface water environmental carrying capacity and surface water quality based on economy-society-environment nexus—Evidence from China. Water Energy Nexus 2023, 6, 231–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.-Y.; Tong, H.-J.; Liu, X.-C.; Feng, Y.; Zhu, Y.-M.; Wu, Y.; Chu, Z.-S.; Zheng, B.-H. Comprehensive evaluation of water resources and environmental carrying capacity based on dualistic water cycle analysis and its application in the Tuo River Basin, China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 146, 109897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Xi, H.-J.; Hu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Li, T.-H.; Wen, Z.-Q. Impact of local environmental standards on water environmental carrying capacity in large water diversion project: A system dynamics analysis in Shandong, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 362, 132423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.-X.; Lei, K.; Meng, W.; Khu, S.T.; Zhao, J.; Wang, M.-N.; Yang, J.-F. Space-time approach to water environment carrying capacity calculation. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 149, 302–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, D.; Wang, T.; Li, C.-M.; Wang, W.-Q. mpact of coal energy development on the surrounding environmental water resources carrying capacity. Desalination Water Treat. 2024, 319, 10518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, A.; Tian, L.; Li, Y.-F.; Xiong, B.-Y.; Yu, J.-H.; Gao, Y.; Li, Q.; Fan, C.-J.; Liu, L.-X.-E.; Duan, X.-J.; et al. Regional complex system simulation optimization through linking governance and environment performance: A case study of water environmental carrying capacity based on the SDES model. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2024, 104, 107356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.-T.; Welden, N.; Renaud, F.G. A framework for integrating ecosystem services indicators into vulnerability and risk assessments of deltaic social-ecological systems. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 326, 116682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, J.-Y.; Dai, C.-L.; Liu, G.-W.; Feng, X.; Wei, Y.-R.; Su, Q.-C. Analysis on the evolution law of precipitation and runoff in Sanjiang Plain: A case study of the lower Songhua River Basin. Res. Cold Arid. Reg. 2025; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murillas-Maza, A.; Broszeit, S.; Pouso, S.; Bueno-Pardo, J.; Ruiz-Frau, A.; Terrados, J.; Jernberg, S.; Iriondo, A.; Dolbeth, M.; Katsanevakis, S.; et al. Ecosystem indicators to measure the effectiveness of marine nature-based solutions on society and biodiversity under climate change. Nat. Based Solut. 2023, 4, 100085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lü, D.; Lü, Y. Spatiotemporal variability of water ecosystem services can be effectively quantified by a composite indicator approach. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 130, 108061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuentes-Cortés, L.F.; Rodríguez-Gutiérrez, J.E.; Valencia-Márquez, D. The renewable energy–water–environment nexus analysis. In The Renewable Energy-Water-Environment Nexu; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2024; pp. 361–398. [Google Scholar]
- Song, D.-D.; Zhang, C.; Saber, A. Integrating impacts of climate change on aquatic environments in inter-basin water regulation: Establishing a critical threshold for best management practices. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 913, 169297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.-L.; Zhang, Y. Coupling analysis of ecological environment evaluation and urbanization using projection pursuit model in Xi’an, China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 156, 111078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Zhu, J.-W.; Gao, M.; Xie, J.-C.; Yang, L.; Lu, N.; Wang, B. Do the protection and harnessing of river systems promote the society, economy, and ecological environment of cities? A case study of Xi’an, China. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2023, 97, 104761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilalova, S.; Newig, J.; Tremblay-Lévesque, L.C.; Roux, J.; Herron, C.; Crane, S. Pathways to water sustainability? A global study assessing the benefits of integrated water resources management. J. Environ. Manage. 2023, 343, 118179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, M.; Liu, Y.; Du, H.; Yang, X.-Y. Advances in Study on Water Resources Carrying Capacity in China. Procedia Env. Sci. 2021, 2, 1894–1903. [Google Scholar]
- Ba, W.-X.; Wang, D.-J.; Gong, B.-H.; Dai, Y.-H.; Yang, Z.-P.; Liu, Z.-F. Urban water scarcity in China: A systematic review of research advances and future directions. Appl. Geogr. 2023, 159, 103069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Liu, Y.-M.; Wu, J.; Wang, T.-T. Index system of urban resource and environment carrying capacity based on ecological civilization. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2018, 68, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB3838-2002; Environmental Quality Standards for Surface Water. Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2002.
- Gómez-Llanos, E.; Durán-Barroso, P.; Matías-Sánchez, A. Management effectiveness assessment in wastewater treatment plants through a new water footprint indicator. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 198, 463–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.; Dai, X.-Y.; Ye, S.-F.; Guo, Z.-Y.; Wu, J.-P. Prediction analysis model of integrated carrying capacity using set pair analysis. Ocean. Coast. Manag. 2016, 120, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.-J.; Hao, J. The evaluation of environmental capacity: Evidence in Hunan province of China. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 60, 514–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.-G.; Huang, C.; Lam, P.T.I.; Yuan, Z. A review on urban carrying capacity assessment. Habitat. Int. 2015, 46, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kılkış, S.; Krajačić, G.; Duić, N.; Rosen, M.A.; Al-Nimr, M.A. Sustainable development of energy, water and environment systems in the critical decade for climate action. Energy Convers. Manag. 2015, 296, 117644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, P.; Wu, H.-Q.; Yang, T.-T.; Jiang, F.-L.; Zhang, W.-J.; Zhu, Z.-L.; Yue, Q.-M.; Liu, M.-X.; Xu, X.-Y. Evaluation of urban water ecological civilization: A case study of three urban agglomerations in the Yangtze River Economic Belt, China. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 123, 107351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.-X.; Wu, D.-S.; Bian, Y. A systematic approach of determining compensation and allocation for river basin water environment based on total pollutants control. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 271, 110896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steiniger, S.; Wagemann, E.; Barrera, F.; Molinos-Senante, M.; Villegas, R.; Fuente, H.; Vives, A.; Arce, G.; Herrera, J.C.; Carrasco, J.A.; et al. Localising urban sustainability indicators: The CEDEUS indicator set, and lessons from an expert-driven process. Cities 2020, 101, 102683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juwana, I.; Muttil, N.; Perera, B.J.C. Indicator-based water sustainability assessment—A review. Sci Total Env. 2012, 438, 357–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galvis, A.; Zambrano, D.A.; Steen, N.P.; Gijzen, H.J. Evaluation of pollution prevention options in the municipal water cycle. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 66, 599–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Huang, H.; Deng, J.; Zhang, Y.-N.; Wang, Q. A spatio-temporal temperature prediction model for coal spontaneous combustion based on back propagation neural network. Energy 2024, 294, 130824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, R.R.; Rahman, A. Development and application of regional urban water security indicators. Util. Policy 2023, 84, 101637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semenov, M.Y.; Semenov, Y.M.; Silaev, A.V.; Begunova, L.A. Assessing the Self-Purification Capacity of Surface Waters in Lake Baikal Watershed. Water 2019, 11, 1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bui, L.T.; Pham, H.T.H. Linking hydrological, hydraulic and water quality models for river water environmental capacity assessment. Sci. Total Env. 2023, 857, 159490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Ma, S.; Liu, S.; Chen, Y.; Gao, W.; Zhang, Y. Study on Temporal and Spatial Distribution Characteristics of Biogenic Pollutant Fluxes in Ten Main Rivers Discharging into the Sea in Eastern China. Sustainability 2025, 17, 4239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazer, N.; Chithra, K.; Bimal, P. Framework for the application of ecosystem services based urban ecological carrying capacity assessment in the urban decision-making process. Environ. Chall. 2023, 13, 100745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.-X.; Jiang, L.-L.; Ouyang, X.-T.; Wang, Z.-L.; Jiang, Q.-X. Sustainable evaluation of the water footprint in Heilongjiang Province, China, based on correlation-matter element analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 408, 137231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, H.-L.; Liu, M.; Xu, M.-Y.; Zhang, M.-X.; Mo, L.; Chen, T.; Tan, X.-Y.; Liu, Z.-Y. Study on the integrated protection strategy of water environment protection: The case of Hainan Province of China. Env. Technol. Innov. 2021, 24, 101990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, T.-Z.; Gong, Z.-P.; Zhang, Z.-X.; Wang, T.-Y.; Sun, N.; Tang, Y.; Chen, P.; Li, T.; Yin, S.; Zhang, M.; et al. Irrigation Scheduling for Maize under Different Hydrological Years in Heilongjiang Province, China. Plants 2023, 12, 1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, N.; Yao, Z.-B.; Xie, Y.-P.; Wang, T.-Y.; Yang, J.-Z.; Li, X.-Y.; Fu, Q. Sustainability Analysis of the Water Environment Carrying Capacity of Harbin City Based on an Optimized Set Pair Analysis Posture-Deviation Coefficient Method Evaluation Model. Water 2023, 15, 1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Wen, Z.-G.; Wang, Y.-H. Nitrogen flow patterns in the food system among cities within urban agglomeration: A case study of the Pearl River Delta region. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 703, 135506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.-C.; Chen, Z.; Wang, B.; Xu, C.; Jia, Z.-Z.; Li, L.; Hu, J.-T. Spatiotemporal variations and controlling mechanism of low dissolved oxygen in a highly urbanized complex river system. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2024, 52, 101691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Water Quality Indicators | I | II | III | IV | V | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dissolved oxygen | 7.5 | 6 | 5 | 3 | 2 | 4.7 |
| Permanganate index | 2 | 4 | 6 | 10 | 15 | 7.4 |
| Biochemical oxygen demand | 3 | 3 | 4 | 6 | 10 | 5.2 |
| Total nitrogen | 0.2 | 0.5 | 1.0 | 1.5 | 2.0 | 1.04 |
| Total phosphorus | 0.02 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.204 |
| Ammonia nitrogen | 0.15 | 0.5 | 1 | 1.5 | 2.0 | 1.03 |
| Postures | SE | Level |
|---|---|---|
| Homotopy | [1.0, 1.4] | Quasi 1 |
| Partial isotropy | (1.4, 1.8] | Bias positive 2 |
| Homogeneous potential | (1.8, 2.2] | Quasi 2 |
| Partial antipathy | (2.2, 2.6] | Bias minus 2 |
| Countertrend | (2.6, 3.0] | Quasi 3 |
| Year | Contact Number | SE | Level |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2021 | 0.24+0.369I+0.391J | 2.151190386 | Quasi 2 |
| 2022 | 0.262+0.368I+0.37J | 2.108041479 | Quasi 2 |
| 2023 | 0.288+0.364I+0.348J | 2.060940913 | Quasi 2 |
| 2024 | 0.334+0.386I+0.281J | 1.946995856 | Quasi 2 |
| 2025 | 0.203+0.279I+0.518J | 2.315210071 | Bias minus 2 |
| 2026 | 0.213+0.305I+0.483J | 2.269849672 | Bias minus 2 |
| 2027 | 0.225+0.271I+0.505J | 2.279660537 | Bias minus 2 |
| 2028 | 0.28+0.321I+0.399J | 2.119063574 | Quasi 2 |
| 2029 | 0.228+0.243I+0.53J | 2.302087332 | Bias minus 2 |
| 2030 | 0.243+0.33I+0.427J | 2.183602842 | Quasi 2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yao, Z.; Wang, X.; Sun, N.; Wang, T.; Yan, H. A Study on the Associative Regulation Mechanism Based on the Water Environmental Carrying Capacity and Its Impact Indicators in the Songhua River Basin in Harbin City, China. Sustainability 2025, 17, 7636. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17177636
Yao Z, Wang X, Sun N, Wang T, Yan H. A Study on the Associative Regulation Mechanism Based on the Water Environmental Carrying Capacity and Its Impact Indicators in the Songhua River Basin in Harbin City, China. Sustainability. 2025; 17(17):7636. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17177636
Chicago/Turabian StyleYao, Zhongbao, Xuebing Wang, Nan Sun, Tianyi Wang, and Hao Yan. 2025. "A Study on the Associative Regulation Mechanism Based on the Water Environmental Carrying Capacity and Its Impact Indicators in the Songhua River Basin in Harbin City, China" Sustainability 17, no. 17: 7636. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17177636
APA StyleYao, Z., Wang, X., Sun, N., Wang, T., & Yan, H. (2025). A Study on the Associative Regulation Mechanism Based on the Water Environmental Carrying Capacity and Its Impact Indicators in the Songhua River Basin in Harbin City, China. Sustainability, 17(17), 7636. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17177636






