The Nexus of Environmental Protection and Economic Growth in Northern Minority Areas of China Under the Background of Sustainable Climate Policies
Abstract
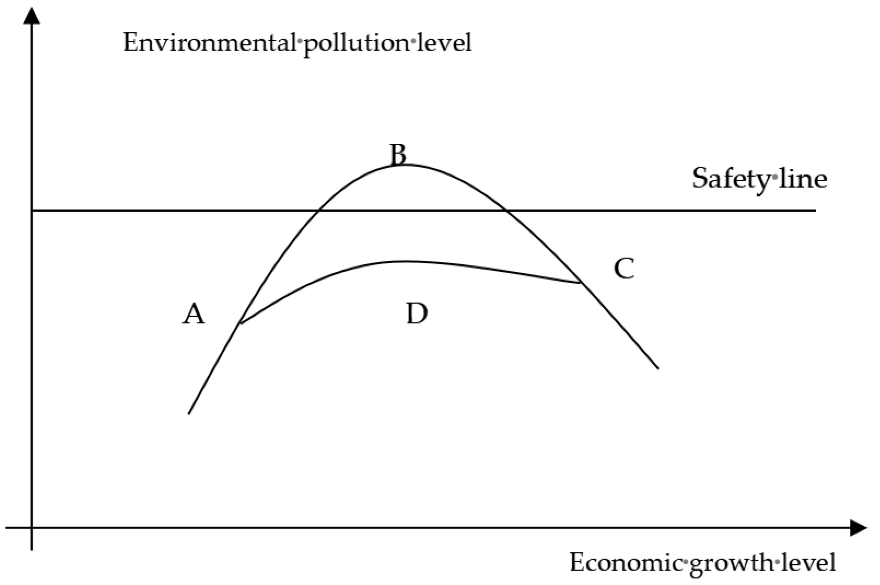
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
3. Empirical Model Design
3.1. Model
3.1.1. Explanatory Variable
3.1.2. Dependent Variable
3.1.3. Control Variable
3.1.4. Data Source
4. Results
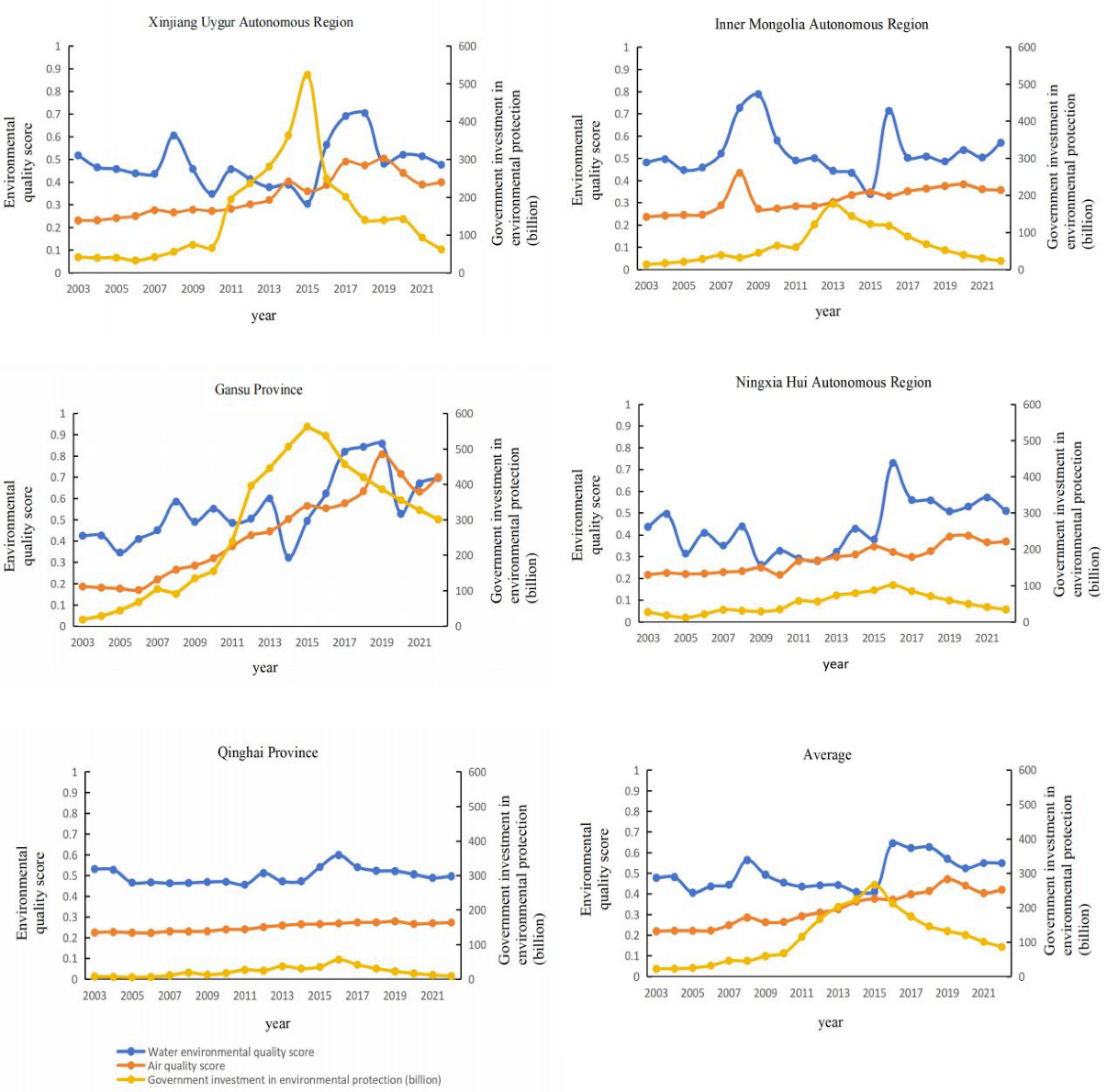
4.1. Analysis of Environmental Quality Characteristics
4.2. Results of Empirical Analysis
5. Conclusions and Policy Recommendations
5.1. Conclusions
5.2. Policy Recommendations
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aruga, K.; Islam, M.M.; Jannat, A. Assessing the CO2 Emissions and Energy Source Consumption Nexus in Japan. Sustainability 2024, 16, 5742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekun, F.V.; Gyamfi, B.A.; Köksal, C.; Taha, A. Impact of financial development, trade flows, and institution on environmental sustainability in emerging markets. Energy Environ. 2024, 35, 3253–3272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saud, S.; Haseeb, A.; Zaidi, S.A.H.; Khan, I.; Li, H. Moving towards green growth? Harnessing natural resources and economic complexity for sustainable development through the lens of the N-shaped EKC framework for the European Union. Resour. Policy 2024, 91, 104804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharb, R.; Suneja, V.; Aggarwal, S.; Singh, P.; Shahzad, U.; Saini, N.; Kumar, D. The relationship between investment determinants and environmental sustainability: Evidence through meta-analysis. Q. Rev. Econ. Financ. 2024, 94, 267–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikari, R.; Niroula, B.; Singh, S.K. Navigating Nepal’s Economic Growth and Carbon Emissions: Insights into the Environmental Kuznets Curve (EKC). Nat. Environ. Pollut. Technol. 2024, 23, 1221–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdogan, S. On the impact of natural resources on environmental sustainability in African countries: A comparative approach based on the EKC and LCC hypotheses. Resour. Policy 2024, 88, 104492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, J.; Ho, Y.K. The impact of government policy, natural resources and ecological innovations on energy transition and environmental sustainability: Insights from China. Resour. Policy 2024, 89, 104531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horobet, A.; Belascu, L.; Radulescu, M.; Lorente, D.B.; Botoroga, C.A.; Negreanu, C.C. Exploring the Nexus between Greenhouse Emissions, Environmental Degradation and Green Energy in Europe: A Critique of the Environmental Kuznets Curve. Energies 2024, 17, 5109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozcan, B.; Esmaeili, P.; Rafei, M.; Lorente, D.B. Uncovering the drivers of CO2 emissions in the United States: The hidden spillover effects. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 369, 122332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xu, W.; Sheng, Z.; Zhu, Z.; Tang, H. Eco-environmental effect and driving factors of changing “production-living-ecological space” in northern Xinjiang, China. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2023, 11, 1248702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Zhao, R. The Impact and Mechanism of Digital Villages on Agricultural Resilience in Ecologically Fragile Ethnic Areas: Evidence from China’s Provinces. Agriculture 2024, 14, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, F.; Saleem, H.; Ding, X.; Nazir, S.; Tariq, S. Do natural resource rents, green technological innovation, and renewable energy matter for ecological sustainability? Role of green policies in testing the environmental kuznets curve hypothesis. Resour. Policy 2024, 91, 104844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muratoğlu, Y.; Songur, M.; Uğurlu, E.; Şanlı, D. Testing the environmental Kuznets Curve hypothesis at the sector level: Evidence from PNARDL for OECD countries. Front. Energy Res. 2024, 12, 1452906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahbaz, M.; Nejati, M.; Du, A.M.; Jiao, Z. A recursive dynamic CGE approach to investigate environmental Kuznets curve. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 370, 122359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, Y. Environmental kuznets curve in the iron and steel industry: Evidence from 30 major steel-producing countries. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2024, 27, 12233–12257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Zhang, J.; Yang, H. Sustainable Development of Farmers in Minority Areas after Poverty Alleviation Relocation: Based on an Improved Sustainable Livelihood Analysis Framework. Land 2023, 12, 1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tai, L.; Yang, H. Evolution Characteristics and Influencing Factors of the Human-Earth System in Minority Areas of Yunnan, China. J. Resour. Ecol. 2024, 15, 372–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, W.; Weiguang, W.; Lichun, X.; Fengting, W. Is there an environment and economy tradeoff for the National Key Ecological Function Area policy in China? Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2024, 104, 107347. [Google Scholar]
- Min, K.S.; Ying, W.; Guang, T. Making Economic Policy for the Development of Minority Regions: Localization and Contribution of Economic Anthropology in China. Anthropologist 2016, 23, 323–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X. Research on the Path of Inclusive Poverty Alleviation in the Minority Regions of the West China. Stud. Sociol. Sci. 2016, 6, 55–61. [Google Scholar]
- Hua, H.; Pan, Y.; Yang, X.; Wang, S.; Shi, Y. Dynamic Relations between Energy Carbon Footprint and Economic Growth in Ethnic Minority Autonomous Regions, China. Energy Procedia 2012, 17, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J. Technological Innovation Study for China Western Ethnic Areas. Front. Educ. Res. 2019, 2, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Z. Do natural resources promote carbon neutrality: The role of green finance. Resour. Policy 2024, 88, 104424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, G.; Yubo, L.; Changde, Z. Analysis of the Influence of Human Resources on the Economic Development of Minority Areas Based on Data Mining. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2022, 2022, 8147537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, Z.; Chen, D.; Fang, C.; Gao, M.; Cheng, J. How green governance empowers high-quality development: An EKC framework-based analysis of ESG and green total factor productivity. Sci. Prog. 2024, 107, 342259278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qamruzzaman, M.; Karim, S.; Kor, S. Does environmental degradation matter for poverty? Clarifying the nexus between FDI, environmental degradation, renewable energy, education, and poverty in Morocco and Tunisia. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2023, 30, 52872–52894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desen, Z.; Yao, D.; Lu, T. Effect of fiscal decentralization and dual environmental regulation on green poverty reduction: The case of China. Resour. Policy 2022, 79, 102990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Z.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Z.; Deng, C. The impact of climate change and environmental regulation on energy poverty: Evidence from China. Energy Sustain. Soc. 2024, 14, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Feng, Z.; Wu, H.; Wang, S. Every rose has its thorn: Do environmental regulations exacerbate regional energy poverty? J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 419, 138285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, J. Ethnic Minorities in China’s Western Development Plan. J. Int. Area Stud. 2015, 22, 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, H.; Hunt, A. Impact of Climate Policy Uncertainty on Regional New Quality Productive Forces in China. Urban Sci. 2025, 9, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Wang, J.; Guan, J. How does the energy consumption structure affect the green economic development? A spatial impact analysis. Front. Environ. Sci. 2024, 12, 1412612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baba, H.; Asami, Y. Cost-efficient factors in local public spending: Detecting relationships between local environments, population size and urban area category. Environ. Plan. B Urban Anal. City Sci. 2022, 49, 241–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, P.; Wang, C.; Jiang, Q.; Liu, X.; Wang, J. Symbol or substance? Environmental regulations and corporate environmental actions decoupling. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 346, 118950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, S.; Li, H.; Cheng, B.; Gao, Z. The value of environmental base flow in water-scarce basins: A case study of Wei River Basin, Northwest China. Water 2018, 10, 848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.; Shi, P. Coordination Relationship and Spatial Differentiation between Industrial Structure and Water Use Structure in Gansu Province. Acad. J. Manag. Soc. Sci. 2024, 7, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y. Evaluation analysis on industrial green total factor productivity and energy transition policy in resource-based region. Energy Environ. 2022, 33, 419–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Primary Indicator | Secondary Indicator | Unit | Indicator Attribute |
|---|---|---|---|
| Air Quality (air) | Total Emission of Sulfur Dioxide | 10,000 tons | Negative |
| Industrial Waste Gas Emission Volume | 100 million standard cubic meters | Negative | |
| Number of Industrial Waste Gas Treatment Facilities | Sets | Positive | |
| Operating Costs of Industrial Waste Gas Treatment Facilities | CNY 10,000 | Positive | |
| Water Quality (water) | Total Industrial Wastewater Emission | 100 million tons | Negative |
| Industrial Chemical Oxygen Demand Emission | 10,000 tons | Negative | |
| Industrial Ammonia Nitrogen Emission | 10,000 tons | Negative | |
| Investment in Completed Industrial Wastewater Pollution Control Projects | CNY 10,000 | Positive | |
| Government Environmental Protection Investment (enin) | Total Investment in Pollution Control | CNY 10,000 | Positive |
| Variable | Sample Size | Mean Value | Minimum Value | Maximum Value | Standard Deviation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| lnpgdp | 100 | 10.2003 | 8.6170 | 11.4770 | 0.4680 |
| water | 100 | 0.4992 | 0.2614 | 0.8581 | 0.1175 |
| air | 100 | 0.3262 | 0.1693 | 0.8078 | 0.1226 |
| lnenin | 100 | 13.2987 | 10.8781 | 15.5424 | 1.3135 |
| lntech | 100 | 7.1933 | 3.4012 | 9.9977 | 2.6858 |
| inst | 100 | 2.3158 | 2.1600 | 2.4307 | 0.0604 |
| lnurba | 100 | 3.8736 | 3.3098 | 4.2283 | 0.0463 |
| lnpopu | 100 | 7.2432 | 6.2804 | 7.8813 | 0.4693 |
| enre | 100 | 0.0078 | 0.0002 | 0.04764 | 0.0070 |
| Variables | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Air | Air | Water | Water | Lnenin | Lnenin | |
| lnpgdp | −3.2248 *** | 13.3591 *** | −2.6300 ** | 30.8496 *** | −10.6729 *** | 76.7467 ** |
| −6.4493 | −3.1598 | −2.2762 | −3.0756 | −3.0136 | −2.4413 | |
| lnpgdp2 | 0.1551 *** | −1.5152 *** | 0.1373 ** | −3.2347 *** | 0.5581 *** | −8.2469 ** |
| −6.5365 | −3.5744 | −2.5046 | −3.2164 | −3.3204 | −2.6163 | |
| lnpgdp3 | 0.0560 *** | 0.1131 *** | 0.2954 *** | |||
| −3.9454 | −3.3573 | −2.797 | ||||
| inst | 0.3252 | 0.2467 | −0.1019 | −0.2604 | 3.6965 ** | 3.2827 ** |
| −1.5512 | −1.288 | −0.2103 | −0.5730 | −2.4895 | −2.305 | |
| enre | −0.7187 | −0.124 | 3.8119 * | 5.0124 *** | 10.5300 * | 13.6646 ** |
| −0.8399 | −0.1565 | −1.928 | −2.6676 | −1.7374 | −2.3203 | |
| lntech | −0.0734 *** | −0.0760 *** | −0.0446 | −0.0497 | 0.2422 | 0.2288 |
| −2.8787 | −3.2764 | −0.7558 | −0.9031 | −1.3401 | −1.3266 | |
| lnurba | −0.2865 | 0.0673 | 0.6029 | 1.3171 ** | −2.4676 | −0.6026 |
| −1.2395 | −0.2945 | −1.1287 | −2.4308 | −1.5072 | −0.3548 | |
| lnpopu | −0.8978 *** | −0.7105 *** | −0.2346 | 0.1435 | −2.3789 *** | −1.3916 * |
| −8.2731 | −6.4920 | −0.9355 | −0.5528 | −3.0950 | −1.7101 | |
| Constant | 24.4032 *** | −32.9821 ** | 12.8638 ** | −102.9852 *** | 80.2458 *** | −222.2517 ** |
| −10.1267 | −2.2423 | −2.3102 | −2.9512 | −4.7015 | −2.0321 | |
| Observations | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| R-squared | 0.9395 | 0.9508 | 0.6484 | 0.6984 | 0.9653 | 0.9689 |
| Year fe | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes |
| Prov fe | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cao, W.; Zhang, Z.; Feng, Y. The Nexus of Environmental Protection and Economic Growth in Northern Minority Areas of China Under the Background of Sustainable Climate Policies. Sustainability 2025, 17, 7178. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17167178
Cao W, Zhang Z, Feng Y. The Nexus of Environmental Protection and Economic Growth in Northern Minority Areas of China Under the Background of Sustainable Climate Policies. Sustainability. 2025; 17(16):7178. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17167178
Chicago/Turabian StyleCao, Weifang, Zhenhua Zhang, and Yanchao Feng. 2025. "The Nexus of Environmental Protection and Economic Growth in Northern Minority Areas of China Under the Background of Sustainable Climate Policies" Sustainability 17, no. 16: 7178. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17167178
APA StyleCao, W., Zhang, Z., & Feng, Y. (2025). The Nexus of Environmental Protection and Economic Growth in Northern Minority Areas of China Under the Background of Sustainable Climate Policies. Sustainability, 17(16), 7178. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17167178








