The Addition of Exogenous Compost Humus Shortens the Composting Cycle of New Corn Stalks, Thereby Promoting Plant Growth
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
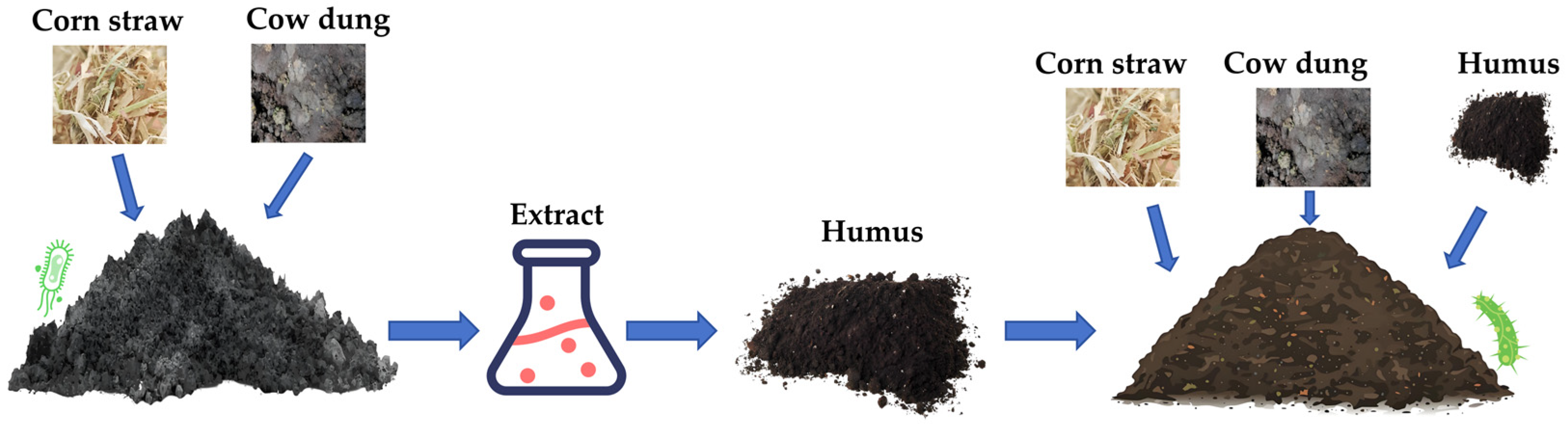
2.2. Compost Design
2.3. Experimental Methods
2.4. Pot Experiment
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussions
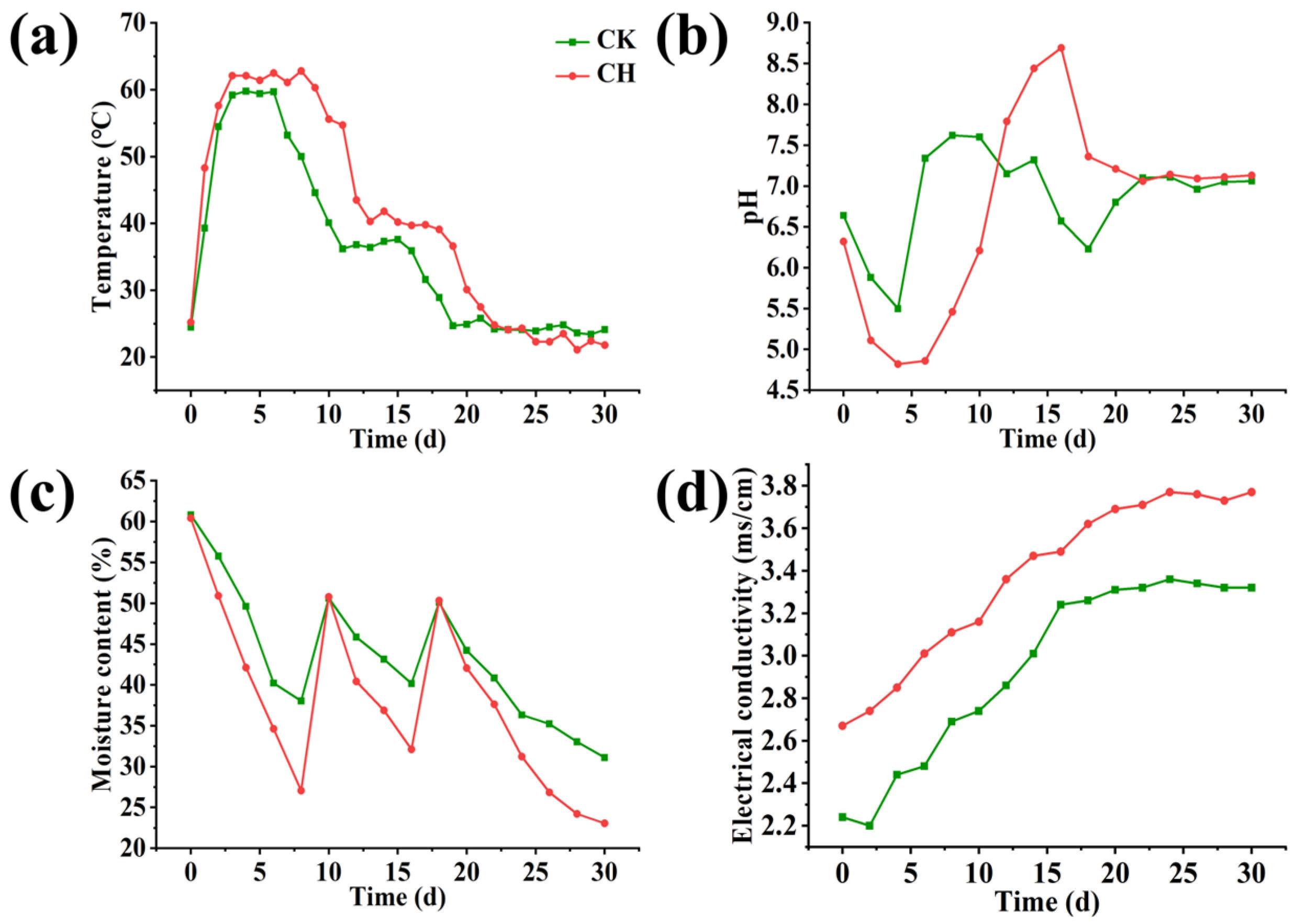
3.1. Physicochemical Properties of Compost
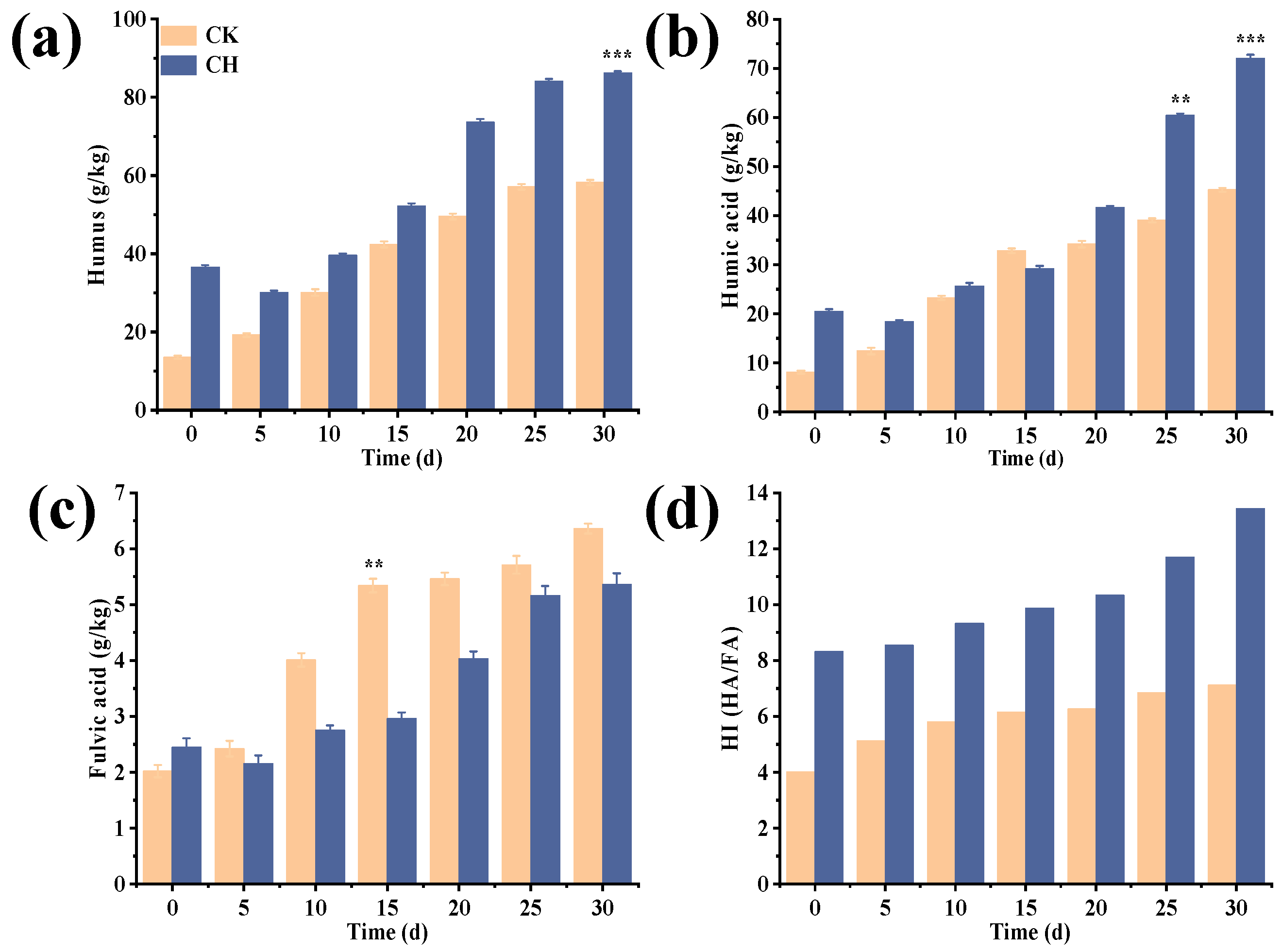
3.2. Compost Humus
3.3. Characteristics of Compost Structure
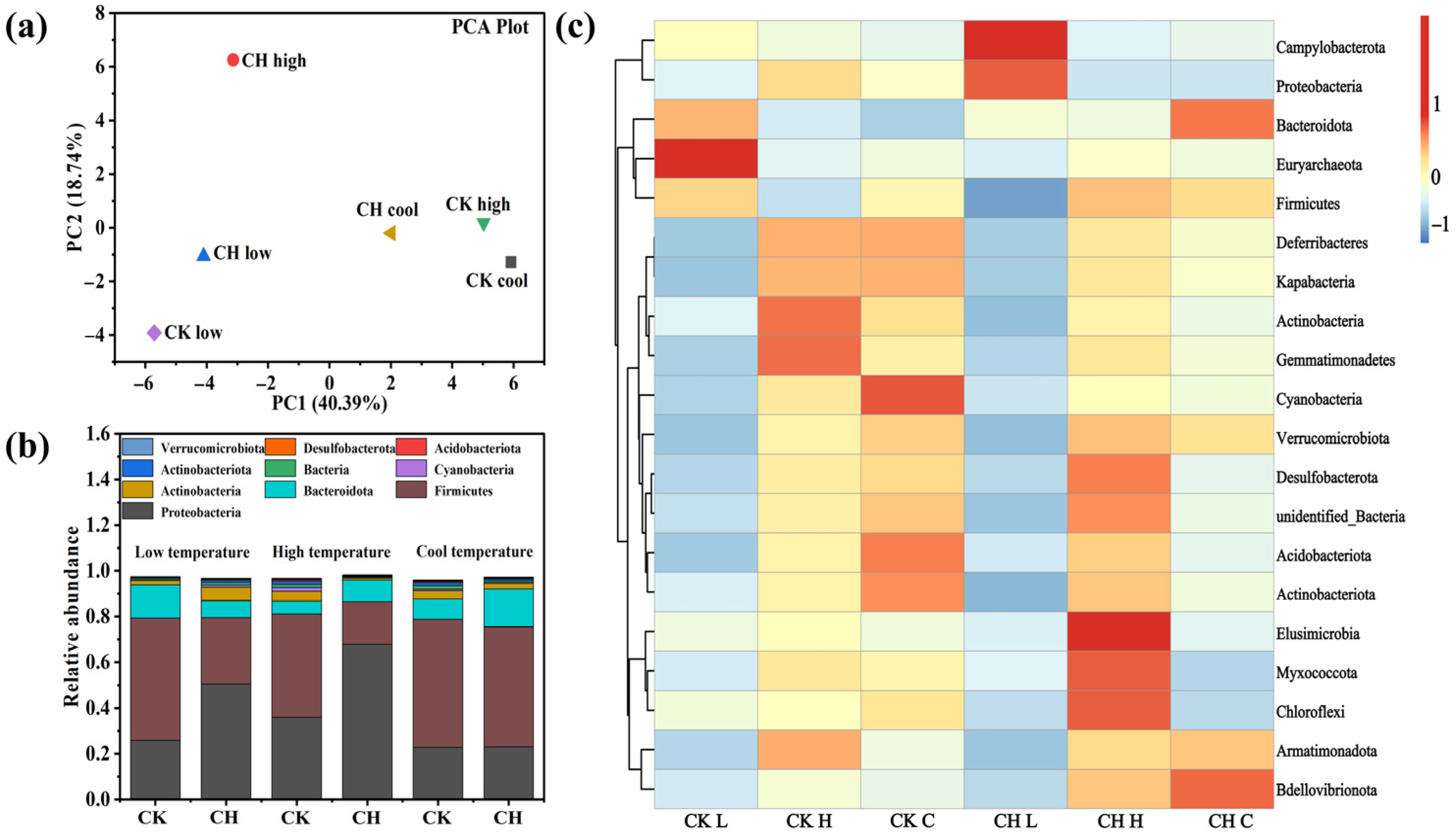
3.4. Microbial Characteristics
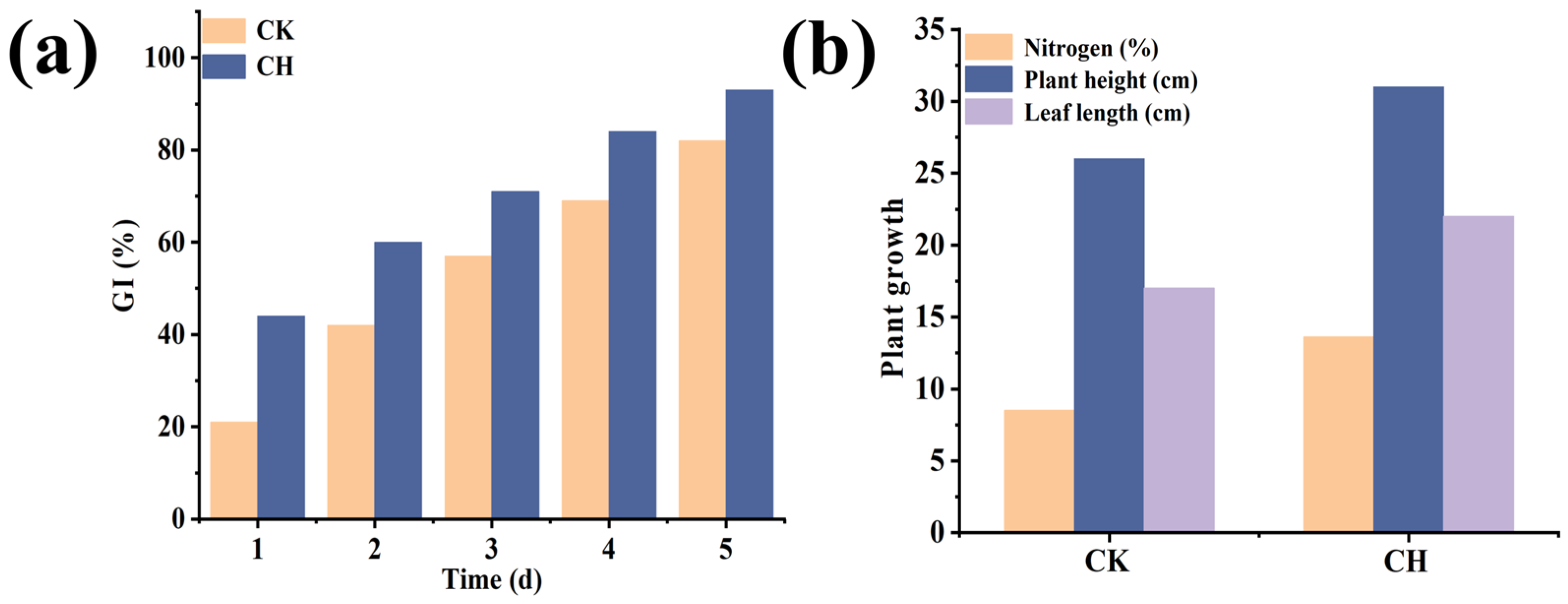
3.5. GI and Plant Growth
3.6. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Prado, E.; Rial, R. Biohydrogen production from residual biomass: The potential of wheat, corn, rice, and barley straw-recent advances. Bioresour. Technol. 2025, 432, 132638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Ren, T.; Cao, X.; Wu, T.; Hu, Z.; Ai, J.; Zhang, N.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, Z.; Du, L.; et al. Emerging and innovative utilisation of herbal medicine residues in anaerobic fermentation of corn straw: Cellulose degradation, fermentation characteristics, and microbial community structure and co-occurrence network. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2025, 227, 120802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhang, W.; Qiu, X.; Xu, C. Hydrothermal treatment of lignocellulosic biomass towards low-carbon development: Production of high-value-added bioproducts. Energychem 2024, 6, 100133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okori, F.; Schwarzböck, T.; Neuburg, S.; Komakech, A.; Lederer, J.; Fellner, J. Macro- and microplastics in composts from municipal solid waste industrial composting Plants in Uganda. Waste Manag. 2025, 204, 114942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendonça, R.; Souza, A.; Leal, R.; Osti, J.; Oliveira, R.; Regitano, J. Industrial composting of sewage sludge mitigates antimicrobial resistance risks and preserves bacterial dynamics in tropical soils. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 391, 126656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Jiang, Z.; Feng, W.; Zhao, Y.; Tang, P.; Cui, J.; Zhao, Z.; Lu, Q. Dual role of multistage inoculation in manipulating bacterial community assembly patterns to improve degradation of lignocellulose during rice or corn straw composting. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 505, 159283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Yu, Z.; Zhai, K.; Deng, W.; Zhuang, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Zhou, S. Thermophilic bacteria contributing to humus accumulation in hyperthermophilic aerobic fermentation of mushroom residue. Bioresour. Technol. 2025, 418, 131957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singbah, P.; Huang, J.; Ahmed, I.; Abdelaziz, M.; Tadesse, K.; Daba, N.; Li, J.; Yan, J.; Liu, S.; Liu, L.; et al. Soil humus and aluminum—Iron interactions enhance carbon sequestration and yield sustainability after long-term fertilization in three different soils. J. Agric. Food Res. 2025, 21, 101995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Li, R.; Zhang, X.; Wang, S.; Xu, X.; Tang, K.; Scriber, K.; Zhang, Z.; Quan, F. Molecular mechanisms of humus formation mediated by new ammonifying microorganisms in compost. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 483, 149341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Pu, Y.; Shi, S.; Zhang, J.; Cao, S.; Xu, X.; Jiao, W.; Zhan, M. Analysis of the effect and mechanism of heavy metals in stabilized landfill humus soil using fly ash-based materials. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2025, 210, 106090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Z.; Lu, B.; Li, D.; Chai, X. Strengthening nitrogen removal of rural wastewater treatment in humus biochemical system under low dissolved oxygen conditions: Sludge and microbial characteristics. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 366, 121762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, X.; Zhang, W.; Deng, J.; Feng, S.; Zhan, H. Pyrite and humus soil-coupled mixotrophic denitrification system for efficient nitrate and phosphate removal. Environ. Res. 2024, 247, 118105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baert, L.; Steven, S.; Toreveyi, E.; Bastiaens, L.; Cornelis, W. Chitin-enriched compost to increase soil moisture retention and resilience against drought. Soil Till. Res. 2025, 254, 106754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdellah, Y.; Yang, S.; Yang, C.; Yang, Z.; Elsheikh, E.; Keiblinger, K.; Mohamed, T.; Rana, M.; Liu, D.; Yu, F. Tobacco waste valorization through composting: A systematic review of biomass conversion efficiency and circular bioeconomy strategies. Biomass Bioenerg. 2025, 201, 108137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Deng, F.; Wang, R.; Li, J.; Liu, X.; Li, D. Bioaugmentation on humification during co-composting of corn straw and biogas slurry. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 374, 128756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Qi, H.; Huang, X.; Wei, D.; Zhao, Y.; Wei, Z.; Lu, Q.; Zhang, R.; Tong, T. How does manganese dioxide affect humus formation during bio-composting of chicken manure and corn straw? Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 269, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Kang, J.; Wu, Z.; Sun, Y.; Tu, X.; Guo, Y.; Mao, L.; Yang, Y.; Yao, W.; Ge, J. Mechanisms of phosphorus conversion in chicken manure and straw composting systems regulated by flax-retting wastewater and a combination of flax-retting wastewater and biochar. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 507, 160773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Li, J.; Zhang, J.; Deng, F.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, P.; Li, D. Bioaugmentation mechanism on humic acid formation during composting of food waste. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 830, 154783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrington, S.; Choinière, D.; Trigui, M.; Knight, W. Effect of carbon source on compost nitrogen and carbon losses. Bioresour. Technol. 2002, 83, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Yu, Q.; Zheng, C.; Wang, Y.; Chen, H.; Dong, S.; Hu, X. The impact of microbial inoculants on large-scale composting of straw and manure under natural low-temperature conditions. Bioresour. Technol. 2024, 400, 130696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Tang, Q.; Xie, W.; Yu, J.; Wang, L.; Wang, B.; Xie, H.; Zhang, M.; Bo, L.; Jin, H.; et al. Application of products derived from pyrolysis and hydrothermal carbonization as conditioners for aerobic composting produced multiple beneficial effects: Evaluation based on 10-ton pilot scale trials. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 505, 159793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Lin, B.; Hao, Y.; Lu, M.; Ding, D.; Niu, S.; Xiang, H.; Huang, Z.; Li, J. Two-stage inoculation with lignocellulose-degrading microorganisms in composting: Enhanced humification efficiency and underlying mechanisms. Environ. Res. 2025, 271, 120906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Fan, R.; Li, W.; Li, G.; Luo, W.; Xu, Z. Unravelling biotic and abiotic mechanisms of mature compost to alleviate gaseous emissions in kitchen waste composting by metagenomic analysis. Bioresour. Technol. 2025, 419, 132102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.; Chung, W.; Hur, J.; Lee, H.; Shin, H. Changes in organic matter composition during poultry manure composting: A new perspective on compost maturity using DAX resin fractionation and spectroscopic analysis. Waste Manag. 2025, 205, 115015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Z.; Kang, Z.; Kong, X.; Qiu, G.; Wang, Q.; Wang, T.; Yang, X.; Zhu, G.; Yue, J.; Han, X.; et al. Synergistic hyperthermophilic microbial consortia in self-elevating ultra-high temperature composting: Mechanism and application investigation for sustainable organic waste upcycling. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 512, 162364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoseini, M.; Cocco, S.; Casucci, C.; Cardelli, V.; Ruello, M.; Serrani, D.; Corti, G. Producing agri-food derived composts from coffee husk as primary feedstock at different temperature conditions. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 373, 123485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Rabaiai, A.; Menezes-Blackburn, D.; Al-Ismaily, S.; Janke, R.; Al-Alawi, A.; Al-Kindi, M.; Bol, R. Biochar pH reduction using elemental sulfur and biological activation using compost or vermicompost. Bioresour. Technol. 2024, 401, 130707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wei, Y.; Zhou, K.; Gao, X.; Chang, Y.; Zhang, K.; Deng, J.; Zhan, Y.; Li, J.; Li, R.; et al. Regulating pH and Phanerochaete chrysosporium inoculation improved the humification and succession of fungal community at the cooling stage of composting. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 384, 129291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Luo, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Yu, W.; Cai, R. The effect of moisture content on dynamics changes of antibiotic resistance genes during sheep manure composting on Qinghai-Tibet Plateau: Insight into changes in potential host microorganisms. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2025, 39, 104251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, W.; Shahab, A.; Sun, X.; Li, J.; Li, K.; Xiao, H. Enhancing municipal sludge composting efficiency: The synergistic impacts of montmorillonite and coconut shell biochar additives on heavy metal passivation and microbial community succession. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2025, 13, 117155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Su, Y.; Zhang, L.; Ren, X. Optimizing green waste composting with Bacillus siamensis inoculant: Impacts on decomposition and microbial dynamics. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 388, 126017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Awasthi, M. Synergistic effect and mechanism analysis of biochar regulator on heavy metal passivation and microplastic degradation in sewage sludge compost. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 494, 138551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Gao, S.; Chen, X.; Chen, Z.; Li, J.; Wang, S.; Gao, Y.; Zhou, H.; Qi, H.; Wei, Z. Improvement in humus synthesis by the humus precursors derived from nitrobenzene degradation during co-composting of nitrobenzene-polluted soil and cow manure. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 457, 142447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, X.; Wang, H.; Liu, L.; Song, C.; Ma, L. Microbial electrochemical composting: A sustainable strategy to enhance lignocellulose conversion into humus. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 481, 148496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Tao, Z.; Liu, X.; Wu, Z. Effects of phosphate-solubilizing bacteria on phosphorus components, humus and bacterial community metabolism during spent mushroom substrate composting. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2023, 32, 103341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, H.; Wang, J.; Zhang, L.; Chen, L.; Zhao, Y.; Wei, Z. Activation effect of catechol on biotic and abiotic factors of humus formation during chicken manure composting. Waste Manag. 2022, 149, 146–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, W.; Li, S.; Liu, J.; Cai, L.; Zhang, W.; Yu, C. Additives change microbiota to promote humic acid formation in composting of vegetable wastes. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2025, 232, 121307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Shahab, A.; Li, J.; Huang, H.; Sun, X.; You, S.; He, H.; Xiao, H. Compost-derived humic and fulvic acid coupling with Shewanella oneidensis MR-1 for the bioreduction of Cr (Ⅵ). J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 345, 118596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Feng, D.; Xie, M.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, D. Phosphate-coupled high-carbon ferromanganese particles synergistically regulate co-composting of seaweed and corn starch residue: Improving nitrogen cycling and accelerating humification. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 381, 125352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baddi, G.; Hafidi, M.; Cegarra, J.; Alburquerque, J.; Gonzálvez, J.; Gilard, V.; Revel, J. Characterization of fulvic acids by elemental and spectroscopic (FTIR and 13C-NMR) analyses during composting of olive mill wastes plus straw. Bioresour. Technol. 2004, 93, 285–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amir, S.; Jouraiphy, A.; Meddich, A.; Gharous, M.; Winterton, P.; Hafidi, M. Structural study of humic acids during composting of activated sludge-green waste: Elemental analysis, FTIR and 13C NMR. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 177, 524–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Y.; Wang, G.; Liu, Y.; Cheng, D.; Fan, S.; Zhao, Q.; Xue, J.; Zhang, S.; Li, Z. The impacts of oxytetracycline on humification during manure composting can be alleviated by adjusting initial moisture contents as illustrated by NMR. J. Integr. Agric. 2021, 20, 2277–2288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayans, B.; P’erez-Esteban, J.; Escolastico, C.; Eymar, E.; Masaguer, A. Evaluation of commercial humic substances and other organic amendments for the immobilization of copper through 13C CPMAS NMR, FT-IR, and DSC analyses. Agronomy 2019, 9, 762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salinas, J.; Martinez-Gallardo, M.; Jurado, M.; Suarez-Estrella, F.; Lopez-Gonzalez, J.; Estrella-Gonzalez, M.; Toribio, A.; Carpena-Istan, V.; Lopez, M. Construction of versatile plastic-degrading microbial consortia based on ligninolytic microorganisms associated with agricultural waste composting. Environ. Pollut. 2025, 366, 125333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.; Lin, B.; Zhang, Y.; Hao, Y.; Li, K.; Huang, Z.; Li, J. Insight into the molecular transformation pathways of humic acid in the co-composting of bagasse and cow manure after adding compound microorganisms. Process Biochem. 2024, 143, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Awasthi, M.; Zhao, J.; Liu, G.; Syed, A.; AL-Shwaiman, H.; Fang, J. Unraveling impacts of inoculating novel microbial agents on nitrogen conversion during cattle manure composting: Core microorganisms and functional genes. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 390, 129887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zubair, M.; Kong, L.; Shi, Y.; Zhou, H.; Tong, L.; Zhu, R.; Lv, Y.; Li, Z. Shifts in bacterial diversity characteristics during the primary and secondary fermentation stages of bio-compost inoculated with effective microorganisms agent. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 382, 129163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, R.; Zuo, S.; Cao, X.; Xu, C. Carbon and nitrogen transformation mechanism and functional microorganisms of sheep manure composting on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau under different moisture content. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 111341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coelho, L.; Reis, M.; Dionísio, L.; Guerrero, C. The influence of the storage period on the suppressive capacity of composts enriched with Trichoderma atroviride. J. Agric. Food Res. 2025, 22, 102048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veliu, M.; López-Romano, H.; Picca, G.; Panettieri, M.; Moreno-Jiménez, E.; Courtier-Murias, D.; Jean-Soro, L.; Gasperi, J.; De Sosa, L. Biochar–Compost blends modulate trace element and nutrient dynamics in rooftop farming systems under Mediterranean conditions. Ecotox. Environ. Saf. 2025, 302, 118663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solaiman, Z.; Yang, H.; Archdeacon, D.; Tippett, O.; Tibi, M.; Whiteley, A. Humus-Rich Compost Increases Lettuce Growth, Nutrient Uptake, Mycorrhizal Colonisation, and Soil Fertility. Pedosphere 2019, 29, 170–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zouari, I.; Masmoudi, F.; Medhioub, K.; Tounsi, S.; Trigui, M. Biocontrol and plant growth-promoting potentiality of bacteria isolated from compost extract. Anton. Leeuw. 2020, 113, 2107–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bao, Y.; Lu, J.; Li, J.; Pang, H. The Addition of Exogenous Compost Humus Shortens the Composting Cycle of New Corn Stalks, Thereby Promoting Plant Growth. Sustainability 2025, 17, 7177. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17167177
Bao Y, Lu J, Li J, Pang H. The Addition of Exogenous Compost Humus Shortens the Composting Cycle of New Corn Stalks, Thereby Promoting Plant Growth. Sustainability. 2025; 17(16):7177. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17167177
Chicago/Turabian StyleBao, Yihang, Jianyu Lu, Jinrong Li, and Hao Pang. 2025. "The Addition of Exogenous Compost Humus Shortens the Composting Cycle of New Corn Stalks, Thereby Promoting Plant Growth" Sustainability 17, no. 16: 7177. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17167177
APA StyleBao, Y., Lu, J., Li, J., & Pang, H. (2025). The Addition of Exogenous Compost Humus Shortens the Composting Cycle of New Corn Stalks, Thereby Promoting Plant Growth. Sustainability, 17(16), 7177. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17167177




