Study on the Effect of pH Modulation on Lactic Acid Production by Electro-Fermentation of Food Waste
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Nature of FW
2.2. EF System
2.3. LA Production by EF in Different pH Regulation Modes
2.4. Analytical Methods
2.5. Statistical Analysis of Data
3. Results and Discussion
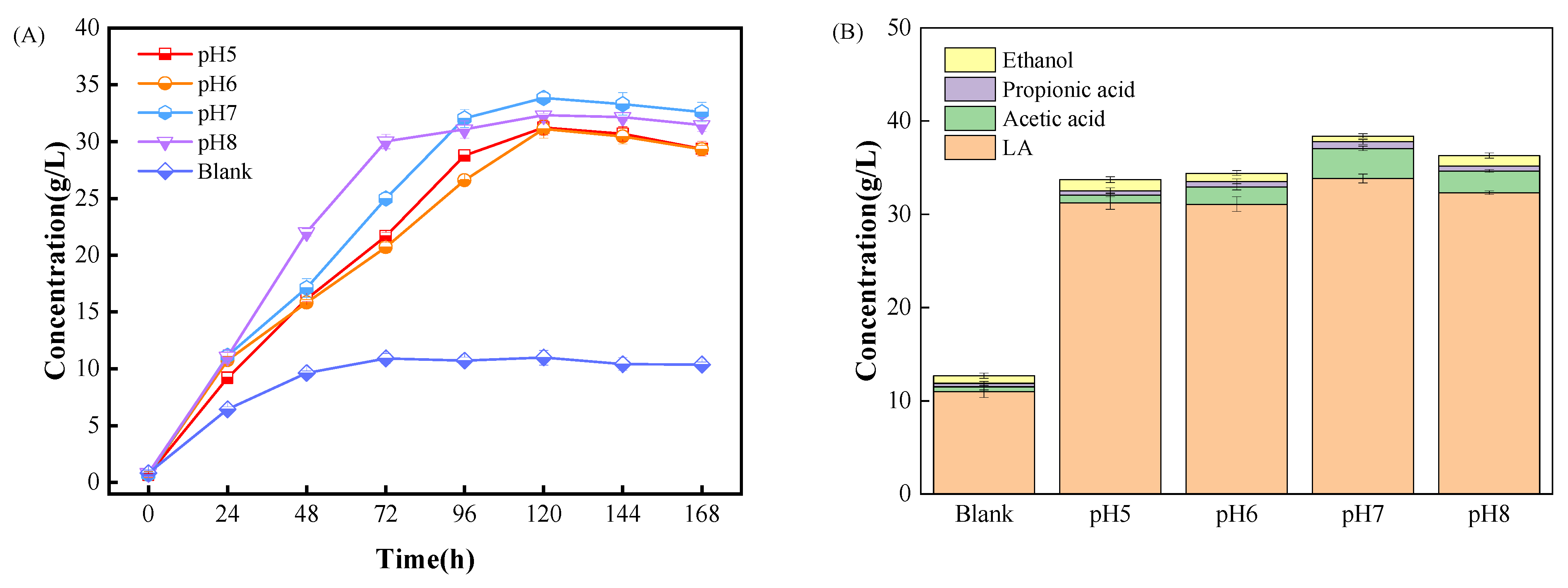
3.1. Effect of pH Regulation on LA Production by EF
- (1)
- Effect of pH regulation frequency on LA production
- (2)
- The effect of pH on LA production
3.2. Effect of pH Regulation on Microbial Community Changes During EF
3.3. Effect of pH Regulation on the Electrochemical Properties of the EF Process
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhou, Y.; Engler, N.; Nelles, M. Symbiotic relationship between hydrothermal carbonization technology and anaerobic digestion for food waste in China. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 260, 404–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Q.; Yang, Y.; Wang, M.; Zhu, Y.; Sun, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Z. Enhancing anaerobic digestion of kitchen wastes via combining ethanol-type fermentation with magnetite: Potential for stimulating secretion of extracellular polymeric substances. Waste Manag. 2021, 127, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, D.; Yu, Y.; Tang, J.; Li, X.; Ke, C.; Yao, Z. Application fields of kitchen waste biochar and its prospects as catalytic material: A review. Sci. Total Env. 2022, 810, 152171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Yang, R.; Sun, M.; Zhang, S.; He, M.; Tsang, D.C.W.; Luo, G. Wood waste biochar promoted anaerobic digestion of food waste: Focusing on the characteristics of biochar and microbial community analysis. Biochar 2022, 4, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Li, H.; Song, Y.; Mu, L.; Pei, L.; Zhou, T.; Qing, Z.; Zeng, Y. Optimization of food-to-microorganism ratio and addition of Tween 80 to enhance biohythane production via two-stage anaerobic digestion of food waste. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2023, 98, 2477–2488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Wang, N.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, X. The Comparison of Biotreatment and Chemical Treatment for Odor Control during Kitchen Waste Aerobic Composting. Separations 2022, 9, 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, C.; Sun, S.; Yang, D.; Sheng, W.; Ma, Y.; He, W.; Li, G. Anaerobic digestion: An alternative resource treatment option for food waste in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 779, 146397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Xu, X.; Yu, P.; Zuo, P.; He, Y.; Chen, H.; Liu, Y.; Xue, G.; Li, X.; Alvarez, P.J.J. Ammonium Enhances Food Waste Fermentation to High-Value Optically Active l-Lactic acid. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 669–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajay, C.M.; Mohan, S.; Dinesha, P. Decentralized energy from portable biogas digesters using domestic kitchen waste: A review. Waste Manag. 2021, 125, 10–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gbiete, D.; Narra, S.; Mani Kongnine, D.; Narra, M.-M.; Nelles, M. Insights into Biohydrogen Production Through Dark Fermentation of Food Waste: Substrate Properties, Inocula, and Pretreatment Strategies. Energies 2024, 17, 6350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.; Wang, Y.; Lin, H.; van Lierop, L.; Hu, B. Facilitating solid-state anaerobic digestion of food waste via bio-electrochemical treatment. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2022, 166, 112637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Zhang, J.; Li, F.; Zhao, X.; Bai, F.; Song, H.; Liu, C. Electrochemical Control of Cell Metabolism Improves Ethanol Production of Zymomonas mobilis in an Electro-Fermentation System. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 2364–2374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahir, K.; Ali, A.S.; Ghani, A.A.; Hussain, M.; Kim, B.; Lim, Y.; Lee, D.S. Enhanced bio-electrochemical performance of microbially catalysed anode and cathode in a microbial electrosynthesis system. Chemosphere 2023, 317, 137770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Zhang, P.; Liu, C.; Zheng, Y.; Chen, X. Feasibility of hydrogen recovery and optimization of gas production from protein-rich food waste by bio-electrochemical system. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2022, 47, 31241–31254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Chen, B.; Su, Z.; Wang, K.; Wang, B.; Wang, Y.; Si, Z.; Wu, Y.; Cai, D.; Qin, P. Efficient lactic acid production from cassava bagasse by mixed culture of Bacillus coagulans and Lactobacillus rhamnosus using stepwise pH controlled simultaneous saccharification and co-fermentation. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2020, 146, 112175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwan, T.H.; Hu, Y.; Lin, C.S.K. Techno-economic analysis of a food waste valorisation process for lactic acid, lactide and poly(lactic acid) production. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 181, 72–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Li, X.; Zhang, T.; Li, J.; Lai, S.; Chen, H.; Gao, P.; Xue, G. High-rate lactic acid production from food waste and waste activated sludge via interactive control of pH adjustment and fermentation temperature. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 328, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadam, S.R.; Patil, S.; Bastawde, K.B.; Khire, J.M.; Gokhale, D.V. Strain improvement of Lactobacillus delbrueckii NCIM 2365 for lactic acid production. Process. Biochem. 2006, 41, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Wang, Q.; Li, Y.; Ma, X.; Zhu, W.; Wang, N.; Sun, H.; Gao, M. Highly efficient oriented bioconversion of food waste to lactic acid in an open system: Microbial community analysis and biological carbon fixation evaluation. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 370, 128398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senila, L.; Cadar, O.; Kovacs, E.; Gal, E.; Dan, M.; Stupar, Z.; Simedru, D.; Senila, M.; Roman, C. L-Poly(lactic acid) Production by Microwave Irradiation of Lactic Acid Obtained from Lignocellulosic Wastes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 9817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swetha, T.A.; Ananthi, V.; Bora, A.; Sengottuvelan, N.; Ponnuchamy, K.; Muthusamy, G.; Arun, A. A review on biodegradable polylactic acid (PLA) production from fermentative food waste—Its applications and degradation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 234, 123703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Gómez, J.P.; Alexandri, M.; Schneider, R.; Venus, J. A review on the current developments in continuous lactic acid fermentations and case studies utilising inexpensive raw materials. Process. Biochem. 2019, 79, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, G.; Lai, S.; Li, X.; Zhang, W.; You, J.; Chen, H.; Qian, Y.; Gao, P.; Liu, Z.; Liu, Y. Efficient bioconversion of organic wastes to high optical activity of l-lactic acid stimulated by cathode in mixed microbial consortium. Water Res. 2018, 131, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, M.; Ma, X.; Song, N.; Wang, Q.; Wu, C. A newly isolated strain, Lactobacillus paracasei subsp. 2, producesl-lactic acid from pilot-scale fermentation of food waste under sterile and nonsterile conditions. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2020, 95, 3193–3201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, Q.; Wang, S.; Zou, D.; Sonomoto, K. Utilisation of microwave-NaOH pretreatment technology to improve performance and l-lactic acid yield from vinasse. Biosyst. Eng. 2012, 112, 6–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, Q.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, W.; Xiang, J. Effect of Fermentation Conditions on L-Lactic Acid Production from Soybean Straw Hydrolysate. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 25, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Gao, M.; Wang, Q.; Wang, J.; Sun, X.; Chang, Q.; Tashiro, Y. Enhancement of l -lactic acid production via synergism in open co-fermentation of Sophora flavescens residues and food waste. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 225, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Liu, Y.; Sun, X.; Wang, Q.; Zou, H.; Wang, J.; Gao, M. Open Fermentative Production of L-Lactic Acid from Distillers’ Grains by Lactobacillus casei CICC 6056. Bioresources 2017, 12, 393–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Wang, J.; Gao, M.; Wang, N.; Li, C.; Wang, Q. Effect of pH regulation mode on byproduct ethanol generated from the lactic acid fermentation of Sophora flavescens residues. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 279, 123536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, S.; Chen, H.; Zheng, X.; Luo, J.; Liu, Y. Efficient production of optically pure l-lactic acid from food waste at ambient temperature by regulating key enzyme activity. Water Res. 2015, 70, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Wang, X.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y. Lactic acid fermentation from food waste with indigenous microbiota: Effects of pH, temperature and high OLR. Waste Manag. 2016, 52, 278–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Wang, X.C.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y. Effect of pH on lactic acid production from acidogenic fermentation of food waste with different types of inocula. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 224, 544–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Chen, L.; Li, H.; Deng, Z.; Liu, J. Lactic acid production from mesophilic and thermophilic fermentation of food waste at different pH. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 304, 114312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schievano, A.; Pepé Sciarria, T.; Vanbroekhoven, K.; De Wever, H.; Puig, S.; Andersen, S.J.; Rabaey, K.; Pant, D. Electro-Fermentation—Merging Electrochemistry with Fermentation in Industrial Applications. Trends Biotechnol. 2016, 34, 866–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, P.; Chandrasekhar, K.; Kumari, A.; Sathiyamoorthi, E.; Kim, B. Electro-Fermentation in Aid of Bioenergy and Biopolymers. Energies 2018, 11, 343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.W.; Chiam, J.A.; Wang, J. Microbial community structure reveals how microaeration improves fermentation during anaerobic co-digestion of brown water and food waste. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 171, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, E.J.Y.; Olias, L.G.; Wuertz, S.; Hinks, J. Bioelectroanalytical Detection of Lactic Acid Bacteria. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores-Rodriguez, C.; Min, B. Enrichment of specific microbial communities by optimum applied voltages for enhanced methane production by microbial electrosynthesis in anaerobic digestion. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 300, 122624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Yao, J.; Min, N.; Sunahara, G.; Duran, R. New insights on the effect of non-ferrous metal mining and smelting activities on microbial activity characteristics and bacterial community structure. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 453, 131301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Yang, L.; Feng, K.; Li, H.; Deng, Z.; Liu, J. Promote lactic acid production from food waste fermentation using biogas slurry recirculation. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 337, 125393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Im, S.; Lee, M.; Yun, Y.; Cho, S.; Kim, D. Effect of storage time and temperature on hydrogen fermentation of food waste. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2020, 45, 3769–3775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Xu, S.; Chen, X.; Sun, H.; Hu, M.; Bai, Z.; Zhuang, G.; Zhuang, X. Bacterial Communities Changes during Food Waste Spoilage. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 8220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersen, S.J.; Candry, P.; Basadre, T.; Khor, W.C.; Roume, H.; Hernandez-Sanabria, E.; Coma, M.; Rabaey, K. Electrolytic extraction drives volatile fatty acid chain elongation through lactic acid and replaces chemical pH control in thin stillage fermentation. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2015, 8, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, N.; Gong, H.; Giwa, A.S.; Yuan, Q.; Wang, K. Metagenomic analysis and characterization of acidogenic microbiome and effect of pH on organic acid production. Arch. Microbiol. 2019, 201, 1163–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakai, K.; Mori, M.; Fujii, A.; Iwami, Y.; Chukeatirote, E.; Shirai, Y. Fluorescent in situ hybridization analysis of open lactic acid fermentation of kitchen refuse using rRNA-targeted oligonucleotide probes. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2004, 98, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Su, X.; Zhang, Y.; Xia, D.; Hou, S.; Zhou, Y.; Fu, H.; Wang, L.; Yin, X. Microbial electrolysis enhanced bioconversion of coal to methane compared with anaerobic digestion: Insights into differences in metabolic pathways. Energy Convers. Manag. 2022, 259, 115553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Q.; Song, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, Z.; Wu, Q. Influence of electrostatic field and conductive material on the direct interspecies electron transfer for methane production. Environ. Res. 2020, 188, 109867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, X.; Sun, B.; Xu, H. Anode decoration with biogenic Pd nanoparticles improved power generation in microbial fuel cells. Electrochim. Acta 2015, 182, 815–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.; Liu, F.; Fu, B.; He, K.; Yang, H.; Zhang, X.; Liang, P.; Huang, X. Onset Investigation on Dynamic Change of Biohythane Generation and Microbial Structure in Dual-chamber versus Single-chamber Microbial Electrolysis Cells. Water Res. 2021, 201, 117326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| pH | 4.37 ± 0.2 |
| TS (%) | 24.74 ± 0.03 |
| VS (%) | 23.58 ± 0.03 |
| C (%) * | 47.8 ± 0.04 |
| H (%) * | 7.11 ± 0.03 |
| O (%) * | 30.8 ± 0.04 |
| N (%) * | 2.9 ± 0.03 |
| Total carbohydrates (%) | 62.14 ± 0.47 |
| Total protein (%) | 14.56 ± 0.31 |
| Total fat (%) | 10.21 ± 0.23 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, N.; Liu, J.; Li, Y.; Ren, Y.; Wang, X.; Zheng, T.; Wang, Q. Study on the Effect of pH Modulation on Lactic Acid Production by Electro-Fermentation of Food Waste. Sustainability 2025, 17, 7160. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17157160
Wang N, Liu J, Li Y, Ren Y, Wang X, Zheng T, Wang Q. Study on the Effect of pH Modulation on Lactic Acid Production by Electro-Fermentation of Food Waste. Sustainability. 2025; 17(15):7160. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17157160
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Nuohan, Jianguo Liu, Yongsheng Li, Yuanyuan Ren, Xiaona Wang, Tianlong Zheng, and Qunhui Wang. 2025. "Study on the Effect of pH Modulation on Lactic Acid Production by Electro-Fermentation of Food Waste" Sustainability 17, no. 15: 7160. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17157160
APA StyleWang, N., Liu, J., Li, Y., Ren, Y., Wang, X., Zheng, T., & Wang, Q. (2025). Study on the Effect of pH Modulation on Lactic Acid Production by Electro-Fermentation of Food Waste. Sustainability, 17(15), 7160. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17157160







