Integrating Spatial Autocorrelation and Greenest Images for Dynamic Analysis Urban Heat Islands Based on Google Earth Engine
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
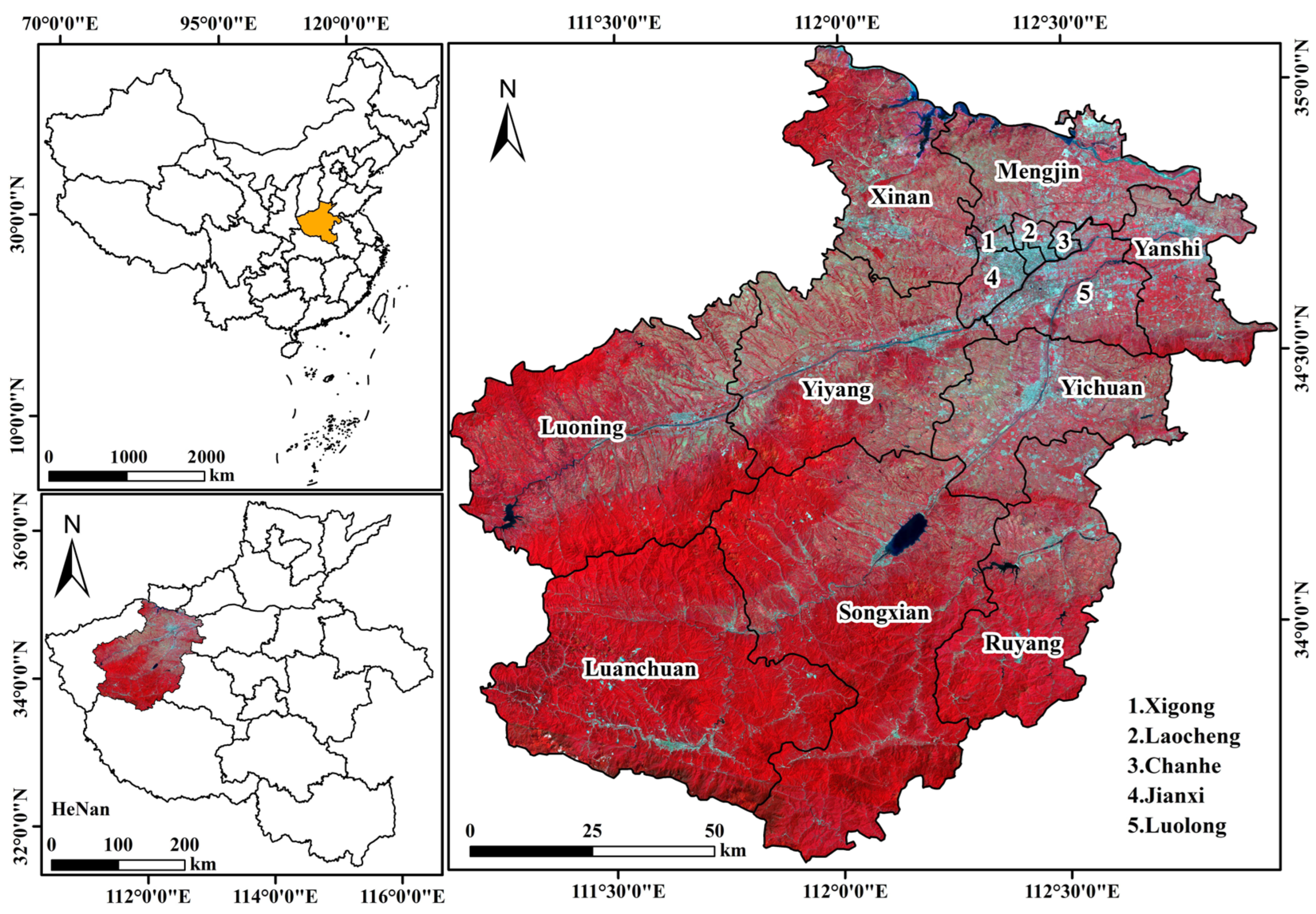
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Datasets
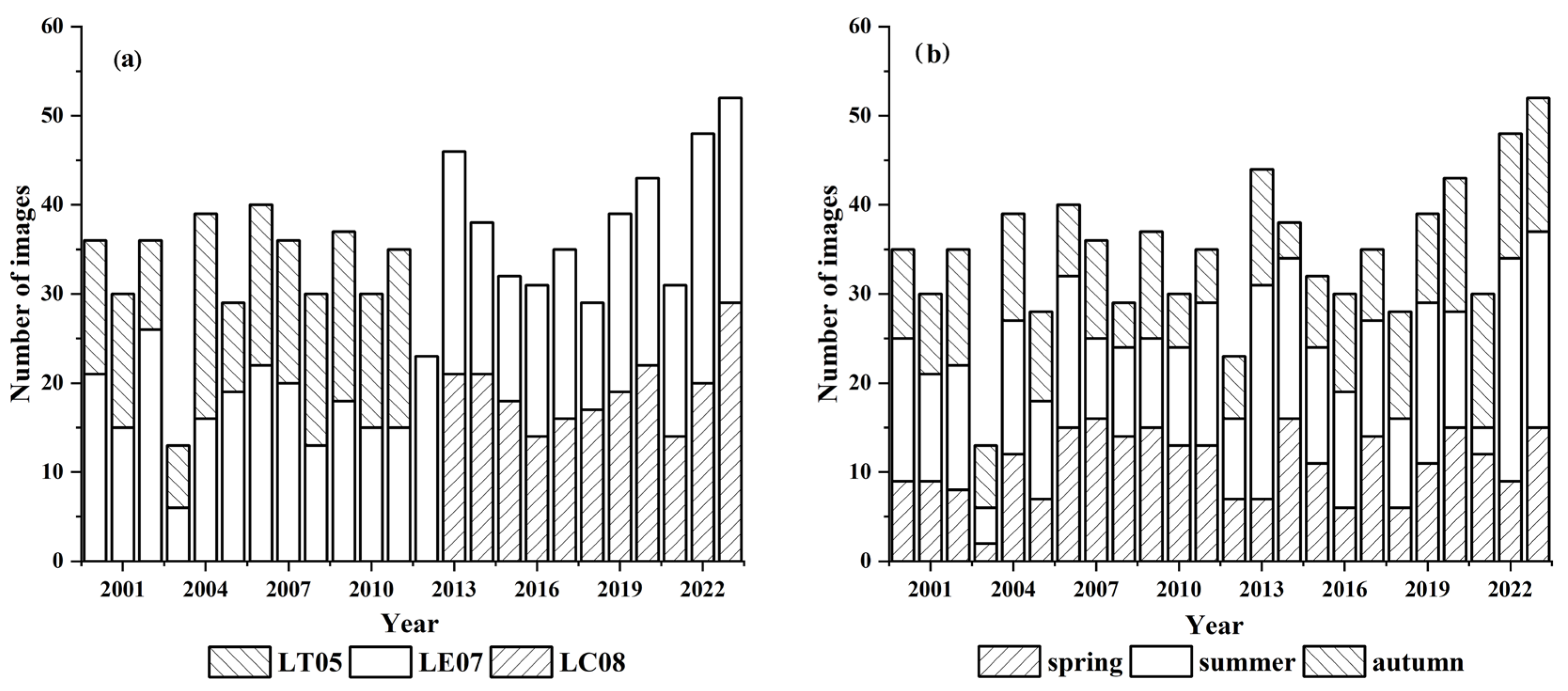
2.2.1. Landsat Image
2.2.2. Additional Data
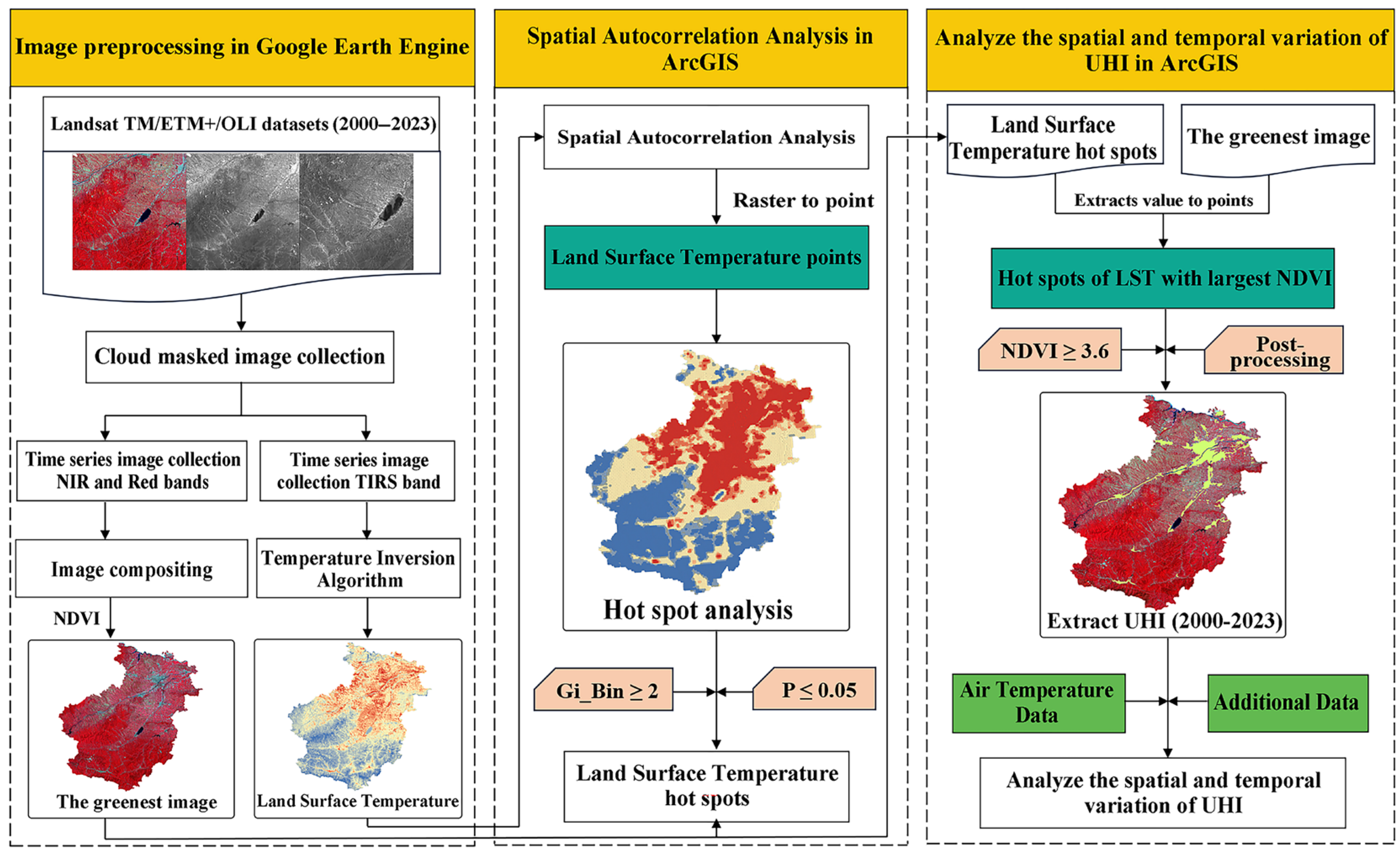
2.3. Methodology
2.3.1. GEE-Based Temperature Inversion
2.3.2. Spatial Autocorrelation Analysis
2.3.3. The Greenest Image
2.3.4. Postprocessing for UHI Extraction
2.3.5. Analysis of Factors Influencing the UHI Effect
3. Results
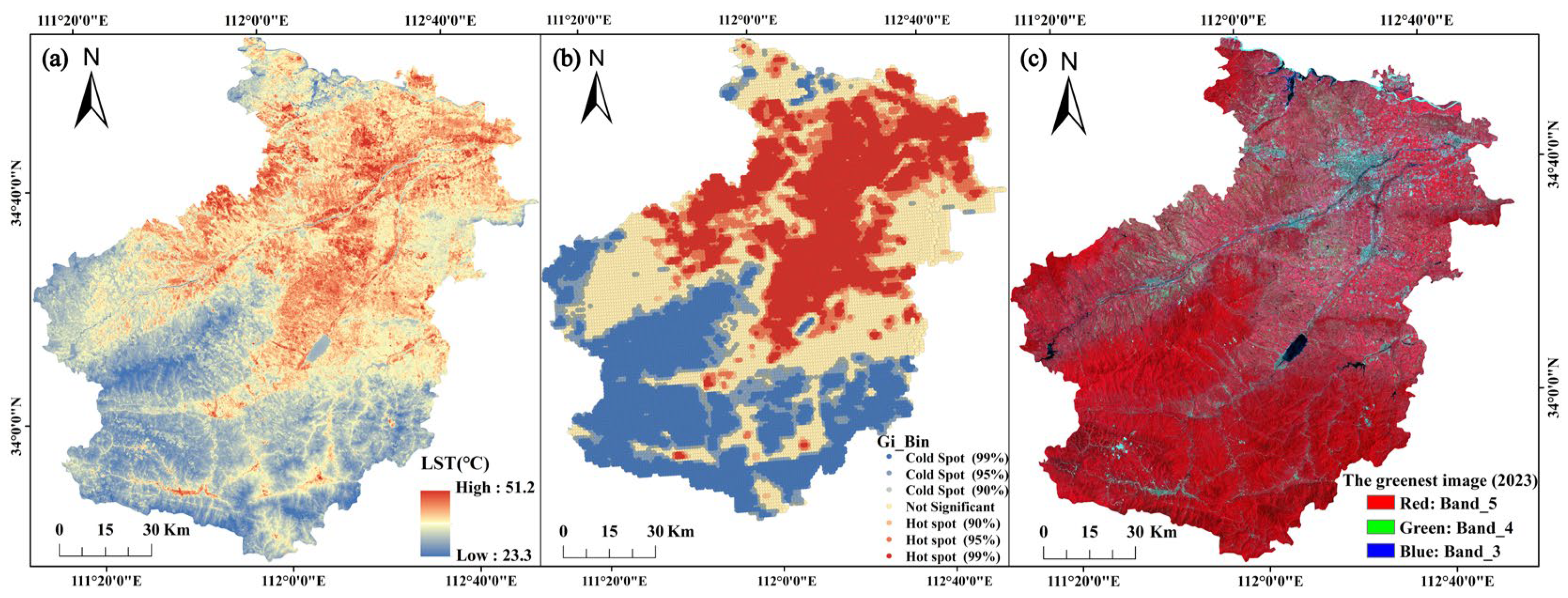
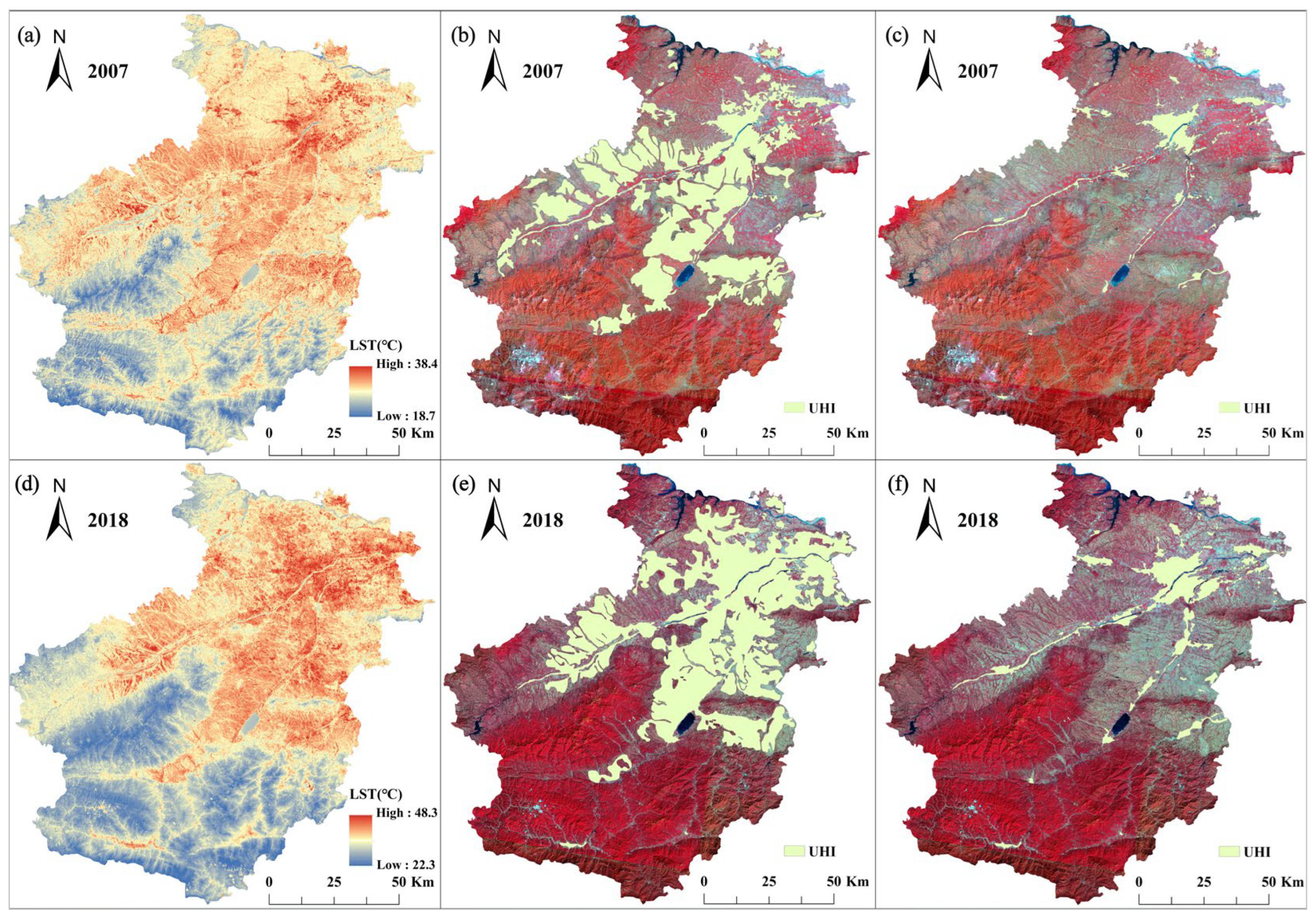
3.1. UHI Effect Spatial Distribution Mapping
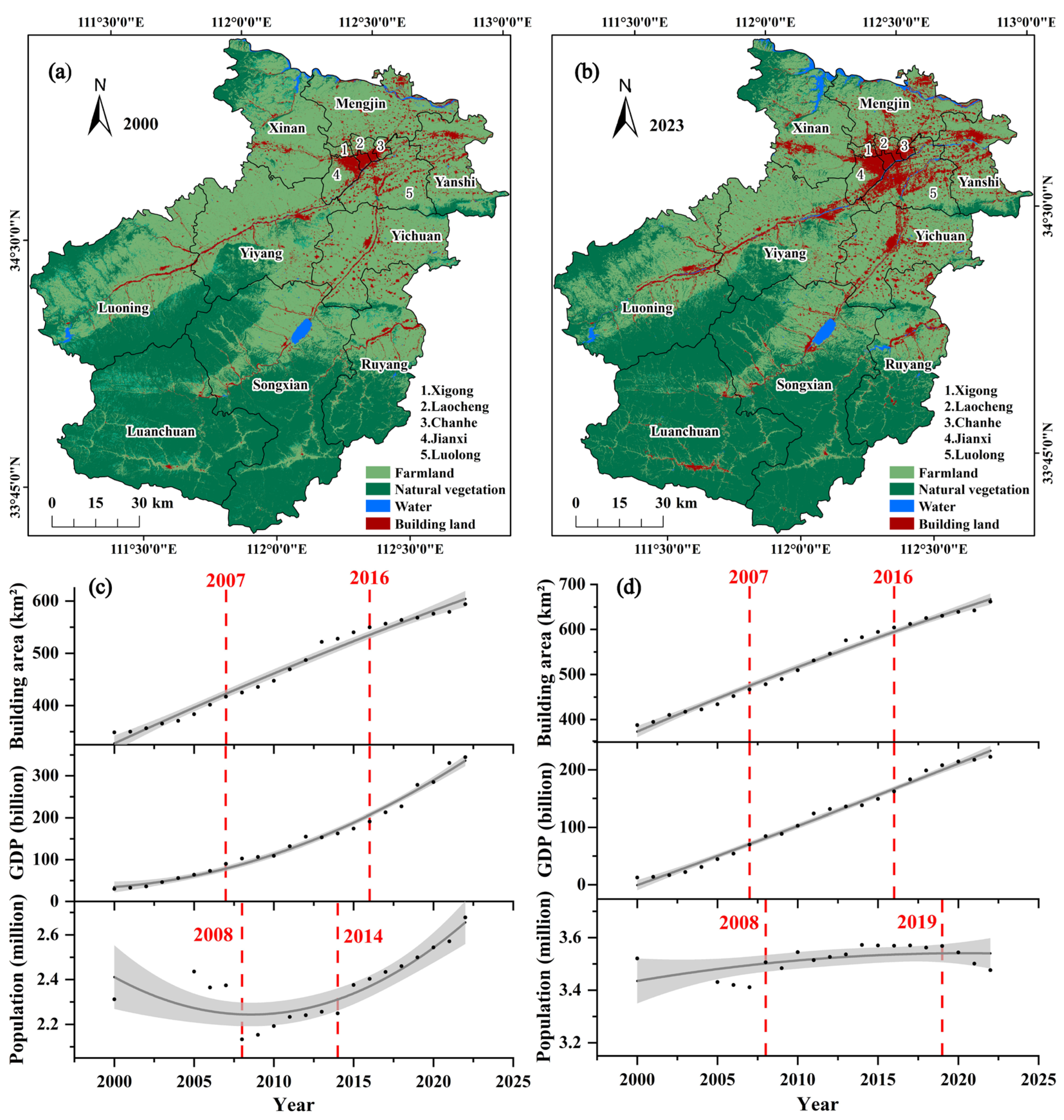
3.2. Spatiotemporal Dynamics of UHI Extent (2000–2023)
3.3. UHI Distribution in Different Regions of Luoyang from 2000 to 2023
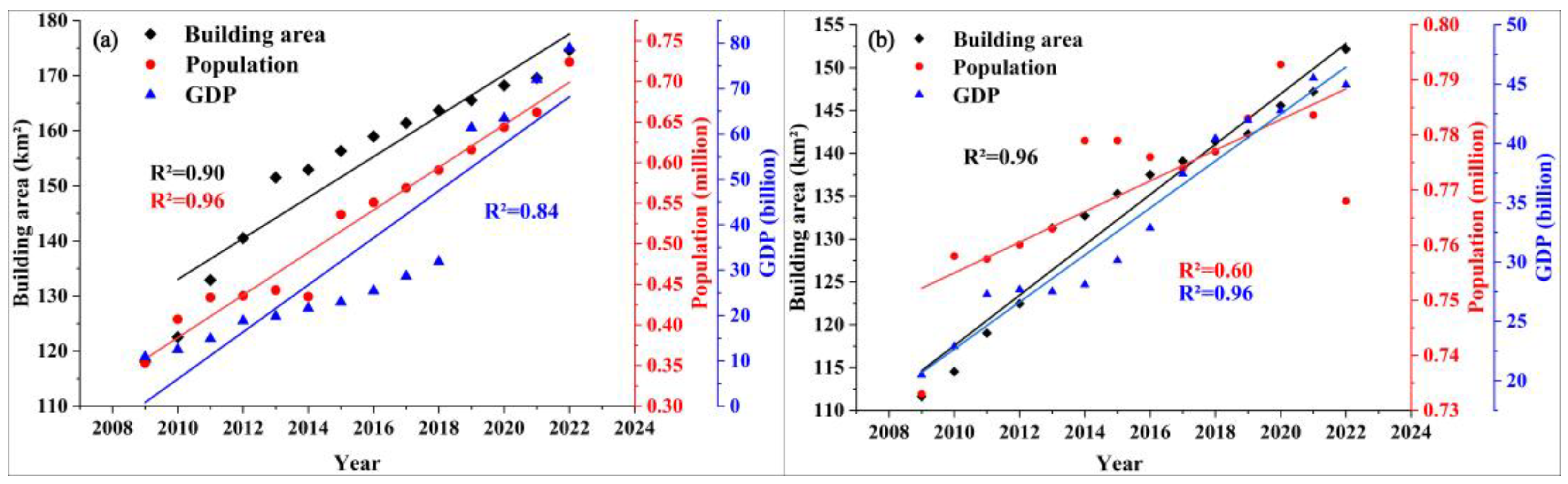
3.4. The Relationship Between UHI Area and Main Driving Factors
4. Discussion
4.1. Extracting the UHI Effect by Combining Spatial Autocorrelation and Greenest Images
4.2. Analysis of the Driving Factors of UHI Expansion
4.3. The Advantages and Disadvantages of Extracting the UHI Area
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kabisch, N.; Remahne, F.; Ilsemann, C.; Fricke, L. The urban heat island under extreme heat conditions: A case study of Hannover, Germany. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 23017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, Z.; Wu, C.; Zhao, D.; Xu, X.; Yang, J.; Feng, L.; Sun, Z.; Liu, L. Determining the boundary and probability of surface urban heat island footprint based on a logistic model. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, C.; Yuan, M.; Lu, Y.; Huang, Y.; Liu, Y. Effects of urban form on the urban heat island effect based on spatial regression model. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 634, 696–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assaf, G.; Assaad, R.H. Modeling the impact of land use/land cover (LULC) factors on diurnal and nocturnal Urban Heat Island (UHI) intensities using spatial regression models. Urban Clim. 2024, 55, 101971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Ma, J.; Liu, Q.; Liu, Y.; Hu, Y.; Li, Y.; Yue, Y. Spatial-temporal change of land surface temperature across 285 cities in China: An urban-rural contrast perspective. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 635, 487–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Chen, Z.; Yu, B.; Wang, L.; Wu, B.; Wu, J.; Zhao, F. Exploring the relationship between 2D/3D landscape pattern and land surface temperature based on explainable extreme Gradient Boosting tree: A case study of Shanghai, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 725, 138229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Yin, Y.; An, H.; Lei, J.; Li, M.; Song, J.; Han, W. Surface urban heat island and its relationship with land cover change in five urban agglomerations in China based on GEE. Environ. Sci. Pollut. R. 2022, 29, 82271–82285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nwakaire, C.; Onn, C.; Yap, S.; Yuen, C.; Onodagu, P. Urban heat island studies with emphasis on urban pavements: A review. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2020, 63, 102476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, B.; Wang, J.; Liu, H.; Ulpiani, G. Localized synergies between heat waves and urban heat islands: Implications on human thermal comfort and urban heat management. Environ. Res. 2021, 193, 110584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, J.; Chen, T.; Wang, L. Heat stress resilience assessment of urban form from physical space dimension: A case study of Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area. Urban Clim. 2024, 55, 101905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Ma, Q.; Ding, H.; Liang, H. Detection of urban expansion and land surface temperature change using multi-temporal landsat images. Resour. Conserv. Recy. 2018, 128, 526–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Jia, J.; Liu, Y.; Li, H.; Wu, J. Seasonal contrast of the dominant factors for spatial distribution of land surface temperature in urban areas. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 215, 255–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Shan, B.; Yu, X. Study on the spatial heterogeneity of urban heat islands and influencing factors. Build. Environ. 2022, 208, 108604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.; Kim, Y.; Sung, H.; Ryu, J.; Jeon, S. Trend analysis of urban heat island intensity according to urban area change in Asian mega cities. Sustainability 2020, 12, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayanlade, A. Seasonality in the daytime and night-time intensity of land surface temperature in a tropical city area. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 557, 415–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baqa, M.; Lu, L.; Chen, F.; Nawaz-Ul-Huda, S.; Pan, L.; Tariq, A.; Qureshi, S.; Li, B.; Li, Q. Characterizing spatiotemporal variations in the urban thermal environment related to land cover changes in Karachi, Pakistan, from 2000 to 2020. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Zhou, W.; Zheng, Z.; Ren, T.; Wang, W. Within-city spatial and temporal heterogeneity of air temperature and its relationship with land surface temperature. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2021, 206, 103979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Zhang, L.; He, B.; Jin, X.; Zhang, Q.; Razafindrabe, B.; You, H. Temporal changes in extreme high temperature, heat waves and relevant disasters in Nanjing metropolitan region, China. Nat. Hazards 2015, 76, 1415–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, F.; Liu, M.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Che, Y. The effects of 3D architectural patterns on the urban surface temperature at a neighborhood scale: Relative contributions and marginal effects. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 258, 120706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z. Reconceptualizing urban heat island: Beyond the urban-rural dichotomy. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2022, 77, 103581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Sun, A.; Niu, R. Effect of land cover fractions on changes in surface urban heat islands using Landsat time-series images. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Huang, L.; Zhang, L.; Wu, P.; Zeng, C. Long-term and fine-scale satellite monitoring of the urban heat island effect by the fusion of multi-temporal and multi-sensor remote sensed data: A 26-year case study of the city of Wuhan in China. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 172, 109–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Zhang, L.; Li, D.; Huang, D.; Zhu, C. Climate-vegetation control on the diurnal and seasonal variations of surface urban heat islands in China. Environ. Res. Lett. 2016, 11, 74009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, R.; Wang, L.; Huang, X.; Niu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Niu, Z. The influence of different data and method on estimating the surface urban heat island intensity. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 89, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Piao, S.; Ciais, P.; Friedlingstein, P.; Ottle, C.; Breon, F.; Nan, L.; Zhou, L.; Myneni, R.B. Surface urban heat island across 419 global big cities. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 696–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Peng, J.; Wang, Y. Diversification of land surface temperature change under urban landscape renewal: A case study in the main city of Shenzhen, China. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, L.; Lu, L.; Fu, P.; Nitivattananon, V.; Guo, H.; Li, Q. Understanding spatiotemporal evolution of the surface urban heat island in the Bangkok metropolitan region from 2000 to 2020 using enhanced land surface temperature. Geomat. Nat. Hazards Risk 2023, 14, 2174904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Lin, T.; Sun, C.; Lin, M.; Zhan, Y.; Chen, Y.; Ye, H.; Yao, X.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, G.; et al. Long-term spatiotemporal characteristics and impact factors of land surface temperature of inhabited islands with different urbanization levels. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.H. Area delineation and spatial-temporal dynamics of urban heat island in Lanzhou city, China using remote sensing imagery. J. Indian Soc. Remote. 2016, 44, 111–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, A.; Sreekumar, S.; Khandelwal, S.; Kumar, R. Prediction of land surface temperatures for surface urban heat island assessment over Chandigarh city using support vector regression model. Sol. Energy 2019, 186, 404–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herbel, I.; Croitoru, A.; Rus, A.; Rosca, C.; Harpa, G.; Ciupertea, A.; Rus, I. The impact of heat waves on surface urban heat island and local economy in Cluj-Napoca city, Romania. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2018, 133, 681–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, D.; Gu, Z.; Meng, X. Summer urban heat island mitigation strategy development for high-anthropogenic-heat-emission blocks. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2022, 87, 104197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, P.; Li, J.; Cao, L.; Pu, R.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Chen, H.; Gong, H. Assessing spatiotemporal characteristics of urban heat islands from the perspective of an urban expansion and green infrastructure. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 74, 103208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, A.; Yang, J.; Xiao, X.; Xia, J.; Jin, C.; Li, X. Influences of urban spatial form on urban heat island effects at the community level in China. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2020, 53, 101972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Guo, X.; Wu, Z. Land surface temperature retrieval from Landsat 8 TIRS-comparison between radiative transfer equation-based method, split window algorithm and single channel method. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 9829–9852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Diao, C.; Xian, G.; Yin, D.; Lu, Y.; Zou, S.; Erickson, T. A summary of the special issue on remote sensing of land change science with Google earth engine. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 248, 112002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, M.; Mao, D.; Wang, Z.; Ren, C.; Zhu, Q.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y. Tracking long-term floodplain wetland changes: A case study in the China side of the Amur River Basin. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. 2020, 92, 102185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, P.; Fu, B.; He, H.; Gao, E.; Fan, D.; Tang, T.; Lin, X.; Bi, L. Quantitative remote sensing analysis of thermal environment changes in the main urban area of Guilin City based on GEE. J. Guilin Univ. Technol. 2020, 40, 330–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, G. Research on Urban Heat Island Effect and Its Causes Supported by GEE. Master’s Thesis, Henan Polytechnic University, Jiaozuo, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Jia, M.; Chen, N.; Wang, W. Long-term surface water dynamics analysis based on Landsat imagery and the Google Earth Engine platform: A case study in the Middle Yangtze River Basin. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, D.; Li, J.; Yao, X.; Luan, Z. Quantifying the long-term expansion and dieback of Spartina alterniflora using Google Earth Engine and object-based hierarchical random forest classification. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Observ. Remote Sens. 2021, 14, 9781–9793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.; Chen, X.; Liu, Y. Impact of urban renewal on urban heat island: Study of renewal processes and thermal effects. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2023, 99, 104995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Gao, J. Comparative analysis of land surface temperature and land cover based on geographically weighted regression. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 2019, 17, 12623–12638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Ding, Z.; Zhao, W. A study on technology integration of ecological environment protection among central plains urban agglomeration. Ecol. Econ. 2014, 30, 170–174. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, Z.; Sun, S.; Xia, C.; Zhou, C.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, W. The effect of “Ecological Restoration and Urban Repair” strategy on urban carbon emission. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2024, 44, 6142–6153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Huang, X. The 30 m annual land cover datasets and its dynamics in China from 1985 to 2023. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2024, 13, 3907–3925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Xu, D.; Zhang, D.; Pu, Y.; Luan, Z. Shoreline dynamics of Chongming island and driving factor analysis based on Landsat images. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liu, H.; Peng, D.; Lv, Q.; Sun, Y.; Huang, H.; Liu, H. The county-scale economic spatial pattern and influencing factors of seven urban agglomerations in the Yellow River Basin-A study based on the integrated nighttime light data. Sustainability 2021, 13, 4220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, D.; Pla, F.; Latorre-Carmona, P.; Myint, S.; Gaetano, M.; Kieu, H. Characterizing the relationship between land use land cover change and land surface temperature. ISPRS J. Photogramm. 2017, 124, 119–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na, N.; Xu, D.; Fang, W.; Pu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, H. Automatic detection and dynamic analysis of urban heat islands based on Landsat images. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 4006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhuyan, U.; Zang, C.; Vicente-Serrano, S.; Menzel, A. Exploring relationships among tree-ring growth, climate variability, and seasonal leaf activity on varying timescales and spatial resolutions. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutman, G.; Skakun, S.; Gitelson, A. Revisiting the use of red and near-infrared reflectances in vegetation studies and numerical climate models. Sci. Remote Sens. 2021, 4, 100025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Peng, J.; Li, G.; Han, W.; Liu, L.; Guan, J.; Ju, X.; Zheng, J. Ecological environment assessment of Kurustai grassland based on GEE. Chin. J. Ecol. 2023, 42, 2776–2785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ermida, S.; Soares, P.; Mantas, V.; Göttsche, F.; Trigo, I. Google Earth Engine open-source code for land surface temperature estimation from the Landsat series. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amani, M.; Ghorbanian, A.; Ahmadi, S.; Kakooei, M.; Moghimi, A.; Mirmazloumi, S.; Moghaddam, S.; Mahdavi, S.; Ghahremanloo, M.; Parsian, S.; et al. Google Earth Engine cloud computing platform for remote sensing big data applications: A comprehensive review. IEEE J.-STARS 2020, 13, 5326–5350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Zhang, Z.; Hu, T.; Wang, G.; He, G.; Zhang, Z.; Li, H.; Wu, Z.; Liu, X. An efficient framework for producing Landsat-based land surface temperature data using Google Earth Engine. IEEE J.-STARS 2020, 13, 4689–4701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Yang, Y.; Xu, Z.; Lin, L.; Huang, S. Spatial distribution characteristics of thermal environment in Fuzhou New District based on RS and GIS. Adm. Tech. Environ. Monit. 2023, 4, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Liu, X.; Wang, H.; Huang, W.; Cai, E. Spatio-temporal variations of ecosystem service values in response to land use/cover change in Luoyang city. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 984888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, S.; Liu, J.; Han, Z. Relationship between urban morphology and land surface temperature-A case study of Nanjing City. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0260205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, M.; Yang, X.; Zhu, M. Inversion Study of Urban Surface Temperature in Luoyang City Based on Landsat Images. Ind. Arch. 2024, 54, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseliou, A.; Melas, E.; Mela, A.; Tsiros, I.; Zervas, E. The effect of green roofs and green facades in the pedestrian thermal comfort of a Mediterranean Urban Residential Area. Atmospheric 2023, 14, 1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Cristo, E.; Evangelisti, L.; Barbaro, L.; Vollaro, R.; Asdrubali, F. A systematic review of green roofs’ thermal and energy performance in the Mediterranean Region. Energies 2025, 18, 2517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorelick, N.; Hancher, M.; Dixon, M.; Ilyushchenko, S.; Thau, D.; Moore, R. Google Earth Engine: Planetary-scale geospatial analysis for everyone. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 202, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, L.; Mutanga, O. Google Earth Engine applications since inception: Usage, trends, and potential. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutanga, O.; Kumar, L. Google Earth Engine applications. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Jia, S. Research on inversion and spatiotemporal variation analysis of surface temperature in Hangzhou based on GEE and Landsat8 data. Stand. Surv. Map. 2024, 40, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| U-UHI | U-Area | U-GDP | U-Population | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| U-UHI | 1 | |||
| U-area | 0.988 ** | 1 | ||
| U-GDP | 0.834 ** | 0.891 ** | 1 | |
| U-population | 0.879 ** | 0.921 ** | 0.972 ** | 1 |
| C-UHI | C-Area | C-GDP | C-Population | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C-UHI | 1 | |||
| C-area | 0.991 ** | 1 | ||
| C-GDP | 0.977 ** | 0.967 ** | 1 | |
| C-population | 0.122 | 0.167 | 0.056 | 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yan, D.; Zhang, Y.; Song, P.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, W.; Du, Q. Integrating Spatial Autocorrelation and Greenest Images for Dynamic Analysis Urban Heat Islands Based on Google Earth Engine. Sustainability 2025, 17, 7155. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17157155
Yan D, Zhang Y, Song P, Zhang X, Wang Y, Zhu W, Du Q. Integrating Spatial Autocorrelation and Greenest Images for Dynamic Analysis Urban Heat Islands Based on Google Earth Engine. Sustainability. 2025; 17(15):7155. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17157155
Chicago/Turabian StyleYan, Dandan, Yuqing Zhang, Peng Song, Xiaofang Zhang, Yu Wang, Wenyan Zhu, and Qinghui Du. 2025. "Integrating Spatial Autocorrelation and Greenest Images for Dynamic Analysis Urban Heat Islands Based on Google Earth Engine" Sustainability 17, no. 15: 7155. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17157155
APA StyleYan, D., Zhang, Y., Song, P., Zhang, X., Wang, Y., Zhu, W., & Du, Q. (2025). Integrating Spatial Autocorrelation and Greenest Images for Dynamic Analysis Urban Heat Islands Based on Google Earth Engine. Sustainability, 17(15), 7155. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17157155






