Study on the Spatio-Temporal Distribution and Influencing Factors of Soil Erosion Gullies at the County Scale of Northeast China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Source
2.3. Extraction of Erosion Gully
2.4. Topographic Information Extraction
2.5. Land Use Type Extraction
2.6. Extraction of Fractional Vegetation Coverage (FVC)
2.7. Kernel Density Evaluation
2.8. Geographic Detector Model
3. Results
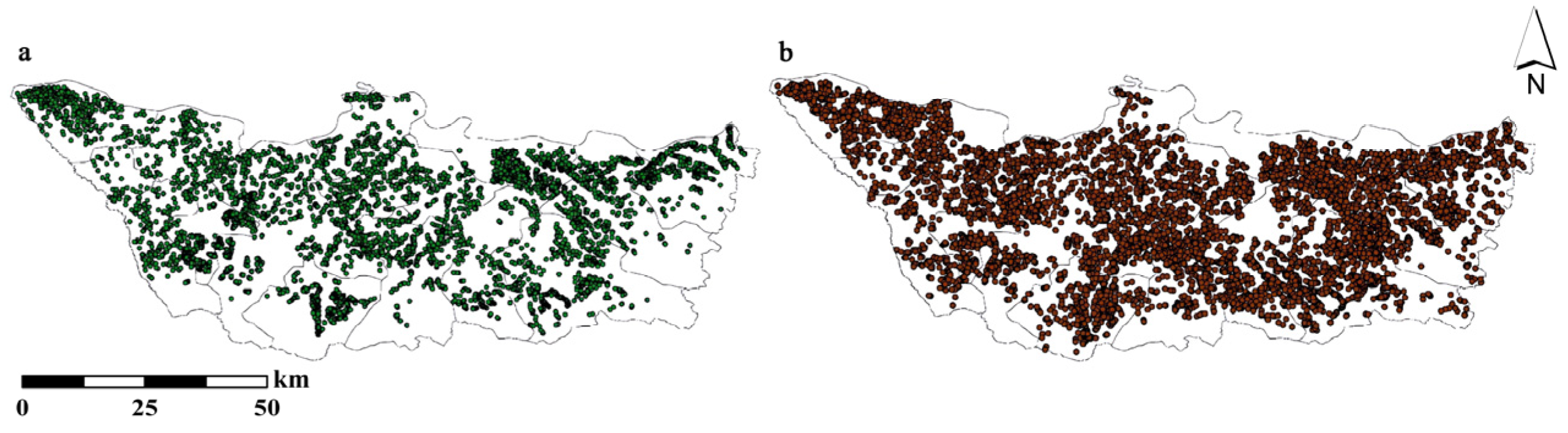
3.1. Extraction Results of Erosion Gullies
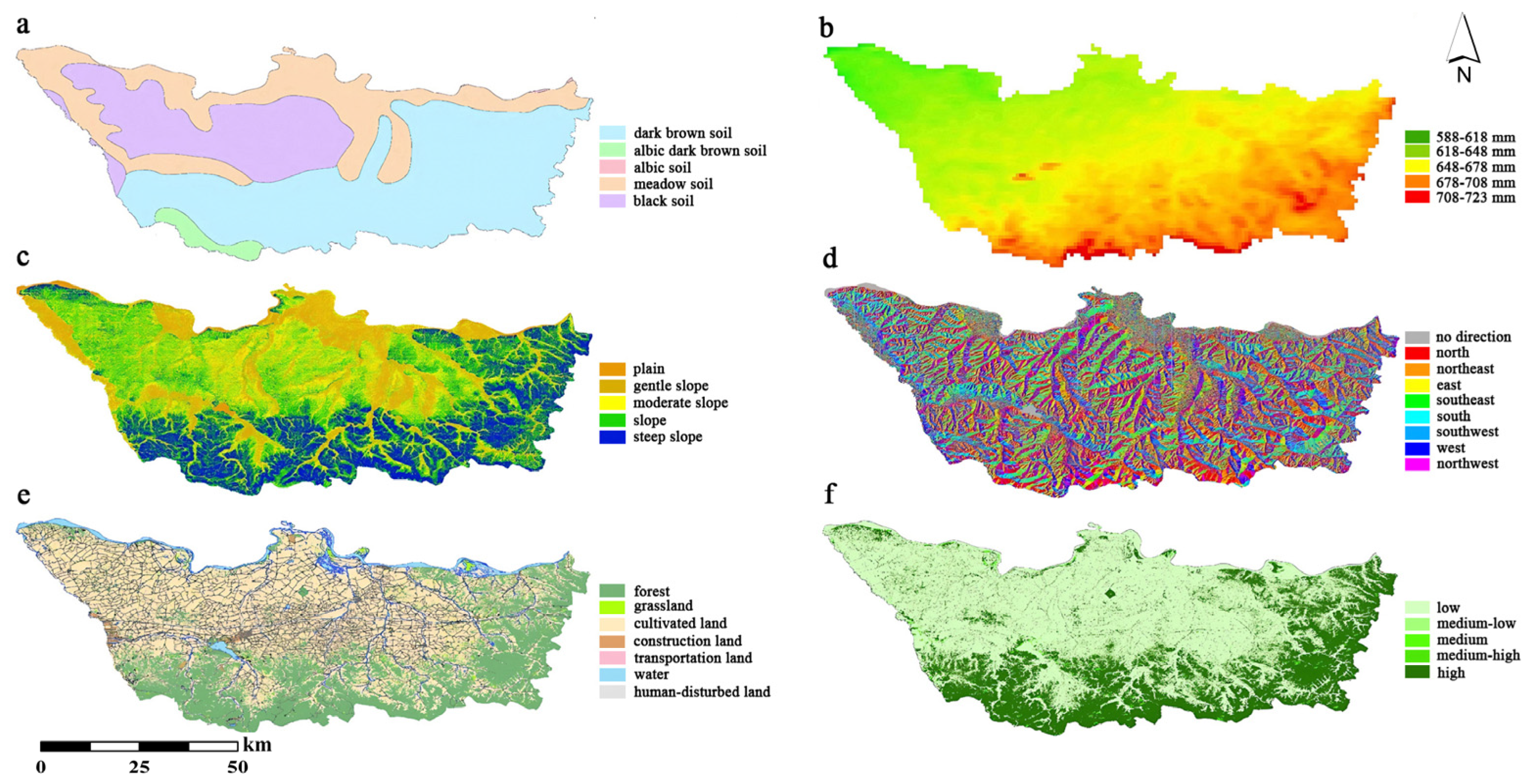
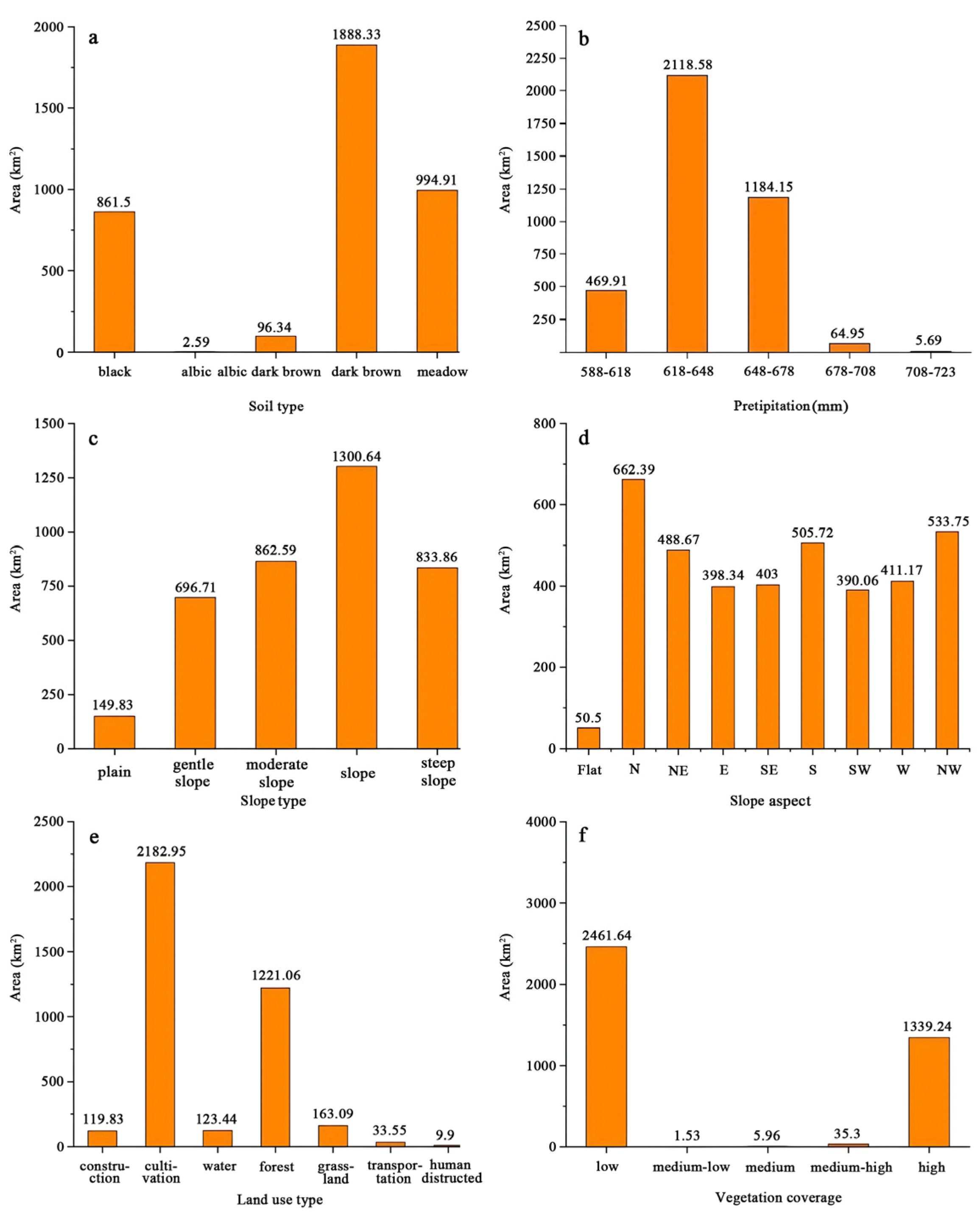
3.2. Extraction Results of Influencing Factors
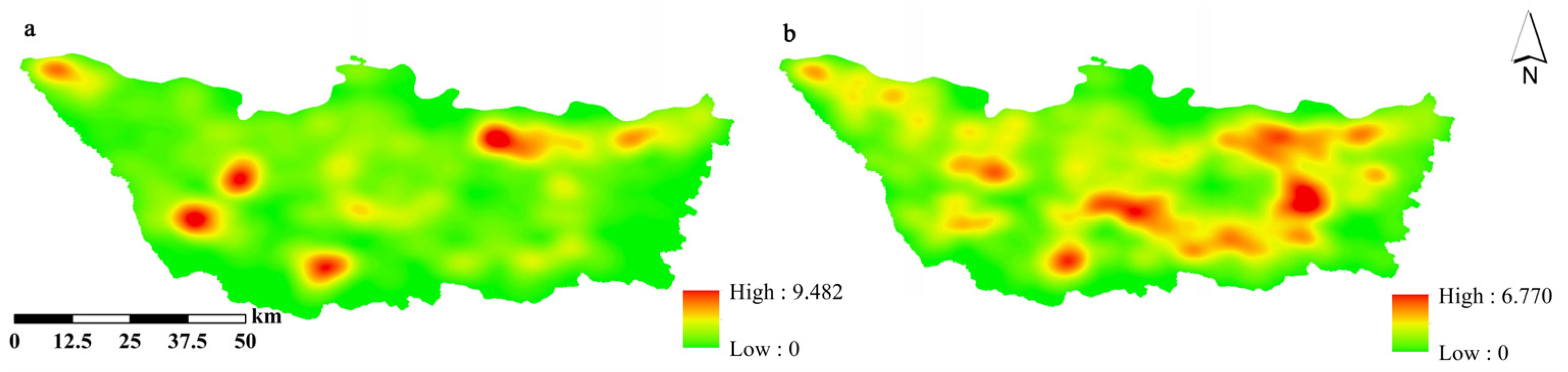
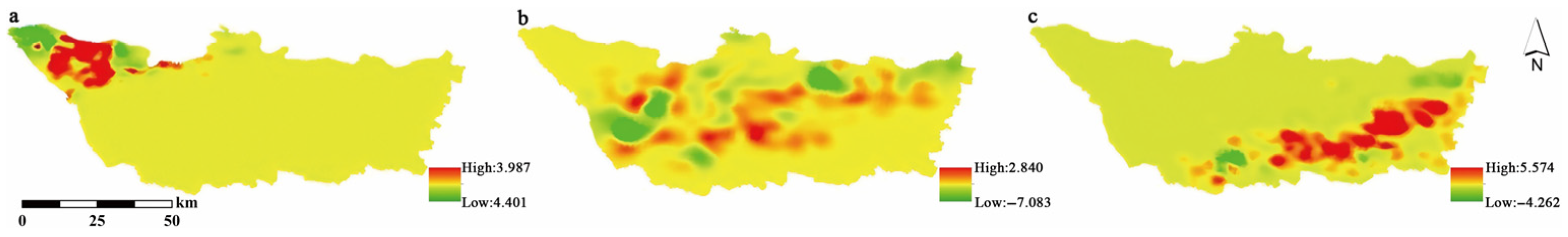
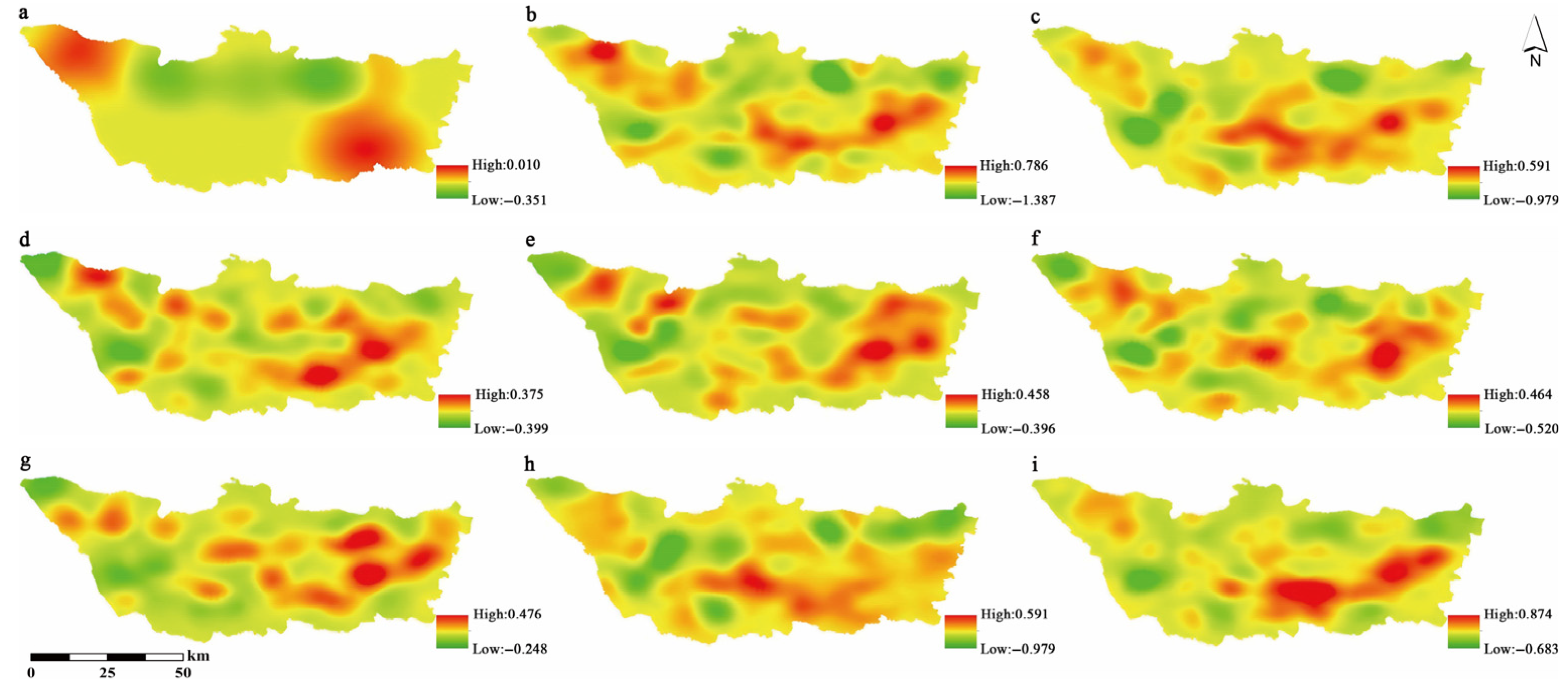
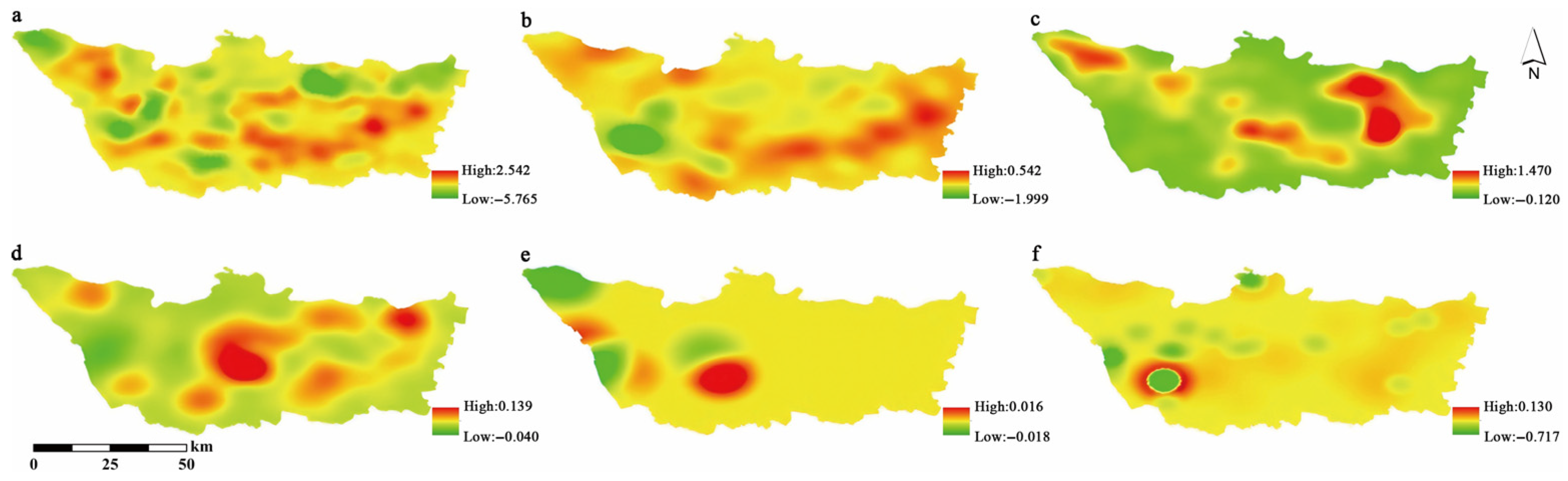
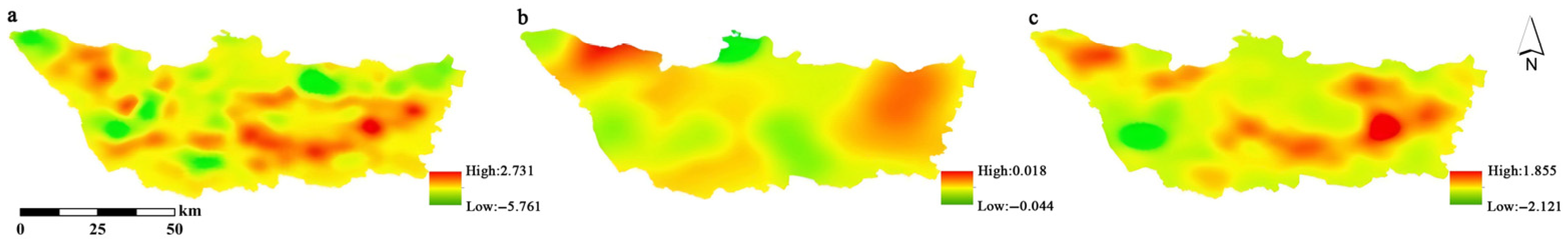
3.3. Results of KDE for Different Factors
3.3.1. Soil Types
3.3.2. Precipitation
3.3.3. Slope Interval
3.3.4. Slope Aspect
3.3.5. Land Use Types
3.3.6. Vegetation Coverage
3.4. Interaction Results of the Geographic Detector
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, Y.; Wu, T.; Lei, L.; Jie, Y. Effects of parent material on soil hydraulic properties in subtropical hilly area of Southern China. Catena 2024, 243, 108210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarrinabadi, E.; Lobb, D.A.; Enanga, E.; Badiou, P.; Creed, I.F. Agricultural activities lead to sediment infilling of wetlandscapes in the Canadian Prairies: Assessment of soil erosion and sedimentation fluxes. Geoderma 2023, 436, 116525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, F.; Nie, L.; Xu, Y.; Rui, X.; He, Y.; Zhang, T.; Wang, Y.; Du, C.; Bao, C. Effects of freeze-thaw cycles on the erodibility and microstructure of soda-saline loessal soil in Northeastern China. Catena 2022, 209, 105812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witharana, C.; Bhuiyan, M.A.E.; Liljedahl, A.K.; Kanevskiy, M.; Jorgenson, T.; Jones, B.M.; Daanen, R.; Epstein, H.E.; Griffin, C.G.; Kent, K. An object-based approach for mapping tundra ice-wedge polygon troughs from very high spatial resolution optical satellite imagery. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, A.; Shen, W.; Yang, J.; Wang, Y.; Li, X. Spatial patterns, determinants, future trends, and implications for the sustainable use of terraces abandonment in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 467, 142860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, J.; Guo, M.; Zhou, P.; Zhang, X.; Xu, J.; Chen, Z.; Liu, X.; Wang, L.; Wan, Z. Soil erosion resistance factors in different types of gully heads developed in four main land-uses in the Mollisols region of Northeast China. Soil Till. Res. 2023, 230, 105697. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, J.; Xie, Y.; Cheng, H.; Liu, G. Impact of farmland landscape characteristics on gully erosion in the black soil region of Northeast China. Catena 2025, 249, 108623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhang, X.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, S.; Cai, C.; Guo, Z.; Wang, J. Assessment of soil quality in a heavily fragmented micro-landscape induced by gully erosion. Geoderma 2023, 431, 116369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayas, A.; Gómez, J.A. Modelling of gully widening, a review. Implications for research on gully evolution and restoration. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2024, 255, 104836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, C.; Zhang, Q.; Lu, C.; Li, H.; Wang, H.; Wu, F. Variations in soil detachment by rill flow during crop growth stages in sloping farmlands on the Loess Plateau. Catena 2022, 216, 106375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valentin, C.; Poesen, J.; Li, Y. Gully erosion: Impacts, factors and control. Catena 2005, 63, 132–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez, Á.G.; Schnabel, S.; Contador, F.L. Gully erosion, land use and topographical thresholds during the last 60 years in a small rangeland catchment in SW Spain. Land Degrad. Dev. 2009, 20, 535–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Li, P.; Hu, J.; Yan, L.; Latifi, H.; Yao, W.; Hao, M.; Gao, J.; Dang, T.; Zhang, S. Development of gully erosion processes: A 3D investigation based on field scouring experiments and laser scanning. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 265, 112683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinsey-Henderson, A.; Hawdon, A.; Bartley, R.; Wilkinson, S.N.; Lowe, T. Applying a hand-held laser scanner to monitoring gully erosion: Workflow and evaluation. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhen, J.; Hu, W.; Chen, S.; Lizaga, I.; Zeraatpisheh, M.; Yang, X. Remote sensing of soil degradation: Progress and perspective. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2023, 11, 429–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polovina, S.; Radić, B.; Ristić, R.; Milčanović, V. Application of remote sensing for identifying soil erosion processes on a regional scale: An innovative approach to enhance the erosion potential model. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Tang, B.; Wang, K.; Shi, J.; Li, M. Evaluation of the gully erosion susceptibility by using UAV and hybrid models based on machine learning. Soil Till. Res. 2024, 244, 106218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cândido, B.M.; James, M.; Quinton, J.; Lima, W.d.; Silva, M.L.N. Sediment source and volume of soil erosion in a gully system using UAV photogrammetry. Rev. Bras. Cienc. Solo. 2020, 44, e0200076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmati, O.; Kalantari, Z.; Ferreira, C.S.; Chen, W.; Soleimanpour, S.M.; Kapović-Solomun, M.; Seifollahi-Aghmiuni, S.; Ghajarnia, N.; Kazemabady, N.K. Contribution of physical and anthropogenic factors to gully erosion initiation. Catena 2022, 210, 105925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Cao, W.; Nie, Y.; Xiong, D.; Cheng, S.; Duan, X. Influence of soil geography on the occurrence and intensity of gully erosion in the Hengduan Mountain region. Catena 2023, 222, 106841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frankl, A.; Nyssen, J.; Vanmaercke, M.; Poesen, J. Gully prevention and control: Techniques, failures and effectiveness. Earth Surf. Proc. Land. 2021, 46, 220–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zare, M.; Soufi, M.; Nejabat, M.; Pourghasemi, H.R. The topographic threshold of gully erosion and contributing factors. Nat. Hazard. 2022, 112, 2013–2035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Guo, M.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, X.; Yang, F.; Zhang, S. Quantifying the contributions of precipitation, topography and human activity and their coupling to the development of permanent gully. Geoderma 2024, 449, 117015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, R.L.; Rowntree, K.M.; Le Roux, J.J. An interrogation of research on the influence of rainfall on gully erosion. Catena 2021, 206, 105482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Shu, J.; Han, L.; Tian, G.; Yang, G.; Lv, J. Modeling the effects of topography and slope gradient of an artificially formed slope on runoff, sediment yield, water and soil loss of sandy soil. Catena 2022, 212, 106060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Liu, G.; Xie, Y.; Wu, Y.; Wang, D.; Gao, Y.; Meng, L. Effect of topographic variations and tillage methods on gully erosion in the black soil region: A case-study from Northeast China. Land Degrad. Dev. 2022, 33, 3786–3800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, B.; Pinheiro, C.; Nunes, A.; Bento-Gonçalves, A.; Hermenegildo, C. Geo-environmental factors controlling gully distribution at the local scale in a Mediterranean environment. Catena 2024, 236, 107712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, A.; Tyeb, M.H.; Mandal, B.B.; Pathak, K.; Tewari, M. Experimental investigation on mobility and deposition characteristics of granular and poly-dispersed mine overburden dump material in inclined channels for hazard assessment. Geomat. Nat. Haz. Risk 2025, 16, 2483803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzaee, S.; Pajouhesh, M.; Imaizumi, F.; Abdollahi, K.; Gomez, C. Gully erosion development and the role of vegetation cover in arid area during an extreme flood (Case study: Dashtiari gully, Iran). Ecol. Eng. 2025, 215, 107600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Zhang, X. Effects of slope vegetation patterns on erosion sediment yield and hydraulic parameters in slope-gully system. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 145, 109723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, X. Current scenario of gully erosion and its control strategy in mollisols areas of Northeast China. T. Chin. Soc. Agr. Eng. 2021, 37, 320–326. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Han, X.; Cruse, R.M.; Zhang, X.; Hu, W.; Yan, Y.; Guo, M. Morphological characteristics and influencing factors of permanent gully and its contribution to regional soil loss based on a field investigation of 393 km2 in mollisols region of Northeast China. Catena 2022, 217, 106467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Hu, W.; Li, J.; Guo, M.; Liu, X. Control of soil and water losses is the critical issue for black earth conservation. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2024, 69, 1401–1405. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, X. Key issues of mollisols research and soil erosion control strategies in China. Bull. Soil Water Conserv. 2020, 40, 340–344. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ding, C.; Zhang, S.; Hu, W.; Yan, Y.; Qi, Z.; Han, X.; Zhang, X. Field validation of gully survey of national census for soil conservation in the black soil region of Northeast China. Sci. Soil Water Conserv. 2021, 19, 77–85. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, K.; Zhang, J.; Yang, R.; Chen, C. Investigation on the effects of gully control in China’s black soil region over a 10-Year scale based on high-resolution remote sensing. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2024, 31, 67–73. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liang, X.; Pang, S.; Lu, T.; Liu, X. Study on soil erosion in typical black soil areas of Heilongjiang Province based on USLE. Geomat. Spat. Inform. Technol. 2025, 48, 112–115. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Wu, K.; Li, X.; Li, X. Classification of land types at provincial level based on the goal of black land protection: A case study of Heilongjiang Province. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2022, 42, 1348–1359. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Almeida, W.S.d.; Seitz, S.; Oliveira, L.F.C.d.; Carvalho, D.F.d. Duration and intensity of rainfall events with the same erosivity change sediment yield and runoff rates. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2021, 9, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H. Gully Characteristics and Influencing Factors in Heilongjiang Province. Master’s Thesis, Northwest A&F University, Xianyang, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Fiorucci, F.; Ardizzone, F.; Mondini, A.C.; Viero, A.; Guzzetti, F. Visual interpretation of stereoscopic NDVI satellite images to map rainfall-induced landslides. Landslides 2018, 16, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Chen, L.; Ban, T.; Lyu, D.; Guan, Y.; Wu, X.; Zhou, X.; Chen, H. Accurate label refinemenft from multiannotator of remote sensing data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Electron. 2023, 61, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Çellek, S. Effect of the slope angle and its classification on landslide. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2020, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleem, N.; Huq, M.E.; Twumasi, N.Y.D.; Javed, A.; Sajjad, A. Parameters derived from and/or used with digital elevation models (DEMs) for landslide susceptibility mapping and landslide risk assessment: A review. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2019, 8, 545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, D.; Shi, W. Modeling the adaptation of agricultural production to climate change. Agriculture 2023, 13, 414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdanaev, E.; Kappas, M.; Wyss, D. The identification of irrigated crop types using support vector machine, random forest and maximum likelihood classification methods with Sentinel-2 data in 2018: Tashkent Province, Uzbekistan. Int. J. Geoinformat. 2022, 18, 37–53. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, H.; Zheng, X.; Lu, X. A supervised segmentation network for hyperspectral image classification. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2021, 30, 2810–2825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Xu, L.; Jing, Y.; Yin, H.; Li, X.; Guan, X. High-quality vegetation index product generation: A review of NDVI time series reconstruction techniques. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2021, 105, 102640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, X.; Yang, Y.; Xu, H.; Guo, Y.; Lai, Y.; McVicar, T.R.; Xie, D.; Yan, G. Improvement of NDVI mixture model for fractional vegetation cover estimation with consideration of shaded vegetation and soil components. Remote Sens. Environ. 2024, 314, 114409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Zheng, X.; Zhao, K.; Xin, X.; Liu, H. Qquantifying the impact of NDVIsoil determination methods and NDVIsoil variability on the estimation of fractional vegetation cover in Northeast China. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, S. Spatial and temporal distribution of vegetation coverage and its response to meteorological factors in frozen soil region of Qinghai-Xizang Plateau. Sci. Surv. Mapp. 2024, 49, 86–96. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ning, X.; Yang, M.; Cao, W.; Wang, S.; Gu, Q.; Wang, Y. Spatial-temporal pattern of vegetation coverage and its climate driving mechanism in the Three Rivers Headwaters region from 2000–2022. Bull. Suv. Mapp. 2024, 12, 70–76. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, S.; Wang, Y.; Qiao, X.; Zhao, T. Spatiotemporal variation and driving factors for FVC in Huaihe River Basin from 1987 to 2021. T. Chin. Soc. Agr. Mach. 2023, 54, 180–190. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Hao, X.; Zhang, Z.; Zheng, H.; Gao, N. Dynamic change of vegetation cover in the economic zone of the northern slopes of Tianshan Mountains. China Environ. Sci. 2024, 4, 1020–1031. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B.; Chen, Z.; Shi, X.; Wu, S.; Feng, H.; Gao, X.; Siddique, K.H.M. Temporal and spatial changes of soil erosion under land use and land cover change based on Chinese soil loss equation in the typical watershed on the Loess Plateau. Soil Use Manag. 2022, 39, 557–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Su, Z.; Deng, Y.; Kurths, J.; Wu, J. Spatial network disintegration based on kernel density estimation. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2024, 245, 110005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, Y.; Yao, W.; Li, X.; Alhudhaif, A. An adaptive highly improving the accuracy of clustering algorithm based on kernel density estimation. Inf. Sci. 2024, 663, 120187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luotamo, M.; Yli-Heikkilä, M.; Klami, A. Density estimates as representations of agricultural fields for remote sensing-based monitoring of tillage and vegetation cover. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silverman, B.W. Density Estimation for Statistics and Data Analysis; Routledge: London, UK, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Shan, J.; Qiu, L.; Tian, M.; Wang, Z.; Wang, J.; Lu, B.; Huang, X. Analysis of spatial distribution characteristics of cultivated land based on landscape indices and kernel density estimation in Jiangsu Province. Jiangsu J. Agr. Sci. 2023, 39, 1872–1882. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wei, C.; Lei, M. Spatio-temporal evolution and its driving factors of non-ferrous mining sites in China. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2023, 78, 1271–1289. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Heidenreich, N.B.; Schindler, A.; Sperlich, S. Bandwidth selection for kernel density estimation: A review of fully automatic selectors. ASTA Adv. Stat. Anal. 2013, 97, 403–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Abuduwaili, J.; Liu, W.; Feng, S.; Saparov, G.; Ma, L. Application of geographical detector and geographically weighted regression for assessing landscape ecological risk in the Irtysh River Basin, Central Asia. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 158, 111540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, L.; Tan, W.; Fang, L.; Ji, L. Spatial analysis of soil aggregate stability in a small catchment of the Loess Plateau, China: II. Spatial prediction. Soil Till. Res. 2018, 179, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Zhao, W.; Wang, J. Research progress on soil erodibility. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2017, 28, 2749–2759. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Chen, Z.; Guo, M.; Zhang, S.; Wang, W. Soil erodibility and its influencing factors of erosion gully banks under different land use types in the typical black soil region of Northeast China. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2025, 32, 18–27. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Dickson, J.L.; Head, J.W.; Levy, J.S.; Morgan, G.A.; Marchant, D.R. Gully formation in the McMurdo Dry Valleys, Antarctica: Multiple sources of water, temporal sequence and relative importance in gully erosion and deposition processes. Geol. Soc. Lond. Spec. Publ. 2019, 467, 289–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai Khuller, A.; Russel Christensen, P. Evidence of exposed dusty water ice within Martian gullies. J. Geophys. Res. Planets 2021, 126, e2020JE006539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modak, P.; Mandal, M.; Mandi, S.; Ghosh, B. Gully erosion vulnerability modelling, estimation of soil loss and assessment of gully morphology: A study from cratonic part of eastern India. Environ. Sci. Pollut. R. 2023, 30, 116656–116687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Fan, H.; Fan, X. Distributions of recent gullies on hillslopes with different slopes and aspects in the Black Soil Region of Northeast China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2017, 189, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Z.; Liu, H.; Hou, Y.; Gao, A.; Niu, Y.; Xu, J.; Xiao, Y. Factors affecting development of erosion gullies on typical slope farmland at Baiquan County of Heilongjiang Province. Bull. Soil Water Conserv. 2024, 44, 166–176. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, L. Morphology and distribution characteristics of erosion gully in the typical black soil region of Northeast China. T. Chin. Soc. Agr. Eng. 2020, 36, 157–165. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Nyssen, J.; Poesen, J.; Moeyersons, J.; Luyten, E.; Veyret Picot, M.; Deckers, J.; Mitiku, H.; Govers, G. Impact of road building on gully erosion risk, a case study from the northern Ethiopian highlands. Earth Surf. Proc. Land. 2022, 27, 1267–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archibold, O.W.; Levesque, L.M.J.; de Boer, D.H.; Aitken, A.E.; Delanoy, L. Gully retreat in a semi urban catchment in Saskatoon, Saskatchewan. Appl. Geogr. 2003, 23, 261–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poesen, J. Soil erosion in the Anthropocene: Research needs. Earth Surf. Process. Land. 2018, 43, 64–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerra, C.A.; Rosa, I.M.D.; Valentini, E.; Wolf, F.; Filipponi, F.; Karger, D.N.; Xuan, A.N.; Mathieu, J.; Lavelle, P.; Eisenhauer, N. Global vulnerability of soil ecosystems to erosion. Landsc. Ecol. 2020, 35, 823–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, M.; Wang, W.; Kang, H.; Yang, B. Changes in soil properties and erodibility of gully heads induced by vegetation restoration on the Loess Plateau, China. J. Arid Land 2018, 10, 712–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Z.; He, Z.; Zhou, T.; Wang, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, L.; Fang, H.; Shi, L.; Liu, Y.; Wu, Z. Impacts of native vegetation on the hydraulic properties of the concentrated flows in bank gullies. J. Mt. Sci. 2021, 18, 907–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Xiong, D.; Guo, M.; Su, Z.; Zhang, B.; Zheng, X.; Zhang, S.; Fang, H. Impact of grass belt position on the hydraulic properties of runoff in gully beds in the Yuanmou Dry-hot Valley Region of Southwest China. Phys. Geogr. 2015, 36, 408–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Wang, W.; Kang, H.; Wang, W. Impacts of different vegetation restoration options on gully head soil resistance and soil erosion in loess tablelands. Earth Surf. Proc. Land 2020, 45, 1038–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, Y.; Kang, H.; Wang, W.; Guo, M.; Guo, W.; Xiao, H. Vertical distribution of vegetation roots and its influence on soil erosion resistance along gully headwalls in the gullied Loess Plateau. J. Soil. Sediment. 2023, 23, 1265–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Guo, D.; Xu, X.; Lu, M.; Bradgett, R.D.; Eissenstat, D.M.; McCormack, M.L.; Hedin, L.O. Evolutionary history resolves global organization of root functional traits. Nature 2018, 555, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
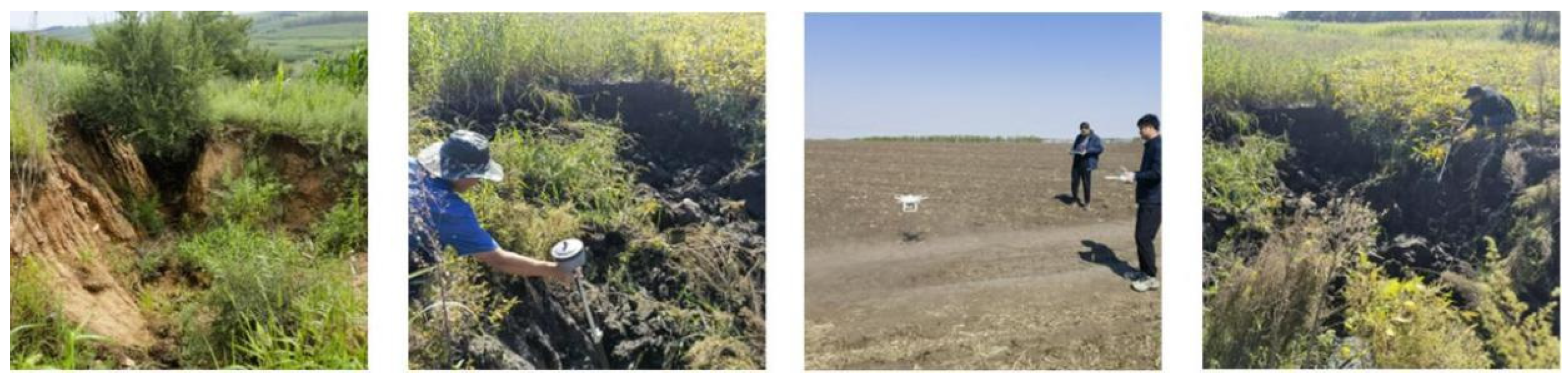




| Position | Category | Photo | Image | Feature |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 127°55′52″ E 45°53′49″ N | Developing gully |  |  | Narrowly striped, light green, with low vegetation coverage at the gully bottom |
| 127°32′27″ E 45°48′37″ N | Stable gully |  |  | Blocky, light green, with high vegetation coverage at the gully bottom |
| 127°32′38″ E 45°47′56″ N | Newly formed gully |  |  | Striped, bare soil color, no vegetation coverage at the gully bottom |
| 127°53′24″ E 45°38′38″ N | Farmland gully |  |  | Narrowly striped, bare soil color, no vegetation coverage at the gully bottom |
| 127°54′56″ E 45°54′24″ N | Forestland gully |  |  | Banded, dark brown, with moderate vegetation coverage at the gully bottom |
| 127°25′02″ E 45°48′30″ N | Road gully |  |  | Narrowly striped, bare soil color, no vegetation coverage at the gully bottom |
| 128°04′39″ E 45°51′27″ N | Grassland gully |  |  | Striped, bare soil color, no vegetation coverage at the gully bottom |
| Interaction Criterion | Interaction |
|---|---|
| Nonlinear attenuation | |
| Single-factor nonlinear attenuation | |
| Two-factor enhancement | |
| Independent | |
| Nonlinear enhancement |
| Soil Type | Gully Number in 2012 | Gully Number in 2022 | Gully Change |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dark brown | 2953 | 3887 | 934 |
| Albic dark brown | 3 | 25 | 22 |
| Albic | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| Meadow | 1480 | 1265 | −215 |
| Black | 1620 | 1848 | 228 |
| Precipitation (mm) | Gully Number in 2012 | Gully Number in 2022 | Gully Change |
|---|---|---|---|
| 588–618 | 672 | 824 | 152 |
| 618–648 | 4092 | 3974 | −118 |
| 648–678 | 1292 | 2226 | 934 |
| 678–708 | 0 | 2 | 2 |
| 708–723 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Slope Interval | Gully Number in 2012 | Gully Number in 2022 | Gully Change |
|---|---|---|---|
| Plain | 45 | 58 | 13 |
| Gentle | 432 | 672 | 240 |
| Moderate | 1513 | 2035 | 522 |
| Slope | 3468 | 3503 | 35 |
| Steep | 598 | 758 | 160 |
| Aspects | Gully Number in 2012 | Gully Number in 2022 | Gully Change |
|---|---|---|---|
| Flat | 9 | 20 | 11 |
| North | 1104 | 1212 | 108 |
| Northeast | 834 | 1059 | 225 |
| East | 833 | 888 | 55 |
| Southeast | 741 | 706 | −35 |
| South | 622 | 716 | 94 |
| Southwest | 559 | 752 | 193 |
| west | 634 | 822 | 188 |
| Northwest | 720 | 851 | 131 |
| Land Use Types | Gully Number in 2012 | Gully Number in 2022 | Gully Change |
|---|---|---|---|
| Transportation land | 51 | 118 | 67 |
| Forest | 732 | 941 | 207 |
| Human-disturbed land | 7 | 4 | −3 |
| Construction land | 50 | 53 | 3 |
| Cultivated land | 4873 | 4730 | −143 |
| Grassland | 343 | 1180 | 837 |
| Vegetation Coverage | Gully Number in 2012 | Gully Number in 2022 | Gully Change |
|---|---|---|---|
| Low | 5012 | 5036 | 24 |
| Medium-low | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| Medium | 1 | 9 | 8 |
| Medium-high | 14 | 24 | 10 |
| High | 1029 | 1956 | 927 |
| Soil Type | Precipitation | Slope Interval | Slope Aspect | Land Use Type | Vegetation Coverage | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| soil type | 0.16 | |||||
| precipitation | 0.17 | 0.06 | ||||
| slope interval | 0.22 | 0.12 | 0.05 | |||
| slope aspect | 0.23 | 0.11 | 0.19 | 0.03 | ||
| land use type | 0.24 | 0.14 | 0.18 | 0.17 | 0.09 | |
| vegetation coverage | 0.21 | 0.11 | 0.11 | 0.11 | 0.15 | 0.06 |
| Soil Type | Precipitation | Slope Interval | Slope Aspect | Land Use Type | Vegetation Coverage | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| soil type | 0.29 | |||||
| precipitation | 0.38 | 0.28 | ||||
| slope interval | 0.31 | 0.32 | 0.03 | |||
| slope aspect | 0.30 | 0.30 | 0.11 | 0.00 | ||
| land use type | 0.30 | 0.32 | 0.13 | 0.07 | 0.02 | |
| vegetation coverage | 0.33 | 0.33 | 0.12 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.05 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ren, J.; Wang, L.; Xu, Z.; Xu, J.; Zheng, X.; Chen, Q.; Li, K. Study on the Spatio-Temporal Distribution and Influencing Factors of Soil Erosion Gullies at the County Scale of Northeast China. Sustainability 2025, 17, 6966. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17156966
Ren J, Wang L, Xu Z, Xu J, Zheng X, Chen Q, Li K. Study on the Spatio-Temporal Distribution and Influencing Factors of Soil Erosion Gullies at the County Scale of Northeast China. Sustainability. 2025; 17(15):6966. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17156966
Chicago/Turabian StyleRen, Jianhua, Lei Wang, Zimeng Xu, Jinzhong Xu, Xingming Zheng, Qiang Chen, and Kai Li. 2025. "Study on the Spatio-Temporal Distribution and Influencing Factors of Soil Erosion Gullies at the County Scale of Northeast China" Sustainability 17, no. 15: 6966. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17156966
APA StyleRen, J., Wang, L., Xu, Z., Xu, J., Zheng, X., Chen, Q., & Li, K. (2025). Study on the Spatio-Temporal Distribution and Influencing Factors of Soil Erosion Gullies at the County Scale of Northeast China. Sustainability, 17(15), 6966. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17156966






