A Spatiotemporal Dynamic Evaluation of Soil Erosion at a Monthly Scale and the Identification of Driving Factors in Hainan Island Based on the Chinese Soil Loss Equation Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
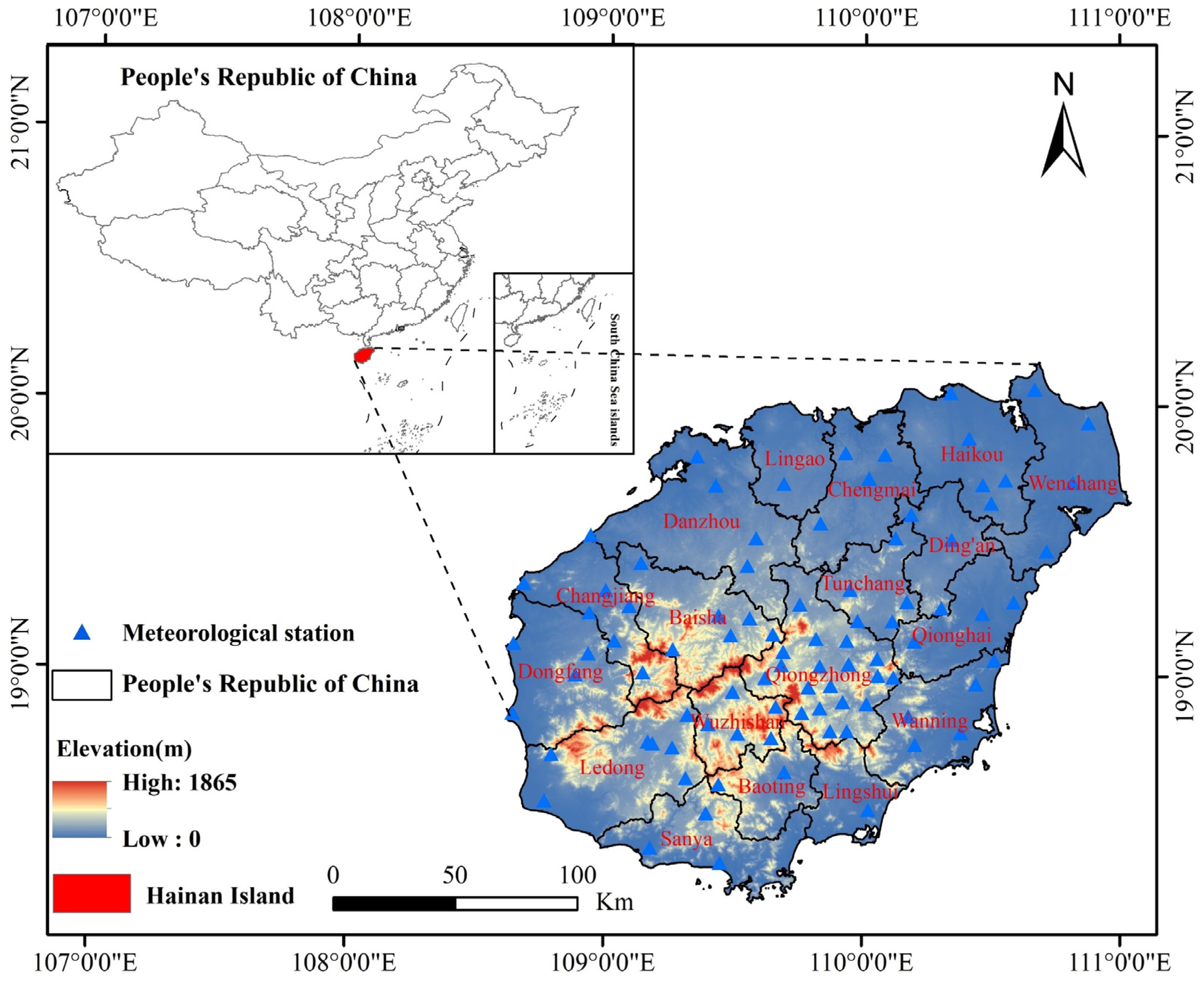
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. CSLE Model
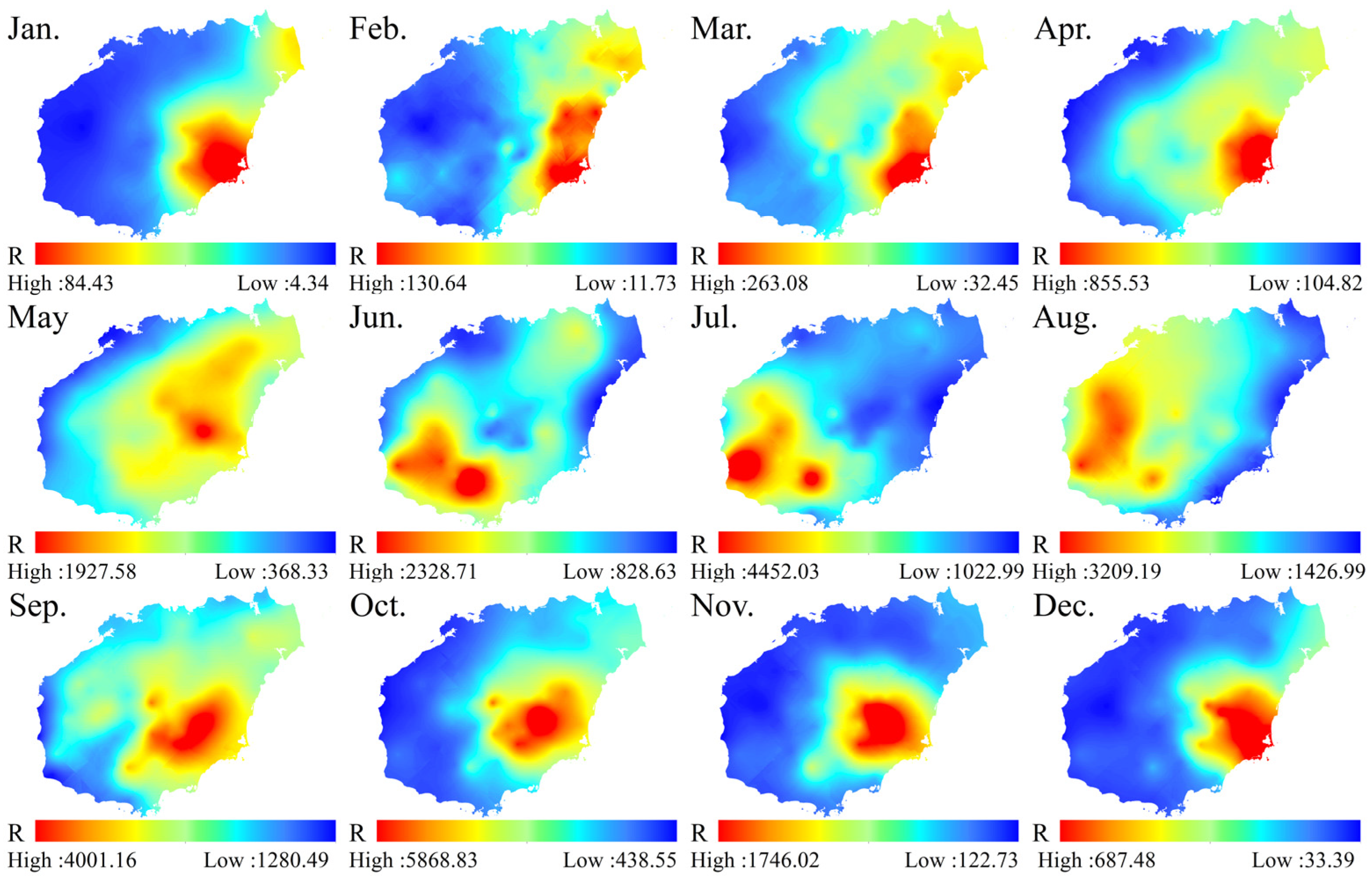
2.4. Rainfall Erosivity Factor (R)
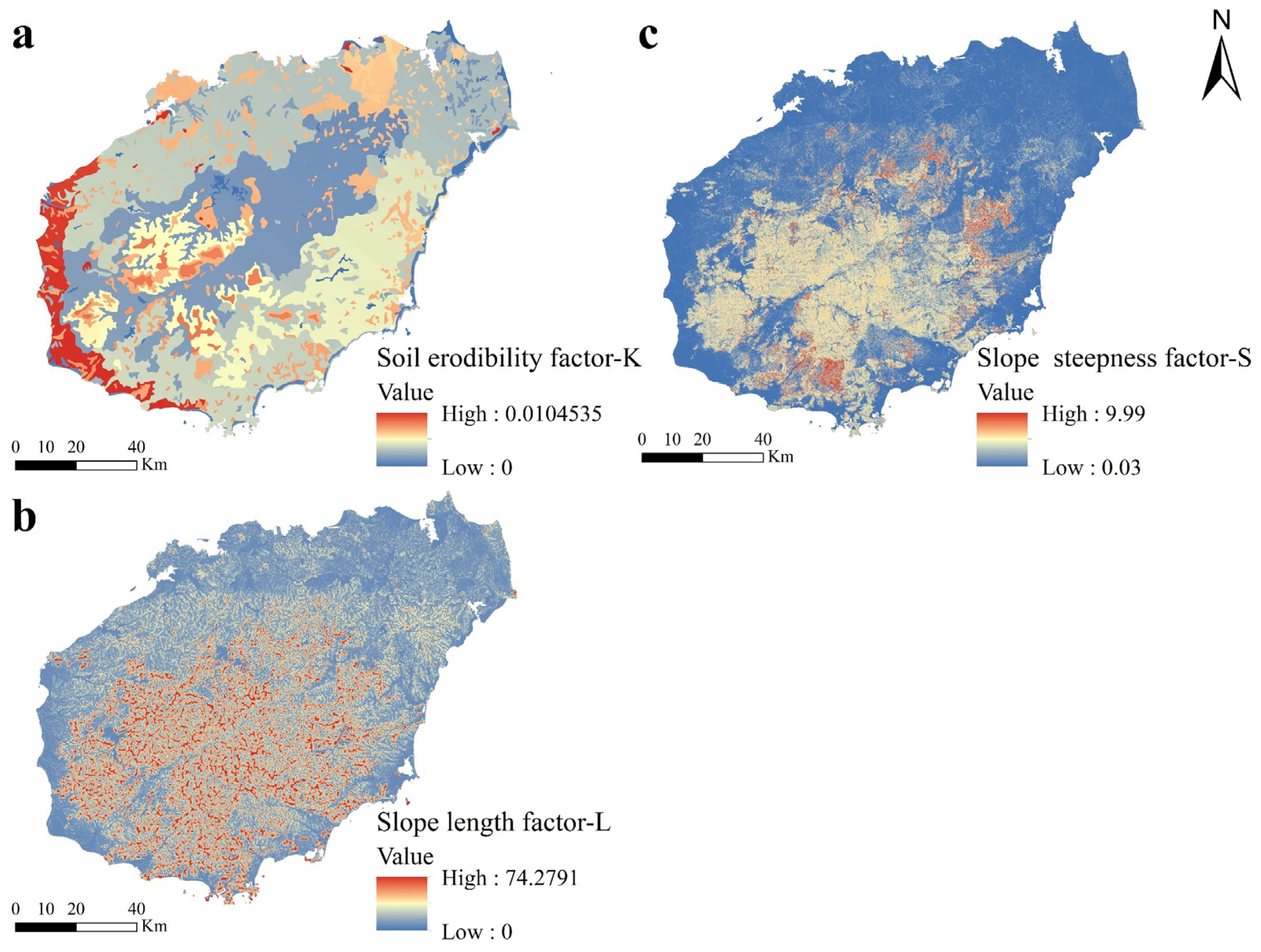
2.5. Soil Erodibility Factor (K)
2.6. Slope Length Factor (L) and Slope Steepness Factor (S)
2.7. Vegetation Cover and Biological Practices Factor (B)
2.8. Engineering Practices Factor (E) and Tillage Practices Factor (T)
2.9. Importance of Random Forest Calculation of Erosion Factors
2.10. Decomposition Analysis of LMDI Model Change
3. Results
3.1. Spatial Layout of Each Static Element in the CSLE Model
3.2. Spatial Distribution of Dynamic Factors in CSLE Model
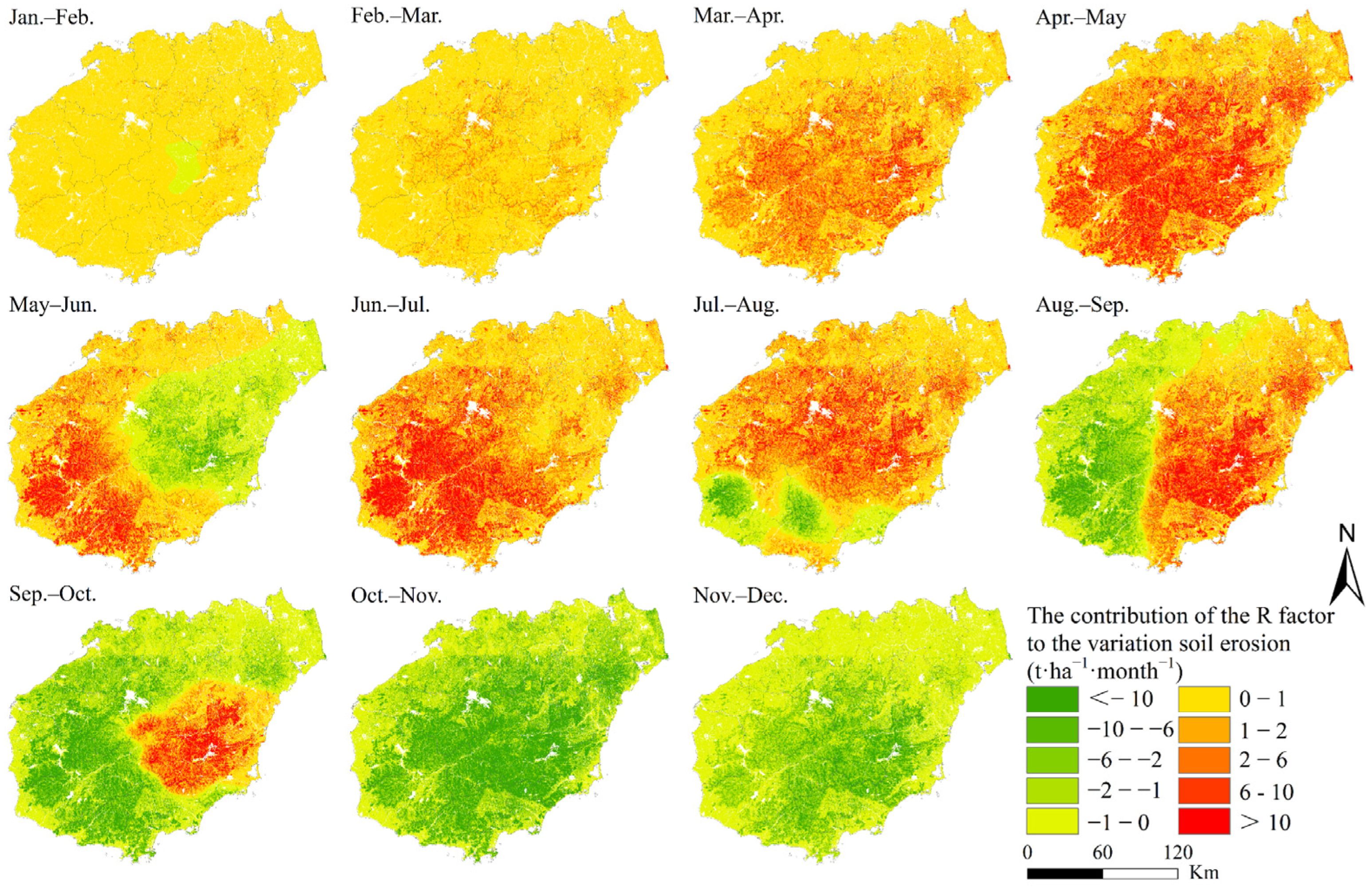
3.2.1. Rainfall Erosivity Factor (R)
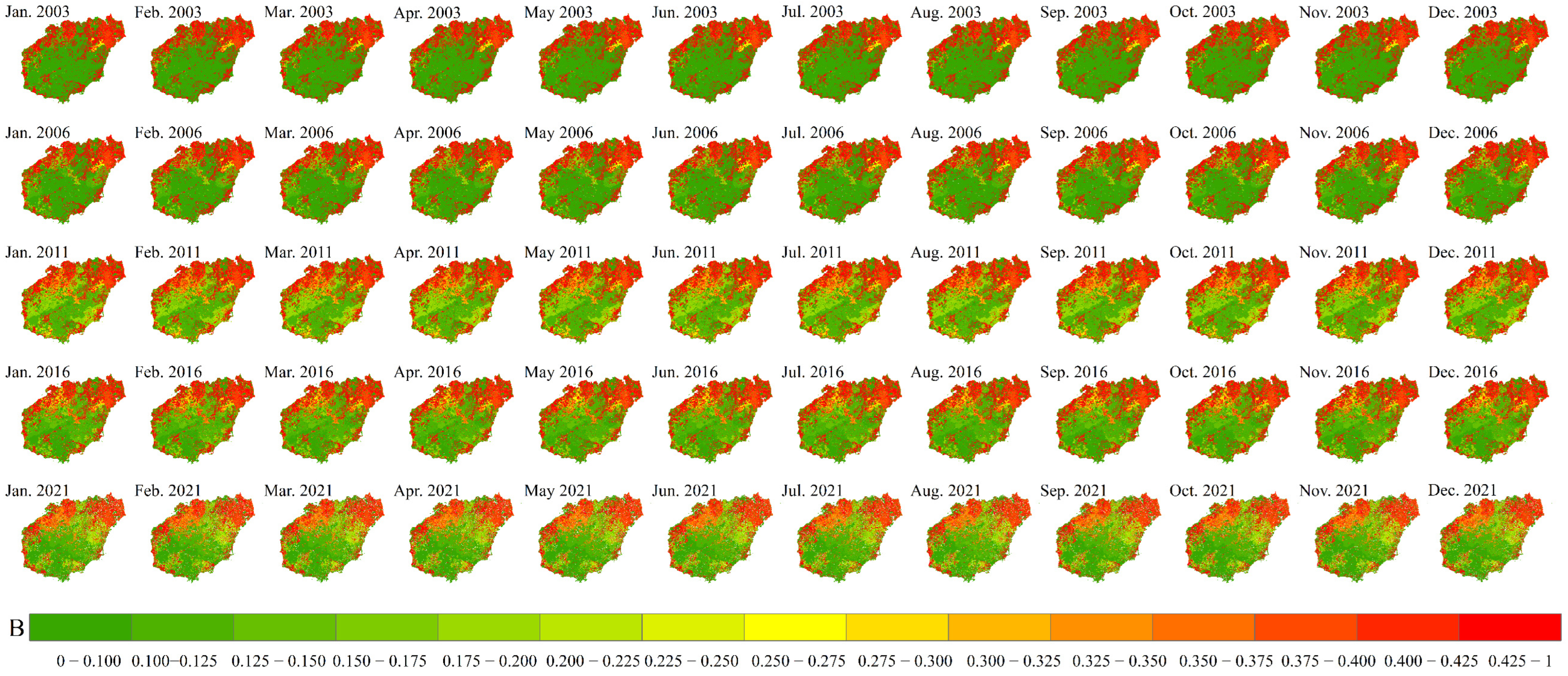
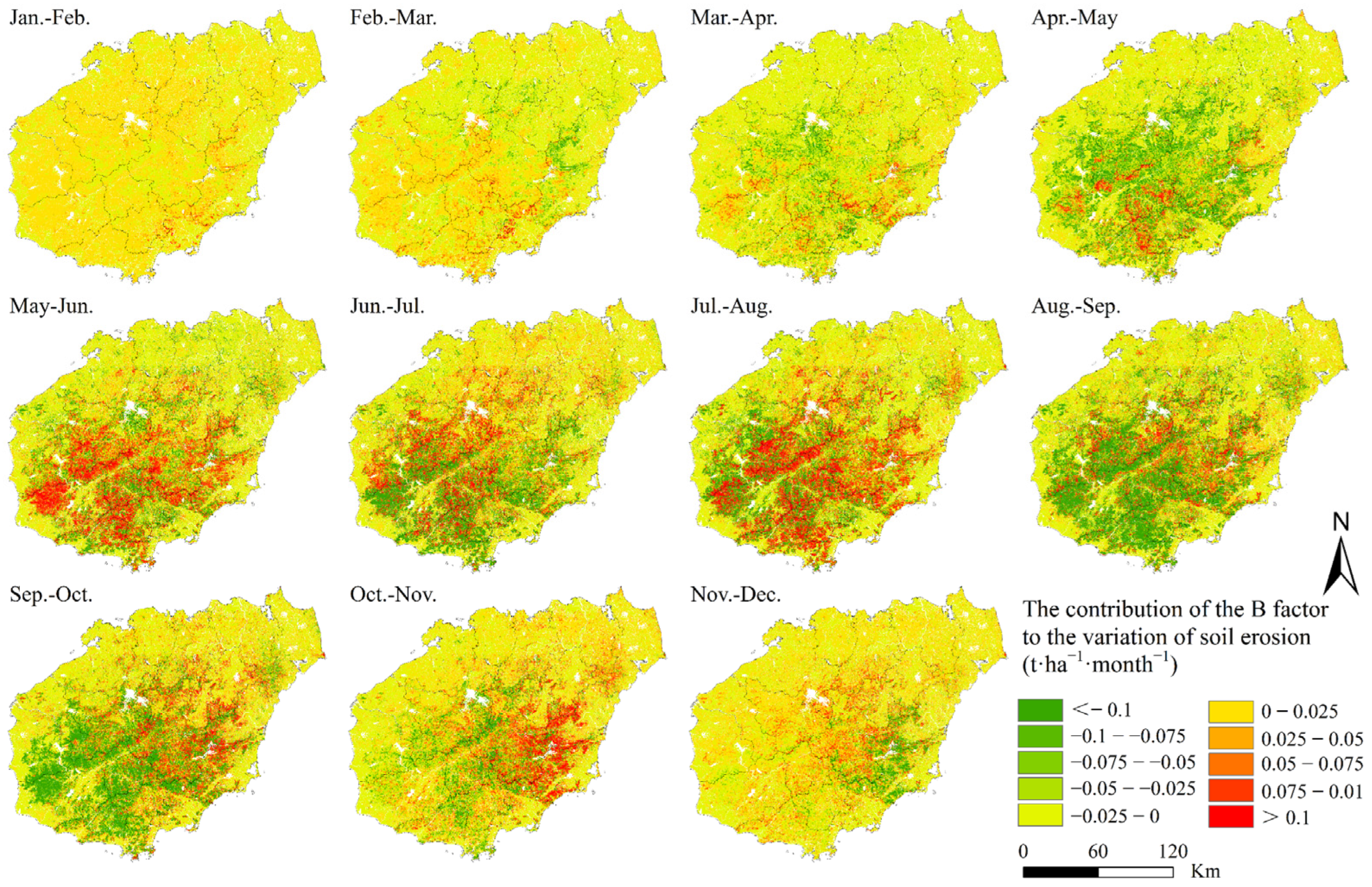
3.2.2. Vegetation Cover and Biological Practice Factor (B)
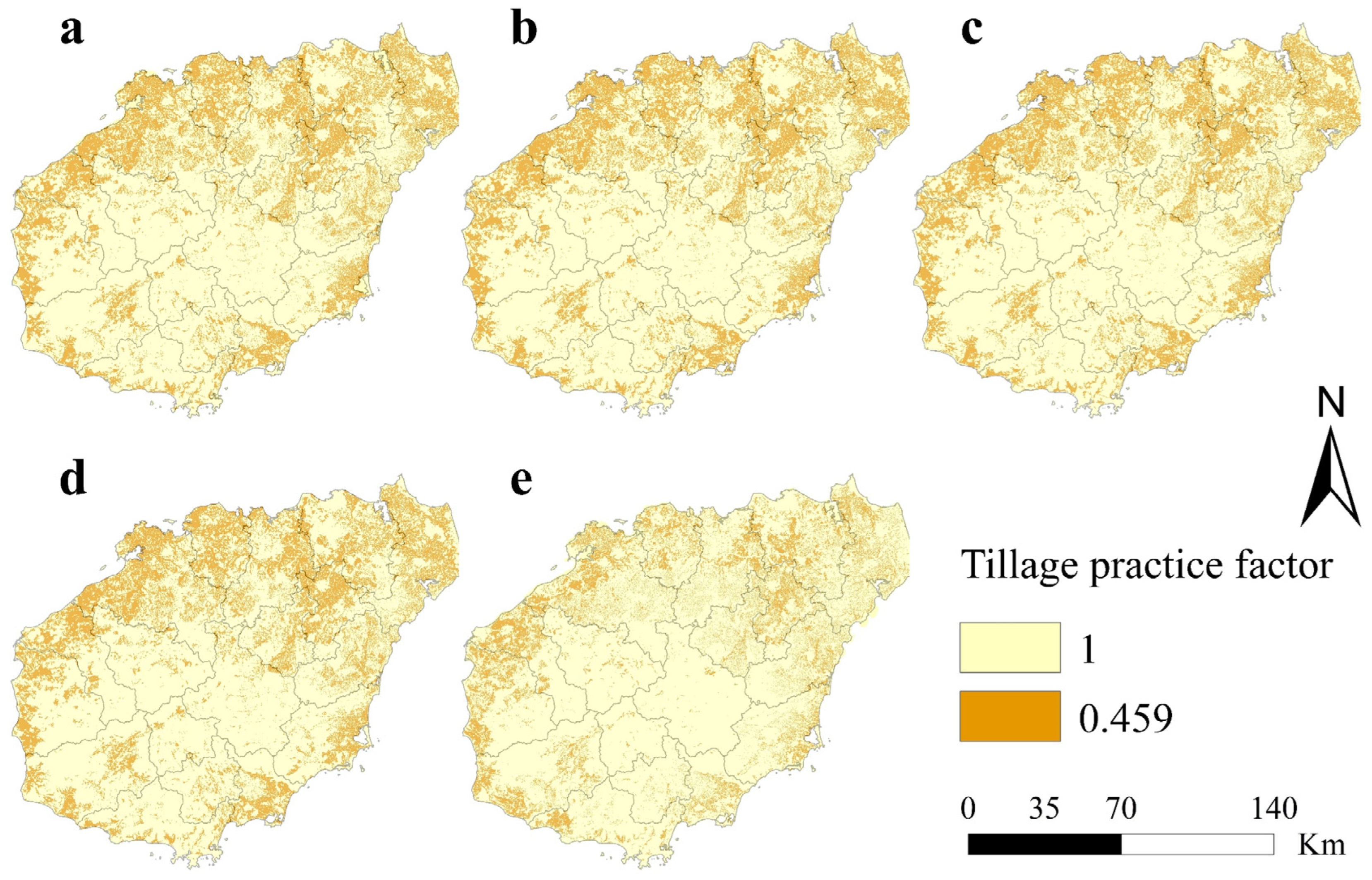
3.2.3. Tillage Practice Factor (T)
3.3. Average Monthly Soil Erosion in Hainan Island and Its Variation Trend
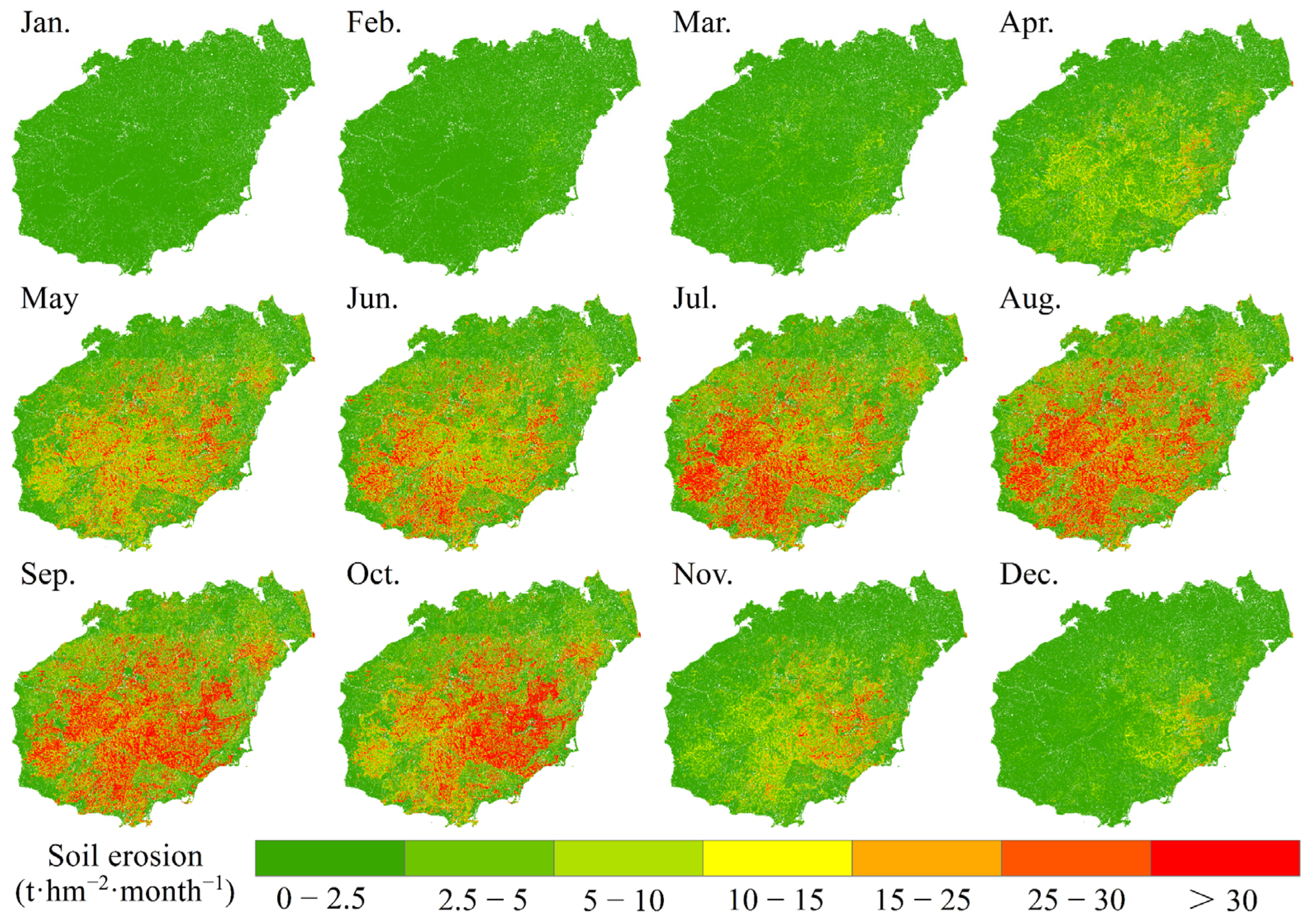
3.3.1. Average Monthly Soil Erosion in Hainan Island
3.3.2. Regularity of Terrain, Slope, and Land Use/Cover on Monthly Erosion
3.4. Identification of Main Controlling Factors of Monthly Soil Erosion
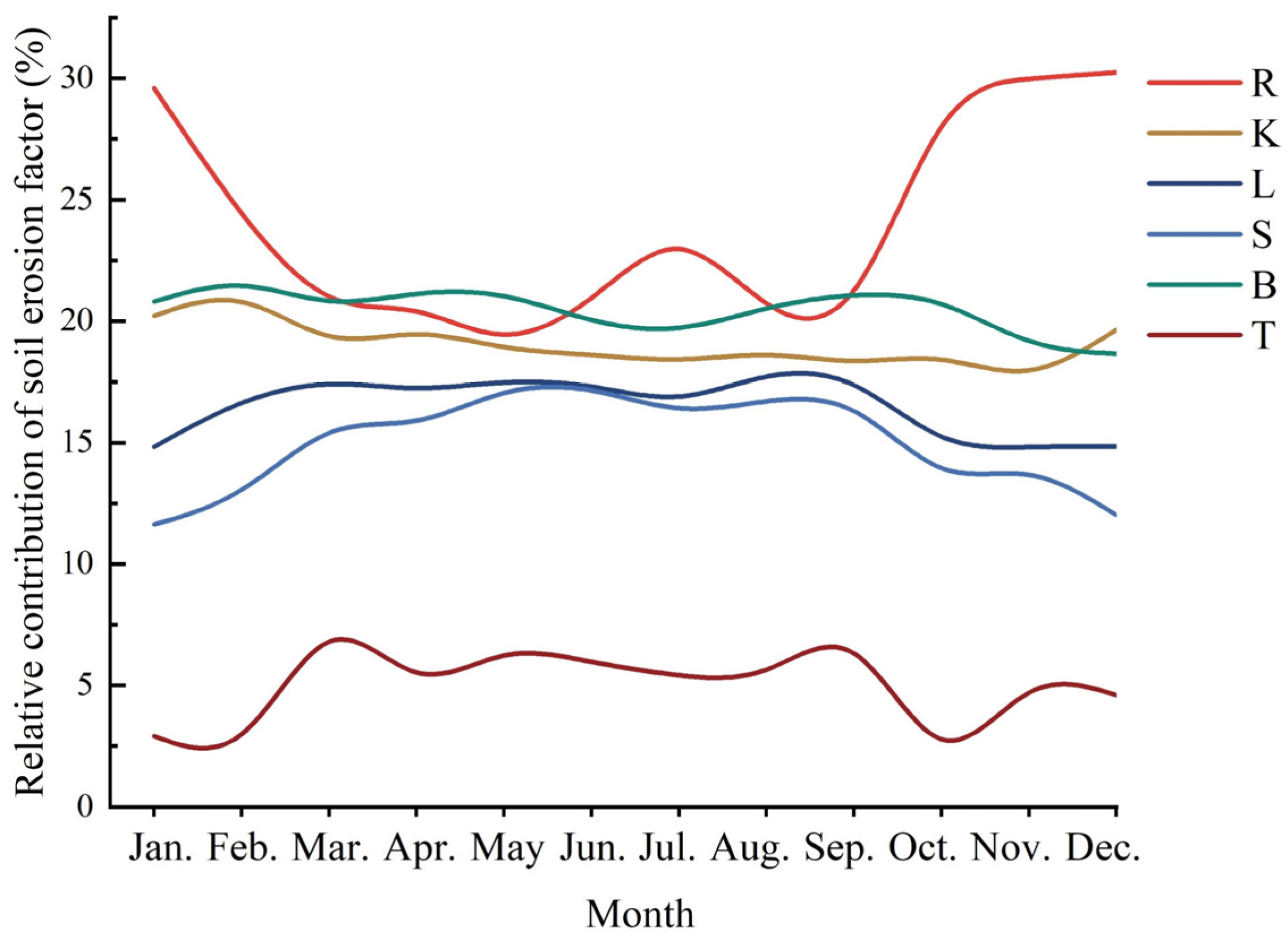
3.4.1. Relative Importance of Soil Erosion Factors
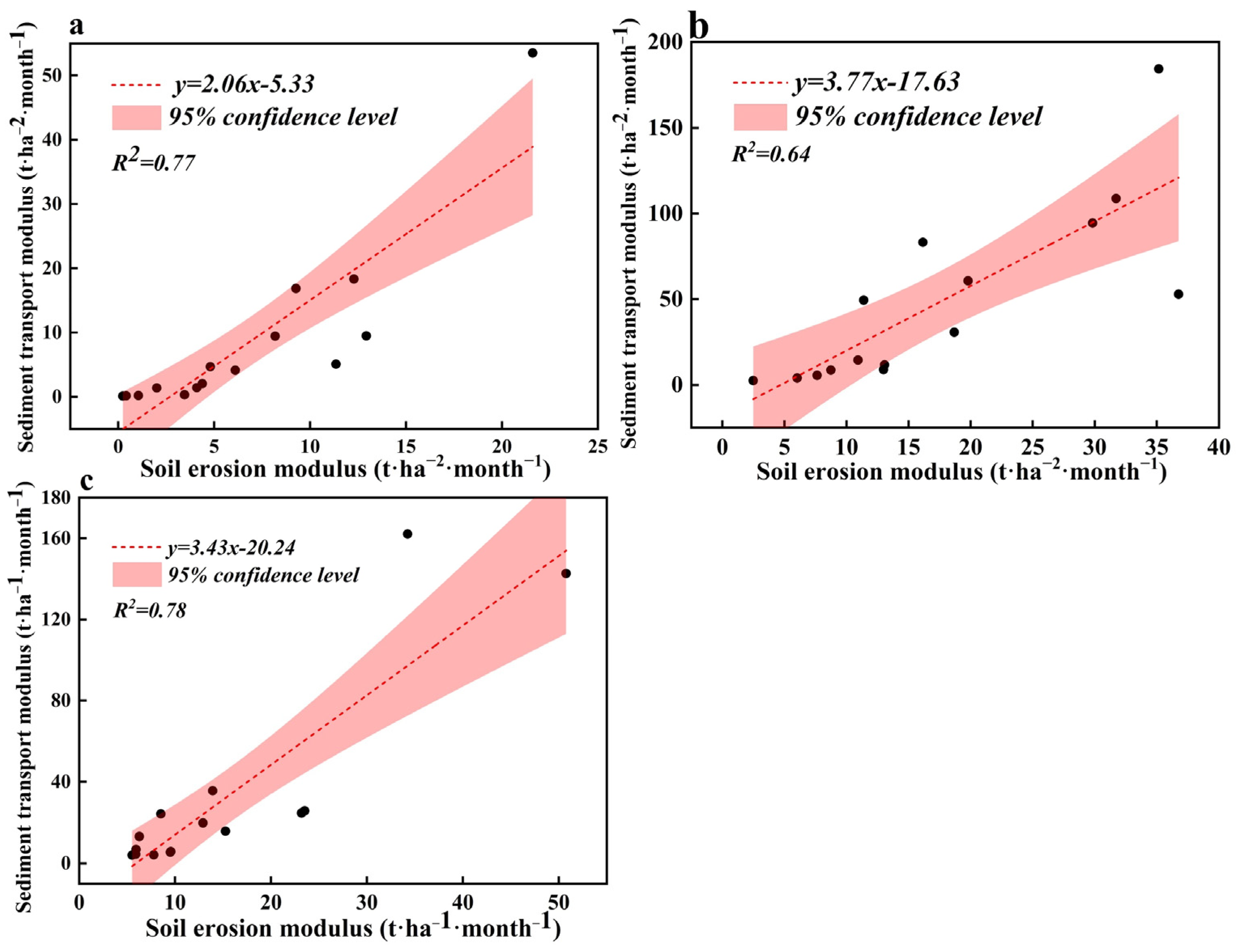
3.4.2. Relationship Between Key Drivers, Including Precipitation and Vegetation Changes, and Soil Erosion
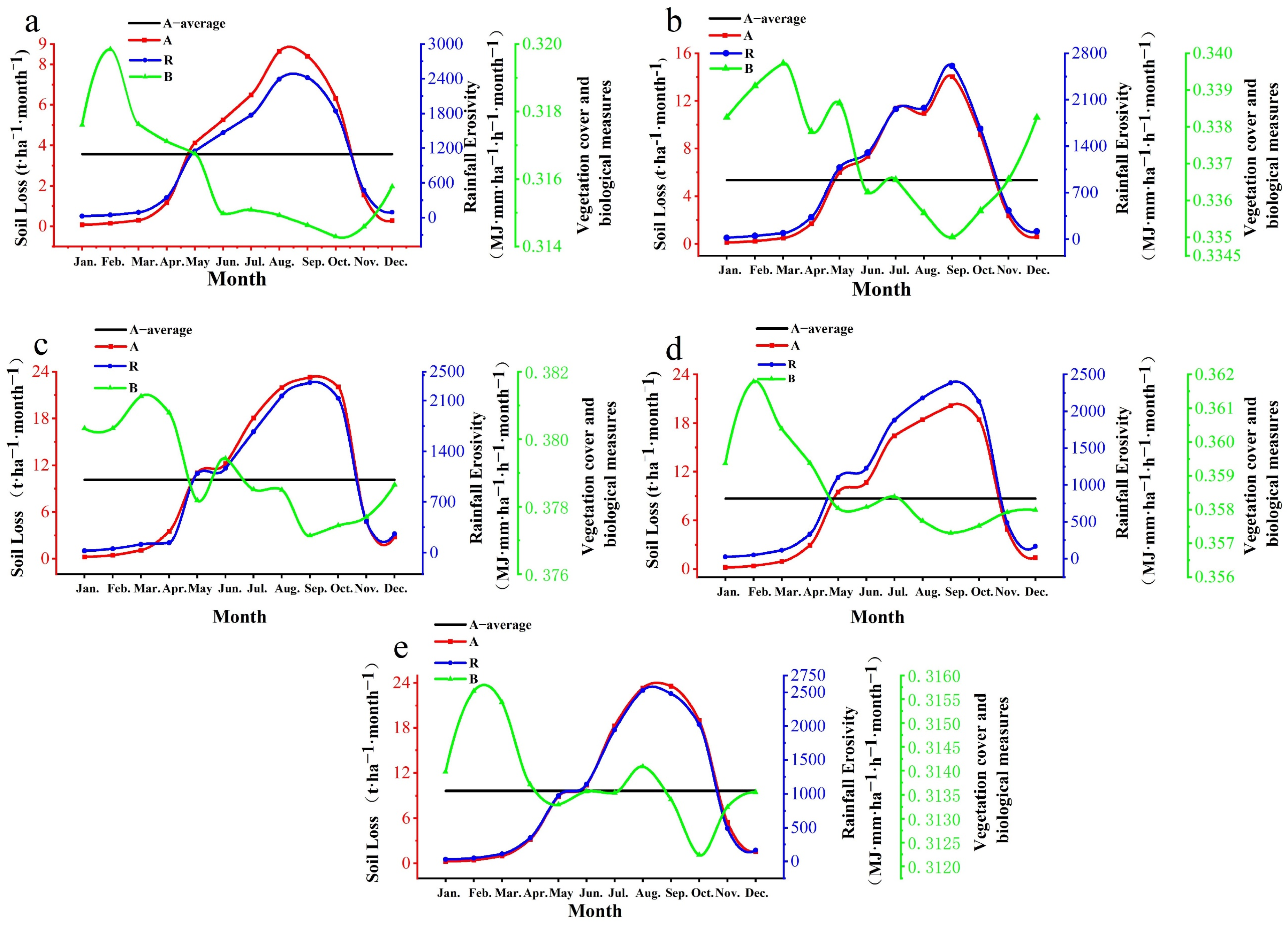
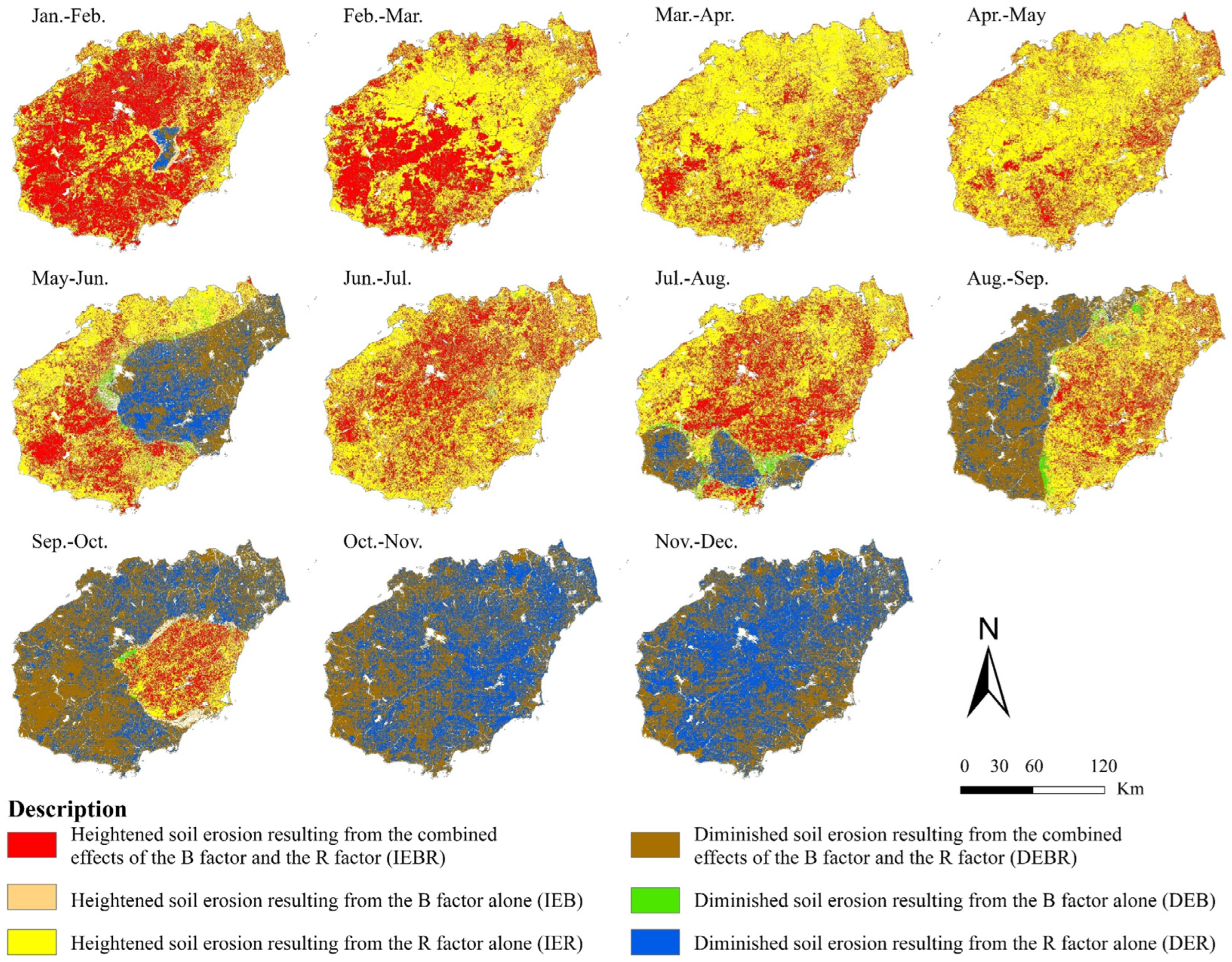
3.4.3. Impact of Driving Factors on Monthly Erosion Variation
4. Discussion
4.1. Availability of the CSLE Model
4.2. Identify Periods Prone to Soil Erosion
4.3. Response of Monthly Soil Erosion to Different Topography and Land Use/Cover
4.4. Suggestions Based on the Factors That Influence Soil Erosion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Panagos, P.; Ballabio, C.; Borrelli, P.; Meusburger, K.; Klik, A.; Rousseva, S.; Tadic, M.P.; Michaelides, S.; Hrabalíková, M.; Olsen, P.; et al. Rainfall erosivity in Europe. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 511, 801–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borrelli, P.; Robinson, D.A.; Fleischer, L.R.; Lugato, E.; Ballabio, C.; Alewell, C.; Meusburger, K.; Modugno, S.; Schutt, B.; Ferro, V.; et al. An assessment of the global impact of 21st century land use change on soil erosion. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gianinetto, M.; Aiello, M.; Vezzoli, R.; Polinelli, F.N.; Rulli, M.C.; Chiarelli, D.D.; Bocchiola, D.; Ravazzani, G.; Soncini, A. Future Scenarios of Soil Erosion in the Alps under Climate Change and Land Cover Transformations Simulated with Automatic Machine Learning. Climate 2020, 8, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montanarella, L.; Pennock, D.J.; McKenzie, N.; Badraoui, M.; Chude, V.; Baptista, I.; Mamo, T.; Yemefack, M.; Aulakh, M.S.; Yagi, K.; et al. World’s soils are under threat. Soil 2016, 2, 79–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Jiang, X.; Shi, X.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Cai, W. Spatiotemporal evolution characteristics of soil erosion and its driving mechanisms—A case Study: Loess Plateau, China. CATENA 2024, 242, 108075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wischmeier, W.H.; Smith, D.D. Predicting rainfall-erosion losses from cropland east of the Rocky Mountains. In Agricultural Handbook; Agricultural Research Service, US Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 1965; Volume 282. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y. Spatiotemporal Analysis of the Soil Erosion Based on CSLE and CA-Markov Model: A Case Study in the Laohekou City. Master’s Thesis, Central China Normal University, Wuhan, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Borrelli, P.; Alewell, C.; Alvarez, P.; Anache, J.A.A.; Baartman, J.; Ballabio, C.; Bezak, N.; Biddoccu, M.; Cerdà, A.; Chalise, D.; et al. Soil erosion modelling: A global review and statistical analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 780, 146494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, M.; Sun, R.; Chen, L. Effects of soil conservation techniques on water erosion control: A global analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 645, 753–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, X.; Deng, X.Z. Current soil erosion assessment in the Loess Plateau of China: A mini-review. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 276, 123091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vente, J.d.; Poesen, J. Predicting soil erosion and sediment yield at the basin scale: Scale issues and semi-quantitative models. Earth Sci. Rev. 2005, 71, 95–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirci, A.; Karaburun, A. Estimation of soil erosion using RUSLE in a GIS framework: A case study in the Buyukcekmece Lake watershed, northwest Turkey. Environ. Earth Sci. 2012, 66, 903–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karamesouti, M.; Petropoulos, G.P.; Papanikolaou, I.D.; Kairis, O.; Kosmas, K. Erosion rate predictions from PESERA and RUSLE at a Mediterranean site before and after a wildfire: Comparison & implications. Geoderma 2016, 261, 44–58. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, B.; Zhang, K.; Yun, X. An Empirical Soil Loss Equation. In Proceedings of the 12th ISCO Conference, Beijing, China, 26–31 May 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, B.; Nearing, M.; Risse, M. Slope Gradient Effects on Soil Loss for Steep Slopes. Trans. ASAE 1994, 37, 1835–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.L.; Liu, B.Y.; He, L.; Dong, L.X.; Yin, B.; Zhao, Y.E. Response of soil erosion to vegetation and terrace changes in a small watershed on the Loess Plateau over the past 85 years. Geoderma 2024, 443, 116837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.X.; Wang, N.A.; Wang, Y.F.; Wang, L.H.; Hu, A.P.; Zhang, D.Y.; Su, X.B.; Chen, J.H. Responses of soil erosion to land-use changes in the largest tableland of the Loess Plateau. Land Degrad. Dev. 2021, 32, 3598–3613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, W.E.; Shen, Z.H.; Duan, X.W. Spatiotemporal patterns and drivers of soil erosion in Yunnan, Southwest China: RULSE assessments for recent 30 years and future predictions based on CMIP6. CATENA 2023, 220, 106703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Guo, J.W.; Zhang, X.P.; Liu, B.Y.; Guzman, G.; Gomeza, J.A. Vegetation restoration dominated the attenuated soil loss rate on the Loess Plateau, China over the last 50 years. CATENA 2023, 228, 07149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.H.; Cao, L.X.; Liu, B.Y.; Wu, Z.P.; Savabi, M.R. Effects of DEM grid size on predicting soil loss from small watersheds in China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 73, 2141–2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, X.W.; Bai, Z.W.; Rong, L.; Li, Y.B.; Ding, J.H.; Tao, Y.Q.; Li, J.X.; Li, J.S.; Wang, W. Investigation method for regional soil erosion based on the Chinese Soil Loss Equation and high-resolution spatial data: Case study on the mountainous Yunnan Province, China. CATENA 2020, 184, 104237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.H.; Huang, M.B.; Barbour, S.L. Storm-based CSLE that incorporates the estimated runoff for soil loss prediction on the Chinese Loess Plateau. Soil Tillage Res. 2018, 180, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.K.; Zhao, J.J.; Duan, X.W.; Tang, B.H.; Zuo, L.J.; Wang, X.; Guo, Q.K. Spatial Quantification of Cropland Soil Erosion Dynamics in the Yunnan Plateau Based on Sampling Survey and Multi-Source LUCC Data. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.G.; He, Y.H.; Tan, Q. Improvement of sediment yield index model through incorporating rainfall erosivity. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 38141–38156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Shi, H.; Yang, X. Estimating the CSLE Biological Conservation Measures’ B-Factor Using Google Earth’s Engine. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.Y.; Zhang, J.; Sun, Z.Y.; Yu, J.A.; Liu, W.J.; Yu, R.; Wang, P. Attribution analysis of land degradation in Hainan Island based on geographical detector. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 141, 109119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, T.; Yang, S.Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhou, Q. Coupling coordination degree measurement and spatiotemporal heterogeneity between economic development and ecological environment—Empirical evidence from tropical and subtropical regions of China. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 244, 118739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, J.; Zhang, L.; Wu, T.; Chen, X.; Li, Y.; Chen, Z. Spatial-temporal evolution and driving factors of water yield in three major drainage basins of Hainan Island based on land use change. Front. For. Glob. Change 2023, 6, 1131262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.; Li, L.J.; Liu, Q.; Wang, X.; Li, Y.D.; Hui, D.F.; Jian, S.G.; Wang, J.; Yang, H.; Lu, H.F.; et al. Spatial and Temporal Patterns of Carbon Storage in Forest Ecosystems on Hainan Island, Southern China. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, 108163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, R.; Wu, Z.X.; Chen, B.Q.; Yang, C.; Qi, D.L.; Lan, G.Y.; Fraedrich, K. Effects of land-use change on eco-environmental quality in Hainan Island, China. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 109, 105777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Wang, L.l.; Cao, J.h.; Dai, S.p.; Li, H.; Xie, Z.; Li, M. NDVl Variables and lts Relationship with Temperature and Precipitation in Hainan Island from 2001 to 2014 Basedon MODIS NDVI. Southwest China J. Agric. Sci. 2018, 31, 856–861. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Lu, X.; Chen, J.; Guo, J.; Qi, S. Variation characteristics of rainfall erosivity in tropical China and its impact on river sediment load. Front. Environ. Sci. 2023, 11, 1084503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.F.; Hua, L.; Tang, Q.; Liu, L.; Cai, C.F. Evaluation of monthly-scale soil erosion spatio-temporal dynamics and identification of their driving factors in Northeast China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 150, 110187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, R.M.; Alves, W.d.S.; Marcionilio, S.M.L.d.O.; De Moura, D.M.B.; Oliveira, D.M.d.S. Soil losses related to land use and rainfall seasonality in a watershed in the Brazilian Cerrado. J. S. Am. Earth Sci. 2022, 119, 104020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polykretis, C.; Alexakis, D.D.; Grillakis, M.G.; Manoudakis, S. Assessment of Intra-Annual and Inter-Annual Variabilities of Soil Erosion in Crete Island (Greece) by Incorporating the Dynamic “Nature” of R and C-Factors in RUSLE Modeling. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphrey, O.S.; Osano, O.; Aura, C.M.; Marriott, A.L.; Dowell, S.M.; Blake, W.H.; Watts, M.J. Evaluating spatio-temporal soil erosion dynamics in the Winam Gulf catchment, Kenya for enhanced decision making in the land-lake interface. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 815, 151975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, S.; Alewell, C.; Meusburger, K. Monthly RUSLE soil erosion risk of Swiss grasslands. J. Maps 2019, 15, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.L.; Chen, L.; Peng, W.X.; Yu, J.H.; He, J.K.; Jiang, H.S. Temperature and historical land connectivity jointly shape the floristic relationship between Hainan Island and the neighbouring landmasses. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 769, 144629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enmin, R.; Yi, X.; Zhiyun, O.; Hua, Z. Spatial characteristics of soil conservation service and its impact factors in Hainan Island. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2013, 33, 746–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagos, P.; Karydas, C.G.; Gitas, I.Z.; Montanarella, L. Monthly soil erosion monitoring based on remotely sensed biophysical parameters: A case study in Strymonas river basin towards a functional pan-European service. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2012, 5, 461–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Yin, S.-Q.; Liu, B.-Y.; Nearing, M.A.; Zhao, Y. Models for estimating daily rainfall erosivity in China. J. Hydrol. 2016, 535, 547–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, J.R.; Renard, K.G.; Dyke, P.T. EPIC: A new method for assessing erosion’s effect on soil productivity. J. Soil Water Conserv. 1983, 38, 381. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, S.P.; Jing, C.W.; Coles, N.A.; Chaplot, V.; Moore, N.J.; Wu, J.P. Evaluating DEM source and resolution uncertainties in the Soil and Water Assessment Tool. Stochastic Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2013, 27, 209–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Random Forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ang, B.W. Decomposition analysis for policymaking in energy: Which is the preferred method? Energy Policy 2004, 32, 1131–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ang, B. The LMDI Approach to Decomposition Analysis: A Practical Guide. Energy Policy 2005, 33, 867–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ang, B.W. LMDI decomposition approach: A guide for implementation. Energy Policy 2015, 86, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koulouri, M.; Giourga, C. Land abandonment and slope gradient as key factors of soil erosion in Mediterranean terraced lands. CATENA 2007, 69, 274–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.; Wang, H.; Fu, B.; Zhu, L.; Wang, Y.; Li, Z. Effects of plant diversity on soil erosion for different vegetation patterns. CATENA 2016, 147, 632–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.F.; Liu, W.J.; Jiang, X.J.; Wu, J.E. Effects of rubber-based agroforestry systems on soil aggregation and associated soil organic carbon: Implications for land use. Geoderma 2017, 299, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Yuan, X.; Lu, E.; Yang, B.; Wang, H.; Du, Y.; Singh, A.K.; Liu, W. Soil splash erosion: An overlooked issue for sustainable rubber plantation in the tropical region of China. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2023, 11, 30–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, X.L.; Qiu, J.L.; Cao, B.W.; Cai, S.R.; Niu, K.L.; Yang, X.K. Mapping Soil Erosion Dynamics (1990–2020) in the Pearl River Basin. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.P.; Zhang, M.F.; Liu, S.R.; Sun, P.S.; Yin, L.H.; Yang, T.L.; Li, Y.D.; Li, Q.; Wei, X.H. The Hydrological Impact of Extreme Weather-Induced Forest Disturbances in a Tropical Experimental Watershed in South China. Forests 2018, 9, 734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Wang, Y.; He, Y.; Zhu, L.; Xue, S.; Liang, X.; Ye, C. Soil Erosion Characteristics in Tropical Island Watersheds Based on CSLE Model: Discussion of Driving Mechanisms. Land 2024, 13, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, F.M.; Yang, W.C.; Fu, J.X.; Li, Z. Effects of vegetation and climate on the changes of soil erosion in the Loess Plateau of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 773, 145514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.Q.; Sun, B.P.; Yu, X.X.; Xin, Z.B.; Jia, G.D. The driver-pattern-effect connection of vegetation dynamics in the transition area between semi-arid and semi-humid northern China. CATENA 2020, 194, 104713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baiamonte, G.; Minacapilli, M.; Novara, A.; Gristina, L. Time Scale Effects and Interactions of Rainfall Erosivity and Cover Management Factors on Vineyard Soil Loss Erosion in the Semi-Arid Area of Southern Sicily. Water 2019, 11, 978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.J.; Yan, Y.J.; Dai, Q.H.; Yi, X.S.; Hu, Z.Y.; Cen, L.P. Spatial and temporal dynamics of rainfall erosivity in the karst region of southwest China: Interannual and seasonal changes. CATENA 2023, 221, 106763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, L.; Yu, K.X.; Li, Z.B.; Li, P.; Zhang, J.Z.; Wang, A.N.; Ma, L.; Xu, G.C.; Zhang, X. Temporal and spatial variation of rainfall erosivity in the Loess Plateau of China and its impact on sediment load. CATENA 2022, 210, 105931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Zhang, X.C.; Liu, B.Y. Effects of DEM resolutions on soil erosion prediction using Chinese Soil Loss Equation. Geomorphology 2021, 384, 107706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, P.; Zhang, G.; Wang, C.; Chen, S.; Wan, Y. Variation in soil infiltration properties under different land use/cover in the black soil region of Northeast China. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2024, 12, 379–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.D.; Guo, J.C.; Chen, J.D.; Wu, H.; Zuo, Q.; Chen, Y.Z.; Lai, J.L.; Liu, S.D.; Wang, M.Y.; Zhang, P.; et al. Study on Functional Effectiveness of Soil and Water Conservation Measures in Rubber Plantations on Hainan Island. Forests 2024, 15, 1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; He, Y.; Tan, Q.; Zheng, Y. Land-use simulation for synergistic pollution and carbon reduction: Scenario analysis and policy implications. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 356, 120603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Wang, H.; Zheng, F. Temporal and Spatial Variations of Vegetation Phenology in the Three Provinces (Regions) of South China from 2001 to 2020. J. Trop. Subtrop. Bot. 2024, 32, 330–338. [Google Scholar]
- Li, G.; Kou, W.; Chen, B.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Yuan, T.; Ma, J.; Sun, R.; Li, Y. Spatio-temporal changes of rubber plantations in Hainan Island over the past 30 years. J. Nanjing For. Univ. 2023, 47, 189–198. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Tan, Z.H.; Zhang, Y.P.; Song, Q.H.; Liu, W.J.; Deng, X.B.; Tang, J.W.; Deng, Y.; Zhou, W.J.; Yang, L.Y.; Yu, G.R.; et al. Rubber plantations act as water pumps in tropical China. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2011, 38, L24406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Fu, R.; Cheng, S.; Qiao, D.; Hu, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Dai, L. Effects of the conversion of natural tropical rainforest to monoculture rubber plantations on soil hydrological processes. J. Plant Ecol. 2024, 17, rtae021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SL 190-2007; Standards for Classification and Gradation of Soil Erosion. China Water & Power Press: Beijing, China, 2007.
- Feng, A.; Qiubo, C.; Guishui, X.; Weifu, L.; Xianhai, Z. Summary on Hydroecological Effects of Artificial Rubber Plantations. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull. 2010, 26, 359–365. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, H. Spatial-Temporal Variation and Driving Factors of Soil Water Erosion in the Upper Reaches of the Yellow River Basin in Recent 40 Years. Master’s Thesis, Lanzhou University, Lanzhou, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, H.; Ko, C.; Ma, Y. Characteristics of Soil Erosion and Proposals for Prevention and Control Projects in Hainan Province. Pearl River 2017, 38, 31–33. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]




| Data | Source | Resolution |
|---|---|---|
| Rainfall data | Hainan Hydrology and Water Resources Survey Bureau | / |
| MODIS-MOD13Q1 product (provides the Normalized Difference Vegetation Index) | NASA (https://ladsweb.modaps.eosdis.nasa.gov/search, accessed on 23 August 2023) | 250 m |
| Digital Elevation Model (DEM) | Hainan Provincial Bureau of Surveying, Mapping and Geographic Information | 10 m |
| Land use | Data Center for Resources and Environment, Chinese Academy of Sciences (http://www.resdc.cn, accessed on 23 August 2023) | 30 m |
| Soil data | World Soil Database (HWSD) (https://www.trade.gov/harmonized-system-hs-codes, accessed on 13 January 2021) | 1000 m |
| Type | Value | Explanations |
|---|---|---|
| Wet rice field | 1 | Benefits related to soil and water conservation are observed through the T reaction |
| Irrigated land | 1 | |
| Dry land | 1 | |
| Urban building land | 0.01 | Similar to land that has 80% FVC |
| Rural building land | 0.025 | Similar to land that has 60% FVC |
| Other construction land | 0.01 | Similar to land that has 80% FVC |
| Rural road | 1 | Similar to land that has 60% FVC |
| Other important traffic areas | 0.01 | Similar to land that has 80% FVC |
| Waterbody and hydrological infrastructure | 0 | |
| Other land | 0 |
| Description | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| + | + | + | Heightened soil erosion resulting from the combined effects of the B factor and the R factor (IEBR) |
| + | − | Heightened soil erosion resulting from the B factor alone (IEB) | |
| − | + | Heightened soil erosion resulting from the R factor alone (IER) | |
| − | − | − | Diminished soil erosion resulting from the combined effects of the B factor and the R factor (DEBR) |
| − | + | Diminished soil erosion resulting from the B factor alone (DEB) | |
| + | − | Diminished soil erosion resulting from the R factor alone (DER) |
| Month/Year | 2003 | 2006 | 2011 | 2016 | 2021 | Average | Standard Deviation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| January | 24.35 | 22.97 | 23.93 | 25.03 | 30.38 | 25.33 | 2.92 |
| February | 45.36 | 50.69 | 54.10 | 51.59 | 51.18 | 50.58 | 3.20 |
| March | 91.25 | 93.17 | 112.64 | 113.53 | 111.44 | 104.41 | 11.18 |
| April | 346.76 | 328.99 | 337.31 | 335.15 | 347.35 | 339.11 | 7.87 |
| May | 1152.92 | 1080.97 | 1092.08 | 1102.84 | 972.69 | 1080.30 | 66.15 |
| June | 1469.09 | 1303.31 | 1165.09 | 1226.21 | 1138.21 | 1260.38 | 132.83 |
| July | 1773.39 | 1959.03 | 1672.66 | 1879.47 | 1943.51 | 1845.61 | 121.16 |
| August | 2391.26 | 1975.33 | 2163.33 | 2180.59 | 2527.65 | 2247.63 | 214.94 |
| September | 2418.24 | 2606.35 | 2350.08 | 2388.66 | 2480.67 | 2448.80 | 100.76 |
| October | 1839.35 | 1662.88 | 2134.32 | 2134.15 | 2024.45 | 1959.03 | 204.76 |
| November | 475.28 | 432.78 | 433.09 | 490.23 | 491.29 | 464.53 | 29.53 |
| December | 92.88 | 117.37 | 257.83 | 168.48 | 166.69 | 160.65 | 63.26 |
| Level | Altitude/m | Degree of Slope |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | <100 m | Flat slope |
| 2 | 100~300 | Gentle slope land |
| 3 | 300~500 | Ground of slope |
| 4 | 500~800 | Steep slope |
| 5 | 800~1000 | Sharp steep slope |
| 6 | >1000 | Dangerous slope land |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, S.; Zou, Y.; He, Y.; Xue, S.; Zhu, L.; Ye, C. A Spatiotemporal Dynamic Evaluation of Soil Erosion at a Monthly Scale and the Identification of Driving Factors in Hainan Island Based on the Chinese Soil Loss Equation Model. Sustainability 2025, 17, 2361. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17062361
Lin S, Zou Y, He Y, Xue S, Zhu L, Ye C. A Spatiotemporal Dynamic Evaluation of Soil Erosion at a Monthly Scale and the Identification of Driving Factors in Hainan Island Based on the Chinese Soil Loss Equation Model. Sustainability. 2025; 17(6):2361. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17062361
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Shengling, Yi Zou, Yanhu He, Shiyu Xue, Lirong Zhu, and Changqing Ye. 2025. "A Spatiotemporal Dynamic Evaluation of Soil Erosion at a Monthly Scale and the Identification of Driving Factors in Hainan Island Based on the Chinese Soil Loss Equation Model" Sustainability 17, no. 6: 2361. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17062361
APA StyleLin, S., Zou, Y., He, Y., Xue, S., Zhu, L., & Ye, C. (2025). A Spatiotemporal Dynamic Evaluation of Soil Erosion at a Monthly Scale and the Identification of Driving Factors in Hainan Island Based on the Chinese Soil Loss Equation Model. Sustainability, 17(6), 2361. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17062361







