Effect of Window Structure and Mounting on Sound Insulation: A Laboratory-Based Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Research Objectives and Questions
3. Materials and Methods
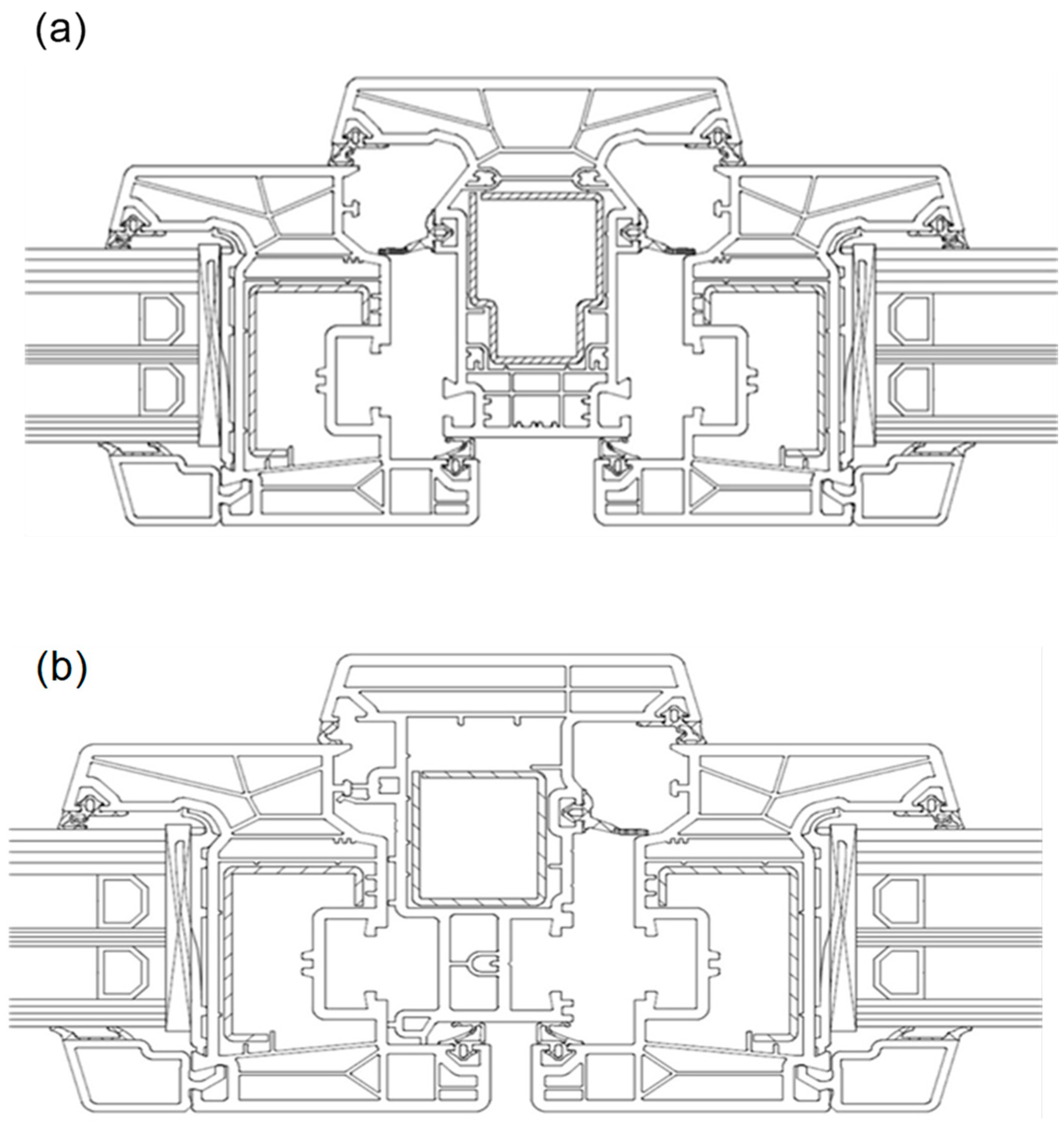
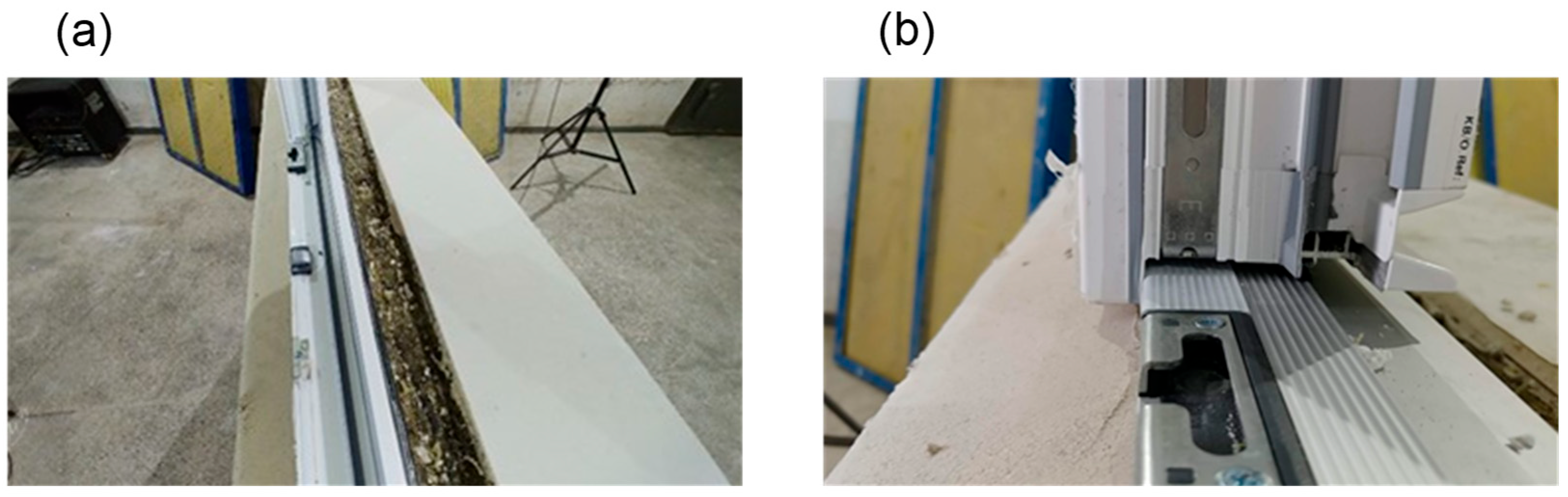
3.1. Window Characteristics
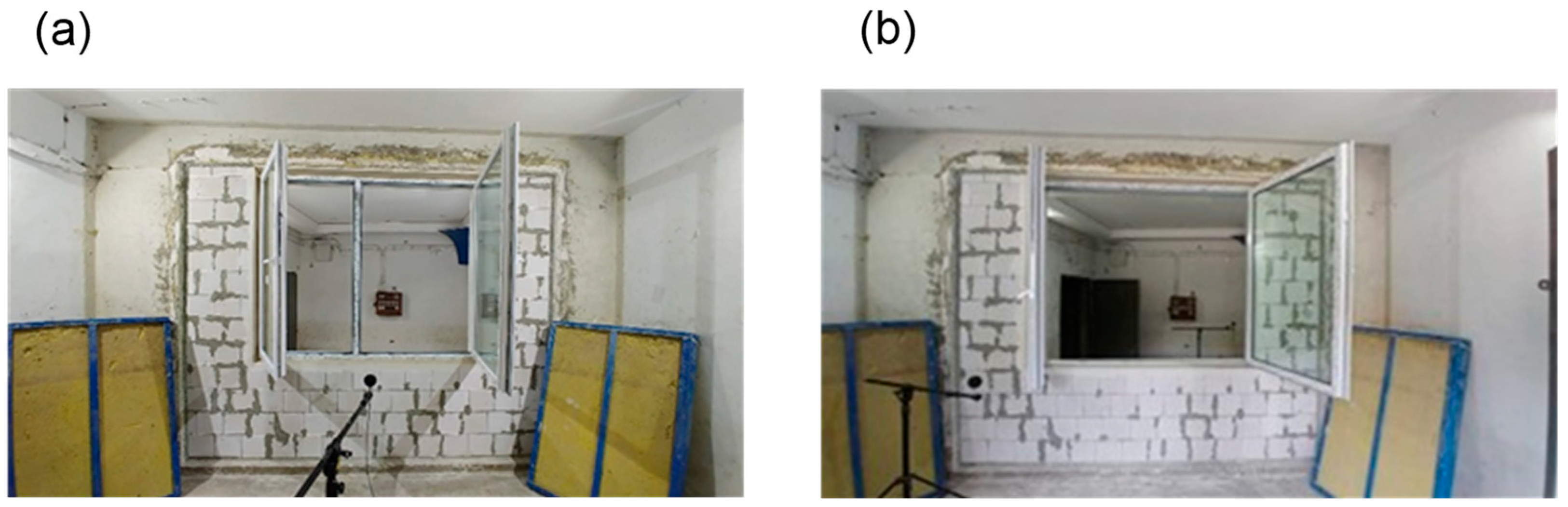
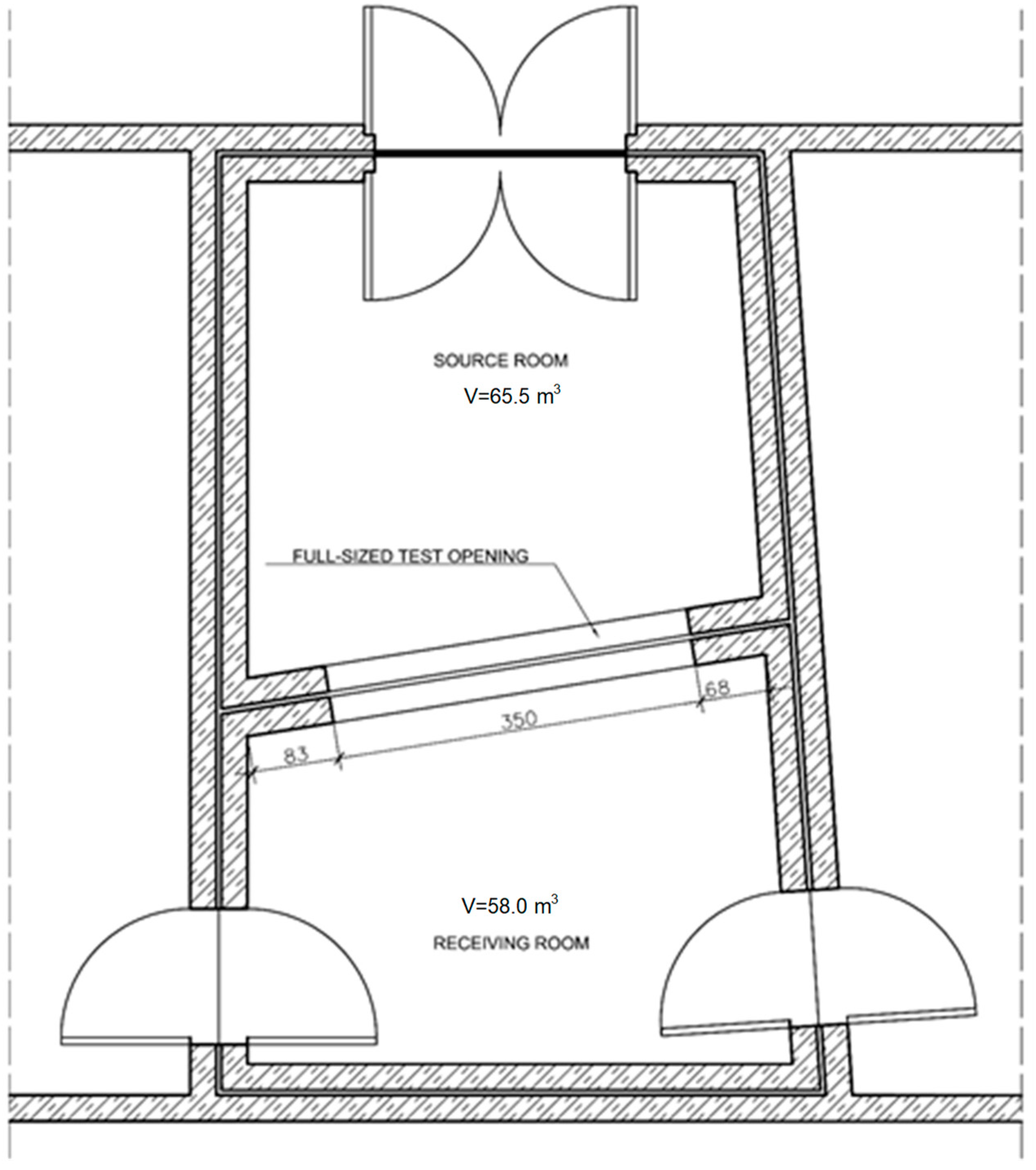
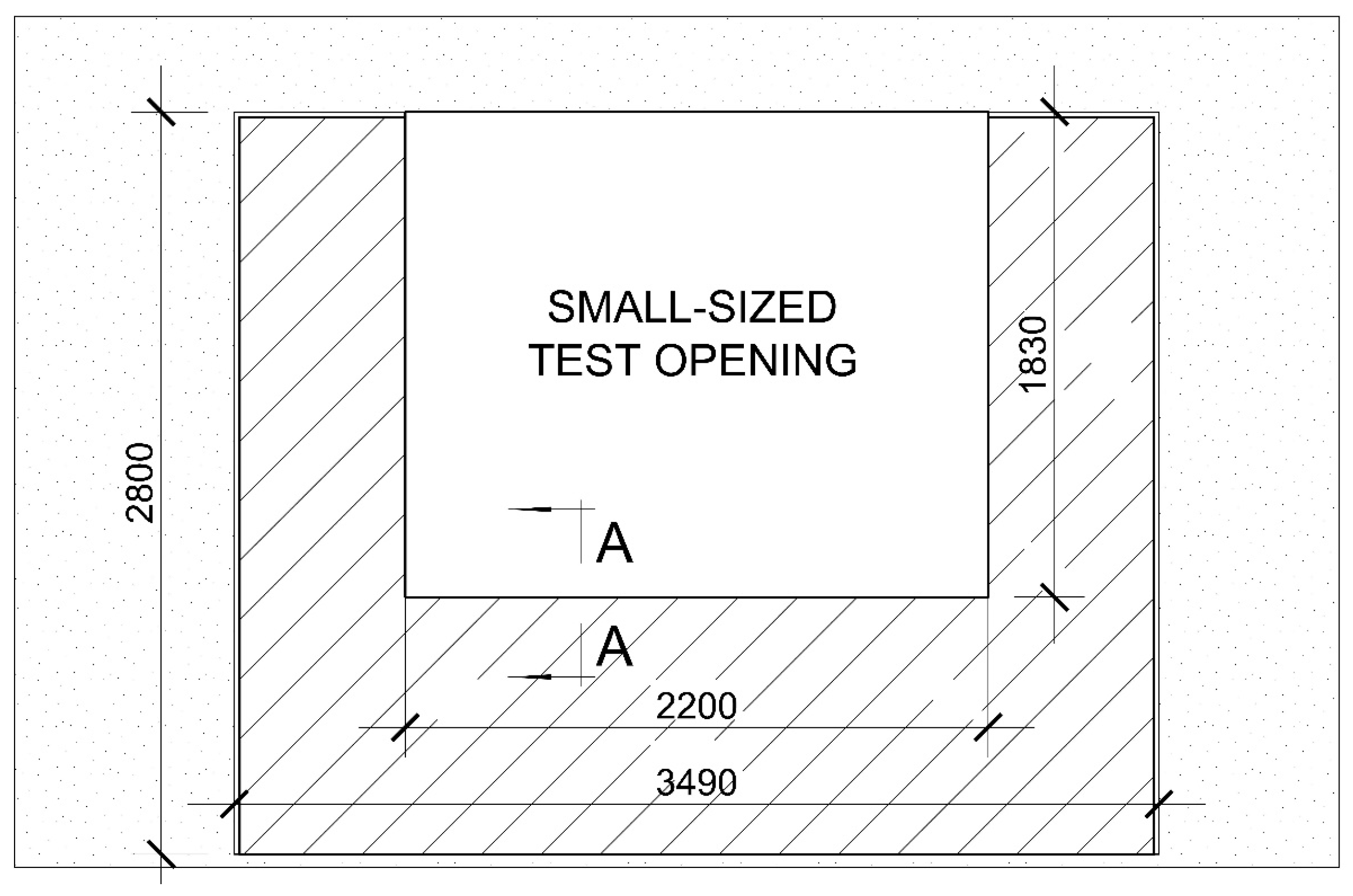
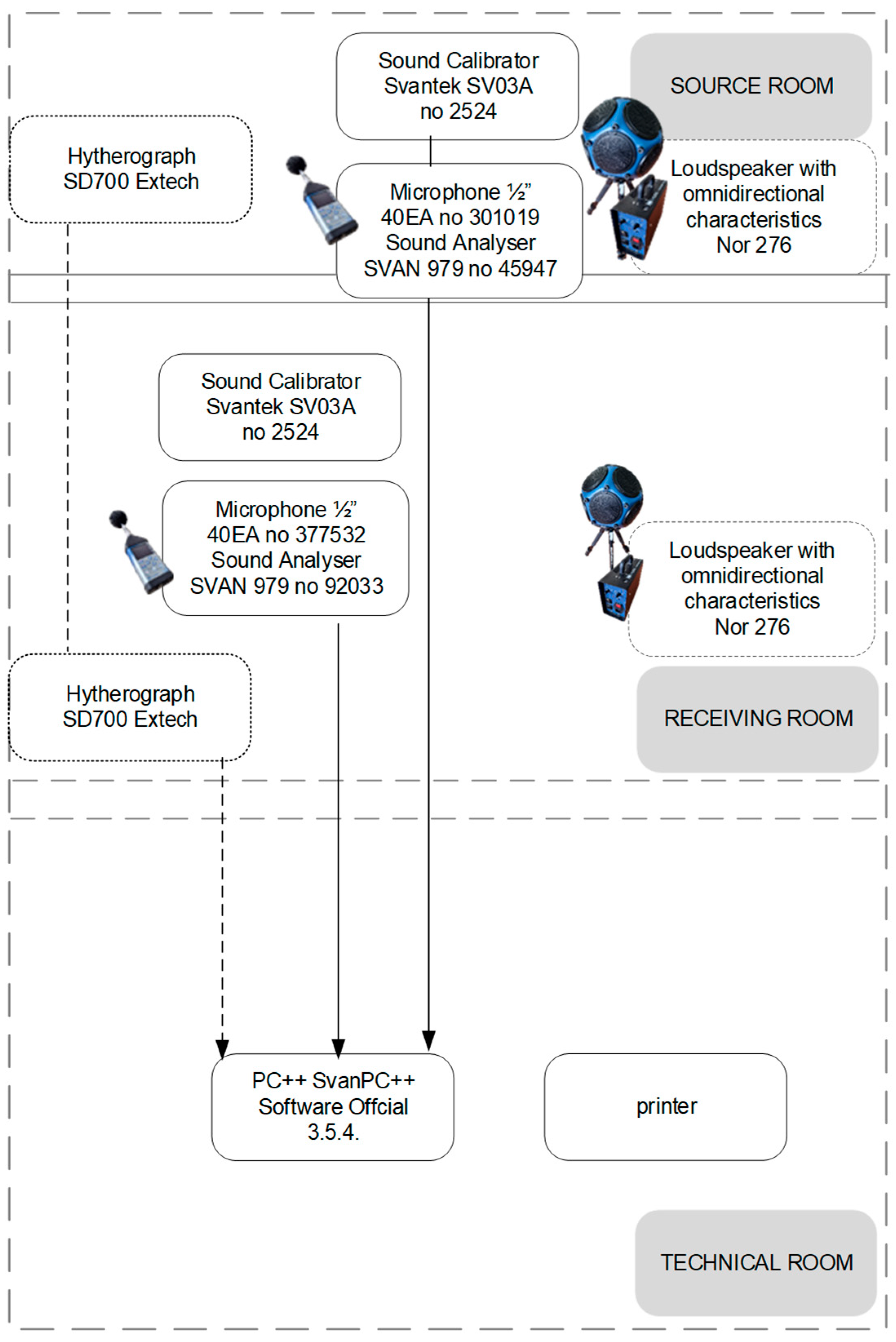
3.2. Test Rooms
3.3. Measurement of Airborne Sound Insulation
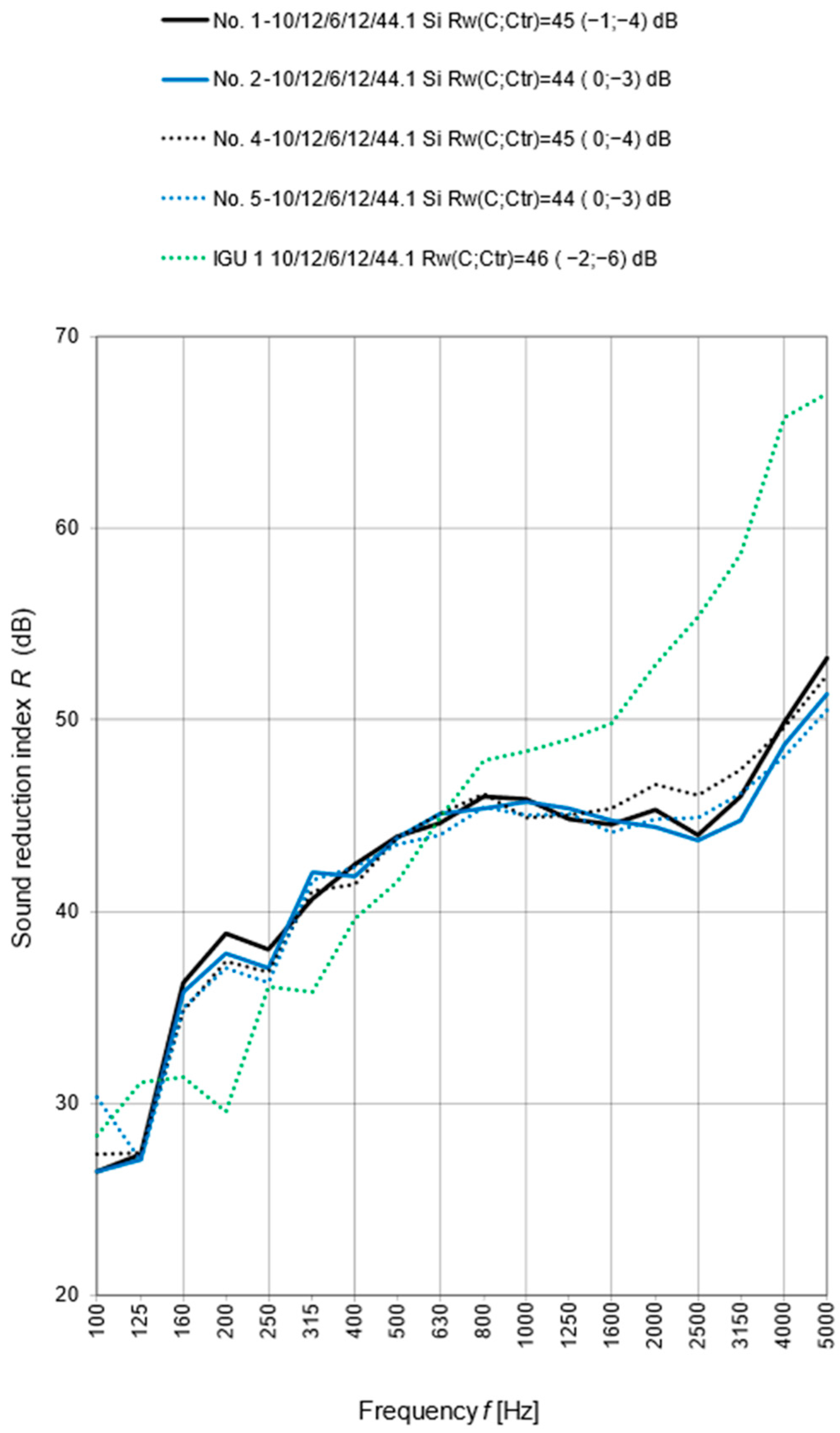
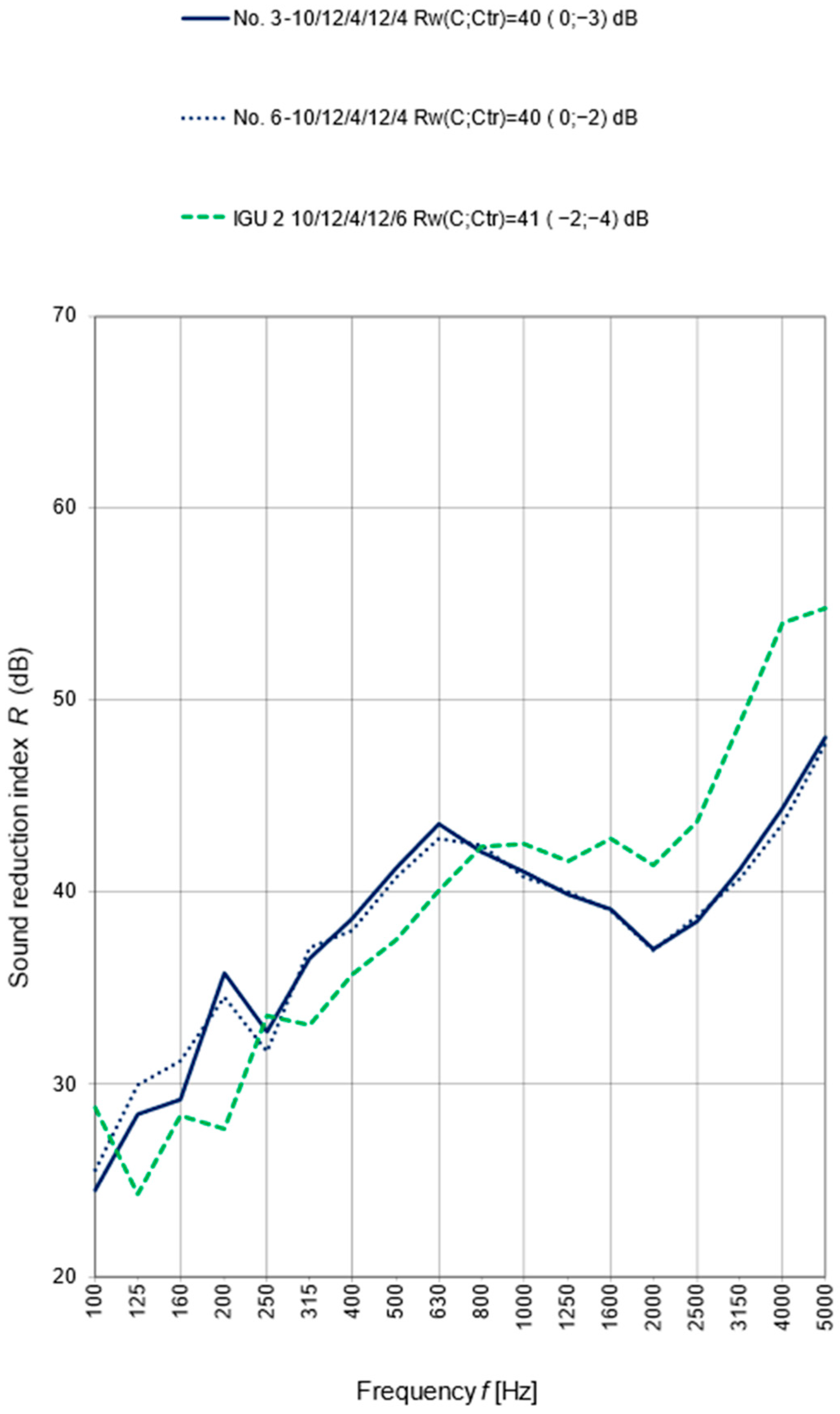
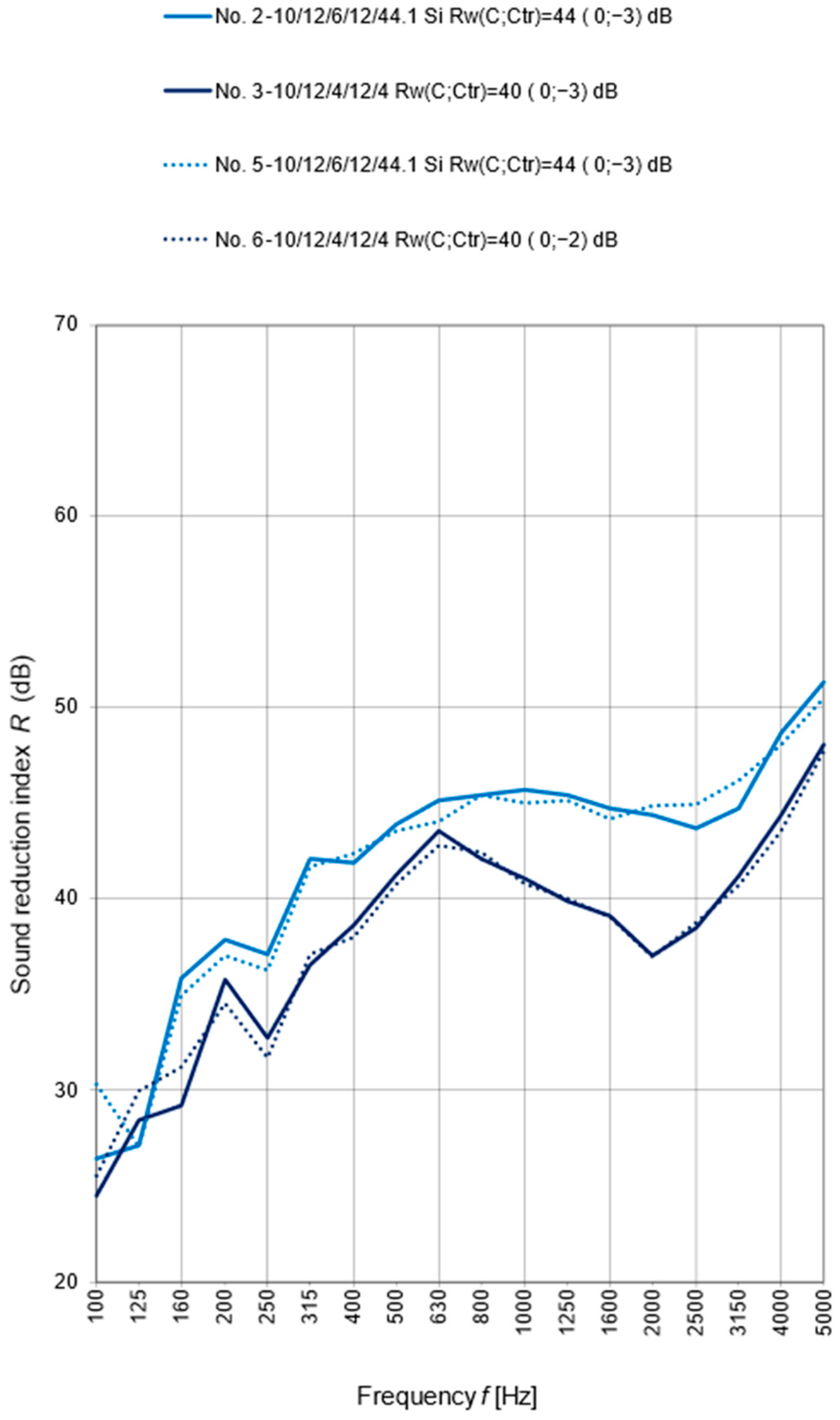
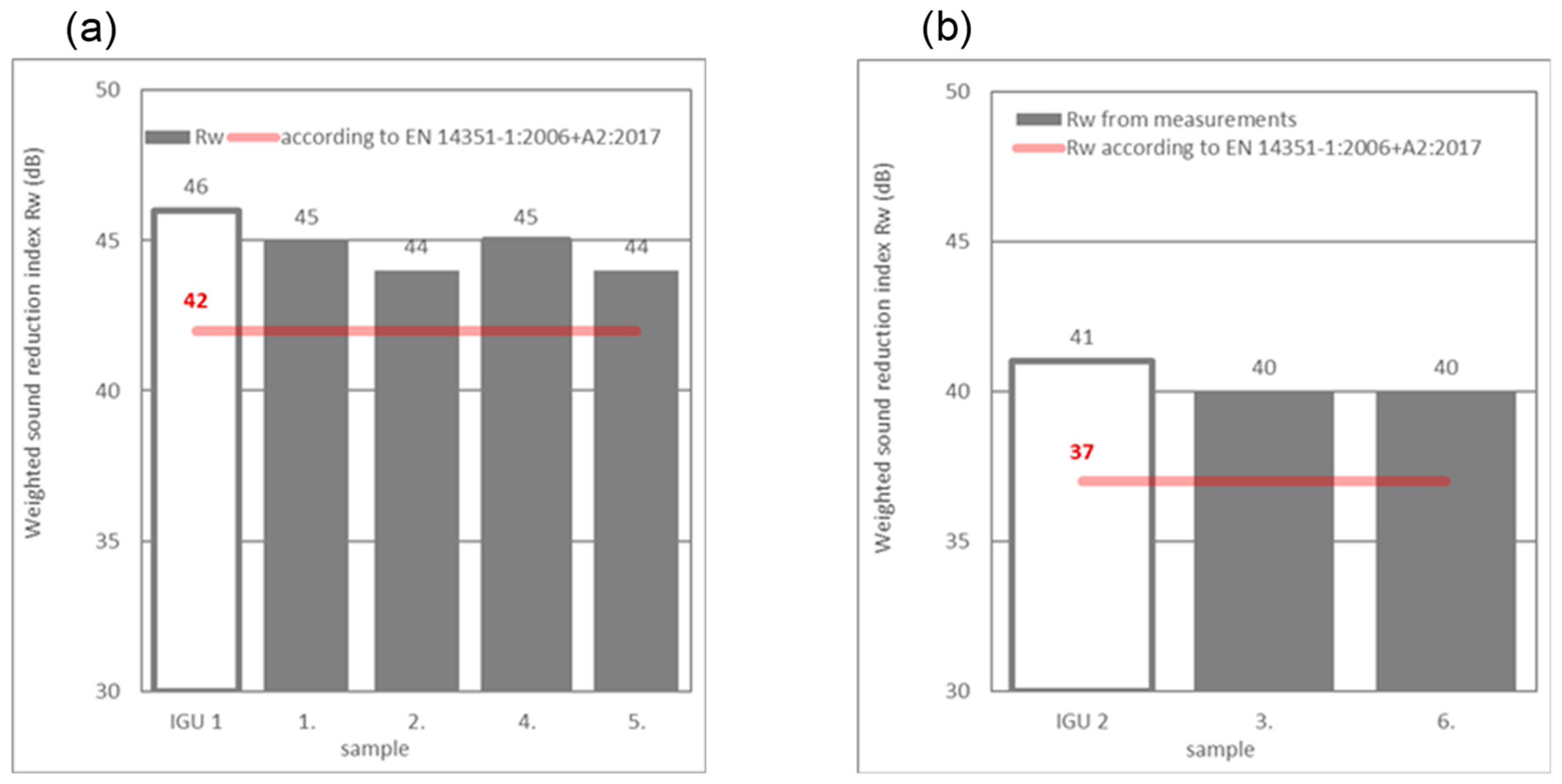
4. Results and Discussions
5. Conclusions and Recommendations
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- ISO 10140-5: 2021; Acoustics–Laboratory measurement of sound insulation of building elements–Part 5: Requirements for test facilities and equipment. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021.
- Ozturk, Z.S.; Kang, J.; Aletta, F. Soundscape research in streets. A scoping review. Sustainability 2025, 17, 3329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, M.; Wu, H.; Liu, J.; Shen, Y.; Wu, G. Improved sound absorption performance of synthetic fiber materials for industrial noise reduction: A review. J. Porous Mater. 2022, 29, 869–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowoświat, A.; Sorociak, w.; Żuchowski, R. The impact of the application of thin emulsion mat microsurfacing on the level of noise in the environment. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 263, 120626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Żuchowski, R.; Nowoświat, A.; Marchacz, M.; Górski, M. Noise assessment of expansion joints built perpendicularly and angled in the direction of traffic. Measurement method: Case study. Appl. Acoust. 2025, 235, 110674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grassie, S.L. Rail irregularities, corrugation and acoustic roughness: Characteristics, significance and effects of reprofiling. J. Rail Rapid Transit 2012, 226, 542–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Żuchowski, R.; Nowoświat, A.; Kucharski, I. Reduction of tram noise by using a rail lubrication device. Appl. Acoust. 2023, 210, 109429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowoświat, A.; Bochen, J.; Dulak, L.; Żuchowski, R. Study on ound absorption of road acoustic screens under simulated weathering. Arch. Acoust. 2018, 43, 323–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andargie, M.S.; Touchie, M.; O’brien, W.; Müller-Traped, M. Assessment of indoor exposure to outdoor environmental noise and effects on occupant comfort in multi-unit residential buildings. Build. Acoust. 2023, 30, 293–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, P.; Wang, K.I.K.; Abdulla, W.H. Robust classification of urban sounds in noisy environments: A novel approach using SPWVD-MFCC and dual-stream classifier. Acoust. Aust. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balderrama, A.; Kang, J.; Prieto, A.; Luna-Navaro, A.; Arztmann, D.; Knaack, U. Effects of Facades on urban acoustic environment and soundscape: A systematic Review. Sustainabillity 2022, 14, 9670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buratti, C.; Barelli, L.; Moretti, E. Wooden windows: Sound insulation evaluation by means of artificial neural networks. Appl. Acoust. 2013, 74, 740–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Sánchez, R.; Barba-Lobo, A.; Isati-Aizpurua, G.; Bolivar, J.P. Evaluation of environmental noise and prevention measures for a standard hospital area from Spain. Acoustics 2025, 7, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhandari, N.; Tadepalli, S.; Gopalakrishnan, P. The combined influence of thermal and acoustic environment on overall comfort and productivity in naturally ventilated University classrooms in India. Build. Environ. 2025, 267, 112212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forssén, J.; Zachos, G.; Perez, C.R.; Kropp, W. A model study low-frequency noise exposure indoors due to road traffic. Build. Acoust. 2023, 30, 3–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badache, K.; Guedouh, K.S.; Haddad, D. A multi-objective optimization of window Surface and glass thickness determination for daylight factor, thermal resistance and acoustic insulation of a test room performances under an avercast sky. J. Build. Eng. 2025, 101, 111717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ford, R.; Kerry, G. The sound insulation of partially open double glazing. Appl. Acoust. 1973, 6, 57–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerry, G.; Ford, R.D. The field performance of partially open dual glazing. Appl. Acoust. 1974, 7, 213–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J. Numerical simulation of an acoustic window system using finite element method. Acta Acust. United Acustics 2007, 93, 152–163. [Google Scholar]
- Yuya, N.; Tsuyoshi, N.; Takashi, Y. Sound propagation in soundproofing casement windows. Appl. Acoust. 2009, 70, 1160–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Y.G.; Tang, S.K. Plenum window insertion loss in the presence of a line source-a scale model study. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2013, 133, 1458–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mucci, N.; Traversini, V.; Lorini, C.; De Sio, S.; Galea, R.P.; Bonaccorsi, G.; Arcangeli, G. Urban noise and psychological distress: A symetric revive. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 6621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berardi, U.; Ivina, C.; Stasi, R. Sound insulation improvements in lift-and-slide window systems. Build. Environ. 2025, 282, 113258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haase, M.; Amato, A. Performance evaluation of three different Façade models for sustainable office buildings. J. Green Build 2006, 1, 89–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fusaro, G.; Kang, J. Participatory approach to draw ergonomic criteria for window design. Int. J. Ind. Erg. 2021, 82, 103098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubino, C.; Liuzzi, S.; Fusaro, G.; Martellotta, F.; Scrosati, C.; Garai, M. Balancing ventilation and sound insulation in windows by means of metamaterials: A review of the state of the art. Built. Environ. 2025, 275, 112780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsukamoto, Y.; Tomikawa, Y.; Sakagami, K.; Okuzono, T.; Maikawa, H.; Komoto, Y. Experimental assessment of sound insulation performance of a double window with porous absorbent materials its cavity perimeter. Appl. Acoust. 2020, 165, 107317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, D.; Sawaki, S.; Mu, R.L. Improvement of sound insulation performance of double-glazed window by using viscoelastic connectors. J. Sound Vib. 2016, 371, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Lau, S.-K.; Cheng, L. A numerical investigation on the sound insulation of ventilation windows. Appl. Acoust. 2017, 117, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EN 14351-1:2006+A2:2017; Windows and Doors–Product Standard, Performance Characteristics–Part 1: Windows and External Pedestrian Doorsets. Available online: https://www.en-standard.eu/une-en-14351-1-2006-a2-2017-windows-and-doors-product-standard-performance-characteristics-part-1-windows-and-external-pedestrian-doorsets/?srsltid=AfmBOopDHiBysxljvfzUNzXanJ3wTuBp8DEyRfdAiUSYLCIxYFOYC_N1 (accessed on 20 June 2025).
- ISO 10140-2:2021; Acoustics—Laboratory measurement of sound insulation of building elements–Part 2: Measurement of airborne sound insulation. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021.
- ISO 10140-4:2021; Acoustics—Laboratory measurement of sound insulation of building elements–Part 4: Measurement procedures and requirements. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021.
- ISO 717-1:2020; Acoustics–Rating of sound insulation in buildings and of building elements–Part 1: Airborne sound insulation. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020.
- ASTM-E413-22; Classification for Rating Sound Insulation. Available online: https://store.astm.org/e0413-22.html (accessed on 20 June 2025).
- ISO 354:2003; Measurement of sound absorption in a reverberation room. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2003.
- Bartnik, W.; Nieradka, P.; Jóska, J.; Chmielewski, B. Predicting Acoustic performance of window with high sound insulation. Forum Acusticum 2023, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowoświat, A. Determination of the reverberation time using the measurement of sound decay curves. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 8607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



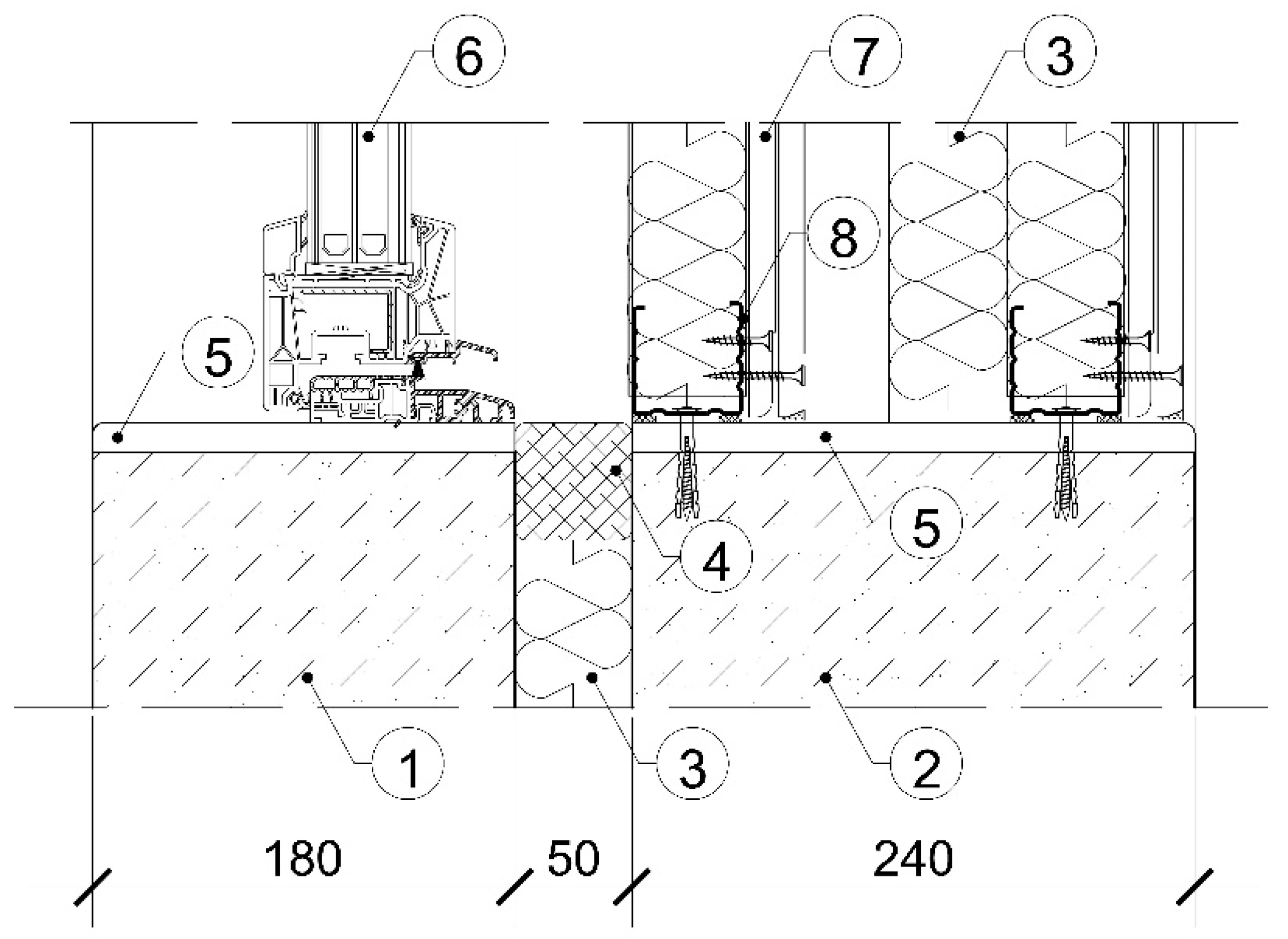


| Sample Number | Mounting | IGUs (Insulating Glass Units) Rw (C; Ctr) [dB] | Mullion Structure | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Foam | Tape | IGU 1 10/12/6/12/44.1 46 (−2; −6) dB | IGU 2 10/12/4/12/6 (−2; −4) dB | Movable | Permanent | |
| 1 | + | + | + | |||
| 2 | + | + | + | |||
| 3 | + | + | + | |||
| 4 | + | + | + | |||
| 5 | + | + | + | |||
| 6 | + | + | + | |||
| f [Hz] | 100 | 125 | 160 | 200 | 250 | 315 | 400 | 500 | 630 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RF′ [dB] | 35 | 40 | 42 | 47 | 50 | 52 | 54 | 56 | 58 |
| f [Hz] | 800 | 1000 | 1250 | 1600 | 2000 | 2500 | 3150 | 4000 | 5000 |
| RF′ [dB] | 60 | 62 | 63 | 65 | 67 | 68 | 70 | 72 | 73 |
| Sample Number | Mounting | IGUs (Insulating Glass Units) Rw (C; Ctr) dB | Mullion Structure | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Foam | Tape | IGU 1 10/12/6/12/44.1 46 (−2; −6) dB | IGU 2 10/12/4/12/6 41 (−2; −4) dB | Movable | Permanent | |
| 1 | + | 45 (−1; −4) | + | |||
| 2 | + | 44 (0; −3) | + | |||
| 3 | + | 40 (0; −3) | + | |||
| 4 | + | 45 (0; −4) | + | |||
| 5 | + | 44 (0; 3) | + | |||
| 6 | + | 40 (0; −2) | + | |||
| f | Sample 1 | Sample 2 | Sample 3 | Sample 4 | Sample 5 | Sample 6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100 | 2.56 | 2.31 | 2.10 | 2.29 | 8.52 | 2.42 |
| 125 | 1.43 | 1.51 | 1.49 | 3.92 | 2.04 | 1.77 |
| 160 | 1.57 | 2.02 | 2.31 | 1.60 | 1.38 | 2.54 |
| 200 | 1.23 | 1.59 | 1.25 | 1.25 | 1.41 | 1.40 |
| 250 | 1.04 | 1.04 | 1.66 | 0.79 | 0.81 | 1.11 |
| 315 | 0.94 | 0.97 | 1.16 | 1.01 | 0.69 | 1.07 |
| 400 | 0.74 | 0.76 | 0.87 | 0.74 | 0.61 | 0.58 |
| 500 | 0.61 | 0.59 | 0.72 | 0.60 | 0.52 | 0.6 |
| 630 | 0.67 | 0.62 | 0.50 | 0.51 | 0.62 | 0.57 |
| 800 | 0.42 | 0.55 | 0.63 | 0.50 | 0.45 | 0.53 |
| 1000 | 0.57 | 0.42 | 0.52 | 0.43 | 0.45 | 0.50 |
| 1250 | 0.58 | 0.47 | 0.44 | 0.39 | 0.39 | 0.41 |
| 1600 | 0.39 | 0.40 | 0.43 | 0.30 | 0.41 | 0.45 |
| 2000 | 0.30 | 0.42 | 0.38 | 0.37 | 0.27 | 0.39 |
| 2500 | 0.32 | 0.41 | 0.35 | 0.36 | 0.38 | 0.34 |
| 3150 | 0.28 | 0.33 | 0.71 | 0.35 | 0.34 | 0.36 |
| 4000 | 0.41 | 0.47 | 0.55 | 0.31 | 0.37 | 0.32 |
| 5000 | 0.40 | 0.49 | 0.66 | 0.31 | 0.38 | 0.32 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dulak, L.; Nowoświat, A. Effect of Window Structure and Mounting on Sound Insulation: A Laboratory-Based Study. Sustainability 2025, 17, 6892. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17156892
Dulak L, Nowoświat A. Effect of Window Structure and Mounting on Sound Insulation: A Laboratory-Based Study. Sustainability. 2025; 17(15):6892. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17156892
Chicago/Turabian StyleDulak, Leszek, and Artur Nowoświat. 2025. "Effect of Window Structure and Mounting on Sound Insulation: A Laboratory-Based Study" Sustainability 17, no. 15: 6892. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17156892
APA StyleDulak, L., & Nowoświat, A. (2025). Effect of Window Structure and Mounting on Sound Insulation: A Laboratory-Based Study. Sustainability, 17(15), 6892. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17156892






