Effects of Replacing Nitrogen Fertilizer with Organic Fertilizer on Soil Physicochemical Properties and Maize Yield in Yunnan’s Red Soil
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Site
2.2. Experiment Design
2.3. Sample Collection and Index Determination
2.4. Economic Analysis
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results
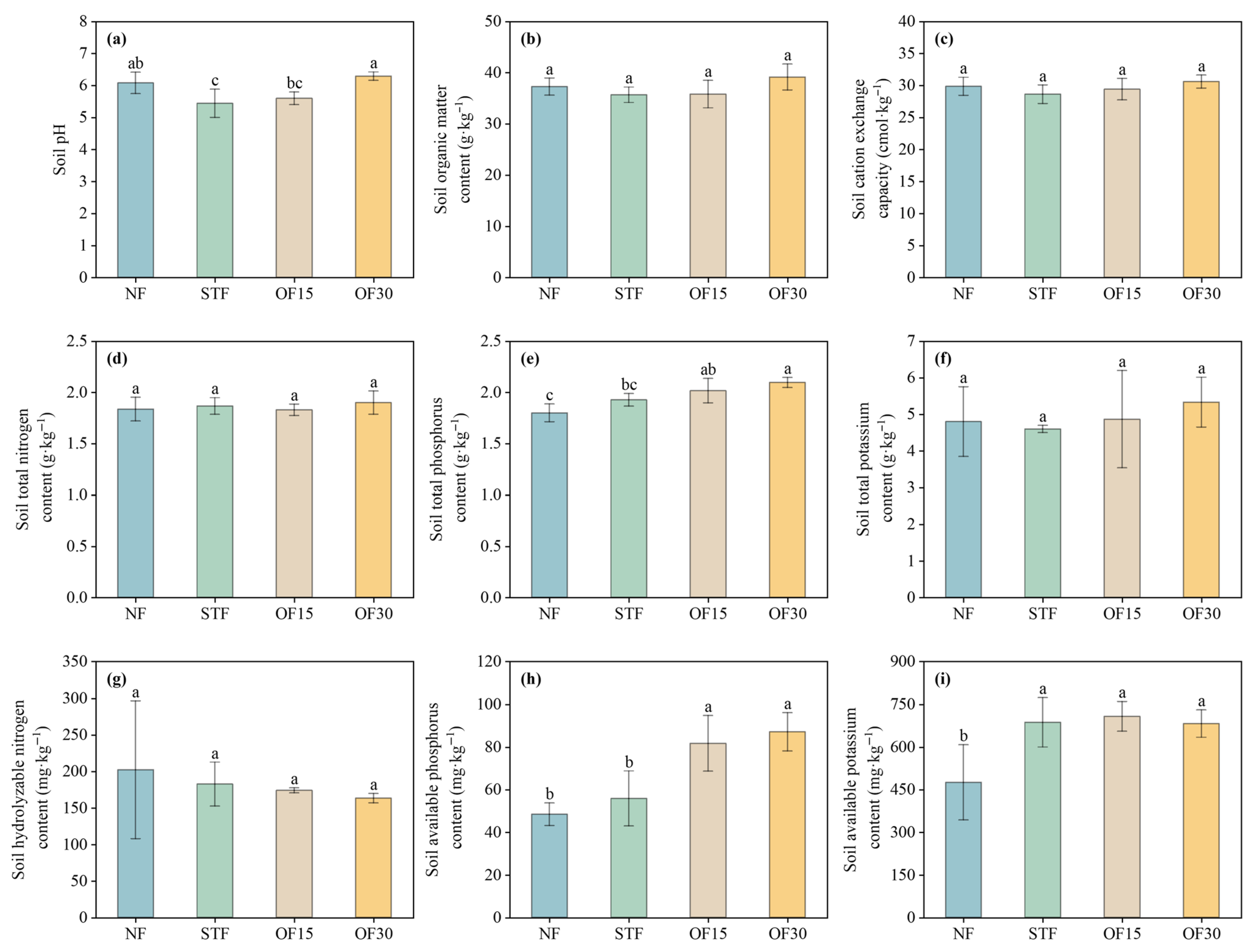
3.1. Physicochemical Properties of Soil
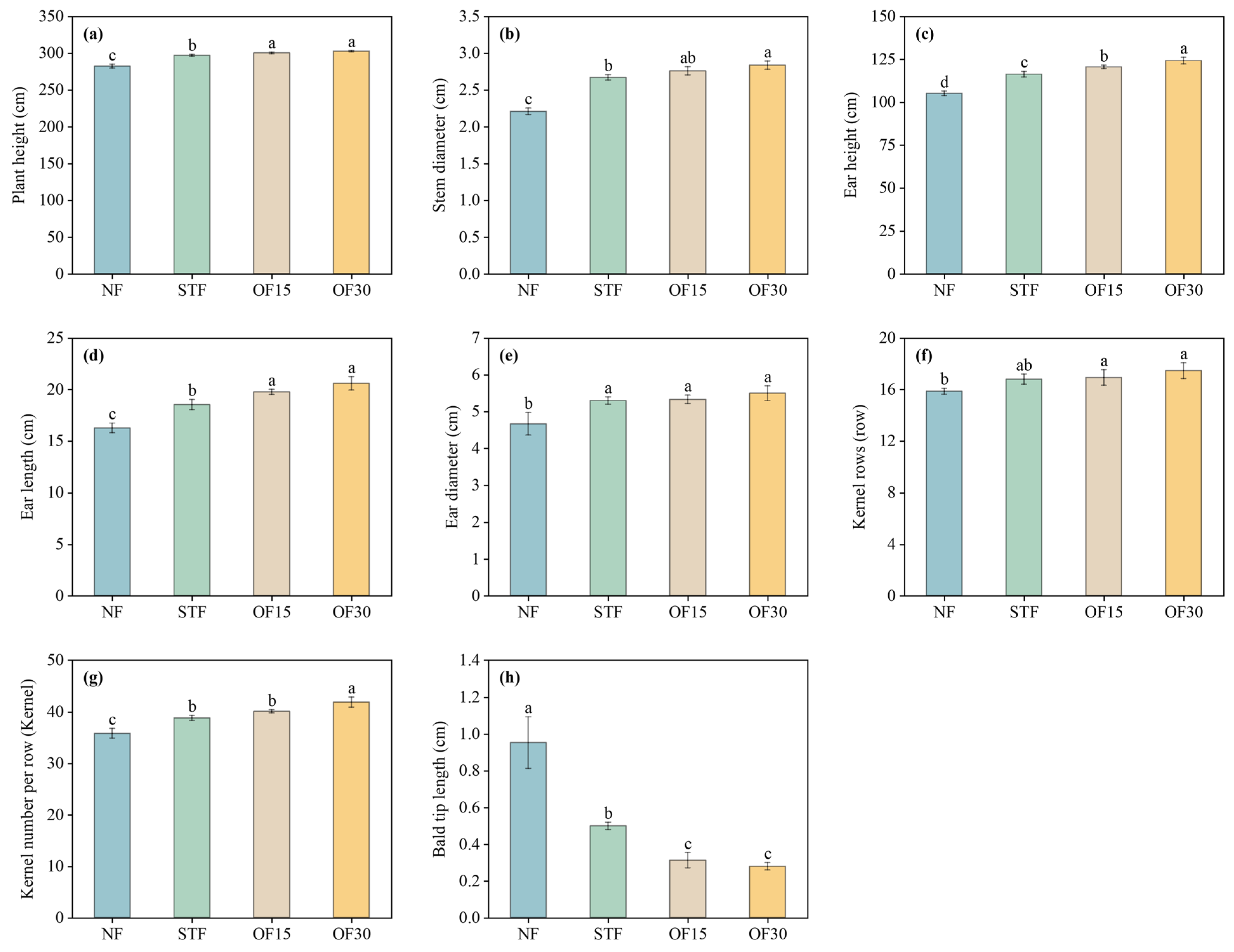
3.2. Agronomic Traits of Maize
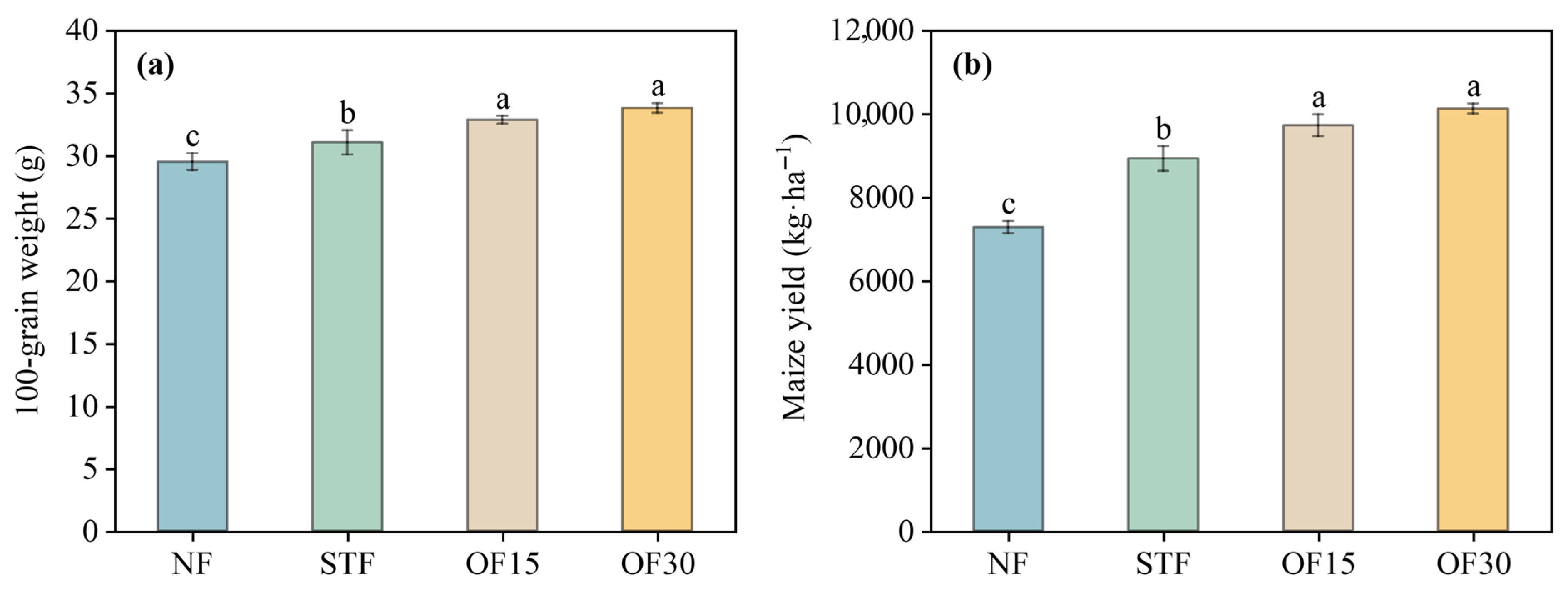
3.3. Maize Yield
3.4. Crop Economic Benefit
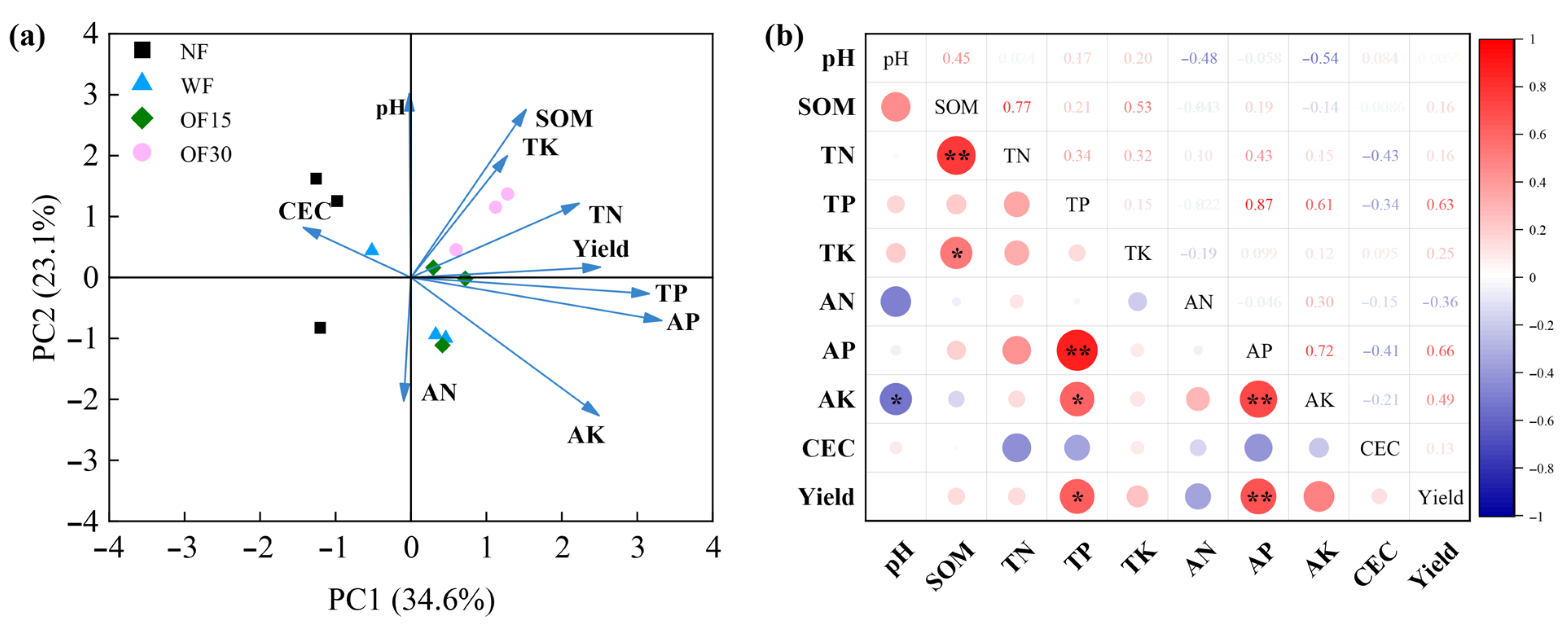
3.5. Correlation Analysis Between Yield and Soil Physicochemical Properties
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of Different Fertilization Treatments on Soil Physicochemical Properties
4.2. Effects of Different Fertilization Treatments on Maize Agronomic Characteristics
4.3. Effects of Different Fertilization Treatments on Maize Yield and Economic Benefit
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tan, S.J.; Xie, D.T.; Ni, J.P.; Chen, F.X.; Ni, C.S.; Shao, J.A.; Zhu, D.; Wang, S.; Lei, P.; Zhao, G.Y.; et al. Characteristics and influencing factors of chemical fertilizer and pesticide applications by farmers in hilly and mountainous areas of Southwest, China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 143, 109346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.Q.; Yan, X.Y. Ecologically optimal nitrogen application rates for rice cropping in the Taihu Lake region of China. Sustain. Sci. 2012, 7, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.H.; He, P.; Jia, L.L.; Ding, W.C.; Ullah, S.; Zhao, R.R.; Zhang, J.J.; Xu, X.P.; Liu, M.C.; Zhou, W. Improving nitrogen use efficiency and reducing environmental cost with long-term nutrient expert management in a summer maize-winter wheat rotation system. Soil Tillage Res. 2021, 213, 105117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Chu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Ju, M.; Wang, Y. Contrasting eutrophication risks and countermeasures in different water bodies: Assessments to support targeted watershed management. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, H.; Riaz, M.; Zhang, M.; Liu, B.; El-Desouki, Z.; Jiang, C. Biochar increases nitrogen use efficiency of maize by relieving aluminum toxicity and improving soil quality in acidic soil. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 196, 110531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, Q.; Ledo, A.; Cheng, K.; Albanito, F.; Lebender, U.; Sapkota, T.B.; Brentrup, F.; Stirling, C.M.; Smith, P.; Sun, J.F.; et al. Re-assessing nitrous oxide emissions from croplands across Mainland China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2018, 268, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, N.X.; Cai, M.; Zhang, X.; Abdelhafez, A.A.; Zhou, L.; Sun, H.F.; Chen, G.F.; Zou, G.Y.; Zhou, S. Runoff loss of nitrogen and phosphorus from a rice paddy field in the east of China: Effects of long-term chemical N fertilizer and organic manure applications. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2020, 22, e01011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curci, P.L.; Bergès, H.; Marande, W.; Maccaferri, M.; Tuberosa, R.; Sonnante, G. Asparagine synthetase genes (AsnS1 and AsnS2) in durum wheat: Structural analysis and expression under nitrogen stress. Euphytica 2018, 214, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frink, C.R.; Waggoner, P.E.; Ausubel, J.H. Nitrogen fertilizer: Retrospect and prospect. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 1175–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Tang, S.; Han, S.; Li, M.; Cheng, W.L.; Bu, R.Y.; Cao, W.D.; Wu, J. Effects of long-term substitution of chemical fertilizer with Chinese milk vetch on soil phosphorus availability and leaching risk in the double rice systems of Eastern China. Field Crops Res. 2023, 302, 109047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carver, R.E.; Nelson, N.O.; Roozeboom, K.L.; Kluitenberg, G.J.; Tomlinson, P.J.; Kang, Q.; Abel, D.S. Cover crop and phosphorus fertilizer management impacts on surface water quality from a no-till corn-soybean rotation. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 301, 113818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, R.N.; Trivedi, A.; Sharma, V.K.; Chobhe, K.A.; Dey, P.; Chandra, S. Soil test-based fertilizer prescription for targeted yield of sesame (Sesamum Indicum, L.). Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2023, 54, 2572–2578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.C.; Li, F.; Zhou, J.; Sun, X.L.; Wang, Y.; Jing, L.Q.; Hou, J.F.; Bao, F.; Wang, G.Y.; Chen, B. Soiltesting formula fertilization with organic fertilizer addition for target yield cannot stand long due to stem lodging of rice. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 1091156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, D.G.P. An Assessment of the Site-Specific Nutrient Management (SSNM) Strategy for Irrigated Rice in Asia. Agriculture 2020, 10, 559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bebber, D.P.; Richards, V.R. A meta-analysis of the effect of organic and mineral fertilizers on soil microbial diversity. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2022, 175, 104450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.P.; Li, K.R.; Chen, S.F.; Fu, X.L.; Feng, S.Y.; Zhuang, Z.S. A sustainable agricultural supply chain considering substituting organic manure for chemical fertilizer. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2022, 29, 432–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.L.; Yang, W.P.; Li, W.G.; Ali, A.; Chen, J.; Sun, M.; Gao, Z.Q.; Yang, Z.P. Moderate organic fertilizer substitution for partial chemical fertilizer improved soil microbial carbon source utilization and bacterial community composition in rain-fed wheat fields: Current year. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1190052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.L.; Ma, Y.Q.; He, W.H.; Kuzyakov, Y.; Bol, R.; Chen, H.Q.; Fan, M.S. Soil quality and ecosystem multifunctionality after 13-year of organic and nitrogen fertilization. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 931, 172789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, X.; Ju, X. Organic fertilizer resources and utilization in China. J. Plant Nutr. Fert. 2017, 23, 1462–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, W.; Tang, S.; Wang, H. The status of organic fertilizer industry and organic fertilizer resources in China. Soil Fertil. Sci. China 2020, 3, 210–219. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Y.J.; Shen, S.Z.; Wan, C.; Wang, S.Q.; Yang, F.X.; Zhang, K.Q.; Gao, W.X. Organic fertilizer substitution over six years improves the productivity of garlic, bacterial diversity, and microbial communities network complexity. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2023, 182, 104718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; Jin, N.; Wang, S.Y.; Li, J.W.; Meng, X.; Xie, Y.D.; Wu, Y.; Luo, S.L.; Lyu, J.; Yu, J.H. Changes in the Microbial Structure of the Root Soil and the Yield of Chinese Baby Cabbage by Chemical Fertilizer Reduction with Bio-Organic Fertilizer Application. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e01215-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chao, S.; Hua, Z.; Shuxia, H.; Qing, Z.; Yuxi, L.; Hai, L. Partial substitution of chemical fertilizer by organic fertilizer increases yield, quality and nitrogen utilization of Dioscorea polystachya. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0301108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, F.; Sha, Z.; Cao, L. Enhancing soil nitrogen supply and maintaining rice yield through partial replacement of chemical nitrogen with food waste-derived organic fertilizer. Plant Soil 2023, 492, 625–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, M.; Guo, A.; Kang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Fan, Y.; Yang, X.; Zhang, R.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Qin, S. Partial substitution of chemical fertilizer with organic manure enhances yield attributes and tuber quality in potato. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2023, 23, 3932–3943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, L.; Feng, W.-t.; He, X.-h.; Ping, Z.; Gao, H.-j.; Nan, S.; Xu, M.-g. Chemical fertilizers could be completely replaced by manure to maintain high maize yield and soil organic carbon (SOC) when SOC reaches a threshold in the Northeast China Plain. J. Integr. Agric. 2017, 16, 937–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Guo, S.; Lei, B.; Guo, Y. Effects of green manure production and utilization on the physiochemical properties of red soil and maize yield in Yunnan Plateau. J. Plant Nutr. Fert. 2022, 28, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.Y.; Zhou, H.Y.; Xu, Y.F.; Ouyang, T.P.; Deng, Q.L. Environmental problems of red soil along the coast of South China. Soil Use Manag. 2002, 18, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Ding, X.; Xue, S.; Li, S.; Liao, X.; Wang, R. Effects of organic-matter application on phosphorus adsorption of three soil parent materials. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2013, 13, 1003–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Liang, F.; Liu, Z.B.; Jiang, G.J.; Zhang, Q. Acidification characteristics and its influencing factors of red paddy soil derived from four parent materials in Southeast of China. Geoderma Reg. 2023, 34, e00673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; de Vries, W.; Liu, X.; Hao, T.; Zeng, M.; Shen, J.; Zhang, F. Enhanced acidification in Chinese croplands as derived from element budgets in the period 1980–2010. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 618, 1497–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- do Carmo Horta, M.; Torrent, J. Phosphorus desorption kinetics in relation to phosphorus forms and sorption properties of Portuguese acid soils. Soil Sci. 2007, 172, 631–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ao, W. Research on soil testing and formulated fertilization techniques for main crops in Fuyuan County. Prim. Agric. Technol. Ext. 2019, 7, 44–46. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, Y.H.; Guo, J.J.; Fan, L.Y.; Ji, Y.; Liu, Z.; Wang, F.; Pu, Z.X.; Ling, N.; Shen, Q.R.; Guo, S.W. The source-sink balance during the grain filling period facilitates rice production under organic fertilizer substitution. Eur. J. Agron. 2022, 134, 126468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, B.; Liao, P.; Hu, R.; Cai, T.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, Q.; Zhang, B.; Shu, Y.; Wang, J.; Luo, Y.; et al. Mitigating ammonia volatilization in rice cultivation: The impact of partial organic fertilizer substitution. Chemosphere 2023, 344, 140326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.F.; Ma, R.H.; Wei, J.L.; Fu, X.Y.; Zhang, S.S.; Zhao, Z.C.; Lin, H.T.; Xu, Y.; Tan, D.S.; Gao, X.B.; et al. Enhancing micronutrient bioavailability in wheat grain through organic fertilizer substitution. Front. Nutr. 2025, 12, 1559537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, M.L.; Liu, H.J.; Liu, X.G.; Guo, T.T.; Guo, J.; Yin, Y.J.; Ji, Y.; Li, Z.X.; Zhang, J.H.; Wang, X.Q.; et al. Complex genetic architecture underlying the plasticity of maize agronomic traits. Plant Commun. 2023, 4, 100473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Shen, T.; Jiang, T.; Hu, X.L.; Wen, M.; Qiu, H.B. Quantitative trait loci mapping of maize (Zea mays) ear traits under low-phosphorus stress. Plant Breed. 2023, 142, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, H.; Wang, J.; Wang, J.D.; Zhang, Y.C. Long-term fertilization with high nitrogen rates decreased diversity and stability of diazotroph communities in soils of sweet potato. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2022, 170, 104266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derkowski, A.; Marynowski, L. Reactivation of cation exchange properties in black shales. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2016, 158, 65–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Te, X.; Hassan, M.J.; Cui, K.S.; Xiao, J.H.; Aslam, M.N.; Saeed, A.; Yang, W.Y.; Ali, S. Effect of different planting pattern arrangements on soil organic matter and soil nitrogen content under a maize/soybean strip relay intercropping system. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 995750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, X.W.; Liu, C.J.; Li, J.; Luo, Y.; Yang, Q.H.; Zhang, W.L.; Yang, P.; Feng, B.L. Responses of rhizosphere soil properties, enzyme activities and microbial diversity to intercropping patterns on the Loess Plateau of China. Soil Tillage Res. 2019, 195, 104355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.N.; Xu, N.; Wang, H.; Li, J.B.; Zhong, H.X.; Dong, H.Y.; Zeng, Z.W.; Zong, C. Variations in the diversity of the soil microbial community and structure under various categories of degraded wetland in Sanjiang Plain, northeastern China. Land Degrad. Dev. 2021, 32, 2143–2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, W.; Liang, C.; Zhihuan, L.; Shuyang, D.; Xuerong, Z.; Jun, F.; Yunhua, X. The role of iron-rich organic fertilizer in promoting the growth of Chinese cabbage and inhibiting the transformation of cadmium. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 908, 168430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Arafat, Y.; Wu, L.K.; Xiao, Z.G.; Li, Q.S.; Khan, M.A.; Khan, M.U.; Lin, S.; Lin, W.X. Shifts in soil microbial community, soil enzymes and crop yield under peanut/maize intercropping with reduced nitrogen levels. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2018, 124, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhou, S.; Hu, J.; Zhu, W.; Zhou, Y.; Pan, X.; Wang, Y.; Lei, Y.; Xiao, L.; Huang, C. Density management is more cost effective than fertilization for Chimonobambusa pachystachys bamboo-shoot yield and economic benefits. Forests 2022, 13, 1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, D.; Niu, S. A global analysis of soil acidification caused by nitrogen addition. Environ. Res. Lett. 2015, 10, 024019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.H.; Liu, X.J.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, J.; Han, W.; Zhang, W.; Christie, P.; Goulding, K.; Vitousek, P.; Zhang, F. Significant acidification in major Chinese croplands. Science 2010, 327, 1008–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, T.; Zhu, Q.; Zeng, M.; Shen, J.; Shi, X.; Liu, X.; Zhang, F.; de Vries, W. Quantification of the contribution of nitrogen fertilization and crop harvesting to soil acidification in a wheat-maize double cropping system. Plant Soil 2019, 434, 167–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, P.; Shen, C.; Fan, L.C.; Li, X.; Zhang, L.P.; Zhang, L.; Han, W.Y. Tea planting affects soil acidification and nitrogen and phosphorus distribution in soil. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2018, 254, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, P.; Wu, L.Q.; Wang, D.H.; Fu, J.Y.; Shen, C.; Li, X.; Zhang, L.P.; Zhang, L.; Fan, L.C.; Han, W.Y. Soil acidification in Chinese tea plantations. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 715, 136963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, L.; Li, Q.; Dai, Q.G.; Hu, J. Responses of nitrification and denitrification in the rhizosphere of mudflat paddy to rice genotype and nitrogen fertilization. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2022, 113, 103452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.J.; Wang, B.R.; Xu, M.G.; Zhang, H.M.; He, X.H.; Zhang, L.; Gao, S.D. Intensified soil acidification from chemical N fertilization and prevention by manure in an 18-year field experiment in the red soil of southern China. J. Soils Sediments 2015, 15, 260–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, R.Y.; Liu, Z.D.; Li, Y.; Jiang, T.M.; Xu, M.G.; Li, J.Y.; Xu, R.K. Mechanisms for increasing soil resistance to acidification by long-term manure application. Soil Tillage Res. 2019, 185, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Butterly, C.R.; Tian, W.; Herath, H.; Xi, Y.G.; Zhang, J.B.; Xiao, X.J. Effects of fertilization practices on aluminum fractions and species in a wheat soil. J. Soils Sediments 2016, 16, 1933–1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, H.; Liu, X.; Zhou, W.; Ji, J.; Lan, X.; Lv, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Müller, C. N transformation mechanisms and N dynamics of organic fertilisers as partial substitutes for chemical fertilisers in paddy soils. J. Soils Sediments 2022, 22, 2516–2529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Cui, H.; Liu, Q.; Wang, F.; Liao, H.; Lu, P.; Qin, S. Effect of nitrogen reduction by chemical fertilization with green manure (Vicia sativa L.) on soil microbial community, nitrogen metabolism and and yield of Uncaria rhynchophylla by metagenomics. Arch. Microbiol. 2024, 206, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Zhu, B.; Brüggemann, N.; Dannenmann, M.; Wang, Y.; Butterbach-Bahl, K. Sustaining crop productivity while reducing environmental nitrogen losses in the subtropical wheat-maize cropping systems: A comprehensive case study of nitrogen cycling and balance. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2016, 231, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanden Nest, T.; Ruysschaert, G.; Vandecasteele, B.; Houot, S.; Baken, S.; Smolders, E.; Cougnon, M.; Reheul, D.; Merckx, R. The long term use of farmyard manure and compost: Effects on P availability, orthophosphate sorption strength and P leaching. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2016, 216, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rambaut, L.A.E.; Tillard, E.; Vayssières, J.; Lecomte, P.; Salgado, P. Trade-off between short and long-term effects of mineral, organic or mixed mineral-organic fertilisation on grass yield of tropical permanent grassland. Eur. J. Agron. 2022, 141, 126635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, R.; Maie, N.; Wagai, R.; Hirano, Y.; Matsuda, Y.; Makita, N.; Mizoguchi, T.; Wada, R.; Tanikawa, T. An increase of fine-root biomass in nutrient-poor soils increases soil organic matter but not soil cation exchange capacity. Plant Soil 2023, 482, 89–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guppy, C.N.; Menzies, N.; Moody, P.W.; Blamey, F. Competitive sorption reactions between phosphorus and organic matter in soil: A review. Aust. J. Soil Res. 2005, 43, 189–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Kong, Y.; Guo, E.; Chen, X.; Li, L. Organic acid regulation of inorganic phosphorus release from Mollisols with different organic matter contents. Soil Use Manag. 2022, 38, 576–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, F.; Haderlein, S.B. Potential effects of biochar on the availability of phosphorus—Mechanistic insights. Geoderma 2016, 277, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchison, K.J.; Hesterberg, D. Dissolution of phosphate in a phosphorus-enriched ultisol as affected by microbial reduction. J. Environ. Qual. 2004, 33, 1793–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Niu, J.; Lu, X.; Zhao, Z.; Li, K.; Wang, F.; Zhang, C.; Sun, R. Dosage effects of organic manure on bacterial community assemblage and phosphorus transformation profiles in greenhouse soil. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1188167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tingting, Z.; Shu, W.; Mengyao, W.; Jiao, M.; Yuanmeng, X.; Jiangling, R.; Yuhan, L.; Sichen, L.; Zhijun, Q.; Xiaoning, C. Effect of Different Fertilizer Types on Quality of Foxtail Millet under Low Nitrogen Conditions. Plants 2024, 13, 1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirzad, H.; Moghaddam, S.S.; Rahimi, A.; Rezapour, S.; Xiao, J.B.; Popovic-Djordjevic, J. Combined Effect of Biological and Organic Fertilizers on Agrobiochemical Traits of Corn (Zea mays L.) under Wastewater Irrigation. Plants 2024, 13, 1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaneh, A.; Bohloul, A.; Mohammadi Torkashvand, A.; Ghanbari Jahromi, M. Effect of levels and types of organic, biological, and chemical fertilizers on morphological traits, yield, and uptake rate of elements in Satureja mutica. Ind. Crops Prod. 2022, 181, 114763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myint, A.K.; Yamakawa, T.; Zenmyo, T.; Thao, H.T.B.; Sarr, P.S. Effects of Organic-Manure Application on Growth, Grain Yield, and Nitrogen, Phosphorus, and Potassium Recoveries of Rice Variety Manawthuka in Paddy Soils of Differing Fertility. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2011, 42, 457–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manono, B.O.; Moller, H.; Benge, J.; Carey, P.; Lucock, D.; Manhire, J. Assessment of soil properties and earthworms in organic and conventional farming systems after seven years of dairy farm conversions in New Zealand. Agroecol. Sustain. Food Syst. 2019, 43, 678–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.G.; Yu, X.L.; Zong, Y.T. Nano-microscale porosity and pore size distribution in aggregates of paddy soil as affected by long-term mineral and organic fertilization under rice-wheat cropping system. Soil Tillage Res. 2019, 186, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, X.L.; Qin, S.W.; Zhang, J.B.; Zhu, A.; Yang, W.L.; Zhang, X.F. Yield, phosphorus use efficiency and balance response to substituting long-term chemical fertilizer use with organic manure in a wheat-maize system. Field Crops Res. 2017, 208, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.K.; Zhang, S.Y.; Jiang, N.; Xiu, W.M.; Zhao, J.N.; Yang, D.L. Effects of organic fertilizer incorporation practices on crops yield, soil quality, and soil fauna feeding activity in the wheat-maize rotation system. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 1058071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Peng, M.W.; Ru, S.B.; Hou, Z.A.; Li, J.H. A suitable organic fertilizer substitution ratio could improve maize yield and soil fertility with low pollution risk. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 988663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, F.; Khan, I.; Ashraf, U.; Shahzad, T.; Hussain, S.; Shahid, M.; Abid, M.; Ullah, S. Effects of organic and inorganic manures on maize and their residual impact on soil physico-chemical properties. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2017, 17, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wei, C.; Li, J. Effects of Different Organic Substitution Reducing Fertilizer Patterns on Maize Growth and Soil Fertility. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2019, 33, 281–287. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.L.; Liu, K.L.; Xu, Q.F.; Shen, R.F.; Zhao, X.Q. Organic fertilization sustains high maize yields in acid soils through the cooperation of rhizosphere microbes and plants. Plant Soil 2025, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.J.; Wen, J.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, Y.; Peng, Z.; Tang, C.C.; Wang, Y.A.; Su, S.M.; Zhang, N.; Zeng, X.B. Effects of Five-Year Inorganic and Organic Fertilization on Soil Phosphorus Availability and Phosphorus Resupply for Plant P Uptake during Maize Growth. Agriculture 2023, 13, 858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, P.; Jin, J.; Li, W.; Liu, H.; Huang, S.; Wang, X.; Wang, L.; Xie, J. Comparison of Phosphorous Absorption, Quality and Yield Between High Oil Maize and Common Maize as Influenced by Phosphorous Application. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2005, 38, 538–543. [Google Scholar]
- Chatterjee, D.; Nayak, A.; Mishra, A.; Swain, C.; Kumar, U.; Bhaduri, D.; Panneerselvam, P.; Lal, B.; Gautam, P.; Pathak, H. Effect of long-term organic fertilization in flooded rice soil on phosphorus transformation and phosphate solubilizing microorganisms. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2021, 21, 1368–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.J.; Gao, W.; Luan, H.A.; Tang, J.W.; Li, R.N.; Li, M.Y.; Zhang, H.Z.; Huang, S.W. Effects of a decade of organic fertilizer substitution on vegetable yield and soil phosphorus pools, phosphatase activities, and the microbial community in a greenhouse vegetable production system. J. Integr. Agric. 2022, 21, 2119–2133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carracelas, G.; Guilpart, N.; Cassman, K.G.; Grassini, P. Distinguishing between yield plateaus and yield ceilings: A case study of rice in Uruguay. Field Crops Res. 2023, 292, 108808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, J.D.B.; Reidsma, P.; Giller, K.; Todman, L.; Whitmore, A.; van Ittersum, M. Sustainable development goal 2: Improved targets and indicators for agriculture and food security. Ambio 2019, 48, 685–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Treatment | Chemical Fertilizer (kg·ha−1) | Organic Fertilizer (kg·ha−1) | Total Conversion (kg·ha−1) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Urea | Superphosphate | Potassium Sulphate | N | P2O5 | K2O | ||
| NF | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| STF | 743.55 | 562.50 | 180.00 | 0 | 345.00 | 90.00 | 90.00 |
| OF15 | 631.95 | 1.80 | 16.35 | 4928.55 | 345.00 | 90.00 | 90.00 |
| OF30 | 520.50 | 0 | 0 | 9857.09 | 345.00 | 179.40 | 163.63 |
| Treatment | Yield (kg·ha−1) | Fertilizer Input (CNY·ha−1) | Economic Benefit (CNY·ha−1) | Net Profit (CNY·ha−1) | Economic Benefit Growth (%) | Net Profit Growth (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NF | 7289.89 ± 145.72 c | 0 | 21,869.67 ± 437.14 c | 21,869.67 ± 437.14 c | 0 | 0 |
| STF | 8932.09 ± 298.41 b | 3308.23 | 26,796.26 ± 895.21 b | 23,488.03 ± 895.21 b | 22.52 ± 4.09 | 7.4 ± 4.09 |
| OF15 | 9728.74 ± 261.66 a | 3315.28 | 29,186.23 ± 784.99 a | 25,870.94 ± 784.99 a | 33.45 ± 3.59 | 18.29 ± 3.59 |
| OF30 | 10,132.07 ± 122.22 a | 4414.48 | 30,396.21 ± 366.65 a | 25,981.73 ± 366.65 a | 38.99 ± 1.68 | 18.8 ± 1.68 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Z.; Ao, W.; Wu, S.; Deng, Q.; Ren, H.; Li, Q.; Li, H.; Zhang, P. Effects of Replacing Nitrogen Fertilizer with Organic Fertilizer on Soil Physicochemical Properties and Maize Yield in Yunnan’s Red Soil. Sustainability 2025, 17, 6634. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17146634
Liu Z, Ao W, Wu S, Deng Q, Ren H, Li Q, Li H, Zhang P. Effects of Replacing Nitrogen Fertilizer with Organic Fertilizer on Soil Physicochemical Properties and Maize Yield in Yunnan’s Red Soil. Sustainability. 2025; 17(14):6634. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17146634
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Zhao, Wen Ao, Shenghang Wu, Qiheng Deng, Hao Ren, Qiang Li, Hao Li, and Peng Zhang. 2025. "Effects of Replacing Nitrogen Fertilizer with Organic Fertilizer on Soil Physicochemical Properties and Maize Yield in Yunnan’s Red Soil" Sustainability 17, no. 14: 6634. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17146634
APA StyleLiu, Z., Ao, W., Wu, S., Deng, Q., Ren, H., Li, Q., Li, H., & Zhang, P. (2025). Effects of Replacing Nitrogen Fertilizer with Organic Fertilizer on Soil Physicochemical Properties and Maize Yield in Yunnan’s Red Soil. Sustainability, 17(14), 6634. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17146634






