Optimal Collector Tilt Angle to Maximize Solar Fraction in Residential Heating Systems: A Numerical Study for Temperate Climates
Abstract
1. Introduction
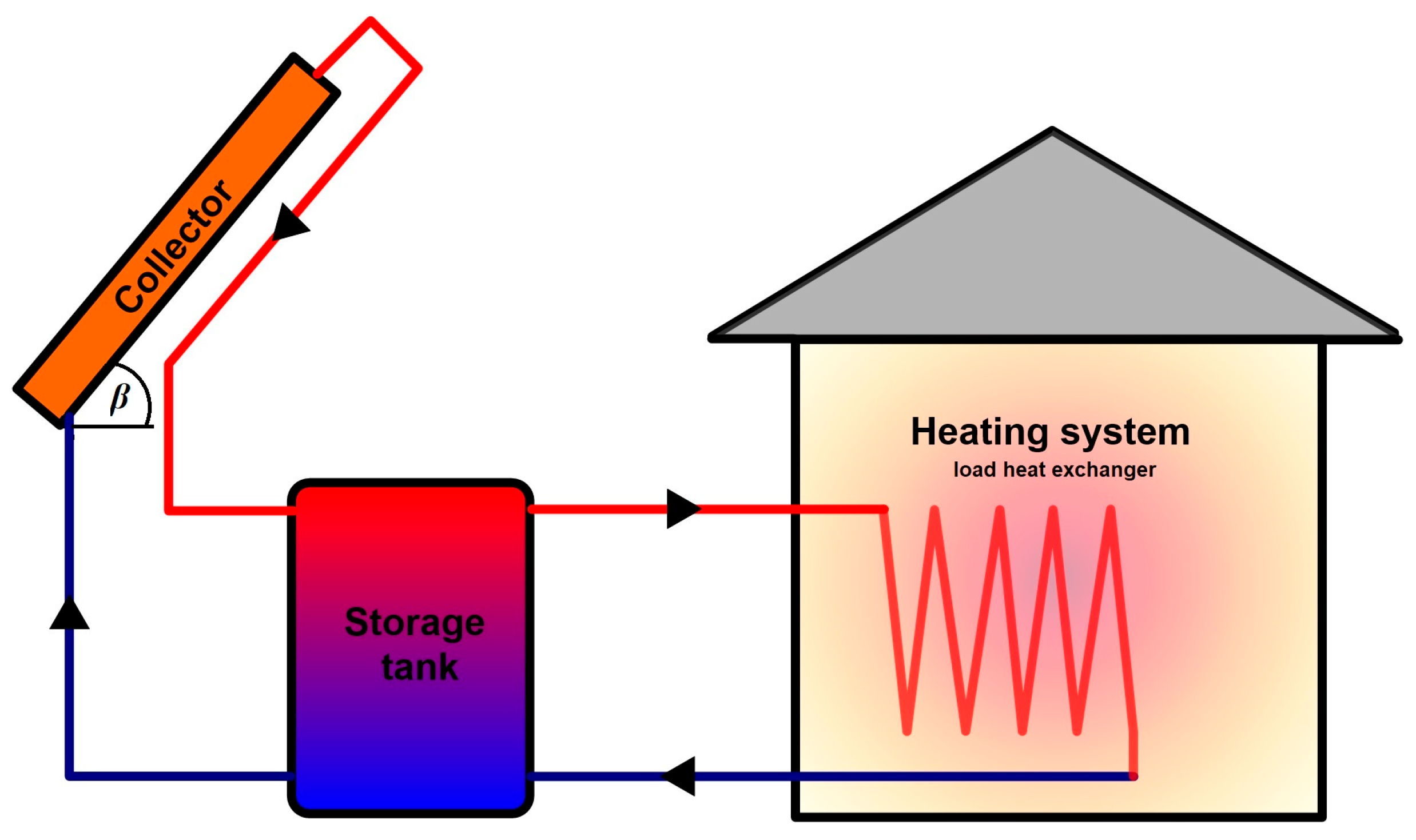
2. Mathematical Model
2.1. Monthly Average Daily Irradiation on a Collector Plane
2.2. Heat Exchanger
2.3. Heat Demand for Heating
2.4. f-Chart Model
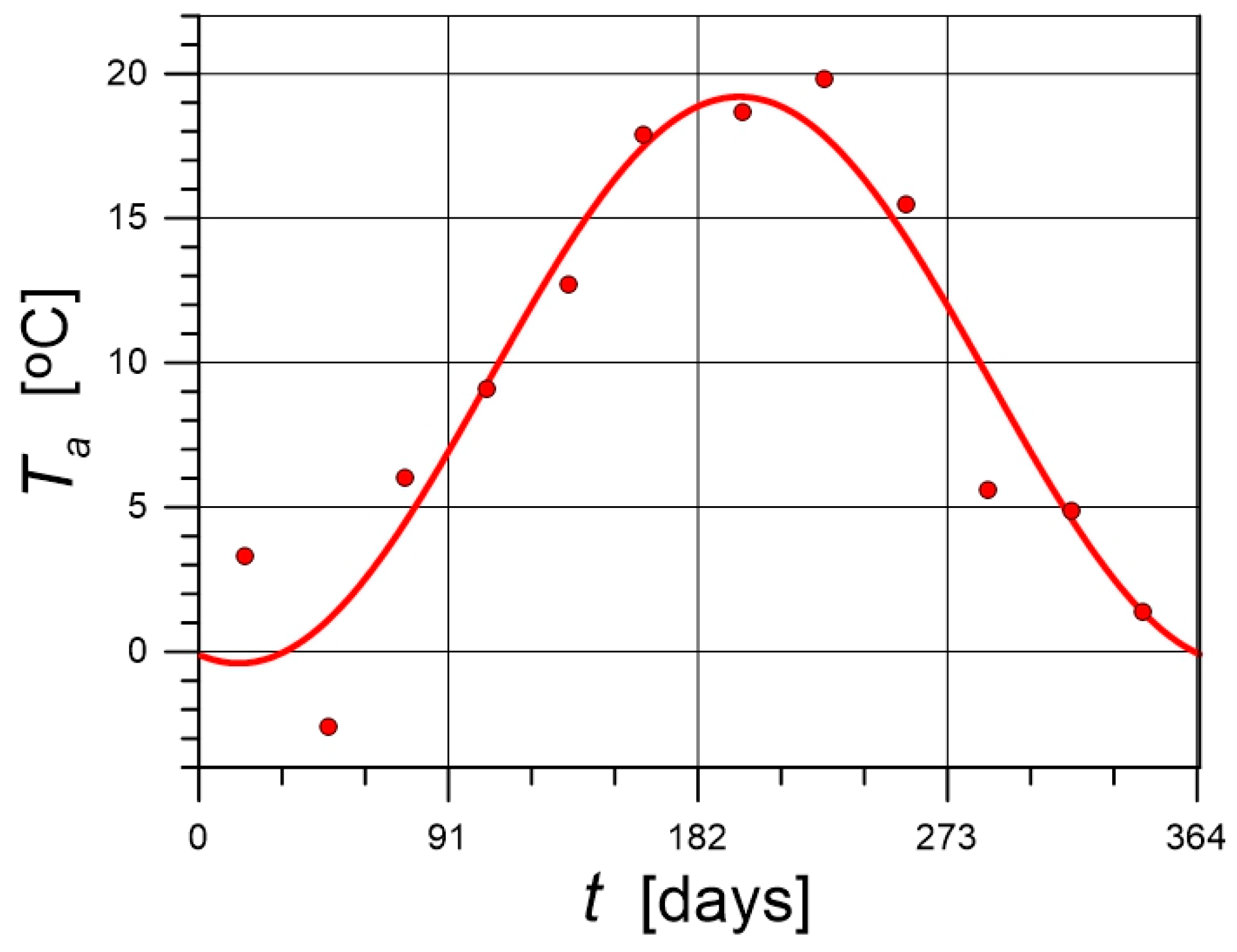
3. Data for Calculations
4. Results
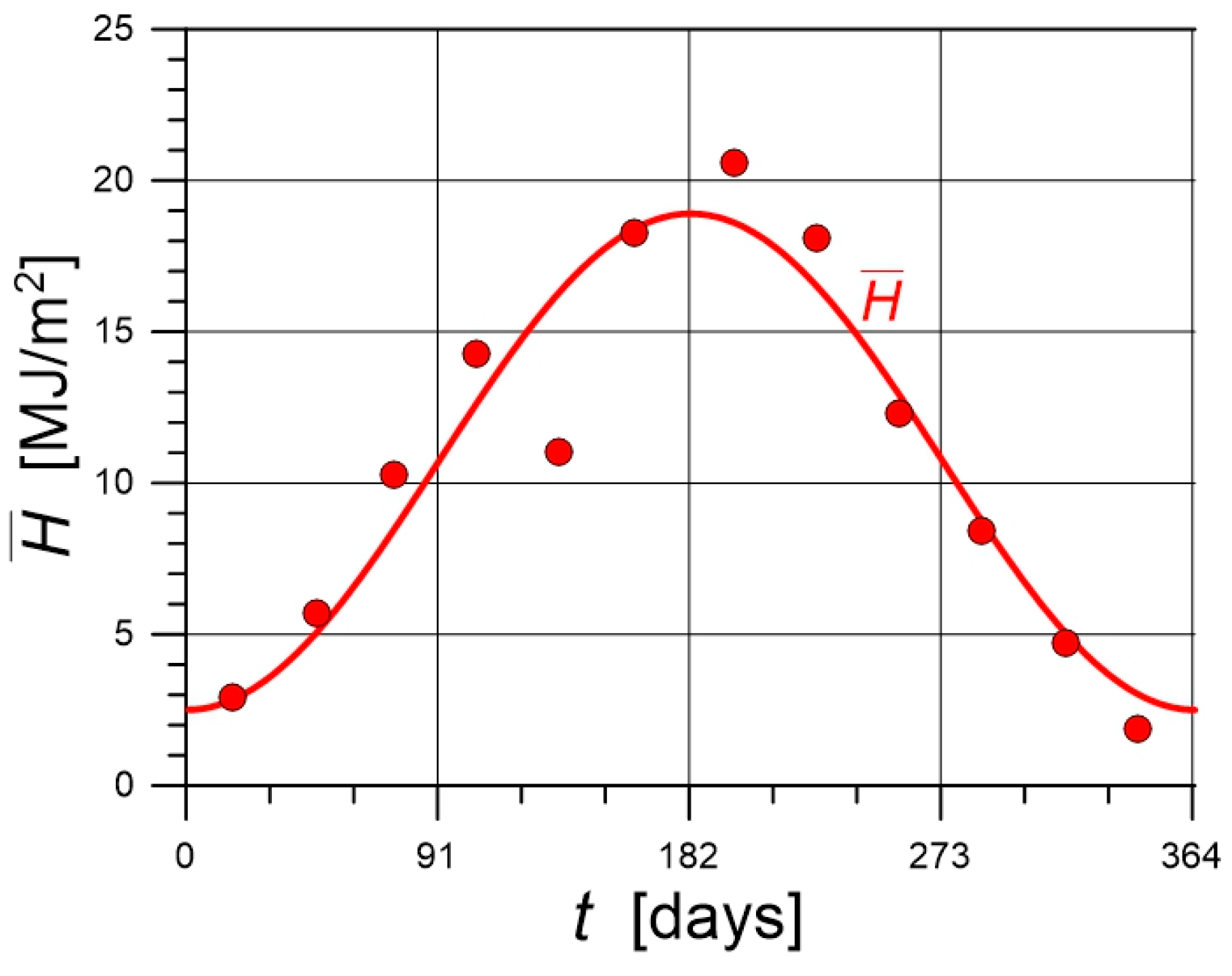
4.1. Solar Irradiation
4.2. Temporal Variations of f
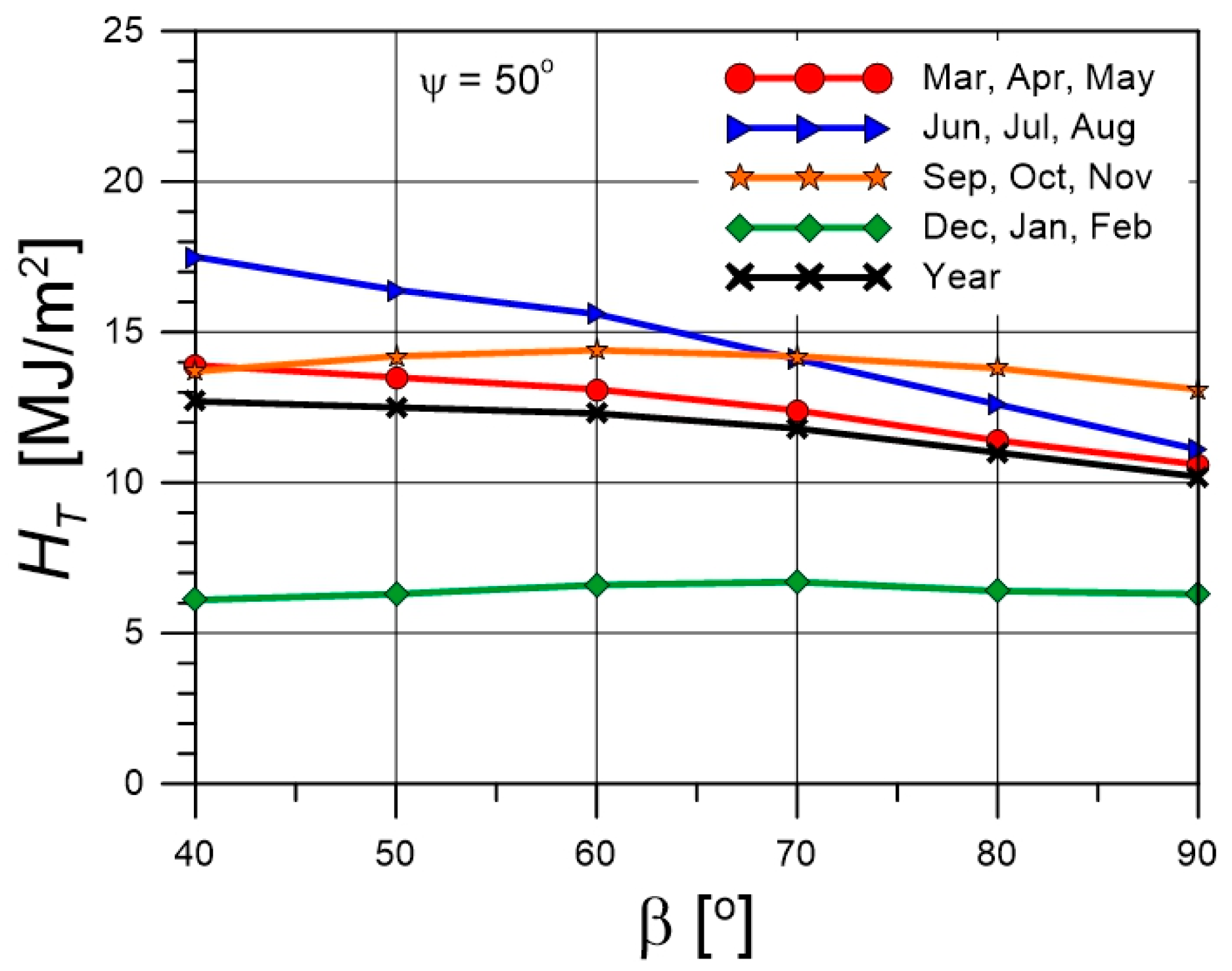
4.3. Solar Fractions for Various Collector Tilt Angles
5. Conclusions
- Avoid steep tilt angles approaching 90°.
- Avoid tilt angles significantly lower than the site’s geographic latitude.
- For locations at a latitude of approximately 50°, an optimal tilt angle of 60° is recommended.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| Ab | envelope of building area, m2 |
| Ac | collectors surface area, m2 |
| c | heat capacity, J/(kgK) |
| DDm, DDa | monthly degree-days and annual degree-days, K·day |
| DHW | fraction of energy for domestic hot water heating |
| f | daily fraction of the load supplied by solar energy |
| collector heat exchanger efficiency factor | |
| FR | collector heat removal factor (including external heat exchanger) |
| H, | daily irradiation and monthly average daily irradiation on a horizontal plane, J/m2; |
| HT, | daily irradiation and monthly average daily irradiation on a collector plane, J/m2 |
| L1, L2 | daily heating load for space heating and hot water respectively, J |
| L | daily total heating load, J |
| flow rate of the heating water, kg/s | |
| monthly average total radiation on the tilted surface to that on a horizontal surface | |
| SE | solar efficiency |
| SF | (annular) solar fraction |
| t | time, s or days |
| Ta | ambient temperature, °C |
| Tref | empirically derived reference temperature (100 °C) |
| Ub | overall heat transfer coefficient of the whole building, W/(m2K) |
| UL | overall heat transfer coefficient between collector and environment, W/(m2K) |
| Uload | load heat exchanger overall heat transfer, W/(m2K) |
| V | volume of tank, m3 |
| X, Xc | dimensionless group and correction dimensionless group (Equations (16) and (18)) |
| Y, Yc | dimensionless group and correction dimensionless group (Equations (17) and (19)) |
| Z | dimensionless parameter defined by Equation (9) |
| β | collectors tilt angle, rad or deg |
| ρg | diffuse reflectance |
| ε | effectiveness of load heat exchanger |
| Δt | time step (=1 day) |
| (τα) | effective transmittance–absorptance product |
| ψ | latitude |
| ω (=2π/365) | frequency, day−1 |
References
- Devabhaktuni, V.; Alam, M.; Depuru, S.S.R.; Green, R.C.; Nims, D.; Near, C. Solar energy: Trends and enabling technologies. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2013, 19, 555–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffie, J.; Beckman, W. Solar Engineering of Thermal Processes; John Wiley & Sons Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- El-Sebaii, A.A.; Al-Hazmi, F.S.; Al-Ghamdi, A.A.; Yaghmour, S.J. Global, direct and diffuse solar radiation on horizontal and tilted surfaces in Jeddah, Saudi Arabia. Appl. Energy 2010, 87, 568–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.H.W.; Lam, T.N.T. Determining the Optimum Tilt Angle and Orientation for Solar Energy Collection Based on Measured Solar Radiance Data. Int. J. Photoenergy 2007, 2007, 85402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heywood, H. Operating experience with solar water heating. IHVE J. 1971, 39, 63–69. [Google Scholar]
- Löf, G.O.G.; Tybout, R.A. Cost of house heating with solar energy. Sol. Energy 1973, 14, 253–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, H.P. Treatise on Solar Energy; Fundamentals of Solar Energy; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1982; Volume I. [Google Scholar]
- Moghadam, H.; Tabrizi, F.F.; Sharak, A.Z. Optimization of solar flat collector inclination. Desalination 2011, 265, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, T.P. The Sun’s apparent position and the optimal tilt angle of a solar collector in the northern hemisphere. Sol. Energy 2009, 83, 1274–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, T.P. Study on the optimal tilt angle of solar collector according to different radiation types. Int. J. Appl. Sci. Eng. 2008, 6, 151–161. [Google Scholar]
- Calabrò, E. Determining optimum tilt angles of photovoltaic panels at typical north-tropical latitudes. J. Renew. Sustain. Energy 2009, 1, 033104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raptis, I.-P.; Moustaka, A.; Kosmopoulos, P.; Kazadzis, S. Selecting Surface Inclination for Maximum Solar Power. Energies 2022, 15, 4784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koray, U.; Arif, H. Prediction of Solar Radiation Parameters Through Clearness Index for Izmir, Turkey. Energy Sources Part A 2002, 24, 773–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakirci, K. General models for optimum tilt angles of solar panels: Turkey case study. Renew. Sust. Energy Rev. 2012, 16, 6149–6159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bari, S. Optimum slope angle and orientation of solar collectors for different periods of possible utilization. Energy Convers. Manag. 2000, 41, 855–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, H.R.; Bhowmik, N.C.; Hussain, M. Determining seasonal optimum tilt angles, solar radiations on variously oriented, single and double axis tracking surfaces at Dhaka. Renew. Energy 2010, 35, 1292–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaldellis, J.; Zafirakis, D. Experimental investigation of the optimum photovoltaic panels tilt angle during the summer period. Energy 2012, 38, 305–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, S.H.; Felton, K.E.; Johnson, A.T. Optimum tilt angles of a solar collector. Energy 1981, 6, 895–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, A.; Vashishtha, V.K.; Mishra, S.N. Comparative approach for the optimization of tilt angle to receive maximum radiation. Int. J. Eng. Res. Technol. 2012, 1, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Jafarkazemi, F.; Saadabadi, S.A.; Pasdarshahri, H. The optimum tilt angle for flat plate solar collectors in Iran. J. Renew. Sustain. Energy 2012, 4, 013118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benghanem, M. Optimization of tilt angle for solar panel: Case study for Madinah, Saudi Arabia. Appl. Energy 2011, 88, 1427–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, R.; Saha, T.K.; Meredith, P.; Goodwin, S. Analysis of year-long performance of differently tilted photovoltaics systems in Brisbane, Australia. Energy Convers. Manag. 2013, 74, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shariah, A.; Al-Akhras, M.A.; Al-Omari, I.A. Optimizing the tilt angle of solar collectors. Renew. Energy 2002, 26, 587–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altarawneh, I.S.; Rawadieh, S.I.; Tarawneh, M.S.; Alrowwad, S.M.; Rimaw, I.F. Optimal tilt angle trajectory for maximizing solar energy potential in Ma’an area in Jordan. J. Renew. Sustain. Energy 2016, 8, 033701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darhmaoui, H.; Lahjouji, D. Latitude based model for tilt angle optimization for solar collectors in the Mediterranean region. Energy Procedia 2013, 42, 426–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunerhan, H.; Hepbasli, A. Determination of the Optimum Tilt Angle of Solar Collectors for Building Applications. Build. Environ. 2007, 42, 779–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ertekin, C.; Evrendilek, F.; Kulcu, R. Modeling spatio-temporal dynamics of optimum tilt angles for solar collectors in Turkey. Sensors 2008, 8, 2913–2931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machidon, D.; Istrate, M. Tilt Angle Adjustment for Incident Solar Energy Increase: A Case Study for Europe. Sustainability 2023, 15, 7015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousazadeh, H.; Keyhani, A.; Javadi, A.; Mobli, H.; Abrinia, K.; Sharifi, A. A review of principle and sun-tracking methods for maximizing solar systems output. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2009, 13, 1800–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomson, T. Discrete two-positional tracking of solar collectors. Renew. Energy 2008, 33, 400–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, D.; Basem, A.; Alizadeh, A.; Jasim, D.J.; Aljaafari, H.A.S.; Fazilati, M.; Mehmandoust, B.; Salahshour, S. Optimum tilt and azimuth angles of heat pipe solar collector, an experimental approach. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2024, 55, 104083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinchilla, M.; Santos-Martín, D.; Carpintero-Rentería, M.; Lemon, S. Worldwide annual optimum tilt angle model for solar collectors and photovoltaic systems in the absence of site meteorological data. Appl. Energy 2021, 281, 116056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatib, A.T.; Samiji, M.E.; Mlyuka, N.R. Optimum Solar Collector’s North-South Tilt Angles for Dar es Salaam and their Influence on Energy Collection. Clean. Eng. Technol. 2024, 21, 100778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Long, E.; Wei, J.; Cheng, Z.; Zheng, H. A new approach to determine the optimum tilt angle and orientation of solar collectors in mountainous areas with high altitude. Energy 2021, 237, 121507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemalili, R.C.; Jhamba, L.; Kiprono Kirui, J.; Sigauke, C. Nowcasting Hourly-Averaged Tilt Angles of Acceptance for Solar Collector Applications Using Machine Learning Models. Energies 2023, 16, 927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Kallioğlu, M.A.; Awasthi, A.; Chauhan, R.; Fekete, G.; Singh, T. Correlation formulation for optimum tilt angle for maximizing the solar radiation on solar collector in the Western Himalayan region. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2021, 26, 101185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Photovoltaic Geographical Information System (PVGIS). Available online: https://joint-research-centre.ec.europa.eu/photovoltaic-geographical-information-system-pvgis_en (accessed on 9 June 2025).
- Chiasson, A.D. Geothermal Heat Pump and Heat Engine System; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Kalogirou, S.A. Solar Energy Engineering, 3rd ed.; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Goswami, D.Y. Principles of Solar Engineering, 4th ed.; CDC Press, Taylor & Francis Group: Abingdon, UK, 2022. [Google Scholar]



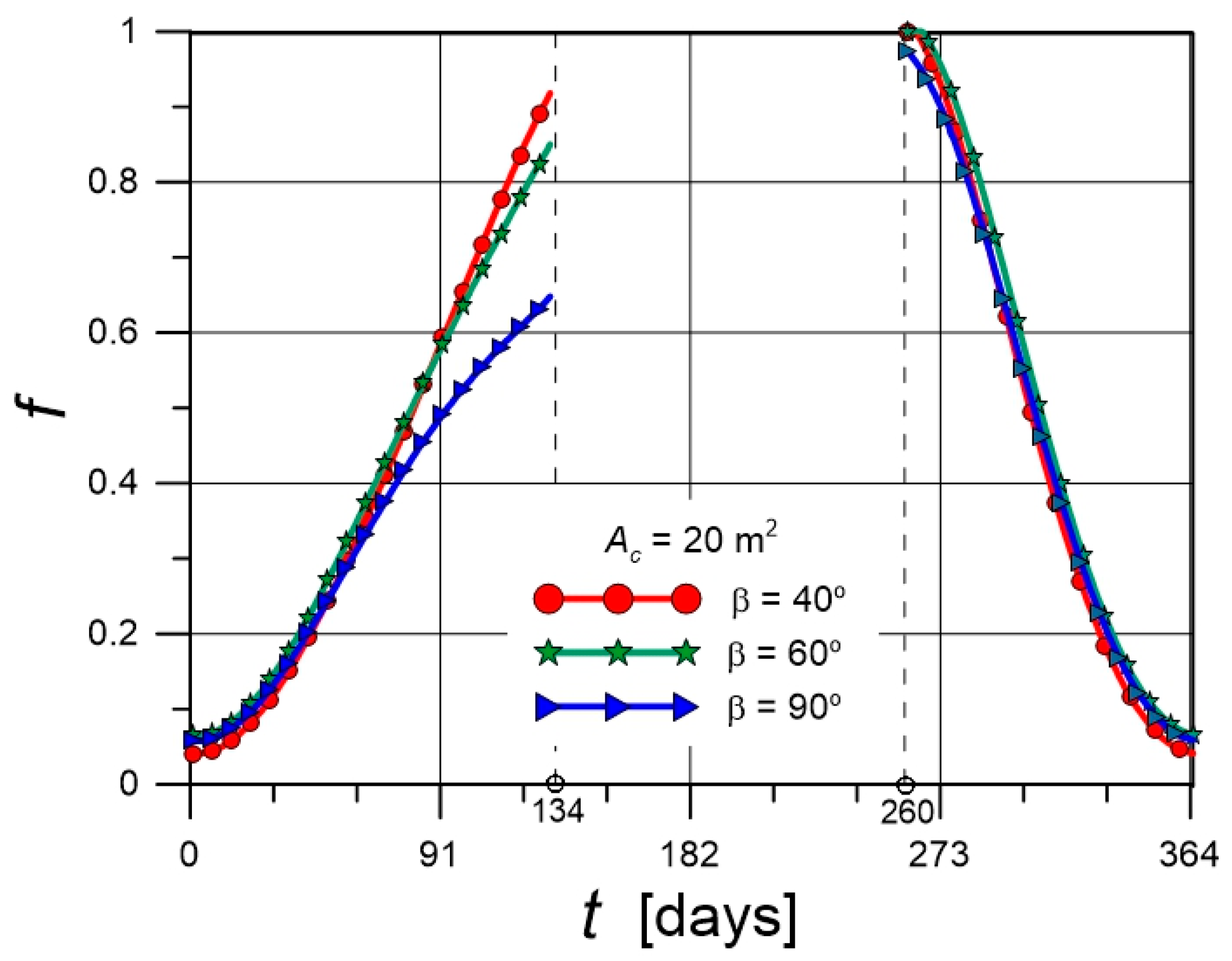


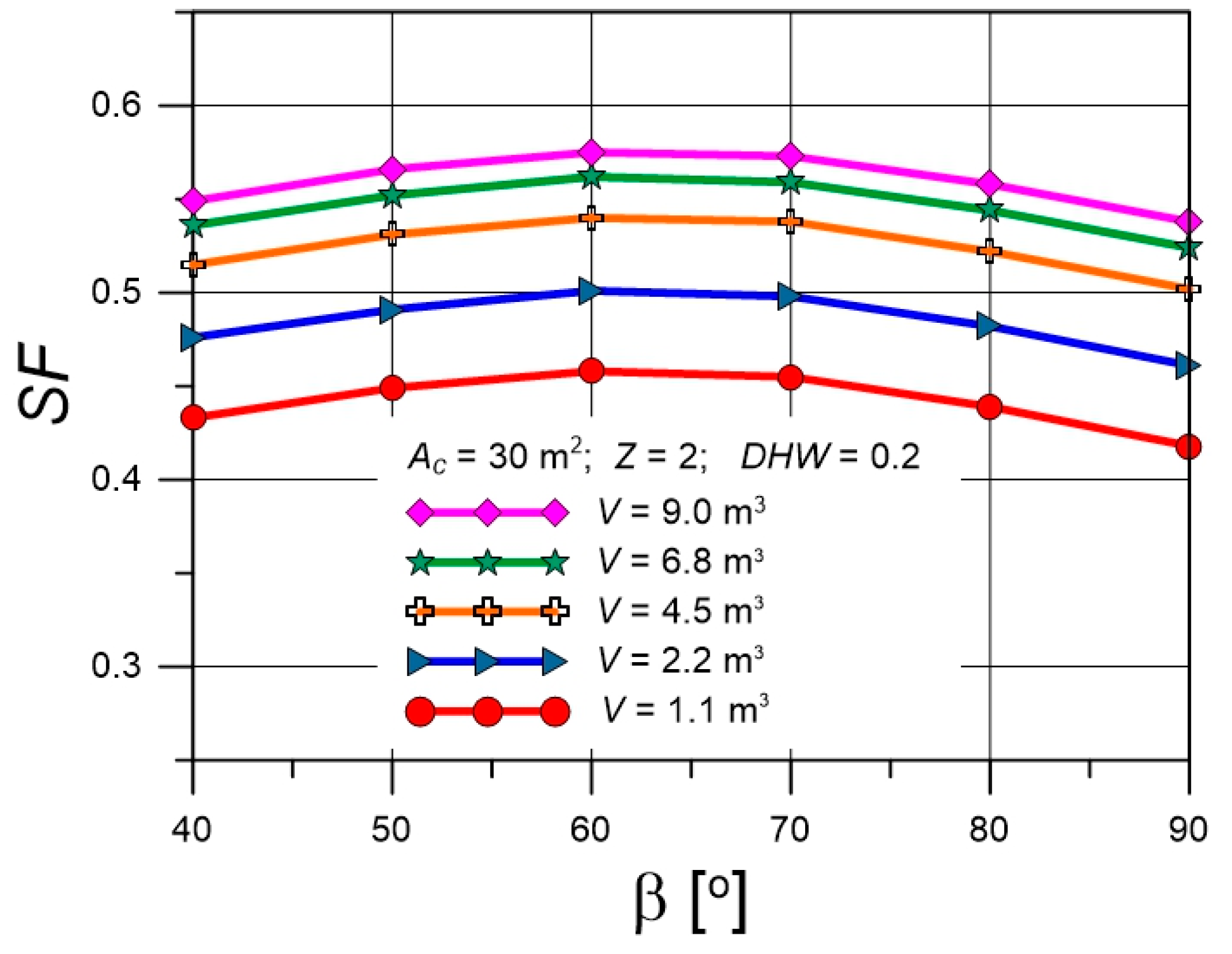
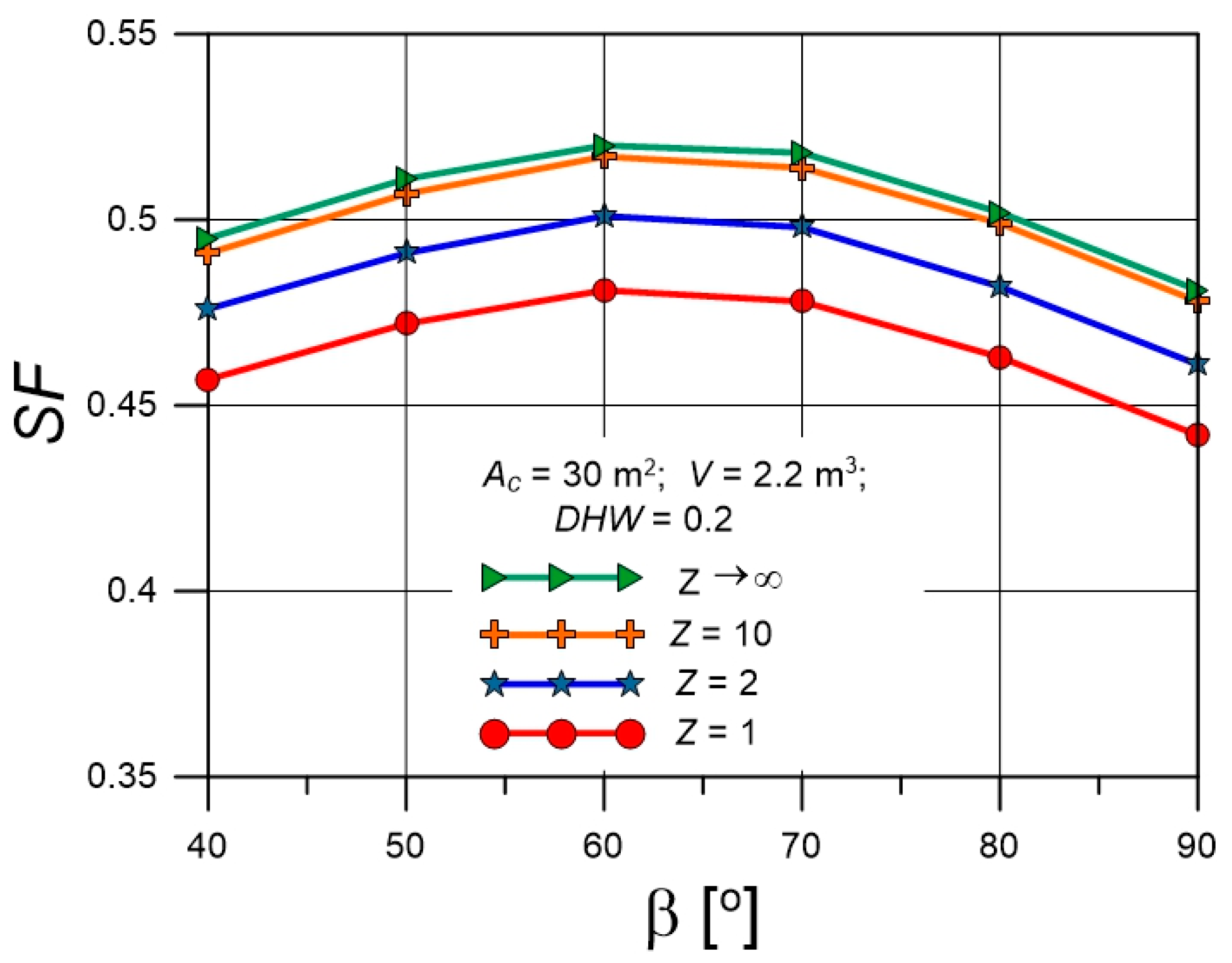
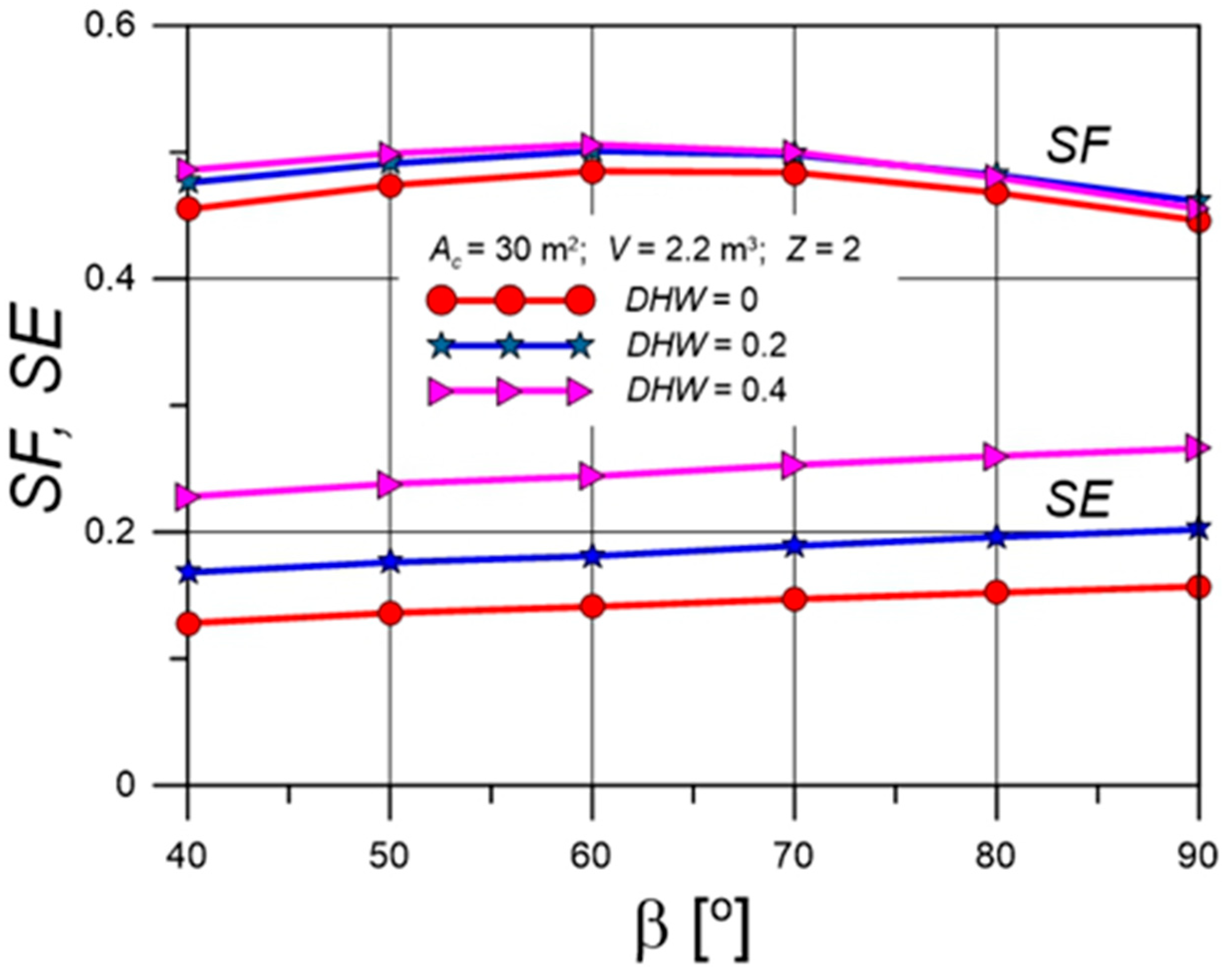
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| 150 W/K | |
| 5.56 W/(m2K) | |
| 0.78 | |
| 0.98 | |
| 100 °C | |
| 0.96 | |
| ρg | 0.4 |
| β | A | B | Ps |
|---|---|---|---|
| 40° | 1.37 | 0.50 | 0.26 |
| 50° | 1.39 | 0.60 | 0.26 |
| 60° | 1.40 | 0.67 | 0.26 |
| 70° | 1.37 | 0.73 | 0.25 |
| 80° | 1.31 | 0.76 | 0.25 |
| 90° | 1.24 | 0.77 | 0.24 |
| Tilt Angle | SF | SE | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| β [o] | Ac = 20 m2 | Ac = 40 m2 | Ac = 20 m2 | Ac = 40 m2 |
| 40 | 0.392 | 0.538 | 0.207 | 0.142 |
| 60 | 0.410 | 0.567 | 0.223 | 0.154 |
| 90 | 0.372 | 0.530 | 0.244 | 0.174 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kupiec, K.; Król, B. Optimal Collector Tilt Angle to Maximize Solar Fraction in Residential Heating Systems: A Numerical Study for Temperate Climates. Sustainability 2025, 17, 6385. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17146385
Kupiec K, Król B. Optimal Collector Tilt Angle to Maximize Solar Fraction in Residential Heating Systems: A Numerical Study for Temperate Climates. Sustainability. 2025; 17(14):6385. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17146385
Chicago/Turabian StyleKupiec, Krzysztof, and Barbara Król. 2025. "Optimal Collector Tilt Angle to Maximize Solar Fraction in Residential Heating Systems: A Numerical Study for Temperate Climates" Sustainability 17, no. 14: 6385. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17146385
APA StyleKupiec, K., & Król, B. (2025). Optimal Collector Tilt Angle to Maximize Solar Fraction in Residential Heating Systems: A Numerical Study for Temperate Climates. Sustainability, 17(14), 6385. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17146385






