Balancing Industrialization with Pollution: Evidence from the Marine Ecological Civilization Demonstration Zone Program in China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Conceptual Framework and Literature Review
2.1. Marine Ecological Civilization Demonstration Zone Policy
2.2. The MECDZ Policy and Upgrading of Industrial Structure
2.3. Environmental Regulation and Green Technology Innovation
2.4. Environmental Regulation and Green Total Factor Productivity
2.5. Environmental Regulation and Local Government Support
3. Data and Model Specification
3.1. Data
3.2. Model Specification
4. Empirical Results
4.1. Baseline Regression Results
4.2. Robustness Check
4.2.1. Propensity Score Matching-Difference-in-Differences
4.2.2. Alternative Measure of Industrial Upgrading
4.3. Underlying Economic Channel
4.4. Environmental Target
5. Geographic Location and Environmental Scrutiny
6. Conclusions, Discussion, and Policy Implication
6.1. Conclusions
6.2. Discussion
6.3. Policy Implication
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Definition
| Variable | Definition | Sources |
|---|---|---|
| MEC | Dummy variable, which equals 1 when a city has become a demonstration city in a time according to the MECDZ policy, otherwise 0 | National Oceanic Administration |
| ISU | The proportion of the tertiary industry in GDP | China City Statistical Yearbook, authors’ own calculation |
| Lnperincome | Per capita income taking natural logarithm | |
| Lnedu | Education expenses taking natural logarithm | |
| Lnenterprises | The number of industrial firms with operating income over 20 million RMB taking natural logarithm | |
| Lnpop | Population density taking natural logarithm | |
| Lnfdi | the amount of foreign direct investment taking natural logarithm | |
| STRAD | Process of industries developing from lower to higher stages | |
| GTI | The number of green patent applications taking natural logarithm | China National Intellectual Property Administration. |
| GTFP | Production efficiency indicator that incorporates environmental factors | CEINET Statistical Database; China City Statistical Yearbook |
| GI | The proportion of fiscal expenditure of prefecture-level cities to provincial fiscal expenditure | China City Statistical Yearbook |
| WQ | The categorical ordinal variable is classified into five levels Class I, Class II, Class III, Class IV, and Class V | Bulletin on Environmental Quality of China’s Coastal Seas |
| LnAP | The concentration of active phosphate taking natural logarithm | |
| LnDIN | The concentration of dissolved inorganic nitrogen taking natural logarithm |
Appendix B. Parallel Trend Tests for STRAD
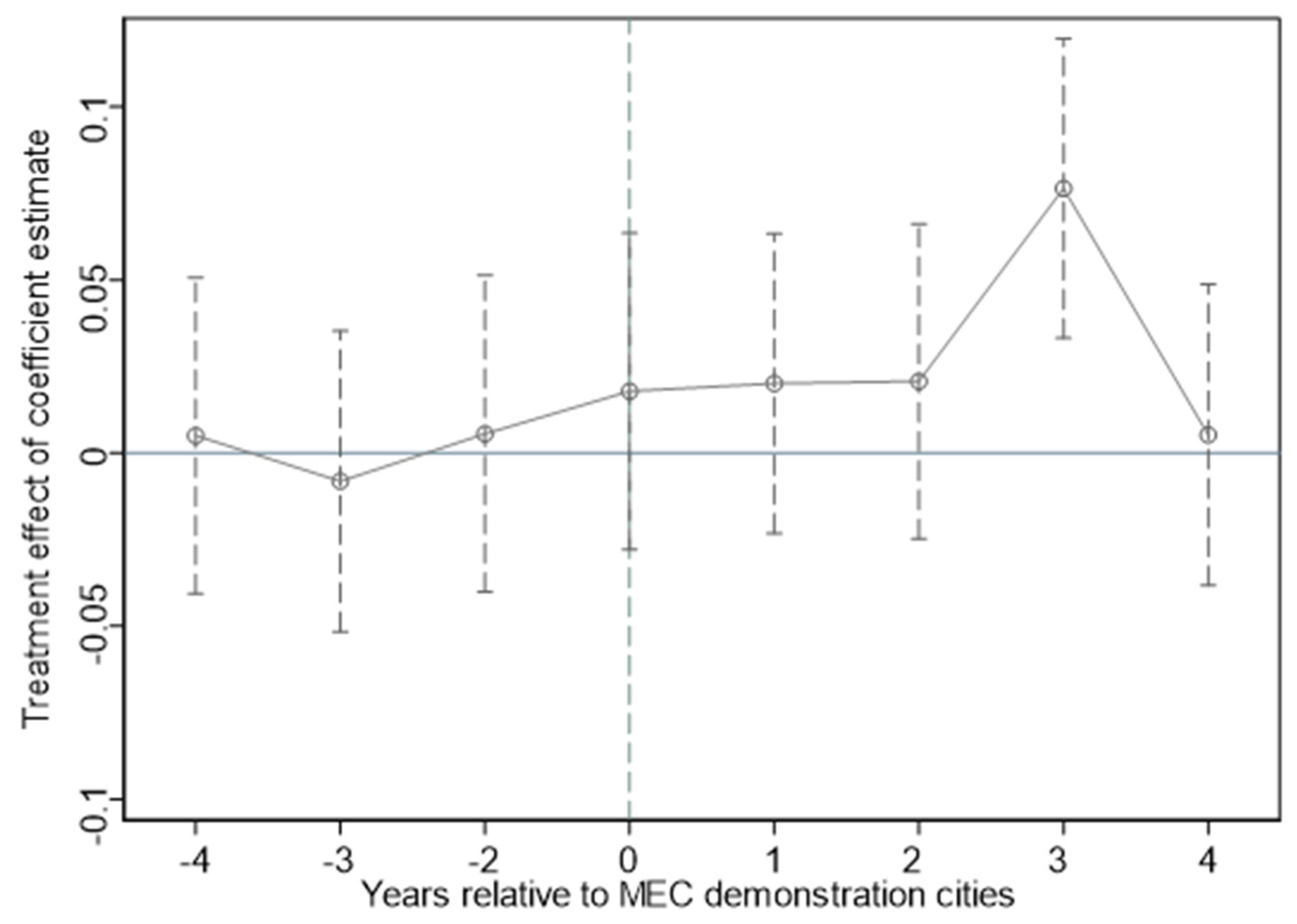
Appendix C. The Construction of GTFP
References
- Smith-Godfrey, S. Defining the blue economy. Marit. Aff. 2016, 12, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bari, A. Our oceans and the blue economy: Opportunities and challenges. Procedia Eng. 2017, 194, 5–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.H.; Noh, J.; Khim, J.S. The Blue Economy and the United Nations’ sustainable development goals: Challenges and opportunities. Environ. Int. 2020, 137, 105528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Q.; Feng, C.; Ding, J.; Bartley, E.; Lin, Y.; Fei, J.; Christakos, G. The decade long achievements of China’s marine ecological civilization construction (2006–2016). J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 272, 111077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, Z.; Yin, X. Environmental regulation, technological innovation and energy consumption—A cross-region analysis in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 203, 885–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Shi, X.; Wu, H.; Liu, L. Trade-off between economic development and environmental governance in China: An analysis based on the effect of river chief system. China Econ. Rev. 2020, 60, 101403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Pei, Z.; Wang, Y. Study on the issue of supplyside reform path in China’s marine ecological civilization construction. Sociology 2019, 9, 20–28. [Google Scholar]
- Qu, Q.; Xu, C. Exploration on marine management under the view of marine eco-civilization. Meteorol. Environ. Res. 2013, 4, 31. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Qian, W. Effect of marine environmental regulation on the industrial structure adjustment of manufacturing industry: An empirical analysis of China’s eleven coastal provinces. Mar. Policy 2020, 113, 103797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Chen, S. Has environmental regulation facilitated the green transformation of the marine industry? Mar. Policy 2022, 144, 105238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhang, C.; Li, R. Does environmental regulation improve marine carbon efficiency? The role of marine industrial structure. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 188, 114669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Liang, C.; Di, Q. Coordination mechanism and empirical research on marine science technology innovation and marine eco-civilization: A case study of coastal areas of China. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2024, 34, 468–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, W.; Xu, Y.; Xiao, H. Research on the impact of marine ecological civilization demonstration zone policies on the green development level of China’s marine economy: A quasi natural experiment based on coastal cities. Mar. Policy 2024, 161, 106048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Shi, J.F. Energy efficiency analysis on Chinese industrial sectors: An improved Super-SBM model with undesirable outputs. J. Clean. Prod. 2014, 65, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- State Oceanic Administration. Opinions on Building a Marine Ecological Civilization Demonstration Zone. 2013. Available online: https://www.gov.cn/gzdt/2012-02/10/content_2063308.htm (accessed on 6 July 2025).
- State Oceanic Administration. Implementation Plan for the Construction of Marine ecological Civilization. 2015. Available online: https://www.gov.cn/xinwen/2015-07/16/content_2898332.htm (accessed on 6 July 2025).
- Cao, Y. Analysis and Policy Recommendations of Marine Ecological Civilization Demonstration Construction. Ecol. Econ. 2016, 32, 207–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, M.A.; Tubb, A. The impact of environmental regulation on firm and country competitiveness: A meta-analysis of the porter hypothesis. J. Assoc. Environ. Resour. Econ. 2018, 5, 371–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, K.; Miao, Y.; Huang, C. Environmental regulation, technological innovation, and industrial structure upgrading. Energy Environ. 2022, 35, 207–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, S.P. The costs of environmental regulation in a concentrated industry. Econometrica 2012, 80, 1019–1061. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, J.; Ji, Y. The Environment, Trade and Innovation with Heterogeneous Firms: A numerical Analysis. In Proceedings of the Agricultural and Applied Economics Association 2011 Annual Meeting, Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 24–26 July 2011; Available online: https://ageconsearch.umn.edu/record/103478/?ln=en&v=pdf (accessed on 19 June 2025).
- Wang, L. Study on the Influence of Marine Environment Control on Industrial Structure Adjustment of Manufacturing Industry in Hainan Province. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2020, 560, 012058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, M.E.; Linde, C.V.D. Toward a new conception of the environment-competitiveness relationship. J. Econ. Perspect. 1995, 9, 97–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanoie, P.; Patry, M.; Lajeunesse, R. Environmental regulation and productivity: Testing the porter hypothesis. J. Product. Anal. 2008, 30, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnstone, N.; Hascic, I.; Popp, D. Renewable energy policies and technological innovation: Evidence based on patent counts. Environ. Resour. Econ. 2010, 45, 133–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calel, R.; Dechezleprêtre, A. Environmental policy and directed technological change: Evidence from the European carbon market. Rev. Econ. Stat. 2016, 98, 173–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, R.; Song, Y.; Sahut, J.M. The impact of environmental regulation on the optimization of industrial structure in energy-based cities. Res. Int. Bus. Finance 2024, 68, 102154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.; Xie, J. Does environmental regulation promote industrial structure optimization in China? A perspective of technical and capital barriers. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2023, 98, 106971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Li, L. Could environmental regulation promote the technological innovation of China’s emerging marine enterprises? Based on the moderating effect of government grants. Environ. Res. 2021, 202, 111682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gollop, F.M.; Roberts, M.J. Environmental regulations and productivity growth: The case of fossil-fueled electric power generation. J. Polit. Econ. 1983, 91, 654–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Sun, P.; Yin, K. Innovation driving effect of marine economic structure transformation. J. Coast. Res. 2020, 115, 184–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, M.E. Towards a dynamic theory of strategy. Strateg. Manag. J. 1991, 12, 95–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, E.Z.; Lee, C.C. The impact of clean energy consumption on economic growth in China: Is environmental regulation a curse or a blessing? Int. Rev. Econ. Finance 2022, 77, 39–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, C.; Hamzah, H.Z.; Yin, J.; Wu, D.; Cao, J.; Mao, X.; Li, H. Impact of environmental regulations on the industrial eco-efficiency in China—Based on the strong porter hypothesis and the weak porter hypothesis. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 44490–44504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, K.; Cheng, Y.; Yao, X. Environmental regulation, green technology innovation, and industrial structure upgrading: The road to the green transformation of Chinese cities. Energy Econ. 2021, 98, 105247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.L.; Shen, M.H.; Ma, R.F.; Yang, H.S.; Chen, Y.N.; Sun, C.Z.; Liu, M.; Han, X.Q.; Hu, Z.D.; Ma, X.G.; et al. Marine resource economy and strategy under the background of marine ecological civilization construction. J. Nat. Resour. 2022, 37, 829–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Ma, J.; Mo, B. Does environmental policy affect green total factor productivity? Quasi-natural experiment based on China’s air pollution control and prevention action plan. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 8216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.C.; Lee, C.C. How does green finance affect green total factor productivity? Evidence from China. Energy Econ. 2022, 107, 105863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; Kong, S. The effect of environmental regulation on green total-factor productivity in China’s industry. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2022, 94, 106757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, S. The influence study on environmental regulation and green total factor productivity of China’s manufacturing industry. Discret. Dyn. Nat. Soc. 2021, 2021, 5580414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Liu, F.; Sun, W.; Tao, X. The relationship between environmental regulation and green total factor productivity in China: An empirical study based on the panel data of 177 cities. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 5287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Peng, X.; Ouyang, M.K. Environmental regulation, green total factor productivity and the transformation of China’s industrial development mode: Analysis based on data of China’s 36 industries. China Ind. Econ. 2013, 56–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Tang, D.; Kong, H.; Boamah, V. Impact of industrial structure upgrading on green total factor productivity in the Yangtze river economic belt. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 3718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Tang, X.; Meng, T.; Chu, J.; Tang, H. Industrial Structure, R&D Staff, and Green Total Factor Productivity of China: Evidence from the Low-Carbon Pilot Cities. Complexity 2021, 2021, 6690152. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, M.; Yang, P.; Li, Q. Impact of environmental regulation on green total factor productivity: A new perspective of green technological innovation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 53785–53800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, J.; Zhang, D. Research on the impact of environmental regulations on industrial green total factor productivity: Perspectives on the changes in the allocation ratio of factors among different industries. Sustainability 2021, 13, 12947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Tao, F. Selection of optimal environmental regulation intensity for Chinese manufacturing industry: Based on the green TFP perspective. China Ind. Econ. 2012, 5, 70–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, Z.; Ma, Y. Heterogeneous environmental regulation and industrial structure upgrading: Evidence from China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 13369–13385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.Y.; Wang, Y. Structural change, industrial upgrading, and middle-income trap. J. Ind. Compet. Trade 2020, 20, 359–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.; Wu, C. Promotion incentives and air pollution: From the political promotion tournament to the environment tournament. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 317, 115491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M. Environmental governance as a new runway of promotion tournaments: Campaign-style governance and policy implementation in China’s environmental laws. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 34924–34936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, W.; Yin, Y.; Bai, X.; Taghizadeh-Hesary, F. Analysis of the upgrading effect of the industrial structure of environmental regulation: Evidence from 113 cities in China. Front. Environ. Sci. 2021, 9, 692478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, J.; Guan, C. Environmental Regulation, Government Behavior and Industrial Structure Upgrading. J. Beijing Inst. Technol. (Soc. Sci. Ed.) 2019, 3, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Wei, X.; Wei, J.; Gao, X. Industrial structure upgrading, green total factor productivity and carbon emissions. Sustainability 2022, 14, 1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Gao, D.; Song, D.; Li, Y. Environmental regulation, pollution reduction and green innovation: The case of the Chinese Water Ecological Civilization City Pilot policy. Econ. Syst. 2021, 45, 100911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, T.; Zhang, W.; Zhou, Q.; Wang, K. Industrial structure, urban governance and haze pollution: Spatiotemporal evidence from China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 742, 139228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.M.; Nepal, R.; Alam, K. Impacts of human capital, exports, economic growth and energy consumption on CO2 emissions of a cross-sectionally dependent panel: Evidence from the newly industrialized countries (NICs). Environ. Sci. Policy 2021, 121, 24–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abid, M.; Sekrafi, H. Pollution haven or halo effect? A comparative analysis of developing and developed countries. Energy Rep. 2021, 7, 4862–4871. [Google Scholar]
- Hoang, D.T.; Do, A.D.; Trinh, M.V. Spillover effects of FDI on technology innovation of vietnamese enterprises. J. Asian Financ. Econ. Bus. 2021, 8, 655–663. [Google Scholar]
- Shevchenko, D.; Zhao, W.; Guo, Q. Financial opening, financial development and industrial restructuring: A mediating effect analysis. Int. J. Dev. Issues 2023, 22, 141–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, Y.; Wang, W.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, J. How does digital economy affect green total factor productivity? Evidence from China. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 857, 159428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.; Zhou, Y. How does vertical fiscal imbalance affect the upgrading of industrial structure? Empirical evidence from China. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2021, 170, 120886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, F.; Xu, J. Green total factor productivity: A re-examination of quality of growth for provinces in China. China Econ. Rev. 2020, 62, 101454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Hu, Q.; Wei, X. Impact of environmental regulation on coastal marine pollution—A case of coastal prefecture-level cities in China. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 882010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.N.; Mobin, M.; Abbas, Z.K.; Alamri, S.A. Fertilizers and their contaminants in soils, surface and groundwater. Encycl. Anthr. 2018, 5, 225–240. [Google Scholar]
- Mainstone, C.P.; Parr, W. Phosphorus in rivers—Ecology and management. Sci. Total Environ. 2002, 282, 25–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.; Wang, Y.; Ye, Y.; Zhang, H.; Huang, G. Relationship between the built environment and the location choice of high-tech firms: Evidence from the Pearl River Delta. Sustainability 2019, 11, 3689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Mello Santos, V.H.; Campos, T.L.R.; Espuny, M.; de Oliveira, O.J. Towards a green industry through cleaner production development. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 349–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, H.; Wen, J.; Choi, Y. How the SDGs are implemented in China—A comparative study based on the perspective of policy instruments. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 291, 125937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tone, K. A slacks-based measure of efficiency in data envelopment analysis. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2001, 130, 498–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.; Zhang, R.P.; Gao, L.H. Can environmental policies improve marine ecological efficiency? Examining China’s Ecological Civilization Pilot Zones. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2024, 203, 116479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Policy Issued Time | Marine Ecological Civilization Demonstration Cities |
|---|---|
| 2013 | Shandong Province: Weihai City, Rizhao City, Yantai City; Zhejiang Province: Ningbo City, Taizhou City, Wenzhou City; Fujian Province: Xiamen City, Quanzhou City, Zhangzhou City; Guangdong Province: Zhuhai City, Shantou City, Zhanjiang City |
| 2015 | Liaoning Province: Panjin City, Dalian City; Shandong Province: Qingdao City; Jiangsu Province: Nantong City, Yancheng City; Zhejiang Province: Zhoushan City; Guangdong Province: Huizhou City, Shenzhen City; Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region: Beihai City; Hainan Province: Sanya City |
| Variable | Obs | Min | p50 | Max | Mean | Std. Dev |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MEC | 689 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0.194 | 0.396 |
| ISU | 689 | 0.156 | 0.459 | 0.792 | 0.465 | 0.105 |
| Lnperincome | 689 | 6.778 | 8.631 | 10.271 | 8.530 | 0.558 |
| Lnedu | 689 | 3.540 | 5.448 | 6.294 | 5.440 | 0.314 |
| Lnenterprises | 689 | 2.996 | 7.440 | 9.841 | 7.291 | 1.237 |
| Lnpop | 689 | 4.904 | 6.311 | 7.923 | 6.323 | 0.564 |
| Lnfdi | 689 | 0.069 | 3.398 | 5.270 | 3.244 | 1.052 |
| STRAD | 689 | 5.956 | 6.638 | 7.836 | 6.652 | 0.330 |
| GTI | 689 | 0 | 3.135 | 7.857 | 3.296 | 1.888 |
| GTFP | 689 | 0.835 | 0.998 | 1.183 | 0.999 | 0.020 |
| GI | 689 | 0.009 | 0.045 | 0.502 | 0.081 | 0.095 |
| WQ | 689 | 1 | 2 | 5 | 2.814 | 1.567 |
| LnAP | 517 | 0 | 0.801 | 2.061 | 0.837 | 0.347 |
| LnDIN | 517 | 0 | 3.060 | 5.441 | 3.165 | 0.683 |
| (1) | (2) | |
|---|---|---|
| ISU | ISU | |
| MEC | 0.0187 *** | 0.0162 *** |
| (0.00635) | (0.00607) | |
| Lnperincome | −0.0134 | |
| (0.0184) | ||
| Lnedu | 0.0050 | |
| (0.0129) | ||
| Lnenterprises | −0.0750 *** | |
| (0.0109) | ||
| Lnpop | −0.0043 | |
| (0.0314) | ||
| Lnfdi | 0.0070 ** | |
| (0.0029) | ||
| Constant | 0.420 *** | 1.0440 *** |
| (0.00582) | (0.2120) | |
| Observations | 689 | 689 |
| R-squared | 0.3997 | 0.4700 |
| Time-fixed effect | Yes | Yes |
| City-fixed effect | Yes | Yes |
| Variable | Unmatched/Matched | Mean | Bias (%) | Reduct Bias (%) | t-Test | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Treated | Control | t | ||||
| Lnperincome | U | 8.535 | 8.527 | 1.500 | 0.190 | |
| M | 8.535 | 8.493 | 7.600 | −417.600 | 0.910 | |
| Lnedu | U | 5.395 | 5.471 | −24.80 | −3.170 | |
| M | 5.395 | 5.421 | −8.400 | 66.200 | −1.090 | |
| Lnenterprises | U | 7.407 | 7.210 | 15.80 | 2.070 | |
| M | 7.407 | 7.336 | 5.700 | 64.000 | 0.680 | |
| Lnpop | U | 6.410 | 6.262 | 26.90 | 3.430 | |
| M | 6.410 | 6.451 | −7.400 | 72.500 | −1.000 | |
| Lnfdi | U | 3.417 | 3.121 | 28.70 | 3.670 | |
| M | 3.417 | 3.397 | 2.000 | 93.200 | 0.260 | |
| Variable | (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ISU | ISU | STRAD | STRAD | |
| MEC | 0.0168 *** | 0.0138 ** | 0.0240 ** | 0.0243 ** |
| (0.0062) | (0.0059) | (0.0117) | (0.0117) | |
| Lnperincome | −0.0029 | 0.0370 | ||
| (0.0188) | (0.0355) | |||
| Lnedu | −0.0002 | −0.0285 | ||
| (0.0148) | (0.0250) | |||
| Lnenterprises | −0.0696 *** | −0.0616 *** | ||
| (0.0110) | (0.0211) | |||
| Lnpop | −0.0071 | −0.1510 ** | ||
| (0.0305) | (0.0606) | |||
| Lnfdi | 0.0071 ** | −0.0031 | ||
| (0.0030) | (0.0056) | |||
| Constant | 0.4210 *** | 0.9720 *** | 6.4940 *** | 7.7600 *** |
| (0.0056) | (0.2130) | (0.0107) | (0.4100) | |
| R-squared | 0.4290 | 0.4850 | 0.6790 | 0.6910 |
| Observations | 659 | 659 | 689 | 689 |
| Time-fixed effect | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| City-fixed effect | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Variables | (1) | (2) | (3) |
|---|---|---|---|
| GTI | GTFP | GI | |
| MEC | 0.3330 *** | 0.0058 * | 0.0017 * |
| (0.0727) | (0.0030) | (0.0009) | |
| Lnperincome | 0.3430 | −0.0291 *** | −0.0030 |
| (0.2200) | (0.0092) | (0.0027) | |
| Lnedu | −0.2360 | −0.0164 ** | −0.0004 |
| (0.1550) | (0.0064) | (0.0019) | |
| Lnenterprises | 0.1000 | 0.0068 | 0.0029 * |
| (0.1310) | (0.0054) | (0.0016) | |
| Lnpop | −0.3450 | −0.0001 | 0.0132 *** |
| (0.3770) | (0.0156) | (0.0046) | |
| Lnfdi | 0.1040 *** | 0.0012 | −0.0001 |
| (0.0351) | (0.0015) | (0.0004) | |
| Constant | 1.3580 | 1.2590 *** | 0.0016 |
| (2.546) | (0.1060) | (0.0311) | |
| Observations | 689 | 689 | 689 |
| R-squared | 0.7900 | 0.0960 | 0.0730 |
| Time-fixed effect | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| City-fixed effect | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Variable | (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | (7) | (8) | (9) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WQ | WQ | WQ | LnAP | LnAP | LnAP | LnDIN | LnDIN | LnDIN | |
| MEC | 0.2490 | 5.0730 | 0.1500 | −0.2660 *** | 0.0090 | −0.2550 *** | −0.0775 | 1.4610 | −0.0463 |
| (0.3510) | (3.7900) | (0.2280) | (0.0760) | (1.4810) | (0.0497) | (0.1240) | (2.4150) | (0.0812) | |
| MEC×GTI | −0.1480 ** | 0.0168 | 0.0157 | ||||||
| (0.0737) | (0.0166) | (0.0271) | |||||||
| MEC×GTFP | −5.4550 | −0.2060 | −1.4730 | ||||||
| (3.7760) | (1.4810) | (2.4140) | |||||||
| MEC×GI | −6.9830 *** | 0.7650 | 0.4450 | ||||||
| (2.2810) | (0.4970) | (0.8120) | |||||||
| Constant | −3.6280 | −2.1690 | −7.1330 | 5.8800 *** | 5.6830 *** | 6.3130 *** | 5.9310 *** | 5.7340 *** | 6.1150 *** |
| (5.0290) | (4.9850) | (5.2140) | (1.3370) | (1.3250) | (1.3830) | (2.1820) | (2.1590) | (2.2600) | |
| Observations | 689 | 689 | 689 | 517 | 517 | 517 | 517 | 517 | 517 |
| R-squared | 0.0670 | 0.0650 | 0.0750 | 0.2090 | 0.2070 | 0.2110 | 0.0220 | 0.0220 | 0.0220 |
| Control Variable | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Time-fixed effect | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| City-fixed effect | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Variable | (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ISU | ||||||
| Bohai Rim Economic Zone | Yangtze River Delta Economic Zone | Pearl River Delta Economic Zone | Other | EP Priority Cities | Non-Priority Cities | |
| MEC | 0.0153 | 0.0006 | 0.0417 *** | 0.0108 | 0.0333 ** | 0.0041 |
| (0.0101) | (0.0080) | (0.0141) | (0.0144) | (0.0138) | (0.0060) | |
| Constant | 0.5320 | 1.1050 ** | 0.3870 | −2.3870 *** | 2.7730 *** | 0.1620 |
| (0.8520) | (0.4450) | (0.3150) | (0.8090) | (0.6280) | (0.2070) | |
| Control Variable | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Time-fixed effect | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| City-fixed effect | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| R-squared | 0.6950 | 0.7490 | 0.4170 | 0.3610 | 0.4410 | 0.6080 |
| Observations | 221 | 143 | 182 | 143 | 286 | 403 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ling, J.; Jin, Y. Balancing Industrialization with Pollution: Evidence from the Marine Ecological Civilization Demonstration Zone Program in China. Sustainability 2025, 17, 6352. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17146352
Ling J, Jin Y. Balancing Industrialization with Pollution: Evidence from the Marine Ecological Civilization Demonstration Zone Program in China. Sustainability. 2025; 17(14):6352. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17146352
Chicago/Turabian StyleLing, Jinxuan, and Yi Jin. 2025. "Balancing Industrialization with Pollution: Evidence from the Marine Ecological Civilization Demonstration Zone Program in China" Sustainability 17, no. 14: 6352. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17146352
APA StyleLing, J., & Jin, Y. (2025). Balancing Industrialization with Pollution: Evidence from the Marine Ecological Civilization Demonstration Zone Program in China. Sustainability, 17(14), 6352. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17146352




