Improving Anaerobic Digestion Process of Sewage Sludge in Terms of Energy Efficiency and Carbon Emission: Pre- or Post-Thermal Hydrolysis?
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Functional Units and Accounting Boundaries
2.2. Calculation Method
2.2.1. Direct Carbon Emission
2.2.2. Indirect Carbon Emission
2.2.3. Carbon Compensation
2.3. Parameter Selection
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Mass Flow Analysis of Typical Sludge Disposal Pathways
3.2. Evolution of Energy Input and Output of Typical Sludge Disposal Pathways
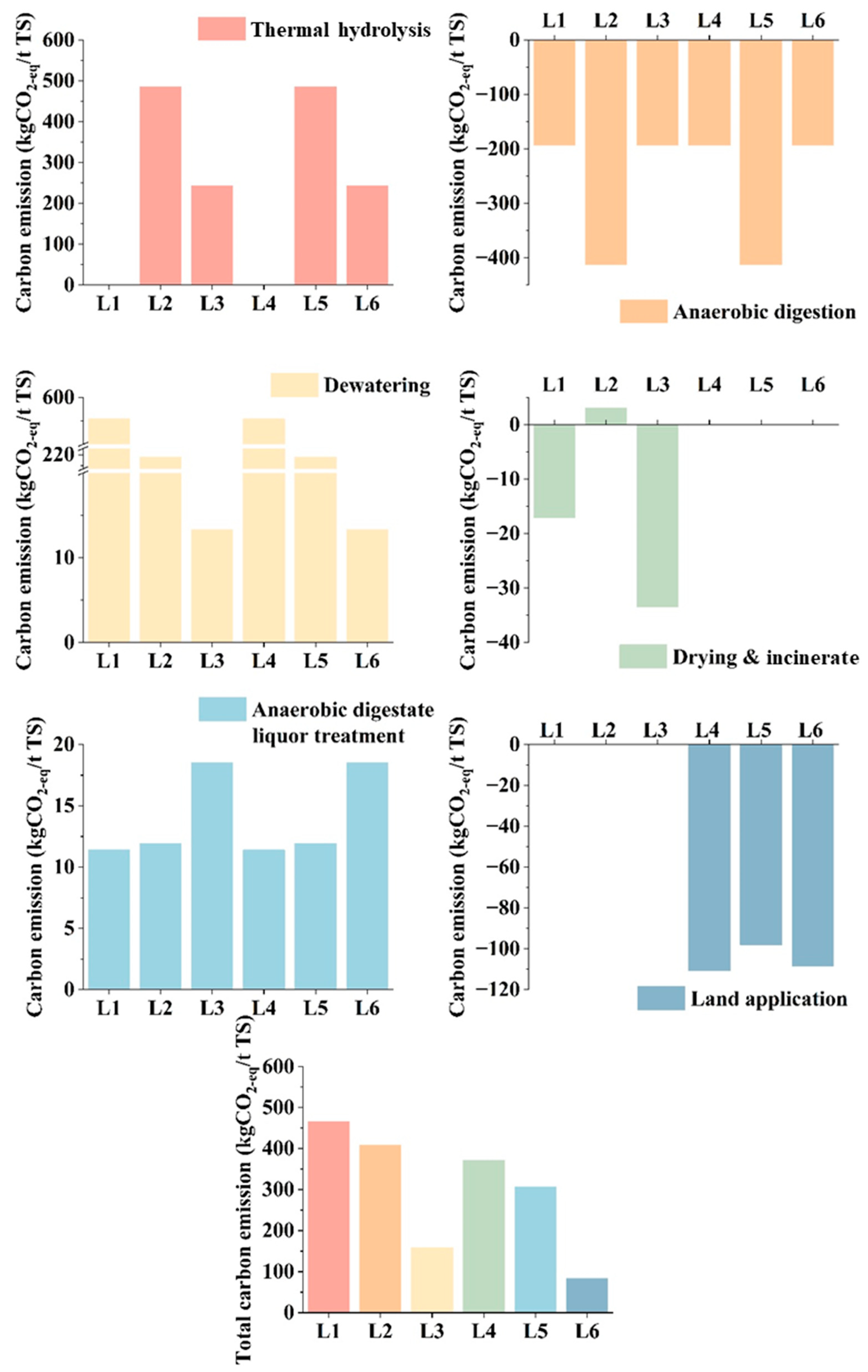
3.3. Carbon Emission and Reduction Potential Analysis for Typical Sludge Disposal Pathways
4. Conclusions
- Compared with conventional anaerobic digestion, applying TH as a post-treatment process leads to a substantial reduction in carbon emissions by 65.9–77.6%, while pretreatment integration yields only moderate improvements.
- Post-treatment TH significantly enhances the dewaterability of anaerobic digestate, and the elimination of chemical flocculants in the dewatering stage and the energy consumption in the drying stage plays a pivotal role in reducing carbon emissions.
- The combination of TH as a post-treatment step with land application as the final disposal method yields the lowest overall carbon emission (83.45 kg CO2-eq/t TS) among the evaluated pathways.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huang, D.N.; Wu, Y.H.; Zhang, L.; Tang, Y.L.; Liu, C.; Zhang, R.X.; Wang, Y.Y.; Gao, Y.N. Life cycle assessment of sewage sludge treatment and disposal technologies based on carbon emissions and environmental impacts. Environ. Technol. 2025, 46, 477–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Dai, X.; Chai, X. Critical review on dewatering of sewage sludge: Influential mechanism, conditioning technologies and implications to sludge re-utilizations. Water Res. 2020, 180, 115–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, A.; Zhang, R.R.; Ngo, H.H.; He, X.; Ma, J.; Nan, J.; Li, G.B. Life cycle assessment of sewage sludge treatment and disposal based on nutrient and energy recovery: A review. Sci. Total Env. 2021, 769, 144451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Cheng, J.J.; Creamer, K.S. Inhibition of anaerobic digestion process: A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 4044–4064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, S.; Jain, S.; Wolf, I.T.; Lee, J.; Tong, Y.W. A comprehensive review on operating parameters and different pretreatment methodologies for anaerobic digestion of municipal solid waste. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 52, 142–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilli, S.; Bhunia, P.; Yan, S.; LeBlanc, R.J.; Tyagi, R.D.; Surampalli, R.Y. Ultrasonic pretreatment of sludge: A review. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2011, 18, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barber, W. Thermal hydrolysis for sewage treatment: A critical review. Water Res. 2016, 104, 53–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, N.; Dai, X.; Tao, W.; Jenkinson, I.R.; Li, Z. Enhanced dewaterability of sludge during anaerobic digestion with thermal hydrolysis pretreatment: New insights through structure evolution. Water Res. 2018, 131, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Dai, X.; Song, L.; Dai, L.; Dong, B. Effects of stepwise thermal hydrolysis and solid-liquid separation on three different sludge organic matter solubilization and biodegradability. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 290, 121753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Li, N.; Dong, B.; Zhao, W.; Dai, L.; Dai, X. New insights into the enhanced performance of high solid anaerobic digestion with dewatered sludge by thermal hydrolysis: Organic matter degradation and methanogenic pathways. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 342, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.; Liu, H.; Chen, S.; Dichtl, N.; Dai, X.; Li, N. Effects of thermal hydrolysis on organic matter solubilization and anaerobic digestion of high solid sludge. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 264, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C. The Effect of the Post High Temperature Thermai Hydroiysis on Anaerobic Digestion of Dewatered Siudge and the Performance of Biogas Residue; Tongji University: Shanghai, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, N.; Dong, B.; Wu, B.; Dai, X. High-solid anaerobic digestion of sewage sludge under mesophilic conditions: Feasibility study. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 104, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svennevik, O.K.; Solheim, O.E.; Beck, G.; Srland, G.H.; Nilsen, P.J. Effects of post anaerobic digestion thermal hydrolysis on dewaterability and moisture distribution in digestates. Water Sci. Technol. 2019, 80, 1338–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qrenawi, L.I.; Rabah, F.K.J. Sludge management in water treatment plants: Literature review. Int. J. Envir Waste Ma 2021, 27, 93–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, W.; Laha, S. Biosolids and sludge management. Water Environ. Res. 2005, 77, 1464–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swierczek, L.; Cieslik, B.M.; Konieczka, P. The potential of raw sewage sludge in construction industry—A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 200, 342–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Z.Y.; Long, G.C.; Zhou, J.L.; Ma, C. Valorization of sewage sludge in the fabrication of construction and building materials: A review. Resour. Conserv. Recy. 2020, 154, 104606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, L.; Porro, J.; Nopens, I. Quantification and Modelling of Fugitive Greenhouse Gas Emissions from Urban Water Systems: A Report from the IWA Task Group on GHG; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2022; pp. 1–260. [Google Scholar]
- Yona, L.; Cashore, B.; Jackson, R.B.; Ometto, J.; Bradford, M.A. Refining national greenhouse gas inventories. Ambio 2020, 49, 1581–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Technical Support Unit of the IPCC National Greenhouse Gas Inventories Programme. 2006 IPCC Guidelines for national greenhouse gas inventories. Available online: https://www.ipcc-nggip.iges.or.jp/meeting/pdfiles/Washington_Report.pdf (accessed on 3 June 2025).
- Piippo, S.; Lauronen, M.; Postila, H. Greenhouse gas emissions from different sewage sludge treatment methods in north. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 177, 483–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Li, P.; Song, K.; Liu, G.F.; Li, L.M.; Zhang, P.H.; Gong, J.; Huang, Q.X. New model for evaluating greenhouse gas emissions from sludge treatment based on fossil and biogenic carbon migration. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 425, 138845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.; Kim, S.; Lee, J.; Jeon, Y.; Kim, K.H.; Jeon, E.C. A Study on Applying Biomass Fraction for Greenhouse Gases Emission Estimation of a Sewage Sludge Incinerator in Korea: A Case Study. Sustain. Basel 2017, 9, 557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillenwater, M. Forgotten carbon: Indirect CO in greenhouse gas emission inventories. Env. Sci. Policy 2008, 11, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.N.; Luo, D. Carbon Emissions from Sludge Treatment in a Sewage Treatment Plant: Field Study Investigation in Guangzhou, China. J. Env. Eng. 2024, 150, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.A.; Hoque, M.A.; Kim, P.J. Mitigating global warming potentials of methane and nitrous oxide gases from rice paddies under different irrigation regimes. Ambio 2013, 42, 357–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, T.Y.; Choi, S.S. Evaluation of methane production by the thermal pretreatment of waste activated sludge in an anaerobic digester. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2007, 13, 856–863. [Google Scholar]
- Pilli, S.; Yan, S.; Tyagi, R.D.; Surampalli, R.Y. Thermal Pretreatment of Sewage Sludge to Enhance Anaerobic Digestion: A Review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 45, 669–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bougrier, C.; Delgenès, J.P.; Carrère, H. Effects of thermal treatments on five different waste activated sludge samples solubilisation, physical properties and anaerobic digestion. Chem. Eng. J. 2008, 139, 236–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svensson, K.; Kjørlaug, O.; Higgins, M.J.; Linjordet, R.; Horn, S.J. Post-anaerobic digestion thermal hydrolysis of sewage sludge and food waste: Effect on methane yields, dewaterability and solids reduction. Water Res. 2018, 132, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Li, Z.; Gu, J.; Wang, F.; Hou, B.; Yu, R. Carbon emissions of municipal sludge “deep dehydration-drying-incineration” processes under different sludge preconditioning methods. China Environ. Sci. 2023, 43, 6651–6656. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, X.; Chen, Q.; van Loosdrecht, M.C.M.; Li, J.; Jiang, H. Sustainable disposal of excess sludge: Incineration without anaerobic digestion. Water Res. 2020, 170, 115298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, X.; Li, J.; van Loosdrecht, M.C.M.; Jiang, H.; Liu, R. Energy recovery from wastewater: Heat over organics. Water Res. 2019, 161, 74–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, X.; Wang, X.; Liu, R.; Li, S.; van Loosdrecht, M.C.M.; Jiang, H. Environmental impacts of resource recovery from wastewater treatment plants. Water Res. 2019, 160, 268–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantaleo, A.; Gennaro, B.D.; Shah, N. Assessment of optimal size of anaerobic co-digestion plants: An application to cattle farms in the province of Bari (Italy). Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2013, 20, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Duan, N. Characteristics of sludge anaerobic digestion effluent in municipal sewage plant. Water Wastewater Eng. 2020, 46, 237–241. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Laurent, J.; Casellas, M.; Carrère, H.; Dagot, C. Effects of thermal hydrolysis on activated sludge solubilization, surface properties and heavy metals biosorption. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 166, 841–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomsen, T.P.; Sárossy, Z.; Ahrenfeldt, J.; Henriksen, U.B.; Frandsen, F.J.; Müller-Stöver, D.S. Changes imposed by pyrolysis, thermal gasification and incineration on composition and phosphorus fertilizer quality of municipal sewage sludge. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 198, 308–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viau, E.; Bibby, K.; Paez-Rubio, T.; Peccia, J. Toward a consensus view on the infectious risks associated with land application of sewage sludge. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 5459–5469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.-L.; Ding, J.; Yang, S.-S.; Pang, J.-W.; Lu, M.-Y.; Zhao, X.; He, S.-S.; Zhang, L.-Y.; Ren, N.-Q. Strategic carbon emission assessment in sludge treatment: A dynamic tool for low-carbon transformation. Environ. Int. 2024, 193, 109124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Guo, Y.; Fang, N.; Dong, B. Life cycle assessment of greenhouse gas emissions of typical sewage sludge incineration treatment route based on two case studies in China. Env. Res. 2023, 231, 115959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, M.; Sun, Y.; Huang, Z.; Li, H.; Zhang, X.; Wu, X.; Zhao, C.; Yao, S.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, W.; et al. Energy economy evaluation of sludge pretreatment-anaerobic digestion system. Huagong Jinzhan/Chem. Ind. Eng. Prog. 2022, 41, 1503–1516. [Google Scholar]
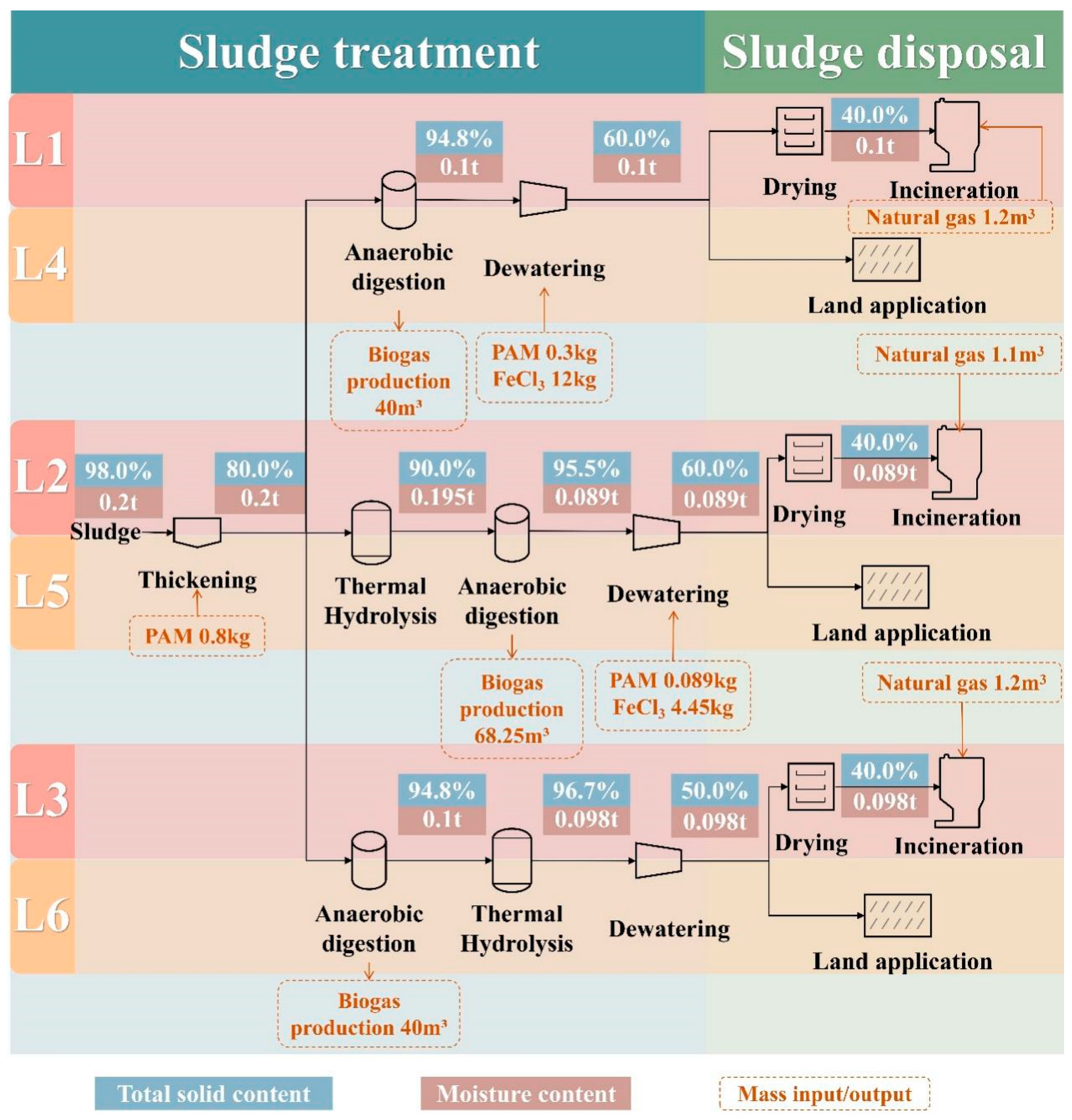

| Pathway | Step 1 | Step 2 | Step 3 | Step 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thickening | AD and TH Sequence | Dewatering | Final Disposal | |
| L1 (N/A TH) | Included | AD | Included | Drying → Incineration |
| L2 (Pre-TH) | Pre-TH → AD | Drying → Incineration | ||
| L3 (Post-TH) | AD → Post-TH | Drying → Incineration | ||
| L4 (N/A TH) | AD | Land Application | ||
| L5 (Pre-TH) | Pre-TH → AD | Land Application | ||
| L6 (Post-TH) | AD → Post-TH | Land Application |
| Processing Unit | Parameter | Unit | Value | Emission Factor | Emission Factor Unit | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L1/L4 | L2/L5 | L3/L6 | |||||
| Thickening | Energy consumption | kW·h/tDS | 15 | 0.68 | kg CO2/kW·h | ||
| PAM dosage | kg/tDS | 4 | 25 | kg CO2/kgPAM | |||
| AD [28,29] | Biogas production | m3/tDS | 200 | 350 | 200 | 0.056 | kg CO2/MJ |
| Energy consumption | kW·h/tDS | 100 | 50 | 100 | 0.68 | kg CO2/kW·h | |
| TH [30,31] | Energy consumption | kW·h/tDS | N/A | 260 | 260 | 0.68 | kg CO2/kW·h |
| Steam consumption | tSteam/tDS | N/A | 1.6 | 1.6 | 193.39 | kg CO2/tSteam | |
| Dewatering [29] | Energy consumption | kW·h/tDS | 55 | 40 | 40 | 0.68 | kg CO2/kW·h |
| PAM dosage | kg/tDS | 3 | 1 | N/A | 25 | kg CO2/kgPAM | |
| FeCl3 dosage | kg/tDS | 120 | 50 | N/A | 8.3 | kg CO2/kgFeCl3 | |
| Drying [32] | Energy consumption | kW·h/kgH2O | 0.125 | 0.68 | kg CO2/kW·h | ||
| Incinerate [33,34,35] | Energy consumption | kW·h/tDS | 300 | 0.68 | kg CO2/kW·h | ||
| Auxiliary fuel consumption | m3/tDS | 12.25 | 1.879 | kg CO2/m3 | |||
| Land application [36] | N | kg/tDS | 30 | 7.759 | kg CO2/kgN | ||
| P | kg/tDS | 15.75 | 2.332 | kg CO2/kgP | |||
| K | kg/tDS | 2.4 | 0.660 | kg CO2/kgK | |||
| Biogas slurry treatment [37] | Energy consumption | kW·h/m3 | 2 | 0.68 | kg CO2/kW·h | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ye, Y.; Msuya, A.S.; Dai, X.; Chai, X.; Wu, B. Improving Anaerobic Digestion Process of Sewage Sludge in Terms of Energy Efficiency and Carbon Emission: Pre- or Post-Thermal Hydrolysis? Sustainability 2025, 17, 6147. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17136147
Ye Y, Msuya AS, Dai X, Chai X, Wu B. Improving Anaerobic Digestion Process of Sewage Sludge in Terms of Energy Efficiency and Carbon Emission: Pre- or Post-Thermal Hydrolysis? Sustainability. 2025; 17(13):6147. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17136147
Chicago/Turabian StyleYe, Yawen, Azizi Selemani Msuya, Xiaohu Dai, Xiaoli Chai, and Boran Wu. 2025. "Improving Anaerobic Digestion Process of Sewage Sludge in Terms of Energy Efficiency and Carbon Emission: Pre- or Post-Thermal Hydrolysis?" Sustainability 17, no. 13: 6147. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17136147
APA StyleYe, Y., Msuya, A. S., Dai, X., Chai, X., & Wu, B. (2025). Improving Anaerobic Digestion Process of Sewage Sludge in Terms of Energy Efficiency and Carbon Emission: Pre- or Post-Thermal Hydrolysis? Sustainability, 17(13), 6147. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17136147










