Analysis of the Spatial–Temporal Characteristics, Regional Differences, and Obstacle Factors of Agricultural Modernization Development in Gansu Province, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Research Design
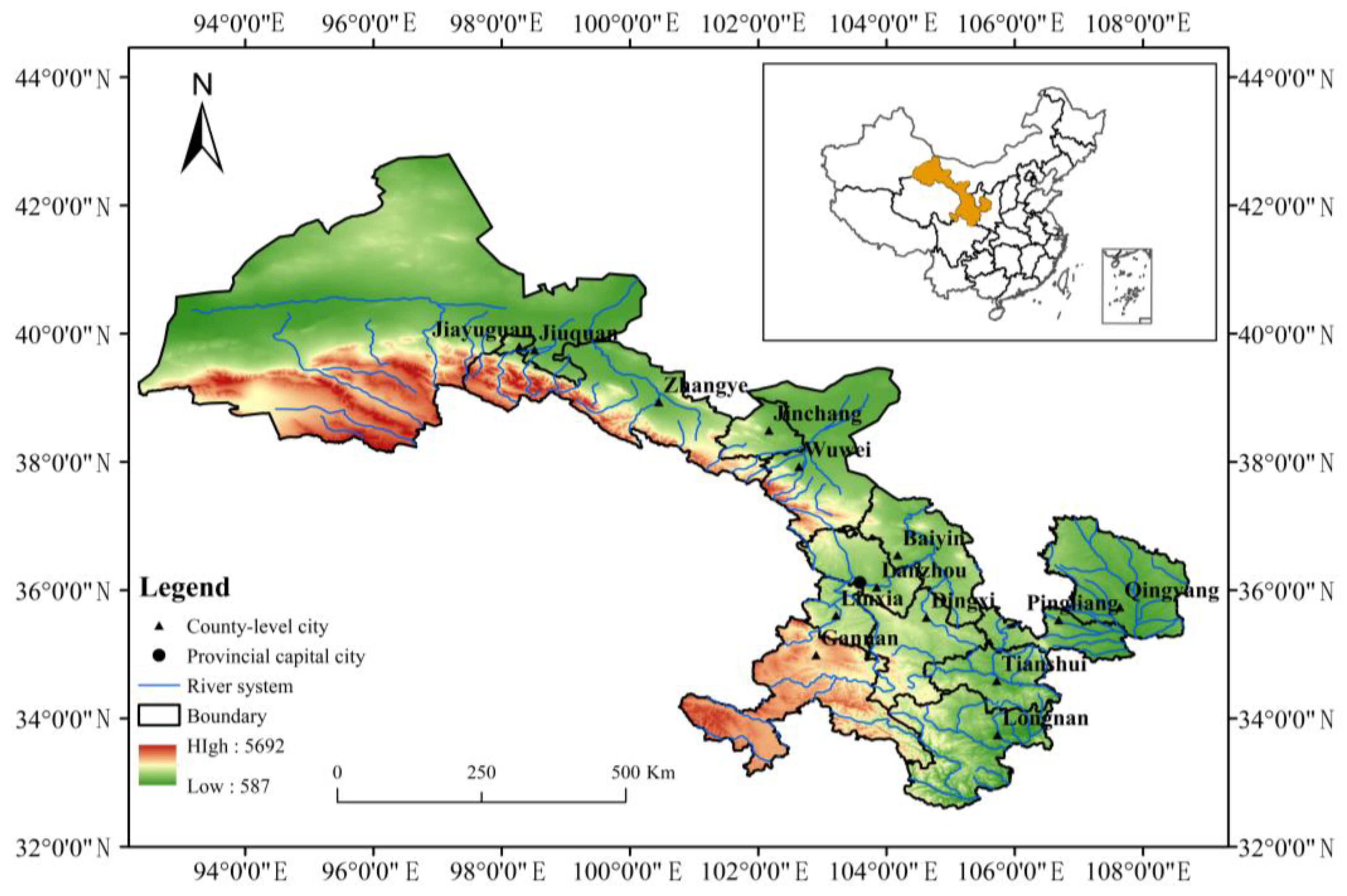
2.1. Overview of the Study Area and Data Sources
2.2. Evaluation Index System Construction
2.3. Research Methods
2.3.1. Multi-Index Comprehensive Evaluation Method
- (1)
- Data standardization: Firstly, standardize the data to eliminate the influence of units and dimensions.
- (2)
- Calculate the feature contribution degree of the i-th evaluation object under the j-th indicator as follows:
- (3)
- The information entropy ej of each indicator is calculated as follows:
- (4)
- Calculate the specific weight Wj of each indicator as follows:
- (5)
- Calculate the index of agricultural modernization level as follows:
2.3.2. Theil Index Analysis Method
2.3.3. Obstacle Degree Model
3. Data Processing and Result Analysis
3.1. Analysis of the Development Level of Agricultural Modernization in Gansu Province, China
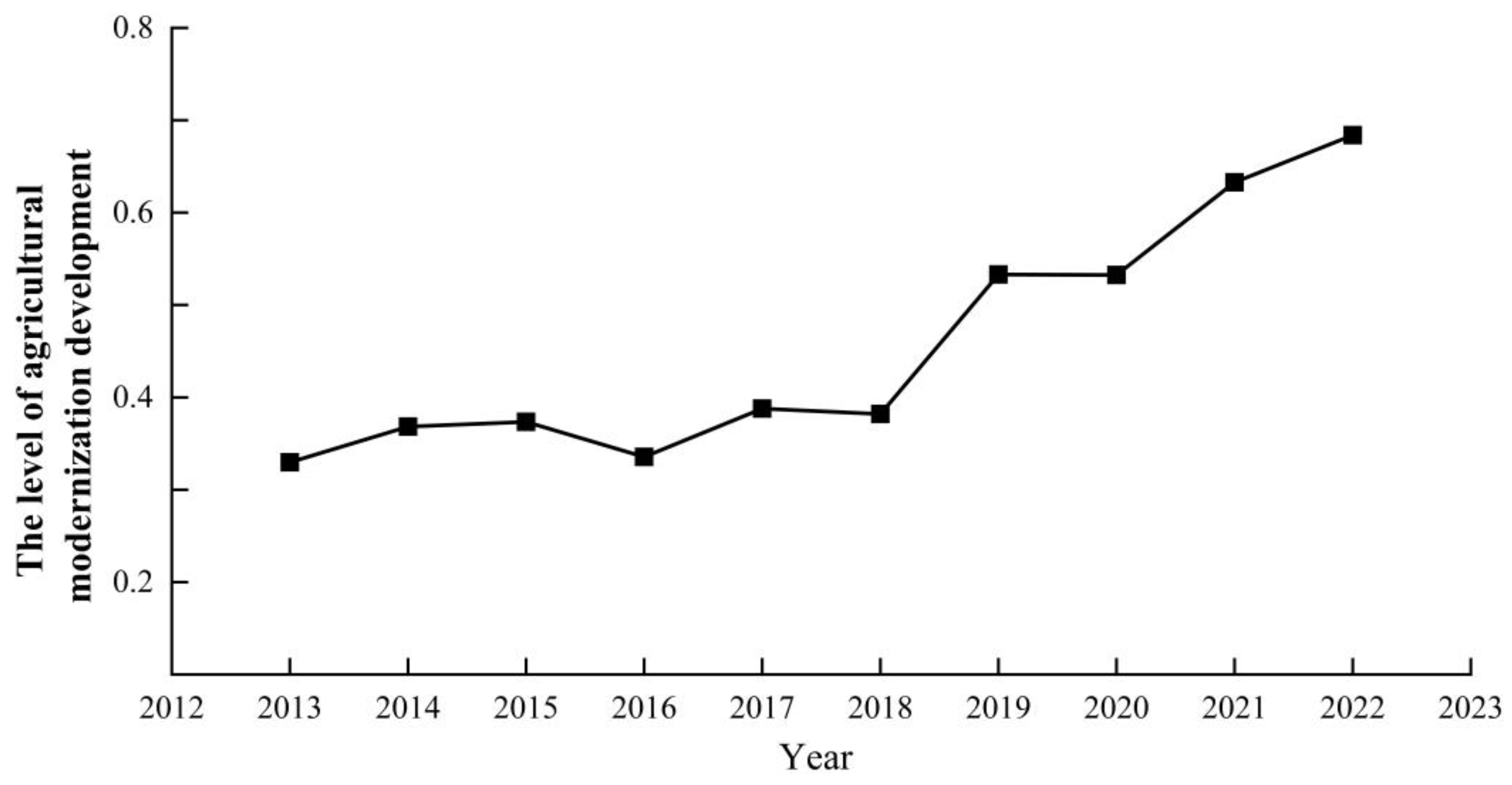
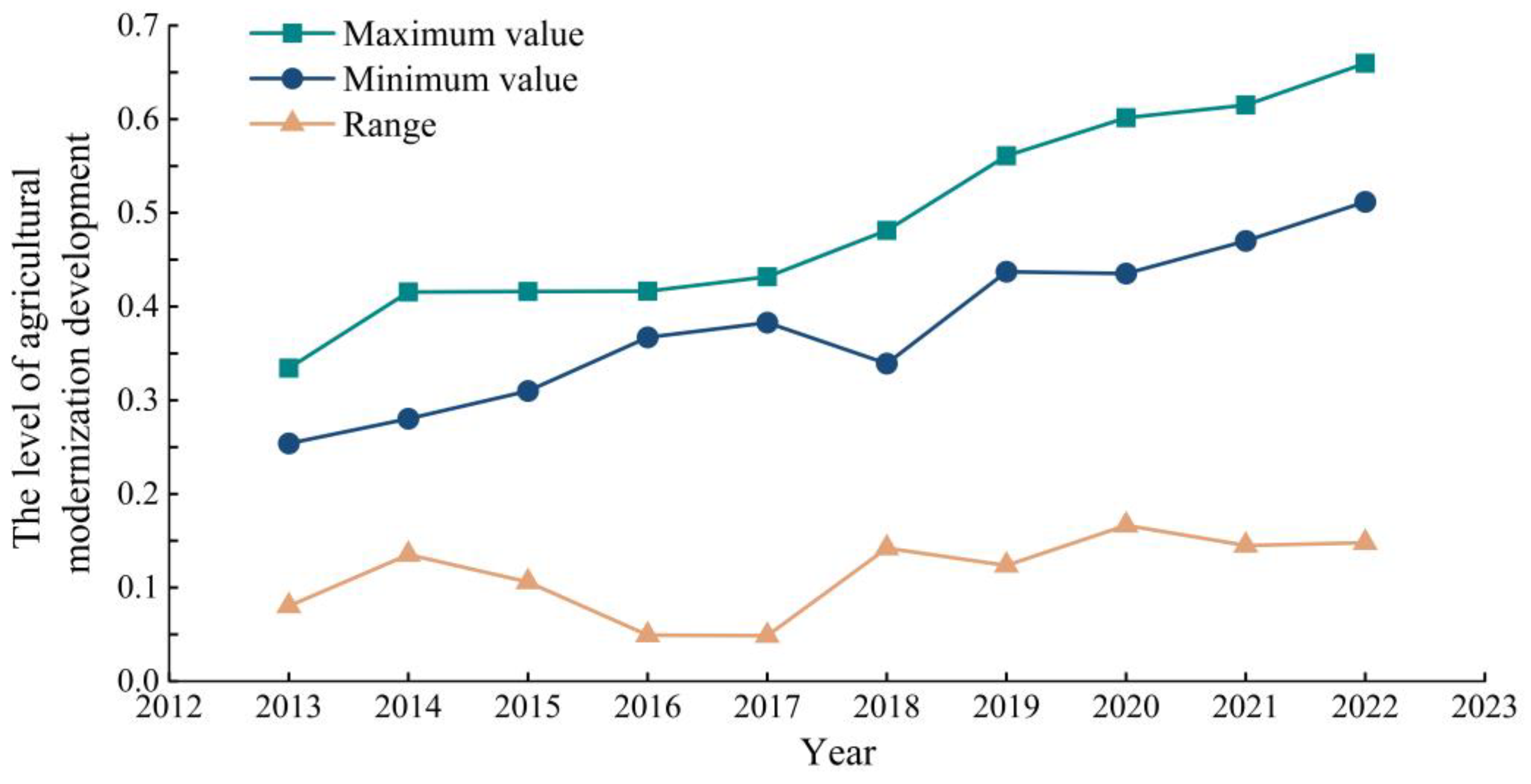
3.1.1. General Characteristics
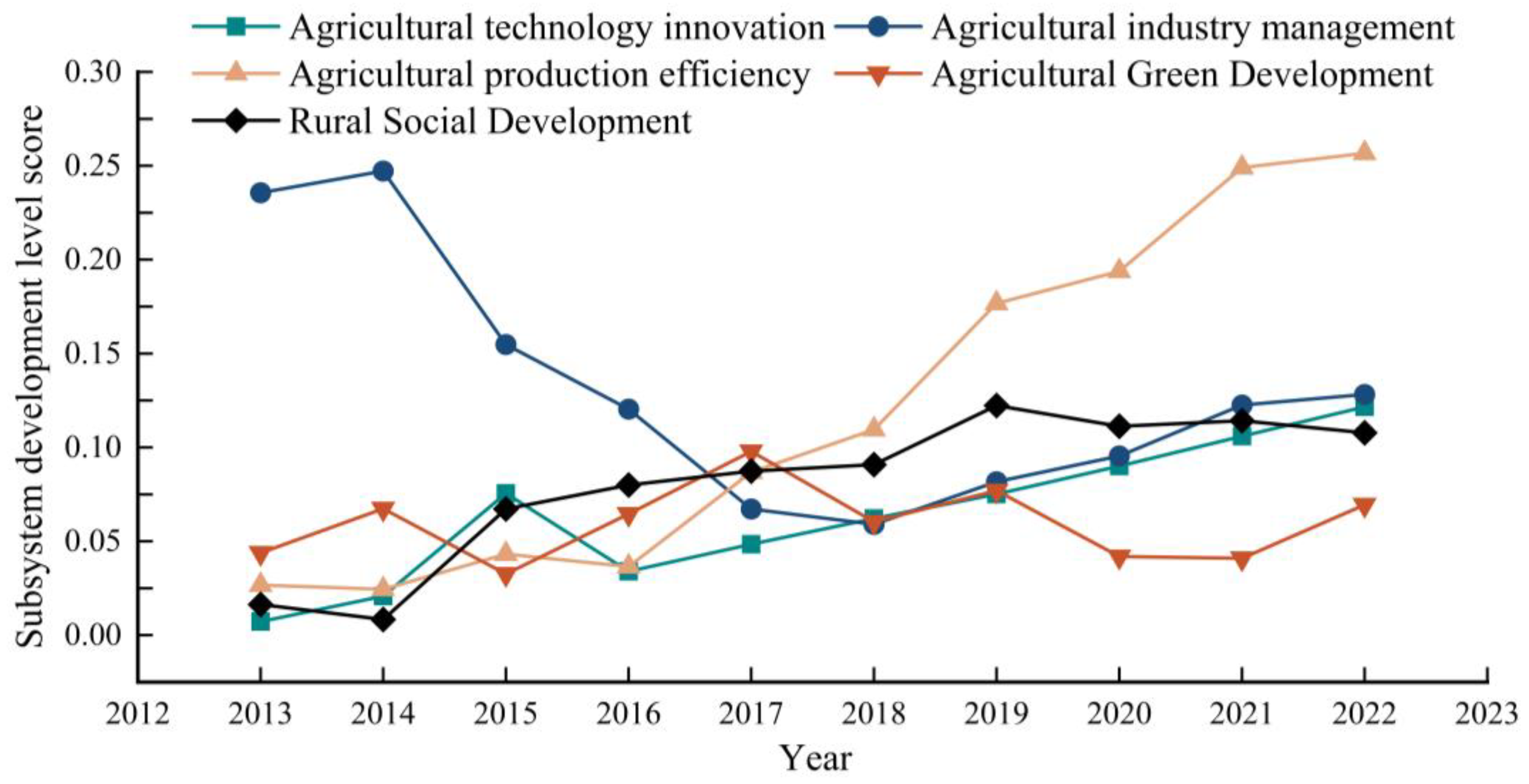
3.1.2. Analysis of Subsystem Characteristics
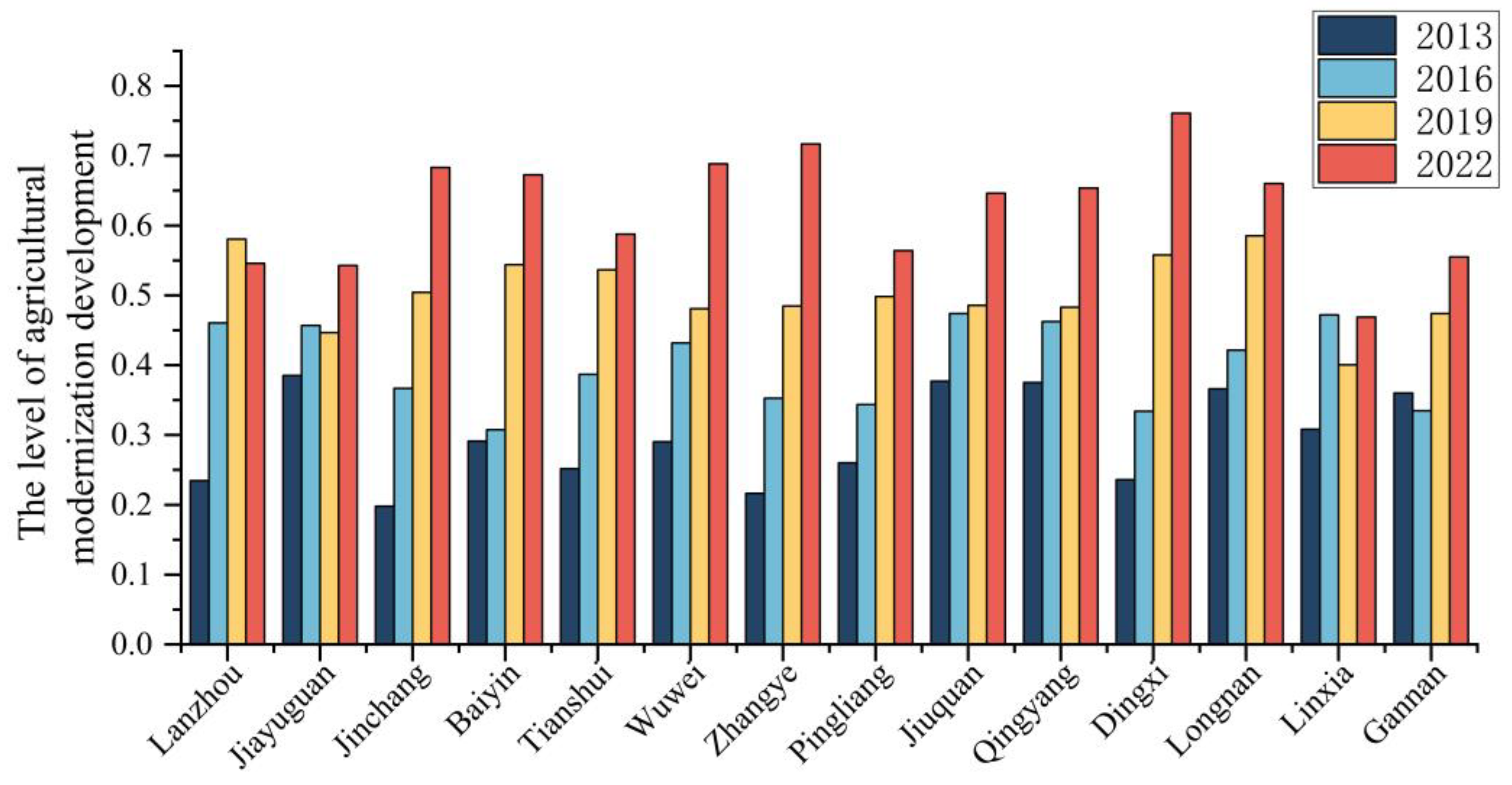
3.1.3. The Temporal Characteristics of Agricultural Modernization Development Levels in Various Cities and Prefectures
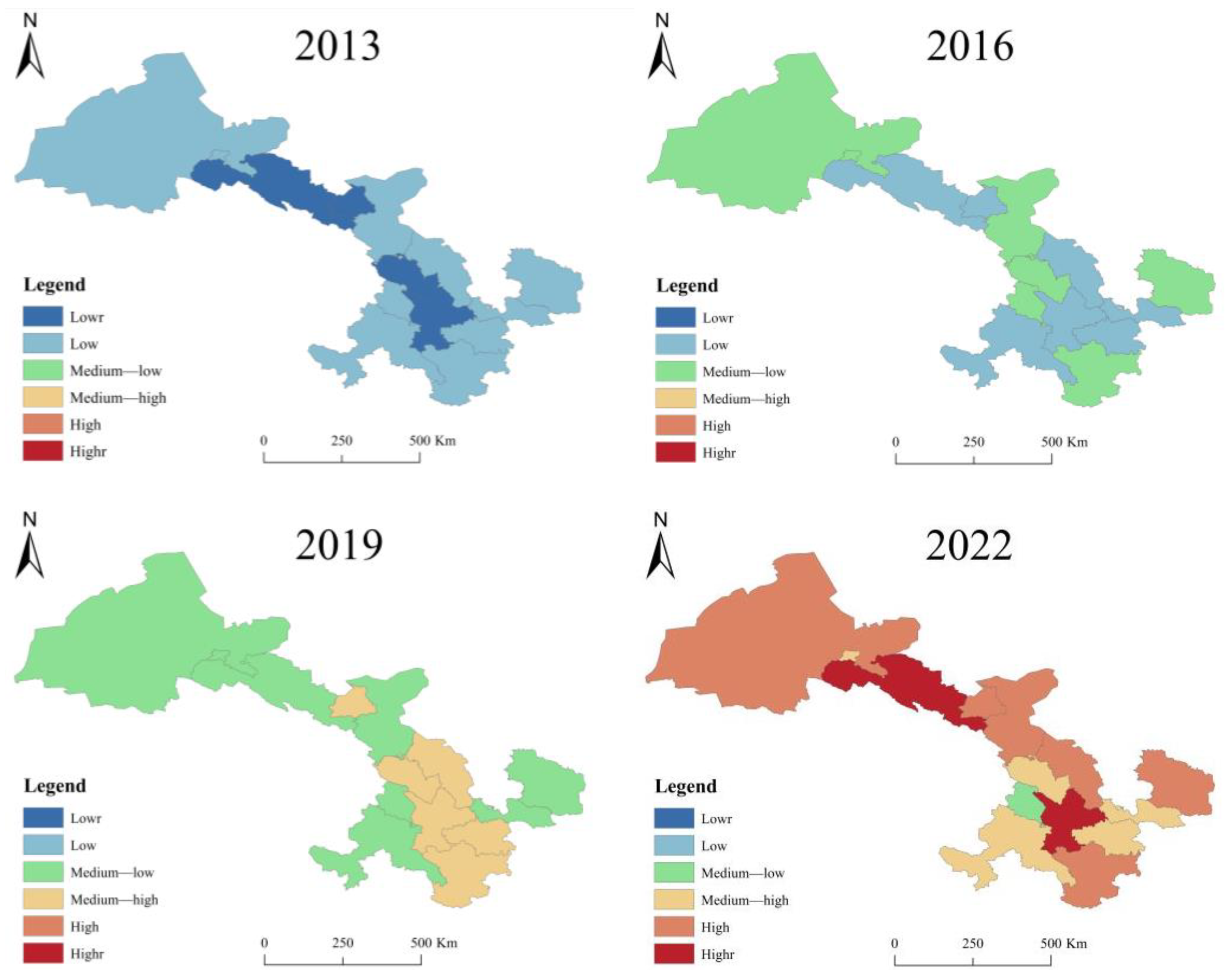
3.2. Spatio-Temporal Differentiation Analysis of Agricultural Modernization Development Level in Gansu Province, China
3.3. Analysis of Regional Disparities in the Development Level of Agricultural Modernization in Gansu Province, China
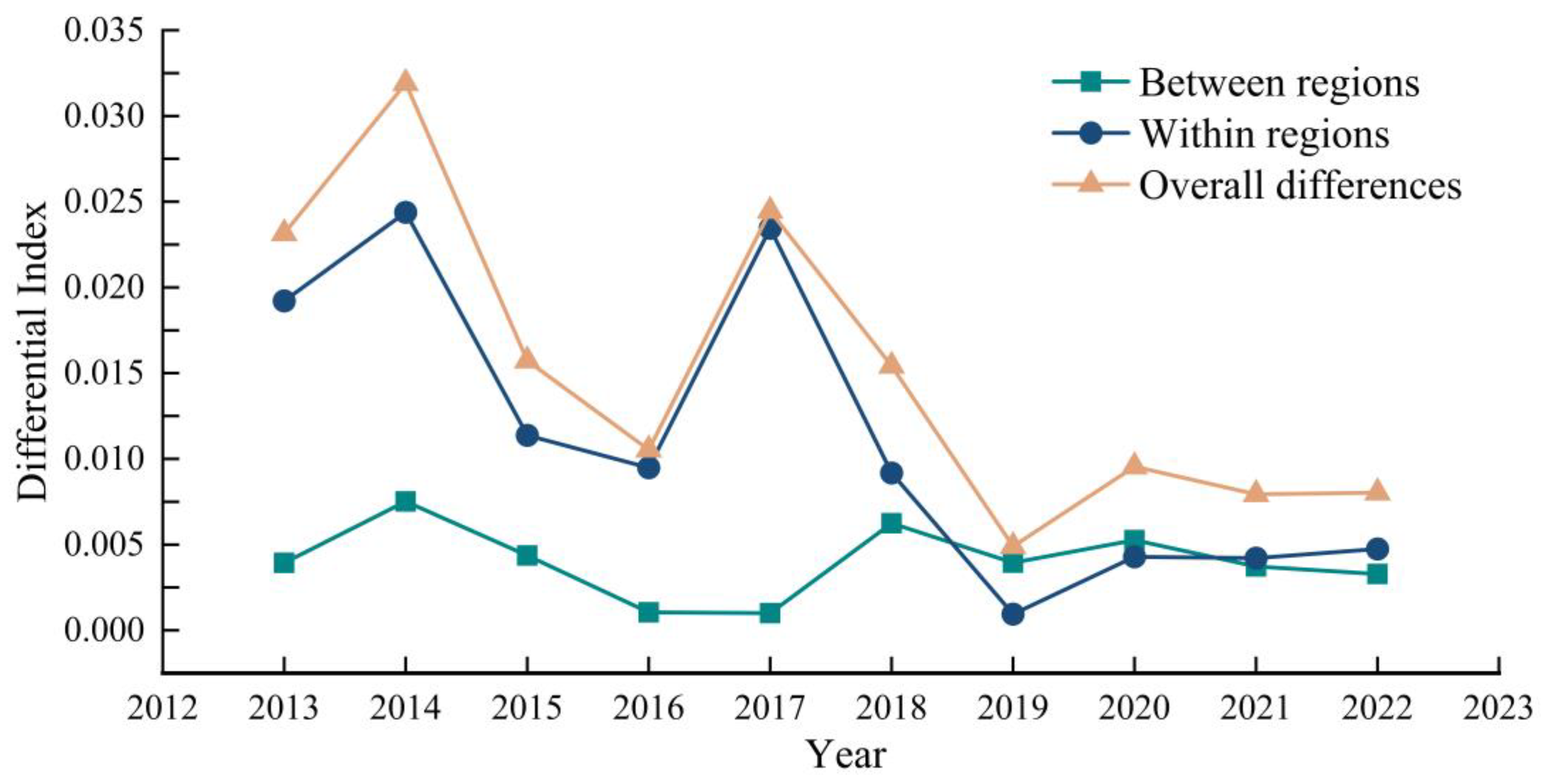
3.3.1. Overall Difference Analysis
3.3.2. Analysis of Inter-Regional Differences
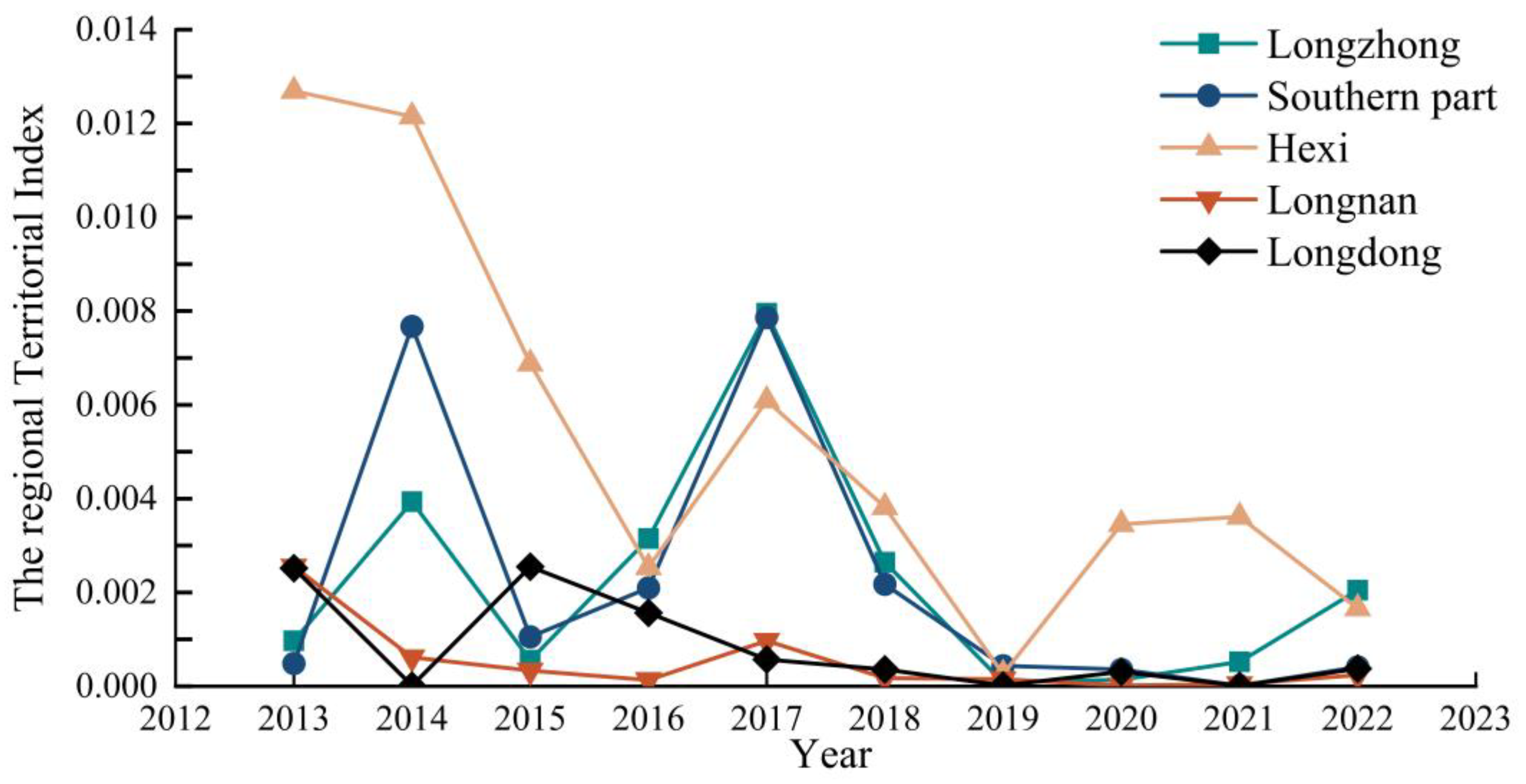
3.3.3. Analysis of Internal Regional Disparities
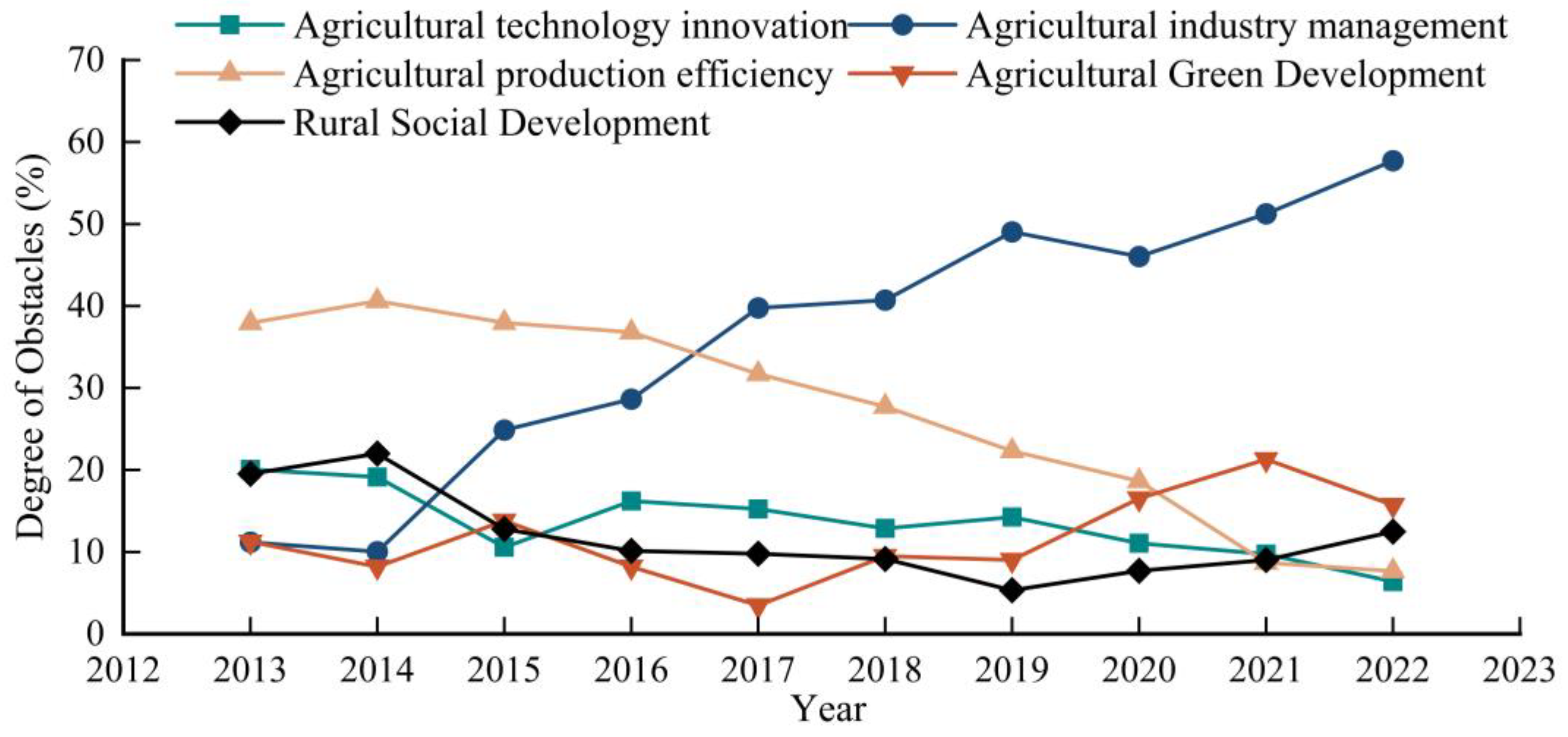
3.4. Analysis of Obstacle Factors for the Development of Agricultural Modernization in Gansu Province, China
4. Conclusions and Recommendations
4.1. Conclusions and Discussion
4.2. Countermeasures and Suggestions
4.3. Research Expectations
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Du, Z. Agricultural and Rural Modernization: Connotation Analysis, Challenges, and Realization Paths. J. Nanjing Agric. Univ. (Soc. Sci. Ed.) 2021, 21, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhuo, Y. The necessary way for the development of China’s rural areas in the new era-rural revitalization strategy. Open J. Soc. Sci. 2018, 6, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Long, H.; Lin, W.; Qiao, J.; Tan, H.; Yang, K.; Yue, W.; Yun, W.; Huang, X.; Lu, H.; et al. Theoretical debates and practical development of the “three rural issues” and rural revitalization in the New Era. J. Nat. Resour. 2023, 38, 1919–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Zhang, P.; Zhao, K.; Zhou, Y.; Zhao, S. A dynamic performance and differentiation management policy for urban construction land use change in Gansu, China. Land 2022, 11, 942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.; Li, L. Evaluation of agricultural modernization in Gansu province. Acad. J. Bus. Manag. 2022, 4, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhou, L. Quantification of restricting factors of agricultural development in Min County of Gansu, China. J. Mt. Sci. 2020, 17, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Li, W.; Zhao, K.; Zhao, S. Spatial Pattern and Driving Mechanism of Urban–Rural Income Gap in Gansu Province of China. Land 2021, 10, 1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardey, P.G.; Alston, J.M. Transforming Traditional Agriculture Redux. In The Oxford Handbook of Structural Transformation; Monga, C., Lin, J.Y., Eds.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2019; pp. 362–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mellor, J.W. The Economics of Agricultural Development; Cornell University Press: Ithaca, NY, USA, 1966. [Google Scholar]
- Deere, C.D.; Gonzales, E.; Pérez, N.; Rodríguez, G. Household incomes in Cuban agriculture: A comparison of the state, cooperative, and peasant sectors. ISS Work. Pap. Ser. 1993, 143, 209–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, R. Conway. The properties of agroecosystems. Agric. Syst. 1987, 24, 95–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, F. Land System: Connotation and Types. Jiangsu Econ. Res. 1996, 5, 33–37. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, H. On the ten major relationships in the process of China’s agricultural modernization towards the 21st century. Chin. Rural Econ. 1997, 7, 5–9. [Google Scholar]
- Van Ittersum, M.K.; Ewert, F.; Heckelei, T.; Wery, J.; Olsson, J.A.; Andersen, E.; Bezlepkina, I.; Brouwer, F.; Donatelli, M.; Flichman, G.; et al. Integrated assessment of agricultural systems–A component-based framework for the European Union (SEAMLESS). Agric. Syst. 2008, 96, 150–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sands, G.R.; Podmore, T.H. A Generalized Environmental Sustainability Index for Agricultural Systems. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2000, 79, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carof, M.; Colomb, B.; Aveline, A. A guide for choosing the most appropriate method for multi-criteria assessment of agricultural systems according to decision-makers’ expectations. Agric. Syst. 2013, 115, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Gu, Z. The path and indicators of Chinese-style agricultural modernization. Econ. Res. J. 1980, 12, 49–51. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X. Evaluation index system of agricultural modernization. Chin. Stat. 2004, 2, 11–13, 10. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Hao, F. Does digital inclusive finance narrow the development gap in agricultural modernization? J. Agri-For. Econ. Manag. 2023, 22, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Meng, X. Spatio-temporal characteristics of agricultural modernization development: Differentiation and agglomeration—An analysis based on Shandong Province data from 2010 to 2019. Chin. Agric. Resour. Reg. Plan. 2022, 43, 202–214. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, B.; Wu, S. Analysis of influencing factors of agricultural and rural modernization based on structural equation modeling. Jiangsu Agric. Sci. 2021, 49, 231–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Wen, F.; Zhang, H.; Li, H.; Yang, K.; Duan, L. Evaluation of agricultural modernization development level in Henan Province based on improved TOPSIS method. Chin. Agric. Resour. Reg. Plan. 2020, 41, 92–97. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Q.; Sun, X.; Lü, J.; Li, X. Measurement and constraint factors of agricultural modernization level in Gansu Province. Res. Agric. Mod. 2018, 39, 369–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Liu, S. Spatio-temporal evolution and obstacle factor analysis of agricultural modernization level in the Yellow River Basin. Res. Agric. Mod. 2023, 44, 624–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, Y.; Elahi, E.; Wang, Y. Comprehensive evaluation of agricultural modernization levels. Sustainability 2022, 14, 5069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Rui, Y.; Li, J.; Li, T. Spatio-temporal characteristics and obstacle factors of agricultural modernization level in Shaanxi Province. Resour. Sci. 2020, 42, 172–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazell, P.; Wood, S. Drivers of change in global agriculture. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2008, 363, 495–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahiigwa, G.; Rigby, D.; Woodhouse, P. Right target, wrong mechanism? Agricultural modernization and poverty reduction in Uganda. World Dev. 2005, 33, 481–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldron, S.; Brown, C.; Longworth, J. A critique of high-value supply chains as a means of modernising agriculture in China: The case of the beef industry. Food Policy 2010, 35, 479–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, K.; Yang, N.; Sun, X.; Yang, S. Ideas and countermeasures for promoting agricultural modernization in Jilin Province through scientific and technological innovation. Northeast Agric. Sci. 2018, 43, 44–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, K.; Lin, J.; Liu, X. Direct financing, spatial spillover, and agricultural modernization: An empirical analysis based on inter-provincial data. J. Jishou Univ. Soc. Sci. Ed. 2018, 39, 79–88. [Google Scholar]
- Dibua, J.I. Agricultural Modernization, the Environment and Sustainable Production in Nigeria, 1970–1985. Afr. Econ. Hist. 2002, 30, 107–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otchia, C.S. Agricultural modernization, structural change and pro-poor growth: Policy options for the Democratic Republic of Congo. J. Econ. Struct. 2014, 3, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Pan, C.; Song, S. Evaluation of agricultural modernization development levels across regions in China: Based on provincial agricultural statistics. Technol. Econ. 2018, 2018, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.; Liu, Y.; Gao, Y.; Zong, G. Evaluation of agricultural modernization in China and evolution of its spatial pattern. Acta Agric. Zhejiangensis 2019, 31, 1012–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, C.; Wang, B.; Chen, D. Evaluation of Regional Agricultural and Rural Modernization Development Levels in China. Chin. Agric. Resour. Reg. Plan. 2022, 43, 173–182. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Zhang, T.; Hou, J. Spatio-Temporal Evolution and Obstacle Factors of Agricultural Modernization Development Level in Shandong Province. Chin. Agric. Resour. Reg. Plan. 2023, 44, 238–247. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Q.; Zhang, P.; Li, J.; Liu, W.; He, X. Measurement and spatio-temporal evolution analysis of agricultural modernization development level in Northeast China. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2022, 42, 1588–1599. [Google Scholar]
- Lü, W. Measurement of Agricultural Modernization Process and Development Path Selection of Characteristic Agriculture in Gansu Province. Master’s Thesis, Lanzhou University, Lanzhou, China, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Gong, D.; Dou, X. Cluster Analysis of Modern Agricultural Development Levels in Different Regions of Gansu Province. Chin. Agric. Resour. Reg. Plan. 2010, 31, 39–42. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, A.; Liu, Y. Evaluation Study on Regional Modern Agricultural Development Level: An Empirical Analysis Based on Data from Gansu Province. Econ. Forum 2016, 8, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Wang, J.; Wu, M. Temporal and Spatial Pattern of Pulmonary Tuberculosis in Gansu Province and Its Environmental Factors Detection and Analysis. Atmosphere 2025, 16, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knickel, K.; Ashkenazy, A.; Chebach, T.C.; Parrot, N. Agricultural modernization and sustainable agriculture: Contradictions and complementarities. Int. J. Agric. Sustain. 2017, 15, 575–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarjuelo, J.M.; Rodriguez-Diaz, J.A.; Abadía, R.; Camacho, E.; Rocamora, C.; Moreno, M.A. Efficient water and energy use in irrigation modernization: Lessons from Spanish case studies. Agric. Water Manag. 2015, 162, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, S.K.; Prabha, S.S.R.; Rai, J.P.; Singh, S.N. Agricultural Mechanization for Sustainable Agricultural and Rural Development in Eastern UP—A Review. Agric. Sustain. Dev. 2014, 2, 192–198. [Google Scholar]
- Scolaro, E.; Beligoj, M.; Estevez, M.P.; Alberti, L.; Renzi, M.; Mattetti, M. Electrification of agricultural machinery: A review. Ieee Access 2021, 9, 164520–164541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Nanseki, T.; Chomei, Y.; Kuang, J. A review of smart agriculture and production practices in Japanese large-scale rice farming. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2023, 103, 1609–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, T.; Liu, B.; Wei, Y.; Xu, Y.; Zheng, H.; Ni, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Fan, X.; Zhou, Z. Research on the low-carbon path of regional industrial structure optimization. Energy Strategy Rev. 2024, 54, 101485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, T.H.; Quang, T.N.; Bui, T.; Thi, H.N. Structure of Agricultural, Forestry and Fishery Sector in the Vietnam Economy: An Input–Output Analysis. J. Account. Bus. Financ. Res. 2022, 14, 8–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogoviz, A.V.; Lobova, S.V.; Ragulina, J.V.; Chutcheva, Y.V.; Bykovskaya, N.V. Increase of labor productivity in the agrarian sector: A view from the standpoint of a modern man. Qual. Access Success 2018, 19, 103–107. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.; Solangi, Y.A. Analyzing the relationship between natural resource management, environmental protection, and agricultural economics for sustainable development in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 450, 141862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redclift, M. The Role of Agricultural Technology in Sustainable Development. In Technological Change and the Rural Environment; Routledge: Oxfordshire, UK, 2023; pp. 81–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubarevich, N.V.; Safronov, S.G. People and Money: Incomes, Consumption, and Financial Behavior of the Population of Russian Regions in 2000–2017. Reg. Res. Russ. 2019, 9, 359–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Easterlin, R.A.; Angelescu, L.; Zweig, J.S. The impact of modern economic growth on urban–rural differences in subjective well-being. World Dev. 2011, 39, 2187–2198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C. Comprehensive Evaluation of Agricultural Modernization Development Level in Gansu Province. E3S Web Conf. 2019, 131, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Feng, Y. Research on China’s agricultural carbon emission efficiency evaluation and regional differentiation based on DEA and Theil models. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 18, 1453–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.; Zheng, J.; Feng, L.; Zhou, Y. Analysis of the Development Level and Obstacles of Agricultural Rural Modernization in Guangdong Province. Adv. Transdiscipl. Eng. 2023, 42, 860–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Scholar | Core Point | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Pardey and Alston | The root cause of the difficulty for traditional agriculture to drive economic growth lies in the price fluctuations of the “income flow” caused by the imbalance between market supply and demand. Modern agriculture, after reasonable transformation, can become an important engine for economic growth. It is emphasized that there is an urgency to transform from traditional agriculture to modern agriculture. | [8] |
| John W. Mellor | The path to agricultural modernization varies among countries due to differences in resources, economic levels, and cultures, and it typically goes through three stages: traditional agriculture → low-capital technology agriculture → high-capital technology agriculture. | [9] |
| Carmen D. Deere et al. | Agricultural modernization is a modernization process with an advanced distribution mechanism. | [10] |
| Gordon R. Conway | From the perspective of agricultural multifunctionality, it emphasizes the role of agriculture in cultural inheritance, social development, and environmental protection; it advocates new models, such as ecological agriculture, urban agriculture, and leisure agriculture, promoting the comprehensive upgrading of agriculture and the integration of urban and rural areas. | [11] |
| Jiang, Fuxin | Agricultural modernization is an organic unity composed of the agricultural mechanism system, the productive forces system, and the production materials production and circulation system. | [12] |
| Gu, Huanzhang | Agricultural modernization is a dynamic process in which traditional production sectors gradually evolve into modern industrial sectors, emphasizing the optimization and upgrading of industrial structure. | [13] |
| Province | Sub-Regions | City and State |
|---|---|---|
| Gansu province | Longzhong Region | Lanzhou City |
| Baiyin City | ||
| Dingxi City | ||
| Southern Ethnic Region | Linxia Hui Autonomous Prefecture | |
| Gannan Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture | ||
| Hexi Region | Jiuquan City | |
| Jiayuguan City | ||
| Jinchang City | ||
| Wuwei City | ||
| Zhangye City | ||
| Longdongnan Region | Longnan City | |
| Tianshui City | ||
| Longdong Region | Qingyang City | |
| Pingliang City |
| First Level Indicators | Second Level Indicators | Calculation and Connotation of Indicators | Attribute | Weight |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Modernization of agricultural science and technology innovation | A1 Water conservancy construction level (%) | Effective irrigated area/Crop planting area | + | 0.034 |
| A2 Agricultural mechanization level (kilowatts per hectare) | Total power of agricultural machinery/Sown area of crops | + | 0.045 | |
| A3 Agricultural electrification level (KWH/person) | Total rural electricity consumption/Total rural population | + | 0.063 | |
| Modernization of agricultural industry management | A4 Degree of agricultural large-scale production (hectares) | Crop sown area/rural households | + | 0.101 |
| A5 Efficiency of agriculture, forestry, animal husbandry, and fishery services (%) | The output value of the agricultural, forestry, animal husbandry, and fishery service industry/The total output value of the agricultural, forestry, animal husbandry, and fishery | + | 0.03 | |
| A6 Adjustment of agricultural planting structure (%) | The sown area of non-food crops/the sown area of crops | + | 0.047 | |
| A7 Agricultural industry integration potential (%) | The output value of the primary industry/Regional gross domestic product | - | 0.064 | |
| A8 Optimization of agricultural industrial structure (%) | The output value of animal husbandry/The total output value of agriculture, forestry, animal husbandry, and fishery | + | 0.101 | |
| Modernization of agricultural production efficiency | A9 Land productivity (yuan) | Total output value of agriculture, forestry, animal husbandry, and fishery/Total sown area of crops | + | 0.053 |
| A10 Labor productivity (Yuan/person) | Total output value of agriculture, forestry, animal husbandry, and fishery/Number of employees in agriculture, forestry, animal husbandry, and fishery | + | 0.063 | |
| A11 Growth rate of agricultural output (%) | (Current year’s agricultural output value—Previous year’s agricultural output value)/Previous year’s agricultural output value) | + | 0.047 | |
| A12 Comprehensive grain production capacity (tons/hectare) | Total grain output/Grain planting area | + | 0.071 | |
| A13 Farmers’ income level (yuan) | Per capita disposable income of farmers | + | 0.046 | |
| Modernization of green development in agriculture | A14 Ecological construction level (%) | The added value of forestry/The added value of agriculture, forestry, animal husbandry, and fishery | + | 0.05 |
| A15 Fertilizer application level (tons/hectare) | Total output value of agriculture, forestry, animal husbandry, and fishery/Number of employees in agriculture, forestry, animal husbandry, and fishery | - | 0.029 | |
| A16 Disaster resistance and prevention capacity (%) | Area affected by disaster/Area stricken by disaster | - | 0.041 | |
| Modernization of rural social development | A17 Urban–rural income ratio (%) | Per capita disposable income of rural residents/Per capita disposable income of urban residents | + | 0.043 |
| A18 Proportion of operating income (%) | Rural residents’ operating income/Per capita disposable income of rural residents | + | 0.033 | |
| A19 Engel’s coefficient (%) | Food expenditure/Total expenditure of rural residents | - | 0.037 | |
| A20 Education, culture and entertainment consumption level (%) | Expenditure on education, culture, and entertainment/Total expenditure of rural residents | + | 0.035 |
| City | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 | Average Annual Growth Rate | Annual Average Score | Final Ranking | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Central Gansu Region | Lanzhou | 0.235 | 0.199 | 0.372 | 0.46 | 0.554 | 0.582 | 0.581 | 0.629 | 0.596 | 0.546 | 9.82 | 0.4754 | 3 |
| Baiyin | 0.291 | 0.338 | 0.36 | 0.307 | 0.375 | 0.422 | 0.544 | 0.58 | 0.577 | 0.673 | 11.87 | 0.4467 | 8 | |
| Dingxi | 0.236 | 0.303 | 0.425 | 0.334 | 0.287 | 0.44 | 0.558 | 0.596 | 0.673 | 0.761 | 13.89 | 0.4613 | 6 | |
| Southern Ethnic Region | Linxia | 0.308 | 0.261 | 0.268 | 0.472 | 0.265 | 0.274 | 0.401 | 0.402 | 0.462 | 0.469 | 4.78 | 0.3582 | 14 |
| Gannan | 0.36 | 0.5 | 0.352 | 0.335 | 0.527 | 0.404 | 0.474 | 0.469 | 0.478 | 0.555 | 4.93 | 0.4454 | 9 | |
| Hexi Region | Jiuquan | 0.377 | 0.451 | 0.511 | 0.474 | 0.454 | 0.462 | 0.486 | 0.528 | 0.568 | 0.646 | 6.17 | 0.4957 | 1 |
| Jiayuguan | 0.385 | 0.46 | 0.5 | 0.457 | 0.261 | 0.301 | 0.447 | 0.408 | 0.492 | 0.543 | 3.89 | 0.4254 | 11 | |
| Jinchang | 0.198 | 0.23 | 0.358 | 0.367 | 0.452 | 0.458 | 0.504 | 0.629 | 0.748 | 0.683 | 14.75 | 0.4627 | 5 | |
| Wuwei | 0.29 | 0.377 | 0.403 | 0.432 | 0.373 | 0.403 | 0.481 | 0.506 | 0.588 | 0.688 | 12.26 | 0.4541 | 7 | |
| Zhangye | 0.216 | 0.281 | 0.309 | 0.353 | 0.374 | 0.386 | 0.485 | 0.485 | 0.577 | 0.717 | 14.26 | 0.4183 | 13 | |
| Southeastern Gansu Region | Tianshui | 0.252 | 0.327 | 0.385 | 0.387 | 0.375 | 0.432 | 0.536 | 0.502 | 0.58 | 0.588 | 9.87 | 0.4364 | 10 |
| Longnan | 0.366 | 0.393 | 0.44 | 0.422 | 0.471 | 0.475 | 0.585 | 0.519 | 0.551 | 0.66 | 6.98 | 0.4882 | 2 | |
| Eastern Gansu Region | Pingliang | 0.26 | 0.41 | 0.333 | 0.344 | 0.469 | 0.359 | 0.498 | 0.438 | 0.522 | 0.564 | 10.54 | 0.4197 | 12 |
| Qingyang | 0.375 | 0.421 | 0.483 | 0.462 | 0.395 | 0.415 | 0.483 | 0.503 | 0.535 | 0.654 | 6.35 | 0.4726 | 4 | |
| Average | 0.296 | 0.354 | 0.393 | 0.4 | 0.402 | 0.415 | 0.505 | 0.514 | 0.568 | 0.625 | 7.299 | 0.447 |
| Sort | 2013 | 2016 | 2019 | 2022 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Obstacle Index | Obstacle Degree | Obstacle Index | Obstacle Degree | Obstacle Index | Obstacle Degree | Obstacle Index | Obstacle Degree | |
| 1 | Comprehensive grain production capacity | 10.469 | Degree of agricultural large-scale production | 13.616 | Degree of agricultural large-scale production | 20.3 | Efficiency of agriculture, forestry, animal husbandry, and fishery services | 21.686 |
| 2 | Labor productivity | 9.476 | Comprehensive grain production capacity | 10.709 | Efficiency of agriculture, forestry, animal husbandry and fishery services | 11.969 | Degree of agricultural large-scale production | 18.141 |
| 3 | Electrification level | 9.376 | Labor productivity | 7.98 | Optimization of agricultural industrial structure | 9.977 | Ecological construction level | 5.725 |
| 4 | Land productivity | 7.947 | Agricultural electrification level | 7.882 | Labor productivity | 7.395 | Agricultural industry integration potential | 14.944 |
| 5 | Optimization of agricultural industrial structure | 7.531 | Optimization of agricultural industrial structure | 7.238 | Agricultural electrification level | 6.933 | Growth rate of agricultural output | 7.673 |
| 6 | Farmers’ income level | 6.829 | Growth rate of agricultural output | 7.12 | Agricultural mechanization level | 6.806 | Agricultural mechanization level | 6.38 |
| 7 | Urban–rural income ratio | 6.351 | Agricultural mechanization level | 6.762 | Disaster resistance and prevention capacity | 5.516 | Engel’s coefficient | 5.776 |
| 8 | Agricultural mechanization level | 5.625 | Land productivity | 6.052 | Agricultural industry integration potential | 5.235 | Education, culture, and entertainment consumption level | 5.384 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shi, M.; Guo, S.; Zhong, S.; Ma, S. Analysis of the Spatial–Temporal Characteristics, Regional Differences, and Obstacle Factors of Agricultural Modernization Development in Gansu Province, China. Sustainability 2025, 17, 5461. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17125461
Shi M, Guo S, Zhong S, Ma S. Analysis of the Spatial–Temporal Characteristics, Regional Differences, and Obstacle Factors of Agricultural Modernization Development in Gansu Province, China. Sustainability. 2025; 17(12):5461. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17125461
Chicago/Turabian StyleShi, Mingting, Shunli Guo, Sheng Zhong, and Shenao Ma. 2025. "Analysis of the Spatial–Temporal Characteristics, Regional Differences, and Obstacle Factors of Agricultural Modernization Development in Gansu Province, China" Sustainability 17, no. 12: 5461. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17125461
APA StyleShi, M., Guo, S., Zhong, S., & Ma, S. (2025). Analysis of the Spatial–Temporal Characteristics, Regional Differences, and Obstacle Factors of Agricultural Modernization Development in Gansu Province, China. Sustainability, 17(12), 5461. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17125461






