Assessing the Impact of Rice Husk Ash on Soil Strength in Subgrade Layers: A Novel Approach to Sustainable Ground Engineering
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Research Significance
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Material Preparation
3.3. Testing Methods
3.3.1. Compaction Tests
3.3.2. Triaxial Compression Test
3.3.3. Microstructural Study on Shear Strength Development
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Influence of Stabilizers on Compaction Behavior
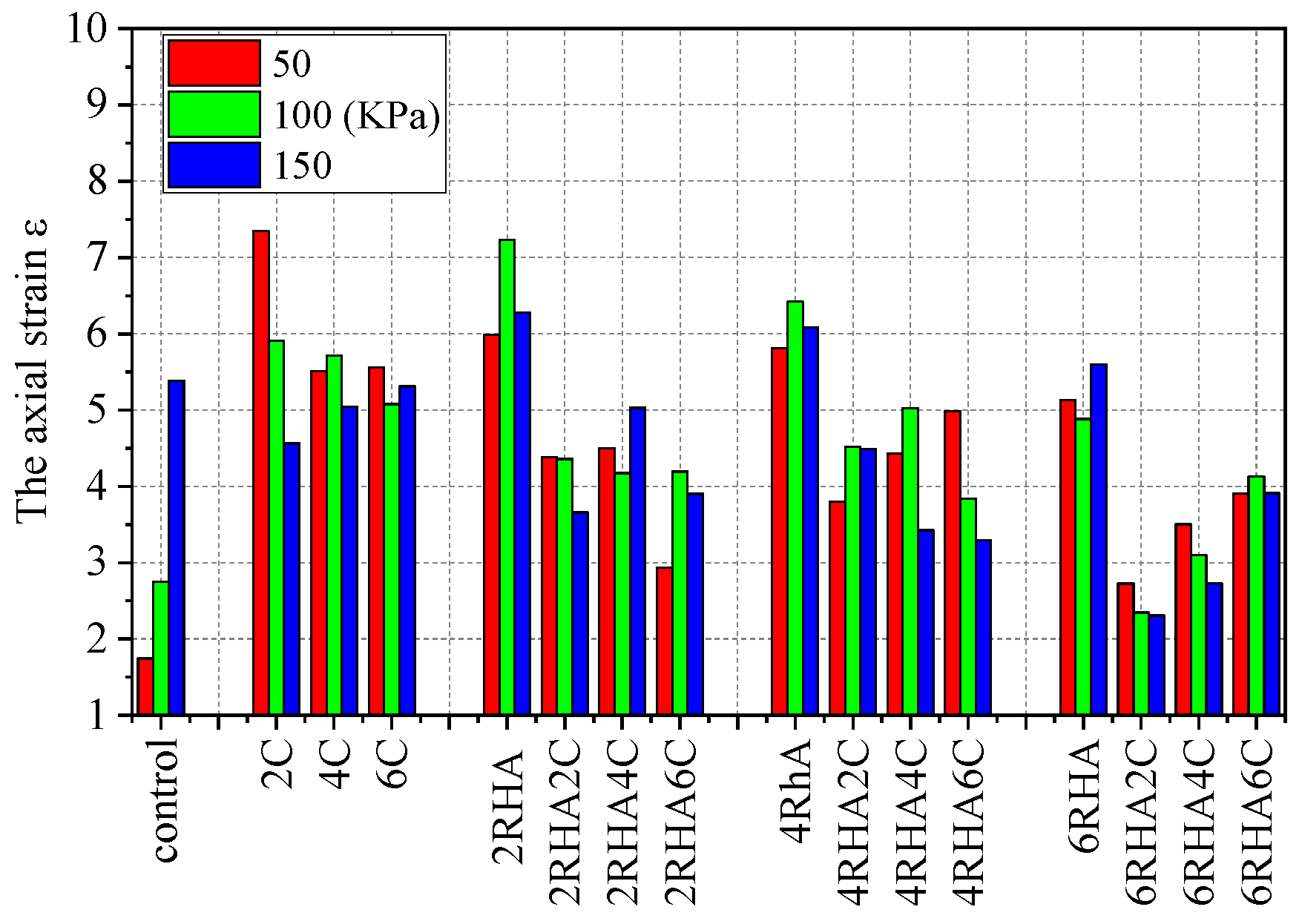
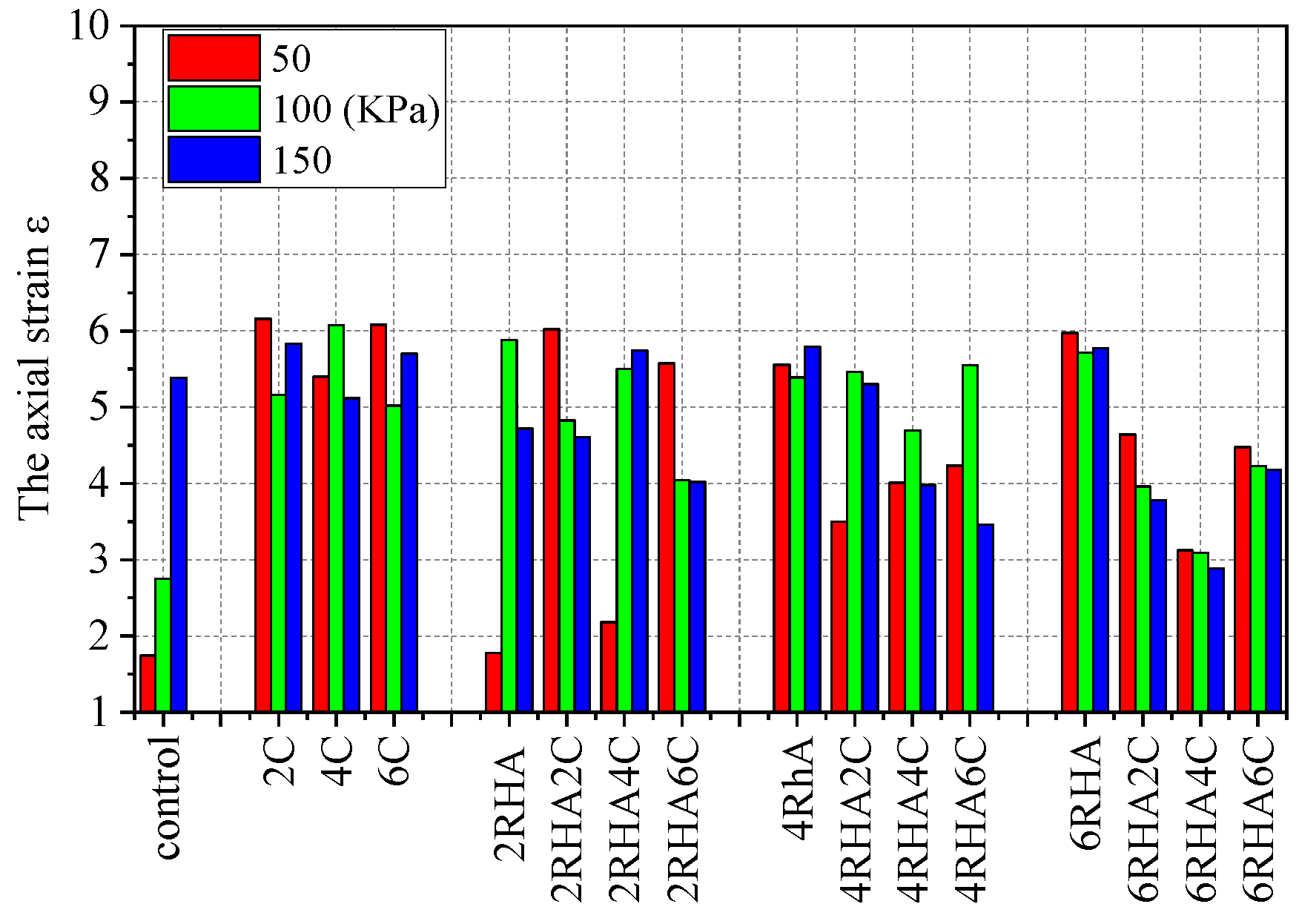
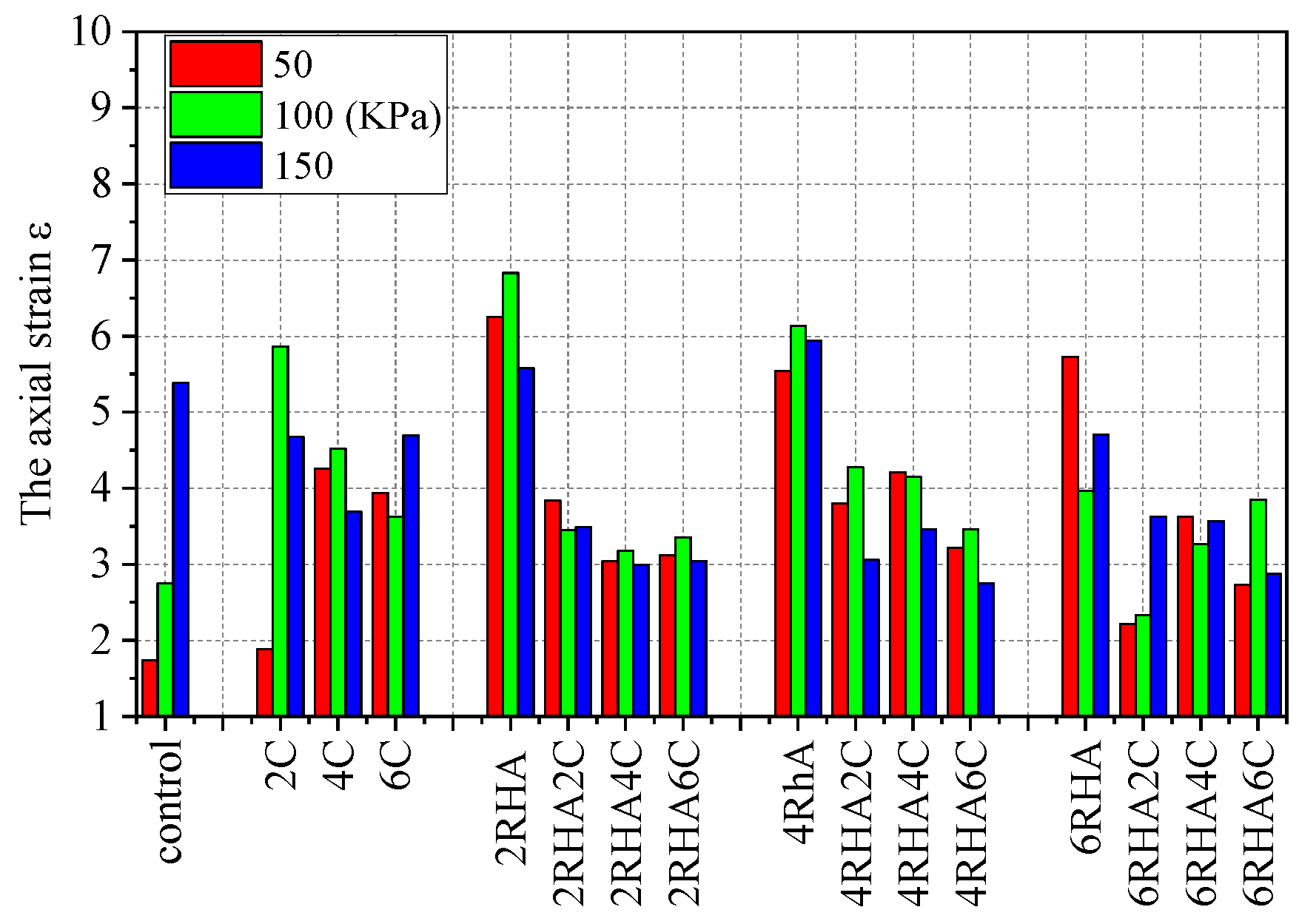
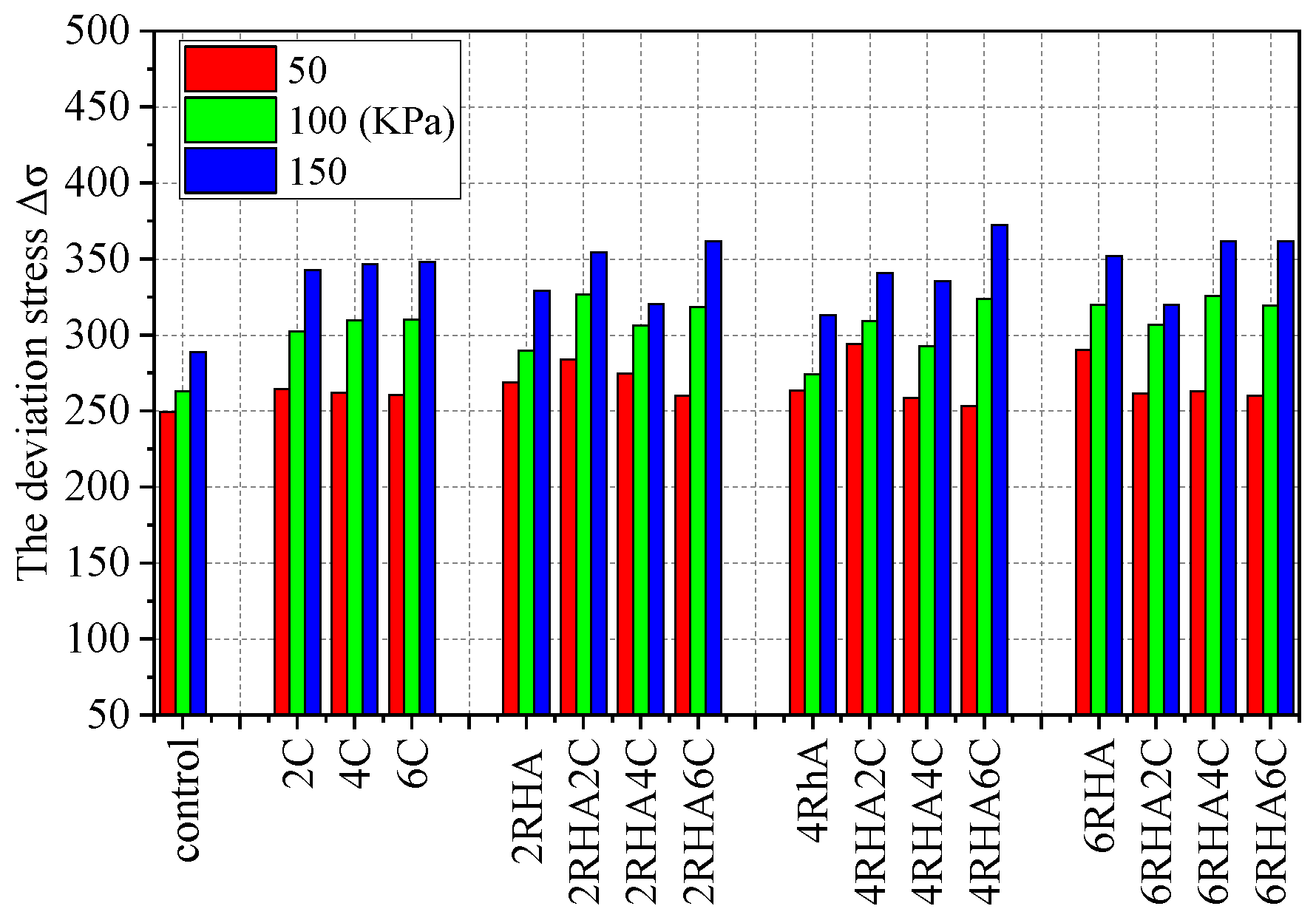
4.2. The Axial Strain and Deviatoric Stress Relationship Curves for Different Types of Soil–RHA–Cement Combinations
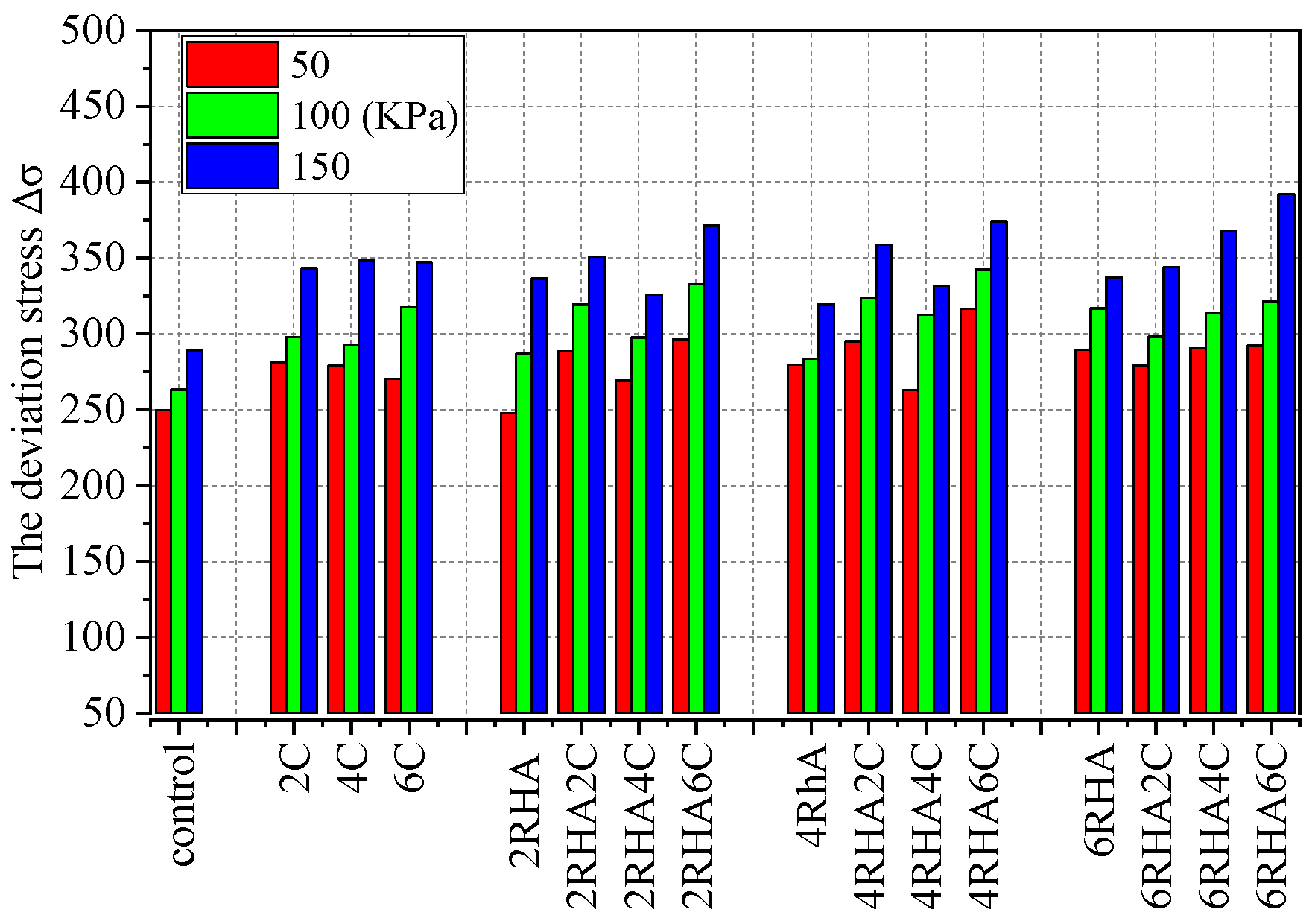
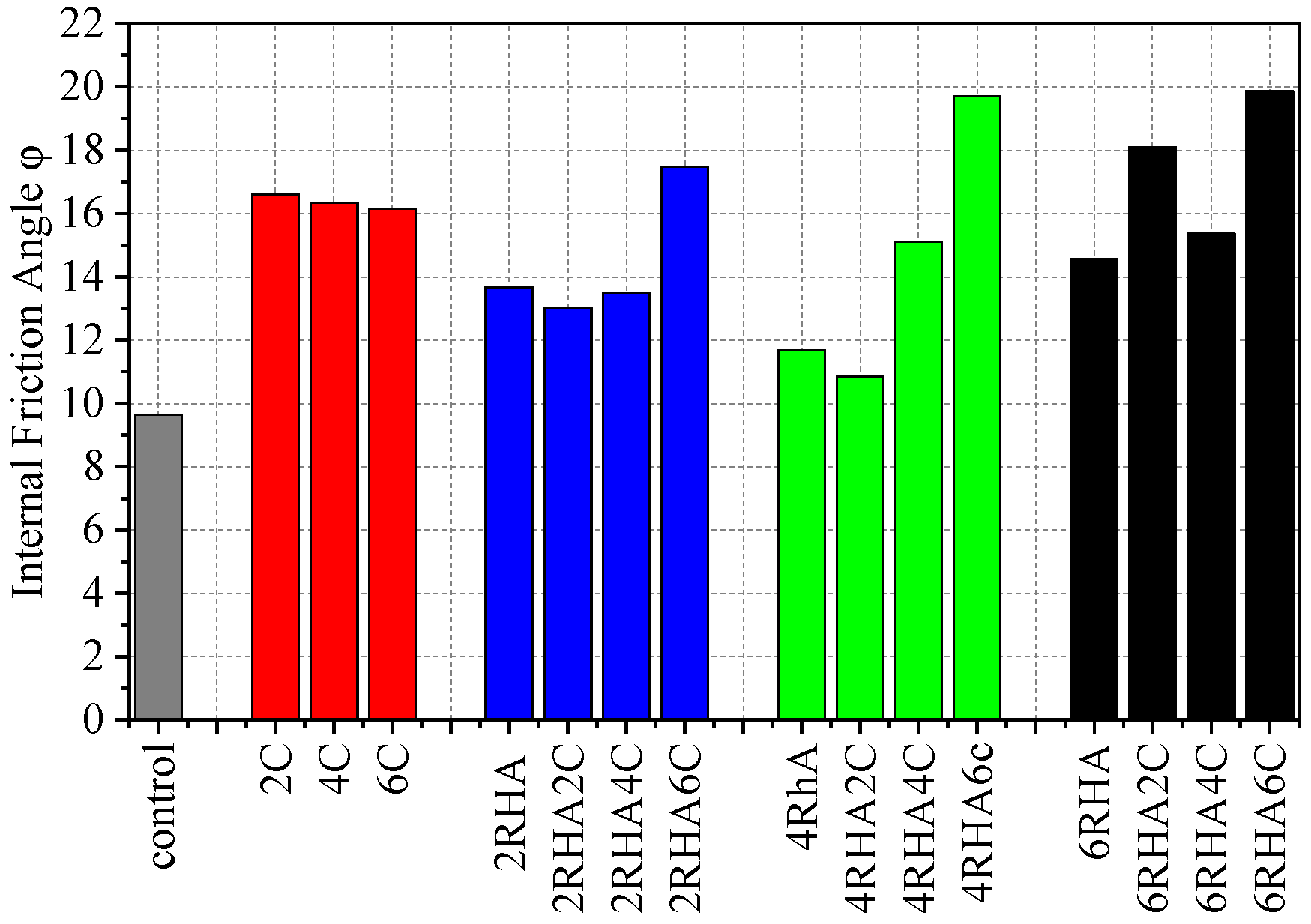
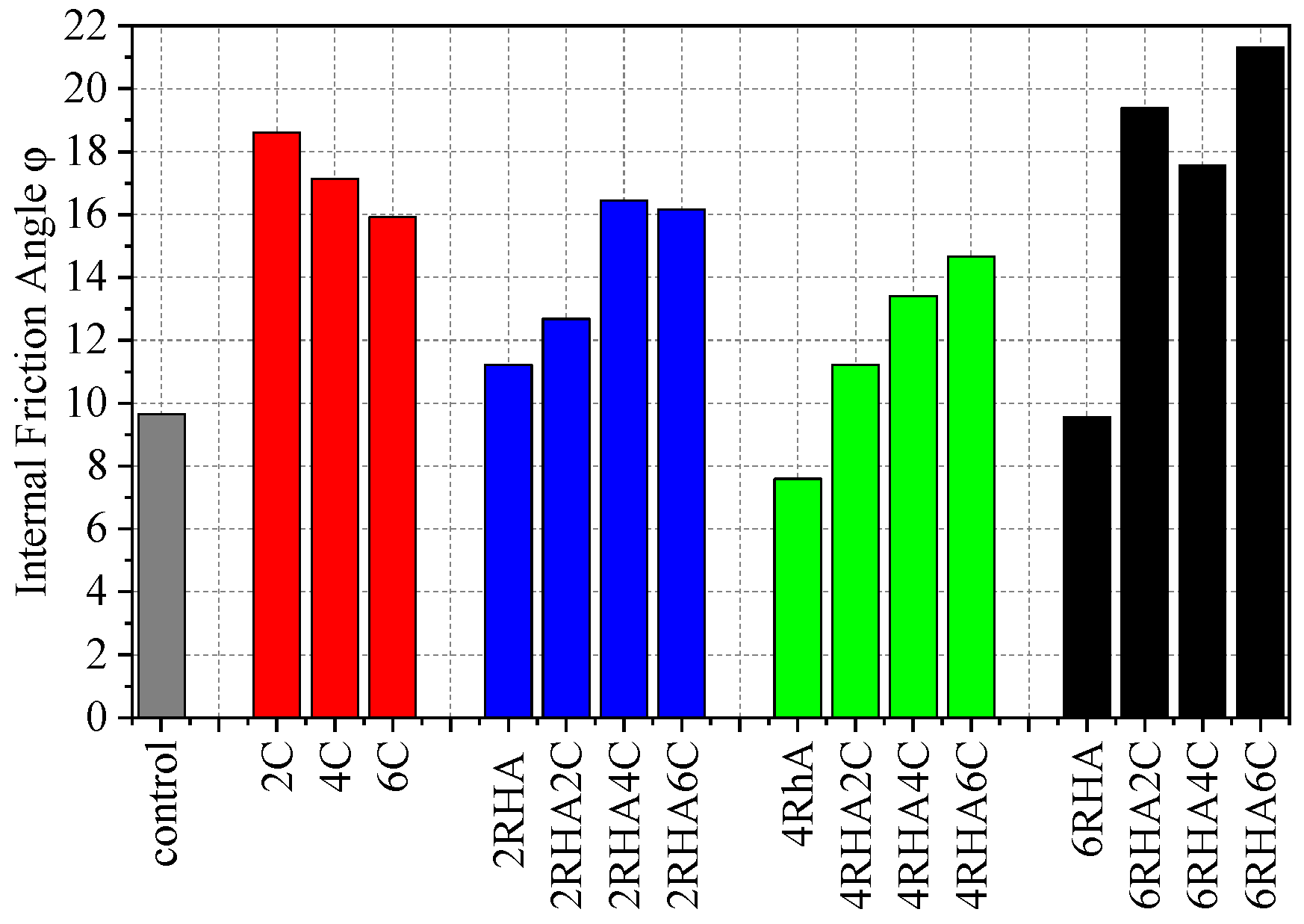
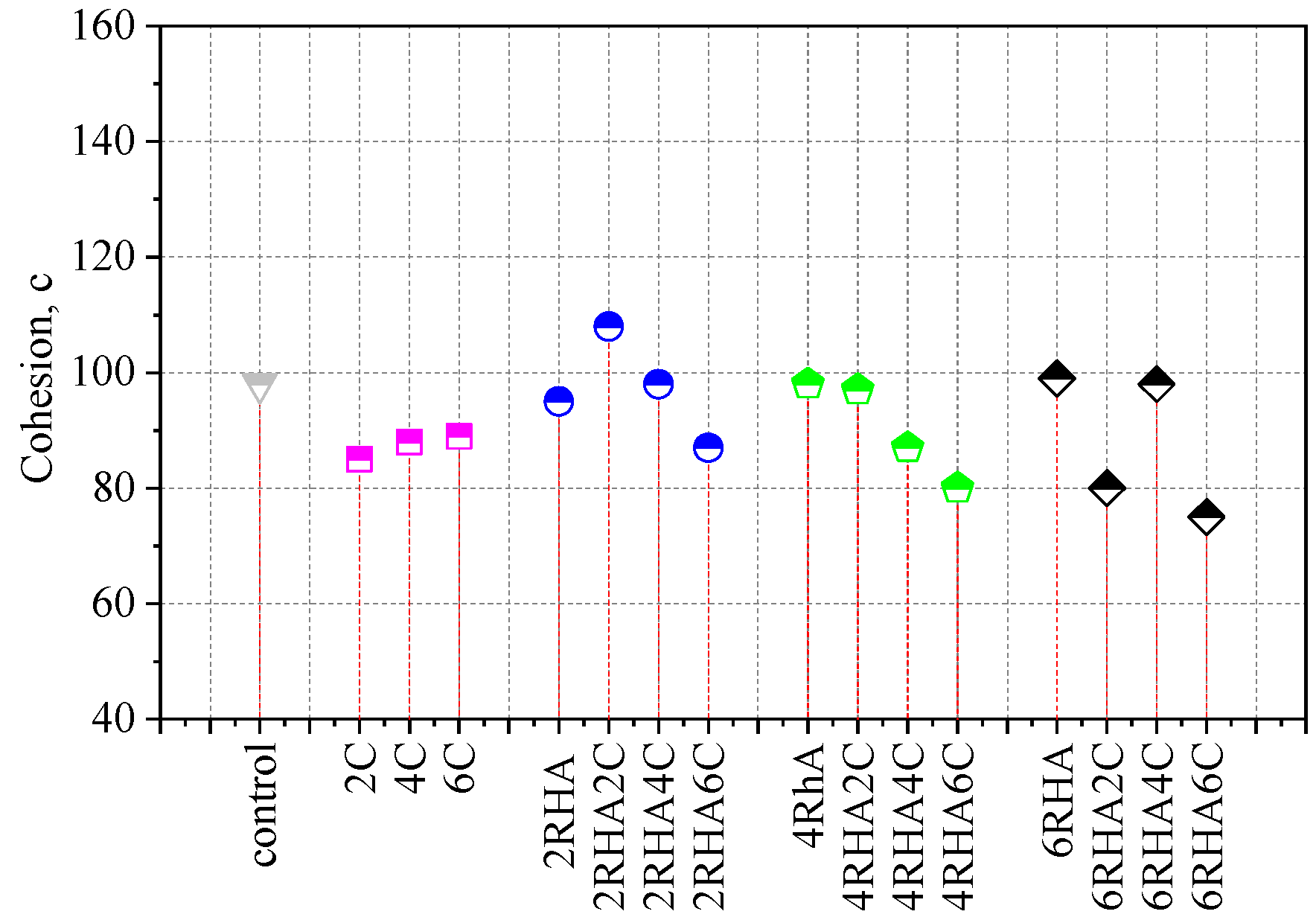
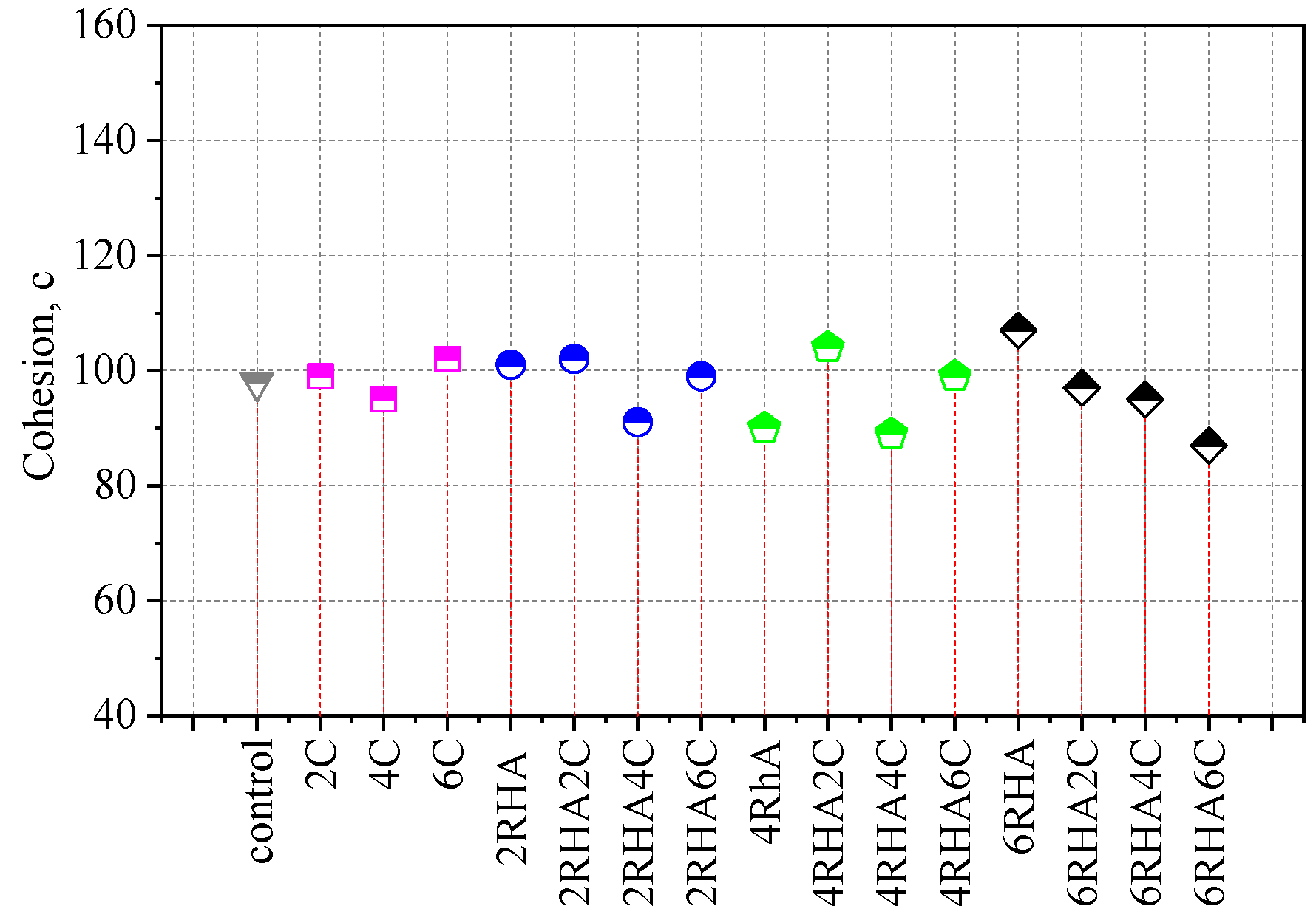
4.3. Shear Strength of Soil Combination with Rice Husk Ash Percentages
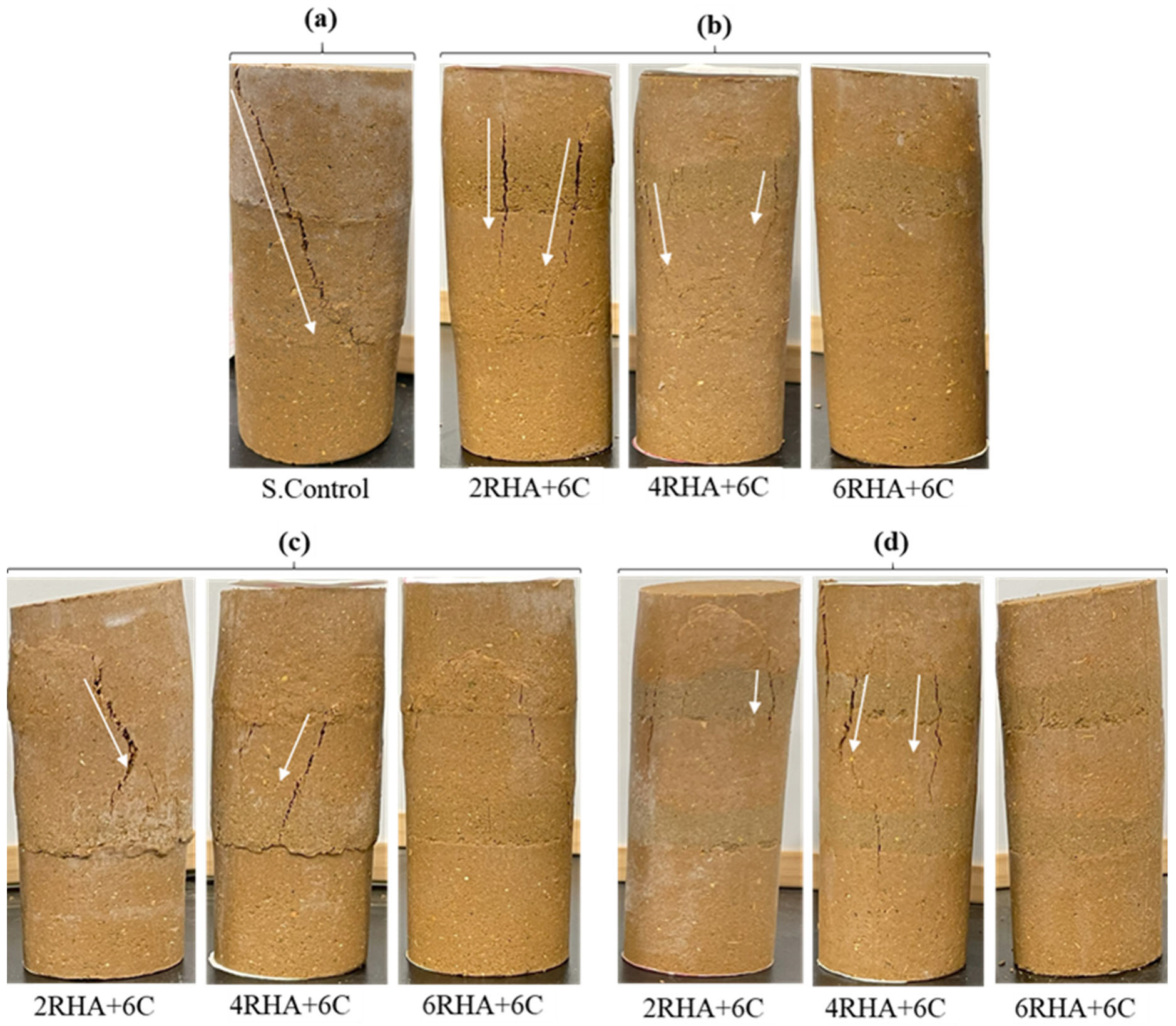
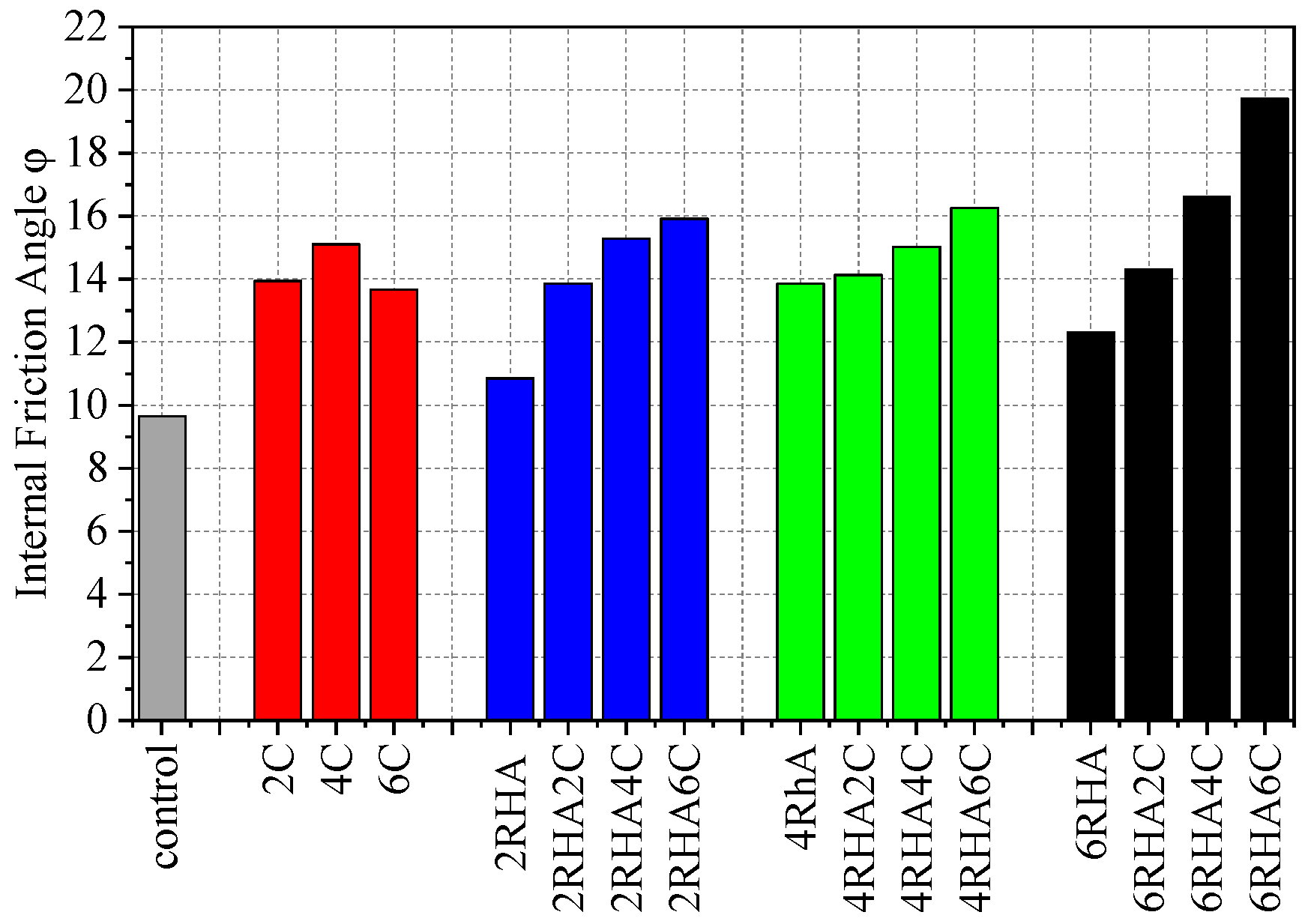
4.4. Effects on Different Layers
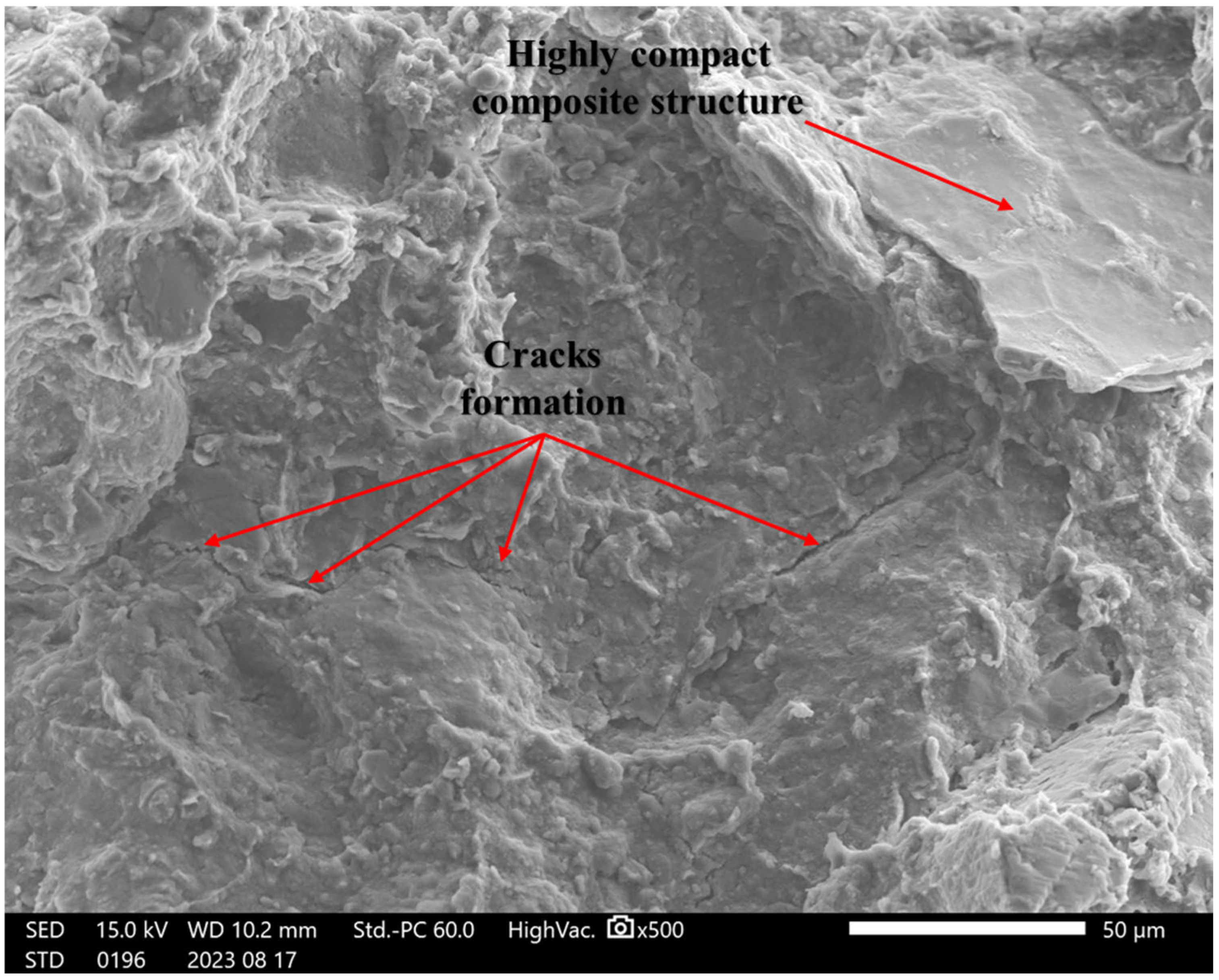
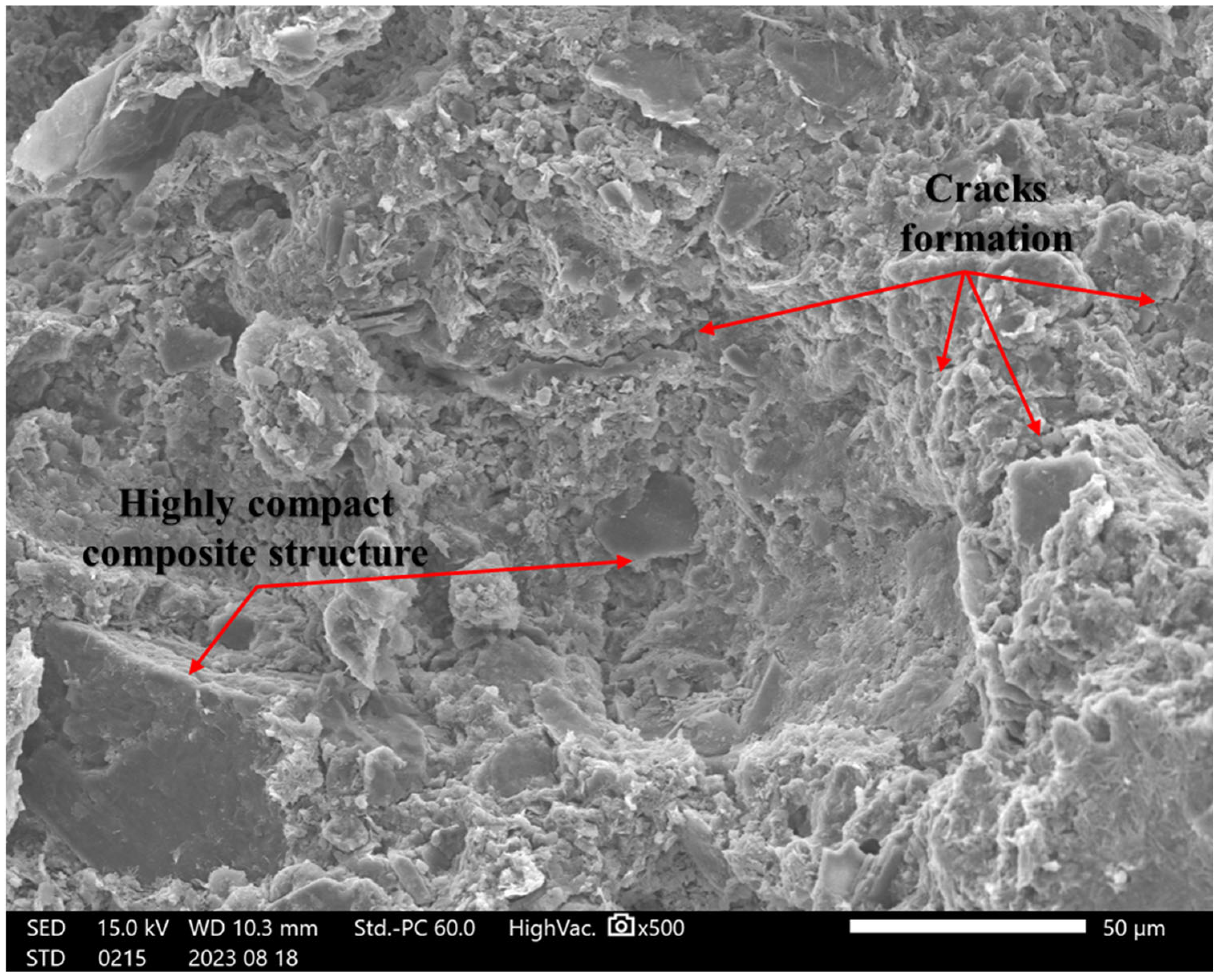
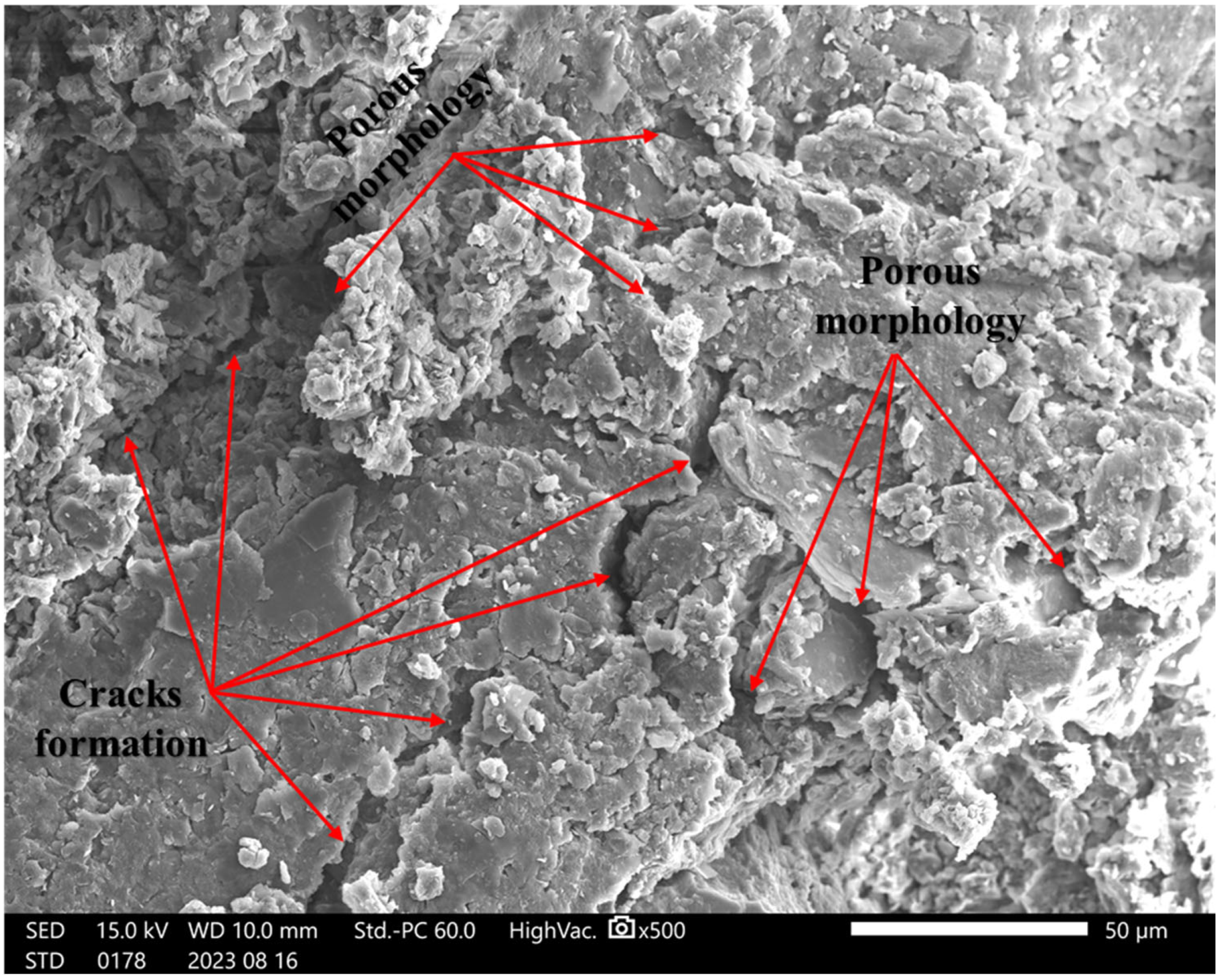
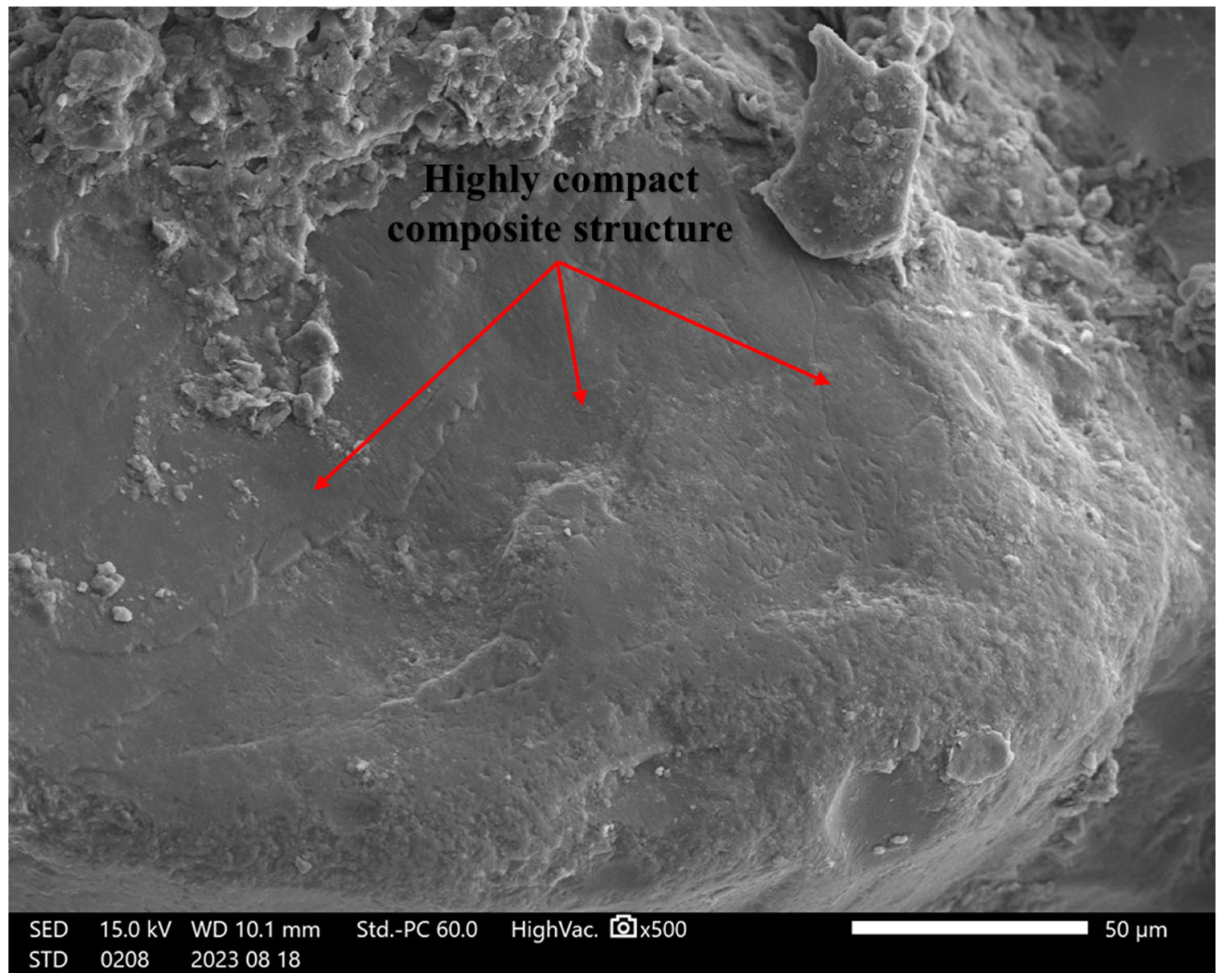
4.5. SEM Analysis
4.6. The Strengthening Mechanisms of RHA and Cement
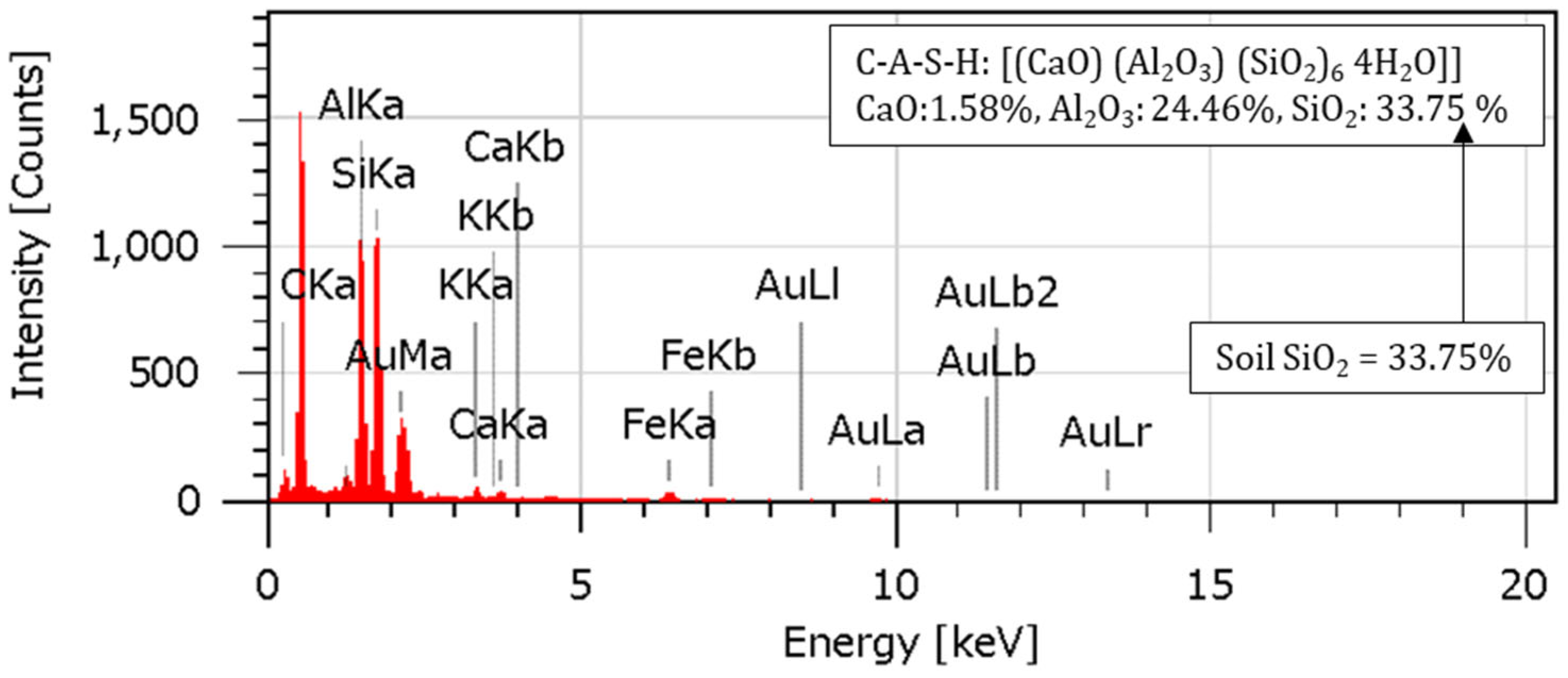
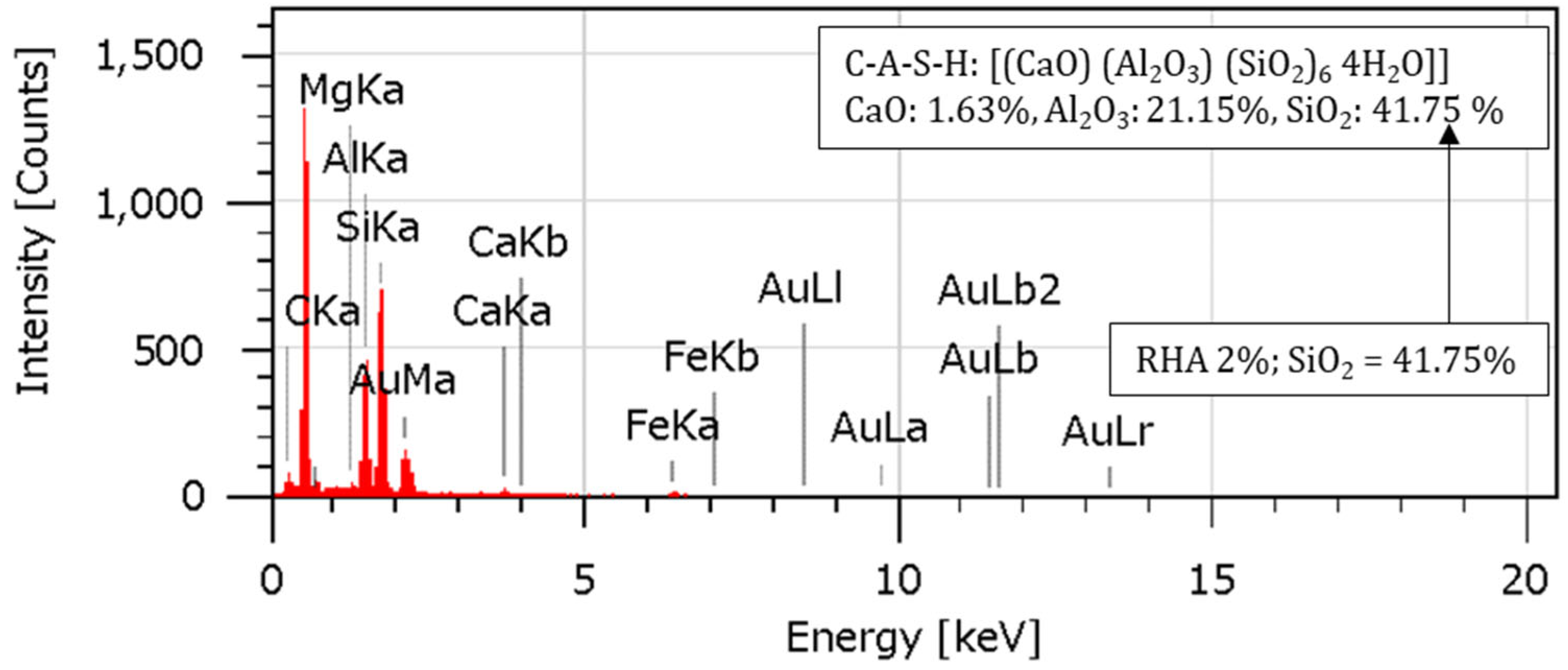
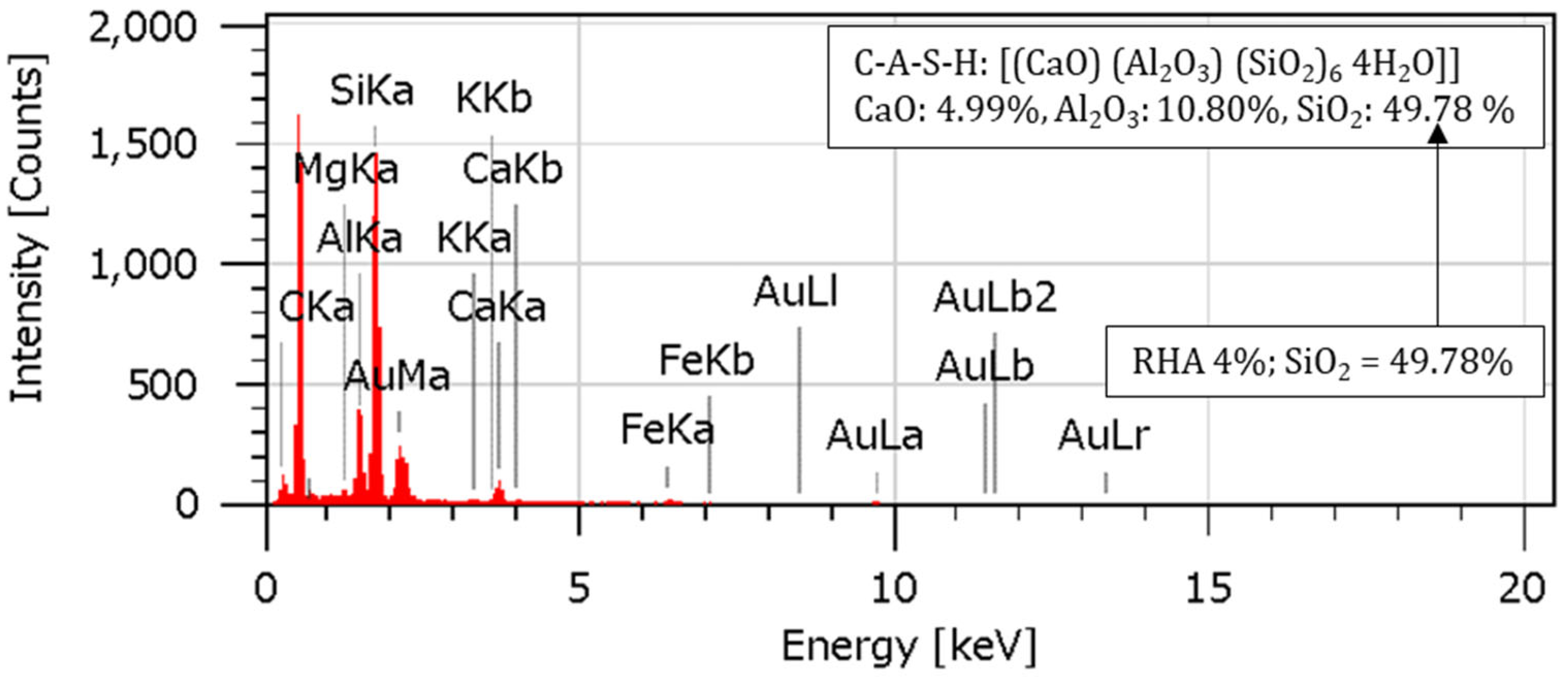
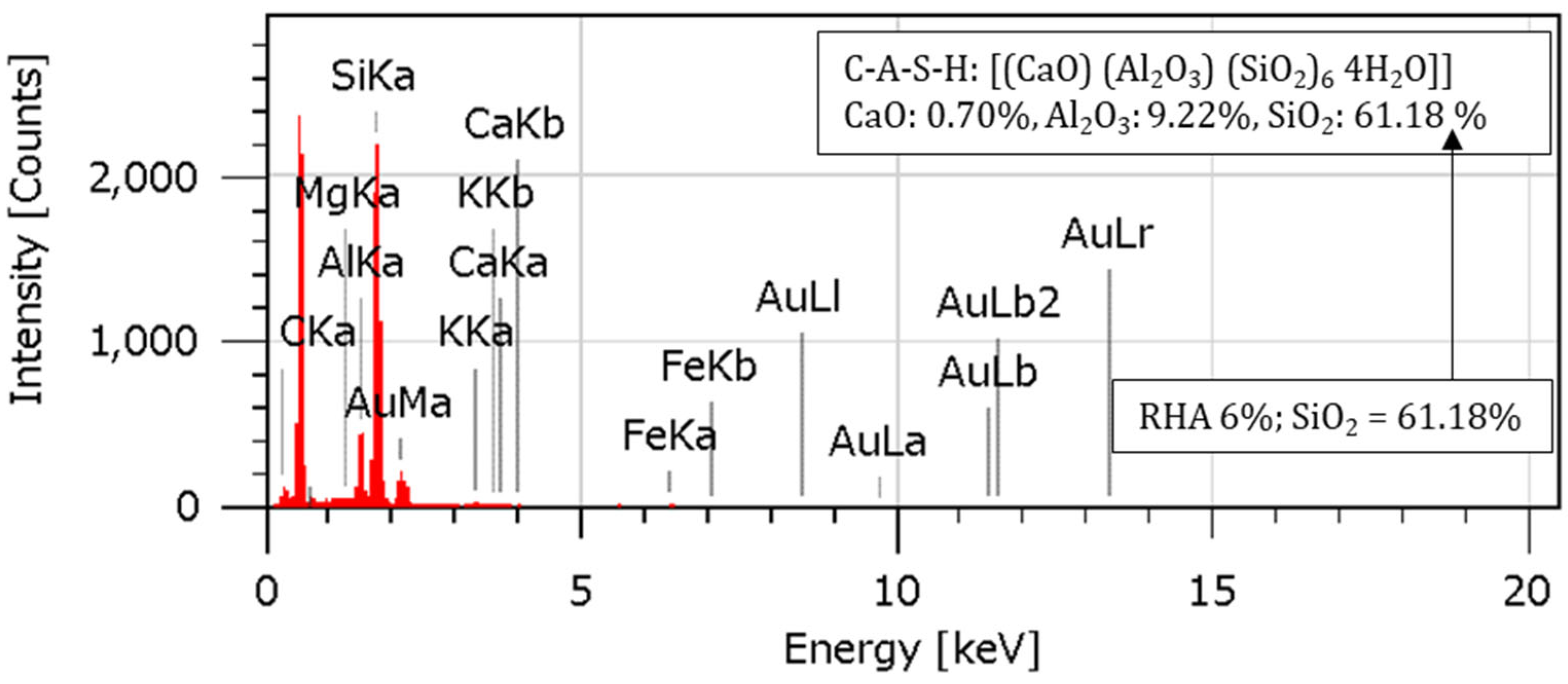
4.7. EDS Analysis
5. Future Research Directions
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| RHA | Rice Husk Ash |
| S | Soil |
| C | Cement |
| SEM | Scanning Electron Microscopy |
| EDS | Energy-Dispersive X-ray Spectroscopy |
| OMC | Optimum Moisture Content |
| MDD | Maximum Dry Density |
References
- Galvin, J. Critical role of risk management in ground engineering and opportunities for improvement. Int. J. Min. Sci. Technol. 2017, 27, 725–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, D.; Misra, A.; Puppala, A.J. Sustainability and geotechnical engineering: Perspectives and review. Can. Geotech. J. 2015, 52, 96–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Ru, J. Goals of sustainable infrastructure, industry, and innovation: A review and future agenda for research. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 28446–28458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina-Martinez, C.J.; Sandoval-Herazo, L.C.; Zamora-Castro, S.A.; Vivar-Ocampo, R.; Reyes-Gonzalez, D. Natural fibers: An alternative for the reinforcement of expansive soils. Sustainability 2022, 14, 9275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afrin, H. A review on different types soil stabilization techniques. Int. J. Transp. Eng. Technol. 2017, 3, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.Y.; Han, R.; Yu, B.; Wei, Y.M. Accounting process-related CO2 emissions from global cement production under Shared Socioeconomic Pathways. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 184, 451–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imbabi, M.S.; Carrigan, C.; McKenna, S. Trends and developments in green cement and concrete technology. Int. J. Sustain. Built Environ. 2012, 1, 194–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jittin, V.; Bahurudeen, A.; Ajinkya, S.D. Utilisation of rice husk ash for cleaner production of different construction products. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 263, 121578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nzereogu, P.U.; Omah, A.D.; Ezema, F.I.; Iwuoha, E.I.; Nwanya, A.C. Silica extraction from rice husk: Comprehensive review and applications. Hybrid Adv. 2023, 4, 100111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Saffar, F.Y.; Wong, L.S.; Paul, S.C. An Elucidative Review of the Nanomaterial Effect on the Durability and Calcium-Silicate-Hydrate (CSH) Gel Development of Concrete. Gels 2023, 9, 613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Pang, Y.; Wang, W.; Wu, E.; Fan, M.; Jiang, P.; Mei, G. Enhancement effect of calcium carbide residue and rice husk ash on soft soil: Small-strain property and micro mechanism. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2024, 32, 774–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malpani, S.K.; Goyal, D. Synthesis, analysis, and multi-faceted applications of solid wastes-derived silica nanoparticles: A comprehensive review (2010–2022). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 28321–28343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abolhasani, A.; Samali, B.; Aslani, F. Rice husk ash incorporation in calcium aluminate cement concrete: Life cycle assessment, hydration and strength development. Sustainability 2022, 14, 1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pode, R. Potential applications of rice husk ash waste from rice husk biomass power plant. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 53, 1468–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endale, S.A.; Taffese, W.Z.; Vo, D.H.; Yehualaw, M.D. Rice husk ash in concrete. Sustainability 2022, 15, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shehata, A.A.A.; Owino, A.O.; Islam, M.Y.; Hossain, Z. Shear strength of soil by using rice husk ash waste for sustainable ground improvement. Discov. Sustain. 2024, 5, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owino, A.O.; Hossain, Z. Correlation between one-dimensional consolidation coefficients and different basalt fiber lengths and RHA-cement contents in fiber-reinforced stabilized expansive soils. Soils Found. 2023, 63, 101351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saad, A.H.; Nahazanan, H.; Yusuf, B.; Toha, S.F.; Alnuaim, A.; El-Mouchi, A.; Elseknidy, M.; Mohammed, A.A. A systematic review of machine learning techniques and applications in soil improvement using green materials. Sustainability 2023, 15, 9738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunasekaran, V.; Sathiparan, N. Combine the use of rice husk ash and quarry waste for sustainable masonry blocks: Mechanical characteristics, durability and eco-benefits. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 98, 111194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atef, A.; Hossain, Z. Sustainable Soil Reinforcement by Maximizing Geotechnical Performance with Rice Husk Ash in Subgrade Layers. Materials 2025, 18, 873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, H.; Bi, K.; Chen, W.; Pham, T.M.; Li, J. Towards next generation design of sustainable, durable, multi-hazard resistant, resilient, and smart civil engineering structures. Eng. Struct. 2023, 277, 115477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.; McNally, C. A holistic review on the contribution of civil engineers for driving sustainable concrete construction in the built environment. Dev. Built Environ. 2023, 16, 100273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okalebo, J.R.; Gathua, K.W.; Woomer, P.L. Laboratory methods of soil and plant analysis: A working manual second edition. Sacred Afr. Nairobi 2002, 21, 25–26. [Google Scholar]
- Obalum, S.E.; Chibuike, G.U. Air-drying effect on soil reaction and phosphorus extractability from upland-lowland tropical soils as related to their colloidal stability. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 2017, 15, 525–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gee, G.W.; Or, D. 2.4 Particle-size analysis. In Methods of Soil Analysis: Part 4 Physical Methods; Soil Science Society of America, Inc.: Madison, WI, USA, 2002; Volume 5, pp. 255–293. [Google Scholar]
- Erich, M.S.; Hoskins, B.R. Effects of Soil drying on soil pH and nutrient extractability. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2011, 42, 1167–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haluschak, P. Laboratory methods of soil analysis. Can.-Manit. Soil Surv. 2006, 3, 133. [Google Scholar]
- JIS A 1210; Test Method for Soil Compaction Using a Rammer. Japanese Industrial Standard, Guidance and Basic—Soil Test. The Japanese Geotechnical Society: Tokyo, Japan, 2010; pp. 71–78. (In Japanese)
- Owino, A.O.; Hossain, Z. The influence of basalt fiber filament length on shear strength development of chemically stabilized soils for ground improvement. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 374, 130930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nahar, N.; Hossain, Z.; Tamaki, N. Optimum utilization of rice husk ash waste for ground improvement. Int. Agric. Eng. J. 2021, 30, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- JGS 0524; Method for Consolidated-Drained Triaxial Compression Test on Soils. The Japanese Geotechnical Society (Dositsu Shiken Hou Dositsu Kogakkai): Tokyo, Japan, 2001; pp. 233–243. (In Japanese)
- Mazumder, M.; Ahmed, R.; Ali, A.W.; Lee, S.J. SEM and ESEM techniques used for analysis of asphalt binder and mixture: A state of the art review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 186, 313–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Zhang, X.; Liu, X.; Gao, H.; Pan, Y. Stabilization of micaceous residual Soil with industrial and agricultural by-products: Perspectives from hydrophobicity, water stability, and durability enhancement. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 430, 136450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Zhang, B.; Dai, Q.; Yu, X. Investigation of internal curing effects on microstructure and permeability of interface transition zones in cement mortar with SEM imaging, transport simulation and hydration modeling techniques. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 76, 366–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polo-Mendoza, R.; Martinez-Arguelles, G.; Walubita, L.F.; Moreno-Navarro, F.; Giustozzi, F.; Fuentes, L.; Navarro-Donado, T. Ultraviolet ageing of bituminous materials: A comprehensive literature review from 2011 to 2022. Constr. Build. Mater 2022, 350, 128889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheraghian, G.; Wistuba, M. Ultraviolet aging study on bitumen modified by a composite of clay and fumed silica nanoparticles. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 11216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A. Compressive strength and microstructure of soft clay soil stabilized with recycled basanite. Appl. Clay Sci. 2015, 104, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azad, N.M.; Samarakoon, S.M.S.M.K. Utilization of industrial by-products/waste to manufacture geopolymer cement/concrete. Sustainability 2021, 13, 873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, S.; Singh, S.P. Strength and durability properties of expansive soil treated with geopolymer and conventional stabilizers. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 328, 127078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haeri, S.M.; Khosravi, A.; Garakani, A.A.; Ghazizadeh, S. Effect of soil structure and disturbance on hydromechanical behavior of collapsible loessial soils. Int. J. Geomech. 2017, 17, 04016021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maddalena, R.; Li, K.; Chater, P.A.; Michalik, S.; Hamilton, A. Direct synthesis of a solid calcium-silicate-hydrate (CSH). Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 223, 554–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choobbasti, A.J.; Samakoosh, M.A.; Kutanaei, S.S. Mechanical properties soil stabilized with nano calcium carbonate and reinforced with carpet waste fibers. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 211, 1094–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasanzadeh, A.; Shooshpasha, I. PET fiber reinforcement efficiency in the mechanical and microstructural characteristics of cemented sand modified with silica fume. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 397, 132363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Zhao, H.; Liu, J.; Song, Z.; Che, W.; Ma, K.; Wang, Y. Study on mechanical properties and microstructure of porous organic polymer reinforced low-grade sand under wetting–drying cycles. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 409, 134042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Meyer, C. Utilization of rice husk ash in green natural fiber-reinforced cement composites: Mitigating degradation of sisal fiber. Cem. Concr. Res. 2016, 81, 94–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthukrishnan, S.; Gupta, S.; Kua, H.W. Application of rice husk biochar and thermally treated low silica rice husk ash to improve physical properties of cement mortar. Theor. Appl. Fract. Mech. 2019, 104, 102376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Li, G.; Lu, S.; Wang, J.; Chi, L. Enhance mechanical damping behavior of RHA-cement mortar with bionic inorganic-organic laminated structures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 323, 126521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goud, G.N.; Umashankar, B. Interface shear strength properties of gravel bases and subgrades with various reinforcements. Int. J. Geosynth. Ground Eng. 2018, 4, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikechukwu, A.F.; Hassan, M.M. Assessing the extent of pavement deterioration caused by subgrade volumetric movement through moisture infiltration. Int. J. Pavement Res. Technol. 2022, 15, 676–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abhishek, A.; Guharay, A.; Raghuram, A.S.S.; Hata, T. A state-of-the-art review on suitability of rice husk ash as a sustainable additive for geotechnical applications. Indian Geotech. J. 2024, 54, 910–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Othman, R.; Putra Jaya, R.; Duraisamy, Y.; Sulaiman, M.A.; Chong, B.W.; Ghamari, A. Efficiency of waste as cement replacement in foamed concrete—A review. Sustainability 2023, 15, 5163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.; Jin, Z.; Bao, X.; Tang, W.; Dong, B. Effect of carbon fiber and nanosilica on shear properties of silty soil and the mechanisms. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 189, 286–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munirwan, R.P.; Taha, M.R.; Mohd Taib, A.; Munirwansyah, M. Shear strength improvement of clay soil stabilized by coffee husk ash. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 5542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, K.; Fauchille, A.L.; Di Filippo, E.; Kotronis, P.; Sciarra, G. A review of sand–clay mixture and soil–structure interface direct shear test. Geotechnics 2021, 1, 260–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratnaweera, P.; Meegoda, J.N. Shear strength and stress-strain behavior of contaminated soils. Geotech. Test. J. 2006, 29, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Roy, L.B. Rainfall induced geotextile reinforced model slope embankment subjected to surcharge loading: A review study. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 2022, 29, 3203–3221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Indraratna, B.; Nguyen, T.T.; Atapattu, S.; Ngo, T.; Rujikiatkamjorn, C. Subgrade soil response to rail loading: Instability mechanisms, causative factors, and preventive measures. Transp. Geotech. 2024, 46, 101267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhou, Y. Dynamic vertical displacement for ballastless track-subgrade system under high-speed train moving loads. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2020, 129, 105911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maheepala MM AL, N.; Nasvi MC, M.; Robert, D.J.; Gunasekara, C.; Kurukulasuriya, L.C. A comprehensive review on geotechnical properties of alkali activated binder treated expansive soil. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 363, 132488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Kogbara, R.B.; Hariharan, N.; Masad, E.A.; Little, D.N. A state-of-the-art review of polymers used in soil stabilization. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 305, 124685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najm, H.M.; Ahmad, S.; Khan, R.A. Mechanical and microstructural analysis of waste ceramic optimal concrete reinforced by hybrid fibers materials: A comprehensive study. J. Archit. Environ. Struct. Eng. Res. 2022, 5, 11–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramesh, H.N.; Manjunatha, B.V. Justification of strength properties of microstructural changes in the black cotton soil stabilized with rice husk ash and carbide lime in the presence of sodium salts. SN Appl. Sci. 2020, 2, 457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramadan, M.; Kohail, M.; Abadel, A.A.; Alharbi, Y.R.; Soliman, A.M.; Mohsen, A. Exploration of mechanical performance, porous structure, and self-cleaning behavior for hydrothermally cured sustainable cementitious composites containing de-aluminated metakaolin waste and TiO2 nanoparticles. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 25, 3998–4019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Alengaram, U.J.; Ibrahim, Z. Effect of treated and untreated rice husk ash, palm oil fuel ash, and sugarcane bagasse ash on the mechanical, durability, and microstructure characteristics of blended concrete–A comprehensive review. J. Build. Eng. 2023, 78, 107500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zajac, M.; Song, J.; Ullrich, P.; Skocek, J.; Haha, M.B.; Skibsted, J. High early pozzolanic reactivity of alumina-silica gel: A study of the hydration of composite cements with carbonated recycled concrete paste. Cem. Concr. Res. 2024, 175, 107345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, S.S.; Mishra, U.; Biswal, S.K. Mechanical and microstructural study of slag based alkali activated concrete incorporating RHA. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 400, 132685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Duan, Y.; Lu, X.; Li, M.; Chen, J.; Jin, Z.; Hou, D.; Hong, S.; Wang, P.; Dong, B. Molecular-scale insights into the leaching of Ca ions and carbonate deposition behavior in CSH under carbonation. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 98, 111358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Ding, Q.; Zhang, G.; Hou, D.; Zhao, M.; Cao, J. Effect of sulfate attack on the composition and micro-mechanical properties of CASH gel in cement-slag paste: A combined study of nanoindentation and SEM-EDS. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 345, 128275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldovino, J.A.; Nuñez de la Rosa, Y.E.; Namdar, A. Sustainable cement stabilization of plastic clay using ground municipal solid waste: Enhancing soil properties for geotechnical applications. Sustainability 2024, 16, 5195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
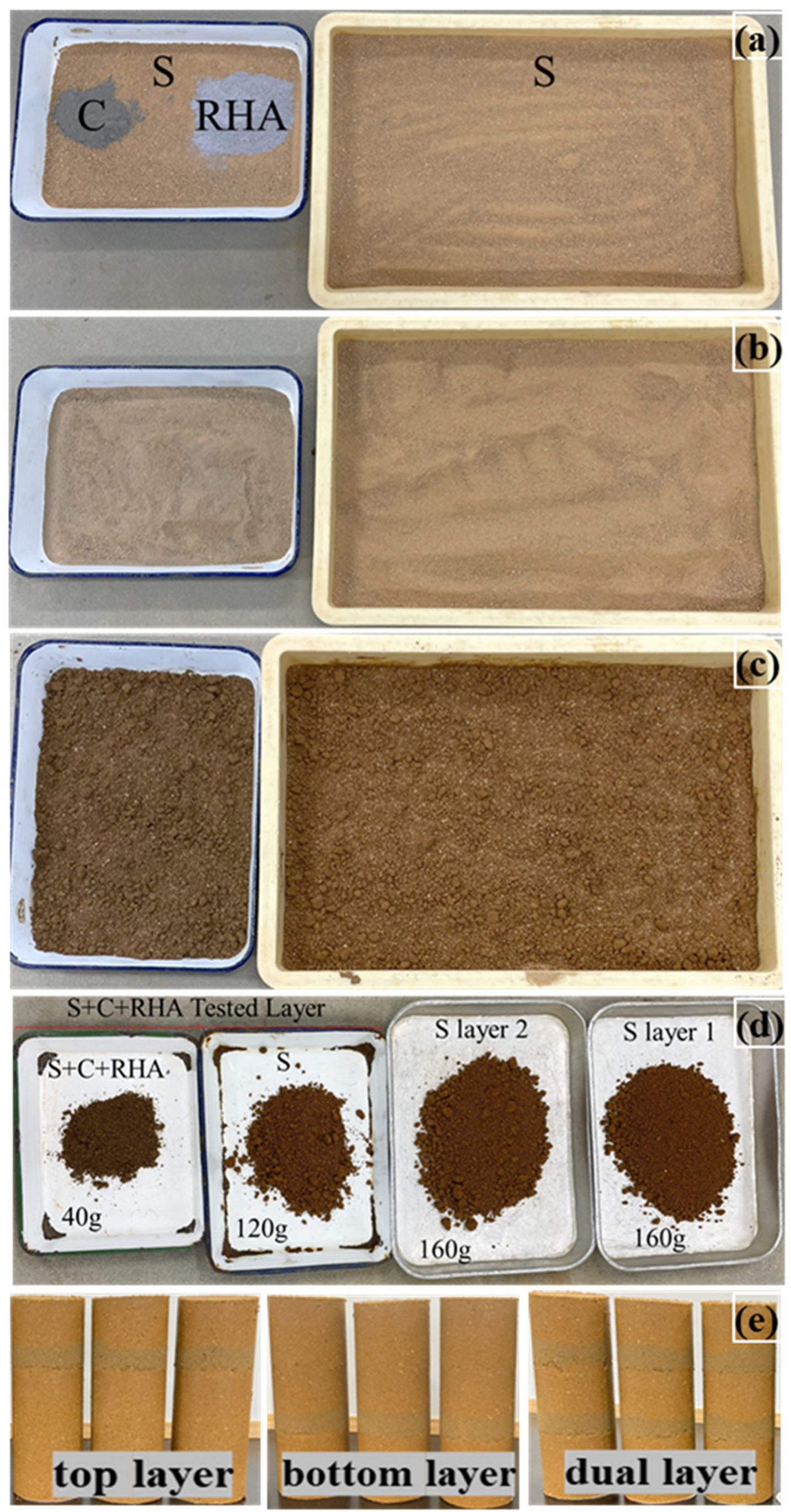
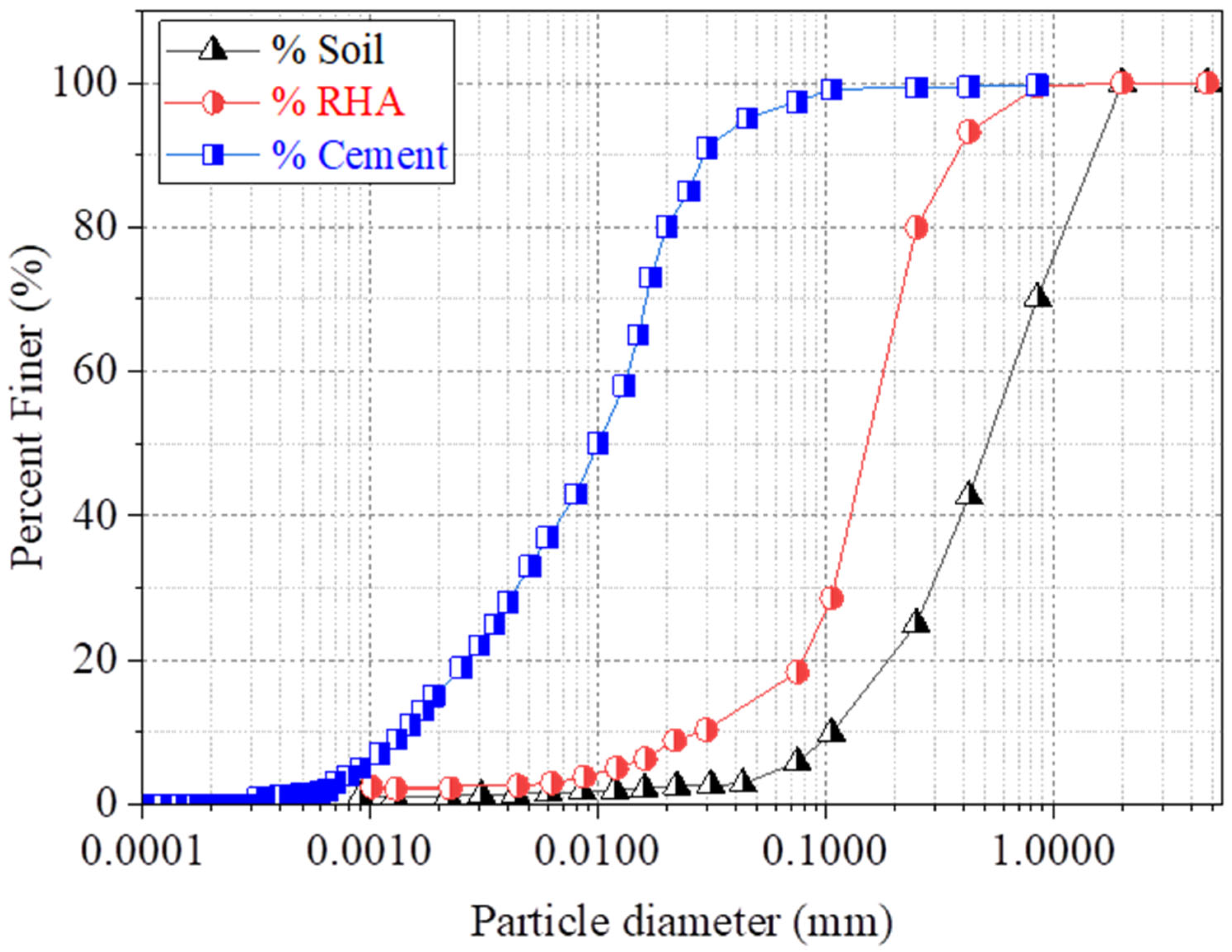

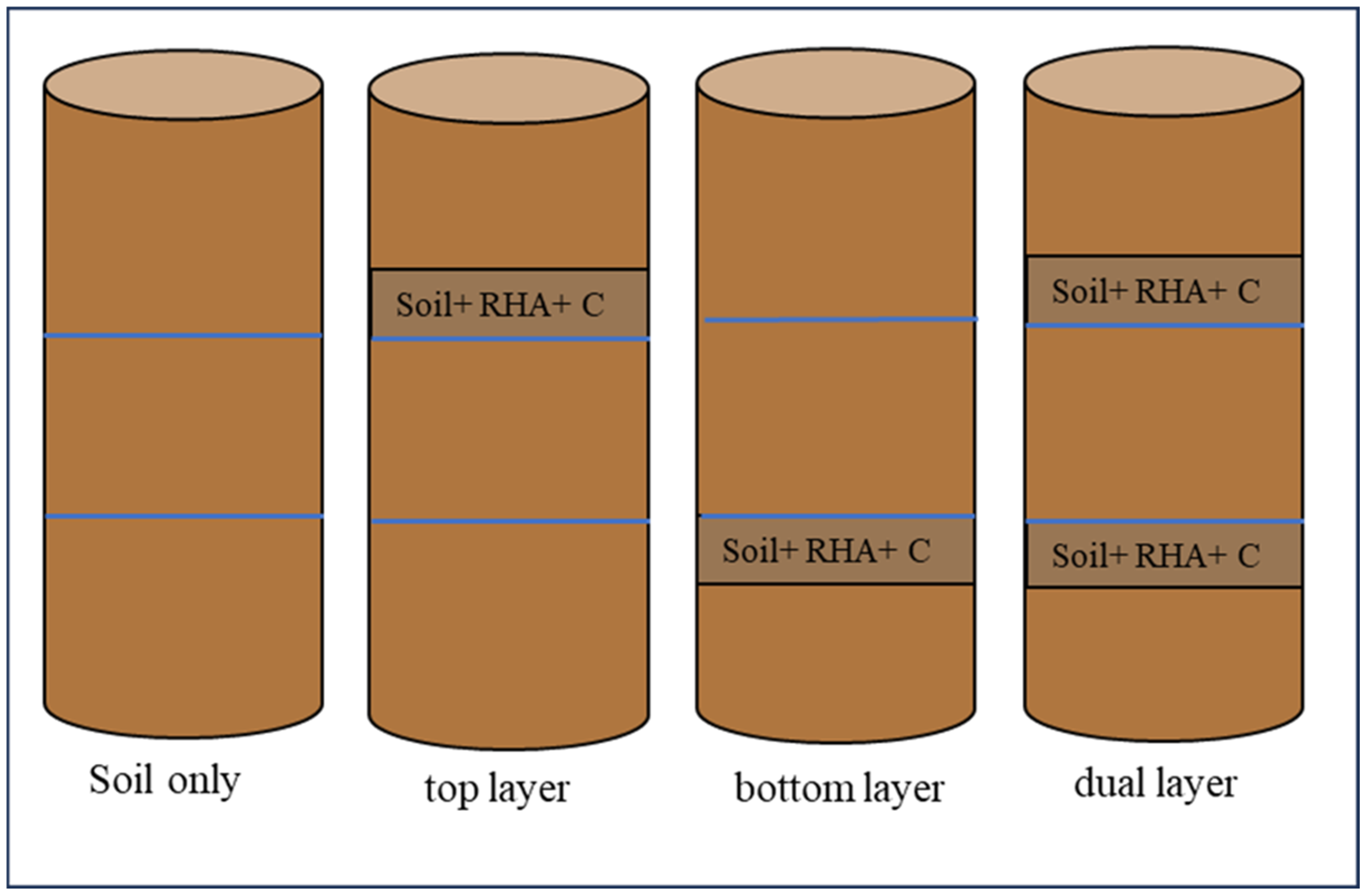
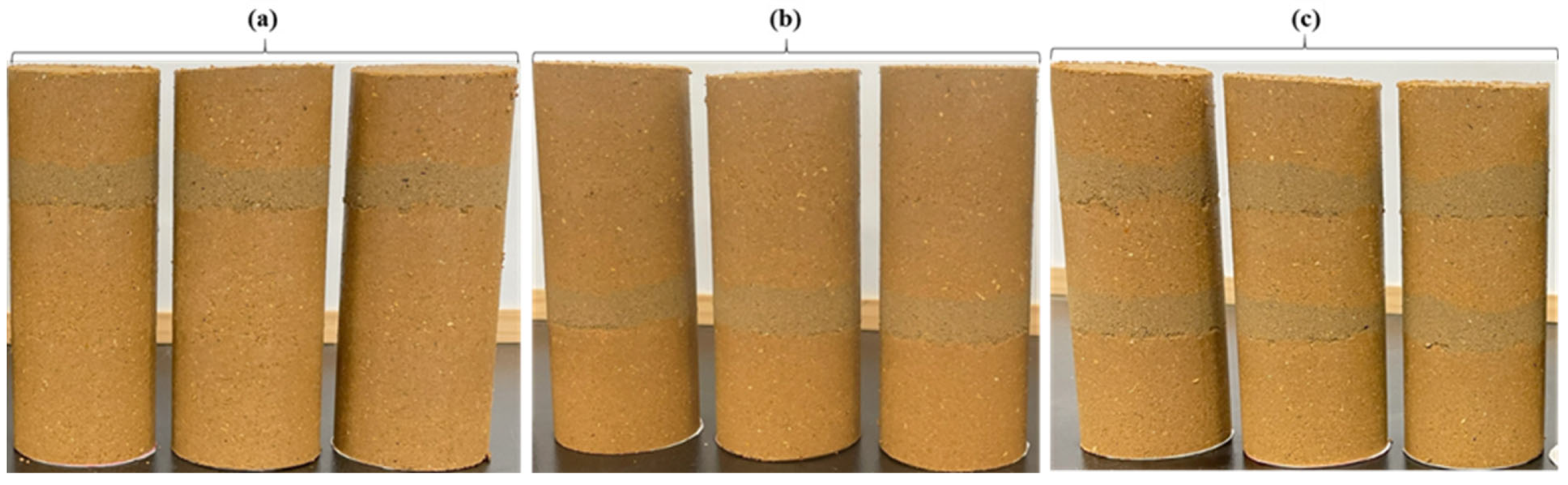
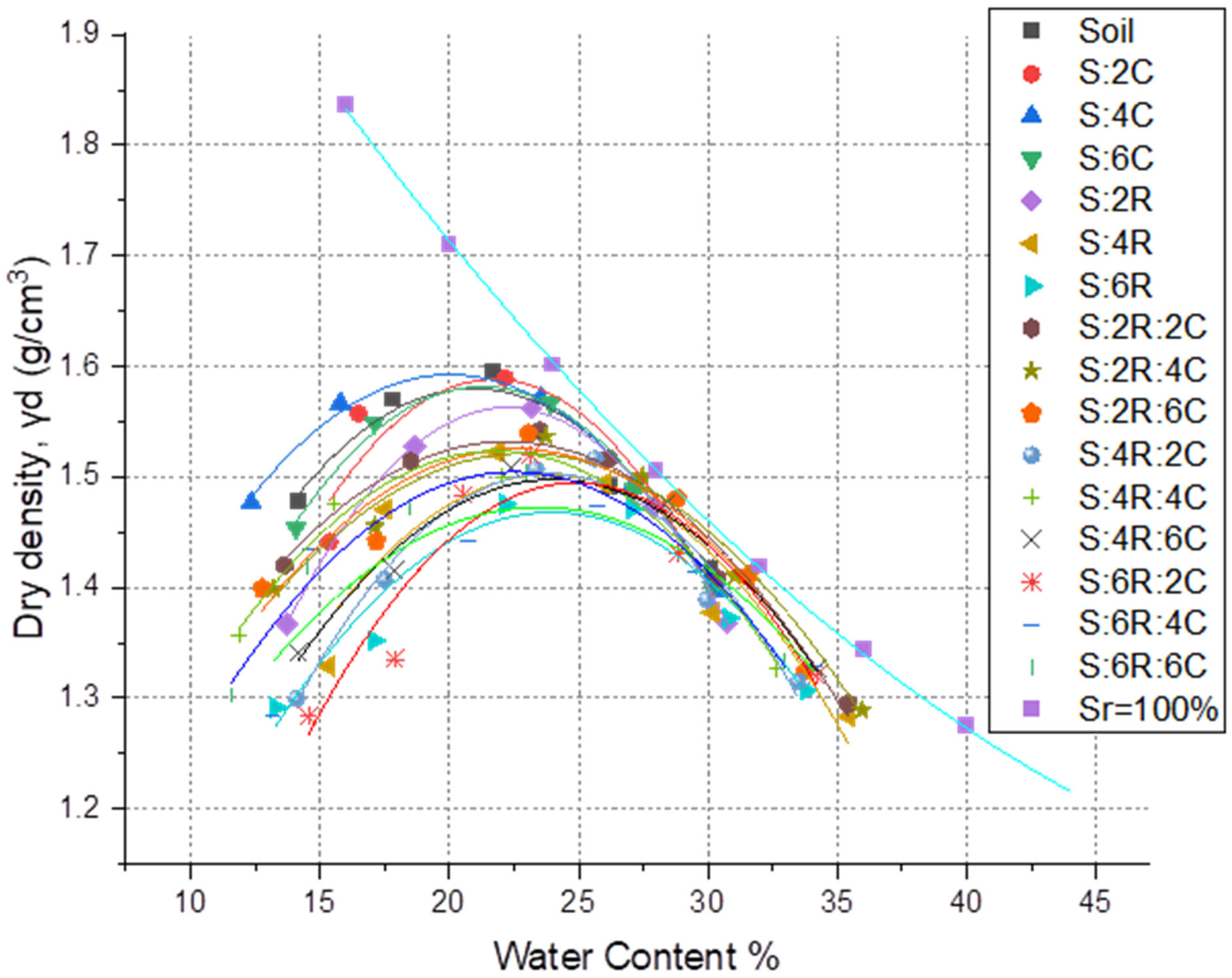





| Data | Basic Characteristics of Soil | Worth |
|---|---|---|
| Basic Characteristics of Soil | sand (75 μm–2 mm), % | 0.02 |
| silt (5–75 μm), % | 57.28 | |
| clay < 5 μm, % | 42.7 | |
| liquid limit, LL, % | 48.5 | |
| plastic limit, PL, % | 28.5 | |
| plasticity Index, PI, % | 19.9 | |
| maximum dry density, g/cm3 | 1.58 | |
| AASHTO classification | A-7–6(5) |
| Data | Basic Characteristics of RHA | Worth |
|---|---|---|
| Basic Characteristics of RHA | average particle size, mm | 0.001 to 0.3 |
| loss of ignition, % | 4–6 | |
| specific gravity, g/cm3 | 2.12 | |
| burning temperature, °C | 650–700 | |
| burning time, hour | 27 | |
| silica (SiO2), % | 91.10 | |
| carbon dioxide (CO2) % | 4.35 | |
| potassium oxide (K2O), % | 2.40 | |
| calcium oxide (CaO), % | 0.57 | |
| iron oxide (Fe2O3), % | 0.05 | |
| alumina (Al2O3), % | 0.03 | |
| others, % | 1.50 |
| Combinations | Soil | RHA | Cement |
|---|---|---|---|
| control | 100 | 0 | 0 |
| soil + 2RHA | 98 | 0 | 2 |
| soil + 4RHA | 96 | 0 | 4 |
| soil + 6RHA | 94 | 0 | 6 |
| soil + 2C | 98 | 2 | 0 |
| soil + 4C | 96 | 4 | 0 |
| soil + 6C | 94 | 6 | 0 |
| soil + 2RHA + 2C | 96 | 2 | 2 |
| soil + 2RHA + 4C | 94 | 2 | 4 |
| soil + 2RHA + 6C | 92 | 2 | 6 |
| soil + 4RHA + 2C | 94 | 4 | 2 |
| soil + 4RHA + 4C | 92 | 4 | 4 |
| soil + 4RHA + 6C | 90 | 4 | 6 |
| soil + 6RHA + 2C | 92 | 6 | 2 |
| soil + 6RHA + 4C | 90 | 6 | 4 |
| soil + 6RHA + 6C | 88 | 6 | 6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Atef, A.; Hossain, Z. Assessing the Impact of Rice Husk Ash on Soil Strength in Subgrade Layers: A Novel Approach to Sustainable Ground Engineering. Sustainability 2025, 17, 5457. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17125457
Atef A, Hossain Z. Assessing the Impact of Rice Husk Ash on Soil Strength in Subgrade Layers: A Novel Approach to Sustainable Ground Engineering. Sustainability. 2025; 17(12):5457. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17125457
Chicago/Turabian StyleAtef, Abdelmageed, and Zakaria Hossain. 2025. "Assessing the Impact of Rice Husk Ash on Soil Strength in Subgrade Layers: A Novel Approach to Sustainable Ground Engineering" Sustainability 17, no. 12: 5457. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17125457
APA StyleAtef, A., & Hossain, Z. (2025). Assessing the Impact of Rice Husk Ash on Soil Strength in Subgrade Layers: A Novel Approach to Sustainable Ground Engineering. Sustainability, 17(12), 5457. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17125457






