Abstract
Hydrogen offers a promising solution to reduce emissions in the energy sector with the growing need for decarbonisation. Despite its environmental benefits, the use of hydrogen presents significant challenges in storage and transport. Many studies have focused on the different types of hydrogen production and analysed the pros and cons of each technique for different applications. This study focuses on techno-economic analysis of onsite hydrogen production through ammonia decomposition by utilising the heat from exhaust gas generated by hydrogen-fuelled gas turbines. Aspen Plus simulation software and its economic evaluation system are used. The Siemens Energy SGT-400 gas turbine’s parameters are used as the baseline for the hydrogen gas turbine in this study, together with the economic parameters of the capital expenditure (CAPEX) and operating expenditure (OPEX) are considered. The levelised cost of hydrogen (LCOH) is found to be 5.64 USD/kg of hydrogen, which is 10.6% lower than that of the conventional method, where a furnace is used to increase the temperature of ammonia. A major contribution of the LCOH comes from the ammonia feed cost up to 99%. The price of ammonia is found to be the most sensitive parameter of the contribution to LCOH. The findings of this study show that the use of ammonia decomposition via heat recovery for onsite hydrogen production with ammonic recycling is economically viable and highlight the critical need to further reduce the prices of green ammonia and blue ammonia in the future.
1. Introduction
Global warming poses a significant threat to our planet, and burning fossil fuels is the biggest contributor to global warming. Hydrogen can play a pivotal role in advancing the world toward decarbonisation as hydrogen has the potential to be a clean source of energy that can replace fossil fuels in various sectors. A report published by the International Energy Agency (IEA) stated that the annual use of hydrogen is growing by 6% annually and is expected to continue growing until at least the end of this decade, which suggests more than 150 million tonnes (Mt) of hydrogen use by 2030 [1].
While hydrogen by itself can be a clean source of energy as the only byproduct after combustion is water vapour, the environmental impact caused by using hydrogen depends on its production [2]. The cost of transitioning from grey to green hydrogen would be a barrier, as green hydrogen is about three times more expensive [3]. One of the main factors would be the cost of the storage and transport of hydrogen.
1.1. Storage and Transport of Hydrogen
The storage and transportation of hydrogen fuel is costly because hydrogen is a low-density gas by volume, which makes it challenging to store in large quantities without high pressure or low temperatures. Current technology uses 700 bar and 30 °C to compress hydrogen using highly sophisticated piping and compression systems with high energy consumption, resulting in high hydrogen production costs [4]. In 2021, hydrogen retailed at 8.50 USD/kg to 10.80 USD/kg higher than gasoline prices, matching the same fuel cost per mile for hybrids or conventional gasoline vehicles [5]. Therefore, various hydrogen storage options have been researched to lower the price of hydrogen in the upcoming years.
There are two categories of hydrogen storage, as hydrogen can be stored in physical-based and material-based systems. In the physical-based system, hydrogen is stored by adjusting its physical state. Hydrogen is stored in the form of compressed gas by increasing its pressure, the form of liquified hydrogen by decreasing its temperature, or cryogenic hydrogen. In material-based storage systems, hydrogen carriers are used, like water, ammonia, etc. Hydrogen is produced via the electrolysis of water or ammonia decomposition. High-pressure tube trailers are commonly used to transport hydrogen gas, where hydrogen gas is stored at high pressure up to 5000 psi [6]. However, different storage methods result in different volumetric densities of hydrogen, as described in Table 1.

Table 1.
Hydrogen density for different storage methods.
1.2. Hydrogen Carrier Fuel—Ammonia
Among all the available methods, ammonia can be used to generate hydrogen through a process known as ammonia decomposition, as described in Equation (1)
In this process, ammonia is broken down into hydrogen and nitrogen through chemical reactions, often facilitated using catalysts. The hydrogen produced can then be used in fuel cells, internal combustion engines, or other applications that require hydrogen energy.
Currently, several methods for ammonia decomposition are in use; these methods include thermal decomposition, where ammonia is heated to high temperatures, and catalytic decomposition, which utilises catalysts to lower the activation energy and enable ammonia breakdown at more moderate temperatures. Significant research has been conducted on catalysts that can facilitate ammonia decomposition at lower temperatures, with the aim of improving the efficiency of the process and reducing energy input [9]. Studies have explored various materials, including precious metals, like ruthenium, and non-precious metals, like iron and nickel [10]. In a study conducted by Zikai Su et al. on the progress of ruthenium-based catalysts for hydrogen production from ammonia decomposition, they have achieved metal support interactions over Ru-based catalysts with high ammonia decomposition activity at 500 °C [11]. They made use of the large specific surface area of the metal support to improve the stability of the reaction and the conductivity of the support to modulate the electron to accelerate the adsorption of the nitrogen atoms. A.S. Chellapa et al. suggested that the reaction rate of ammonia decomposition via Ni-Pt/Al2O3 catalysts is highly dependent on the partial pressure of ammonia, whereas hydrogen inhibition could potentially occur at temperatures lower than 520 °C [12]. A study also demonstrated that Ni-based catalysts are more stable than Ru-based catalysts, as Ru-based catalysts suffer from the deactivation problem due to the loss of exposed Ru active sites [13]. Although Ru-based catalysts could achieve higher ammonia conversion, precious metals are not the best option for catalytic ammonia decomposition due to their high cost and limited supply, as shown in Figure 1. Catalysts with precious metals could achieve low activation energy and low decomposition temperatures; however, they are not economically feasible for long-term hydrogen generation, as the price of precious metal catalysts is about twice the price of base metal catalysts, like Fe, Co, Mo, or Ni. Hence, the usage of catalysts based on Ni or Fe is more sustainable in the long run and more common.
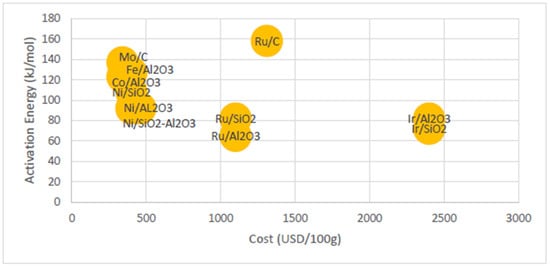
Figure 1.
Cost comparison of different catalysts used in ammonia decomposition [9].
The temperature for ammonia decomposition is a crucial factor for practical applications. Catalysts have been shown to lower the required decomposition temperature, with some research aiming to achieve ammonia breakdown at temperatures below 450 °C, a significant reduction from the 800–1000 °C required in non-catalytic methods [9]. Advancements in catalytic materials and techniques are key to unlocking the full potential of ammonia as a hydrogen carrier fuel [14].
1.3. Techno-Economic Analysis of Various Hydrogen Generation Methods
Hydrogen plays an important role in the low-carbon energy future. Hydrogen council projected that hydrogen has the potential to take up 18% of the share of final energy demand by 2050 [15]. The global hydrogen project investment has increased by seven-fold in 2024 since 2020 [16]. Hence, hydrogen demand/supply has been increasing drastically in recent years. However, it is important to determine a way to reduce hydrogen production costs. Camel et al. stated that the levelised cost of hydrogen (LCOH) will be estimated at USD 6.86/kg with current technology in thermo-catalytic ammonia crackers, and sensitivity analysis suggested that the LCOH would be reduced by almost 50% by 2040 with improved technologies. In addition, the cost of green hydrogen is significantly higher than that of grey hydrogen, as the technologies for green hydrogen production are still in the research stage.
The LCOH is estimated at USD 11.28/kg for hydrogen production via the electrolysis of water based on alkaline electrolysis technology by using 50% energy from grip power and 50% energy from PV plants at a medium production capacity of 100 kg/day [17]. LCOH via water electrolysis could be lower with more efficient technology that has lower electricity consumption. Antonio Villalba-Herreros et al. conducted a techno-economic study on the LCOH of green hydrogen under three different scenarios: (1) producing green hydrogen on-site using water electrolysis, (2) offshore production of hydrogen using electrolysis, liquefying and transporting liquid green hydrogen to the site, and then regasification on-site, and (3) offshore production of hydrogen using electrolysis, conversion of hydrogen into ammonia, then transporting ammonia by ship and cracking ammonia on-site [18]. This study also suggested that blue hydrogen would have a LCOH that is 65% lower than that of green hydrogen and the LCOH for thermos-catalytic ammonia cracking is about 40% lower compared with the LCOH for water electrolysis. In addition, the LCOH of water electrolysis is highly dependent on the electricity tariff. It is worth mentioning that on-site or off-site hydrogen production via ammonia decomposition could be more likely to achieve a greener future. This approach offers significant advantages, including efficient hydrogen storage and transport, and the possibility of reusing energy sources for conversion.
Hence, it is important to develop a better technology that could further reduce the cost of the ammonia cracking session, for example, waste heat recovery. While previous studies have been focusing on water electrolysis or thermal–catalytic ammonia cracking via the burning of carbon fuel, they have not adequately addressed ammonia cracking with the capture of waste heat from other heat sources. In this study, we will conduct a techno-economic analysis of hydrogen production via ammonia decomposition with convective heat transfer and compare the result with that of the conventional method, which is the direct heating of ammonia. The application of reusing exhaust heat from gas turbines to generate hydrogen via ammonia decomposition could be proven to be economically viable through this study and incentivise more research in this field of study.
2. Materials and Methods
The developed methodology in this study for on-site hydrogen production via ammonia decomposition by utilising waste heat recovery is illustrated in Figure 2. In this study, a process simulation was developed by using AspenPlus and the economic analysis obtained from the simulation was compared between the proposed method and the conventional method with the burning of fossil fuel used for ammonia decomposition. A sensitivity analysis of process and economic parameters was conducted. An uncertainty analysis by Monte Carlo simulation was performed.
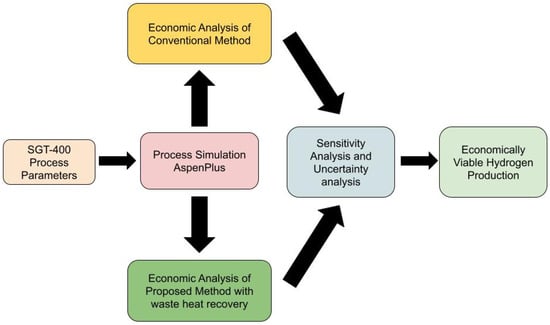
Figure 2.
Flowchart for the methodology.
2.1. Techno-Economic Analysis
2.1.1. Simulation of SGT-400 Gas Turbine
A SGT-400 gas turbine with a twin shaft, shown in Figure 3, was selected as the study gas turbine as this gas turbine has been reported to be capable of operating under 100% hydrogen fuel [19].
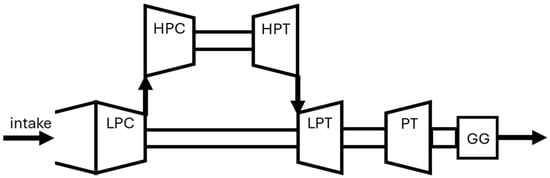
Figure 3.
Schematic drawing of SGT-400 gas turbine.
Due to the limited and confidential information provided by the manufacturer, Siemens Energy, the required hydrogen fuel mass flow rate is assumed to be the same as the natural gas fuel mass flow rate. The simulation of the SGT-400 gas turbine was conducted by using Aspen Plus V14 to determine the required flow rate for natural gas; Figure 4 illustrates the simulation of the SGT-400 gas turbine consisting of 2 stages of compressor and 3 stages of turbine. The parameters for each stage were determined referring to a study by Ajoko et al. [20]. The power output calculated from the simulation result was 12.8 MW, as shown in Table 2, by considering the power output generated from LPT and PT and the power required for LPC. The power output obtained was reported to have less than 1% error compared with the power output reported in the study by Ajoko et al. [20]. The heat released from the combustion of natural gas described in Equation (2) was calculated by applying Equation (3) to verify the result obtained from the simulation. The specific energy of hydrogen at 200 bar was about 2.4 times the specific energy of natural gas at 200 bar [21]. Although hydrogen exhibits a higher specific energy and a lower density compared with natural gas, the hydrogen mass flow rate was conservatively assumed to be equivalent to that of natural gas in this study. This simplifying assumption was made due to the limited availability of performance data and validated operational parameters for hydrogen-fuelled gas turbines, particularly at commercial scales. In addition, differences in combustion characteristics, flame speed, and turbine material compatibility introduce uncertainties that are beyond the scope of this analysis. By assuming a mass flow rate equal to that of natural gas, we avoided overestimating the hydrogen throughput and maintained a conservative basis for techno-economic projections. Hence, in the next techno-economic analysis section, the hydrogen required for the gas turbine was assumed to be the same as the mass flow rate of natural gas obtained from this simulation, which was 38.9 kg/s. The ammonia feed rate will be used as one of the process parameters in the sensitivity analysis as it directly affects the hydrogen production rate and the LCOH.
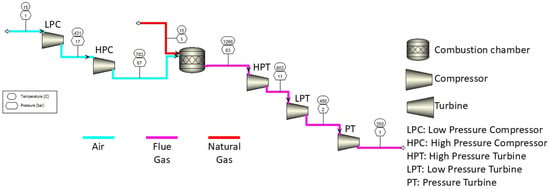
Figure 4.
Schematic diagram of SGT-400 gas turbine.

Table 2.
Simulated power input/output of LPC, LPT, and PT in SGT-400 gas turbine.
: Combustion heat released ;
: Work done ;
,: Molar flow rate of product and reactant, respectively ;
: Enthalpy of formation at 25 °C ;
Change in enthalpy between the temperature of the product or reactant and the reference temperature at 25 °C ;
: Universal gas constant (8.314 );
,: Absolute temperature of product or reactant (K).
2.1.2. Basis of Design
This study analyses the LCOH for on-site hydrogen production for a commercial gas turbine, SGT400, that could be converted to a 100% hydrogen-fuelled gas turbine via waste heat recovery [19]. There are 2 case studies here for cost comparisons. In the first case study, ammonia is steadily supplied in the conceptual system shown in Figure 4 with the assumption of an ammonia gas distribution system excluded from this study.
The ammonia is fed at a rate of 480 kg/s at a pressure of 1 bar and temperature of 298 K (25 °C). The ammonia pressure is raised to 3 bar via a pump before it enters the reactor for the ammonia decomposition process. A furnace is used in the simulation to mimic the process where conventional reactors use a burner to increase the temperature of ammonia to the required temperature, set at 923 K (650 °C) in this study [22]. The thermal efficiency of the furnace is set at 80%. REQUIL is used to simulate the reactor with the assumption of using a Ni-based catalyst and activation energy of [22]. The furnace and reactor were set to assume no pressure loss. Theuncracked ammonia is recycled back to the storage tank via ammonia absorption and flash distillation process. Four reactors and an ammonia absorber were used to maximise the conversion rate of ammonia and the absorption rate of uncracked ammonia. Water is used to capture the uncracked ammonia and flash distillation increases the pressure of the ammonia–water mixture to 3 bar in order to transform the ammonia into the vapour phase. The mixture of hydrogen and nitrogen is separated by pressure swing absorption (PSA), which has 7 stages with a pressure of 5 bar set as the condenser pressure [23,24]. The 1st stage is set for nitrogen and 7th stage is set for hydrogen. This PSA is assumed to have zero pressure drop. The hydrogen produced will be heated up to 323 K (50 °C) via a heater for the next phase of use in hydrogen-powered gas turbines. The duty heat and power for the system shown in Figure 5 are reported in Table 3.
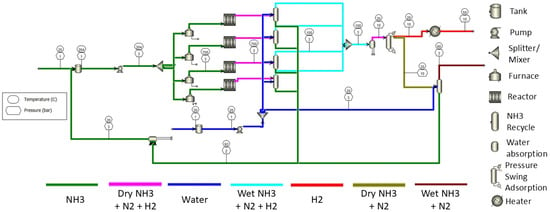
Figure 5.
Schematic diagram for onsite hydrogen production with a conventional ammonia reactor.

Table 3.
Duty heat and power consumption for the process with a conventional reactor.
The second case study shown in Figure 6 used the same flow system as that in the first case study, except for the reactor. The reactor was heated by the convection heat with a target temperature of 923 K (650 °C) (hot gas) and decomposition of ammonia at a temperature of 923 K (650 °C) with the assumption of using a Ni catalyst [9]. The heat transfer efficiency of this reactor design is, according to reference [9], assumed to be 91%. The duty heat and power for the flow in Figure 6 are shown in Table 4.
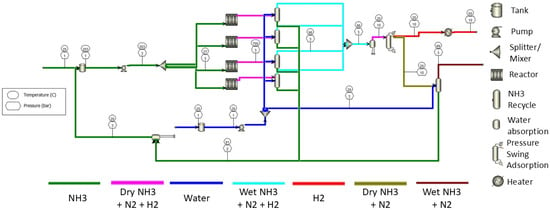
Figure 6.
Schematic diagram for onsite hydrogen production with proposed ammonia reactor via waste heat recovery.

Table 4.
Duty heat and power consumption for the process with a heat recovery system.
The theoretical modelling and simulation were conducted by using the commercial simulation software Aspen Plus V.14 [25]. The thermodynamic properties were solved by using the built-in Peng Robinson model [26].
The main design parameters that impact the LCOH are the usage of natural gas and type of ammonia used. Hence, there were two types of ammonia gas considered in this study, blue ammonia and green ammonia. Blue ammonia gas is produced with carbon capture, while green ammonia gas is produced with no carbon emissions. There were two different configurations of the whole production system. The first configuration was using natural gas for combustion and heating up the ammonia gas for decomposition in the reactor; likewise, the second configuration was assuming that the heat is captured from the exhaust heat generated from the gas turbine, where no combustion of natural gas will take place. The amount of hydrogen delivered differs between the configurations because different cracking processes have different ammonia conversion efficiencies.
2.1.3. Methodology of Techno-Economic Assessment
The techno-economic assessment of hydrogen production via ammonia decomposition with a burner and with convective heat transfer was performed by using the process simulation result. The outcome of the economic assessment includes the capital expenditure (CAPEX) and operating expenditure (OPEX) generated over the lifespan of the plant. The capital cost of the equipment for ammonia decomposition was calculated using the chemical engineering plant cost index (CEPCI) value by using Equation (4) [27].
, : equipment cost for this study and equipment cost obtained from the simulation with baseline from the year 2017;
, : cost index in 2024 and 2017.
CAPEX and OPEX are required to estimate the LCOH. CAPEX is calculated by using Equations (5) and (6) [27].
i: discount rate;
n: plant life;
CRF: cost-recovery factor;
TCI: total capital investment.
OPEX is calculated based on manufacturing costs, local taxes, insurance, financing, and general expenses. The consumption of raw materials and utilities was determined using the simulation results. The number of labourers was assumed to be 15 and the annual salary per person was estimated at an average of 31,111 USD.
The LCOH calculated in accordance with Equation (7) was used to determine the overall cost of hydrogen for each investigated case [28]. Table 5 summarises all the assumptions made for estimating the LCOH for both investigated cases. The hydrogen generated from the system is assumed to be fully utilised by the gas turbine for power generation. The estimations were assumed for a plant based in Singapore, and each unit of cost was converted to USD with an exchange rate of 1SGD to 0.7404 USD.

Table 5.
List of assumptions made for LCOH estimation.
2.1.4. Sensitivity Analysis
Sensitivity analysis was conducted to identify the key parameters for the estimation of LCOH. The sensitivity of process parameters, such as reactor temperature, was analysed by varying this parameter from 823 K to 1073 K. The sensitivity of economic parameters, such as the ammonia price, operating labour cost, purchased equipment cost, building cost, and utilities cost, was analysed by varying these parameters by 30% while keeping the rest constant.
2.1.5. Uncertainty Analysis by Monte Carlo Simulation
Uncertainty analysis was performed by applying the Monte Carlo simulation method. [28]. The key parameters for uncertainty analysis were selected from the sensitivity analysis that were identified as high-sensitivity parameters, such as ammonia cost, utilities cost, and purchased equipment cost. The following steps were taken for the Monte Carlo simulation.
- Identify the key economic parameters;
- Calculate the minimum and maximum for each parameter with variation of ;
- Calculate the range of each parameter;
- Allocate uniform probability distribution for all parameters except for the ammonia cost in step 1. The triangular probability distribution is used for ammonia cost and the cumulative probability distribution is calculated using the cumulative distribution function (CDF) with Equations (8) and (9);
- Generate a random number between 0 and 1 for one of the parameters;
- Using the random number from step 5, assign a value to the probability distribution for that parameter;
- Calculate the LCOH using the sum of the min value and assigned value with the range;
- Repeat step 5 to step 7 for 10,000 iterations;
- Repeat step 2 to step 7 for variations of , and ;
- Repeat steps 1 to 8 for other parameters.
- : minimum value;
- : most likely value;
- : maximum value;
- : random value.
The cumulative probability distribution curves for each key economic parameter were obtained with values for 10,000 iterations with different variations.
2.1.6. Exergy Analysis
Exergy is the maximum work that could be acquired from a system under standard conditions. Exergy has four components, namely physical exergy (, chemical exergy (, potential exergy , and kinetic exergy [33].
This study considered the physical exergy and chemical exergy only as kinetic exergy, and potential exergy is not crucial in the total exergy loss calculation. Physical exergy is the maximum work that can be received from a stream and is calculated in accordance with Equation (10). Chemical exergy is the chemical energy stored in the molecules that can be found in a stream and is obtained from Equation (11).
: enthalpy;
: standard enthalpy;
: entropy;
: standard entropy.
: molar component of th species;
chemical exergy of component of th species;
: universal gas constant, 8.314 J/mol.
The exergy analysis is conducted on the reactor with heat recovery and the reactor with furnace in both case studies. The required initial data, like exergy flow for physical exergy, molar flow rate, molar fraction for ammonia, hydrogen, and nitrogen, were obtained from Aspen Plus. The molar flow rate and molar fraction for a reactor with heat recovery and a reactor with a furnace are tabulated in Table 6 and Table 7.

Table 6.
Molar flow and mass fraction for the reactor with heat recovery.

Table 7.
Molar flow and mass fraction for the reactor with a furnace.
The reference temperature, , and pressure in this study were set at 298.15 K and 1 atm, respectively. The following assumptions are made for this exergy analysis:
- Potential and kinetic exergy are negligible;
- Steady-state model;
- No loss due to pressure in a system.
The total exergy is the summation of physical exergy and chemical exergy. The exergy efficiency is calculated based on Equation (12).
The standard chemical exergies for ammonia, hydrogen, and nitrogen are mentioned in Table 8 [34]. Physical exergies for the inlet and outlet streams are shown in Table 9.

Table 8.
Standard chemical exergy for ammonia, hydrogen, and nitrogen.

Table 9.
Physical exergy for reactor with heat recovery and reactor with furnace.
2.1.7. Climate Change Impacts Based on the Global Warning Potential
A simplified life cycle assessment was conducted to determine the carbon footprint for both case studies. Figure 7 shows the simplified system boundaries of the carbon footprint assessment. The climate change impacts of blue ammonia were assumed to be 1.2 kg CO_2e/kg NH_3, while green ammonia was assumed to have an impact of 0.5 kg CO_2e/kg NH_3 [35]. The carbon emissions from electricity consumption were calculated based on the carbon dioxide emission rate. The electricity used in this study was assumed to be generated via a natural gas fuel source based on the carbon dioxide emission factor data source of EU2018/2066 [36]. The global warming potential based on 100 years (GWP100) was used to calculate the carbon dioxide-equivalent (CO_2e) for 1 kg of hydrogen production, which serves as the functional unit in both case studies. This calculation takes into consideration the natural gas usage and carbon dioxide emission rate.
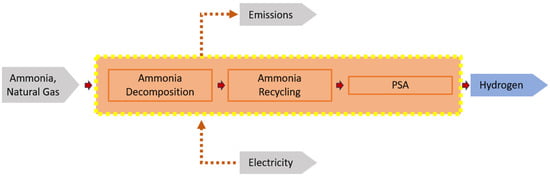
Figure 7.
System boundaries and input parameters of carbon footprint assessment.
3. Results and Discussion
Figure 8 shows the distribution of the purchased equipment costs in both case studies. The ammonia absorber represents the largest portion of 49%, followed by flash distillation with a splitter for separating hydrogen from nitrogen and water, which accounts for 27% when a heat recovery system is used. Likewise, reactors with burning fuel have the highest proportion, accounting for 45%, followed by those with an ammonia absorber, at 31%. There would be a great reduction in equipment cost when fuel combustion is eliminated from the reactor, as a reactor with a heat recovery system would require fewer components and less expensive materials.
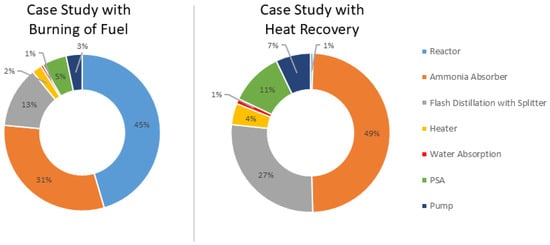
Figure 8.
Distribution cost for all purchased equipment in both case studies.
Table 10 and Table 11 show the LCOH, TCI, CAPEX, and LCOH estimated from the calculations using Equations (5) and (6) for both case studies. The direct costs and indirect costs were obtained from the simulation results. The cost of each piece of equipment calculated using Equation (4) is shown in Appendix A. In the estimation of OPEX, the cost of the consumed raw materials and utilities was obtained from the simulation. The OPEX of both cases was found to be 99.7% of the total cost of hydrogen production, with the remaining 0.3% coming from the CAPEX, with the ammonia cost being the most dominant cost that accounts for 88% of the OPEX in case study 1 and accounts for 99% of the OPEX in case study 2 due to the difference in the utilities used in the heating for case study 1. Figure 9 shows the distribution of OPEX, and the consumable materials cost was the most dominant compared with the other costs, like utilities, operating labour costs, maintenance costs, tax, insurance, etc.

Table 10.
Estimation of TCI from Aspen Plus V14 economic analysis.

Table 11.
Estimation of OPEX.
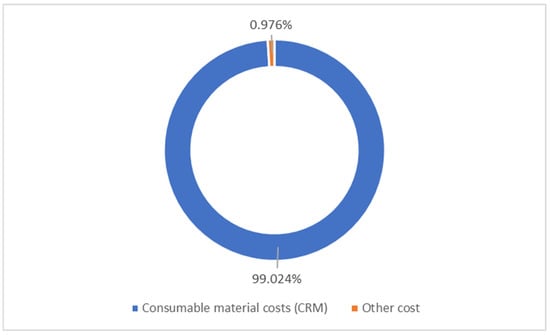
Figure 9.
Distribution of OPEX in case study 2.
From our simulation, we achieved an optimal LCOH of 5.64 USD/kg of when the heat was taken from the waste exhaust heat. The LCOH with the conventional method was 6.31 USD/kg of . It was reduced by 10.5% with the application of heat recovery in the ammonia decomposition process. This LCOH value lies in the range of LCOH values that other studies have found, 5.5 USD/kg to 7.4 USD/kg of [9,10,11]. In addition to this, LCOH with green ammonia feed was about twice the LCOH with blue ammonia feed, as shown in Figure 10. Given that the climate change impact of blue ammonia is more than twice that of green ammonia, green ammonia clearly offers greater potential for decarbonising the energy industry [35]. Hence, green ammonia technologies should aim to further reduce their costs in the future in order to ensure that the supply chain of green hydrogen is completely carbon-free, as also demonstrated in the study by Antonio Villalba-Herreros et al. [18]. The cost of either blue ammonia or green ammonia is highly dependent on location; hence, the ammonia production plant should be set at a place with the lowest energy cost [37].
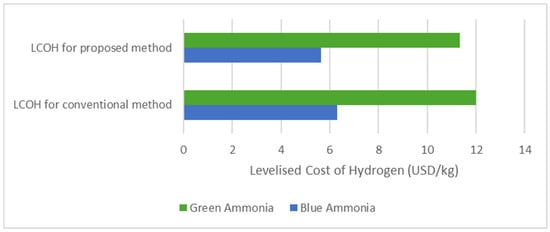
Figure 10.
LCOH for proposed method and conventional method with green ammonia and blue ammonia feed.
3.1. Effect of Economic and Process Parameters on LCOH
This sensitivity analysis was conducted by varying the economic parameters, ammonia cost, utilities cost, purchased equipment cost, building cost, and operational labour by . Figure 11 suggests that the long-term cost of ammonia is a critical factor affecting the economic performance of hydrogen production in this system. The result shows that the most sensitive parameter is the raw material cost, which is the ammonia cost as the ammonia feed cost contributed the most in the techno-economic study for the proposed method. The LCOH varied from 4.00 USD/kg to 7.3 USD/kg of with a variation of for ammonia price. The rest had no impactful effect on LCOH. Given that the ammonia cost is subjected to fluctuations driven by the global energy market, production methods, and carbon policies, making the future price projection highly uncertain for long-term planning. Future strategies in the reduction of ammonia costs must carefully consider price uncertainties and volatile market dynamics to ensure long-term competitiveness and overall energy sustainability.
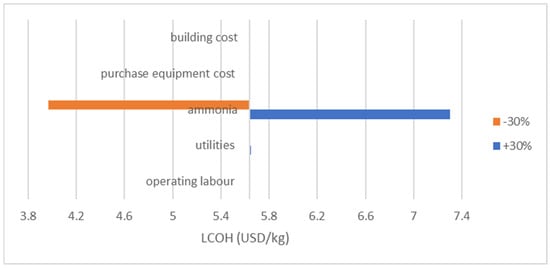
Figure 11.
Effect of economic parameters on the LCOH for variation of .
Figure 12 shows the effect of the process parameter, which is the reactor temperature, on the LCOH. The reactor temperature increases with the temperature of the exhaust gas intake; this will enhance the conversion of ammonia and produce more hydrogen, which resulted in lower LCOH with lower consumption of ammonia. However, this would rely on the thermal efficiency of the designed reactor. High thermal efficiency would result in high reactor temperature, but the degradation of material in the reactor should be taken into consideration. Figure 13 shows the effect of the ammonia recycling percentage on LCOH. LCOH decreases with the ammonia recycling percentage as less ammonia feed is used and leading to lower consumable material costs. To optimise the onsite hydrogen production system, the ammonia feed rate is reduced to 380 kg/s, provided that the hydrogen produced is sufficient for gas turbine usage. Figure 14 depicts the effect of varying water flow rate on the ammonia recycling percentage and LCOH. In addition, the results show that the LCOH for an ammonia feed rate of 380 kg/s was about 17% lower than the LCOH for an ammonia feed rate of 480 kg/s, which produced sufficient hydrogen output with higher water demand for ammonia recycling process.
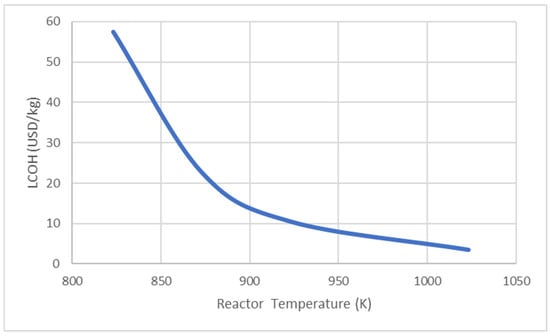
Figure 12.
Effect of reactor temperature on LCOH.
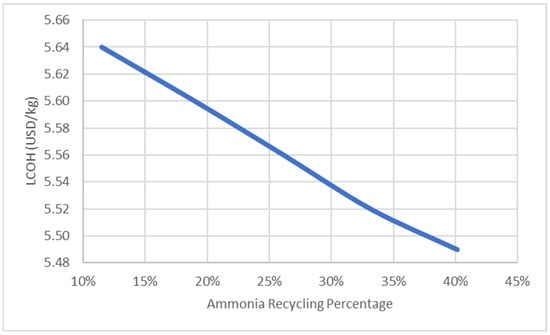
Figure 13.
Effect of ammonia recycling percentage on LCOH.
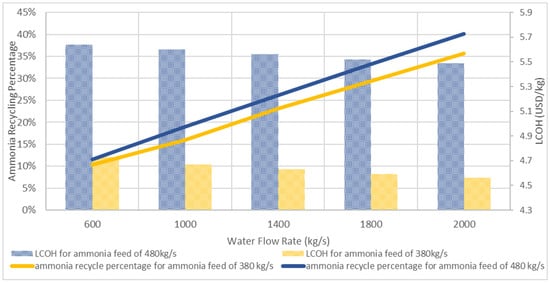
Figure 14.
LCOH and ammonia recycling percentage at different water flow rates.
3.2. Uncertainty Analysis with Monte Carlo Simulation
The raw material cost, which is the ammonia feed cost in our consideration, had the largest fluctuations after running for 10,000 iterations. The results of the uncertainty analysis are shown in Figure 15 and Figure 16. The LCOH can go as low as 2.90 to as high as 8.41 USD/kg of hydrogen if ammonia changes by 10% to 50% in price. While other parameters are less sensitive, coming in next is the utility cost. With 50% movement in utility price. The LCOH value will range by 0.04 USD/kg of hydrogen.
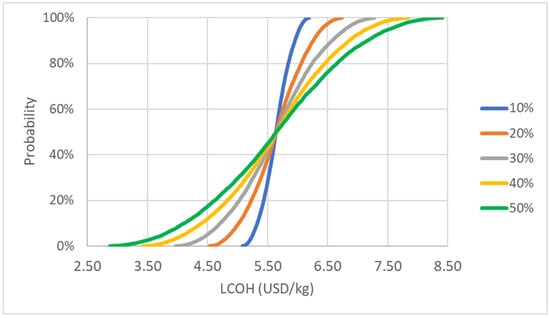
Figure 15.
Probability curve of LCOH for raw material cost variation.
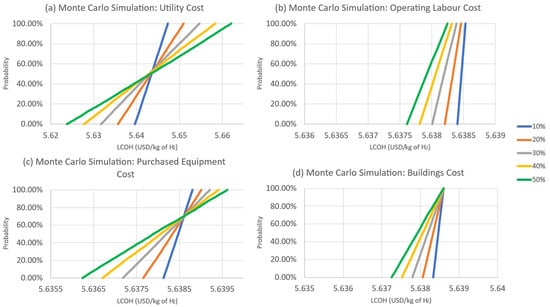
Figure 16.
Probability curve of LCOH for variation in (a) utility cost, (b) labour cost, (c) purchased equipment cost, and (d) buildings cost.
3.3. Exergy Analysis Result
Table 12 presents a comparison of the exergy analysis results. There was no significant difference between the exergy efficiency for the two reactors used in this study. One of the reasons could be the use of the furnace, as the furnace is set to heat the ammonia at a specific temperature without the simulation of the burning of fuel for heating purposes. Hence, this would be one of the limitations of this study. Part of future studies would be the study of the exergy analysis of a pilot experiment when the burning of fuel is used and compare it with the application of heat recovery.

Table 12.
Exergy analysis result.
3.4. Carbon Emission Comparison
The results of the carbon footprint assessment are shown in Figure 17. The life-cycle emissions are mainly caused by the natural gas combustion used in heating up the ammonia for the decomposition reaction. The system with waste heat recovery achieved a lower carbon footprint than the conventional system with burning fuel. However, the results in this study are significantly lower than the carbon footprint of steam methane reforming with carbon capture (2.8 kg CO2/kg H2) reported in a study conducted by Florian et al. [38]. It is important to note that a detailed life cycle assessment should be included in future studies, specifically addressing the flow of hydrogen to the gas turbine and the associated carbon emissions from hydrogen-fired gas turbines.
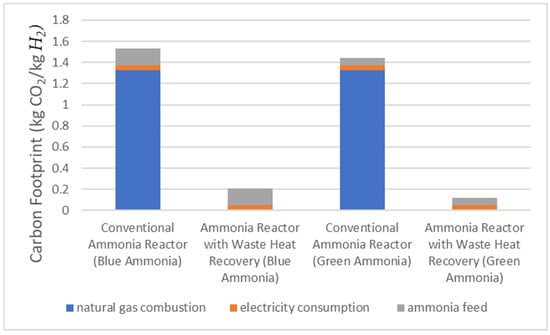
Figure 17.
Carbon footprint result for conventional reactor and reactor with heat recovery.
4. Conclusions
The aim of this study was to conduct a techno-economic analysis to analyse the economic suitability of the proposed ammonia cracker and compare it with that of a conventional ammonia cracker. The simulated process produced an estimated amount of 41.5 kg/s of 99.99% hydrogen from 480 kg/s of ammonia feed. The process demonstrates that it is capable of recycling 10% of the ammonia feed from the uncracked ammonia. This study presents an economic analysis, including detailed cost estimation, sensitivity analysis of economic and process parameters, and uncertainty analysis with Monte Carlo simulation using the outcome of the simulation. The effects of the reactor temperature were selected as the process parameter for investigation, and it was found that the LCOH improved as the temperature increased. The temperature increase allowed the ammonia decomposition rate to increase and peak at 1023 K, having the optimal LCOH of 3.52 USD/kg of hydrogen. However, this study focused on 973 K only, as the chosen Ni-based catalyst would reduce the temperature required for ammonia decomposition to below 973 K with high ammonia conversion. The costs of the ammonia feed, utilities, equipment, labour, and buildings were selected as the economic parameters to be examined. The cost of ammonia was found to be the most sensitive parameter, which contributes to 88% and 99% of the operating expenditure in the two separate simulations conducted. The fluctuation in ammonia price will greatly affect the LCOH. To forecast the variations in LCOH caused by the economic parameters, uncertainty analysis using the Monte Carlo simulation method was carried out. The results suggest that the LCOH will be reduced by approximately 10.5% with the application of ammonia decomposition with heat recovery. One of the goals of future studies would be the setup of a pilot experiment for result validation and system optimisation in terms of exergy analysis. Last, but not least, this study highlights the need for more research and technology development in ammonia for reducing the price of ammonia and making it competitive with the conventional ammonia production method. Future policies concerning ammonia supply and demand should be implemented with caution, as fluctuations in its price could significantly impact the future of green energy systems.
Author Contributions
Conceptualisation, methodology, software, validation, investigation, formal analysis, draft preparation, and writing—original draft preparation, J.T.L. and H.X.O.; visualisation, H.X.O.; Conceptualisation, supervision, and writing—review and editing, E.Y.-K.N.; project administration, J.T.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets presented in this article are not readily available because the data are part of an ongoing study. Requests to access the datasets should be directed to the authors.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to express their gratitude to Nanyang Technological University (NTU), Singapore, for the opportunity to study this topic.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Appendix A

Table A1.
Purchased equipment cost list for case study of reactor with heat recovery.
Table A1.
Purchased equipment cost list for case study of reactor with heat recovery.
| Equipment Name | Simulated Purchased Equipment Cost, USD | Calculated Purchased Equipment Cost in 2024, USD |
|---|---|---|
| Reactor 1 | 18,100 | 25,486.13 |
| Ammonia Absorber 1 | 1,652,700 | 2,327,122.79 |
| Ammonia Flash Distillate with Splitter | 3,650,800 | 5,140,594.11 |
| PSA | 1,469,000 | 2,068,459.72 |
| Water Pump | 104,800 | 147,566.08 |
| Ammonia Pump | 851,600 | 1,199,115.25 |
| Water Absorption | 137,900 | 194,173.31 |
| Ammonia Absorber 5 | 2,358,300 | 3,320,659.33 |
| Reactor 2 | 18,100 | 25,486.13 |
| Ammonia Absorber 2 | 1,652,700 | 2,327,122.79 |
| Ammonia Absorber 4 | 1,652,700 | 2,327,122.79 |
| Reactor 4 | 18,100 | 25,486.13 |
| Ammonia Absorber 3 | 1,652,700 | 2,327,122.79 |
| Reactor 3 | 18,100 | 25,486.13 |
| HEATER | 585,400 | 824,286.13 |
| Total | 22,305,289.62 | |
References
- IEA. Global Hydrogen Review 2023; International Energy Agency: Paris, France, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Roy, R.; Antonini, G.; Hayibo, K.S.; Rahman, M.M.; Khan, S.; Tian, W.; Boutilier, M.S.; Zhang, W.; Zheng, Y.; Bassi, A. Comparative techno-environmental analysis of grey, blue, green/yellow and pale-blue hydrogen production. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2025, 116, 200–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Hunger, R.; Berrettoni, S.; Sprecher, B.; Wang, B. A review of hydrogen storage and transport technologies. Clean Energy 2023, 7, 190–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sdanghi, G.; Maranzana, G.; Celzard, A.; Fierro, V. Review of the current technologies and performances of hydrogen compression for stationary and automotive applications. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2019, 102, 150–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yowell, G. How Does the Cost of Hydrogen Stack Up Against Gasoline. Stillwate Associates. 2022. Available online: https://stillwaterassociates.com/how-does-the-cost-of-hydrogen-stack-up-against-gasoline/ (accessed on 2 May 2025).
- Zhang, L.; Jia, C.; Bai, F.; Wang, W.; An, S.; Zhao, K.; Li, Z.; Li, J.; Sun, H. A comprehensive review of the promising clean energy carrier: Hydrogen production, transportation, storage, and utilization (HPTSU) technologies. Fuel 2024, 355, 129455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashcroft, J.; Goddin, H. Centralised and Localised Hydrogen Generation by Ammonia Decomposition: A technical review of the ammonia cracking process. Johns Matthey Technol. Rev. 2022, 66, 375–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usman, M.R. Hydrogen storage methods: Review and current status. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2022, 167, 112743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucentini, I.; Garcia, X.; Vendrell, X.; Llorca, J. Review of the decomposition of ammonia to generate hydrogen. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2021, 60, 18560–18611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafie, P.; DeChamplain, A.; Lepine, J. Thermal Ammonia Decomposition for Hydrogen-Rich Fuel Production and the Role of Waste Heat Recovery. Int. J. Energy Res. 2024, 2024, 9534752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Z.; Guan, J.; Liu, Y.; Shi, D.; Wu, Q.; Chen, K.; Zhang, Y.; Li, H. Research progress of ruthenium-based catalysts for hydrogen production from ammonia decomposition. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2024, 51, 1019–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chellappa, A.; Fischer, C.; Thomson, W. Ammonia decomposition kinetics over Ni-Pt/Al2O3 for PEM fuel cell applications. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2002, 227, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucentini, I.; Casanovas, A.; Llorca, J. Catalytic ammonia decomposition for hydrogen production on Ni, Ru and NiRu supported on CeO2. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 12693–12707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, S.; Devaguptapu, S.V.; Sviripa, A.; Lund, C.R.; Wu, G. Low-temperature ammonia decomposition catalysts for hydrogen generation. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2018, 226, 162–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Council, H. Hydrogen Scaling Up: A Sustainable Pathway for the Global Energy Transition; Hydrogen Council: Davos, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Council, H. Hydrogen Insights 2024; Hydrogen Council: Davos, Switzerland, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Minutillo, M.; Perna, A.; Forcina, A.; Di Micco, S.; Jannelli, E. Analyzing the levelized cost of hydrogen in refueling stations with on-site hydrogen production via water electrolysis in the Italian scenario. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2021, 46, 13667–13677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villalba-Herreros, A.; d’Amore-Domenech, R.; Crucelaegui, A.; Leo, T.J. Techno-economic assessment of large-scale green hydrogen logistics using ammonia as hydrogen carrier: Comparison to liquified hydrogen distribution and in situ production. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 4716–4726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Energy, S.; Centrax. HYFLEXPOWER Consortium Successfully Operates a Gas Turbine with 100 Percent Renewable Hydrogen, a World First; Siemens Energy Munich: Munich, Germany, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Ajoko, T.J.; Awusa, G.T.; Ogbonnaya, E.A. The Effects of Intrinsic Parameters on the Performance of Industrial Gas Turbines. The Effects of Intrinsic Parameters on the Performance of Industrial Gas Turbines. Int. J. Sci. Res. Eng. Technol. (IJSRET) 2018, 7, 758–764. [Google Scholar]
- Edwards, P.P.; Kuznetsov, V.L.; David, W.I. Hydrogen energy. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2007, 365, 1043–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamb, K.E.; Dolan, M.D.; Kennedy, D.F. Ammonia for hydrogen storage; A review of catalytic ammonia decomposition and hydrogen separation and purification. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 3580–3593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, F.; Ma, S.; Tong, L.; Xiao, J.; Bénard, P.; Chahine, R. Artificial neural network based optimization for hydrogen purification performance of pressure swing adsorption. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 5334–5344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sircar, S.; Golden, T. Purification of hydrogen by pressure swing adsorption. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2000, 35, 667–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inc, A.T. Aspen Plus V14; Aspen Technology Inc.: Bedford, MA, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, D.-Y.; Robinson, D.B. A new two-constant equation of state. Ind. Eng. Chem. Fundam. 1976, 15, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, M.S.; Timmerhaus, K.D. Plant Design and Economics for Chemical Engineers; McGraw-Hill International: New York, NY, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Devkota, S.; Cha, J.-Y.; Shin, B.-J.; Mun, J.-H.; Yoon, H.C.; Mazari, S.A.; Moon, J.-H. Techno-economic and environmental assessment of hydrogen production through ammonia decomposition. Appl. Energy 2024, 358, 122605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singapore Energy Market Authority Organization. Buying at Regulated Tariff. Available online: https://www.ema.gov.sg/consumer-information/electricity/buying-electricity/buying-at-regulated-tariff (accessed on 2 May 2025).
- Simon Property Group, Inc. Interactive: Ammonia Price Chart. Available online: https://cilive.com/commodities/energy-transition/news-and-insight/051023-interactive-ammonia-price-chart-natural-gas-feedstock-europe-usgc-black-sea (accessed on 2 May 2025).
- Singapore’s National Water Agency. Water Price. Available online: https://www.pub.gov.sg/Public/WaterLoop/Water-Price (accessed on 2 May 2025).
- City Energy. Gas Tariffs. Available online: https://www.cityenergy.com.sg/gas-tariffs/ (accessed on 2 May 2025).
- Mehrpooya, M.; Asadnia, M.; Karimi, A.H.; Allahyarzadeh-Bidgoli, A. Hybrid Poly-Generation Energy Systems: Thermal Design and Exergy Analysis; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Szargut, J. Egzergia: Poradnik Obliczania i Stosowania; Wydawnictwo Politechniki Śląskiej: Gliwice, Poland, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Mayer, P.; Ramirez, A.; Pezzella, G.; Winter, B.; Sarathy, S.M.; Gascon, J.; Bardow, A. Blue and green ammonia production: A techno-economic and life cycle assessment perspective. iScience 2023, 26, 107389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Commission Implementing Regulation (EU). 2018/2066 of 19 December 2018 on the monitoring and reporting of greenhouse gas emissions pursuant to Directive 2003/87/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council and amending Commission Regulation (EU) No 601/2012. Off. J. Eur. Union 2018, 31, 1–93. [Google Scholar]
- Del Pozo, C.A.; Cloete, S. Techno-economic assessment of blue and green ammonia as energy carriers in a low-carbon future. Energy Convers. Manag. 2022, 255, 115312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerscher, F.; Stary, A.; Gleis, S.; Ulrich, A.; Klein, H.; Spliethoff, H. Low-carbon hydrogen production via electron beam plasma methane pyrolysis: Techno-economic analysis and carbon footprint assessment. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2021, 46, 19897–19912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).