Abstract
The emphasis on sustainable and environmentally friendly practices in geotechnical engineering has generated interest in alternative soil stabilizing techniques. The present study examines the application of xanthan gum (XG) and guar gum (GG) to enhance the strength of a sand–bentonite composite and explore their potential for use as landfill liners or impervious barriers. The mixtures, consisting of 25% bentonite and 75% sand, were treated with XG and GG concentrations of different percentages (0.5%, 1%, 2%, and 3% by dry mass). The test results indicated that a 2% addition was optimal for both biopolymers. Using this optimum value of XG and GG significantly increased the unconfined compressive strength (UCS) by almost 3-fold compared to the strength of untreated samples. Meanwhile, XG demonstrated a slightly higher impact on strength attributed to its robust gel-forming and binding properties. Comparisons between the two biopolymers highlighted XG’s superior performance, with UCS improvements of up to 20% over GG-treated samples. These results underscore the potential of biopolymers as effective, sustainable alternatives to traditional stabilizers, providing both mechanical enhancements and environmental benefits. The present study contributes valuable insights into green soil stabilization techniques, supporting the development of more sustainable construction practices. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR) was conducted to analyze the chemical interactions between sand–bentonite mixtures and biopolymers, which possibly provide insights into the bonding mechanisms responsible for the observed improvements in mechanical and volumetric behavior.
Keywords:
xanthan gum; guar gum; soil stabilization; sand–bentonite; biopolymers; UCS; sustainable engineering 1. Introduction
Soil stabilization is a technique used in geotechnical engineering practices to improve the mechanical characteristics of soils and satisfy the demanding standards of various construction and infrastructure projects. Conventional stabilizers, including cement, lime, and fly ash, have been widely employed owing to their demonstrated efficacy in enhancing soil strength, durability, and workability [1]. Nonetheless, the environmental repercussions of these materials, especially cement, must not be disregarded. Cement production significantly contributes to global carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions, representing almost 5–7% of total worldwide emissions, highlighting its substantial impact on global warming and climate change [2,3]. These environmental concerns have prompted the search for more sustainable alternatives to reduce the carbon footprint linked to soil stabilizing methods.
In this context, biopolymers have emerged as a viable environmentally sustainable approach for soil stabilization. Biopolymers, sourced from renewable resources like plants, microbes, and animals, are biodegradable, non-toxic, and possess a reduced environmental impact relative to conventional stabilizers [4]. Their capacity to improve soil characteristics, such as strength, permeability, and erosion resistance, has generated growing interest in geotechnical research. Xanthan gum and guar gum are notable biopolymers that have considerable potential owing to their distinctive features and efficacy in soil enhancement [5,6]. These biopolymers operate by creating gel-like structures that aggregate soil particles, thereby enhancing cohesion and overall stability.
Biopolymers such as xanthan gum, guar gum, and agar interact with clay-rich soils through hydration, swelling, and electrostatic attraction, enhancing the binding between particles and contributing to improved shear strength [7]. Nonetheless, although these mixes perform exceptionally in specific engineering roles, their mechanical strength, especially unconfined compressive strength (UCS), frequently does not meet the standards for more rigorous applications. This constraint has necessitated the development of new stabilizing methods that can improve the mechanical properties of sand–bentonite mixes while maintaining their environmental sustainability. The integration of biopolymers such as xanthan gum and guar gum provides an effective solution to this issue, enhancing soil strength while conforming to the increasing focus on sustainable engineering methods [8].
Despite recent advancements, the full potential of biopolymers in enhancing sand–bentonite mixtures remains underexplored, especially concerning long-term behavior and molecular-level interactions. Most studies have either focused on untreated soils or single-point strength evaluations. Few have assessed how different biopolymer dosages influence strength development over extended curing durations or investigated the chemical bonding mechanisms using spectral analysis.
The effectiveness of biopolymers in soil stabilization is closely linked to their chemical interactions with soil particles. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR) is a widely used analytical technique for identifying functional groups and understanding molecular interactions within treated soils. Several studies have demonstrated its reliability in detecting the presence of functional groups such as hydroxyl (-OH), carboxylate (-COO−), and amide (-CONH) groups, which are characteristic of biopolymers like xanthan gum and guar gum [9,10]. These functional groups contribute significantly to enhancing cohesion and water retention in the soil matrix. FTIR analysis not only confirms the presence of these groups but also provides insight into the bonding mechanisms between the biopolymer and the soil minerals [11,12]. Therefore, FTIR serves as a valuable tool in assessing the efficiency and durability of biopolymer treatment in geotechnical applications.
FTIR analysis was also performed on sand–bentonite mixtures treated with varying concentrations of xanthan gum and guar gum, along with individual component materials, to elucidate the structural modifications and interaction mechanisms. The comparative analysis of FTIR spectra allows for the identification of key interactions between biopolymer-treated soils and their potential effects on strength and volumetric stability. The use of FTIR in geotechnical applications, particularly in biopolymer-treated soils, provides a deeper understanding of the stabilization process at the molecular level, complementing the mechanical and volumetric assessments conducted in this research.
The innovation of this study lies in its dual approach, combining extended mechanical testing with chemical analysis to evaluate the stabilization performance of sand–bentonite mixtures treated with two widely available biopolymers—xanthan gum and guar gum. By testing multiple concentrations (0.5%, 1%, 2%, and 3%) and curing durations up to 180 days, this work provides one of the most comprehensive assessments of biopolymer-based stabilization to date. Furthermore, the use of FTIR to interpret bonding interactions offers new insights into the durability and cohesion mechanisms underlying strength development.
The present study focuses on addressing critical gaps in the application of biopolymers for soil stabilization, particularly in sand–bentonite mixtures. Preliminary assessments determined that a 25% bentonite content, balanced with sand, provided optimal unconfined compressive strength (UCS), aligning with the existing literature which emphasizes the positive correlation between bentonite concentration and improved soil stability [8,13]. While research on biopolymers such as xanthan gum and guar gum has highlighted their potential for enhancing soil performance, limited studies have explored their application in sand–bentonite mixtures across a range of concentrations [4,6]. This work systematically evaluates the impact of xanthan gum and guar gum at 0.5%, 1%, 2%, and 3% concentrations on the UCS of sand–bentonite mixtures, providing insights into optimal dosages and long-term behavior. The study incorporates curing durations of 1, 7, 14, 28, 60, and 180 days to assess the temporal progression of mechanical properties under controlled conditions [5,8]. By advancing the understanding of sustainable soil stabilization techniques, this research contributes to the adoption of biodegradable and renewable materials in geotechnical engineering, supporting international efforts to mitigate climate change [1,3]. The findings offer practical guidance for engineers seeking to implement environmentally friendly alternatives to conventional stabilizers while ensuring the resilience and reliability of biopolymer-treated soils for applications such as landfill liners and foundational materials.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.1.1. Sand
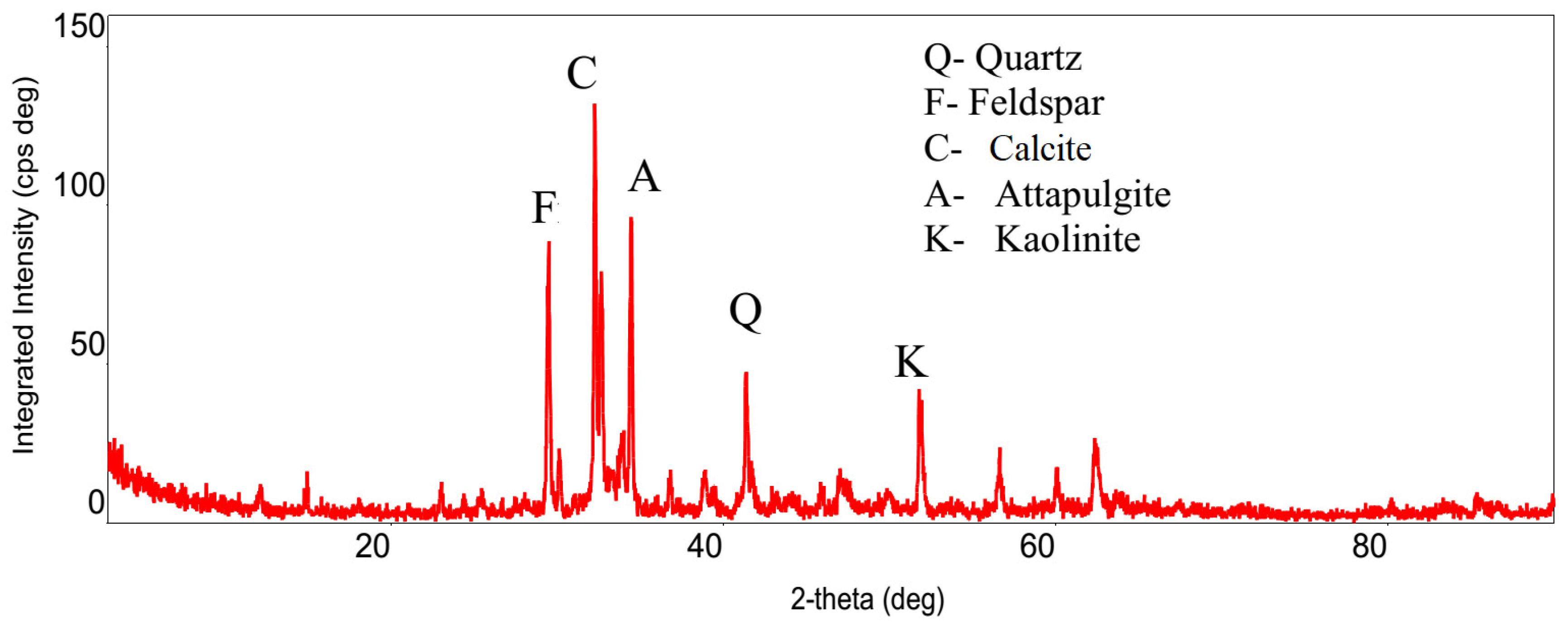
Sand for the present study was collected from Silver Beach in Famagusta, North Cyprus (35°10′18.78″ N, 33°54′33.42″ E). To ensure sample purity, the uppermost 30 cm of surface sediment was removed during collection. The sand samples were immediately sealed in airtight polyethylene bags and transported to the Geotechnical Laboratory at Cyprus International University. Upon laboratory arrival, the sample underwent thorough preparation—first, it was washed with distilled water to remove marine salts and potential surface contaminants, then it was subsequently dried in a laboratory oven at 105 °C for complete moisture elimination. The particle size distribution characteristics are detailed in Table 1. The soil is classified as poorly graded sand (SP) according to the Unified Soil Classification System (USCS) [13]. The mineralogical analysis of the sand revealed a predominantly quartz composition, as indicated by the sharp diffraction peaks in the XRD pattern (Figure 1).

Table 1.
Soil Gradation Parameters.
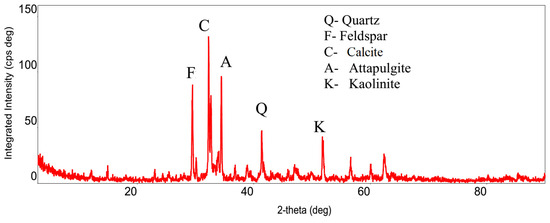
Figure 1.
XRD image of sand [14].
2.1.2. Na–Bentonite Clay
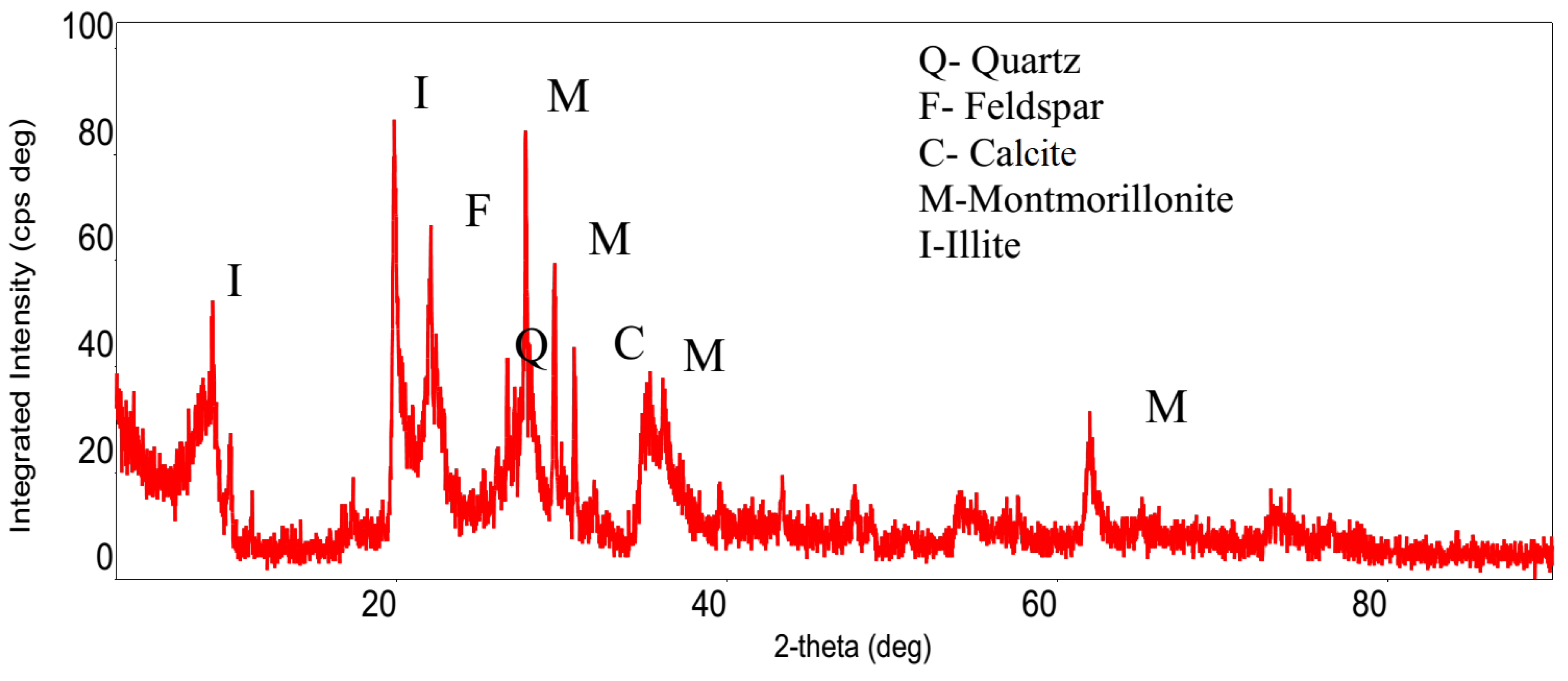
The Na–bentonite used in this study was obtained from Karakaya Ltd. Şti., a company located in Çankaya, Ankara, Türkiye. The Na–bentonite displayed fundamental attributes consistent with API 13A drilling fluid requirements and TS EN 13500 norms for untreated bentonite. The sample exhibited significant swelling potential and remarkably low permeability, with hydraulic conductivity values routinely provided by the supplier ranging from 10−7 to 10−10 cm/s, indicating its geotechnical appropriateness for specialized applications. The material demonstrated a liquid limit of 456%, a plastic limit of 38.5%, and a shrinkage limit of 19.5%. Specific gravity was ascertained to be 2.66. The total dissolved solids concentration was noted at 359 ppm, while the electrical conductivity was measured at 0.73 S/m. The material exhibited a pH of 9.60 and a salinity of 0.4 PSU [15]. It mostly consists of smectite minerals (about 71%), along with zeolite (19.5%), quartz (5%), feldspar (2.5%), and mica (2%) [16]. The XRD results for bentonite confirmed the presence of montmorillonite as the primary mineral, along with traces of quartz and calcite (Figure 2).
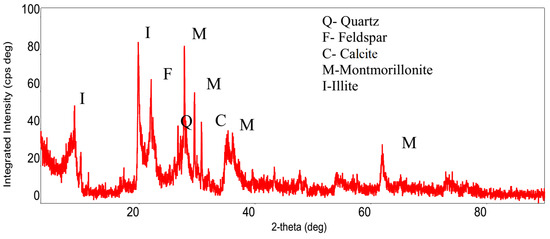
Figure 2.
XRD image of bentonite [14].
2.1.3. Biopolymers
In this study, two biopolymers, xanthan gum (XG) and guar gum (GG) were used to examine their influence on the strength characteristics of sand–bentonite mixes. Both biopolymers were procured from Katkı Deposu (Istanbul, Türkiye), a specialized chemical supplier in Türkiye, and were chosen for their well-documented rheological features and demonstrated efficacy in geotechnical applications [17,18].
2.1.4. Xanthan Gum (XG)
Xanthan gum (XG) is a biopolymer composed of polysaccharides, sourced from the bacterium Xanthomonas campestris [18]. It is generated via the fermentation of carbohydrate-dense substrates, such as sugars obtained from agricultural products like corn or soybeans. XG possesses a distinctive molecular structure, featuring a cellulose backbone with trisaccharide side chains made up of D-glucuronic acid and two D-mannose units [19]. This configuration allows XG to dissolve easily in both hot and cold water, markedly enhancing the viscosity of the medium [20]. XG demonstrates multiple beneficial characteristics, such as pH stability, compatibility with ionic salts, pseudo-plasticity, and robust shear stability at low concentrations [19,21]. In geotechnical applications, XG is recognized for diminishing soil permeability by occupying pore spaces and augmenting erosion resistance through enhanced water retention [13].
2.1.5. Guar Gum (GG)
Guar gum is a natural polysaccharide derived from the seeds of the guar plant (Cyamopsis tetragonoloba). The structure comprises a linear sequence of β-d-mannopyranose units with α-d-galactose branches, resulting in a galactomannan configuration [22,23]. GG consists of 75–85% galactomannan, in addition to moisture (8–14%), protein, fiber, and ash [24]. It is soluble in both hot and cold water and is recognized for its elevated viscosity and thickening characteristics. GG is extensively utilized in sectors including food manufacturing, cosmetics, oil and gas extraction, and civil engineering because of its non-toxic nature, environmental neutrality, and economic efficiency [4,24]. In geotechnical applications, GG has demonstrated the capacity to enhance soil stability and improve mechanical properties by forming robust hydrogen bonds with soil particles.
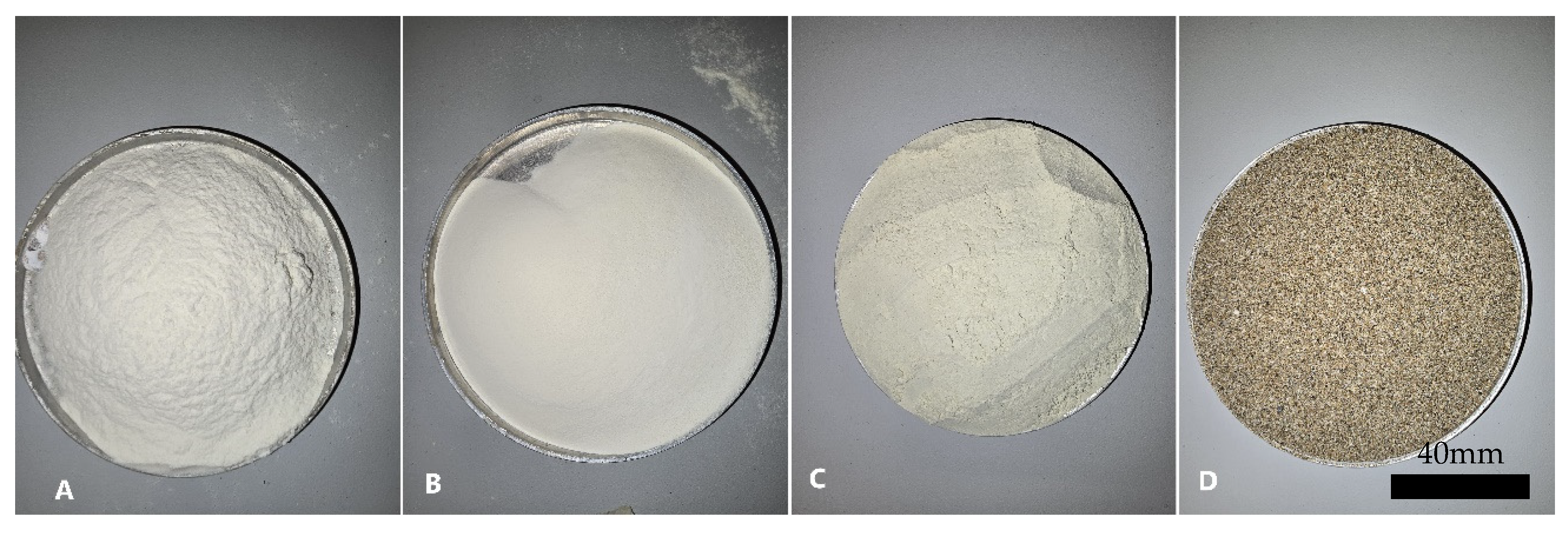
Figure 3 depicts powdered forms of GG, GG, Na–bentonite, and sand, respectively.
Figure 3.
Materials used in the study: (A) GG, (B) XG, (C) Na–bentonite, and (D) sand.
2.2. Sample Preparation and Testing Protocol
2.2.1. Material Proportioning
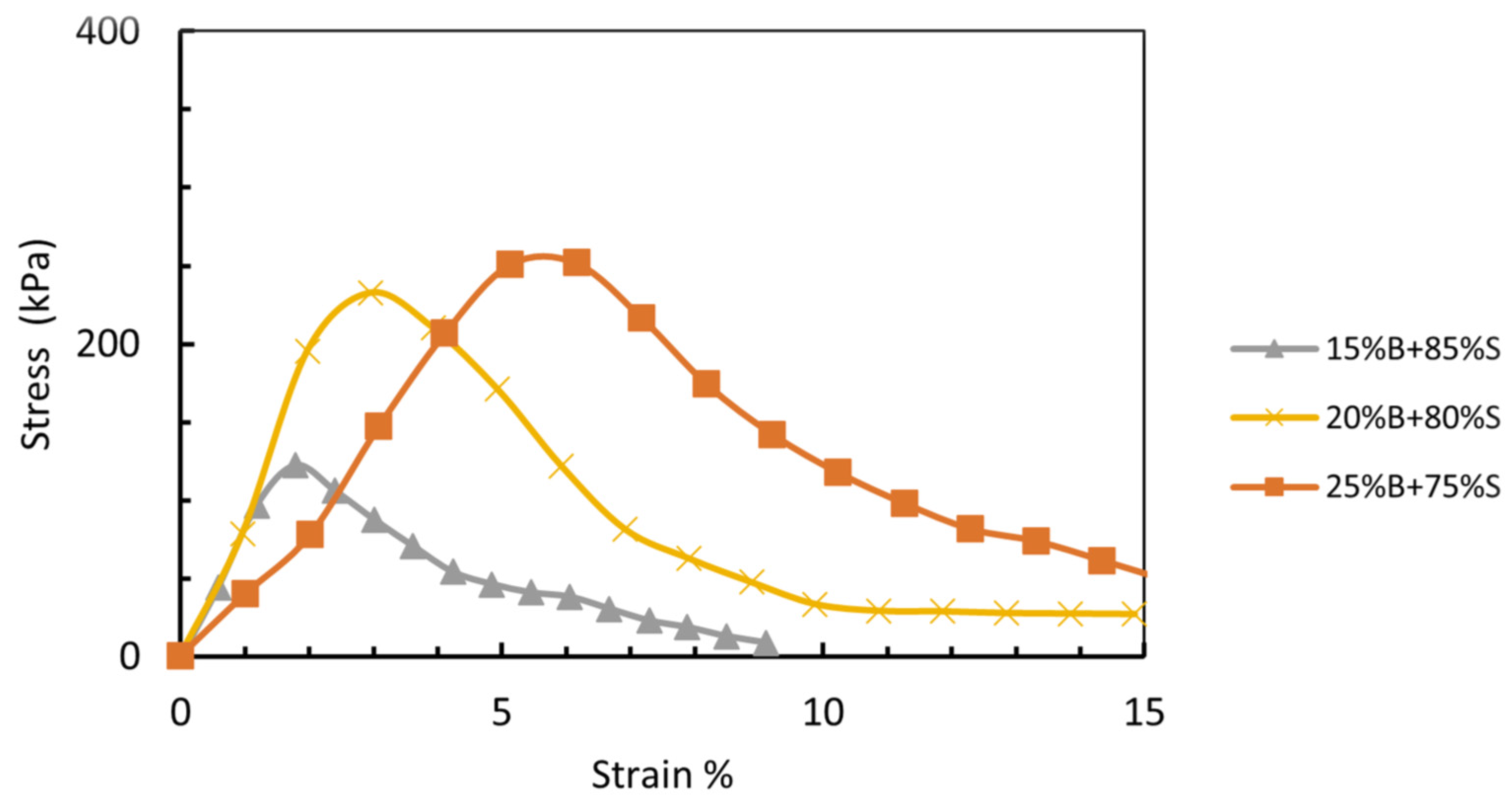
The sand–bentonite combination was formulated with a constant ratio of 25% bentonite and 75% sand by dry weight. This ratio was determined from initial unconfined compressive strength (UCS) testing, which indicated that 25% bentonite yielded the highest UCS in comparison to combinations containing 15% and 20% bentonite (Figure 4).
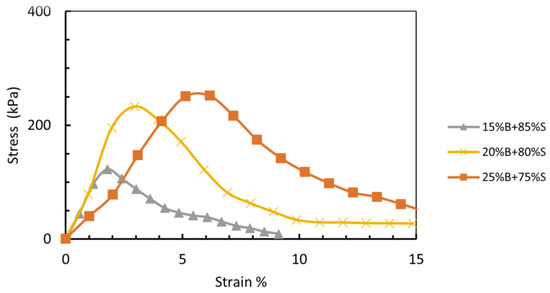
Figure 4.
UCS for sand–bentonite with 3 different percentages of bentonite, 15%, 20%, and 25%.
2.2.2. Material Drying
The bentonite was subjected to drying in an oven at 70 °C for 4 days to achieve total moisture elimination before utilization. The sand was dehydrated at 105 °C for 24 h to remove any remaining moisture. This step was essential for attaining consistent and precise results in the next mixing and testing procedures.
2.2.3. Dry Mixing of Biopolymers
Xanthan gum (XG) and guar gum (GG) were incorporated into the dry sand–bentonite mixture at concentrations of 0.5%, 1%, 2%, and 3% by dry mass of the mixture. The dry constituents (sand, bentonite, and biopolymer) were meticulously blended in a mechanical mixer for 3 min to guarantee consistent distribution.
2.2.4. Incorporation of Distilled Water
Following the dry mixing procedure, distilled water was introduced to the mixture according to the maximum dry density (MDD) and optimum moisture content (OMC) established for each sample. The MDD and OMC values were derived using routine Proctor compaction tests performed before sample preparation. Water was added gradually while mixing persisted for an additional 5 min to attain a uniform soil–biopolymer combination with the requisite moisture content.
2.2.5. Curing Procedure
Following the mixing process, each sample was enclosed in a sealed bag to avert moisture evaporation and subsequently positioned within a vacuum desiccator for a duration of 24 h. The curing process guaranteed complete interaction between the biopolymers and soil particles, hence augmenting the stabilizing effect.
2.2.6. Compaction and Molding
The produced mixtures were compacted utilizing the Proctor compaction test methodology. Owing to the challenges associated with extracting intact specimens from the compaction mold, the samples were compacted into a smaller mold measuring 38 mm in diameter and 76 mm in height. A 2.5 kg hammer was utilized with a drop height of 0.305 m to sustain the same standard compaction energy. The number of blows per layer and the number of layers were modified to maintain an equivalent compaction effort to the conventional Proctor test. The energy required for compaction per unit volume was determined using the following equation:
where E denotes the compaction energy per unit volume, N represents the number of blows per layer, n indicates the number of layers, W signifies the weight of the hammer, H refers to the height of the hammer drop, and V corresponds to the volume of the mold.
A series of trial compactions were performed to compare the outcomes of the large and small molds, verifying that the compaction energy and effort remained consistent.
2.2.7. Control Samples
Control samples were manufactured utilizing the identical sand–bentonite mixture, excluding the incorporation of biopolymers. These samples served as a reference for evaluating the impact of XG and GG on the UCS of the soil mixture.
2.2.8. Examination Protocol
The unconfined compressive strength (UCS) test was performed in compliance with the ASTM D2166 standard [25]. The cured samples underwent uniaxial loading via a compression testing apparatus at a constant strain rate of 1 mm/min. The load and associated deformation were documented until the sample failed. The UCS was computed using the formula
Pmax represents the maximum load at failure, and A is the cross-sectional area of the sample.
2.3. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR) Analysis
FTIR analysis was performed to investigate the chemical interactions between sand–bentonite mixtures and biopolymers, particularly xanthan gum and guar gum, by identifying the functional groups contributing to soil stabilization. The analysis was carried out using a Shimadzu IR Prestige-21 infrared spectrometer equipped with an AIM-8800 infrared microscope (Shimadzu, Kyoto, Japan), providing high resolution and sensitivity [26,27]. Nine different samples were tested, including a control sand––bentonite mixture; sand–bentonite treated with 0.5%, 1%, 2%, and 3% xanthan gum; and individual components such as sand, bentonite, xanthan gum, and guar gum. Before analysis, the mixture samples were oven-dried at 105 °C, finely ground, and prepared using the potassium bromide (KBr) pellet method, in which a small amount of the sample was mixed with KBr and compressed into pellets under a pressure of 8 to 10 tons to ensure spectral clarity. Measurements were conducted in transmission and reflection modes over the 4000 cm−1 to 400 cm−1 range, with a resolution of 4 cm−1 and 32 scans per spectrum to enhance signal clarity. The system was equipped with a 15× Cassegrain lens and a liquid nitrogen-cooled MCT detector to improve sensitivity. The collected spectra were analyzed to identify key functional groups, including hydroxyl (-OH) stretching, carboxyl (-COO-) vibrations, Si-O and Al-O stretching from bentonite minerals, and polysaccharide structures characteristic of biopolymers. Comparison between untreated and biopolymer-treated samples provided insights into stabilization mechanisms by revealing changes in chemical bonding and interactions within the matrix.
3. Results
3.1. Optimum Moisture Content (OMC) and Maximum Dry Density (MDD)
Table 2 presents the outcomes of the typical Proctor compaction tests for sand–bentonite mixtures treated with xanthan gum (XG) and guar gum (GG). The MDD and OMC values offer essential insights into the compaction properties and the effect of biopolymer concentration on the soil mixture.

Table 2.
MDD and OMC for Sand–Bentonite Mixtures Treated with Xanthan Gum and Guar Gum.
3.2. Examination of MDD and OMC Outcomes
3.2.1. Impact of Xanthan Gum on MDD and OMC
The incorporation of xanthan gum into the sand–bentonite combination led to a progressive reduction in maximum dry density as the concentration of the biopolymer rose. The MDD diminished from 1.81 g/cm3 at 0% XG to 1.73 g/cm3 at 3% XG. The decrease in MDD is due to xanthan gum creating a gel-like structure that fills pore gaps and lowers the overall density of the soil combination [1]. The OMC values demonstrated a non-linear pattern, initially declining from 17.5% at 0% XG to 15.5% at 1% XG, followed by an increase to 19.5% at 3% XG. This behavior aligns with the findings of [4], which indicated that biopolymers could modify the water retention characteristics of soil, resulting in fluctuations in OMC.
3.2.2. The Impact of Guar Gum on MDD and OMC
Like xanthan gum, the incorporation of guar gum resulted in a decrease in MDD, but to a lesser extent. The maximum dry density (MDD) diminished from 1.81 g/cm3 at 0% ground granulated blast-furnace slag (GG) to 1.78 g/cm3 at 3% GG. The minor reduction in MDD is due to guar gum’s capacity to bind soil particles and occupy pores, however, to a lesser degree than xanthan gum [6]. The OMC readings for guar gum-treated samples exhibited a steady decline from 17.5% at 0% GG to 15.0% at 3% GG. This pattern indicates that guar gum improves the soil’s moisture retention capacity at reduced water levels, aligning with the conclusions of [5].
3.2.3. Comparison Between Xanthan Gum and Guar Gum
The findings demonstrate that xanthan gum exerts a more pronounced effect on MDD and OMC than guar gum. The disparity can be ascribed to the elevated viscosity and gel-forming ability of xanthan gum, which occupies additional pore spaces and significantly modifies the soil’s compaction properties [28]. Conversely, the reduced viscosity and distinct molecular configuration of guar gum leads to less impact on MDD and OMC.
3.3. Unconfined Compressive Strength (UCS)
3.3.1. Unconfined Compressive Strength (UCS) of Sand–Bentonite Mixtures Treated with Guar Gum and Xanthan Gum
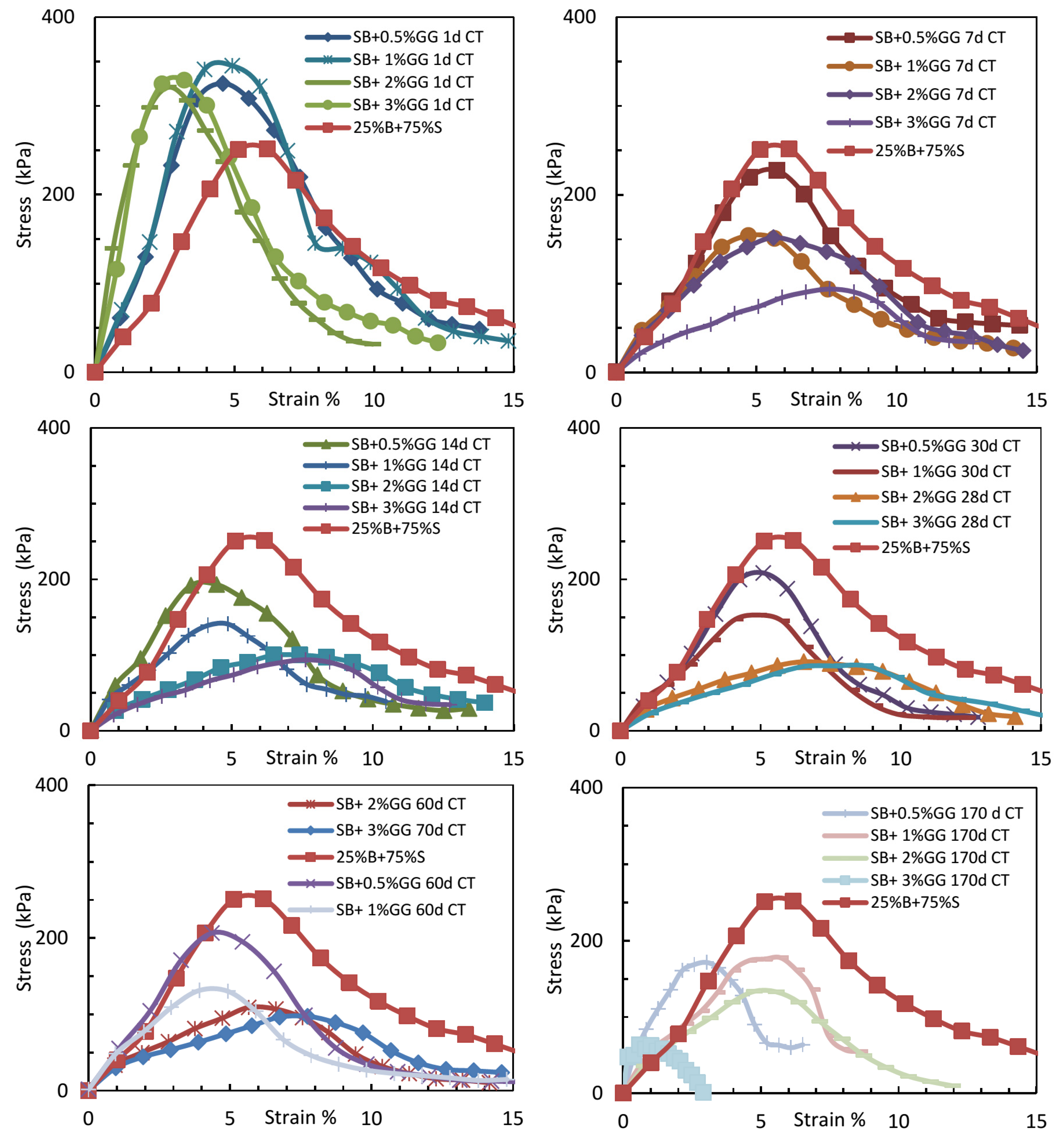
The unconfined compressive strength (UCS) of sand–bentonite mixture treated with guar gum (GG) and xanthan gum (XG) was assessed at concentrations of 0%, 0.5%, 1%, 2%, and 3% over curing durations of 1, 7, 14, 30, 60, and 180 days. The findings are displayed in Figure 5 and Figure 6. The processing and storage conditions were meticulously regulated to replicate authentic environmental conditions for landfill liner applications. Upon preparation, the samples were encased in thermal bags to preserve uniform moisture levels and positioned in a vacuum desiccator at a regulated temperature of 25 °C for curing. Images of the samples, especially those treated with guar gum after 180 days, exhibit evident decay and mold proliferation, which considerably affected the UCS outcomes.
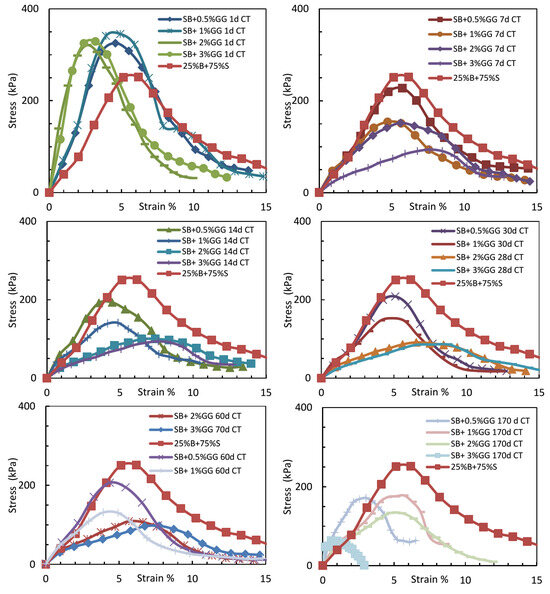
Figure 5.
UCS of sand–bentonite treated with guar gum (comparison by concentration at identical curing time).
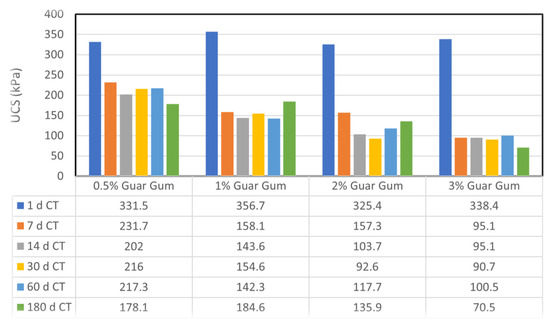
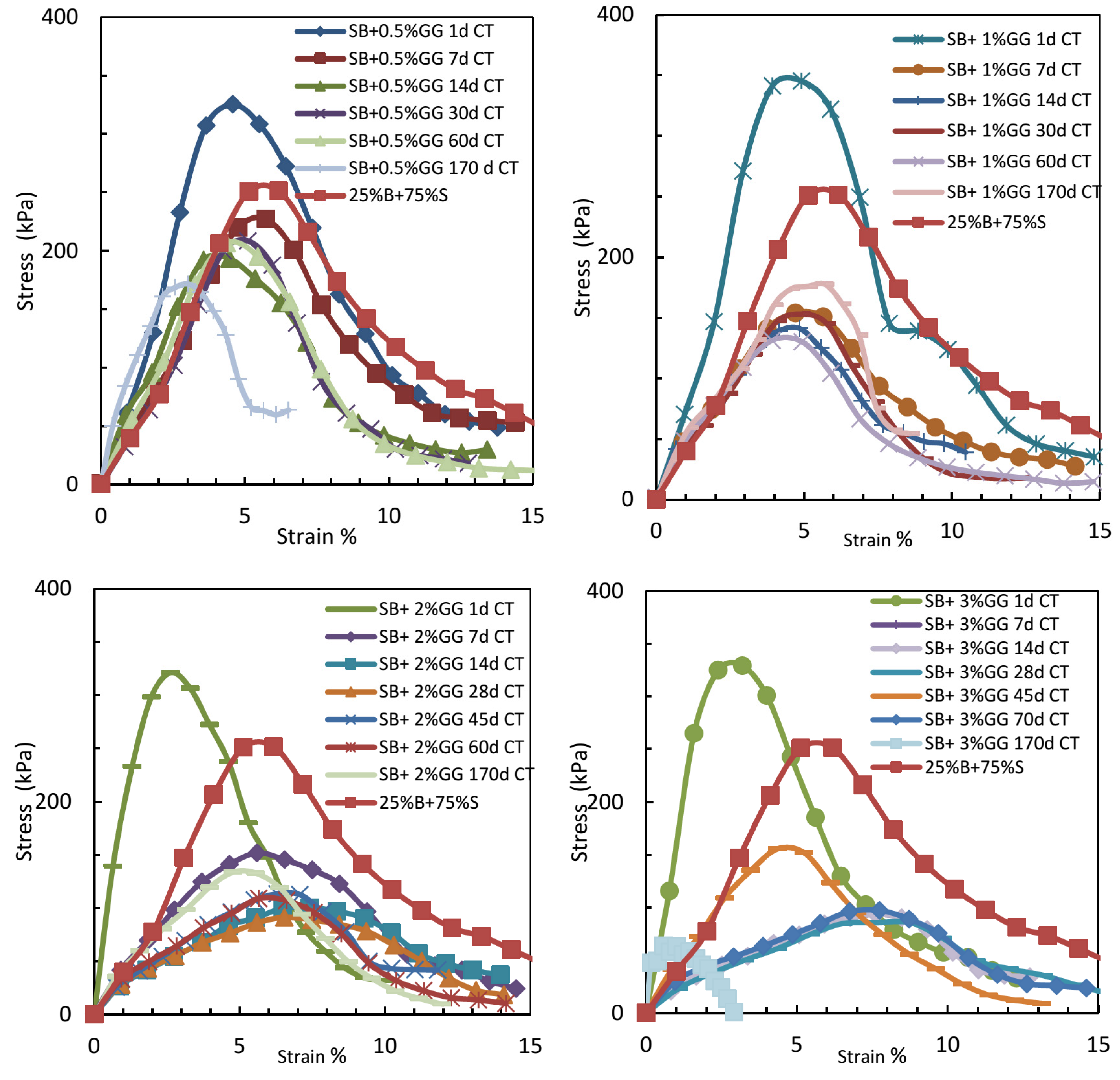
Figure 6.
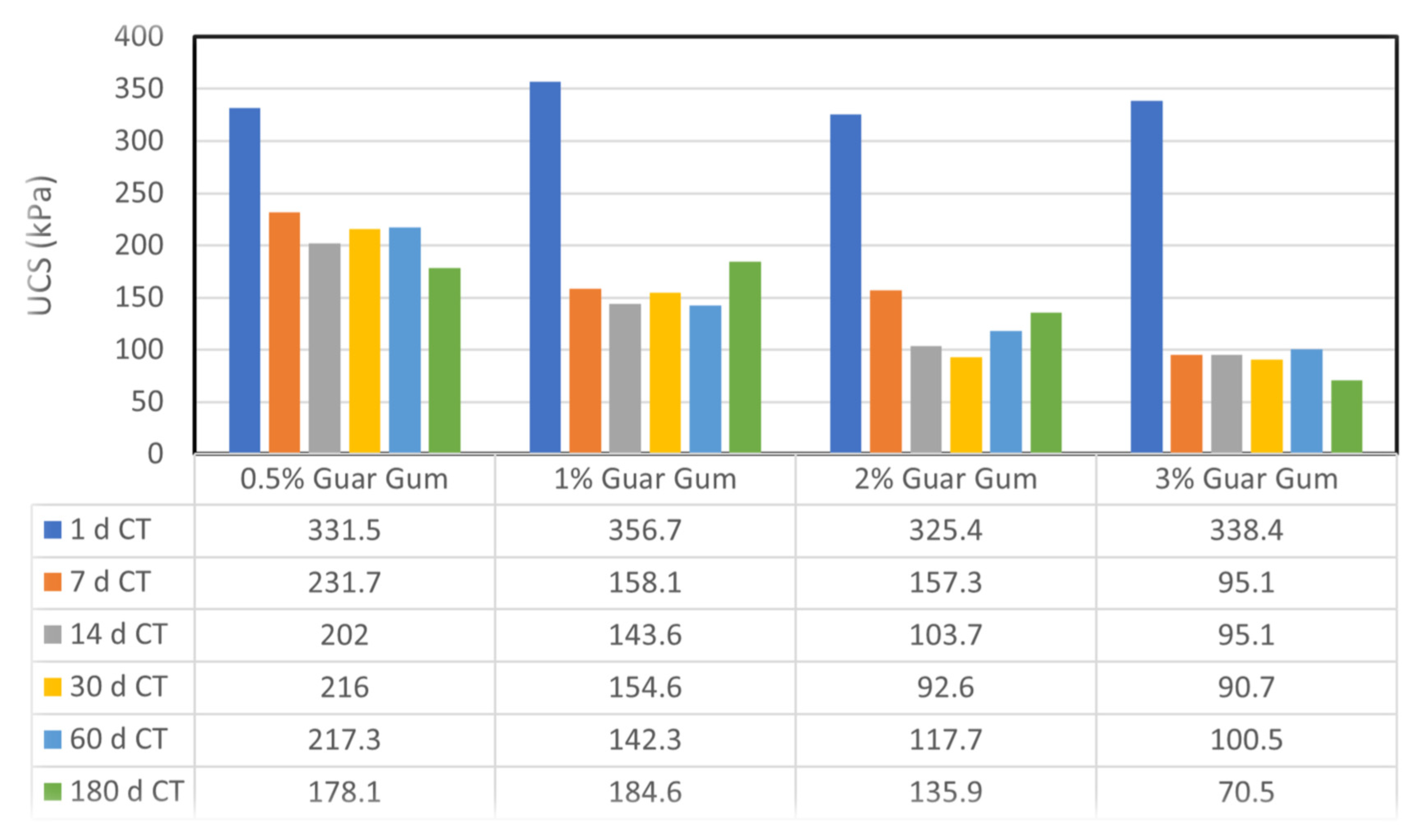
Variation in unconfined compressive strength (UCS) with curing time for sand–bentonite mixtures treated with different concentrations of guar gum.
3.3.2. Impact of Guar Gum Concentration and Curing Time on Unconfined Compressive Strength
The UCS of samples treated with guar gum notably decreased as curing time increased, especially at elevated concentrations. At 3% GG, the UCS decreased from 338.4 kPa after 1 day to 70.5 kPa after 180 days. The decline in strength was followed by evident decay and mold proliferation, which intensified with increased guar gum concentrations and extended curing periods, as illustrated in Figure 6. Guar gum’s organic composition renders it vulnerable to microbial deterioration when exposed to moisture and ambient temperatures for extended periods [6]. These findings underscore the inadequacies of guar gum for prolonged applications, such as landfill liners, where longevity is essential.
Figure 7 illustrates the correlation between UCS and curing time for samples treated with guar gum. The findings demonstrate a steady decrease in UCS with time, especially at elevated values. The reduction in UCS for guar gum-treated samples is due to the biodegradation of the biopolymer, which compromises the soil–biopolymer matrix. This behavior aligns with other research indicating analogous problems with guar gum in soil stabilization applications [4]. To address these issues, it is advisable to employ auxiliary chemicals, such as antibacterial agents or preservatives, to inhibit mold proliferation and enhance the longevity of guar gum-treated soils.
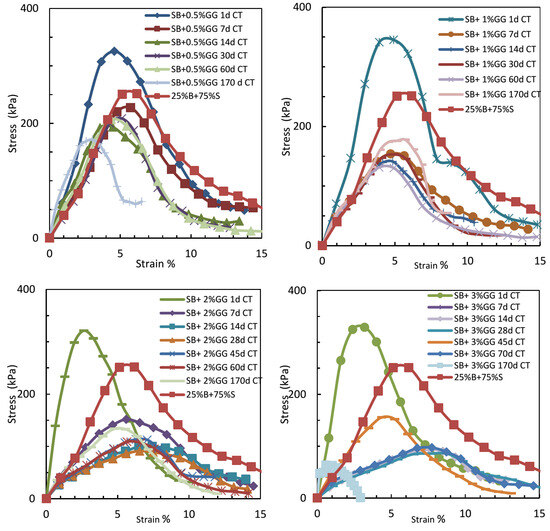
Figure 7.
The relationship between UCS and strain for sand–bentonite mixtures treated with guar gum at different curing times.
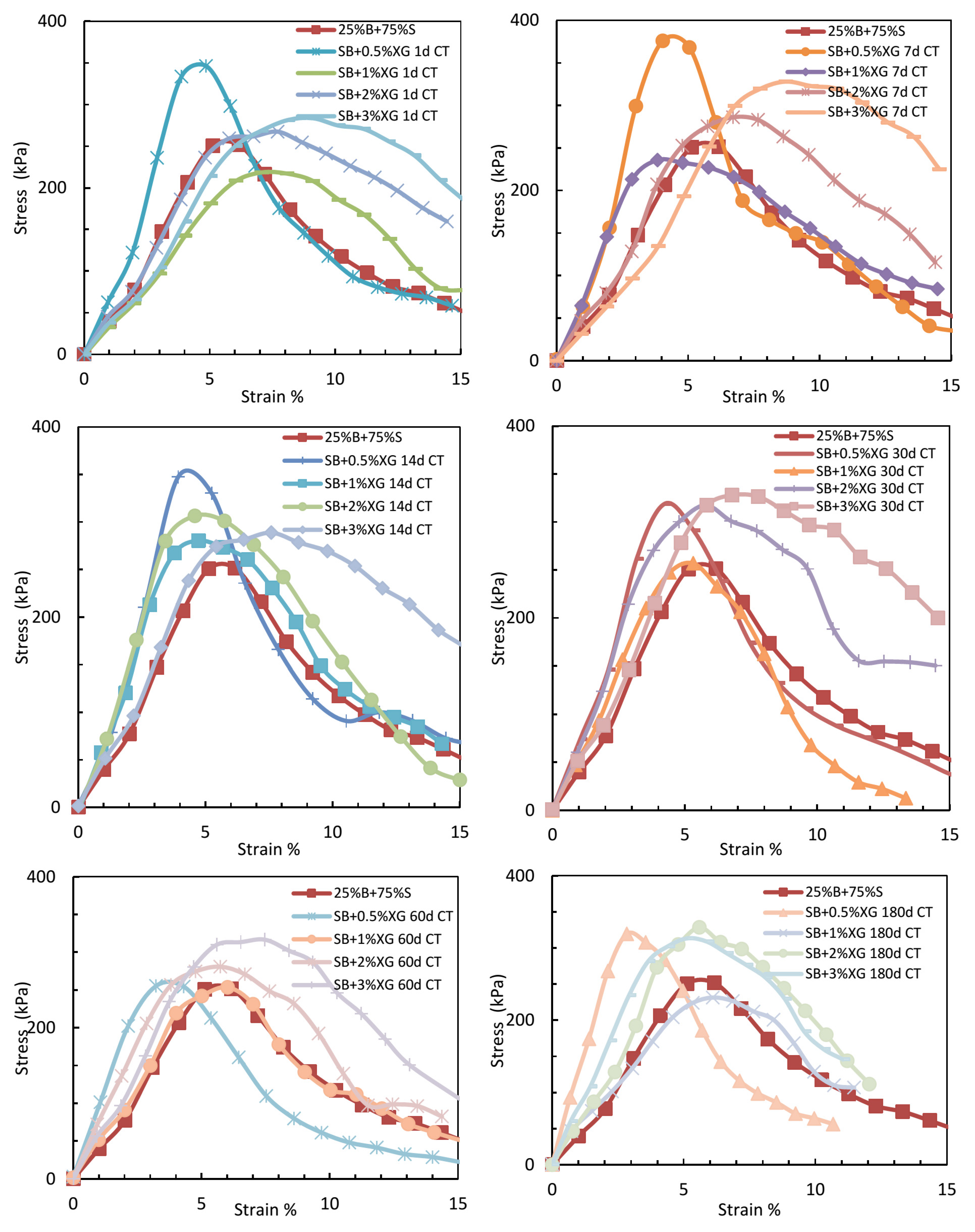
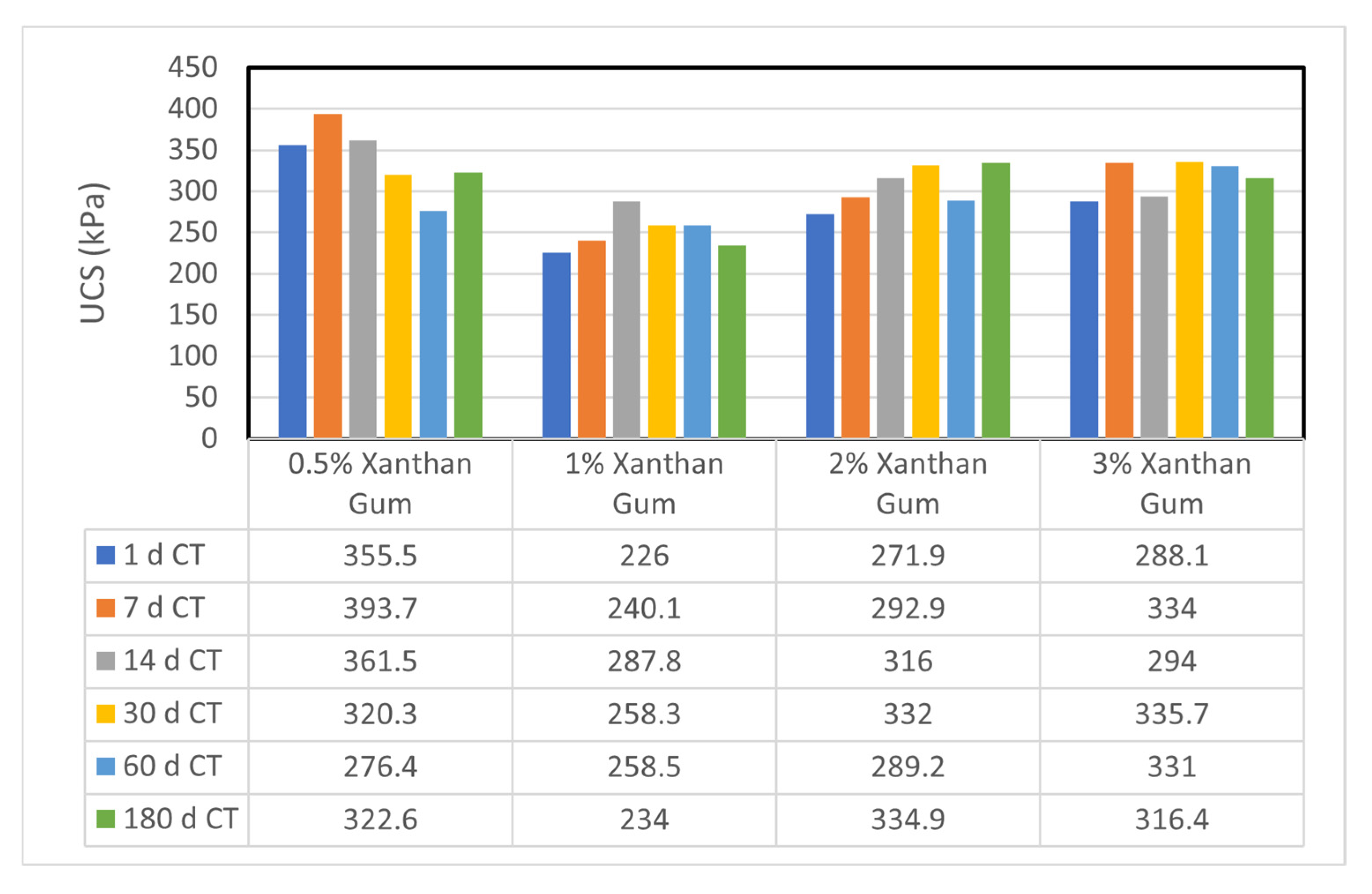
Figure 8 presents the UCS results of sand–bentonite mixtures treated with different concentrations of xanthan gum at various curing times, showing a general trend of strength improvement with increased biopolymer content.
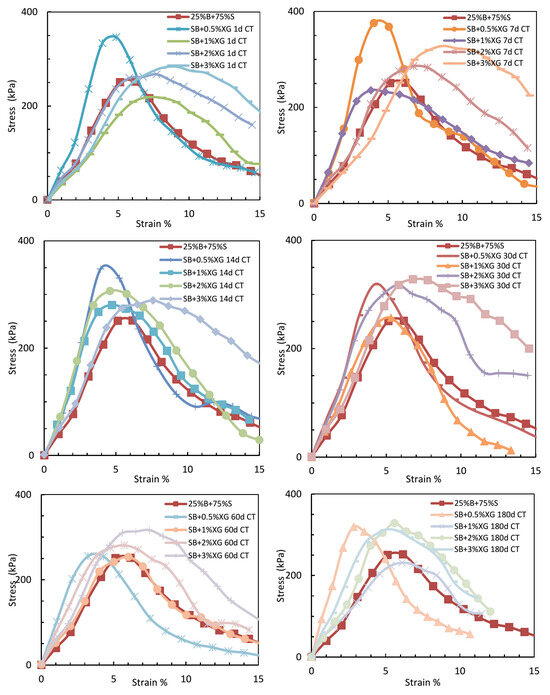
Figure 8.
UCS for sand–bentonite treated by xanthan Gum (comparison by concentration at identical curing time).
Figure 9 shows the development of unconfined compressive strength (UCS) over time for sand–bentonite mixtures treated with different concentrations of xanthan gum, highlighting strength gains particularly at 2% and 3% contents as curing progresses.
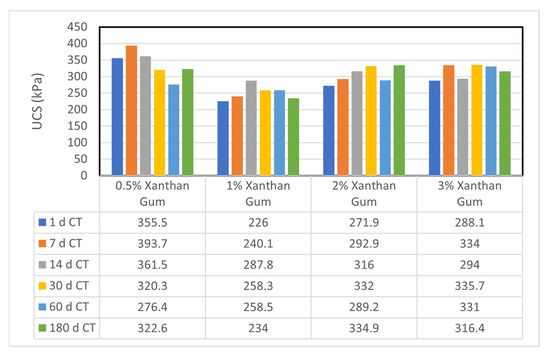
Figure 9.
Development of UCS Over Curing Time for Xanthan Gum-Treated Sand–Bentonite Mixtures.
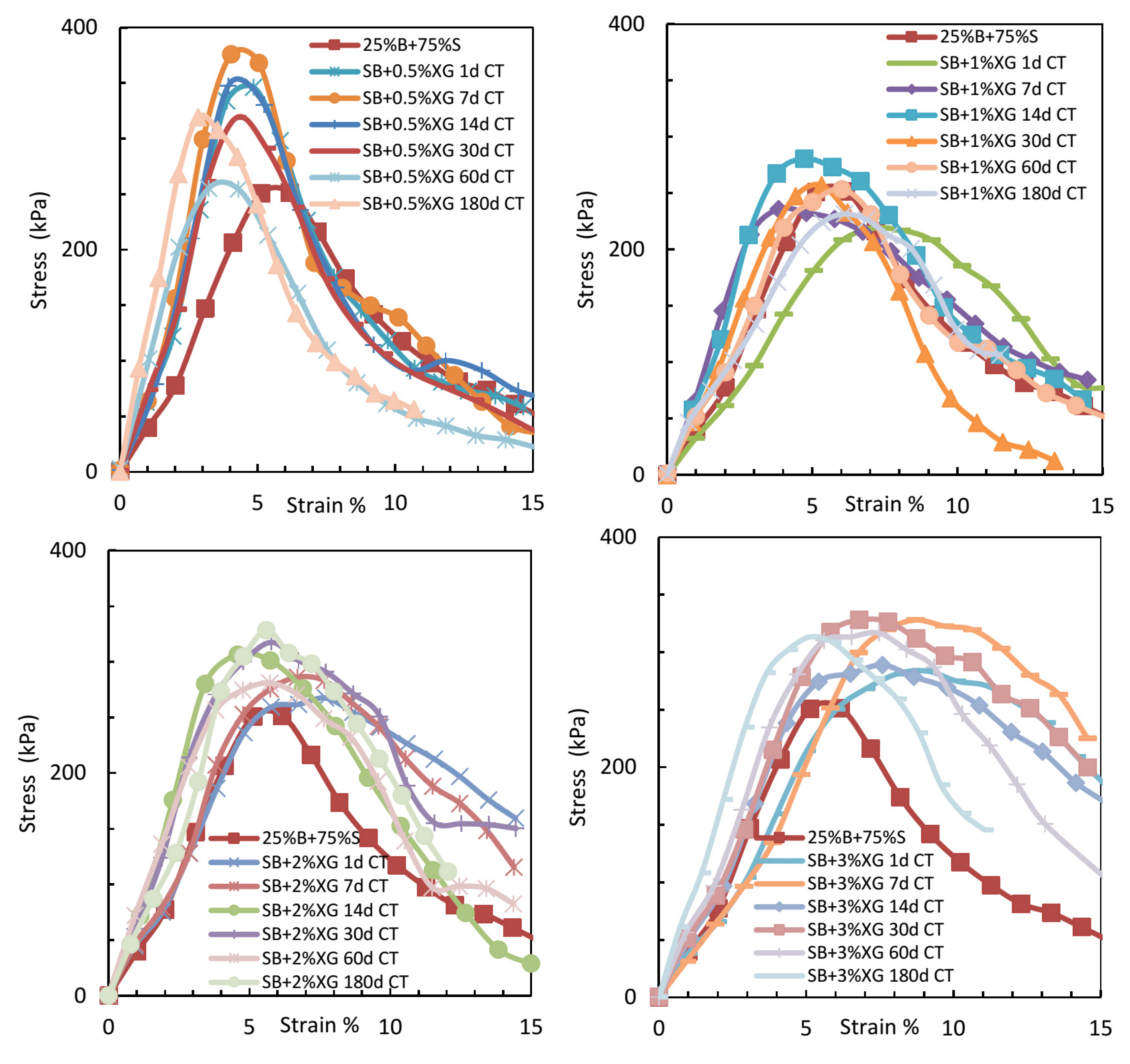
Figure 10 displays the stress–strain behavior of sand–bentonite mixtures treated with varying concentrations of xanthan gum over different curing durations, highlighting the evolution of peak strength and deformation response with time.
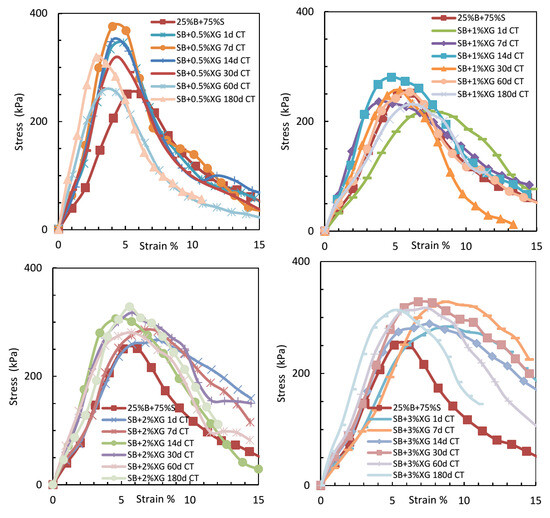
Figure 10.
The relationship between UCS and strain for sand–bentonite mixtures treated with xanthan gum at different curing times.
The xanthan gum-treated samples demonstrated enhanced UCS values with prolonged curing time, especially at elevated concentrations, in contrast to guar gum. At 2% XG, the UCS rose from 271.9 kPa after 1 day to 334.9 kPa after 180 days. The elevated viscosity and enhanced gel-forming ability of xanthan gum establish a more robust and resilient soil–biopolymer matrix, which is resistant to microbial degradation [1]. The findings indicate that xanthan gum is a more dependable choice for long-term soil stabilization in applications like landfill liners.
3.3.3. Relationship Between UCS and Strain for Guar Gum and Xanthan Gum
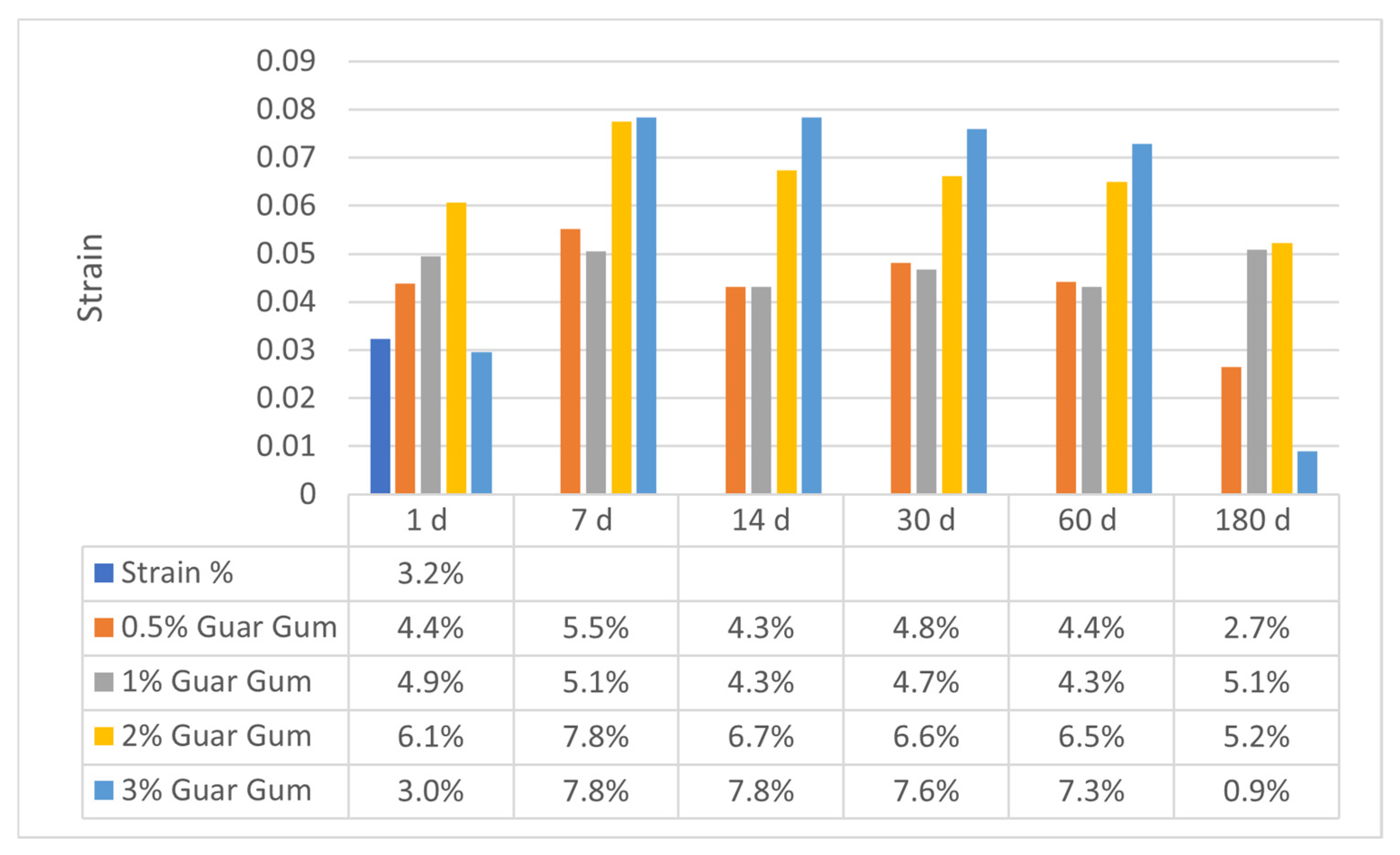
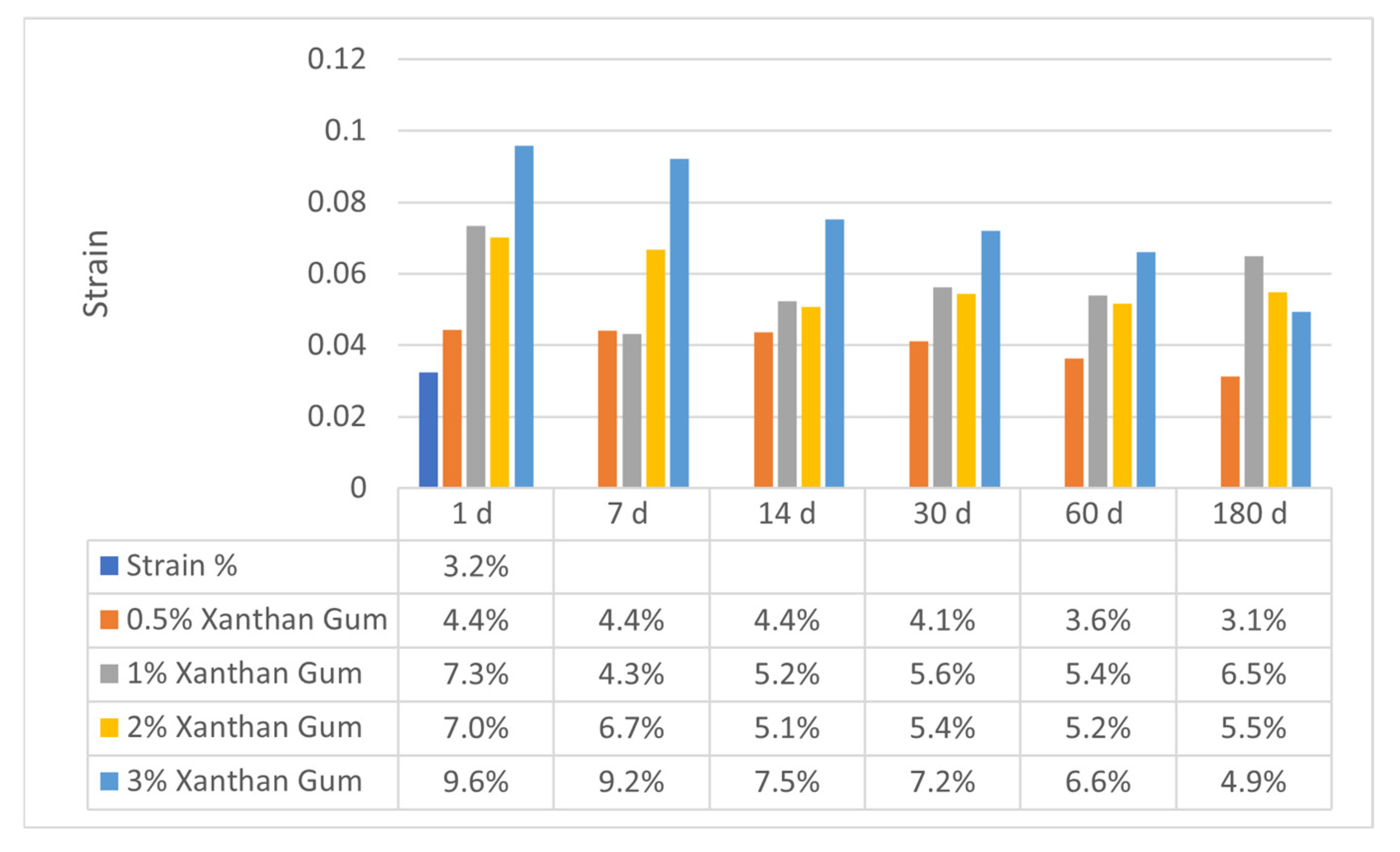
Figure 11 and Figure 12 exhibit the axial strain values for sand–bentonite mixes treated with xanthan gum (XG) and guar gum (GG) at various concentrations and curing durations. The results offer vital insights into the deformation characteristics and rigidity of the treated soils, which are crucial for comprehending their mechanical performance in applications like landfill liners.
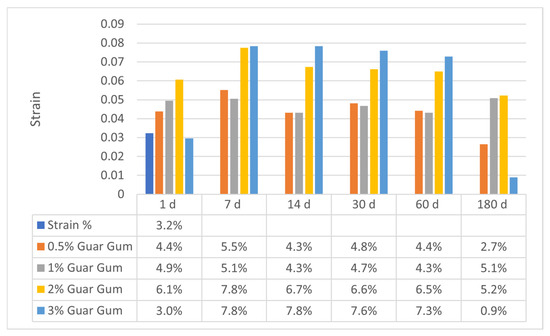
Figure 11.
Variation in Axial Strain for Sand–Bentonite Mixtures Treated with Guar Gum.
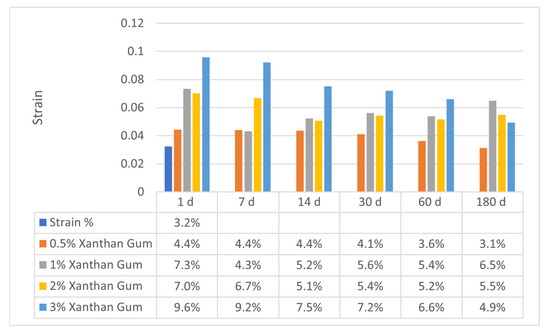
Figure 12.
Variation in Axial Strain for Sand–Bentonite Mixtures Treated with Xanthan Gum.
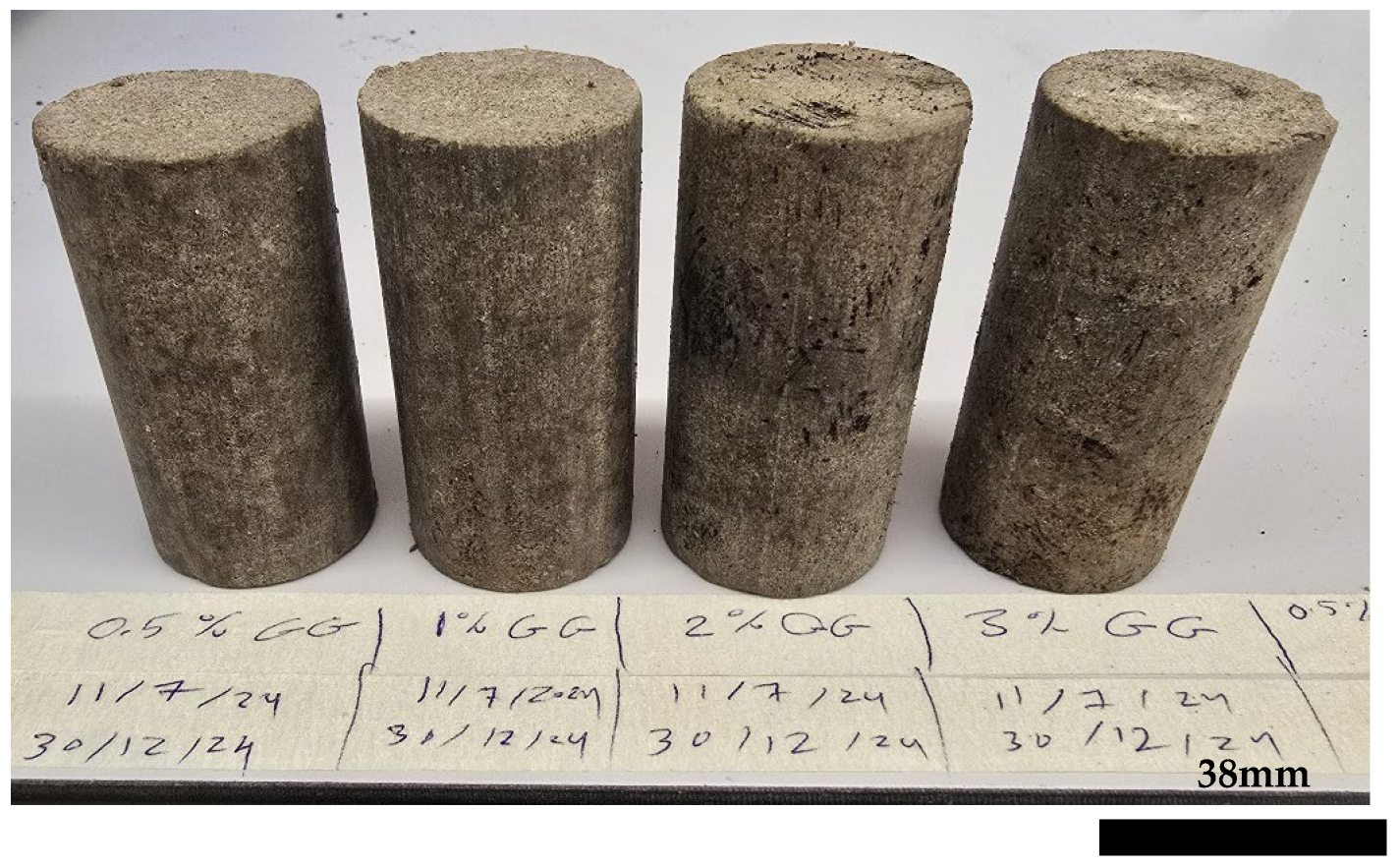
The axial strain values for guar gum-treated samples typically rose with extended curing time, especially at elevated concentrations. At 2% GG, the axial strain rose from 6.1% on day 1 to 6.7% on day 14 and stabilized at the rather high level of 6.5% by day 60. This trend signifies a decline in soil stiffness with time, aligning with the documented biodegradation of guar gum. The organic composition of guar gum renders it vulnerable to microbial degradation, resulting in the deterioration of the soil–biopolymer matrix and heightened deformation under stress [6]. At 3% GG, the axial strain exhibited a significant reduction to 0.9% at 180 days, which may appear paradoxical. This can be attributable to the substantial decay and mold proliferation detected in the samples, which undermined their structural integrity and led to early failure under minimal strain settings. This tendency is apparent in the images of the samples after 180 days (refer to Figure 13), where significant degradation is observable.

Figure 13.
Guar gum-treated sand–bentonite samples after 180 days of curing. Each cylindrical sample has a diameter of 38 mm and a height of 76 mm.
The xanthan gum-treated samples demonstrated more stable axial strain values over time compared to guar gum, especially at elevated doses. At 2% XG, the axial strain diminished from 7.0% on day 1 to 5.1% on day 14 and stabilized at approximately 5.2% by day 60, indicating that xanthan gum preserves soil stiffness over time due to its resistance to microbial degradation and its ability to form a robust soil–biopolymer matrix [1]. At 3% XG, the axial strain values were initially elevated (9.6% at 1 day) but diminished considerably to 4.9% by 180 days. This decrease in strain suggests that xanthan gum-treated soils undergo progressive strengthening as the biopolymer fully hydrates and forms more durable bonds with soil particles. This trend is supported by UCS data, which show increased strength with curing time for xanthan gum-treated samples.
The axial strain data underscore the differing efficacy of xanthan gum and guar gum in soil stabilization. Samples treated with guar gum demonstrated escalating strain values over time, signifying a decline in stiffness and structural integrity attributable to biodegradation. The xanthan gum-treated samples exhibited steady or declining strain levels, indicating enhanced durability and resistance to microbial invasion. The results align with the UCS findings, indicating a reduction in strength for samples treated with guar gum and an enhancement in strength for samples treated with xanthan gum over time. The images of the guar gum-treated samples after 180 days (refer to Figure 13) corroborate these findings as they distinctly exhibit significant decay and mold proliferation, which are not present in the xanthan gum-treated samples. The axial strain results significantly influence the design of landfill liners, where enduring stability and resistance to deformation are essential. The biodegradation of guar gum, along with the resultant increase in axial strain, renders it less appropriate for such applications unless supplementary compounds are employed to inhibit microbial deterioration. Xanthan gum’s capacity to sustain steady strain values and enhance strength over time renders it a more dependable choice for long-term soil stabilization in waste containment systems.
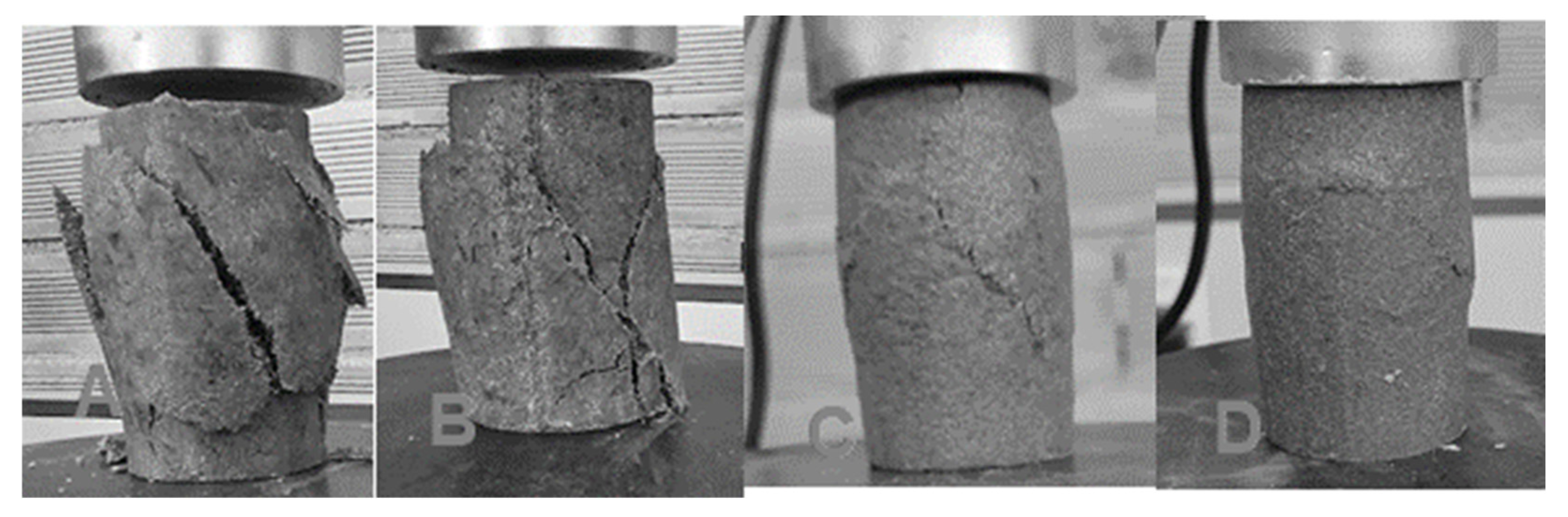
3.4. Failure Patterns in UCS Tests
The failure patterns noted in unconfined compressive strength (UCS) tests on sand–bentonite mixes treated with xanthan gum exhibited various characteristics based on the biopolymer concentration. At low concentrations (0.5% and 1%), the samples exhibited brittle failure characterized by irregular cracks and partial fragmentation, signifying diminished cohesiveness. At 2%, the failure exhibited greater cohesion, characterized by distinct shear planes and reduced random cracks, indicating excellent structural integrity. At 3%, the samples exhibited smoother fractures and d0uctile failure, indicating enhanced ductility. These patterns underscore the function of xanthan gum in enhancing cohesiveness and diminishing brittleness, particularly at approximately 2% concentration, which exhibited the most optimal mechanical performance Figure 14.

Figure 14.
Failure pattern of samples treated by XG. (A) 0.5%XG, (B) 1%XG, (C) 2%XG, and (D) 3%XG.
3.5. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR) Analysis Results
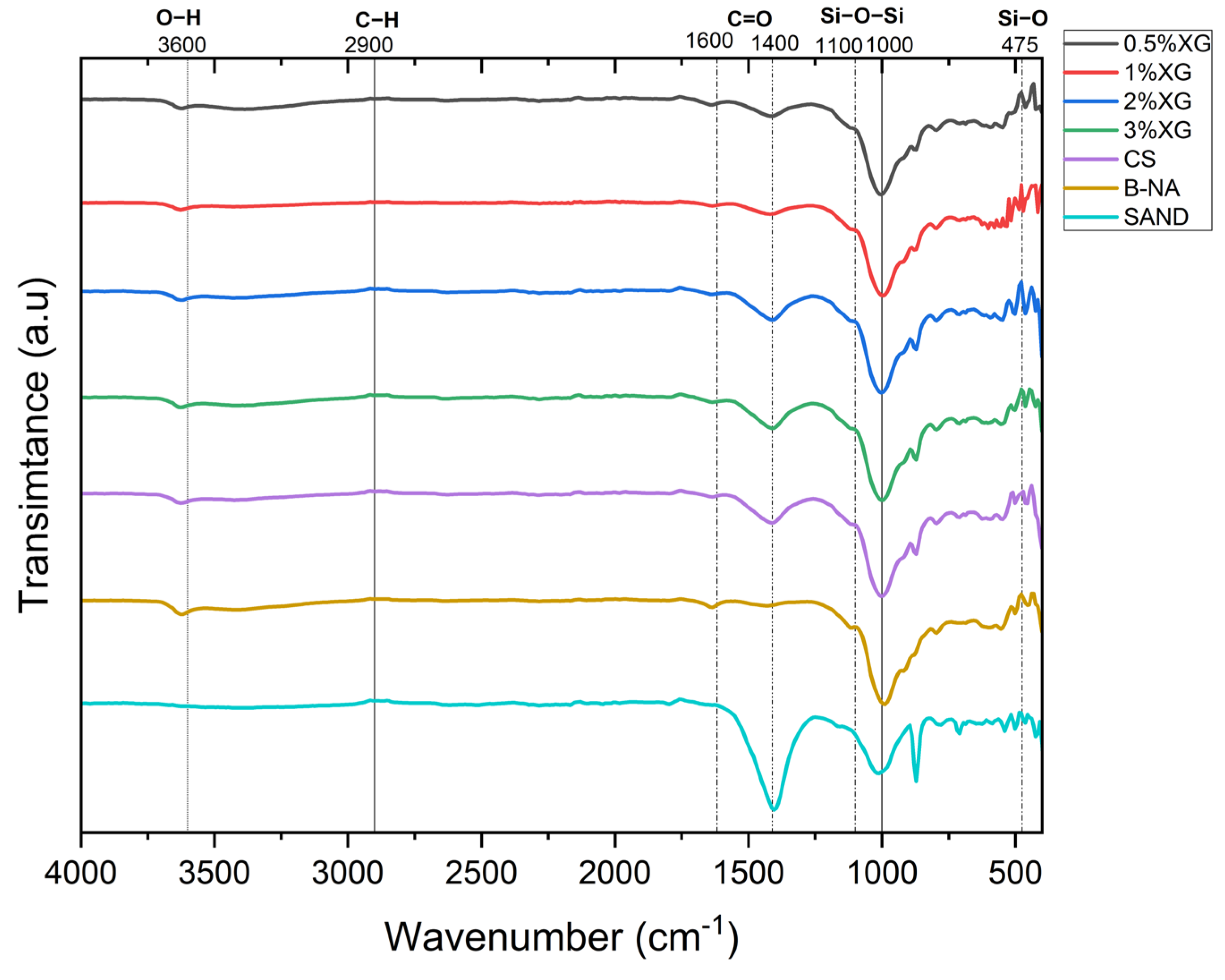
FTIR was conducted to analyze the chemical interactions and functional groups present in the sand–bentonite mixtures treated with xanthan gum and guar gum. The spectra were obtained for samples containing different biopolymer concentrations (0.5%, 1%, 2%, and 3%) and compared to the control sample. The results provide insights into the molecular structure modifications and interactions induced by biopolymer addition.
3.6. FTIR Spectral Characteristics
The FTIR spectra of all samples exhibited distinct absorption bands corresponding to the primary functional groups present in bentonite, sand, and the biopolymers (Figure 15). The following characteristic peaks were identified:
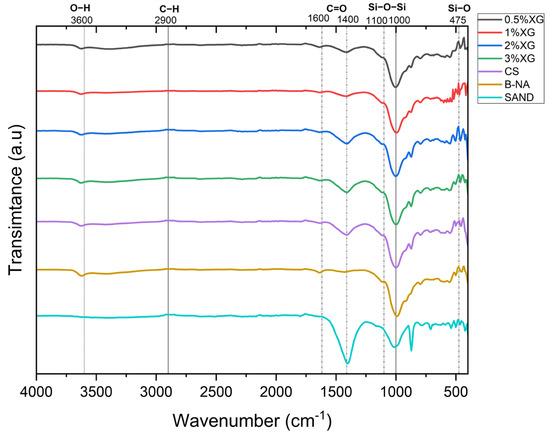
Figure 15.
FTIR Spectra of Sand–Bentonite Samples with Different Biopolymer Contents.
- Si-O-Si stretching vibrations: A strong absorption band was observed around 1000–1100 cm−1, corresponding to the silicate framework of sand and bentonite. This peak remained prominent across all samples, indicating the structural integrity of the mineral phase [29].
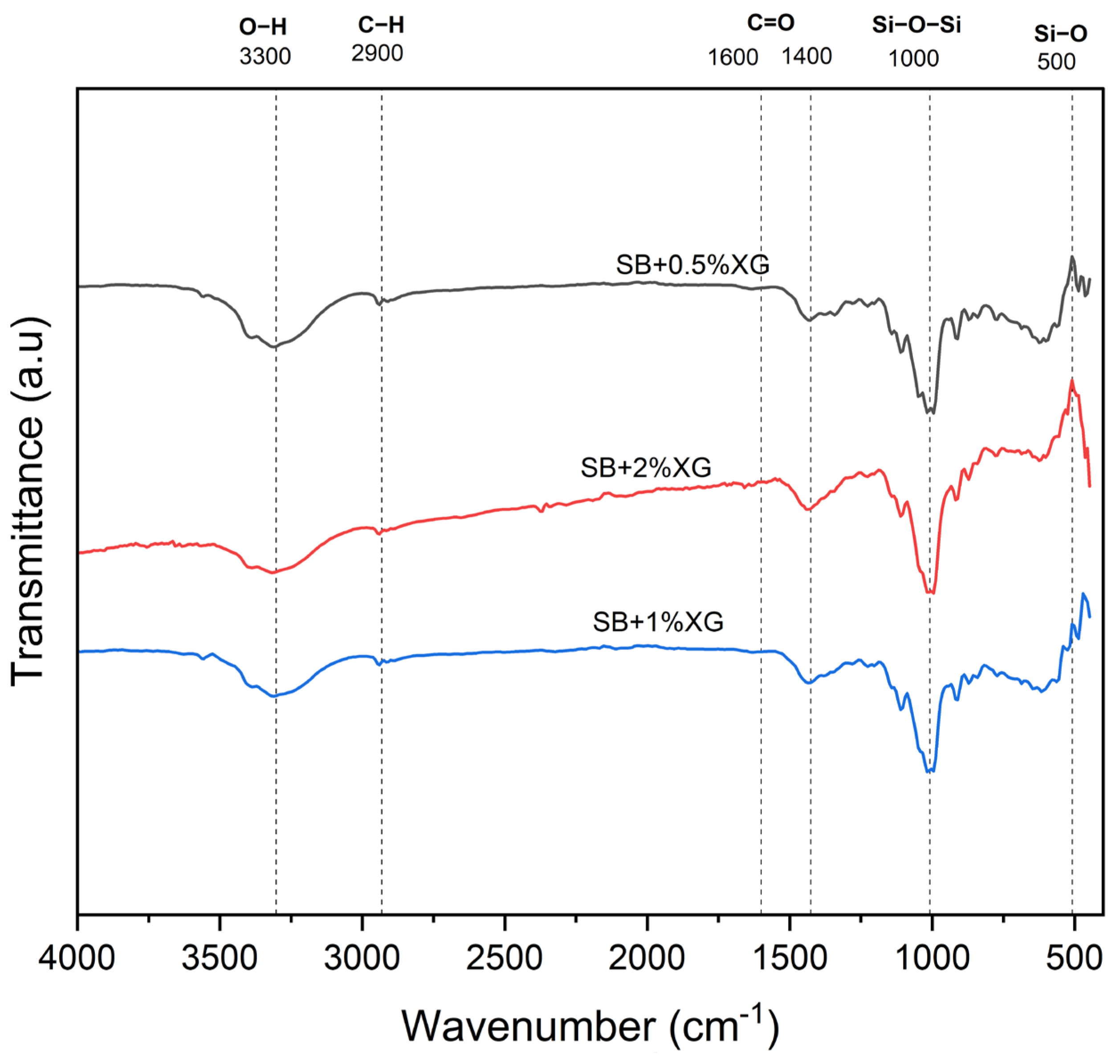
- O-H stretching vibrations: The broad absorption band around 3200–3600 cm−1 corresponds to hydroxyl (-OH) groups found in both the bentonite and the biopolymer matrix. In the original FTIR spectra obtained from oven-dried samples, this peak appeared relatively weak, which raised concerns regarding the possible thermal degradation or suppression of hydrogen bonding. To address this, a second FTIR analysis was conducted on selected samples (SB + 0.5%, 1%, and 2% XG) that were air-dried at room temperature. As shown in Figure 16, the resulting spectra revealed clearer and more intense O-H absorption bands, indicating that these functional groups are better preserved under milder drying conditions. The increasing peak intensity with higher biopolymer content further supports the role of xanthan gum in enhancing hydrophilicity and promoting hydrogen bonding within the soil matrix [29].
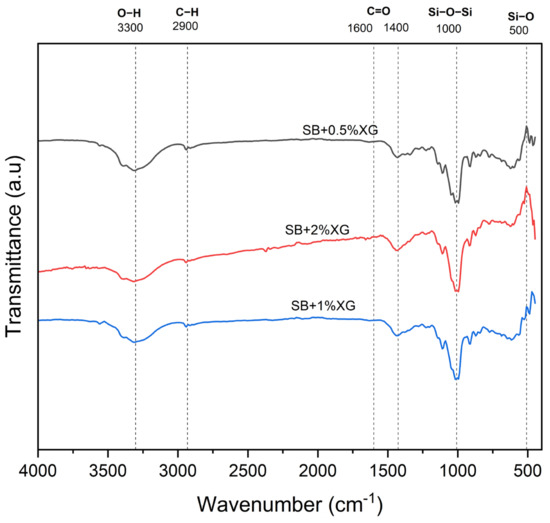 Figure 16. FTIR spectra of air-dried sand–bentonite mixtures with 0.5%, 1%, and 2% XG, showing enhanced O−H and C=O bands.
Figure 16. FTIR spectra of air-dried sand–bentonite mixtures with 0.5%, 1%, and 2% XG, showing enhanced O−H and C=O bands. - C-H stretching vibrations: Peaks observed around 2800–2950 cm−1 correspond to the aliphatic C-H stretching vibrations from the biopolymers, particularly xanthan gum and guar gum [29].
- C=O stretching vibrations: The absorption band near 1600–1650 cm−1 was attributed to the carboxyl (-COO−) functional groups from the biopolymers. The peak intensity increased with higher biopolymer content, signifying enhanced organic interactions [29].
- Si-O bending vibrations: The peak around 470–500 cm−1, characteristic of Si-O bending, was detected in all samples, confirming the presence of silicate minerals [30].
3.7. Effect of Biopolymer Addition on FTIR Spectra
The incorporation of xanthan gum and guar gum altered the FTIR spectra, indicating notable interactions between the biopolymers and the sand–bentonite matrix. The most significant spectral changes include the following:
- Increase in O-H Absorption: A noticeable enhancement in the 3200–3600 cm−1 band suggests increased hydrogen bonding due to the presence of hydrophilic biopolymers (Figure 15). This implies greater water retention, which may influence swelling and consolidation behavior.
- Shift in C=O Absorption: A slight shift in the 1600–1650 cm−1 region suggests interactions between the biopolymers and bentonite, potentially forming new hydrogen bonds or ionic interactions.
- Intensity Variations in Si-O-Si Peaks: Although the Si-O-Si peak remained present, slight intensity changes were observed with increasing biopolymer content, which may be linked to surface modifications or interactions between the biopolymers and the mineral phase.
These spectral shifts correlate with the observed strength gains in the XG-treated samples, supporting the conclusion that hydrogen bonding and biopolymer–mineral interactions play a key role in mechanical enhancement.
3.8. Interpretation of the Mechanical Behavior of Xanthan Gum-Treated Sand–Bentonite Based on UCS and E50
The relationship between unconfined compressive strength (UCS) and secant modulus (E50) offers key insights into the mechanical behavior of xanthan gum (XG)-treated sand–bentonite mixtures. As shown in Table 3, both UCS and E50 values are influenced by curing time and XG content. The highest UCS values were generally observed within the first 7 to 14 days of curing, reflecting the early formation of a biopolymer network and increased cohesion due to gelation and hydration processes [9,28]. After 28 days, the UCS gains tend to plateau, suggesting that the biopolymer structure reaches a state of stabilization. E50 values follow a similar trend, with a noticeable increase during early curing stages and relatively stable values afterward, indicating the establishment of a stiff soil matrix in the early curing phase [30].

Table 3.
Variation in Secant Modulus (E50) and Unconfined Compressive Strength (UCS) with Curing Time for Sand–Bentonite Mixtures Treated with Different Xanthan Gum (XG) Concentrations.
The 0.5% XG-treated sample reached the peak UCS of 393.7 kPa after 7 days, demonstrating that a moderate dosage of XG enhances soil strength efficiently. Higher concentrations, such as 2% and 3% XG, showed diminishing returns in UCS at later curing stages, which may be attributed to oversaturation and non-uniform distribution of the polymer, consistent with observations in loess soils and other fine-grained materials [30]. The stiffness of the mixtures, represented by E50, was highest at lower XG concentrations and declined with increased biopolymer content, likely due to increased ductility and reduced brittleness of the treated soils [9,28]. Interestingly, after 180 days, E50 values slightly increased again for higher XG contents, possibly due to continued polymer–soil interaction or moisture redistribution that led to re-stiffening.
The correlation between UCS and E50 is strong, aligning with the trends reported for biopolymer-modified soil systems, where strength and stiffness tend to improve together due to enhanced interparticle bonding and biofilm development [9]. These findings suggest that an optimal XG content of around 0.5% to 1% and a curing period of 7 to 28 days provide a practical balance between strength and stiffness. Such mixtures are promising for applications such as landfill liners or containment barriers, where mechanical integrity and durability under varying environmental conditions are critical. However, minor declines in performance at later stages, especially in higher XG contents, indicate the importance of long-term monitoring to evaluate the effects of moisture fluctuations and possible biodegradation [30].
4. Discussion
The experimental results clearly demonstrate that adding biopolymers has a significant impact on both the mechanical and physical behavior of sand–bentonite mixtures. Among the materials tested, xanthan gum (XG) showed the most consistent and favorable performance. Due to its high viscosity and ability to form gel-like networks, XG altered the compaction characteristics by reducing the maximum dry density (MDD) and influencing the optimum moisture content (OMC). This change suggests that the biopolymer enhances bonding between particles and improves moisture retention within the soil matrix.
Unconfined compressive strength (UCS) data reinforced the benefits of XG, particularly at the 2% dosage, where strength increased steadily with curing time, reaching its peak at 180 days. In contrast, guar gum (GG) did not perform as well under long-term conditions. While initial strength gains were observed, they declined over time, and this was accompanied by an increase in axial strain. The appearance of mold and surface decay in GG-treated samples confirmed the material’s susceptibility to biodegradation, which undermines its effectiveness for applications requiring long-term stability.
When analyzing stiffness using the secant modulus (E50), a strong correlation was observed with UCS, especially during the early stages of curing. However, at higher XG concentrations, a slight reduction in stiffness was noted—likely due to the increased ductility provided by the biopolymer. This observation was supported by the failure patterns recorded during UCS testing—at lower XG contents, samples showed brittle failure, while at 2%, the failure became more ductile and cohesive, suggesting improved structural performance.
FTIR analysis added a molecular perspective to these findings. Peaks associated with hydroxyl (-OH), carboxyl (-COO−), and polysaccharide groups confirmed the presence of biopolymers in the treated soils. While the positions and intensities of these peaks did not shift significantly with curing time—indicating minimal chemical cross-linking—the data still point to meaningful interactions at the molecular level. These interactions, most likely hydrogen bonding and electrostatic attractions, contribute to the enhanced cohesion and mechanical stability observed in XG-treated specimens.
Taken together, the results make a strong case for the use of xanthan gum, particularly at a 2% concentration, in improving the mechanical behavior and long-term durability of sand–bentonite barriers. This makes it a viable alternative for applications such as landfill liners and containment systems where strength and reliability over time are essential. Moving forward, further research is recommended to explore ways of improving the durability of guar gum, possibly through chemical treatment or additives, and to apply more advanced analytical tools like X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) or nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) for a deeper understanding of the bonding mechanisms involved.
5. Conclusions
This study investigated the influence of xanthan gum (XG) and guar gum (GG) on the unconfined compressive strength (UCS) and mechanical performance of sand–bentonite mixtures, with a focus on their application as sustainable alternatives for landfill liners. The results demonstrated that xanthan gum significantly enhanced UCS over time, particularly at a 2% concentration, where the strength increased from 271.9 kPa after 1 day to 334.9 kPa after 180 days. This improvement was accompanied by stable axial strain values, indicating maintained soil stiffness and resistance to deformation during long-term curing. The stability of xanthan gum is attributed to its resistance to microbial degradation and strong gel-forming capacity, making it suitable for durable soil reinforcement.
In contrast, guar gum-treated samples exhibited reduced strength and increased deformation over time. Visual observations confirmed biological degradation, such as mold formation and rotting, especially after 180 days. These limitations suggest that guar gum may not be ideal for long-term soil stabilization unless supported by additional treatments, such as antimicrobial agents. Additionally, FTIR analysis confirmed the presence of functional groups such as hydroxyl and carboxyl in biopolymer-treated soils, indicating strong molecular interactions with soil particles. These interactions contribute directly to improved cohesion and mechanical integrity of the treated sand–bentonite mixtures.
The comparative performance of XG and GG emphasizes the importance of biopolymer selection when targeting long-term geotechnical applications. The consistent strength gain and molecular stability observed in XG-treated specimens underline its reliability, particularly under extended curing conditions.
Overall, the study highlights the 2% concentration of xanthan gum as the optimal dosage, offering a balanced approach between strength development and material efficiency. By combining long-term mechanical evaluation with FTIR-based molecular insights, the study offers a comprehensive view of how biopolymers interact within the soil matrix, reinforcing both cohesion and durability. The findings support its practical use in landfill liner design, where durability under varying environmental conditions is crucial. Further large-scale field testing is recommended to confirm laboratory findings, assess long-term performance, and evaluate economic feasibility. Future research should also explore alternative biopolymers, assess their environmental impacts, and develop standardized application protocols to ensure consistent and sustainable practices in geotechnical engineering.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.A.-J. and H.B.; Methodology, A.A.-J.; Writing—original draft preparation, A.A.-J.; Writing—review and editing, H.B.; Supervision, H.B.; Funding acquisition, A.A.-J. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Chang, I.; Im, J.; Cho, G.C. Geotechnical engineering behaviors of gellan gum biopolymer treated sand. Can. Geotech. J. 2016, 53, 1658–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, T.; Shen, L.; Shen, M.; Chen, F.; Liu, L.; Gao, L. Analysis on differences of carbon dioxide emission from cement production and their major determinants. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 103, 160–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrew, R.M. Global CO2 emissions from cement production, 1928–2018. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2019, 11, 1675–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayeldeen, M.; Negm, A.; El-Sawwaf, M.; Kitazume, M. Enhancing mechanical behaviors of collapsible soil using two biopolymers. J. Rock Mech. Geotech. Eng. 2017, 9, 329–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabalar, A.F.; Awraheem, M.H.; Khalaf, M.M. Geotechnical properties of a low-plasticity clay with biopolymer. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2018, 30, 04018170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Wu, L.; Perdjon, M.; Huang, X.; Peng, Y. The drying effect on xanthan gum biopolymer treated sandy soil shear strength. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 197, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Yadav, B.D.; Raj, R. A review on the application of biopolymers (xanthan, agar and guar) for sustainable improvement of soil. SN Appl. Sci. 2024, 6, 393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soldo, A.; Miletić, M.; Auad, M.L. Biopolymers as a sustainable solution for the enhancement of soil mechanical properties. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, I.; Im, J.; Prasidhi, A.K.; Cho, G.C. Effects of xanthan gum biopolymer on soil strengthening. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 74, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudgil, D.; Barak, S.; Khatkar, B.S. X-ray diffraction, IR spectroscopy and thermal characterization of partially hydrolyzed guar gum. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2012, 50, 1035–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagheri, P.; Gratchev, I.; Rybachuk, M. Effects of xanthan gum biopolymer on soil mechanical properties. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, A.S.A.; Latifi, N.; Meehan, C.L.; Manahiloh, K.N. Sustainable improvement of tropical residual soil using an environmentally friendly additive. Geotech. Geol. Eng. 2017, 35, 2613–2623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghadr, S.; Assadi-Langroudi, A. Structure-based hydro-mechanical properties of sand-bentonite composites. Eng. Geol. 2018, 235, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iravanian, A. Hydro-Mechanical Properties of Compacted Sand-Bentonite Mixtures Enhanced with Cement. Ph.D. Thesis, Eastern Mediterranean University, Gazimağusa, North Cyprus, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Garoushi, A.H.B.; Uygar, E. Biopolymer and gypsum added Na bentonite for a more effective clay liner. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alibrahim, B.; Garoushi, A.H.B.; Uygar, E. The role of calcium-based additives in bentonite stabilization: A comparative evaluation. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, X.; Deng, S.; Liang, B.; Zhuang, J.; Yu, Y.; Wu, Z. Mechanical behavior and strengthening mechanism of loess stabilized with xanthan gum and guar gum biopolymers. Mater. Res. Express 2024, 11, 105305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehghan, H.; Tabarsa, A.; Latifi, N.; Bagheri, Y. Use of xanthan and guar gums in soil strengthening. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2019, 21, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassler, R.A.; Doherty, D.H. Genetic engineering of polysaccharide structure: Production of variants of xanthan gum in Xanthomonas campestris. Biotechnol. Prog. 1990, 6, 182–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nsengiyumva, E.M.; Alexandridis, P. Xanthan gum in aqueous solutions: Fundamentals and applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 216, 583–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, J.; Liu, C.; Xiao, H.; Lin, W.; Tang, Z.; Jia, Y. Study on planting and mechanical properties of clay modified by xanthan gum and guar gum. Preprints 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seema, M.; Phool, C.; Neelkant, P.; Hina, C.; Tajdar, S.A.; Mahor, S. A review on natural plant-based polymers: A brilliant pharmaceutical excipient. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Rev. Res. 2022, 75, 24–30. [Google Scholar]
- Prajapati, V.D.; Jani, G.K.; Moradiya, N.G.; Randeria, N.P. Pharmaceutical applications of various natural gums, mucilages and their modified forms. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 92, 1685–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mudgil, D.; Barak, S.; Khatkar, B.S. Guar gum: Processing, properties and food applications—A review. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 51, 409–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ASTM D2166/D2166M-16; Standard Test Method for Unconfined Compressive Strength of Cohesive Soil. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2010. [CrossRef]
- Madejová, J. FTIR techniques in clay mineral studies. Vib. Spectrosc. 2003, 31, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM D6348-12; Standard Test Method for Determination of Gaseous Compounds by Extractive Direct Interface Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) Spectroscopy. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2020. [CrossRef]
- García-Ochoa, F.; Santos, V.E.; Casas, J.A.; Gómez, E. Xanthan gum: Production, recovery, and properties. Biotechnol. Adv. 2000, 18, 549–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuart, B. Infrared Spectroscopy: Fundamentals and Applications; John Wiley & Sons: Chichester, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Lemboye, K.; Almajed, A. Effect of varying curing conditions on the strength of biopolymer modified sand. Polymers 2023, 15, 1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).