1. Introduction
Over the past several decades, addressing global environmental challenges has emerged as a central priority within the framework of the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). Notably, SDG 7 underscores the necessity of transitioning toward sustainable energy sources to supplant polluting fossil fuels, thereby promoting a more equitable and ecologically resilient world [
1,
2]. The adoption of renewable energy is particularly critical in mitigating atmospheric CO
2 emissions, considering that the energy sector is responsible for nearly two-thirds of global carbon emissions. Consequently, advancing low-carbon energy technologies and scaling up the utilization of renewable sources such as solar, hydropower, and biomass are essential strategies for addressing climate change [
3].
International climate agreements have established binding regulations on energy consumption, thereby compelling significant polluters such as the United States and China to delineate explicit carbon neutrality targets [
4,
5]. Nevertheless, the widespread adoption of renewable energy continues to be impeded by high costs [
6,
7], technological constraints [
8], and financial barriers [
9]. Therefore, policy interventions, investments in innovation, and financial incentives are imperative to expedite this transition. Recent advancements in wind turbines, solar photovoltaics, battery storage, and smart grid technologies have significantly enhanced efficiency, reduced costs, and improved the competitiveness of renewable energy [
3].
In the realm of renewable energy, technological innovation is pivotal in enhancing market accessibility and advancing sustainability standards [
10]. Its significance has grown increasingly prominent in contemporary discussions on environmental management. The surge in patents for low-carbon technologies underscores a heightened focus on innovation as a key strategy for gaining competitive advantages in the global energy market [
11]. However, despite this trend, the share of green innovation and environmental governance remains notably unstable in Middle Eastern nations (see
Figure 1). Similarly,
Figure 2 illustrates pronounced, irregular fluctuations in environmental governance among Middle Eastern countries from 1990 to 2023, indicating episodic, event-driven policy responses rather than consistent and sustained advancements in environmental regulation and governance. This instability poses significant challenges to transitioning away from fossil fuel dependency, driving a global shift toward a greener economy, and fostering the development of groundbreaking technologies [
12].
The Middle East occupies a distinctive position at the intersection of environmental sustainability and economic development. With extensive oil reserves and challenging climate conditions, the region confronts pressing challenges, including desertification, water scarcity, and elevated carbon emissions. The Middle East Green Initiative (MGI) and the Saudi Green Initiative (SGI) represent significant efforts to address these environmental concerns through afforestation, pollution control, and investments in renewable energy [
13]. Nevertheless, the implementation of these strategies remains complex, hindered by persistent reliance on fossil fuels, geopolitical tensions, and economic barriers.
Historically, Middle Eastern economies have been heavily reliant on natural resource exploitation, particularly in nations such as Saudi Arabia, Kuwait, Iraq, and Iran, which have dominated global oil exports for decades. While this dependence has conferred economic benefits, it has also exacerbated environmental degradation and heightened the region’s vulnerability to climate change [
14,
15]. The region’s exposure to extreme weather events, including prolonged droughts and severe heatwaves, further underscores the urgency of sustainable environmental management.
Environmental vulnerabilities differ significantly across Middle Eastern nations, reflecting diverse socio-political contexts. For example, Yemen, Bahrain, Israel, Jordan, and Lebanon experience severe water shortages due to a combination of natural limitations and geopolitical conflicts over resource access. In response, regional initiatives such as the MGI aim to promote environmental governance and sustainability; however, challenges persist, including weak regulatory frameworks, economic disparities, and inadequate infrastructure [
3,
16].
In response, the MGI, led by Saudi Arabia, signifies a paradigm shift in regional environmental governance. By emphasizing afforestation, pollution abatement, and the development of renewable energy infrastructure, the initiative seeks to mitigate the adverse effects of climate change. Complementary efforts, such as the SGI, are aimed at accelerating transitions toward sustainability. Nonetheless, the implementation of these initiatives encounters substantial challenges, including entrenched dependency on fossil fuels, political and economic barriers, and technological limitations [
13].
Despite increasing international pressure for climate action, many Middle Eastern nations continue to grapple with structural and institutional barriers that hinder effective environmental governance and the transition to sustainable energy systems. These challenges include inadequate regulatory frameworks, limited regional coordination, and an entrenched dependence on fossil fuels, which collectively slow the adoption of renewable energy technologies and sustainability initiatives [
13,
17]. Additionally, political instability in conflict-affected countries such as Syria, Lebanon, and Iraq compound these obstacles, undermining long-term policy planning and deterring foreign investment in green infrastructure. Infrastructure deficiencies and persistent economic constraints in territories like Gaza and the West Bank further weaken environmental governance capacity, worsening problems related to pollution, waste management, and resource scarcity [
2].
Even in more developed economies such as the UAE, Saudi Arabia, and Qatar, oil dependency constitutes a significant barrier to achieving a green transition. Although these nations have articulated ambitious commitments to diversify their economies and reduce emissions, progress is often hindered by fragmented environmental policies and a lack of regional coordination [
18,
19]. Furthermore, the renewable energy sector remains in its early stages, requiring substantial investments in innovation and financing to ensure the scalability and affordability of clean energy solutions [
20,
21]. Addressing these challenges necessitates a holistic approach that integrates environmental, economic, and technological strategies. Enhancing investments in renewable energy, strengthening governance frameworks, and promoting innovative sustainability practices are critical to overcoming obstacles and advancing the transition to a green economy.
A critical challenge in the Middle East’s sustainability transition lies in the interconnected dynamics of environmental governance, resource dependence, and pollution. The region’s vast natural resource wealth, particularly in fossil fuels, has historically shaped its economic trajectory, but weak governance structures have often resulted in unsustainable extraction practices and high pollution levels [
15,
22]. Resource-rich nations that lack strong regulatory frameworks frequently experience environmental degradation, as reliance on fossil fuels discourages investment in green technologies [
23,
24]. However, governance plays a crucial mediating role in breaking this cycle. Effective environmental policies can mitigate the adverse effects of resource dependence by promoting cleaner production methods, reinvesting resource revenues into sustainable innovation, and enforcing stricter pollution controls [
25,
26]. Without integrated governance mechanisms, pollution levels will continue to rise, hindering the effectiveness of green innovation in addressing environmental challenges [
8]. Recognizing this interdependence is essential for crafting policies that balance economic growth, resource sustainability, and environmental protection in the Middle East.
This study aims to evaluate the interplay between environmental governance, renewable energy transitions, and sustainable innovations in shaping the Middle East’s green future. By focusing on key regional actors—including Bahrain, Iraq, Iran, Israel, Jordan, Kuwait, Lebanon, Oman, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, Syria, the West Bank and Gaza, and Yemen—this research offers a comprehensive analysis of how policy, technology, and governance converge to drive environmental transformation. The inclusion of diverse nations with distinct political and economic contexts yields valuable insights into shared challenges and opportunities in regional sustainability efforts. While the existing literature extensively discusses the environmental consequences of fossil fuel dependency, this study provides new insights into how a coordinated strategy combining innovation, renewable energy, and governance can effectively address the Middle East’s environmental challenges.
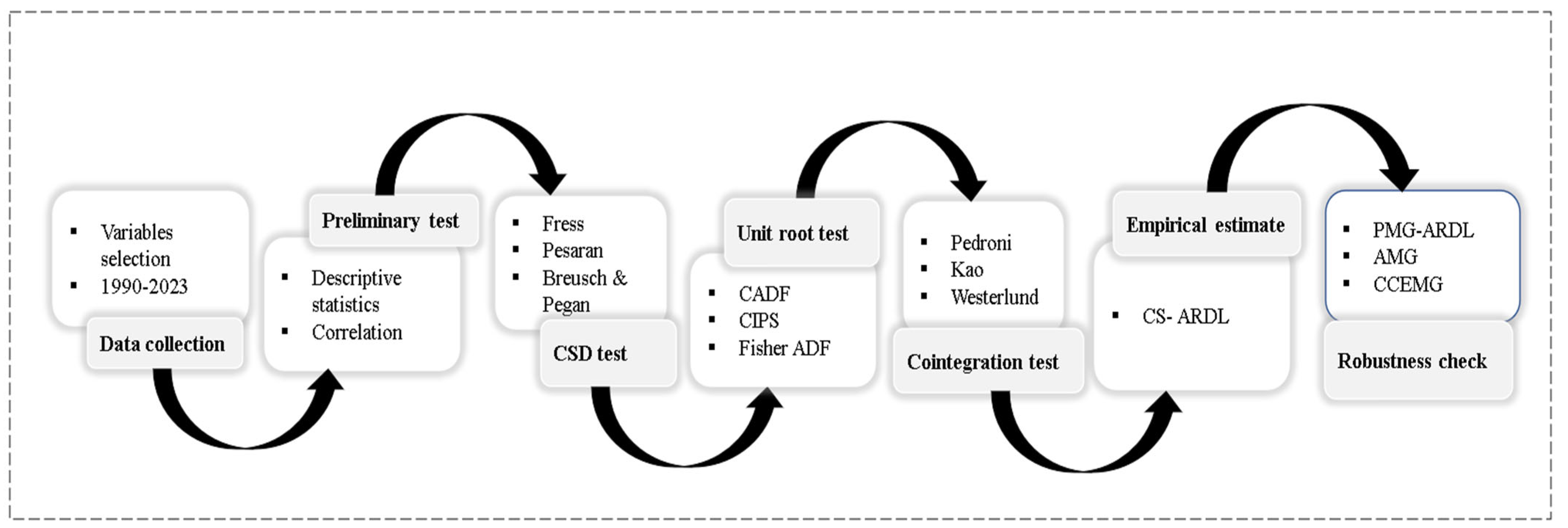
Our research unfolds through the following stages: Firstly, we compile a panel dataset that includes environmental governance indicators, renewable energy metrics, innovation indices, and socio-economic variables from selected Middle Eastern countries. Secondly, we use the cross-sectional autoregressive distributed lag (CS-ARDL) model as our main analysis tool because it can manage differences between countries, allow for various time delays for each variable, and show strong long-term connections even when there are dependencies between countries [
27,
28]. Thirdly, we use other methods like the Pooled Mean Group (PMG-ARDL), Average Mean Group (AMG), and Common Correlated Effects Mean Group (CCEMG) to check how accurate and reliable the results from the CS-ARDL model are [
28,
29,
30]. Fourthly, we examine both the short-term and long-term effects of the identified variables on green innovation, focusing on understanding the dynamics and causal relationships within the regional context. Finally, we derive practical insights and suggestions to guide Middle Eastern nations in their national green initiatives, helping them strike a balance between economic growth and environmental sustainability.
This study is structured as follows:
Section 2 provides a review of the relevant literature.
Section 3 outlines the methodology employed, detailing the analytical framework and data processing techniques. In
Section 4, we present, interpret, and discuss the results of this study, analyzing their implications. Finally,
Section 5 concludes this study and offers policy recommendations based on the findings, highlighting their significance for sustainable development and green innovation in the region.
2. Literature Review
Environmental governance, resource dependence, and pollution are intricately linked, shaping the path of green innovation and sustainability in the Middle East. Weak governance structures often exacerbate the negative effects of resource dependence, leading to high pollution levels and environmental degradation. In many Middle Eastern economies, natural resource wealth, primarily from fossil fuels—has driven economic expansion but has also created governance challenges that hinder environmental sustainability [
13,
31]. The absence of strong regulatory frameworks allows pollution-intensive industries to thrive, reinforcing a cycle where resource exploitation fuels environmental degradation without adequate innovation incentives. Conversely, countries with well-developed governance structures have demonstrated that effective policies can redirect resource revenues toward sustainable innovation, mitigating pollution while sustaining economic growth [
32,
33].
The “resource curse” hypothesis suggests that economies highly dependent on natural resource revenues often experience slower innovation growth and weaker institutional capacity, which, in turn, limits effective pollution control [
24]. In the Middle East, oil and gas dependence has historically constrained efforts to transition toward a green economy, as fossil fuel revenues reduce the immediate economic pressure to invest in renewable energy and emissions reduction technologies [
23,
25]. However, governance plays a mediating role in breaking this pattern. Countries that strategically reinvest resource wealth into research and development (R&D) for green technologies have achieved more sustainable outcomes [
34]. For example, Norway’s sovereign wealth fund model redirects oil revenues into sustainable projects, a model Middle Eastern economies could adopt to enhance green innovation while reducing pollution.
The lack of strict environmental regulations in resource-rich economies has also contributed to significant pollution levels, particularly in oil-dependent nations such as Saudi Arabia, Iraq, and Kuwait. Without governance mechanisms enforcing sustainable resource extraction practices, industries continue to prioritize short-term gains over long-term environmental stability [
35]. Studies indicate that countries with robust environmental policies, such as carbon pricing, emissions caps, and investment in clean energy—are more likely to successfully integrate resource management with pollution control, reducing their reliance on fossil fuels while incentivizing green innovation [
36,
37]. In contrast, Middle Eastern countries with weak governance structures often struggle to implement these measures, leading to unchecked pollution despite growing awareness of environmental concerns [
17].
Another critical factor is international climate governance and trade regulations, which increasingly pressure Middle Eastern economies to adopt cleaner technologies. Export-dependent oil economies face mounting challenges as global markets shift toward carbon border adjustment mechanisms, making green innovation essential for maintaining economic competitiveness [
2]. Without proactive policy alignment between governance, resource dependence, and pollution control, Middle Eastern nations risk economic stagnation as global demand for fossil fuels declines. The European Union’s Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM) serves as an example of how external governance structures are influencing domestic environmental policies, forcing oil-exporting nations to reconsider their sustainability strategies [
20].
Green innovation acts as the bridge between these interconnected issues, offering technological solutions to reduce pollution while ensuring economic resilience. However, without governance mechanisms that align resource revenues with sustainability investments, green innovation adoption remains slow [
33]. Strengthening regional environmental policies—such as coordinated carbon pricing across GCC nations—could create incentives for businesses to shift toward low-carbon technologies while reducing pollution [
38]. Furthermore, digital innovations, such as AI-driven emissions monitoring and blockchain-based resource tracking, offer new governance tools to ensure transparency and efficiency in managing pollution and resource use [
39,
40].
Ultimately, achieving a regional green future in the Middle East requires a holistic policy approach that integrates governance, natural resource management, and pollution control rather than treating them as separate challenges. Countries must transition from viewing resource wealth as an economic end goal to leveraging it as a tool for sustainable innovation. Establishing regional governance bodies to enforce unified pollution standards, reinvesting resource revenues into green technology R&D, and developing cross-border energy transition policies are essential steps toward breaking the resource–pollution cycle and fostering long-term environmental resilience.
2.1. Conceptual Framework
The transition to a sustainable future in the Middle East hinges on the interplay between environmental governance, renewable energy adoption, and innovative sustainability solutions. Environmental governance provides the institutional, legal, and regulatory foundation necessary to drive sustainability policies, enforce compliance, and manage resource use efficiently [
41,
42]. In Saudi Arabia and the broader Middle Eastern region, recent policy shifts—including the SGI and MGI—demonstrate a growing commitment to balancing economic growth with environmental responsibility [
13]. However, governance effectiveness varies across the region, affecting the speed and success of sustainable transitions.
A critical dimension of this transition is renewable energy adoption, which serves as a primary mechanism for reducing carbon emissions, diversifying energy sources, and decreasing fossil fuel dependency [
21]. The energy transition model emphasizes the role of legislative support, technological innovation, and financial incentives in shifting from hydrocarbon-based economies to renewable energy systems [
20]. Despite ambitious national policies, challenges such as high investment costs, technological limitations, and entrenched oil-based economic structures hinder rapid transformation [
2].
At the same time, innovative sustainability strategies—including carbon capture technologies, green hydrogen, and smart infrastructure—offer pathways for mitigating climate risks while promoting economic resilience. Innovation theory suggests that technological breakthroughs, institutional adaptation, and market-driven solutions are central to achieving long-term environmental sustainability [
19]. Middle Eastern economies increasingly integrate circular economy principles and digital sustainability tools to reduce carbon footprints, enhance resource efficiency, and address environmental challenges such as urbanization and water scarcity [
43].
These three pillars—governance, renewable energy transition, and innovation—are deeply interconnected. Effective governance not only establishes regulatory frameworks and financial incentives for renewable energy adoption but also ensures that technological innovations are strategically implemented to support sustainability goals. In turn, successful renewable energy transitions and sustainability innovations reinforce governance by providing proof of concept for long-term environmental policies and encouraging further institutional reforms. Without strong governance mechanisms, renewable energy initiatives may remain underfunded, and sustainability innovations may fail to reach full-scale implementation [
34].
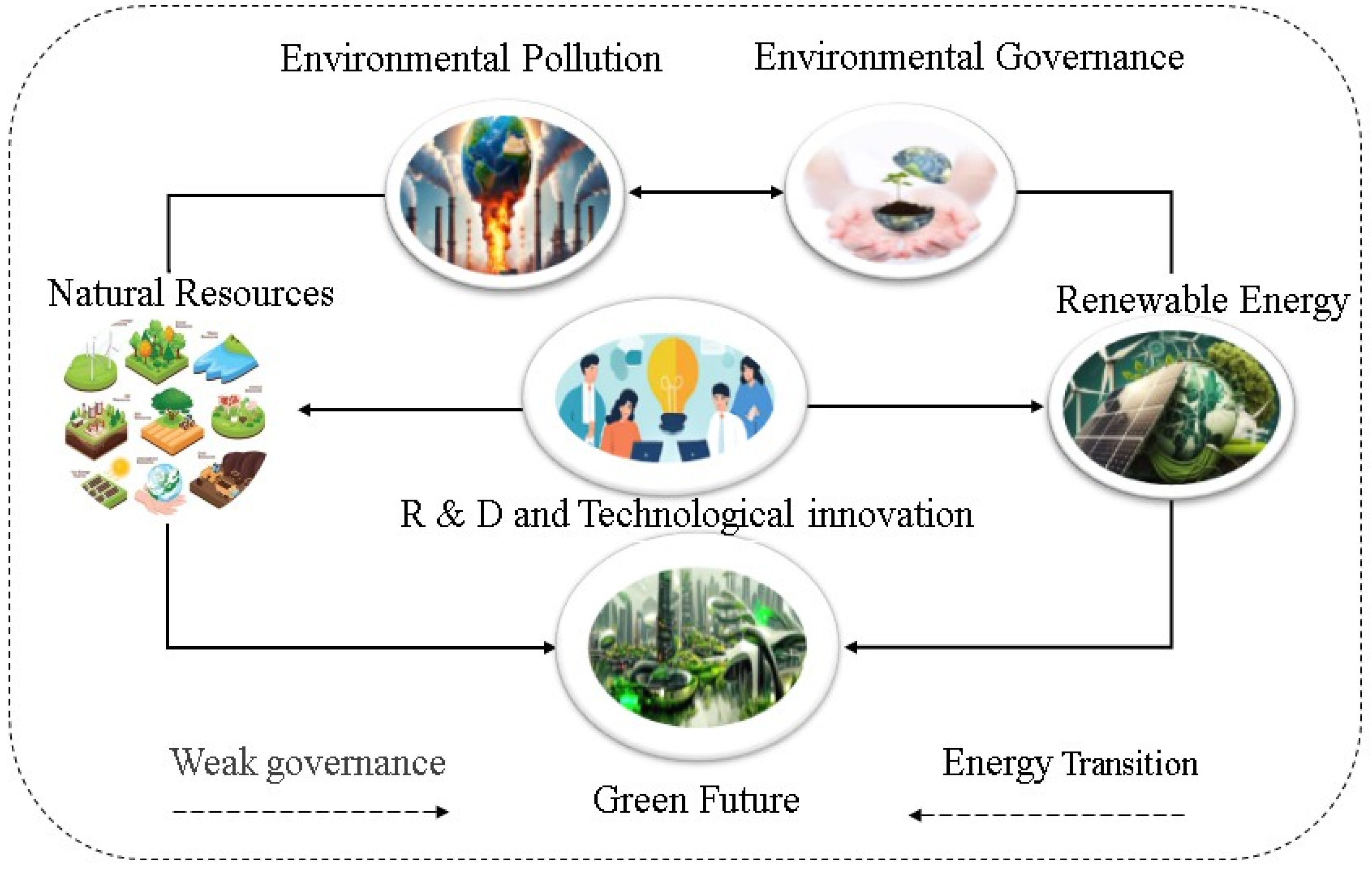
Figure 3 illustrates how environmental governance, pollution control, renewable energy, and natural resources shape a sustainable future. Governance structures drive energy transitions, resource management, and sustainability efforts, while renewable energy adoption and innovation improve governance by influencing policy. Research and technological advancements act as moderators, enhancing the effectiveness of renewable energy and natural resources in achieving environmental goals. The model highlights the interconnected feedback loop where governance impacts sustainability, and innovation accelerates green progress through energy strategies and policy improvements.
2.2. Theoretical Framework
The Saudi and Middle East Green Initiatives represent a transformative policy shift in historically fossil fuel-dependent economies, aligning with the broader global energy transition movement. The energy transition model serves as a foundational theory for understanding this shift, as it describes how economies move from carbon-intensive energy systems to renewables through technological, institutional, and policy transformations [
44]. This transition involves not only technological innovation but also changes in economic incentives, governance structures, and social acceptance of renewable energy solutions [
45,
46].
A key theoretical underpinning of this shift is environmental governance theory, which highlights the role of institutional quality, regulatory enforcement, and policy coordination in shaping sustainability outcomes [
41]. Strong governance ensures that renewable energy policies are effectively implemented, compliance is enforced, and investments in sustainability are strategically allocated. In Saudi Arabia, for instance, government-led initiatives such as Vision 2030 and SGI demonstrate how governance can drive systemic energy transformations [
13]. However, the region still faces institutional challenges, such as weak cross-border collaboration, policy inconsistencies, and slow regulatory adaptation [
2].
Moreover, innovation theory provides a complementary perspective, emphasizing that technological advancements and market-based solutions are essential for achieving sustainable transitions [
18]. Innovations such as solar PV efficiency improvements, energy storage breakthroughs, and AI-driven grid management play a pivotal role in ensuring that the energy transition is both technologically viable and economically competitive [
47]. These advancements are not isolated but are deeply influenced by governance and policy frameworks, which determine the pace of adoption and diffusion [
48].
The integration of these three theoretical pillars—energy transition, environmental governance, and innovation—creates a holistic analytical framework for assessing the effectiveness of Saudi and Middle East Green Initiatives. A key insight from transition studies is that successful energy shifts are not purely technological but also socio-political, requiring public support, economic incentives, and robust governance structures [
46]. The challenge in the Middle East lies in navigating the complexities of economic diversification while maintaining political and financial stability [
22,
49].
By adopting a multidimensional theoretical framework, this study seeks to understand not only the technical feasibility of renewable energy transitions but also the governance and innovation strategies necessary to sustain these efforts. The success of these initiatives depends on whether environmental policies, institutional frameworks, and market-driven innovations can align to create a self-reinforcing cycle of sustainable transformation [
45].
5. Conclusions and Policy Implications
This study examines the roles of environmental governance, renewable energy transition, economic growth, and natural resource abundance in driving green innovations across 13 Middle Eastern countries from 1990 to 2023. Using a panel dataset, we first detected cross-sectional dependency (CSD) through Frees, Friedman, and Pesaran CSD tests. Consequently, second-generation unit root tests were employed to confirm data stationarity and address the issue of CSD. Both first- and second-generation cointegration tests were utilized to validate long-run relationships among the variables. The analysis relied on the CS-ARDL model as the baseline, with PMG-ARDL, AMG, and CCEMG estimators used to corroborate the findings.
The results reveal that environmental governance, economic growth, total population, and natural resource abundance consistently exert a positive influence on green innovation in both the short and long term. In contrast, the human development index and environmental pollution negatively affect green innovation, with these adverse effects becoming significant only in the long run. This pattern suggests that, while governance, economic expansion, and demographic dynamics stimulate innovation, rising human development may at times prioritize immediate economic gains over sustainability goals, while persistent pollution progressively undermines innovation capacity over time.
Based on the findings of this study, the following policy recommendations are proposed to promote green innovation in the Middle Eastern region: First, it is imperative for governments to implement robust environmental regulations and policies that incentivize sustainable practices. Establishing transparent monitoring systems and enforcing compliance can create an environment conducive to green innovation. Second, policymakers should prioritize investments in renewable energy infrastructure, including solar, wind, and hydropower. The provision of subsidies, tax incentives, and the establishment of public–private partnerships can encourage the adoption of clean energy technologies. Third, it is recommended to redirect revenues from natural resource exploitation toward funding green innovation projects. The establishment of sovereign wealth funds or green investment funds could facilitate support for research and development in sustainable technologies. Fourth, it is essential to integrate green growth strategies into national development plans. Industries should be encouraged to adopt eco-friendly practices through grants, low-interest loans, and carbon pricing mechanisms. Fifth, stricter pollution control measures should be implemented, along with investments in waste management systems. Promoting circular economy models would contribute to waste reduction and resource efficiency. Sixth, aligning human capital development programs with sustainability goals is crucial. Incorporating green skills training and environmental education into curricula can foster a workforce capable of driving green innovation. Seventh, the launch of public awareness campaigns to highlight the benefits of green innovation is necessary. Encouraging community participation in sustainability initiatives can help build a culture of environmental responsibility. Finally, it is advisable for Middle Eastern countries to collaborate on regional green innovation initiatives, sharing knowledge, technology, and best practices to address common environmental challenges. By adopting these policies, Middle Eastern economies can leverage their strengths, address existing challenges, and position themselves as leaders in green innovation and sustainable development.