The Future Climate Change Projections for the Hengduan Mountain Region Based on CMIP6 Models
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Research Region, Data and Methodology
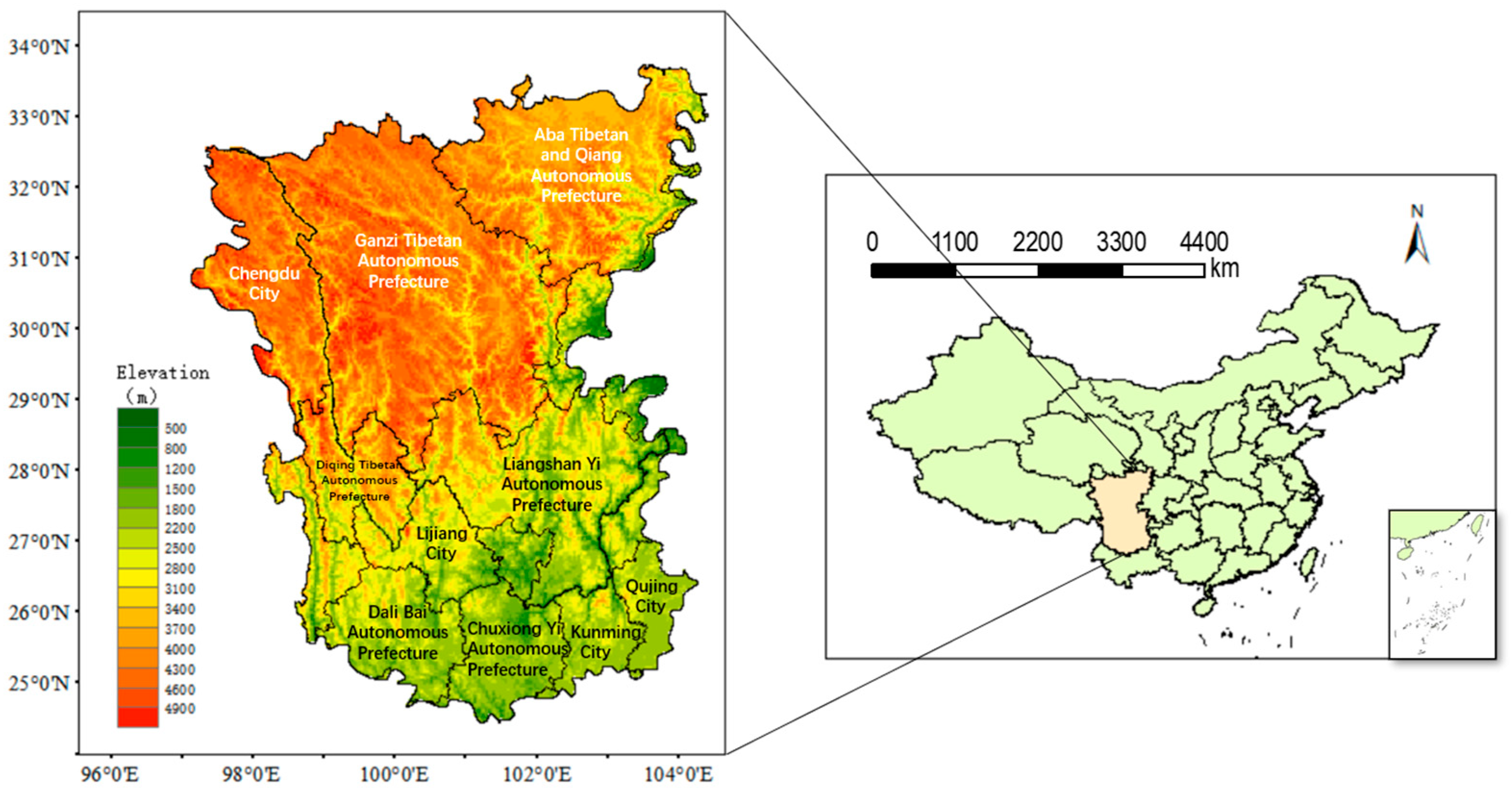
2.1. Overview of the Study Area
2.2. Data and Methods
2.2.1. Overall Technical Route
2.2.2. Data Sources
2.2.3. Data Resolution Standardization
2.2.4. Ensemble Strategy and Threshold Setting
2.2.5. Multi-Model Ensemble (MME)
2.2.6. Inverse Distance Weighting (IDW) Interpolation Method
2.2.7. Seasonal Classification Criteria
3. Results and Analysis
3.1. Current Climate Analysis
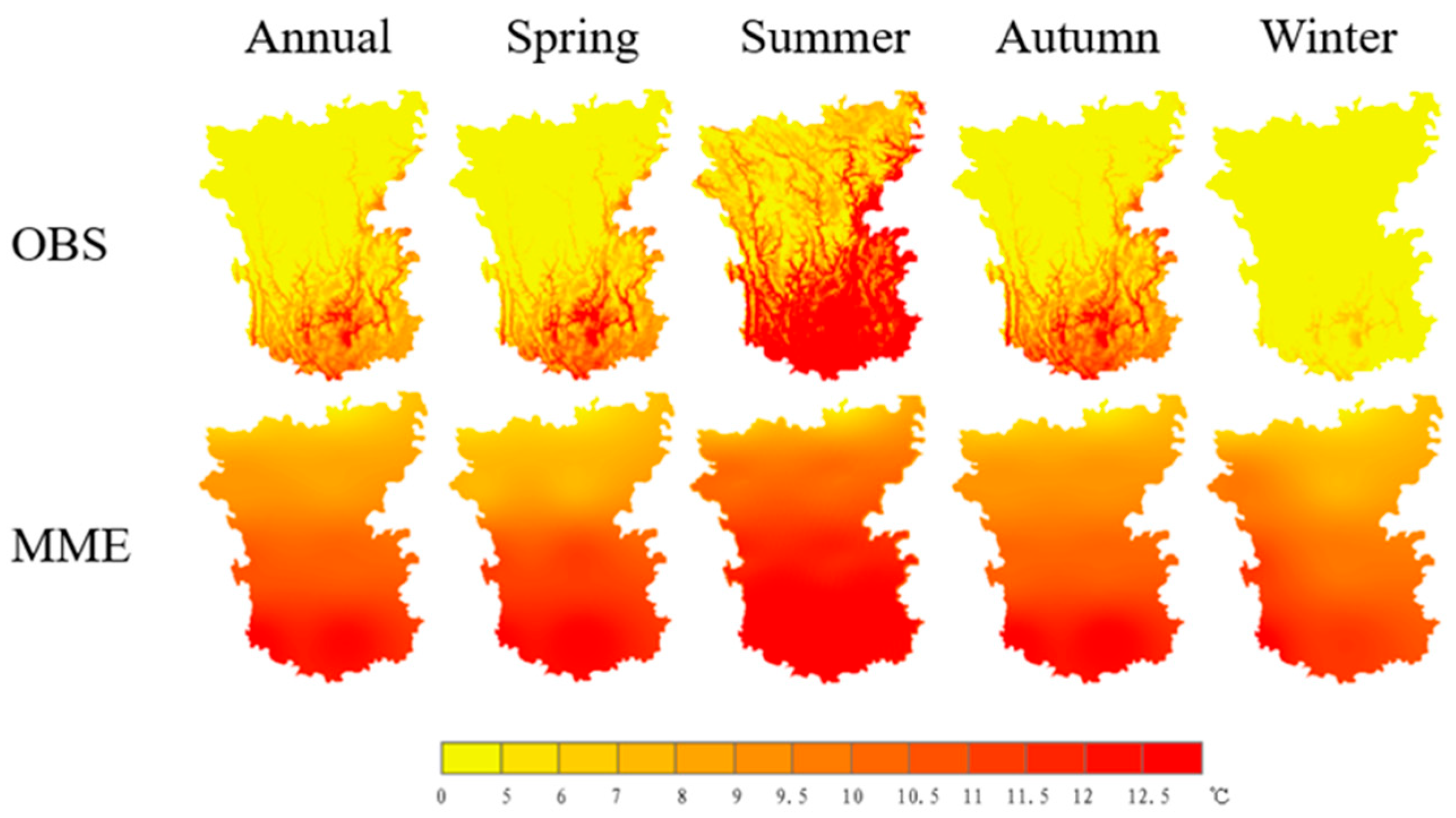
3.1.1. Spatial Distribution Characteristics of Temperature and Precipitation
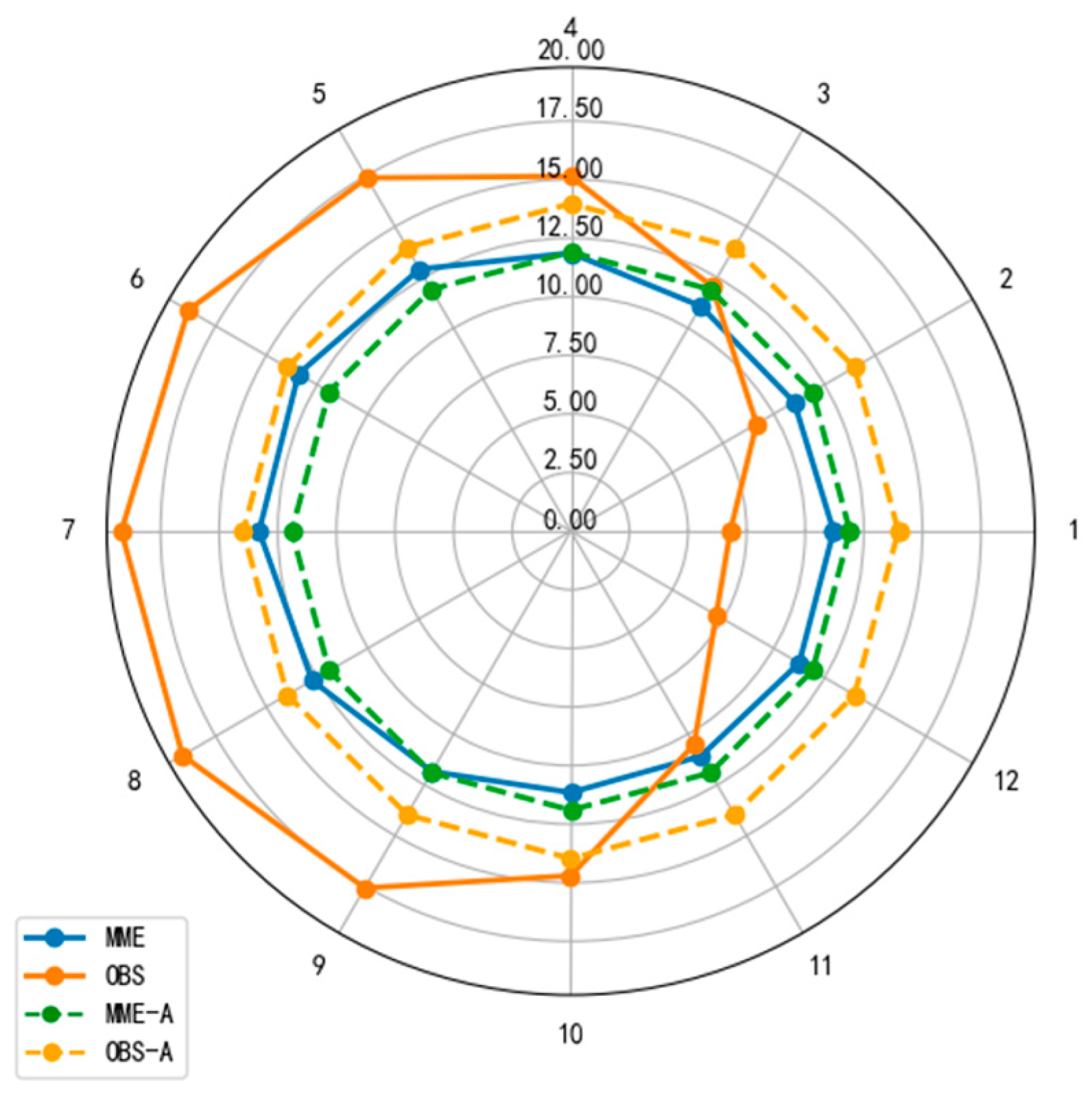
3.1.2. Annual Cyclical Variation in Temperature and Precipitation
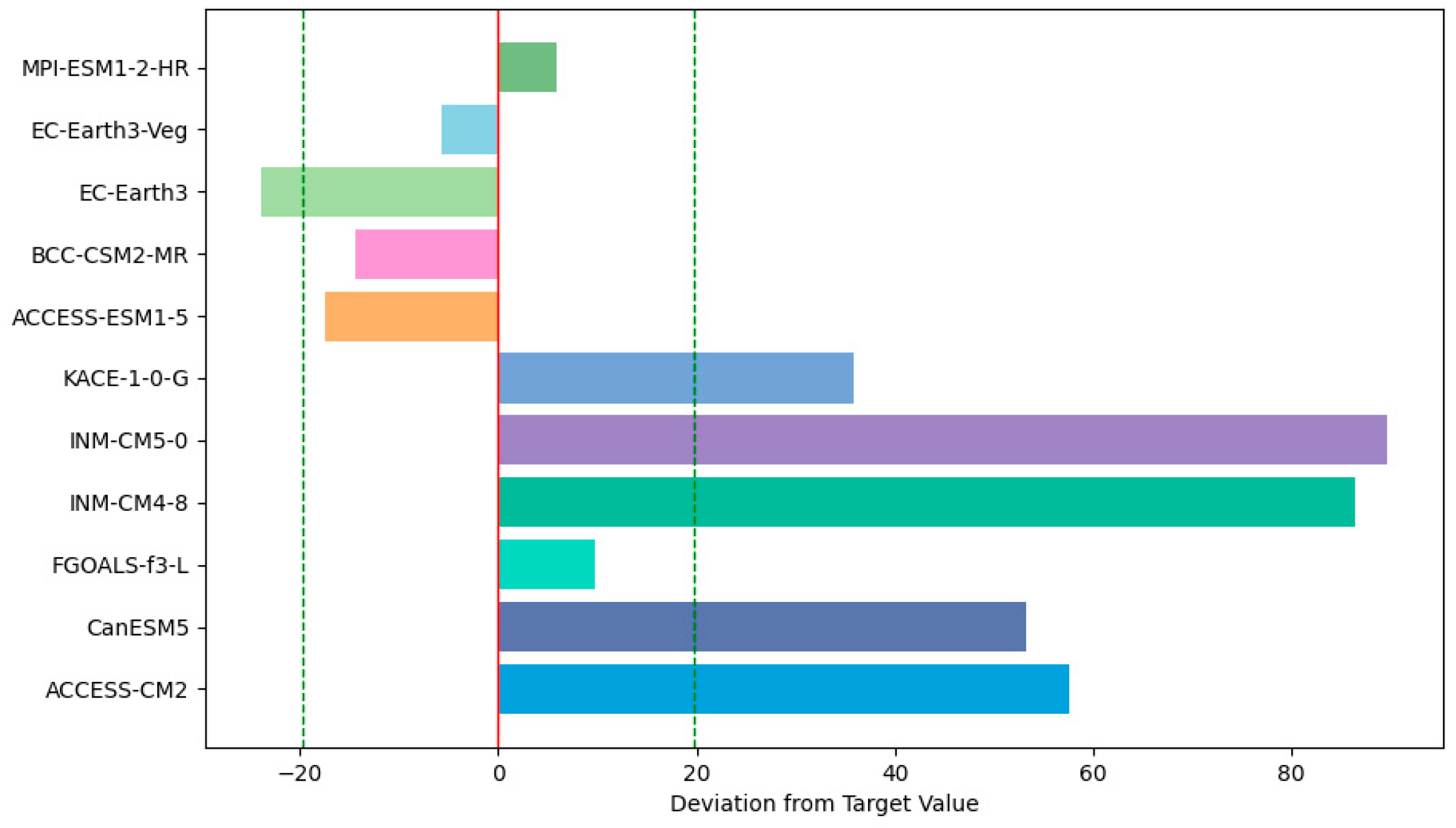
3.1.3. Comprehensive Evaluation of Model Performance
3.2. Model Selection
3.2.1. Temperature Simulation Performance Evaluation
3.2.2. Precipitation Simulation Performance Evaluation
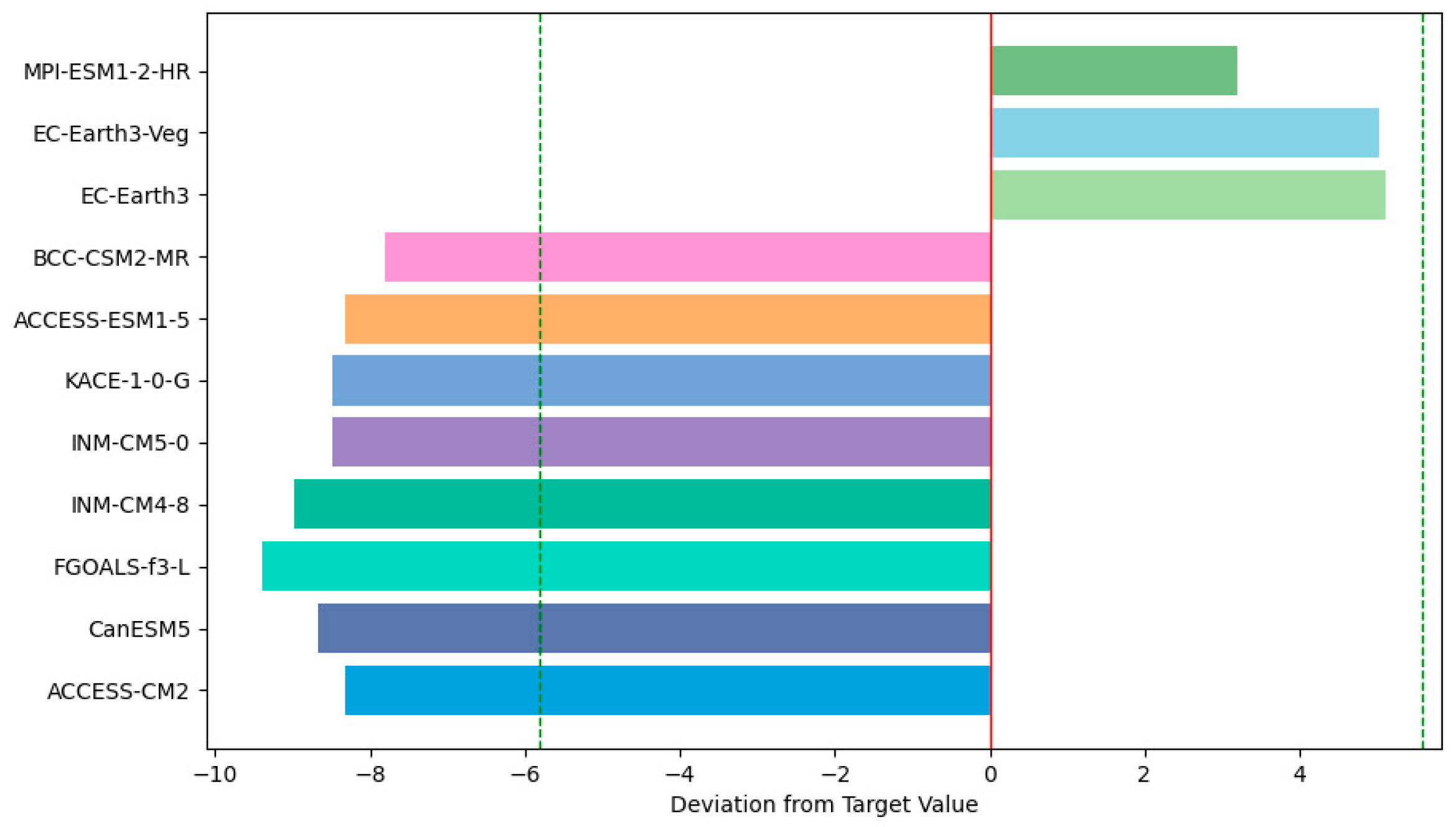
3.2.3. Multi-Model Ensemble Construction
3.2.4. Uncertainty Quantification and Directions for Improvement
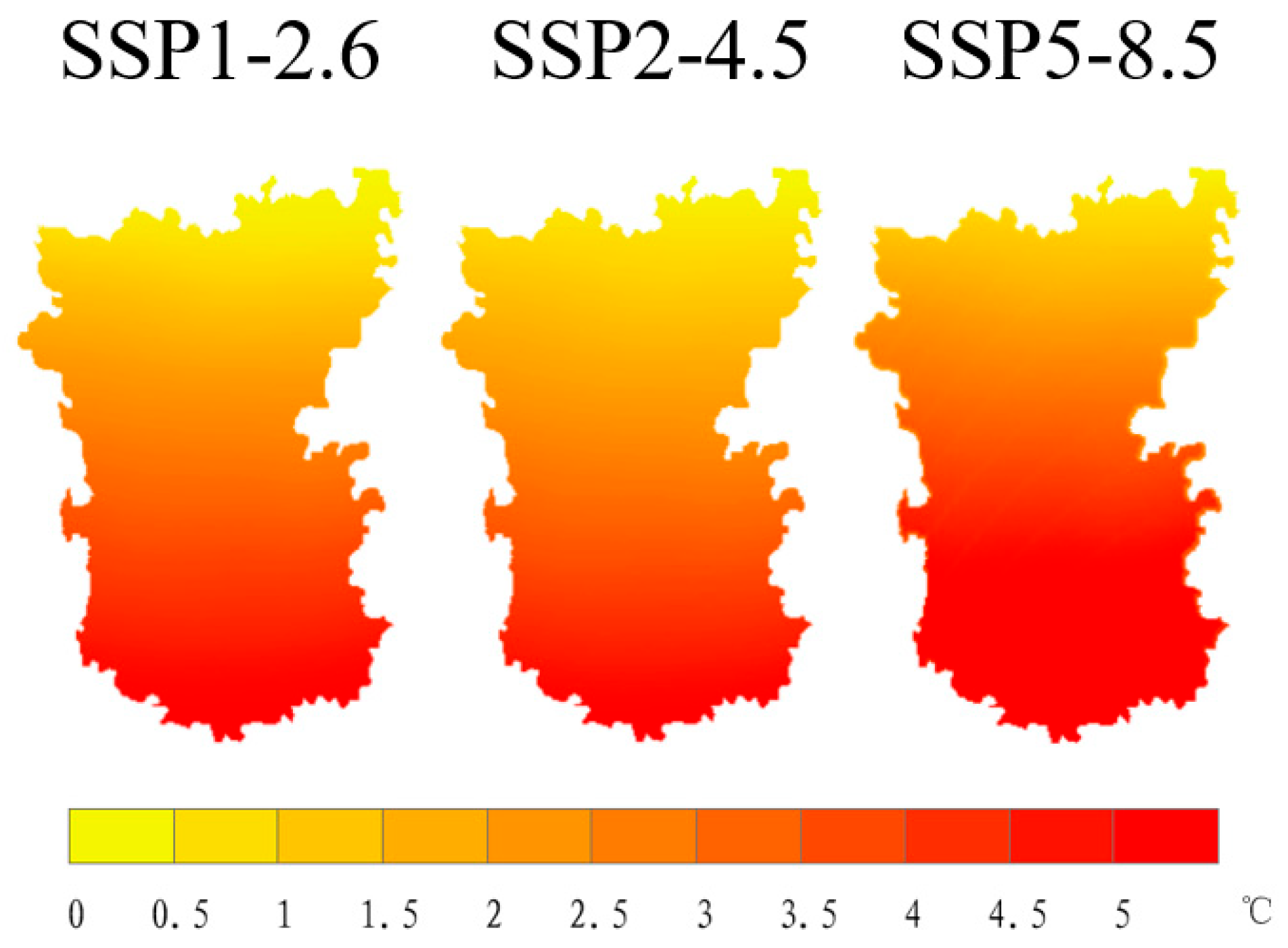
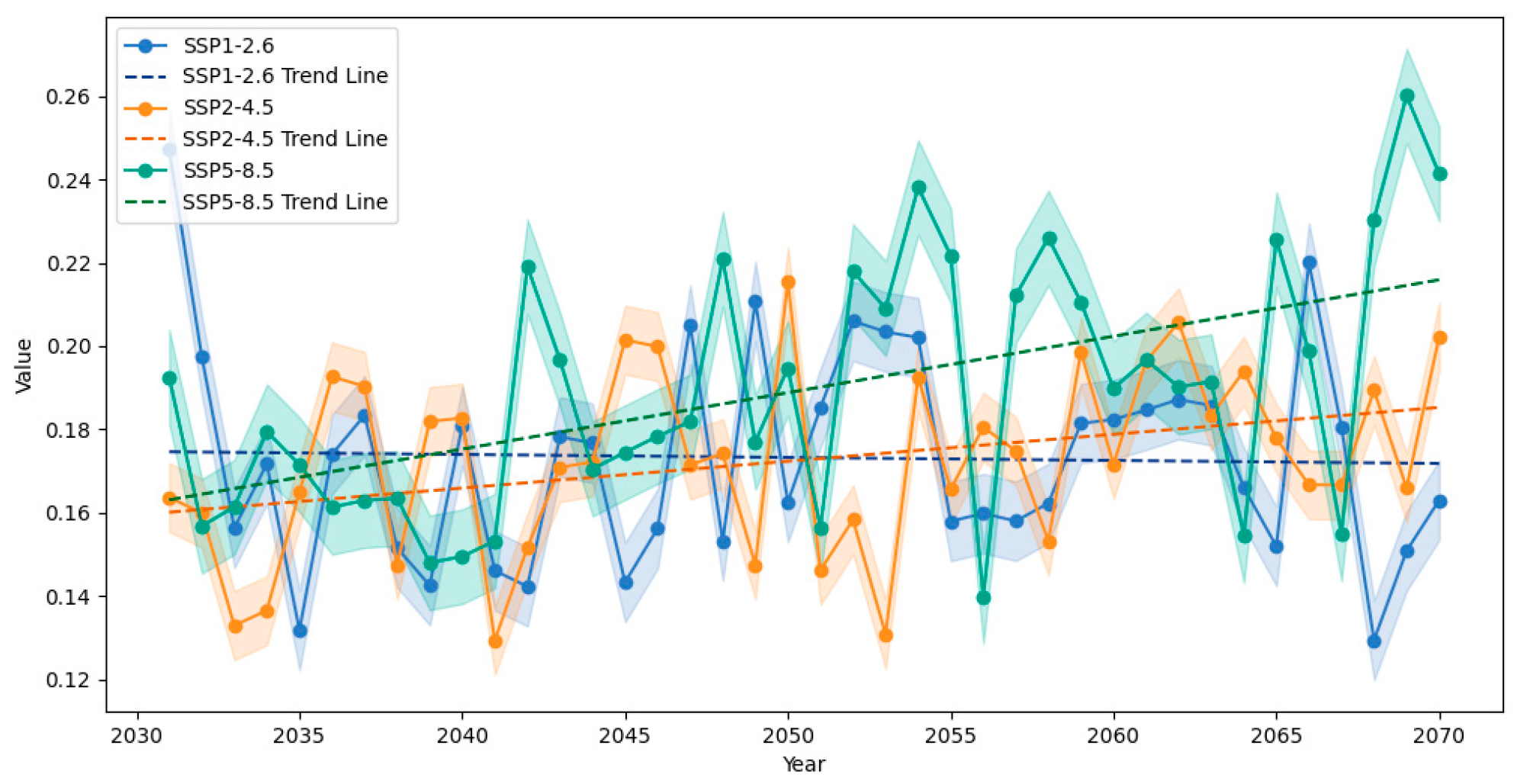
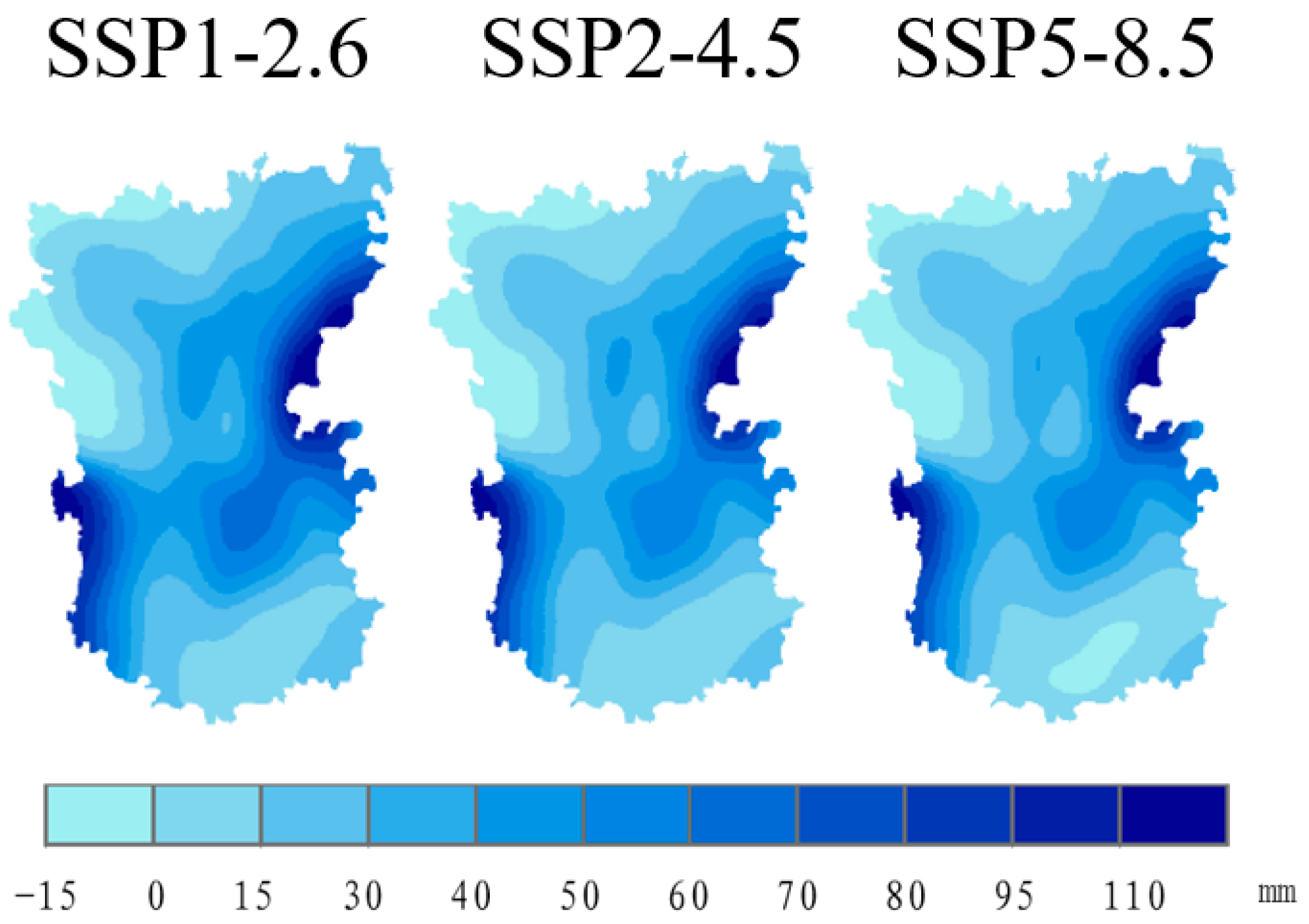
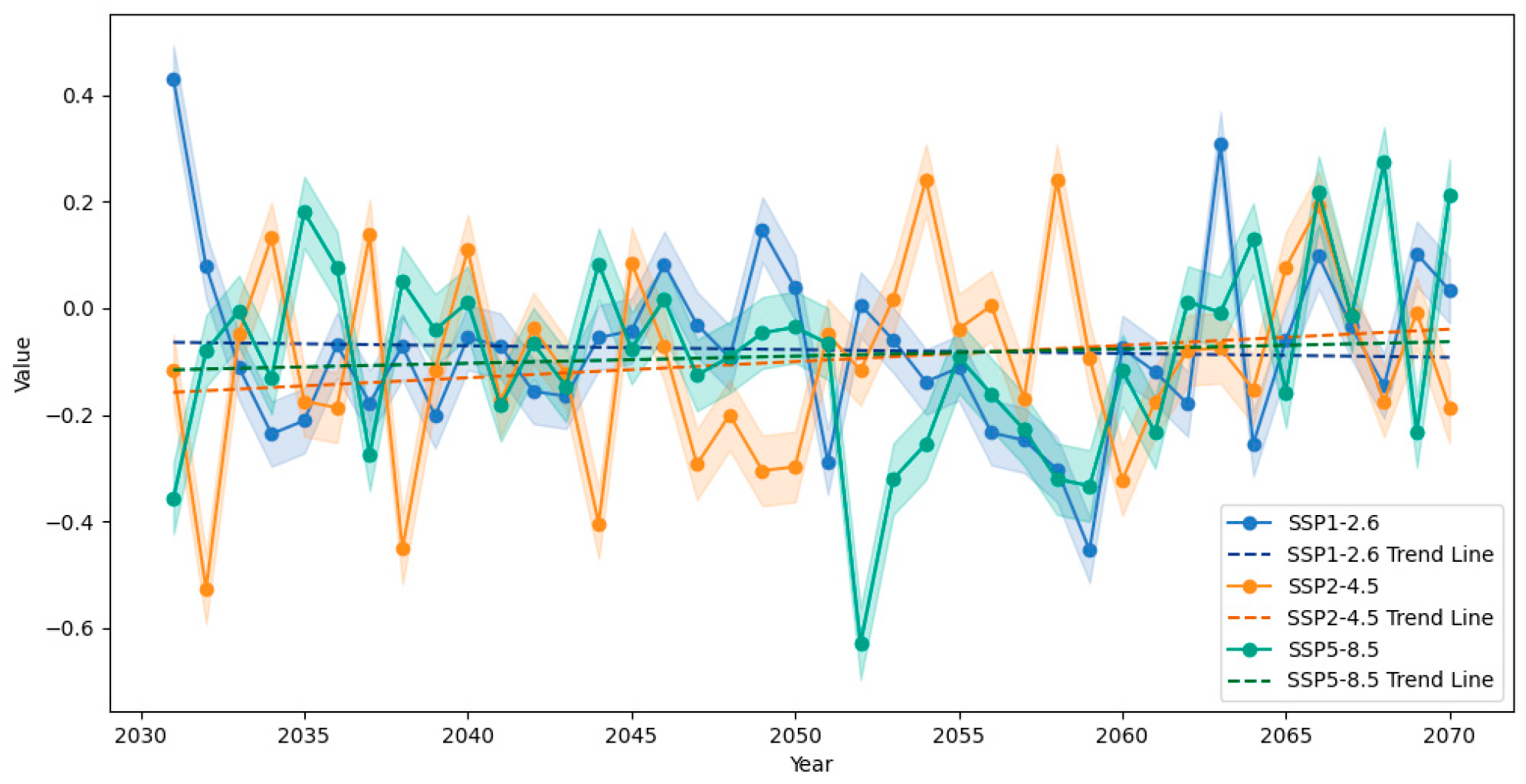
3.3. Future Changes in Annual Average Temperature and Precipitation
3.3.1. Spatial Patterns and Temporal Evolution of Temperature Changes
3.3.2. Spatial Distribution and Dynamic Mechanisms of Precipitation Changes
3.3.3. Physical Attribution of Climate Response
4. Discussion
4.1. Limitations of CMIP6 Model Performance and Improvement Paths
4.2. Cascade Effects of Climate Change on Regional Systems
4.3. Challenges and Solutions for Sustainable Implementation in the Hengduan Mountains
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Maletjane, M.; Manandhar, R. Climate Change Adaptation in Mountain Regions. In Safeguarding Mountain Social-Ecological Systems; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2024; pp. 109–114. [Google Scholar]
- Rogora, M.; Frate, L.; Carranza, M.L.; Freppaz, M.; Stanisci, A.; Bertani, I.; Bottarin, R.; Brambilla, A.; Canullo, R.; Carbognani, M. Assessment of Climate Change Effects on Mountain Ecosystems through a Cross-Site Analysis in the Alps and Apennines. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 624, 1429–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pepin, N.C.; Arnone, E.; Gobiet, A.; Haslinger, K.; Kotlarski, S.; Notarnicola, C.; Palazzi, E.; Seibert, P.; Serafin, S.; Schöner, W.; et al. Climate Changes and Their Elevational Patterns in the Mountains of the World. Rev. Geophys. 2022, 60, e2020RG000730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telwala, Y.; Brook, B.W.; Manish, K.; Pandit, M.K. Climate-Induced Elevational Range Shifts and Increase in Plant Species Richness in a Himalayan Biodiversity Epicentre. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e57103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khandu; Forootan, E.; Schumacher, M.; Awange, J.L.; Müller Schmied, H. Exploring the Influence of Precipitation Extremes and Human Water Use on Total Water Storage (TWS) Changes in the Ganges-Brahmaputra-Meghna River Basin. Water Resour. Res. 2016, 52, 2240–2258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patton, A.I.; Rathburn, S.L.; Capps, D.M. Landslide Response to Climate Change in Permafrost Regions. Geomorphology 2019, 340, 116–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Climate Change 2022: Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability. Available online: https://www.ipcc.ch/report/ar6/wg2/about/factsheets (accessed on 13 February 2025).
- Alizadeh, O. Advances and Challenges in Climate Modeling. Clim. Change 2022, 170, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, S.; Takemi, T.; Maity, S. Precipitation and Temperature Climatologies over India: A Study with AGCM Large Ensemble Climate Simulations. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoof, J.T.; Pryor, S.C. Assessing the Fidelity of AOGCM-Simulated Relationships between Large-Scale Modes of Climate Variability and Wind Speeds. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 9719–9734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touzé-Peiffer, L.; Barberousse, A.; Le Treut, H. The Coupled Model Intercomparison Project: History, Uses, and Structural Effects on Climate Research. WIREs Clim. Change 2020, 11, e648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, B.C.; Carter, T.R.; Ebi, K.; Harrison, P.A.; Kemp-Benedict, E.; Kok, K.; Kriegler, E.; Preston, B.L.; Riahi, K.; Sillmann, J.; et al. Achievements and Needs for the Climate Change Scenario Framework. Nat. Clim. Change 2020, 10, 1074–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Lu, H.; Yang, K.; Jiang, R.; Yang, Y.; Wang, W.; Zhang, X. Projection of China’s Future Runoff Based on the CMIP6 Mid-High Warming Scenarios. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2023, 66, 528–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, T.; Li, C.; Tian, F. Evaluation of Temperature and Precipitation Simulations in CMIP6 Models Over the Tibetan Plateau. Earth Space Sci. 2021, 8, e2020EA001620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalande, M.; Ménégoz, M.; Krinner, G.; Naegeli, K.; Wunderle, S. Climate Change in the High Mountain Asia in CMIP6. Earth Syst. Dyn. 2021, 12, 1061–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seker, M.; Gumus, V. Projection of Temperature and Precipitation in the Mediterranean Region through Multi-Model Ensemble from CMIP6. Atmos. Res. 2022, 280, 106440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Sun, W.; Wu, J.; Che, J.; Liu, M.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Huai, B.; Wang, Y.; Wang, L. Evaluation and Projection of Precipitation in CMIP6 Models over the Qilian Mountains, China. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 4350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Fan, G. Assessment and Projection of Elevation-Dependent Warming over the Tibetan Plateau by CMIP6 Models. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2022, 147, 1713–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Zhang, G.; Wang, J.; Li, C.; Wu, S.; Li, Y. Spatiotemporal Variation of Flash Floods in the Hengduan Mountains Region Affected by Rainfall Properties and Land Use. Nat. Hazards 2022, 111, 465–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Zhang, X.; Li, X. Evaluation of the Applicability of Three Methods for Climatic Spatial Interpolation in the Hengduan Mountains Region. J. Hydrometeorol. 2022, 24, 35–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Miao, S.; Xie, G.; Guo, X.; Chen, Z.; Favre, A. Contrasting Floristic Diversity of the Hengduan Mountains, the Himalayas and the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau Sensu Stricto in China. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2020, 8, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Jia, Y.W. Annual, Seasonal and Monthly Variation Characteristics of Temperature and Precipitation in the Hengduan Mountains Region. J. Mt. Sci. 2018, 36, 171–183. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.; Wang, G.; Guo, L.; Sun, J.; Sun, X. Evaluation of Three Gridded Precipitation Products in Characterizing Extreme Precipitation over the Hengduan Mountains Region in China. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Li, B.L.; Yuan, Y.C.; Gao, X.Z.; Jiang, Y.H.; Liu, Y. Spatio-Temporal Precipitation Dataset in Hengduan Mountains (1998–2012). J. Glob. Change Data Discov. 2019, 3, 168–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.; Li, J.; An, W.; Qin, N.; Song, H.; Liu, Y. The Recent High Occurrence of Spring Atmospheric Droughts over Central Hengduan Mountains Is Unprecedented in 669-Year Tree-Ring Records. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2024, 649, 112318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Wang, L.; Yang, R.; Yang, M.; Gao, R. Temporal and Spatial Distribution of Maximum Daily Precipitation in Hengduan Mountainous Region of China and Its Probability Characteristics. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2020, 25, 05020039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Guo, B.; Zhang, R.; Zang, W.; Wei, C.; Wu, H.; Yang, X.; Zhen, X.; Li, X.; Zhang, D.; et al. Quantitatively Determine the Dominant Driving Factors of the Spatial—Temporal Changes of Vegetation NPP in the Hengduan Mountain Area during 2000–2015. J. Mt. Sci. 2021, 18, 427–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, E.; Wang, Y. Attribution Analysis for Water Yield Service Based on the Geographical Detector Method: A Case Study of the Hengduan Mountain Region. J. Geogr. Sci. 2020, 30, 1005–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.; Fu, W.; Tao, Y.; Li, M.; Wang, L. Dynamics of the Alpine Timberline and Its Response to Climate Change in the Hengduan Mountains over the Period 1985–2015. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 135, 108589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, W.; Chen, F.; Davi, N.K.; Zhang, H.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, X.; Gao, Z. Little Ice Age Cooling in the Western Hengduan Mountains, China: A 600-Year Warm-Season Temperature Reconstruction from Tree Rings. Clim. Dyn. 2024, 62, 773–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Yang, M.; Chang, R.; Zhan, Q.; Li, Z.-L. Surface Warming Trend Analysis Based on MODIS/Terra Land Surface Temperature Product at Gongga Mountain in the Southeastern Tibetan Plateau. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2021, 126, e2020JD034205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zu, K.; Chen, F.; Li, Y.; Shrestha, N.; Fang, X.; Ahmad, S.; Nabi, G.; Wang, Z. Climate Change Impacts Flowering Phenology in Gongga Mountains, Southwest China. Plant Divers. 2024, 46, 774–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Y.; Ree, R.H. Uplift-Driven Diversification in the Hengduan Mountains, a Temperate Biodiversity Hotspot. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E3444–E3451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, L.; Dai, E.; Guan, M.; Zhang, B. A Novel Approach for the Identification of Conservation Priority Areas in Mountainous Regions Based on Balancing Multiple Ecosystem Services—A Case Study in the Hengduan Mountain Region. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2022, 38, e02195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, C.X.; Jiang, C.; Zhang, X.Y. Simulation and Projection of Temperature in Southwest China by CMIP6 Models. J. China Agric. Meteorol. 2022, 43, 597–611. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.T.; Qu, Z.Y.; Wang, B.; Suacho. Downscaled Precipitation Projection Analysis of Summers in Liaoning Based on CMIP6 Models. Henan Sci. (In Chinese). 2023, 41, 1469–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Shen, Y.-J.; Wang, L.; Guo, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, X. Multi-Model Ensemble Enhances the Spatiotemporal Comprehensive Performance of Regional Climate in China. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.; Ahn, J.-B.; Kryjov, V.N.; Lee, W.-S.; Kim, D.-J.; Kumar, A. Assessment of MME Methods for Seasonal Prediction Using WMO LC-LRFMME Hindcast Dataset. Int. J. Climatol. 2020, 41, E2462–E2481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; He, Y.; Wang, C.; Wang, X.; Xin, H.; Zhang, W.; Cao, W. Spatial and Temporal Trends of Temperature and Precipitation during 1960–2008 at the Hengduan Mountains, China. Quat. Int. 2011, 236, 127–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Wang, L.; Yang, R.; Yang, M.; Gao, R. Temporal and Spatial Variation of Precipitation in the Hengduan Mountains Region in China and Its Relationship with Elevation and Latitude. Atmos. Res. 2018, 213, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue-zhao, H.; Dao-yi, G. Interdecadal Change in Western Pacific Subtropical High and Climatic Effects. J. Geogr. Sci. 2002, 12, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, R.; Steger, C.; Sørland, S.; Schär, C. The Impact of Hengduan Mountains Formation on the Regional Monsoon Climate and Extreme Precipitation. In Proceedings of the EGU22, the 24th EGU General Assembly, Online, 23–27 May 2022. EGU22-6986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, Z. Evaluation of Bias Correction Techniques for Generating High-Resolution Daily Temperature Projections from CMIP6 Models. Clim. Dyn. 2023, 61, 3893–3910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D.; Hu, D.; Tian, Z.; Lang, X. Differences between CMIP6 and CMIP5 Models in Simulating Climate over China and the East Asian Monsoon. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2020, 37, 1102–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, Q.; Cai, Z.; Wu, F.; Jiang, Z.; Pepin, N.; Shen, S.S.P. Temperature Dataset of CMIP6 Models over China: Evaluation, Trend and Uncertainty. Clim. Dyn. 2021, 57, 17–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, Z. Assessment of Bias Correction Methods for High Resolution Daily Precipitation Projections with CMIP6 Models: A Canadian Case Study. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2025, 58, 102223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almazroui, M.; Islam, M.N.; Saeed, F.; Saeed, S.; Ismail, M.; Ehsan, M.A.; Diallo, I.; O’Brien, E.; Ashfaq, M.; Martínez-Castro, D.; et al. Projected Changes in Temperature and Precipitation Over the United States, Central America, and the Caribbean in CMIP6 GCMs. Earth Syst. Environ. 2021, 5, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia-wen, L.I.; Yu-lin, Z.; Xing, W.E.I.; Zu-jin, F. Evaluating the Ability of CMIP6 Models in Simulating Precipitation and Temperature in Wanzhou City in the Three Gorges Reservoir. J. Yangtze River Sci. Res. Inst. 2023, 40, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Findell, K.L.; Berg, A.; Gentine, P.; Krasting, J.P.; Lintner, B.R.; Malyshev, S.; Santanello, J.A.; Shevliakova, E. The Impact of Anthropogenic Land Use and Land Cover Change on Regional Climate Extremes. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Hu, Y.; Liu, J. Inter-Model Spreads of the Climatological Mean Hadley Circulation in AMIP/CMIP6 Simulations. Clim. Dyn. 2023, 61, 4411–4427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samset, B.H.; Fuglestvedt, J.S.; Lund, M.T. Delayed Emergence of a Global Temperature Response after Emission Mitigation. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danhong, D.; Huang, G.; Tao, W.; Wu, R.; Hu, K.; Li, C. Interannual Variation of Precipitation over the Hengduan Mountains during Rainy Season. Int. J. Climatol. 2018, 38, 2112–2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Dey, S.; Das, S.; Riemer, N.; Giuliani, G.; Ganguly, D.; Venkataraman, C.; Giorgi, F.; Tripathi, S.N.; Ramachandran, S.; et al. Towards an Improved Representation of Carbonaceous Aerosols over the Indian Monsoon Region in a Regional Climate Model: RegCM. Geosci. Model Dev. 2023, 16, 2119–2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Number | Model Name | Spatial Resolution | Institution | Selection Criteria |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ACCESS-CM2 | 288 × 180 | CSIRO | Accurately simulate temperature and precipitation in mountainous and high-altitude regions around Australia, capturing the local climatic characteristics of complex terrains. |
| 2 | ACCESS-ESM1-5 | 512 × 256 | CSIRO | |
| 3 | BCC-CSM2-MR | 384 × 192 | BCC | Excellently simulates the mean climate and inter-annual variability in regions like China’s Qilian Mountains, capturing circulation and precipitation patterns. |
| 4 | CanESM5 | 320 × 160 | CCCma | High-precision simulation of climate in mountainous regions such as the Canadian Rockies, reflecting the impact of mountains on airflow, temperature, and precipitation. |
| 5 | EC-Earth3 | 192 × 145 | EC-Earth-Consortium | Accurately represent the microclimate of mountainous regions such as the European Alps, taking into account vegetation–climate interactions. |
| 6 | EC-Earth3-Veg | 512 × 256 | EC-Earth-Consortium | |
| 7 | FGOALS-f3-L | 192 × 144 | CAS | Accurately simulates the thermal and dynamic effects of regions such as the Tibetan Plateau, reflecting the influence of topography on atmospheric circulation. |
| 8 | INM-CM4-8 | 128 × 64 | INM | Precisely simulate long-term trends in temperature and precipitation in Russian mountainous regions, capturing internal variability within the climate system. |
| 9 | INM-CM5-0 | 192 × 144 | INM | |
| 10 | KACE-1-0-G | 180 × 120 | NIMS-KMA | Effectively simulates meso-scale and micro-scale weather and local climate in mountainous regions such as the Taebaek Mountains in South Korea, capturing extreme weather events. |
| 11 | MPI-ESM1-2-HR | 180 × 120 | MPI-M | Excellently simulates the climate in regions with complex terrains such as the European Alps, meticulously depicting the influence of topography on climate. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bian, C.; Liang, X.; Li, B.; Hu, Z.; Min, X.; Yue, Z. The Future Climate Change Projections for the Hengduan Mountain Region Based on CMIP6 Models. Sustainability 2025, 17, 5306. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17125306
Bian C, Liang X, Li B, Hu Z, Min X, Yue Z. The Future Climate Change Projections for the Hengduan Mountain Region Based on CMIP6 Models. Sustainability. 2025; 17(12):5306. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17125306
Chicago/Turabian StyleBian, Cuihua, Xinlan Liang, Bingchang Li, Zhiqiang Hu, Xiaofan Min, and Zihao Yue. 2025. "The Future Climate Change Projections for the Hengduan Mountain Region Based on CMIP6 Models" Sustainability 17, no. 12: 5306. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17125306
APA StyleBian, C., Liang, X., Li, B., Hu, Z., Min, X., & Yue, Z. (2025). The Future Climate Change Projections for the Hengduan Mountain Region Based on CMIP6 Models. Sustainability, 17(12), 5306. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17125306






