Sustainable Strategy for Microplastic Mitigation: Fe3O4 Acid-Functionalized Magnetic Nanoparticles for Microplastics Removal
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemical Reagents and Analysis
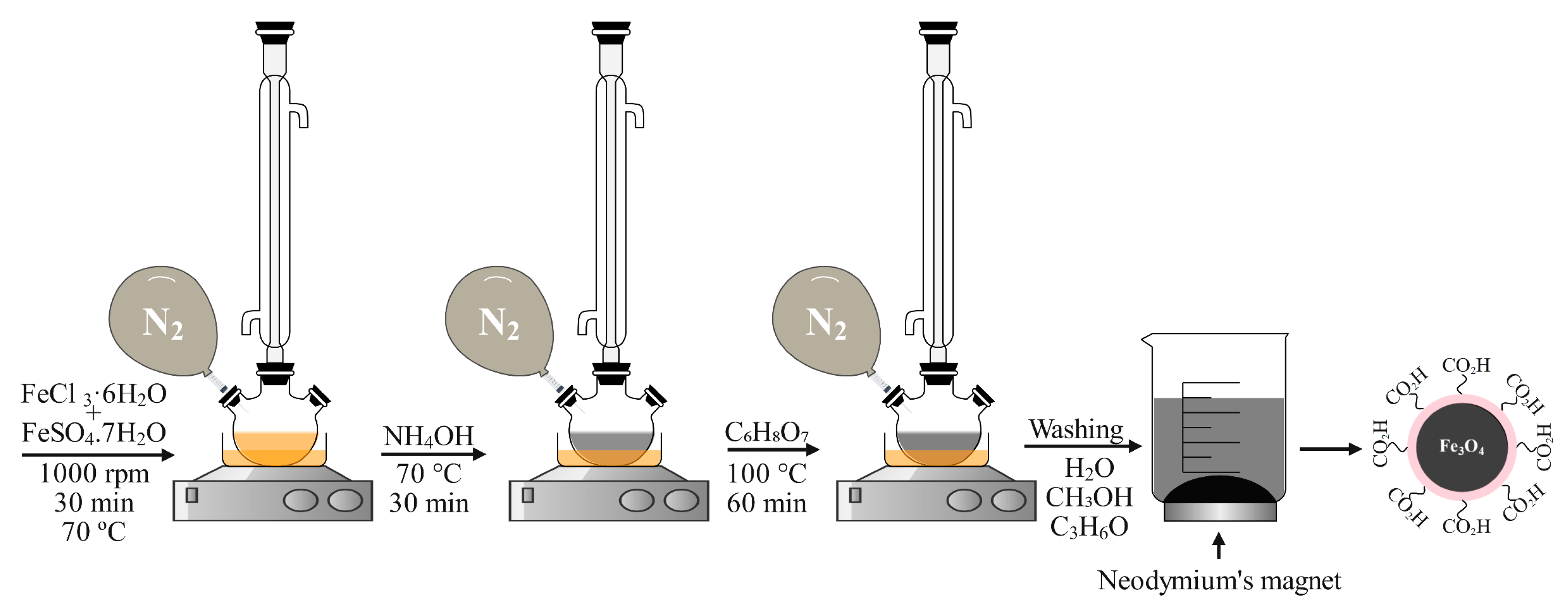
2.2. Synthesis of Magnetic Fe3O4@AC
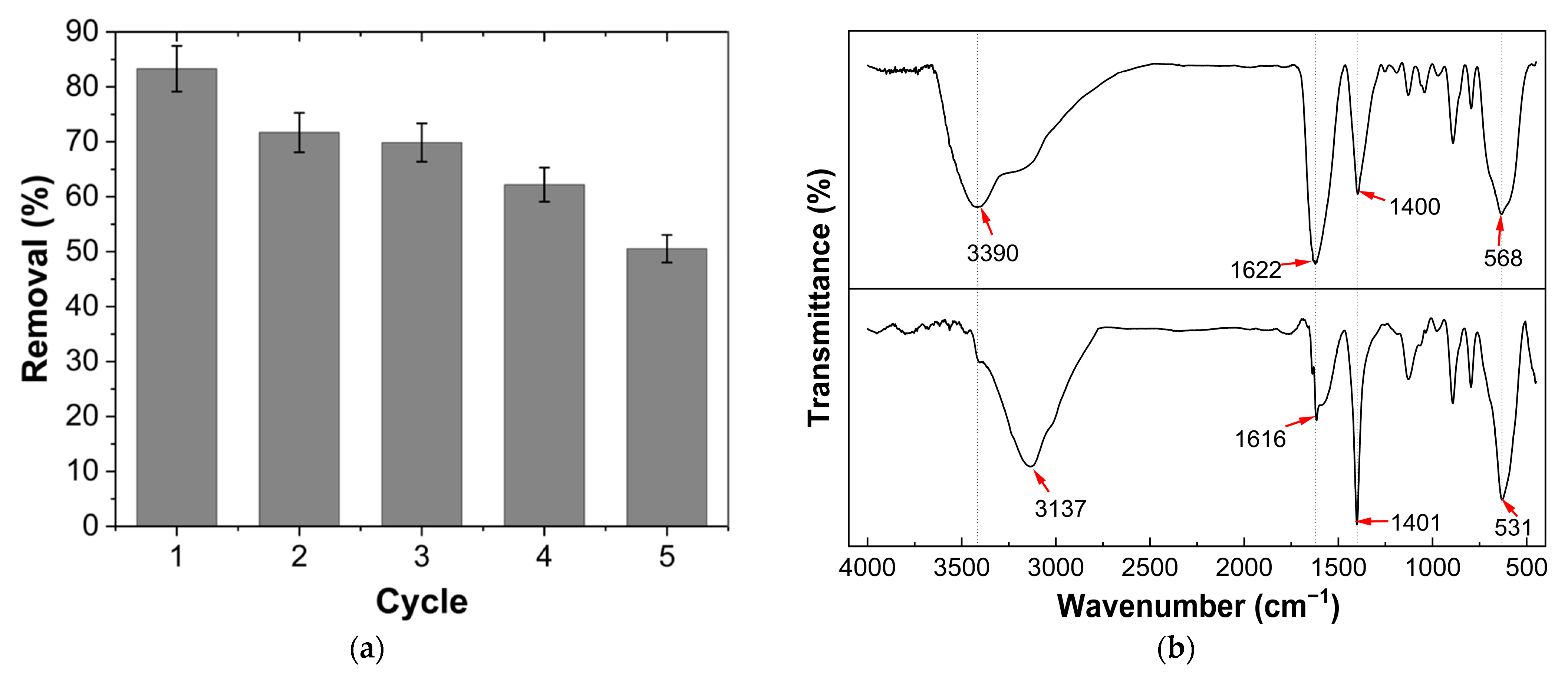
2.3. Characterization of MPs and Fe3O4@AC
2.4. Experimental Procedure for the MPs Removal
2.5. Isothermal and Kinetic Studies
2.6. Reuse Testing
3. Results
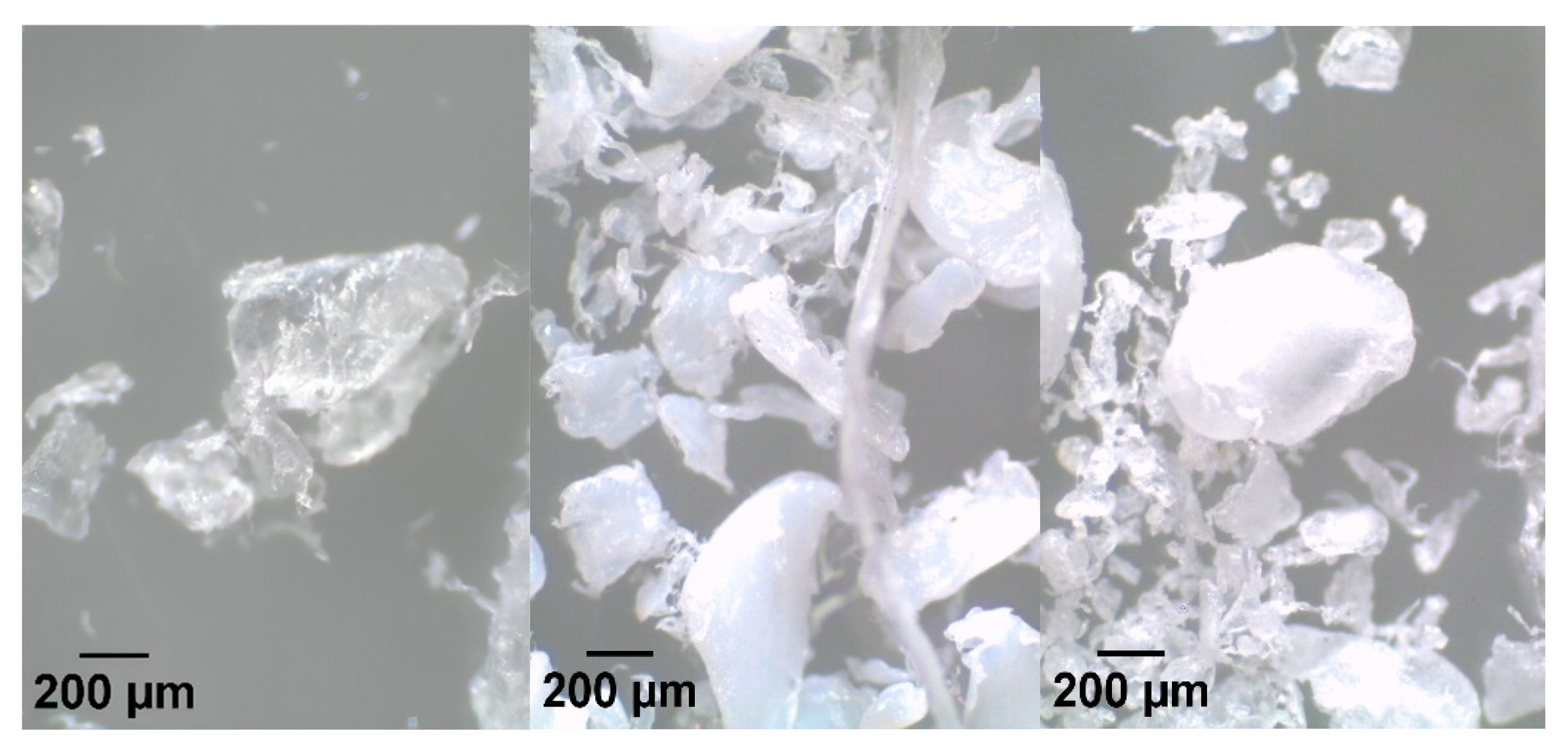
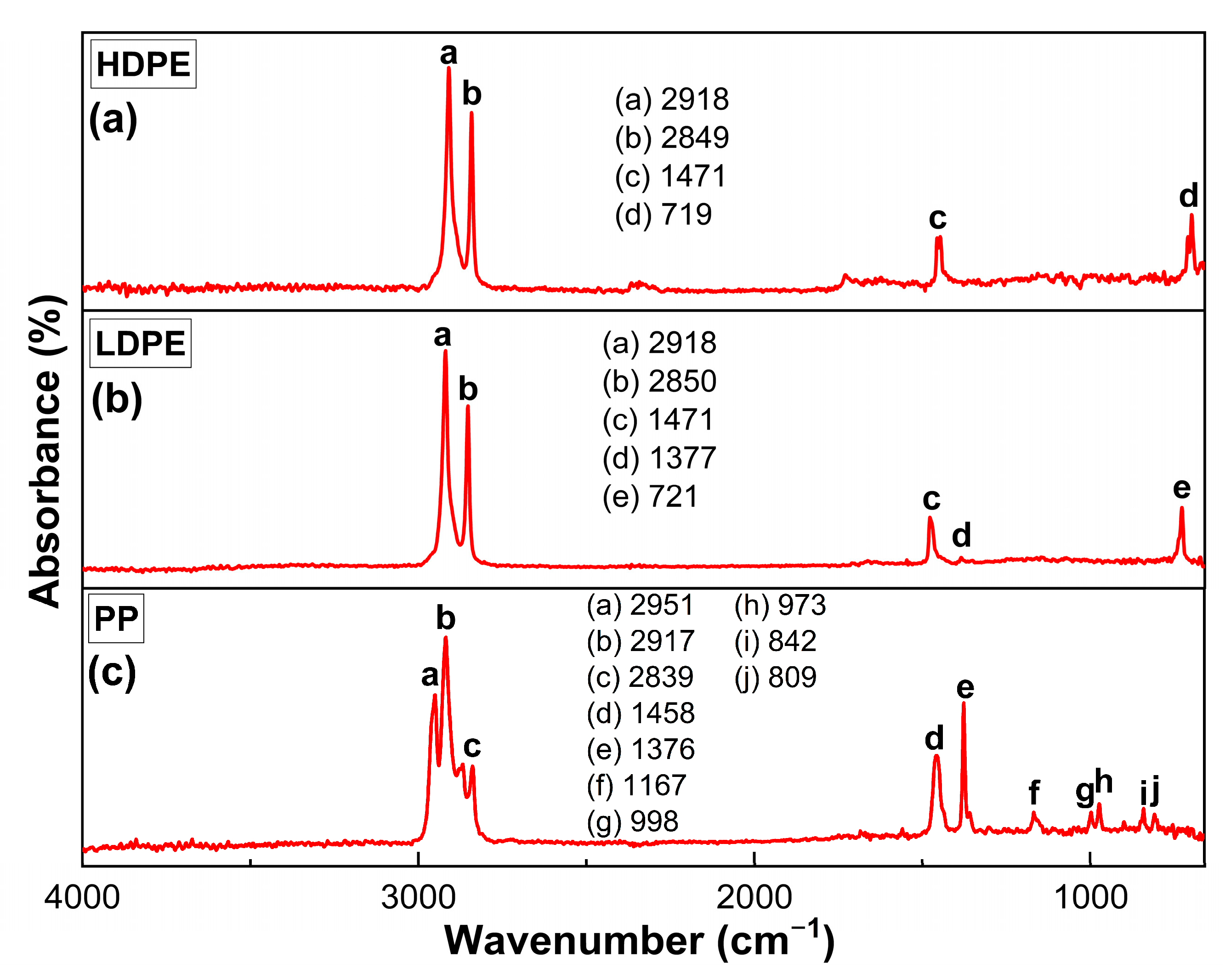
3.1. Characterization of MPs
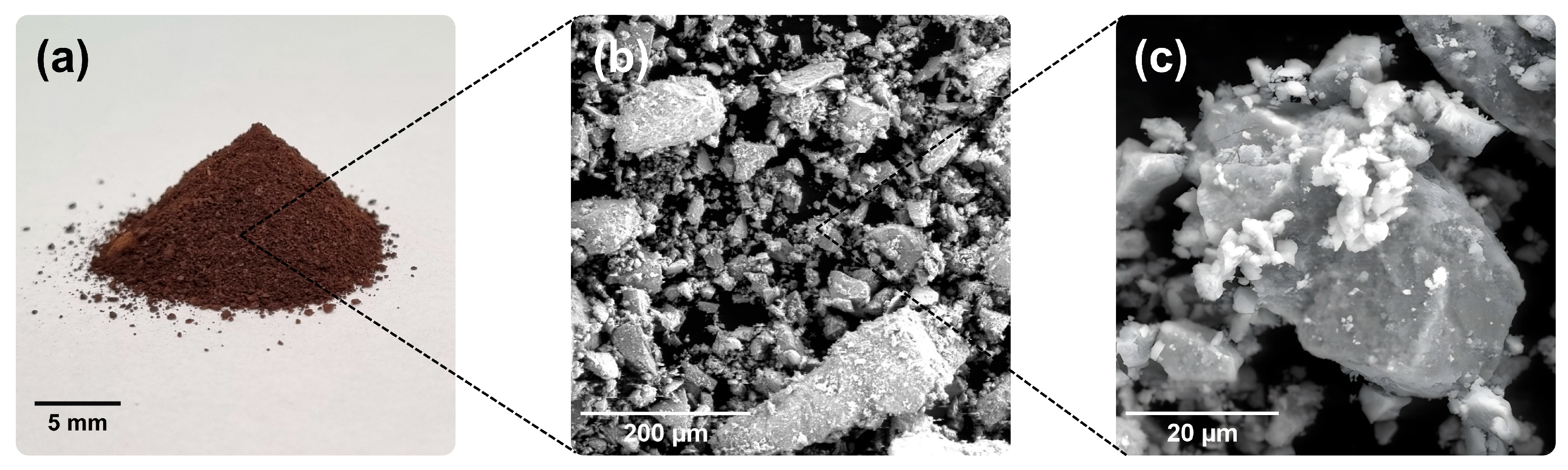
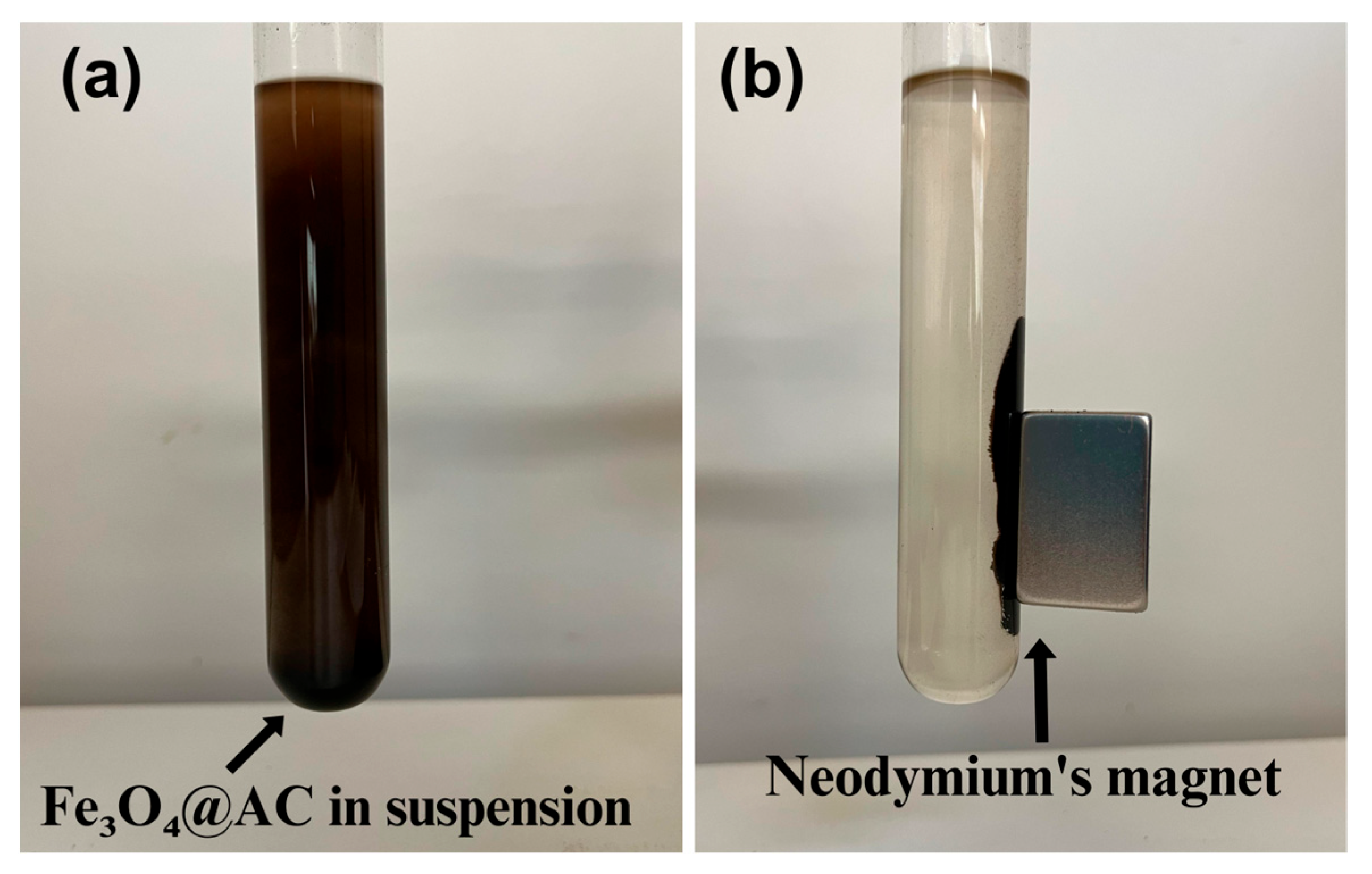
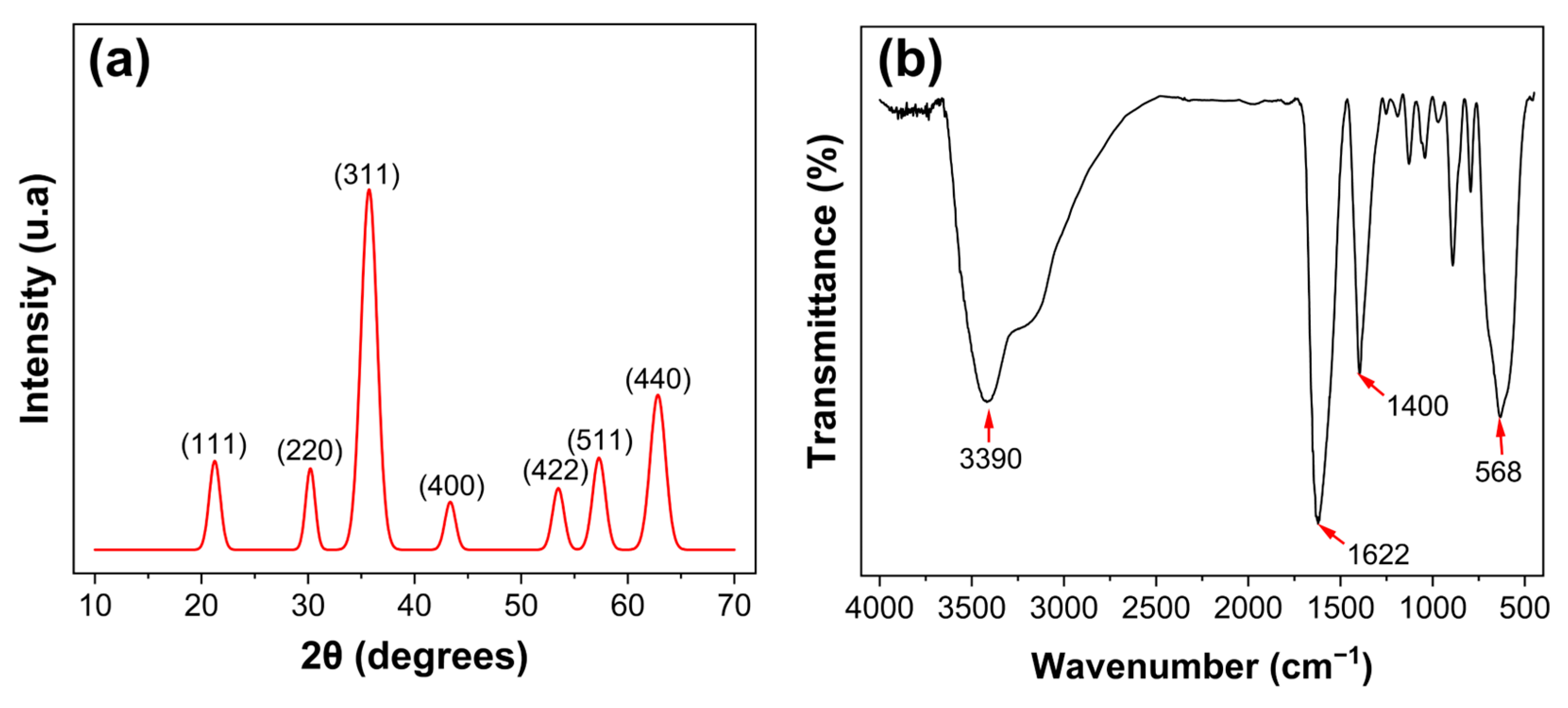
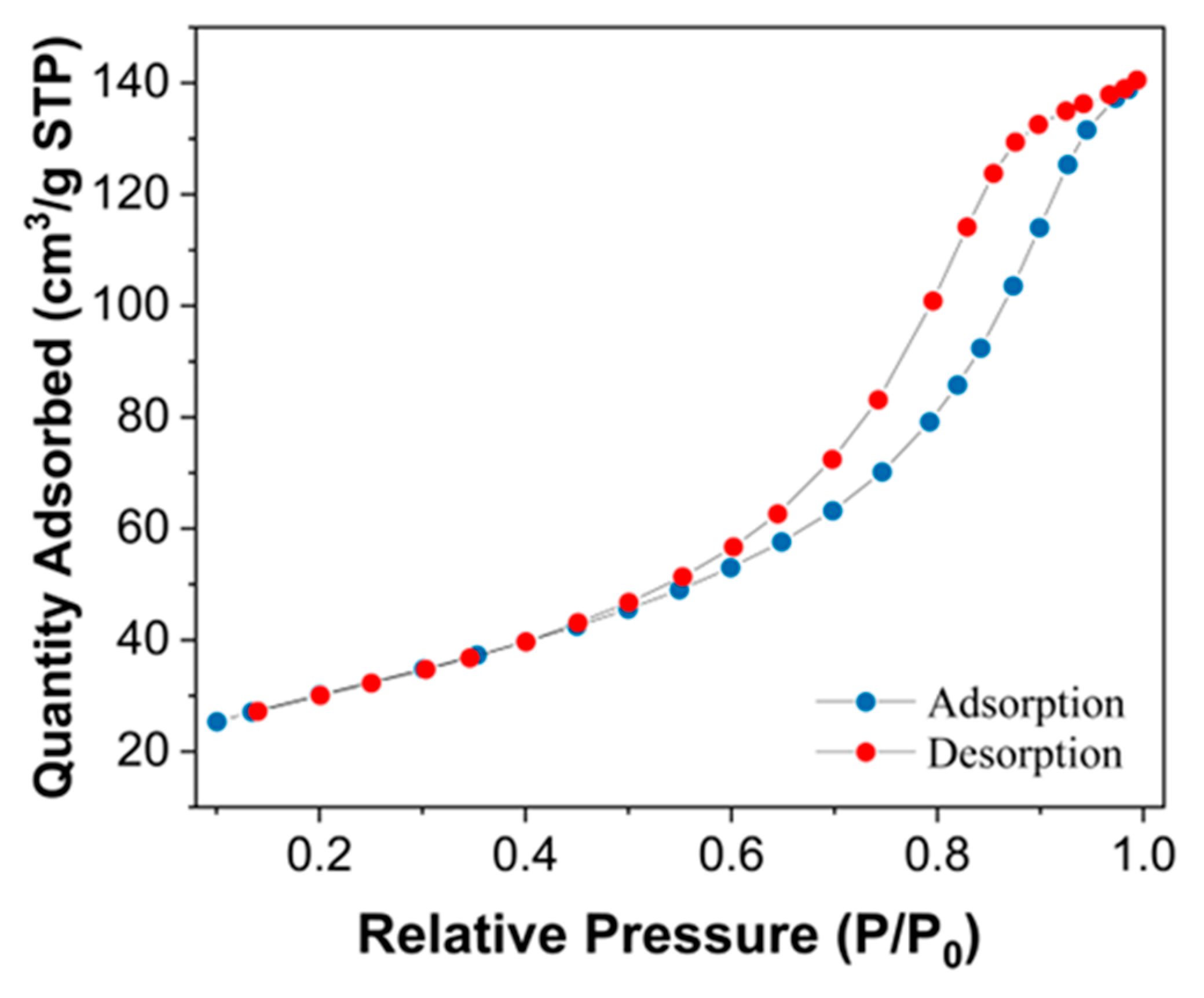
3.2. Morphological, Crystalline and Chemical Analysis of the Fe3O4@AC Nanoparticles
3.3. Removal of the MPs
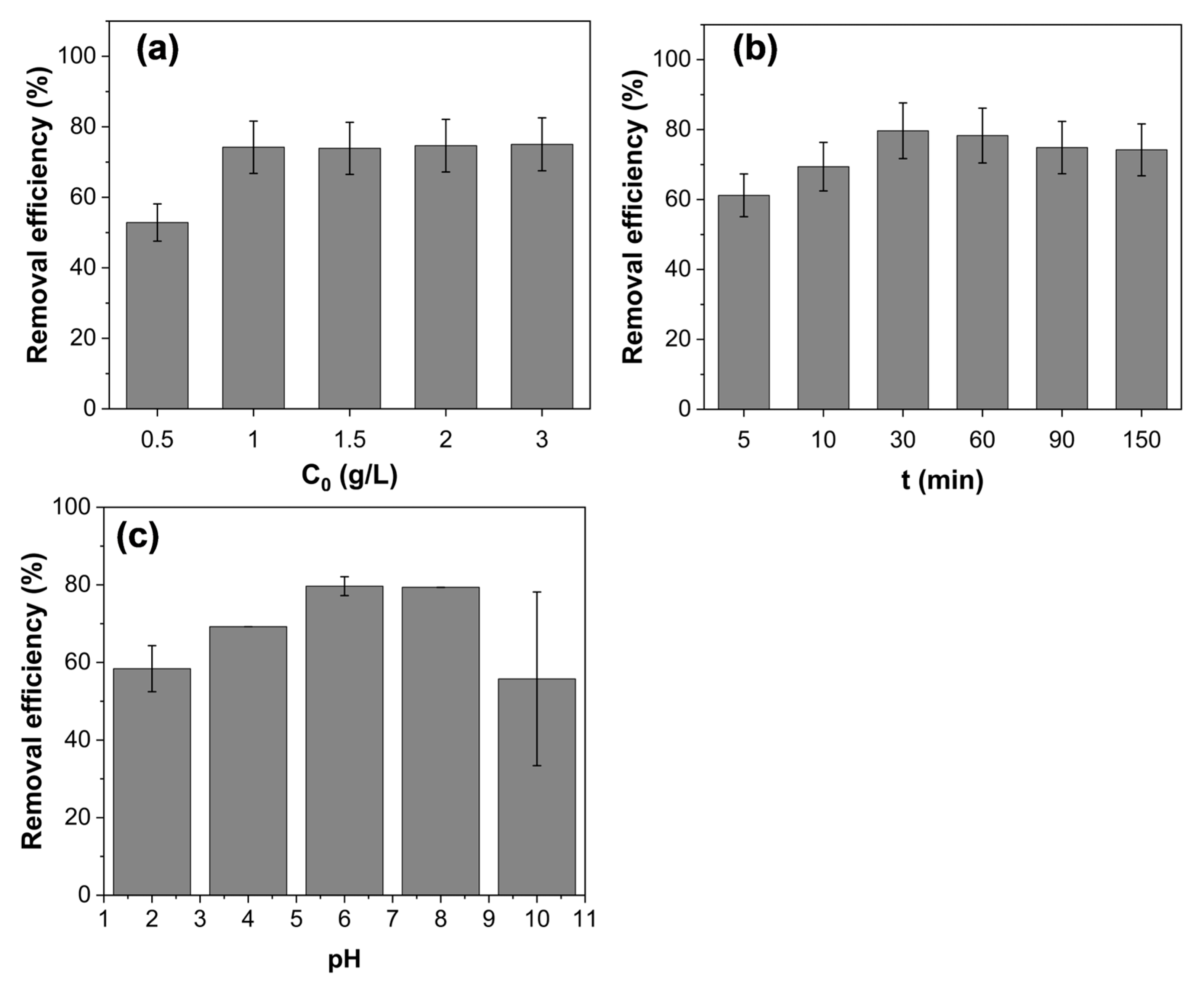
3.3.1. Effect of Fe3O4@AC Nanoparticles Concentration, Contact Time and pH
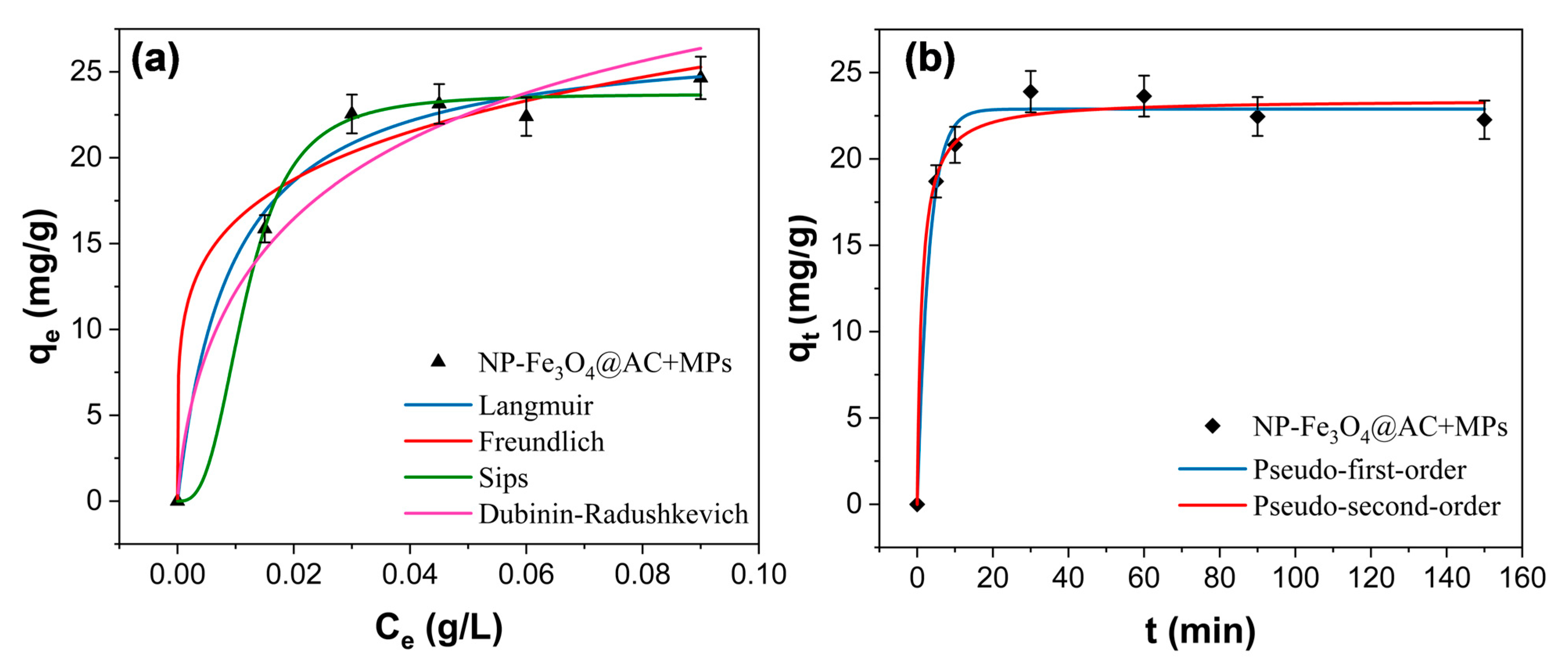
3.3.2. Adsorption Isothermal and Kinetic Study
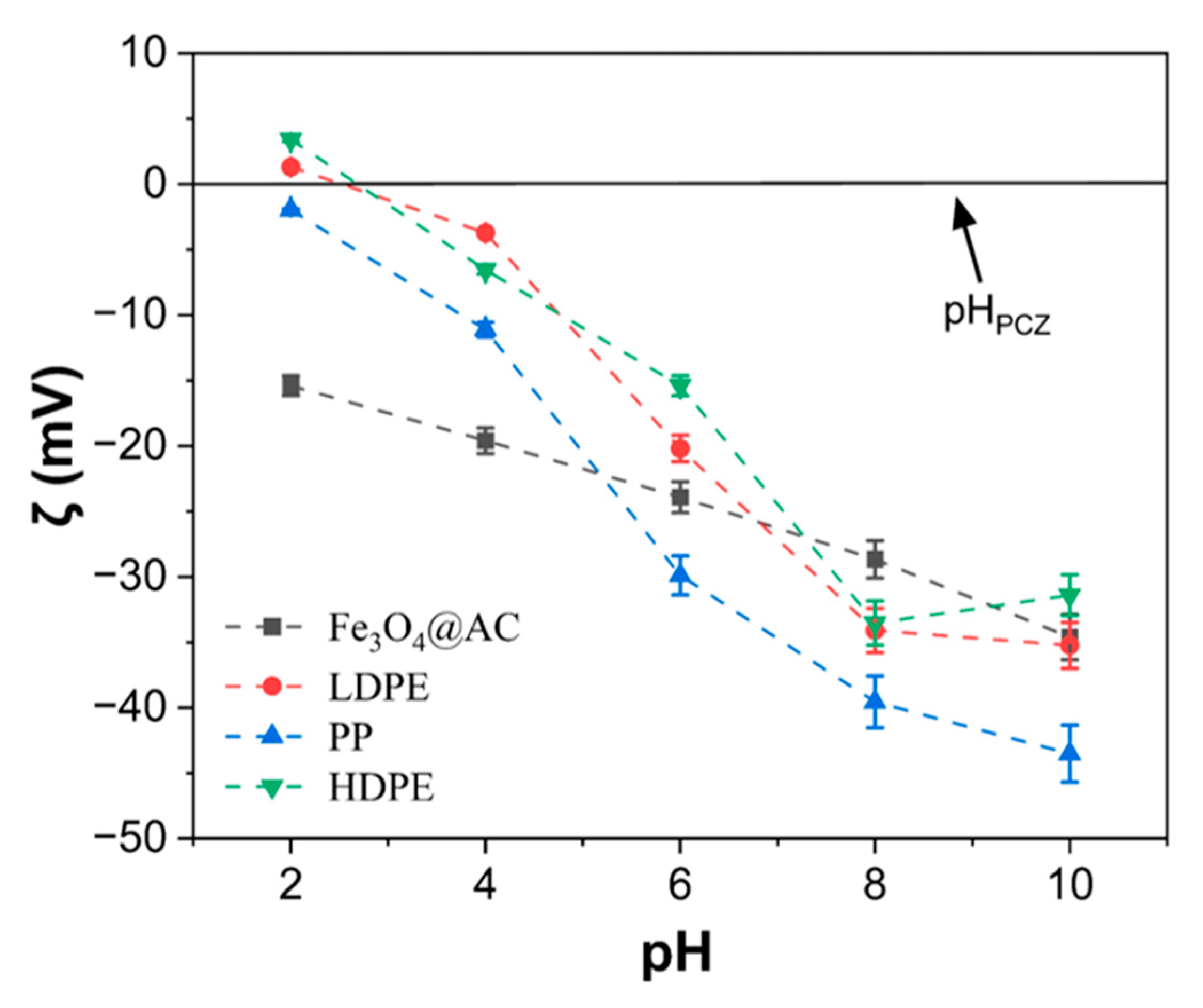
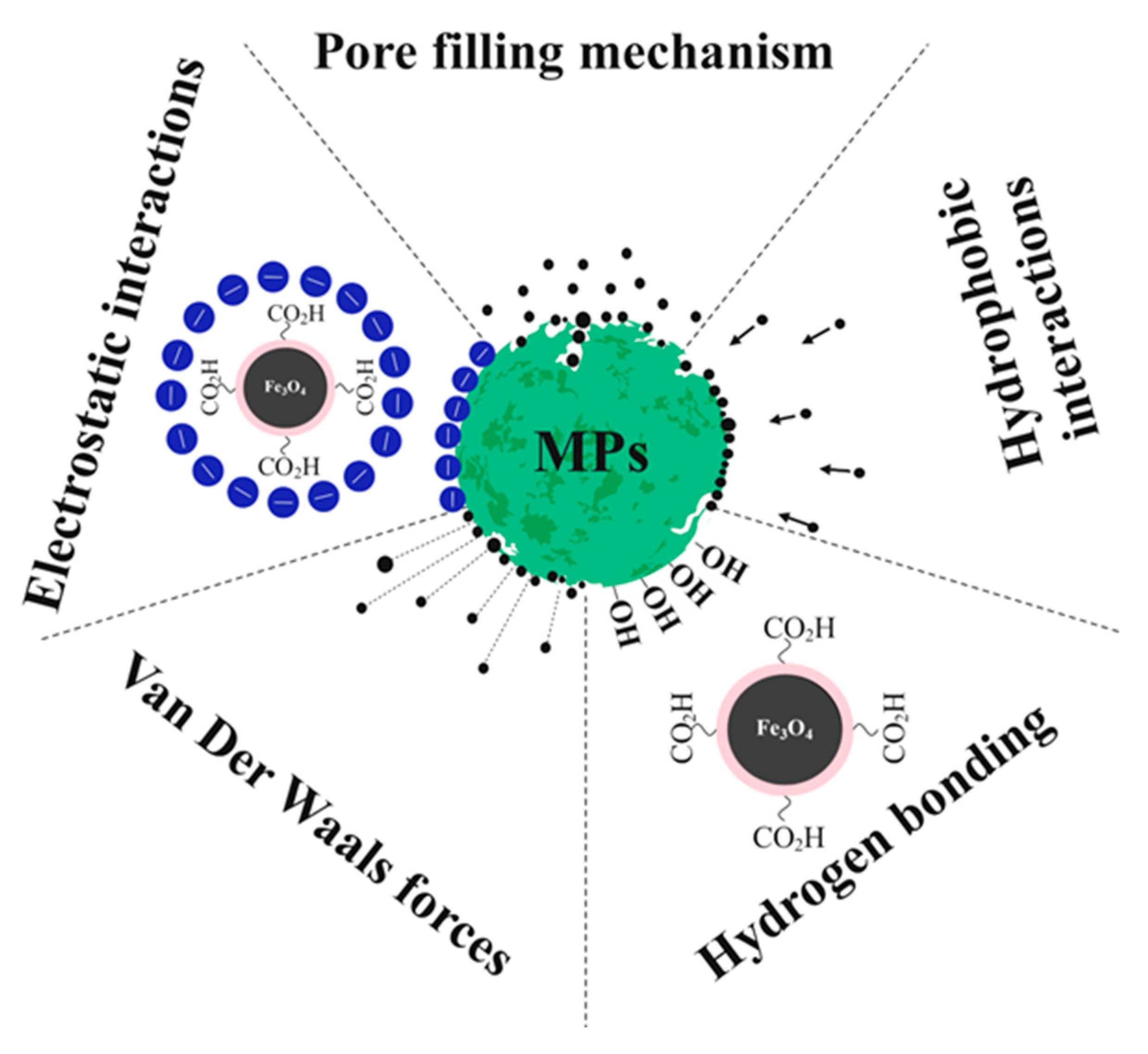
3.4. Insight into the Mechanisms of MPs Removal by Fe3O4@AC Nanoparticles
3.5. Reuse Testing of Fe3O4@AC Nanoparticles
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Suaria, G.; Perold, V.; Lee, J.R.; Lebouard, F.; Aliani, S.; Ryan, P.G. Floating Macro- and Microplastics around the Southern Ocean: Results from the Antarctic Circumnavigation Expedition. Environ. Int. 2020, 136, 105494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Huang, J.; Zhu, F.; Zhou, S. Airborne Microplastics: A Review on the Occurrence, Migration and Risks to Humans. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2021, 107, 657–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Yan, Y.; Yu, Y.; He, Y.; Fu, B.; Wang, J. Distribution, Sources, Migration, Influence and Analytical Methods of Microplastics in Soil Ecosystems. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 243, 114009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, S.; Cui, Y.; Brahney, J.; Mahowald, N.M.; Li, Q. Long-Distance Atmospheric Transport of Microplastic Fibres Influenced by Their Shapes. Nat. Geosci. 2023, 16, 863–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, E.; Gordon, M.; Hanson, R.; Jantunen, L.M. Modelling the Effect of Shape on Atmospheric Microplastic Transport. Atmos. Environ. 2024, 326, 120458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, N.B.; Hüffer, T.; Thompson, R.C.; Hassellöv, M.; Verschoor, A.; Daugaard, A.E.; Rist, S.; Karlsson, T.; Brennholt, N.; Cole, M.; et al. Are We Speaking the Same Language? Recommendations for a Definition and Categorization Framework for Plastic Debris. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 1039–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, M.; Lindeque, P.; Halsband, C.; Galloway, T.S. Microplastics as Contaminants in the Marine Environment: A Review. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2011, 62, 2588–2597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mintenig, S.M.; Int-Veen, I.; Löder, M.G.J.; Primpke, S.; Gerdts, G. Identification of Microplastic in Effluents of Waste Water Treatment Plants Using Focal Plane Array-Based Micro-Fourier-Transform Infrared Imaging. Water Res. 2017, 108, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, M.; Song, B.; Zhu, Y.; Zeng, G.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Wen, X.; Chen, M.; Yi, H. Removal of Microplastics via Drinking Water Treatment: Current Knowledge and Future Directions. Chemosphere 2020, 251, 126612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochman, C.M.; Kross, S.M.; Armstrong, J.B.; Bogan, M.T.; Darling, E.S.; Green, S.J.; Smyth, A.R.; Veríssimo, D. Correction to Scientific Evidence Supports a Ban on Microbeads. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 14740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camacho, M.; Herrera, A.; Gómez, M.; Acosta-Dacal, A.; Martínez, I.; Henríquez-Hernández, L.A.; Luzardo, O.P. Organic Pollutants in Marine Plastic Debris from Canary Islands Beaches. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 662, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De-la-Torre, G.E. Microplastics: An Emerging Threat to Food Security and Human Health. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 57, 1601–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, L.; Fu, D.; Zhao, J.; Wu, W.; Wang, Z.; Su, Y.; Peng, L. Microplastics Aged in Various Environmental Media Exhibited Strong Sorption to Heavy Metals in Seawater. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 169, 112480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Chen, J.; Li, J. The Removal of Microplastics in the Wastewater Treatment Process and Their Potential Impact on Anaerobic Digestion Due to Pollutants Association. Chemosphere 2020, 251, 126360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badola, N.; Bahuguna, A.; Sasson, Y.; Chauhan, J.S. Microplastics Removal Strategies: A Step toward Finding the Solution. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2021, 16, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Duan, J.; Liu, R.; Petropoulos, E.; Feng, Y.; Xue, L.; Yang, L.; He, S. Efficient Magnetic Capture of PE Microplastic from Water by PEG Modified Fe3O4 Nanoparticles: Performance, Kinetics, Isotherms and Influence Factors. J. Environ. Sci. 2025, 147, 677–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Chen, X.; Yu, S.; Cui, M. Removal of Pristine and Aged Microplastics from Water by Magnetic Biochar: Adsorption and Magnetization. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 875, 162647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Liu, N.; Peng, Y.; Wang, G.; Wang, X.; Wang, Q.; Lv, M.; Chen, L. An Ultra-Light Sustainable Sponge for Elimination of Microplastics and Nanoplastics. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 456, 131685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, D.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, W.; Pan, Q.; Li, J. Metal-Organic Framework-Based Wood Aerogel for Effective Removal of Micro/Nano Plastics. Chem. Res. Chin. Univ. 2022, 38, 186–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, R.; Lin, S.; Jiang, W.; Yu, X.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, W.; Sui, Q. Effect of Aggregation Behavior on Microplastic Removal by Magnetic Fe3O4 Nanoparticles. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 898, 165431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khairudin, K.; Abu Bakar, N.F.; Osman, M.S. Magnetically Recyclable Flake-like BiOI-Fe3O4 Microswimmers for Fast and Efficient Degradation of Microplastics. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 108275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Su, Y.; Wu, D.; Zhao, Y.; Xie, B. Removal of Microplastics from Aqueous Solutions by Magnetic Carbon Nanotubes. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 406, 126804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, L.M.A.; Sheng, J.; Zimba, P.V.; Zhu, L.; Fadare, O.O.; Haley, C.; Wang, M.; Phillips, T.D.; Conkle, J.; Xu, W. Testing an Iron Oxide Nanoparticle-Based Method for Magnetic Separation of Nanoplastics and Microplastics from Water. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Zhang, X.; Gao, W.; Zhang, Y.; He, D. Removal of Microplastics from Water by Magnetic Nano-Fe3O4. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 802, 149838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grbic, J.; Nguyen, B.; Guo, E.; You, J.B.; Sinton, D.; Rochman, C.M. Magnetic Extraction of Microplastics from Environmental Samples. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2019, 6, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, Y.; Lee, E.H.; Lee, S.W. Adsorptive Removal of Micron-Sized Polystyrene Particles Using Magnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles. Chemosphere 2022, 307, 135672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazdani, F.; Seddigh, M. Magnetite Nanoparticles Synthesized by Co-Precipitation Method: The Effects of Various Iron Anions on Specifications. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2016, 184, 318–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangaiya, P.; Jayaprakash, R. A Review on Iron Oxide Nanoparticles and Their Biomedical Applications. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 2018, 31, 3397–3413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darwesh, O.M.; Matter, I.A.; Eida, M.F. Development of Peroxidase Enzyme Immobilized Magnetic Nanoparticles for Bioremediation of Textile Wastewater Dye. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 102805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, I.; Ding, T.; Peng, C.; Naz, I.; Sun, H.; Li, J.; Liu, J. Micro- and Nanoplastics in Wastewater Treatment Plants: Occurrence, Removal, Fate, Impacts and Remediation Technologies—A Critical Review. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 423, 130205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zheng, S.; Shao, Y.; Liu, J.; Xu, Z.; Zhu, D. Amino-Functionalized Fe3O4@SiO2 Core–Shell Magnetic Nanomaterial as a Novel Adsorbent for Aqueous Heavy Metals Removal. J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2010, 349, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keller, A.A.; Wang, H.; Zhou, D.; Lenihan, H.S.; Cherr, G.; Cardinale, B.J.; Miller, R.; Zhaoxia, J.I. Stability and Aggregation of Metal Oxide Nanoparticles in Natural Aqueous Matrices. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 1962–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahangaran, F.; Navarchian, A.H. Recent Advances in Chemical Surface Modification of Metal Oxide Nanoparticles with Silane Coupling Agents: A Review. Adv. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2020, 286, 102298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Yu, B.; Wang, S.; Shen, Y.; Cong, H. Preparation, Surface Functionalization and Application of Fe3O4 Magnetic Nanoparticles. Adv. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2020, 281, 102165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rǎcuciu, M.; Creangǎ, D.E.; Airinei, A. Citric-Acid-Coated Magnetite Nanoparticles for Biological Applications. Eur. Phys. J. E 2006, 21, 117–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikelashvili, V.; Kekutia, S.; Markhulia, J.; Saneblidze, L.; Maisuradze, N.; Kriechbaum, M.; Almásy, L. Synthesis and Characterization of Citric Acid-Modified Iron Oxide Nanoparticles Prepared with Electrohydraulic Discharge Treatment. Materials 2023, 16, 746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Huang, P.M. Atomic Force Microscopy and Surface Characteristics of Iron Oxides Formed in Citrate Solutions. Soil. Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1999, 63, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arefi, M.; Kazemi Miraki, M.; Mostafalu, R.; Satari, M.; Heydari, A. Citric Acid Stabilized on the Surface of Magnetic Nanoparticles as an Efficient and Recyclable Catalyst for Transamidation of Carboxamides, Phthalimide, Urea and Thiourea with Amines under Neat Conditions. J. Iran. Chem. Soc. 2019, 16, 393–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dheyab, M.A.; Aziz, A.A.; Jameel, M.S.; Noqta, O.A.; Khaniabadi, P.M.; Mehrdel, B. Simple Rapid Stabilization Method through Citric Acid Modification for Magnetite Nanoparticles. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajinkya, N.; Yu, X.; Kaithal, P.; Luo, H.; Somani, P.; Ramakrishna, S. Magnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticle (IONP) Synthesis to Applications: Present and Future. Materials 2020, 13, 4644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freundlich, H. Über Die Adsorption in Lösungen. Z. Für Phys. Chem. 1907, 57U, 385–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmuir, I. The constitution and fundamental properties of solids and liquids. Part I. Solids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1916, 38, 2221–2295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sips, R. On the Structure of a Catalyst Surface. J. Chem. Phys. 1948, 16, 490–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubinin, M.M. Generalization of the Theory of Volume Filling of Micropores to Nonhomogeneous Microporous Structures. Carbon. N. Y. 1985, 23, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezzati, R.; Ezzati, S.; Azizi, M. Exact Solution of the Langmuir Rate Equation: New Insights into Pseudo-First-Order and Pseudo-Second-Order Kinetics Models for Adsorption. Vacuum 2024, 220, 112790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, Y.S.; McKay, G. Pseudo-Second Order Model for Sorption Processes. Process Biochem. 1999, 34, 451–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanvey, J.S.; Lewis, P.J.; Lavers, J.L.; Crosbie, N.D.; Pozo, K.; Clarke, B.O. A Review of Analytical Techniques for Quantifying Microplastics in Sediments. Anal. Methods 2017, 9, 1369–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nigam, S.; Barick, K.C.; Bahadur, D. Development of Citrate-Stabilized Fe3O4 Nanoparticles: Conjugation and Release of Doxorubicin for Therapeutic Applications. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2011, 323, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, D.; Gautam, R.K.; Kumar, R.; Shukla, B.K.; Shankar, V.; Krishna, V. Citric Acid Coated Magnetic Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Characterization and Application in Removal of Cd(II) Ions from Aqueous Solution. J. Water Process Eng. 2014, 4, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duszyńska, A.; Danielewicz, A.; Kadłubowski, S.; Kozanecki, M.; Maniukiewicz, W.; Sowiński, P.; Szadkowska-Nicze, M. Influence of Electron-Beam Irradiation on Surface Properties of Magnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles Stabilized with Citrate. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2020, 169, 107796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheraghipour, E.; Javadpour, S.; Mehdizadeh, A.R. Citrate Capped Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles Used for Hyperthermia Therapy. J. Biomed. Sci. Eng. 2012, 2012, 715–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Mak, K.Y.; Leung, C.W.; Chan, K.Y.; Chan, W.K.; Zhong, W.; Pong, P.W.T. Effect of Synthesis Conditions on the Properties of Citric-Acid Coated Iron Oxide Nanoparticles. Microelectron. Eng. 2013, 110, 329–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Günay, A.; Arslankaya, E.; Tosun, I. Lead Removal from Aqueous Solution by Natural and Pretreated Clinoptilolite: Adsorption Equilibrium and Kinetics. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 146, 362–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, V.C.; Araújo, M.E.B.; Rodrigues, A.M.; Vitorino, M.D.B.C.; Cartaxo, J.M.; Menezes, R.R.; Neves, G.A. Adsorption Behavior of Crystal Violet and Congo Red Dyes on Heat-Treated Brazilian Palygorskite: Kinetic, Isothermal and Thermodynamic Studies. Materials 2021, 14, 5688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, J.V.; Rodrigues, A.M.; Menezes, R.R.; de Araújo Neves, G. Adsorption of Anionic Dye on the Acid-Functionalized Bentonite. Materials 2020, 13, 3600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, M.R.; Horgen, F.D.; Orski, S.V.; Rodriguez, C.V.; Beers, K.L.; Balazs, G.H.; Jones, T.T.; Work, T.M.; Brignac, K.C.; Royer, S.J.; et al. Validation of ATR FT-IR to Identify Polymers of Plastic Marine Debris, Including Those Ingested by Marine Organisms. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 127, 704–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tourinho, P.S.; Kočí, V.; Loureiro, S.; van Gestel, C.A.M. Partitioning of Chemical Contaminants to Microplastics: Sorption Mechanisms, Environmental Distribution and Effects on Toxicity and Bioaccumulation. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 252, 1246–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chércoles Asensio, R.; San Andrés Moya, M.; De La Roja, J.M.; Gómez, M. Analytical Characterization of Polymers Used in Conservation and Restoration by ATR-FTIR Spectroscopy. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2009, 395, 2081–2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Chen, Y.; Wang, T.; Liu, C.; He, D.; Liu, B.; Liu, Y. Efficient Removal of Petroleum Hydrocarbons from Soil by Percarbonate with Catechin-Promoted Fe(III)/Fe(II) Redox Cycling: Activation of Ferrous and Roles of ·OH and ·CO3−. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 448, 130875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudhoo, A.; Sillanpää, M. Magnetic Nanoadsorbents for Micropollutant Removal in Real Water Treatment: A Review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2021, 19, 4393–4413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lassoued, A.; Dkhil, B.; Gadri, A.; Ammar, S. Control of the Shape and Size of Iron Oxide (α-Fe2O3) Nanoparticles Synthesized through the Chemical Precipitation Method. Results Phys. 2017, 7, 3007–3015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omelyanchik, A.; da Silva, F.G.; Gomide, G.; Kozenkov, I.; Depeyrot, J.; Aquino, R.; Campos, A.F.C.; Fiorani, D.; Peddis, D.; Rodionova, V.; et al. Effect of Citric Acid on the Morpho-Structural and Magnetic Properties of Ultrasmall Iron Oxide Nanoparticles. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 883, 160779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, L.S.; Yeong, Y.F.; Ani, N.C.; Lau, K.K.; Shariff, A.M. Effect of Synthesis Parameters on the Formation of Zeolitic Imidazolate Framework 8 (ZIF-8) Nanoparticles for CO2 Adsorption. Part. Sci. Technol. 2014, 32, 520–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ghouti, M.A.; Da’ana, D.A. Guidelines for the Use and Interpretation of Adsorption Isotherm Models: A Review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 393, 122383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, N.; Shahat, A.; El-Didamony, A.; El-Desouky, M.G.; El-Bindary, A.A. Mesoporous Iron Oxide Nano Spheres for Capturing Organic Dyes from Water Sources. J. Mol. Struct. 2020, 1217, 128361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafa, N.; Ahmed, B.; Zohora, F.; Bakya, J.; Ahmed, S.; Ahmed, S.F.; Mofijur, M.; Chowdhury, A.A.; Almomani, F. Microplastics as Carriers of Toxic Pollutants: Source, Transport, and Toxicological Effects. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 343, 123190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pramanik, B.K.; Pramanik, S.K.; Monira, S. Understanding the Fragmentation of Microplastics into Nano-Plastics and Removal of Nano/Microplastics from Wastewater Using Membrane, Air Flotation and Nano-Ferrofluid Processes. Chemosphere 2021, 282, 131053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Huang, X.; Wang, L.; Zhao, X.; Yan, F.; Yang, Y.; Li, G.; Gao, P.; Ji, P. Removal of Polystyrene Nanoplastics from Aqueous Solutions Using a Novel Magnetic Material: Adsorbability, Mechanism, and Reusability. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 430, 133122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urso, M.; Ussia, M.; Novotný, F.; Pumera, M. Trapping and Detecting Nanoplastics by MXene-Derived Oxide Microrobots. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 3573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zandieh, M.; Liu, J. Removal and Degradation of Microplastics Using the Magnetic and Nanozyme Activities of Bare Iron Oxide Nanoaggregates. Angew. Chem. 2022, 134, e202212013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Liu, S.; Huang, K.; Qin, S.; Liang, B.; Wang, J. Preparation of Magnetic Janus Microparticles for the Rapid Removal of Microplastics from Water. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 903, 166627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Wang, F.; Li, J.; Deng, S.; Zhang, S. Adsorption of Three Pesticides on Polyethylene Microplastics in Aqueous Solutions: Kinetics, Isotherms, Thermodynamics, and Molecular Dynamics Simulation. Chemosphere 2021, 264, 128556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kouchakipour, S.; Hosseinzadeh, M.; Qaretapeh, M.Z.; Dashtian, K. Sustainable Large-Scale Fe3O4/Carbon for Enhanced Polystyrene Nanoplastics Removal through Magnetic Adsorption Coagulation. J. Water Process Eng. 2024, 58, 104919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, G.; Zhang, Y.; Yue, J.; Wang, X.; Yang, Z.; Chen, J.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, J. Mechanisms of Polystyrene Nanoplastics Adsorption onto Activated Carbon Modified by ZnCl2. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 876, 162763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Liu, W.; Zhang, M. Application of Carbon-Based Adsorbents in the Remediation of Micro- and Nanoplastics. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 349, 119522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.; Cai, Z.; Jin, H.; Tang, Y. Adsorption Mechanisms of Five Bisphenol Analogues on PVC Microplastics. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 650, 671–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Wang, L.; Chen, Q.; Kalogerakis, N.; Ji, R.; Ma, Y. Interactions between Microplastics and Organic Pollutants: Effects on Toxicity, Bioaccumulation, Degradation, and Transport. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 748, 142427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atugoda, T.; Vithanage, M.; Wijesekara, H.; Bolan, N.; Sarmah, A.K.; Bank, M.S.; You, S.; Ok, Y.S. Interactions between Microplastics, Pharmaceuticals and Personal Care Products: Implications for Vector Transport. Environ. Int. 2021, 149, 106367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hüffer, T.; Hofmann, T. Sorption of Non-Polar Organic Compounds by Micro-Sized Plastic Particles in Aqueous Solution. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 214, 194–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Liu, F.; Brookes, P.C.; Xu, J. The Sorption Kinetics and Isotherms of Sulfamethoxazole with Polyethylene Microplastics. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 131, 191–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Zhan, X.; Wu, X.; Li, J.; Wang, H.; Gao, S. Effect of Weathering on Environmental Behavior of Microplastics: Properties, Sorption and Potential Risks. Chemosphere 2020, 242, 125193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Hamidian, A.H.; Tubić, A.; Zhang, Y.; Fang, J.K.H.; Wu, C.; Lam, P.K.S. Understanding Plastic Degradation and Microplastic Formation in the Environment: A Review. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 274, 116554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campanale, C.; Savino, I.; Massarelli, C.; Uricchio, V.F. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy to Assess the Degree of Alteration of Artificially Aged and Environmentally Weathered Microplastics. Polymers 2023, 15, 911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez-Pastora, J.; Bringas, E.; Ortiz, I. Recent Progress and Future Challenges on the Use of High Performance Magnetic Nano-Adsorbents in Environmental Applications. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 256, 187–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Magnetic Materials | Size (μm) | MPs | Size MPs (μm) | Removal Capacity (mg/g) | Removal | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fe3O4@AC | - | HDPE, LDPE, PP | 1–3000 | 23.72 | 80% | This work |
| NPs-Fe | 0.025 | PE PS | <20 | - | 92% | [25] |
| Fe3O4 | - | PS | 1 | 2799.2 | 90% | [26] |
| PEG/Fe3O4 | - | PE | 13–149 | 2.202 | 97% | [16] |
| Corn cob magnetic biochar | 63.5 | PA | 27–307 | 1145 | 97% | [17] |
| Nano-Fe3O4 | <0.03 | PE, PP, PS, PET | 200–900 | 367.62 | 98% | [24] |
| Magnetite and cobalt ferrite nano ferrofluid | - | PE, PVC, PES | 0.74–1.88 | - | 55% | [67] |
| Fly ash modified with Fe | - | PS | 0.08 | 83.1 | 94% | [68] |
| Nano-Fe3O4 with hydrophobic coating | ~0.1 | PS | 0.1–1 | - | 93% | [23] |
| Microrobotsγ-Fe2O3/Pt/TiO2 | - | PS | 0.05 | - | 97% | [69] |
| Fe3O4 NPs | 0.01 | PE, PP, PVC, PS, PET | 20–800 | - | 100% | [70] |
| Fe3O4@SiO2-PAC 18 | 1.72 | PE PS | 10 μm | 2.41 | 92% | [71] |
| Isotherm | Parameters | Fe3O4@AC |
|---|---|---|
| Freundlich | Kf (mg1−1/n g/L1/n) | 40.84 |
| n | 5.02 | |
| R2 | 0.969 | |
| Langmuir | qmax (mg/g) | 27.27 |
| Kl (L/mg) | 107.88 | |
| R2 | 0.987 | |
| Sips | qmax (mg/g) | 23.72 |
| Ks (L/mg) | 84.93 | |
| R2 | 0.991 | |
| ns | 2.922 | |
| Dubinin-Radushkevich | qmax (mg/g) | 36.24 |
| EDR (KJ/mol) | 0.05 | |
| R2 | 0.85 | |
| Pseudo-first-order | k1 (min−1) | 0.33 |
| qe (mg/g) | 22.89 | |
| R2 | 0.998 | |
| Pseudo-second-order | K2 (g/(mg·min)) | 0.035 |
| qe (mg/g) | 23.445 | |
| R2 | 0.998 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aquino, I.d.S.d.; Freire, E.d.A.; Rodrigues, A.M.; Vercillo, O.E.; Silva, M.F.P.d.; Rocha, M.F.S.d.; Amaral, M.C.S.; Amorim, A.K.B. Sustainable Strategy for Microplastic Mitigation: Fe3O4 Acid-Functionalized Magnetic Nanoparticles for Microplastics Removal. Sustainability 2025, 17, 5203. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17115203
Aquino IdSd, Freire EdA, Rodrigues AM, Vercillo OE, Silva MFPd, Rocha MFSd, Amaral MCS, Amorim AKB. Sustainable Strategy for Microplastic Mitigation: Fe3O4 Acid-Functionalized Magnetic Nanoparticles for Microplastics Removal. Sustainability. 2025; 17(11):5203. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17115203
Chicago/Turabian StyleAquino, Ivanilson da Silva de, Ester de Araújo Freire, Alisson Mendes Rodrigues, Otilie Eichler Vercillo, Mauro Francisco Pinheiro da Silva, Mateus Faustino Salazar da Rocha, Míriam Cristina Santos Amaral, and Ariuska Karla Barbosa Amorim. 2025. "Sustainable Strategy for Microplastic Mitigation: Fe3O4 Acid-Functionalized Magnetic Nanoparticles for Microplastics Removal" Sustainability 17, no. 11: 5203. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17115203
APA StyleAquino, I. d. S. d., Freire, E. d. A., Rodrigues, A. M., Vercillo, O. E., Silva, M. F. P. d., Rocha, M. F. S. d., Amaral, M. C. S., & Amorim, A. K. B. (2025). Sustainable Strategy for Microplastic Mitigation: Fe3O4 Acid-Functionalized Magnetic Nanoparticles for Microplastics Removal. Sustainability, 17(11), 5203. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17115203









