Innovative Application and Research of Industrial Solid Waste in Mining Filling Materials in China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Search Methodology
2.1. Criterion of Selection and Sources of Data
2.2. Publication Information
3. Research Progress on the Preparation of New Mine-Filling Materials from Solid Mining Waste
3.1. Preparation of Filling Materials from Coal-Based Solid Wastes
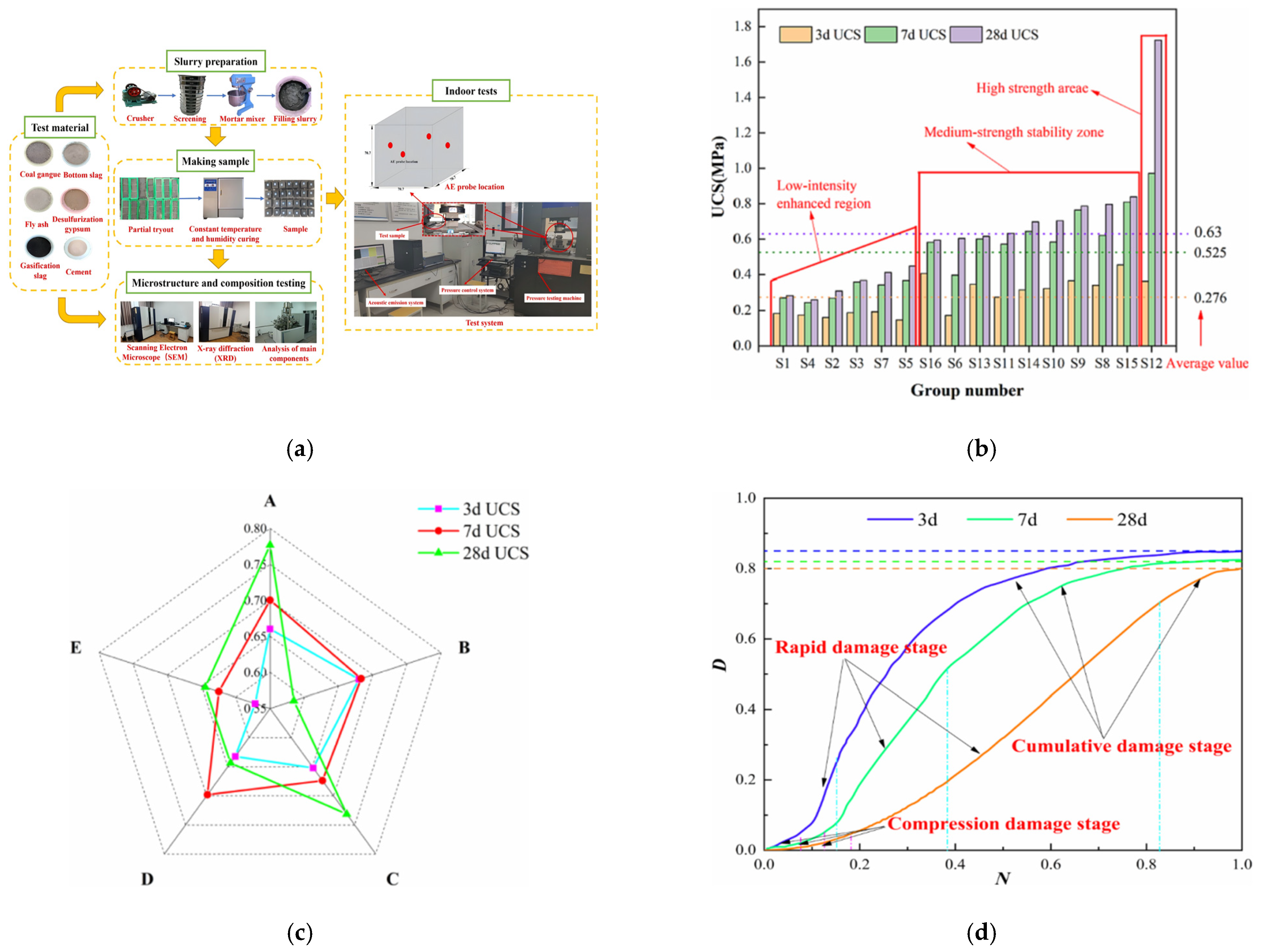
3.1.1. Single Coal-Based Solid Waste
3.1.2. Multi-Source Coal-Based Solid Waste
3.2. Preparation of Filling Materials Based on Smelting Slag
3.2.1. Preparation of Filling Materials Based on Metal Smelting Slag
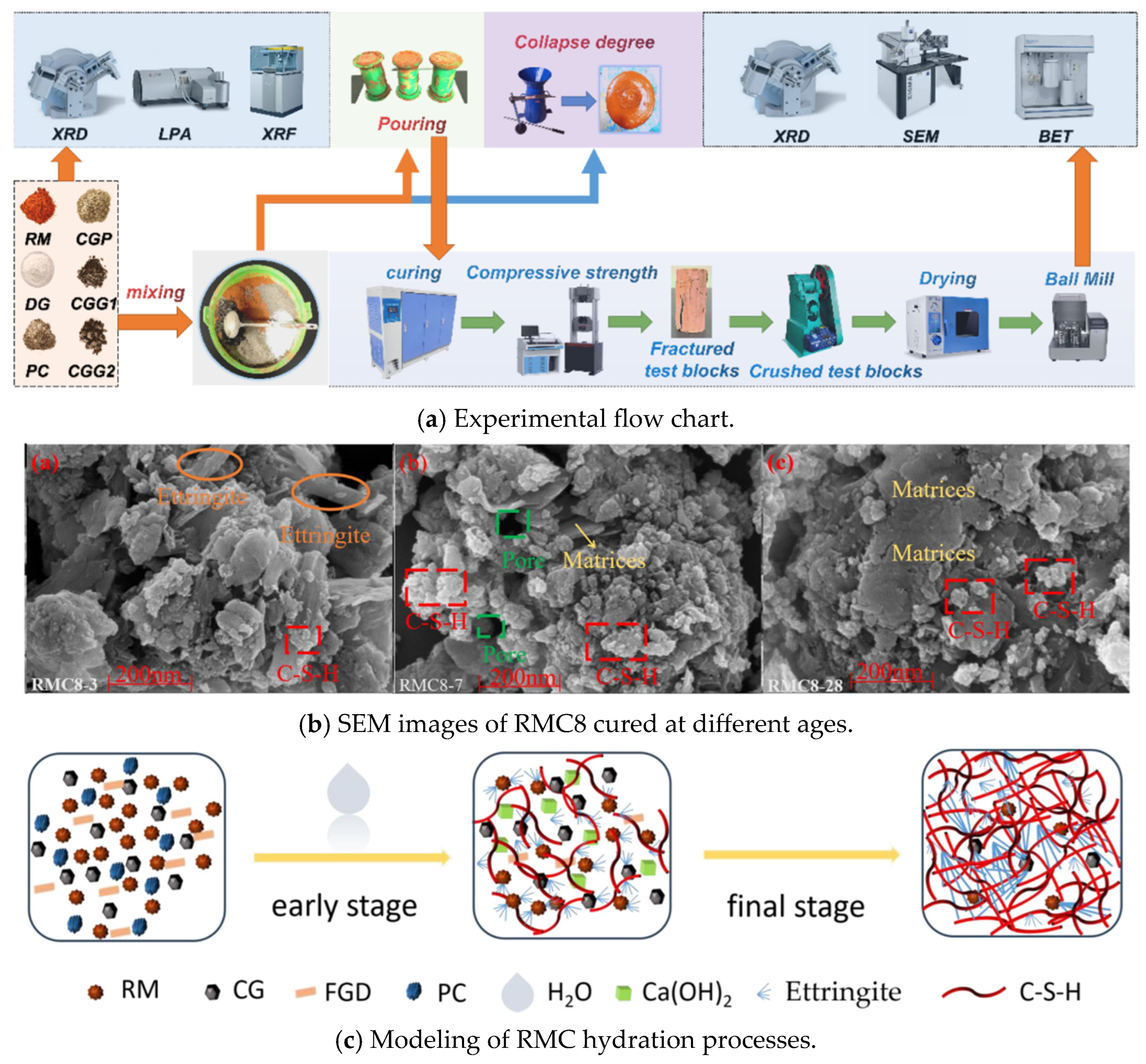
3.2.2. Red-Mud-Based Mineral Filling Materials
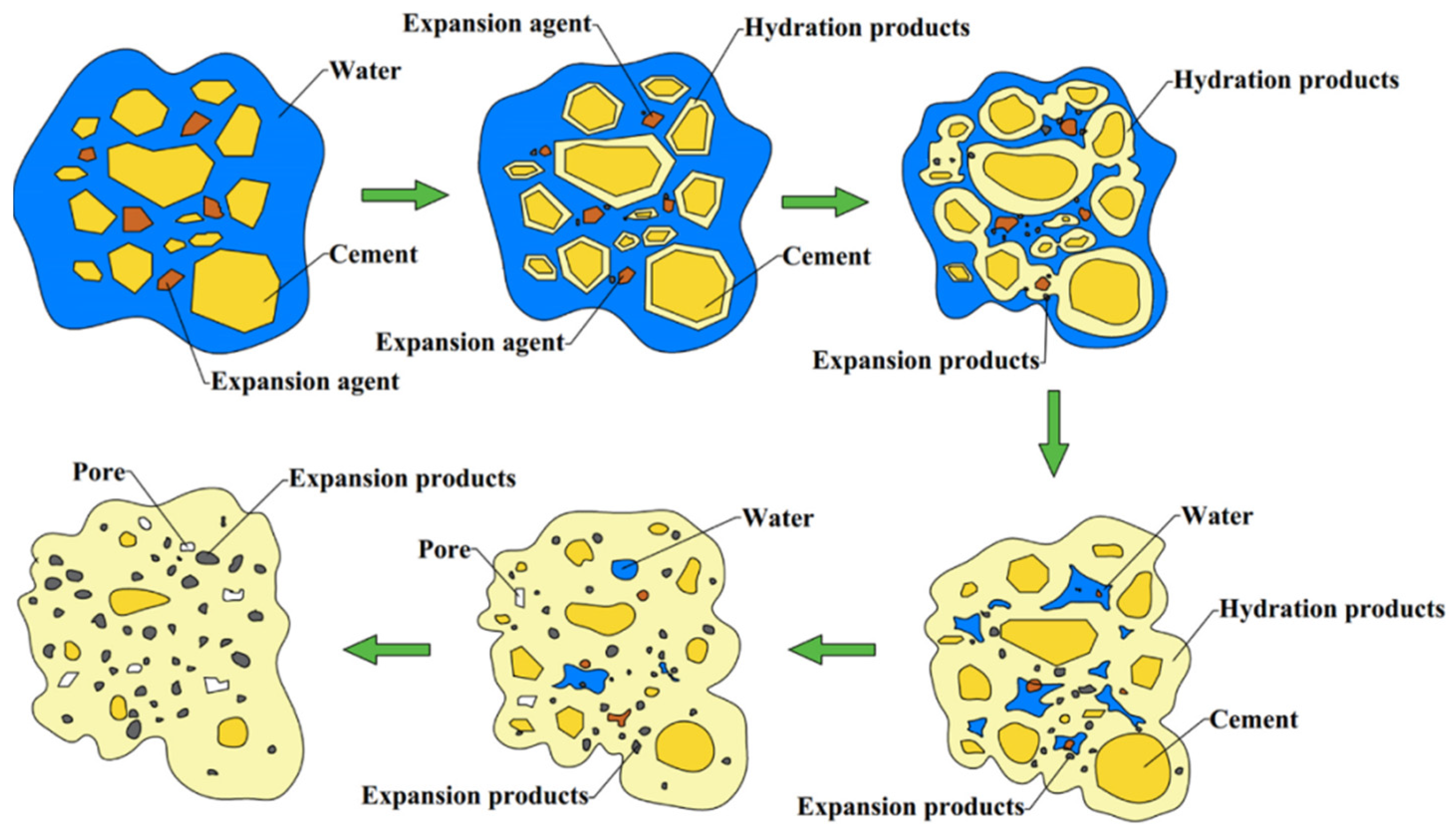
3.3. Preparation of Filling Materials Based on Industrial By-Product Gypsum
3.4. Preparation of Filling Materials Based on Tailings
4. Current Problems and Development Trends
- (1)
- The economy and scale application of solid waste resource utilization are limited
- (2)
- The disconnect between laboratory research and engineering practice is prominent
- (3)
- There is weak research on the mechanism of the synergistic activation of composite solid waste
- (1)
- Multi-source solid waste synergistic utilization and performance customization: based on the geological conditions of the mine and functional requirements (such as seepage resistance, expansion roofing, fast solidification), we build an intelligent model of “solid waste characteristics—ratio design—performance prediction” to achieve the precise control of material performance.
- (2)
- Low-carbon activation technology and environmental safety enhancement: scholars should develop green excitation agents (e.g., bio-based activators), optimize the curing path of harmful components (heavy metals, alkaline substances), and reduce the risk of leaching.
- (3)
- Evaluation of the whole lifecycle and construction of a standardized system: the inventory data encompass the entire lifecycle of materials, spanning from the acquisition of raw materials through pretreatment, material production, transportation, construction, service, dismantling, and ultimately recycling or disposal. The primary indicators within this inventory consist of environmental metrics (such as carbon emissions and heavy metal leaching) and technical metrics (including compressive strength and permeability). In the assessment process, the inventory data, which include emissions of CO2 and SO2, are initially classified into relevant environmental impact categories, such as climate change and acidification. Subsequently, the contributions of various substances to a specific environmental issue can be quantified through scientific modeling and translated into a standardized equivalent. The development of the standardization system is organized into three main components: the formulation of technical performance standards, environmental safety standards, and process management standards.
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ju, J.H.; Wang, Q.; Chen, J.B. Research on high-quality development of China’s mining industry in the new era. China Min. Mag. 2019, 28, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, J.; Hu, R.B.; Zhou, Q.Z.; Cui, R.G.; Lin, B.L.; Zhao, Y. Review and prospect of China’s mineral resources situation in 2024. China Min. Mag. 2025, 34, 37–45. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, K.; Wei, Z.; Zhao, X.Y.; He, X.; Zhang, J.Q. Theory and technology of green filling of solid waste in underground mine at coal power base of Yellow River Basin. J. China Coal Soc. 2021, 46, 925–935. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, H.Y.; Wu, A.X.; Wu, S.C.; Zhu, J.Q.; Li, H.; Liu, J.; Niu, Y.H. Research status and development trend of solid waste backfill in metal mines. Chin. J. Eng. 2022, 44, 11–25. [Google Scholar]
- An, L.; Chen, W.W.; Zhao, T.Y.; Li, L.J.; Wang, Y.C. Research progress on resource utilization of solid waste as roadbed filler in road engineering. Mater. Rep. 2024, 38, 257–263. (In English) [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.T.; Gao, Q.; Xiao, B.L.; Weng, Z.J.; Wu, F. Overview and application prospects of industrial solid waste development of filling cementitious materials. Min. Res. Dev. 2020, 40, 19–25. [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China. 2023 Annual Report of China’s Ecological and Environmental Statistics; Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2024.
- Cao, H.; Gao, Q.; Zhang, X.; Guo, B. Research progress and development direction of filling cementing materials for filling mining in iron mines of China. Gels 2022, 8, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Yao, Z.; Wang, K.; Wang, F.; Jiang, H.; Liang, M.; Wei, J.; Airey, G. Sustainable utilization of bauxite residue (Red Mud) as a road material in pavements: A critical review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 12, 1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Liu, B.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, S.; Liu, J.; Li, Q.; Fan, J.; Wei, S. Mechanical properties and hydration of fly ash-based geopolymers modified by copper slag. Mater. Today Commun. 2024, 39, 108914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldawsari, S.; Kampmann, R. Durability of fly ash/slag geopolymers: Role of OPC and silica under sulfate attack. Constr. Build. Mater. 2025, 465, 139855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Q.H.; Wang, A.; Zhang, J.R. Research on the early fracture behavior of fly ash-based geopolymers modified by molybdenum tailings. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 365, 132759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Wang, B.; Li, T.; Fan, C.; Yu, H. Effect and mechanism of activators on the properties of Yellow River sediment/fly ash/cement-based alkali-activated cementitious materials used for coal mine filling. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 445, 137955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, N.-N.; Liu, Z.; Xu, Y.-Y.; Kong, F.-L.; Wang, D.-M. Fabrication of hollow microspheres filled fly ash geopolymer composites with excellent strength and low density. Mater. Lett. 2015, 161, 451–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshaaer, M.; Alharbi, B.; Alqahtani, O.; Alotaibi, M.S.; Alzayed, A.; Al-Kafawein, J. Synthesis and characterization of metakaolin-wollastonite geopolymer goams for removal of heavy metal ions from water. Materials 2025, 18, 678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.L.; Ding, G.X.; Zhang, S.C.; Weng, A.C.; Wang, X.L. Advances in foaming process and adsorption properties of porous geopolymers. New Chem. Mater. 2023, 51, 272–277. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, X.; Zhang, L.; Huang, J.; Shi, H. Detoxification and solidification of heavy metal of chromium using fly ash-based geopolymer with chemical agents. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 151, 394–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.B.; Sun, Q.Z. Research status and outlook on the preparation of microcrystalline foam glass using industrial solid waste. Bull. Chin. Ceram. Soc. 2017, 36, 3697–3702. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, Z.Y.; Liang, L.S.; Qiao, J.Y.; Chen, J.; Li, Y.; Zhang, L.X. Research progress on the preparation of new glass materials from metallurgical solid wastes. Trans. Mater. Heat Treat. 2023, 44, 16–33. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, M.K.; Sha, H.P.; Wang, H.D. Preparation of fly ash insulating refractory bricks by high temperature foaming method. Bull. Chin. Ceram. Soc. 2017, 36, 2701–2707. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, J.R.; Liu, X.M.; Zhang, Z.Q. Road base materials prepared by multi-industrial solid wastes in China: A review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 373, 130860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.W.; Tang, Y.; Pei, F.; He, D.S.; Li, Z.L.; Qin, F.; Chi, N.A. Current status and prospects of phosphorus tailings application in agriculture. Chem. Bioeng. 2024, 41, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, W.J.; Wei, Z.Y. Progress of research on estimating the benefits of land reclamation and environmental management of nonferrous metal tailings ponds. Res. Environ. Sci. 2019, 32, 1304–1313. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, W.; Li, Y.; Feng, W.G.; Su, Y.; Jie, W.Z.; Zhang, H.; Ni, H.W. Progress of comprehensive utilization of phosphogypsum and its application in the field of building materials. Bull. Chin. Ceram. Soc. 2024, 43, 534–542. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, P.; Fu, Z.Y.; Wang, F.; Sun, J.K.; Lu, Z.H.; Huang, Z.B.; Zhang, L.; Dong, Z.; Gao, T.W. Research progress of multi-source coal-based solid waste for soil remediation. Clean Coal Technol. 2024, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.F.; Zhu, T. Application and prospect of green fill mining technology in China’s coal mines. China Min. Mag. 2021, 30, 5–8. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, X.M.; Ni, W.; Xu, D. Research progress on the preparation of filling binder from industrial solid waste. Met. Mine 2018, 4, 11–17. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, A.X.; Jiang, G.Z.; Wang, Y.M. Overview and development trend of new filling cementitious materials for mines. Met. Mine 2018, 3, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, G.L.; Yilmaz, E.; Wang, Y.D. Progress and prospects of mining with backfill in metal mines in China. Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater. 2023, 30, 1455–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.P.; Zhang, X.W.; Wei, F. Hazards and resource reuse of solid waste from metal mines. Mod. Min. 2017, 33, 122–125. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, X.K. Current status and prospect of the development of green fill mining in mines. Coal Sci. Technol. 2020, 48, 48–55. [Google Scholar]
- Behera, S.K.; Mishra, D.P.; Singh, P.; Mishra, K.; Mandal, S.K.; Ghosh, C.N.; Kumar, R.; Mandal, P.K. Utilization of mill tailings, fly ash and slag as mine paste backfill material: Review and future perspective. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 309, 125120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tebogo, M.; Thandiwe, S. Clean production of sustainable backfill material from waste gold tailings and slag. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 308, 127357. [Google Scholar]
- Yılmaz, T.; Ercikdi, B.; Deveci, H. Utilisation of construction and demolition waste as cemented paste backfill material for underground mine openings. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 222, 250–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monika, M.; Sourava, S.M.; Sanket, N. Efficacy of C&D waste in base/subbase layers of pavement—Current trends and future prospectives: A systematic review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 340, 127726. [Google Scholar]
- Liberati, A.; Altman, D.G.; Tetzlaff, J.; Mulrow, C.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Ioannidis, J.P.A.; Clarke, M.; Devereaux, P.J.; Kleijnen, J.; Moher, D. The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate health care interventions: Explanation and elaboration. Ann. Intern. Med. 2009, 151, W65–W94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, N.S.B.N.; Mustafa, F.B.; Didams, G. A systematic review of soil erosion control practices on the agricultural land in Asia. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2020, 8, 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.L.; Xuan, D.Y.; Li, J. Practice and research outlook of overburden isolation grouting and filling technology. China Coal 2024, 50, 74–80. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y. Experimental Study on the Injectability of Coal Gangue and Fly Ash Mixed Slurry Overburden Off-Layer. Ph.D. Thesis, China University of Mining and Technology, Beijing, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Han, L.; Xu, Q.; Zhang, Y.Q. Research on the performance of slurry filling material for gangue powder-coal slurry overburden. Shandong Coal Sci. Technol. 2024, 42, 157–162. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.; He, X.; Yang, K. Mechanical Properties and Damage Characteristics of Coal-Based Solid Waste Paste Filling Materials with Different Moisture Content. Sustainability 2023, 15, 1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Yu, W.J.; Liu, F.F. The Materialization Characteristics and Ratio of a New Soil Paste Filling Material. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2020, 2020, 6645494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.G.; Liang, W.G.; Han, J.J.; Han, X.H.; Yu, Y.J. Physical and mechanical characterization of paste filling materials with swelling properties. Min. Res. Dev. 2015, 35, 15–20. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.H.; Yang, Z.Q.; Wang, Y.T.; Gao, Q. Research on the strength and hydration mechanism of fly ash composite cementitious material filling body. J. China Univ. Min. Technol. 2015, 44, 650–655, 695. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.S.; Chen, D.F.; Guo, R.H.; Tian, J.H.; Li, B. A preliminary study on the improvement of gangue/tailing cemented fill by bentonite: Flow properties, mechanical properties and permeability. Materials 2023, 16, 6802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Q.; Guan, H.D.; Wang, G.S.; Cheng, J.S. Strength prediction modeling of Na-based bentonite filler based on ultrasonic transverse wave testing. J. Min. Sci. Technol. 2024, 9, 426–434. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.B.; Guo, C.Y.; Guo, J.H.; Zhao, D.; Chen, Y.T.; Wang, F. Effect of coal gasification slag on the performance of gangue paste filling materials. J. Henan Polytech. Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 2024, 43, 165–171. [Google Scholar]
- Qu, H.S.; Su, Y.L.; Liu, L.; Zhou, W.W.; Yang, P.; Zhang, C.X. Preparation and properties of modified coal gasification slag-based mine filling materials. J. China Coal Soc. 2022, 47, 1958–1973. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, D.H.; Li, C.; Zhang, Z.G. Optimization of the performance of gasified slag-based paste filling materials in Ningdong mine. Coal Geol. Explor. 2022, 50, 41–50. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, K.; Ma, L.; Huo, B.; Ngo, I.; Wu, Y.; Zhai, J. Study on the fluidity and mechanical properties of multi-source coal-based solid waste (MCSW) filling material. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2024, 28, 2924–2934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Yang, K.; He, X.; Zhang, L.; Wei, Z.; Zhao, X.; Fang, J. Study on mechanical properties and damage characteristics of coal-based solid waste cemented backfill. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 368, 130373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Du, W.; Jin, Y.; Li, Y. Performance and hydration mechanism of fly ash coal-based solid waste backfill material affected by multiple factors. Mater. Today Commun. 2024, 41, 110639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, P.; Xu, M.; Ma, Z.-G.; Ni, X.-Y. Study on pipe-line flow characteristics of multi-source coal-based solid waste filling materials. Therm. Sci. 2023, 27, 3845–3850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, X.Z.; Chang, G.F.; Liu, X.; Yang, K.; Chen, D.H.; Li, C.; Wang, E.Q. Strength evolution and acoustic emission characteristics of multi-source coal-based solid waste fill. Chin. J. Rock Mech. Eng. 2022, 41, 1536–1551. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, M.C.; Li, C.; Feng, Y.C.; Zhao, F.Q. Preparation and application of fly ash-slag-tar slag composite cementitious material. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 41, 42–48. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.H.; Zhang, W.W. Preparation and properties of cement co-consolidated multi-waste cured ferrochrome slag filling materials. Min. Res. Dev. 2023, 43, 27–33. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.; Zheng, Q.; Zhang, G.; Wang, C.; Cheng, F.; Lin, G. Preparation and hydration mechanism of mine cemented paste backfill material for secondary smelting water-granulated nickel slag. J. New Mater. Electrochem. Syst. 2020, 23, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na, H.; Lv, G.; Wang, L.; Liao, L.; Zhang, D.; Guo, L.; Li, W. A new expansion material used for roof-contacted filling based on smelting slag. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 2607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, S.; Liu, L.; Zhu, M.; Shao, C.; Xie, L. Development and field application of a modified magnesium slag-based mine filling cementitious material. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 419, 138269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, D.Q.; Cao, G.D.; Liang, Y.H. Experimental study on lead-smelting slag as paste filling cementing material. Geofluids 2022, 2022, 6126881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, W.T.; Wu, A.X.; Yu, P. Development of a new controlled low strength filling material from the activation of copper slag: Influencing factors and mechanism analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 246, 119060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.Z.; Zhang, H.Z.; Zhang, S.H.; Li, X.; Wang, C.L.; Chen, J.L.; Zhai, Y.X.; Jing, T.L.; Ma, J.T.; Ping, H.Y.; et al. Preparation and properties of cementitious filler based on mining and metallurgical solid waste. Mater. Rep. 2023, 37, 70–75. [Google Scholar]
- Nan, X.L.; Zhang, T.G.; Liu, Y.; Dou, Z.H. Analysis of comprehensive utilization of red mud in China. Chin. J. Process Eng. 2010, 10, 264–270. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.; Du, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Yin, D.; Feng, F.; Ma, J. Effects of red mud additions on gangue-cemented paste backfill properties. Powder Technol. 2020, 367, 833–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.X.; Sun, X.H.; Zhou, L.B.; Liu, Z.; Wang, D.M. Preparation and properties of red mud-based all-solid waste mine filling materials. J. Build. Mater. 2024, 27, 946–954. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, J.K.; Han, L.; Shu, J.S.; Tan, Z.W.; Chen, T. Optimization of the proportion of expansion material and the effect of filling in end-channel mining. Saf. Coal Mines 2024, 55, 188–196. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, L.S.; Ren, Y.Q.; Yang, F.; Wang, H.F. Compressive strength and electrical resistivity characteristics of concrete recycled aggregate-red mud filling materials. Concrete 2022, 7, 87–90. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Yan, G.; Bai, X.; Kong, S.; Li, J.; Li, G.; Ge, Z.; Huang, J. Resource Utilization Potential of Red Mud: A Study on the Micro-Mechanism of the Synergistic Effect of Multiple Solid Waste Filling Materials. Sustainability 2023, 15, 15532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.L.; Wang, Y.M.; Wu, A.X.; Zhang, M.Z.; Wang, Z.K.; Wu, L.B. Leaching behavior and curing mechanism of red mud composite filling materials. Acta Mater. Compos. Sin. 2023, 40, 6729–6739. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, Z.; Pan, R.; Cao, Y.; Chen, Q.; Yang, M. Study on application and environmental effect of phosphogypsum-fly ash-red mud composite cemented paste backfill. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2023, 30, 108832–108845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.W.; Su, X.D.; Zhang, J.G.; Luo, D.Y.; Chen, Y.; Li, H.J. Leaching of heavy metals from red mud-phosphogypsum composites. Inorg. Chem. Ind. 2022, 54, 133–140. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Duan, P.X.; Ni, W.; Zhang, D.J. Carbon footprint assessment of cementitious materials prepared from industrial by-product gypsum based on life cycle. Bull. Chin. Ceram. Soc. 2023, 42, 1921–1930. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, W.H.; Cui, F.; Liu, P.L.; Wang, H.Y. Study on the properties and microstructure of fly ash-desulfurization gypsum filling materials. China Min. Mag. 2022, 31, 132–138. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, Y.; Liu, X.Z.; San, H.F. Current situation and prospect of resource utilization of industrial by-product gypsum in the field of building materials. China Build. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2023, 32, 23–25. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, D.H.; Qin, H.Y.; Li, C.; Chen, R. Optimization of less hydration ratio of bulk coal-based solid waste paste filling materials. Min. Saf. Environ. Prot. 2024, 51, 146–155. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.M.; Liu, S.L.; Wu, A.X.; Wang, Z.K.; Zhang, M.Z. Macro-fine-microstructure strengthening and damage characteristics of composite-excited paste filling materials under dry and wet cycles. J. Cent. South Univ. (Sci. Technol.) 2024, 55, 665–676. [Google Scholar]
- Ruan, S.; Liu, L.; Zhu, M.; Shao, C.; Xie, L.; Hou, D. Application of desulfurization gypsum as activator for modified magnesium slag-fly ash cemented paste backfill material. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 869, 161631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.L.; Meng, H.; Leng, Z.; Bu, T.; Long, G.X.; Duan, K.R. Properties and microstructure of calcium carbide slag-desulfurization gypsum composite inspired filling materials. J. Civ. Environ. Eng. 2023, 45, 99–106. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.S. Study on the Properties of Desulfurization Gypsum-Based Composite Cementitious Materials Based on Response Surface Methodology. Ph.D. Thesis, Guizhou University, Guiyang, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Z.D.; Zhang, D.M.; Liu, Y.K.; Zhang, Q.L.; Wang, H. Effect of citric acid leaching pretreatment on the properties of phosphogypsum filler. Gold Sci. Technol. 2020, 28, 97–104. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.J.; Yue, W.Q.; Pa, C.; Zhang, S.K. Study on the influence of pretreatment process on the performance of phosphogypsum cement mortar. Non-Met. Mines 2018, 41, 15–17. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.K.; Zhang, Q.L.; Chen, Q.S.; Qi, C.C.; Su, Z. Utilisation of water-washing pre-treated phosphogypsum for cemented paste backfill. Minerals 2019, 9, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, W.T.; Wu, A.X.; Wang, Y.M. Experimental study on factors affecting the filling performance of complex-phase condensate-expanded materials. Adv. Eng. Sci. 2019, 51, 192–198. [Google Scholar]
- Lan, W.T.; Wu, A.X.; Wang, Y.M.; Li, J.Q. Optimization of semi-aqueous phosphogypsum filling ratio based on orthogonal test. Chin. J. Nonferrous Met. 2019, 29, 1083–1091. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Li, X.R.; Cheng, L.P.; Xiong, Z.Q.; Zhan, S.F. Study on the proportion of paste filling materials based on fluorogypsum. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0286872. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.L.; Lu, H.J.; Yang, Y.J. Influence of gypsum fluoride on the performance of high water filling materials. Coal Sci. Technol. 2023, 51, 42–51. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, C.H.; Liu, M.S.; Cheng, L.J.; Lan, R. Research progress and engineering practice of comprehensive utilization of tailings. China Min. Mag. 2024, 33, 107–114. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, S.; Li, W.; Yuan, K.; Rong, C. Properties and application of thixotropic cement paste backfill with molybdenum tailings. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 391, 136169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Zhao, G.Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, H.Y. Optimization of mine filling material ratio based on RSM-DF. J. Basic Sci. Eng. 2019, 27, 453–461. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, D.J. Experimental Study on Flowability and Cement Strength of Red Clay-Ultrafine Copper Tailings Filled Paste. Ph.D. Thesis, Donghua University of Science and Technology, Nanchang, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Wang, Z.; Chen, C.; Wu, A. Insight into the active roof-contact of cemented paste backfill: A high-efficient expansion material. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2024, 20, e03123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, S.; Liu, J.; Cheng, L.; Guo, L.; Zhou, D. Rheological and mechanical properties of full-tailings backfill material prepared by ultrafine-iron-tailings-powder- based consolidation agent. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 417, 135286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



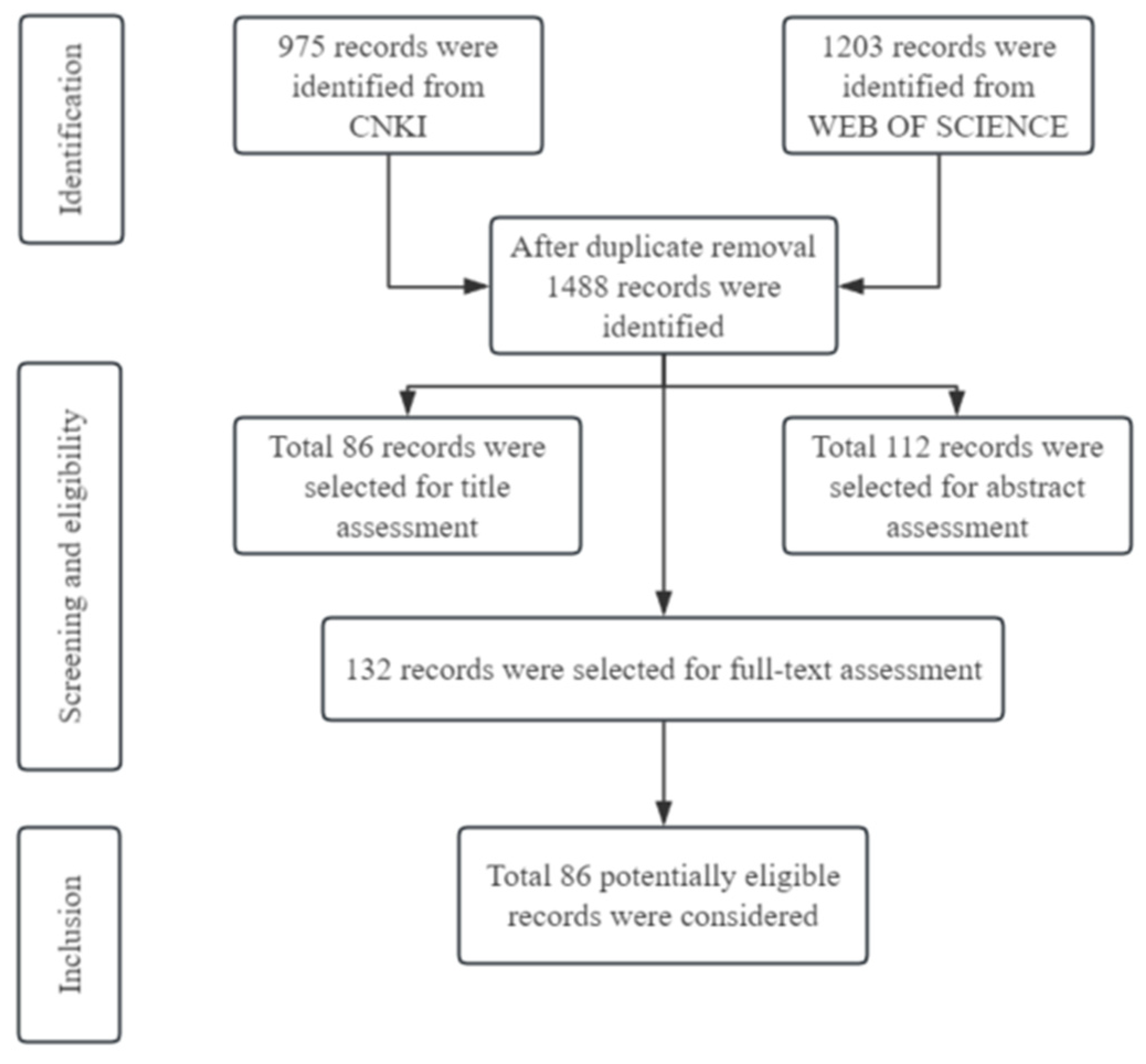








| Data Source | Keywords | No. of Papers |
|---|---|---|
| Documents identified using the CNKI database | TOPIC (((coal-based solid waste) OR (fly ash) OR (coal gangue) OR (coal gasification slag)) AND (filling material)) | 612 |
| TOPIC ((tailings) AND (filling material)) | 142 | |
| TOPIC ((gypsum) OR (by-product gypsum)) AND (filling material)) | 155 | |
| TOPIC (((smelting slag) OR (blast furnace slag) OR (red mud) OR (non-ferrous smelting slag) OR (steel slag)) AND (filling material)) | 66 | |
| Documents identified using the Web of Science database | TOPIC (((coal-based solid waste) OR (fly ash) OR (coal gangue) OR (coal gasification slag)) AND (filling material)) | 511 |
| TOPIC ((tailings) AND (filling AND material)) | 182 | |
| TOPIC ((gypsum) OR (by-product gypsum)) AND (filling material)) | 146 | |
| TOPIC (((smelting slag) OR (blast furnace slag) OR (red mud) OR (non-ferrous smelting slag) OR (steel slag)) AND (filling material)) | 364 | |
| Total= | 2178 |
| Source Link | Solid Waste Products | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Coal Mining Segment | Coal gangue | Rock or low-calorific-value coal with low carbon content and high ash content separated during coal mining and washing. Accounting for 10% to 20% of coal production, the accumulation is prone to spontaneous combustion, dust, and heavy metal pollution. |
| Coal Washing Segment | Washing gangue | Impure and low-quality coal sorted out by coal washing plants. It is similar to gangue but with higher water content, and it is easy to slate. |
| Coal slurry | Fine particles of suspended matter produced in the coal washing process and the mud formed after dewatering. Characteristics: high moisture, high viscosity, difficult to handle. | |
| Coal power generation/heating link | Fly ash | Fine ash collected from boiler flue gas in coal-fired power plants. Rich in silicon, aluminum and iron oxides, it can be used as a raw material for building materials. |
| Desulfurization gypsum | By-product from flue gas desulfurization (e.g., the limestone–gypsum method). | |
| Furnace slag | Molten residue discharged from the bottom of coal-fired boilers. It has coarse particles, a porous structure, and can be used for road building or brick making. | |
| Coal gasification/chemical link | Gasification slag | Residue after the high-temperature gasification of coal in coal gasifiers, divided into coarse residue and fine residue (fly ash). It has a low carbon content and contains silicon, aluminum and other inorganic components; the difficulty of resource utilization is high. |
| Coal chemical waste products | Waste catalyst and tar slag produced in the coal-to-oil, coal-to-gas and coal-to-olefin processes. |
| Low-Carbon-Footprint Activation Technology | Type of Technology | Principle |
|---|---|---|
| Low-temperature thermal activation technology | Low-temperature calcination | Reconstruction of slag’s vitreous structure via low-temperature heat treatment to release reactive SiO2 and Al2O3. |
| Low-carbon chemical stimulation technologies | Industrial by-product exciters | Activate the potential activity of slag/steel slag by utilizing the alkaline or sulfate content of other industrial wastes. |
| Carbon dioxide mineralization activation | Carbon dioxide is employed to react with calcium and magnesium oxides present in the slag, resulting in the formation of carbonates. This process not only sequesters CO2 but also contributes to the densification of the material. | |
| Bio-activation technology | Microbially Induced Carbonate Precipitation | Urease-producing microorganisms facilitate the hydrolysis of urea, resulting in the generation of carbonate ions. These carbonate ions subsequently interact with calcium ions to form a precipitate of calcium carbonate. |
| Mechanical–physical activation technology | Powder grind | Increasing the specific surface area of slag through mechanical energy increases the reactivity. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Song, Z.; Lyu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Song, B.; Liu, S.; Guan, C. Innovative Application and Research of Industrial Solid Waste in Mining Filling Materials in China. Sustainability 2025, 17, 5136. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17115136
Song Z, Lyu J, Zhang Z, Song B, Liu S, Guan C. Innovative Application and Research of Industrial Solid Waste in Mining Filling Materials in China. Sustainability. 2025; 17(11):5136. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17115136
Chicago/Turabian StyleSong, Zhimeng, Jinxing Lyu, Zhiyi Zhang, Bao Song, Songxiang Liu, and Chengyuan Guan. 2025. "Innovative Application and Research of Industrial Solid Waste in Mining Filling Materials in China" Sustainability 17, no. 11: 5136. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17115136
APA StyleSong, Z., Lyu, J., Zhang, Z., Song, B., Liu, S., & Guan, C. (2025). Innovative Application and Research of Industrial Solid Waste in Mining Filling Materials in China. Sustainability, 17(11), 5136. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17115136






